The aim of this study was to investigate the relationships between organizational climate, psychological contract breach and employee outcomes in college employees. Moderated multiple regression analysis was performed to measure the moderator roles of ethical leadership and trust in the organizational climate, psychological contract breaches, and relationships with employee outcomes.
- Background of the study
- Research problem
- Aim of the study
- Objectives of the study
- Hypotheses
- Significance of the study
- Operational definitions
- Outline of the study
To determine the relationship between psychological contract breach and employee outcomes of organizational citizenship behavior and intention to leave. Psychological contract breach (PCB) is a cognitive process where employees perceive a discrepancy in their psychological contracts due to unfulfilled obligations (Baruch & Rousseau, 2019; Chaudhry & Tekleab, 2013; Paillé & Dufour, 2013).
Conceptualising the study variables
- Organisational climate
- Psychological contract
- Organisational citizenship behaviour
- Intention to leave
- Ethical leadership
- Trust
Theoretical framework of the study
- Social exchange theory
- Affective events theory (AET)
- Authentic leadership theory
- Social learning theory
Empirical study
- Organisational climate and employee outcomes
- Psychological contract breach and employee outcomes
- Ethical leadership as a moderator in the relationship between organisational
- Ethical leadership as a moderator in the relationship between psychological
- Trust as a moderator in the relationship between organisational climate and
- Trust as a moderator in the relationship between psychological contract breach
Conceptual framework for this study
Research paradigm, design and approach
However, the quantitative nature of the present study necessitates the use of the positivist's paradigm. This study used a quantitative research design because the objectives of the study involved investigating the relationships between the independent variables and dependent variables. A major advantage of the quantitative research approach is that findings obtained from the study can be generalized to the entire population and the data is objective (Saunders, Lewis & Thornhill, 2012).
Despite these mentioned advantages and disadvantages, in this study, the research objectives justified the use of quantitative research approach.
Research participants and sampling
- Sample size
- Sampling procedure
Leedy and Omrond (2016) define the sampling procedure as a technique of choosing enough elements from the population in such a way that the selected individuals represent the entire population from which they were selected. All sampling methods under the probability sampling procedure randomly select elements from the sample, so all elements in the population have an equal chance of being included in a sample (Sekaran & Bougie, 2016), but non-probability sampling methods do not use a random selection of elements . The strata are formed based on the characteristics or attributes of the population and then a random sample is selected from each stratum in a number proportional to the size of the stratum, compared to the population (Etikan, Musa & . Alkassim, 2016).
This method ensures that both the population and subgroups within it are represented in the sample (Creswell, 2014).
Measuring instruments
- Organisational climate
- Psychological contract breach
- Organisational citizenship behaviour
- Intention to leave
- Ethical leadership
- Trust
Hennicks (2014) also reported a confidence level of 0.90 on the psychological contract breach scale in his study of South African miners. A study by Rothmann (2010) on information technology workers in South Africa found a reliability of 0.82 on the behavioral scale of organizational citizenship. This scale was suitable for this study because it contains extensive questions about the intention to leave and had a reliability of 0.885 in the original study.
The scale items were assessed on a 5-point Likert scale ranging from "disagree" to "strongly agree." A study conducted by Rothmann (2010) on the validation of instruments that measure happiness in South Africa found a reliability of 0.84 on the intention to leave scale.
Data collection procedure
This method was more suitable for the current study because the researcher could follow up the distributed questionnaire and thus ensure a high response rate (Sekaran & Bougie, 2016).
Data analysis
- Descriptive statistics
- Item Analysis
- Exploratory Factor Analysis
- Confirmatory factor analysis
- Correlation analysis
- Hierarchical moderated regression analysis
In addition, the guiding principles of Nunnally (1967) in interpreting reliability coefficients determined the reliability of the scales and subscales used in this current study. The chi-square value is originally an indicator of the differences between the observed and reproduced covariance matrices. The root mean squared residual (RMR) and standardized root mean squared residual (SRMR) present the square roots of the mismatches between the sample covariance matrix and the model implied covariance matrix.
The goodness-of-fit measure serves as a substitute for Chi-square (Hu & Bentler, 1999).
Ethical considerations
In this study, data for visualizing these significant interaction effects on simple slopes were produced by the PROCESS macro for SPSS created by Hayes (2017). The main purpose of the current chapter is to present the results obtained from the statistical procedures performed to test the hypotheses for this study. Finally, results from the structural model and moderated hierarchical regression analysis in hypothesis testing are presented.
Demographic profile of sample
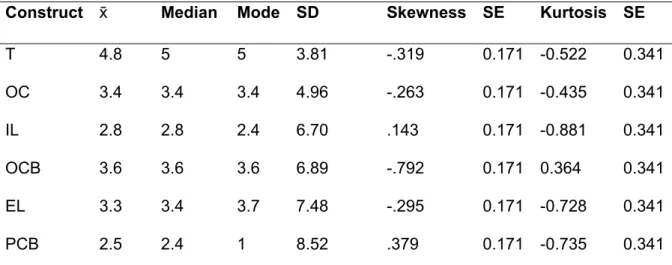
Descriptive statistics (Measure of central tendency, dispersion and normality)
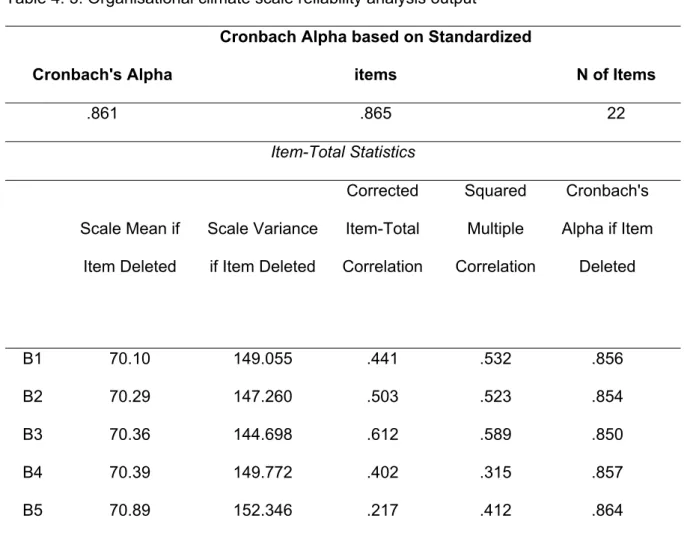
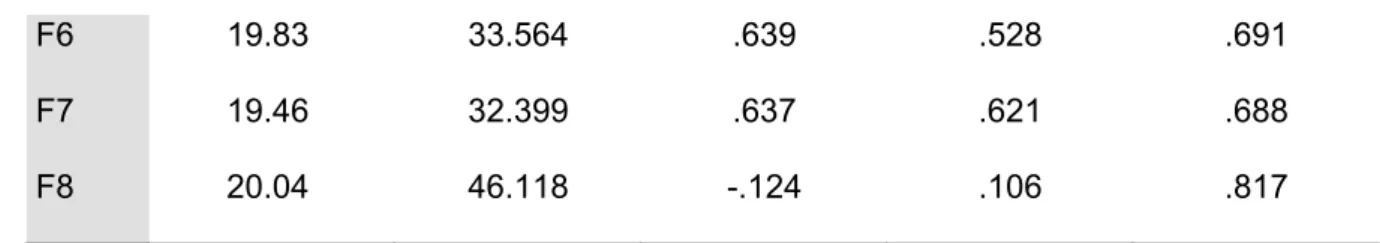
Reliability analysis
- Organisational climate scale
- Psychological contract breach scale
- Organisational citizenship behaviour scale
- Intention to leave scale
- Ethical Leadership scale
- Trust scale
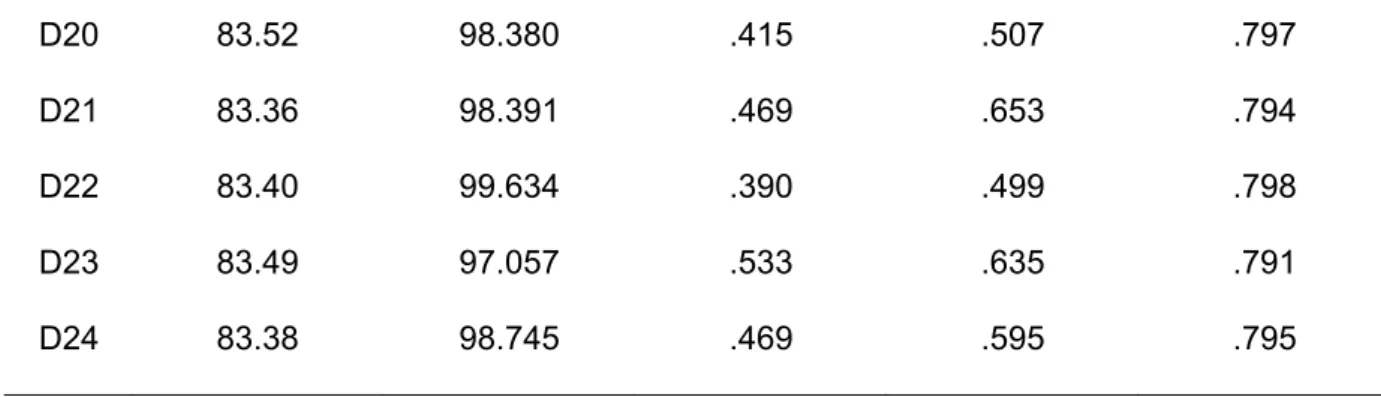
A Cronbach α = 0.939 was found for the psychological contract breach scale, which reflects an excellent coefficient as indicated by Nunnally and Bernstein (1994). Although items D12, D15, D16, D17, D18, and D19 had values below α = 0.3, they were all retained for further analysis because their removal would not significantly increase the scale's Cronbach alpha. However, they were retained for further analysis because the improvement they would make is very marginal.
All item values for the corrected-item total correlation were above α = 0.30, therefore there were no problematic items.
Exploratory factor analysis
A total of 40 items were removed because they either did not contribute to a simple factor structure or failed to meet the recommended minimum criteria of a factor loading of 0.5 or higher (Tabachnick & Fidell, 2013). It was named ethical leadership (EL) and items were developed by Brown, Trevino, and Harrison (2005) to measure ethical leadership. This result was consistent with the literature because the items were originally developed by Freese (2007) to measure intention to leave.
The result was consistent with the literature because the items were originally developed by Robinson and Rousseau (1994) to measure the degree of trust employees have in the organization.
Confirmatory Factor Analysis
- Goodness of fit for the overall measurement model
- Standardised estimates and squared multiple correlations
- Validity and reliability of the measurement model
According to Rose et al. (2017) are standardized estimates of factor loading values for items in the measurement model and should be above 0.6. In this study, the unidimensionality requirement was met when the fitness indices reached the required level in the measurement model. The validity requirement was verified by assessing the convergent validity, construct validity and discriminant validity of the measurement model.
In addition, construct validity for the measurement model was also achieved when the fit indices reached the required level as shown in Table 4.8.
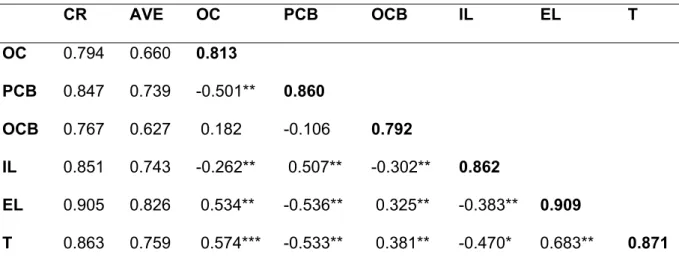
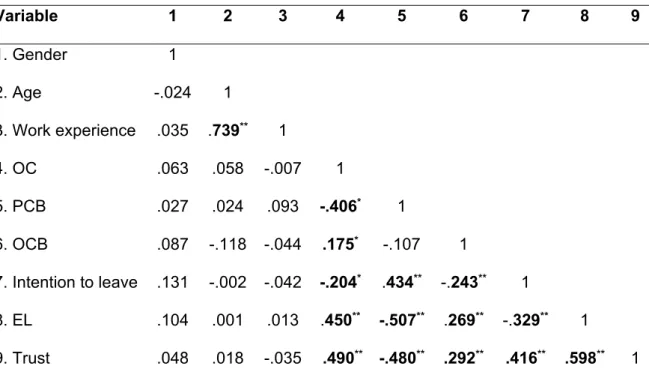
Pearson Correlation Analysis
Discriminant validity for all constructs is achieved when a diagonal value (in bold) is higher than the values in its row and column. Finally, demographic variables; gender, age and work experience were also included in the correlation analysis to see if they were related to any of the variables. As shown in Table 4.12, there was no relationship between demographic variables and other study variables of organizational climate, psychological breach of contract, organizational citizenship behavior, intention to leave, ethical leadership and trust.
OC= organizational climate; PCB= psychological breach of contract; OCB= organizational citizenship behavior; EL= ethical leadership** = p < p < 0.05.
Moderated Multiple Regression Analysis
- The moderating role of ethical leadership and trust on the relationship between
- The moderating role of ethical leadership and trust on the relationship between
As a result, hypothesis 1a was supported, suggesting that ethical leadership moderates the relationship between organizational climate and organizational citizenship behavior (see Table 4.14). As a result, hypothesis 3a is supported, which states that trust moderates the relationship between organizational climate and organizational citizenship behavior. A moderated hierarchical regression analysis was conducted to test the hypothesis that trust moderates the relationship between psychological contract breach and organizational citizenship behavior (Hypothesis 4a).
Therefore, hypothesis 4a that trust moderates the relationship between psychological contract breach and organizational citizenship behavior is supported.
Discussion
Hypothesis 1a stated that ethical leadership moderates the relationship between organizational climate and organizational citizenship behavior. This means that the presence of ethical leadership affects the relationship between organizational climate and organizational citizenship behavior. The results for hypothesis 3a that trust moderates the relationship between organizational climate and organizational citizenship behavior were significant.
The results for Hypothesis 2a that ethical leadership moderates the relationship between psychological contract breach and organizational citizenship behavior were significant.
Conclusions
113 possible explanation is that it is difficult to change the opinion of employees when they decide to leave the organization. 114 However, the moderating effects of ethical leadership and trust on the relationship between psychological breach of contract and intention to leave were not significant. Based on these results, we can conclude that there is insufficient evidence to suggest that both ethical leadership and trust have a moderating effect on turnover intentions among university employees.
It is also concluded that neither ethical leaders nor trustworthy leaders can reduce employees' intentions to leave the organization if the organizational climate is perceived as poor and when the psychological contract is broken.
Recommendations
- Theoretical contributions of the study
- Practical implications of research findings
From the research results, it appears that psychological contract breach is positively correlated to employees' intention to leave. Fourth, this study extends our understanding of organizational climate, psychological contract breach, and employee outcomes. Both ethical leadership and trust were also found to moderate the relationship between psychological contract breach and organizational citizenship behavior.
In addition, trust also emerged as a significant moderator in the relationship between psychological contract breach and organizational citizenship behavior.
Limitations of the study
Based on the findings of this study, the tangible benefits of trust in the organization are evidenced by high organizational citizenship behavior. To gain the trust of employees, it is suggested that managers should honestly communicate any changes that will affect employees. Kouzes and Posner (2013) also emphasize the urgency of clear communication in building trust in leader-subordinate relationships for messages that are easily distorted if communicated vaguely or ambiguously.
Only two universities were included in the study, therefore the results from the current study are only representative of a fairly small percentage of South African universities, therefore the generalizability of the results to the entire population of universities in South Africa in all provinces is limited.
Suggestions for future research
The mediating role of psychological contract fulfillment in the relationship between ethical leadership and employee extra-role performance. Reciprocal Effects of Psychological Contract Violation on Counterproductive Citizenship and Organizational Behaviors: The Role of Time. Psychological contract breach, job satisfaction and turnover intention in the service industry (Unpublished Master's thesis).
Psychological contract breach, organizational trust and organizational citizenship behavior of the employees in a hotel industry in Taiwan. Positive employment relationships and organizational outcomes: the role of the psychological contract and employability (Unpublished master's thesis). How psychological contract breach affects organizational identification and organizational citizenship behavior: The mediating role of psychological capital.