Directory UMM :Data Elmu:jurnal:S:Structural Change and Economic Dynamics:Vol11.Issue1-2.Jul2000:
Teks penuh
Gambar
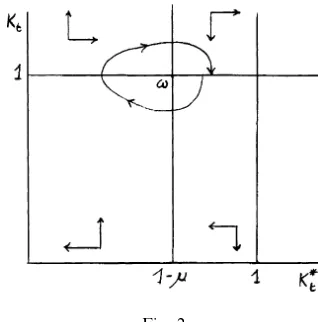
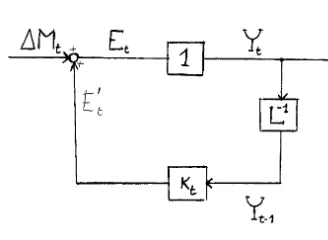
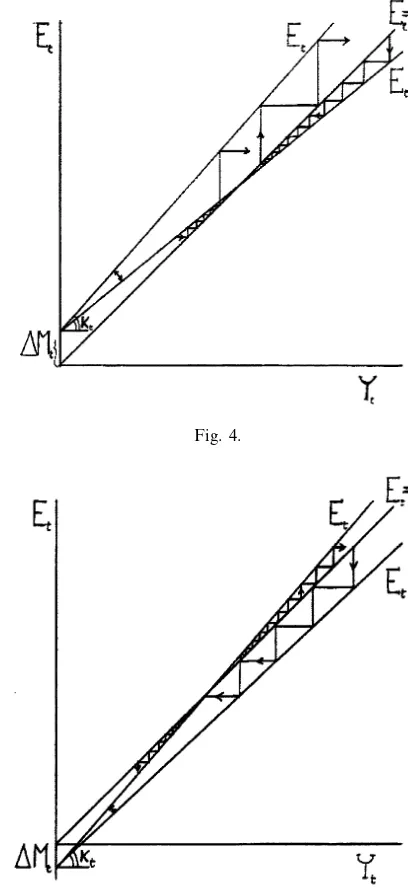
Dokumen terkait
in the relative weights of significant components of systems (Ishikawa, 1987; Pasinetti and Scazzieri, 1987). All rights reserved.. Smith gives two different kinds of illustrations
Currently, the process of economic development is at risk because the nature of global institutions for short term capital flows is robbing developing countries of their
(Marshall, 1873, pp. The restrictions Marshall imposes on this very generous principle — which allows economists to use their own experiences and judgement as part of the
Although Albin demonstrates that appropriate qualitative taxonomies of complex systems (like distinguishing among those with stable equilibria, limit cycles, and strange
The addressed forms are, relations among human beings are reduced to relations of equivalents; economic rationality is reduced to rational choice; the category of happiness is
As Hendry and Doornik (1997) remark, when the long-run mean is non-zero, breaks shift the location of the data, inducing a short-run ‘trend’ to the new equilibrium mean, which is
The proposed new method of HC estimation presented in Section 4 allows, (i) the HC estimation of each economic unit as a latent variable; (ii) the average HC by age; (iii) the
The cornerstone of that framework is the zero - bequest sa 6 ing function which represents the aggregate cross-sectional saving rate that satisfies the zero-bequest