I TIN.
Lill
I
IRA NADYA OCTAVIRA
NIM. 206014000140
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
Experimental Study at the seventh Grade of SMP Pelita YNH Suknbumi") written
by
IRA
NADYA OCTAVIRA, a student's registration number 206014000140 was examined in the examination session of the Faculty of Tarbiya and Teachers' Training,Syarif Hidayatullah
State Islamic University Jakarta on Januari. The"skripsi" has been accepted and declared to have fulfilled one of the requirements for the degree of "S.Pd" (Bachelor of Arts) in English Language Education at the
English Education Department.
Jakarta, January 2013
EXAMINATION COMMITTEE
CHAIRMAN : Drs.Svauki. M.Pd.
NIP. 19641212199103
I
002SECRETARY : Neneng Sunenssih. S.Pd. NIP. 19730625199903 2 001
EXAMINERS: 1.Dr. Alek. M.Pd.
NIP. 196909 12200901 1008
,.r,".
rrn
**
*urro*r,n
r,o.
rror.U NIP. 194407 19196510 1 001' Training Faculty
A "Skripsi"
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teacher's Training
In a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements
For the Degree of S. Pd. (Bachelor of Art) in English Language Education
Ira Nadva Octavira NIM. 206014000140
Ismalilnine Eviyuliwatl NI.Hum NrP.19740723 200003 2 001
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACTJLTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
Jl. Ir. H. Juanda No.95 Telp: (62-21) 7443328, 7401925 Ciputat 15142 Jakarta Email: [email protected]
SURAT PERNYATAAN KARYA SENDIRI
Saya yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini,
Nama : Ira Nadya Octavira
Tempat/Tanggal lahir : Sukabumi, 09 Oktober 1988 NIM : 206014000140
Program Studi : Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris
Judul Skripsi : The Effectiveness of Using Mind Mapping Technique
Toward Comprehension of Descriptive Text.
(An Experimental Study at the Seventh Grade of
SMP Pelita YNH Sukabumi)
Dosen Pembimbing : Ismalianing Eviyuliwati, M.Hum
Dengan ini menyatakan bahwa skripsi yang saya buat benar-benar hasil karya saya sendiri dan saya bertanggung jawab secara akademis atas apa yang saya tulis. Pernyataan ini dibuat sebagai salah satu syarat menempuh Ujian Munaqasah.
Jakarta, Januari 2013 Mahasiswa Ybs.
Praises be to Allah, Lord of the worlds, who has given the writer His love
and compassion to finish the last assignment in her study. Peace and salutation be
upon to the prophet Muhammad SAW, his family, his companion, and his
adherent.
It is a pleasure to acknowledge the help and contribution from all people
who always support me. Hence, this skripsi is processed until it becomes a
complete writing which will be presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and
Teachers’ Training in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of S.
Pd (Bachelor of Art) in English Language Education.
First of all, the writer would like to express her great honor and deepest
gratitude to her beloved parents, Alm. Dr. H. Silahudin, MA. andAlm. E.
Maemunah, S.E.And also best gratitude to her advisor,Ismalianing Eviyuliwati,
M.Hum. whose scholarly suggestions and critical remarks have enabled the writer
to refine this skripsi. The writer’s sincere gratitude also goes to:
1. Drs. Syauki, M. Pd., the Head of English Department
2. Neneng SunengsihS.Pd.,the Secretary of English Department.
3. Prof. Dr. Rif’at Syauqi Namawi, MA.,the Dean of the Faculty of Tarbiyah
and Teachers’ Training Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta.
4. All People in SMP Pelita YNH Sukabumi.
The writer does realize that this skripsi cannot be considered perfect without
critiques and suggestions. Therefore, it is such a pleasure for her to get critiques
and suggestions to make this skripsi better.
Jakarta, Januari 2013
Sukabumi), Skripsi, English Education Department, The Faculty of
Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training, Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta.
Advisor: Ismalianing Eviyuliwati, M.Hum
Keywords: Descriptive Text, Mind Mapping Technique
This study is aimed at knowing the effectiveness toward comprehension of descriptive text of seventh grade students of Junior High School Pelita, Sukabumi who learn descriptive text through mind mapping.
This study is categorized as a quantitative study since it requires numerical data. She conducts experiment in two different classes with two different techniques. Besides, the it using mind mapping technique in one class (experiment class) and explanatory method in another one (controlled class). In analyzing the data, it uses t-test to analyze the students’ achievement test, by holding a pre-test to know whether or not the two different classes are relatively at the same level, and post-test to know whether or not there is any significant different achievement of using mind mapping and explanatory technique in teaching descriptive text. In this study, it takes the sample only two classes taken from class VII-A and VII-B. The sample based on purposive random sampling technique. So, VII-A (35 students) was as experiment class using mind mapping and VII-B (35 students) as controlled class using explanatory technique in teaching descriptive text.
Sukabumi), Skripsi, Jurusan pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Ilmu Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, Universitas Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta.
Pembimbing: Ismalianing Eviyuliwati, M.Hum
Kata Kunci: Teks Deskriptif, Peta Konsep
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui keefektifan pemahaman siswa kelas VII SMP Pelita Sukabumi yang mempelajari teks deskriptif melalui peta konsep.
Penelitian ini di kategorikan sebagai penelitian kuantitatif semenjak ditujukan dalam bentuk data berupa angka.Peneliti bereksperimen di dua kelas yang berbeda dengan dua teknik pengajaran yang berbeda pula. Disamping itu, penelitian ini menggunakan teknik peta konsep di kelas eksperimen dan metode ceramah di kelas terkendali (controlled class).Dalam menganalisa data, peneliti menggunakan t-test untuk menganalisa hasil perolehan tes siswa, melalui pre-test dan post-test. Di dalam penelitian ini, sample yang di ambil adalah dua kelas yaitu di kelas VII-A dan kelas VII-B.Sample tersebut berdasarkan teknik sample acak. Olehsebab itu, kelas VII-A yang terdiri dari 35 siswa sebagai kelas experiment yang menggunakan peta konsep dalam mengajarkan teks deskriptif sedang kan kelas VII-B yang terdiridari 35 siswa sebagai kelas terkendali menggunakan metode ceramah dalam mengajarkan teks deskriptif.
APPROVAL………...
SURAT PERNYATAAN KARYA SENDIRI ………... i
ENDORSEMENT………...…. ii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT………... iii
ABSTRACT………... iv
TABLE OF CONTENT………... viii
LIST OF TABLES ………... x
LIST OF FIGURES………...….. xi
CHAPTER I : INTRODUCTION A.Background of the Study ………... 1
B.The Formulation of Problem………... 4
C.The Objective of Study ………....…... 4
D.The Significance of Study………. ... 4
CHAPTER II : REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE A. Descriptive Text...……….……... 5
1. The General Concept of Descriptive Text……...……. 5
2. The Characteristics of Descriptive Text ……... 7
B. Reading………... 11
1. The General Concept of Reading ………... 11
2. The Purposes of Reading ………... 13
3. The Kinds of Reading ………... 15
C. Mind Mapping ... 18
1. The General Concept of Mind Mapping ... 18
2. The Techniques of Using Mind Mapping... 21
D. Previous Studies... 22
1. Studies on Descriptive Texts... 22
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. The Method of the Research... 29
B. The Place and the Time of the Research... 29
C. The Population and Sample of the Research... 29
D. The Technique of Data Collecting... 29
E. The Technique of Data Analysis... 31
F. The Procedure of the Research... 32
CHAPTER IV: FINDING AND INTERPRETATION A. Finding... 33
1. The Data Description ... 33
2. The Data Analysis . ... 38
B. Interpretation... 43
1. The Interpretation of Data Analysis ... 43
CHAPTER V : CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A. Conclusion ... 45
B. Suggestion ... 45
Table 3.1 The Blue Print Test of Pre-Test for the Experimental and
the Control Class ... ... 30
Table 3.2 The Blue Print Test of Post-Test for the Experimental and the Control Class ... 30
Table 4.1 The Scores of Pre-Test and Post-Test of Experiment Class ... 29
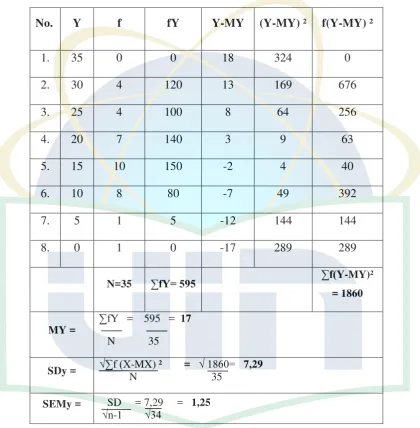
Table 4.2 The Scores of Pre-Test and Post-Test of Controlled Class ... 31
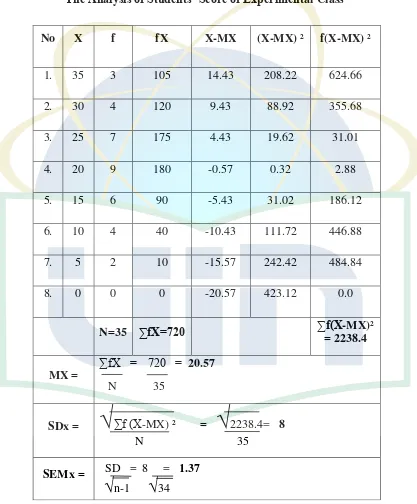
Table 4.3 The Analysis of Students’ Score of Experimental Class ... 34
[image:10.595.103.525.148.567.2]CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
In this chapter, the writer would like to present the general account of study in
which it discusses about background of study, the limitation of study, the
formulation of study, the objective of study and the significance of study.
A. Background of the Study
Nowadays, English has become one of the dominant languages in this
globalization era. Hence, English leads important position for communication
among countries in many fields such as education, advertising, transportation,
tourism, business, banking, industry, and other relationships all over the world.
These also encounter English as an international language.
Meanwhile, in Indonesia English is regarded as a foreign language. According to GBPP 1994, it is stated that “English is the first foreign language in Indonesia which is considered very crucial for the purpose of science development
and absorption of technology and culture, and also construction of relation with
other nations.”1
Therefore, the Indonesian government has determined English as
a lesson that must be learned at school since it has been known its significance
role to interact with other nations in which it functions to develop Indonesian
country. Besides, to acquire those goals, then Indonesia has determined English as
one of the subject initiated to be learned from elementary school up to university
level; as the local content curriculum until it is considered as the compulsory
subject.
Like other foreign language learners, students at Indonesian schools also
need to master English language skills and its language components. The
language skills are divided into four areas; those are listening, speaking, reading,
and writing; meanwhile the language components are learned to support the four
language skills, they are grammar, pronunciation, and vocabulary.2
1Depag RI, GBPP Bahasa Inggris (MTs), (Jakarta: Depag RI, 1993), p. 2. 2
As one of language skills, reading is clearly one of the most important
aspects in many instances around the world. We may argue that reading is the
most important foreign language skill, particularly in cases where students have to
read English material for their own specialist subject, but may never actually have
to speak the language.3
It means that reading has many functions for students. In
this case, reading enables the students understand the massages given in written
form. They read because they wanted to get something from the writing; facts,
ideas, enjoyment, even feelings of family community (from letter). They read to
obtain the information for some purposes. For example, when the students read
the instructions on a ticket machine, they need to know how to operate it, when
the students read the road sign so that they know where to go, when they read the story of Lady Diana‟s life so that they know who Lady Diana is.
Based on that, we exactly know that reading can improve and develop students‟ other skills of English such as writing skill, that is from the information and ideas which are exchanging between the writer and the reader in the act of
communicating. In addition, reading helps the students maintain a competence
and fluency in speaking, writing and grammar. It is because in teaching reading
generally the teacher integrates with other language skills.
In reading selections, it is also taught English texts as one key component
of the new 2006 curriculum, that is what we call as genre. “Genre that appears in the classical literature on rhetoric, from Aristotle to modern day, are those of
narrative, descriptive, procedural, and persuasive discourse.”4
Descriptive text is one of specific instructional objectives in teaching English,
one in a typical genre lesson activities using, includes in factual genres, and as a
competence of achievement target, should to understand by students.5
So it can be
illustrated that descriptive text has a social function is to describe a particular
3
Jo McDonough and Christopher Shaw, Material and Method in ELT; Teacher’s Guide, (Oxford: Blackwell Publishers, 1993), p. 101.
4 Evelyn Hatch, Professor Emerita, Discourse and Language Education, University of California,
(Los Angeles: Cambridge University 1992), p.164.
5 Helena I.R. Agustien, ,New Let’s Talk, Text Book of Eight Grade for Junior High School
person, place, or thing, for instance, description of a particular building, specific
animal, particular place, and specific person.
However, in a fact in teaching – learning process as long as I do research, there are some problems faced by students as they are learning descriptive text
such as; most of them do not understand the schematic structure of the text, they
are difficult to grasp the main idea of the text, they have no interesting enough to
be involved in many kinds of reading activity including in learning descriptive
text, and the last they are easily to lose their concentration as they read, then of
course it will lead them to get boring when they study reading texts. Furthermore,
the teaching reading of descriptive text tends to be boring since the teacher uses
the explanatory method; it seems so monotonous without involving students
active in the class.
Based on the statements above, teachers basically must be able to organize
learning-teaching activities. They have to master the materials and methods. A
good method can help the students in comprehending and mastering the lesson.
One of the teaching failures is caused by an unsuitable method. As it is said by
William F. Mackey “The method used has often been said to be the cause of success or failure in language; for it is ultimately the method that determines the what and the how of language interaction”.6
There are a lot of methods and approaches to get the English teaching
method effectively. To modify positively the situation of the classroom and to
make the teaching-learning process lively in teaching descriptive text, the writer
would like to propose an alternative other than teacher centered approach or others, that is the one which common known under the term “mind mapping”. Mind Mapping is a way getting your ideas together. It is a learning strategy that
can help students to facilitate their learning by generating and organizing the ideas
about the topic they are reading. Mind Mapping also can make students more
imaginative and creative in writing class. It is expected can make a positive
atmosphere in the classroom.
6 William F. Mackey, Language Teaching Analysis, (London: Longman, Greenland Co.Ltd, 1996), p.
Since the writer read some researchers who had already done the
technique of mind mapping in teaching descriptive produced varieties of results either showing improvement toward students‟ achievement in reading test or even not yet successfully. Therefore, in this study the writer is interested in mind
mapping in teaching descriptive text. Compared with the explanatory method,
hopefully mind mapping will obtain good result in teaching descriptive text
B. The Formulation of Problem
Based on the background of the problem of this research can be formulated as below, “was there any effect of using mind mapping technique toward comprehension of descriptive text of seventh grade students of SMP Pelita
YNH Sukabumi?”.
C. The Objective of Study
In accordance with the formulation of the problem above, the objective of
this study was to know whether or not any effect of using mind mapping
technique show better achievement than through non-mind mapping technique.
D. The Significance of Study
The significances of the study were expected to be beneficial both
theoretically and practically go to teachers, the finding of this study is useful to
enrich their teaching strategy to be applied in teaching descriptive text. For the
students, it enables them to improve their reading comprehension of descriptive
text and to increase their participation in reading class activities. This study is also
expected to be a reference for other researchers who have the same problem and
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter covers some theories related to the study. The discussion
focuses on the reading, the descriptive text, and the mind mapping. In addition,
the chapter also reviews some previous studies done other researchers, which
share some similar ideas to the current study.
A.Descriptive Text
1. The General Concept of Descriptive Text
Descriptive text is one of genres in reading selection that is learned by
students either at junior high school or senior high school. There are some
definitions regarding the descriptive text. According to Anderson and Anderson
that state a factual description describes a particular person, place or thing.7
In this
sense, the function is to describe a particular person, place, or thing, for instance,
description of a particular building, specific animal, particular place, and specific
person.
Descriptive is basically embedded in the word description are two words: scribe, meaning “to write” and de, meaning “down” or
“about”. There is a hint in the etymology of the word description that something is being traced or drawn, that in describing you will follow the outline of an object visually and then write it down or “draw” it in words. The word “draws” is not an accidental association. Many writers have likened the process of describing to that of painting.8
Based on that, description text tends to be as a mental process, a way of
perceiving objects in space and time. As it pertains to composition, description is
a way of picturing images verbally in speech or writing and of arranging.9
Those
images in some kinds of logical or associational pattern.
7 Mark Anderson and Anderson Kathy, Text Types in English 3, (Sidney: MacMillan, 1998), p. 26. 8
Frank J. D‟Angelo, Process and Thought in Composition, (Cambridge: Massachusetts, Winthrop Publishers, inc, 1997), p.123.
9
Moreover, description is concerned mostly with people, places, and things.
The student papers reprinted below give you a variety of models to follow, based
on these topics. You might wish to describe a roommate, a close friend, a parent, a
child, a niece or nephew, a teacher, a landlord, a rock star, or a celebrity.
Hence, description must be in living color, like narrative, description has a
predictable pattern. You may start on the left and work to the right, or from the
center outward, or from front to rear, but in any case you owe it to your reader to
keep his or her position clear. Description must follow some kind of spatial
pattern; usually its point of view and perspective are clear.
Furthermore, according to Charlotte Miller, he said that in descriptive text
there consists of some words, standing alone, may seem neutral (neither good nor
bad), but in context with other words, or in a sentence, take on a connotative
meaning.10 Here, the writer may illustrate that for example, the word drugs to an
elderly person suffering the pains of age related disease is positive, but, to parents
with a son hooked on heroin, drugs is negative. Denotative language, on the other hand, means words that don‟t carry any emotional overtones or value judgments.
Examples:
Thin lean slender scrawny slim skinny which of the above words do you consider positive, negative, or neutral?
You may find that because of difference in values, your classmates differ with you.11
Description is the pattern used to convey what you have sensed, what you
have seen, heard, smelled, felt, tasted. Description is more than a visual account,
and certainly it must not be limited to black and white. Therefore, the purpose of
description is to present the reader with a picture of person, subject, or setting.
Although description is sometimes used alone, it more often appears in connection
with one of the other types of writing – exposition, narration, or persuasion.
In sum up, the purpose of descriptive is to tell about the subject by
describing its features without including personal opinion. The aim of description
10
Charlotte Miller. Gwen brewer, with Andrea White, Lila Fink, Phyllis Levy. Choices, A Text for Writing and Reading, (Northridge: Little, Brown and Company Boston Toronto, 1993 ), pp. 41—42 .
11
is to enable the reader what something looks like. It attempts to paint a picture
with words. In this sense, the description also attempts to put the reader directly in touch with the physical world within the readers‟ senses. Description helps the readers visualize a scene or a person and understand the related sensation or an
emotion.
2. The Characteristics of Descriptive Text
As we have already discussed, a descriptive text is a text which lists the
characteristics of something. So, in descriptive paragraph, we must make very
clear the location of the objects being described. It must be exist the attributes of a
thing to present the topic and the forms which are used.12
According to Harry H. Crosby, to understand the descriptive text, we need
to know the characteristics as following:13
a. Communicative Purpose: to describe a particular person, place, or thing b. Generic Structures
- Identification, to identify the phenomenon will describe
- Description; to describe the items, the qualities, subject features, whole attitude, and adjectives.
c. Linguistic Features focus on specific participant, for example my house, my cat, the museum, etc.
When you set out to describe a person, an object, or a scene, you have got
to decide at the outset how you are going to arrange the details. Sometimes the
natural contours of the objects; themselves suggest a way of proceeding.
Description is also a powerful strategy, one that allows the writer to exercise a great deal of control over the reader‟s perceptions. In addition, it is a strategy we use in our daily interaction. In our daily interaction, we may describe different
kind of things, place, and person.14
12
Regina L. Smalley, Mary K. Ruetten, Refining Composition Skills/Rhetoric and Grammar Fourth Edition, (San Francisco: Heinle & Heinle Publishers an Internasional Thompson Publishing Company (ITP), 1997), p.73.
13
Harry H. Crosby - Duncan A. Carter, The Commited Writer Mastering Nonfiction Genres, (Boston: McGraw Hill Book Company, 1996) p. 7.
14
a. Description of Things
In descriptive text, you will occasionally need to describe an animate
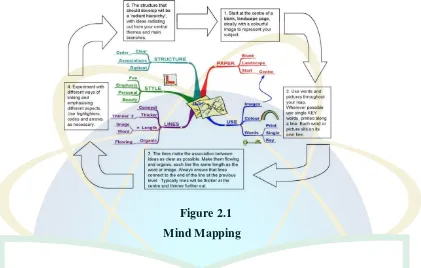
subject, such as a person, animal, or insect. Meanwhile, you can describe a person‟s appearance in many ways. You can tell about the person‟s style of clothing, manner of walking, color and style of many facial appearance, body shape, and expression. You can also describe the person‟s way of talking. Just what you select to describe depends on your topic and purpose. For example, how
would you begin to describe your girlfriend to your cousin? her hair? her eyes?
her voice? The following are some useful vocabulary words and expressions of a
[image:19.595.101.525.145.542.2]person.
Table 2.1
Vocabulary Words and Expression15
Facial Expression
Facial
Shape Eyes Voice Mouth Eyebrow Scowl Frown Smirk Worried Pained Blank Peaceful Round Broad Narrow Oval Flat Beady Smiling Snapping Empty Hard Bulging Staring Booming Growling Deep Melodious Full-lipped Thin-lipped Set Sensuous Thick Arched Neatly plucked uneven
b. Description of Place
The description must be organized so that the reader can imagine the scene
being described. To make the paragraph more interesting, it can be added a
controlling idea that states an attitude or impression about the place being described. “Descriptive text must include the arrangement of the details in your description depend on your subject and purpose.”16
15 Smalley, R.L., Reutten, M.K. &Kozyrev, J.R. Refining Composition Skills: Rhetoric and
Grammar (5th ed.) 1997, p. 71.
16 Regina L. Smalley, Mary K. Ruetten, Refining Composition Skills/Rhetoric and Grammar1997,
The purpose of descriptive texts in Junior High School is to describe current activities or events (running commentaries) and to describe activities in the pictures. And the structure it‟s for identification and description and the language features are specific participants, the use of present continuous tense and action verb.17
c. Description of Person
When you describe something or someone, you give your readers a picture in words. To make this “word picture” as vivid and real as possible, you must observe and record specific details that appeal to your readers‟ senses (sigh, hearing, taste, smell and touch). It is also said by Alice Oshima:
Descriptive writing appeals to the senses, so it tells how something looks, feels, smells, tastes, and / or sounds. A good description is like a “word picture”; the reader can imagine the object, place or person in his or her mind. A writer of a good description is like an artist who paints a picture that can be “seen” clearly in the mind of the reader.18
More than any other type of writing, a descriptive paragraph needs sharp,
colorful details. Here is a description in which only the sense of sight is used. “Sense impressions include sight (thick, reddish-brown shag rug; laid wall to wall; walk through them in your bare feet; sneeze your toes into the deep covering;
push back), hearing (whisper), and touch (bare feet, soft fibers, spongy resilience).”19
In every kinds of genres including descriptive text, it can be analyzed the
two characteristics. Those are the schematic structures in which how the passages
are organized, and the linguistic features in which it functions to construct the text
itself.20
For further explanation such following:
17
Mukarto, Sujatmiko dkk, English On Sky For Junior High School Student Year VIII, (Based On KTSP 2006, Bandung: Erlangga, PT. Gelora Aksara Pratama 2007), p.19.
18
Alice Oshima, Introduction to Academic Writing, Second Edition, (Longman: Addison Wesley, 1997), p. 50.
19
Langan, English Skills with Readings, Fifth Edition, Atlantic Cape Community College, (Boston Burr Ridge: McGraw Hill Companies Inc, 2002), p. 243.
20
1. The Schematic Structures of Descriptive
The schematic structure of descriptive paragraph consists of identification
and description.21
Identification mentions phenomenon to be describe, while the
description describes the parts, the qualities, and the characteristics of what has
been described.
To construct a description usually uses an opening paragraph introducing a
subject of the description, followed by a series of paragraphs each describing one
feature of the subject. There can also be a final concluding section that signals the
end of the description.22
In sum up, the schematic structure is important to organize a good descriptive paragraph. It can help to see the organization of description clearly. So, the reader can easy to get imagination of description.
2. The Linguistic Features of Descriptive
Descriptive paragraph usually include the following linguistic features such
as verb in the present tense, adjectives to describe the features of the subject, and
the topic sentences to begin paragraph and organize the various aspects of the
description.23
Other resources mention that the linguistic features of description are: first,
focus on specific participants. Second, use of attribute and identifying processes.
Next, use of epithets and classifier in nominal groups.The last, use of simple
present tense.24
In conclusion, the linguistic features play significant role to sustain in
producing a good description. For instance, through specific participant, it tells the
readers exactly participant. Next, the use of adjective, it is relatively necessary to
describe the characteristic and the phenomenon in order to get a vivid image.
Hence, all of the linguistic features are conveyed to construct vividly description.
21
Ibid, p. 7.
22 Mark Anderson and Anderson Kathy, Text Types in English 3,1998, p. 26. 23
Ibid. p. 26.
24 Rudi Hartono, SS, M. Pd. Genres of Text, (Unpublished Paper), (Semarang: Semarang State
Shortly, descriptive text is a part of factual genres in which it has social
function to describe a particular person, place or thing. Besides, there are two
characteristics of that text. Those are Schematic Structure it is for identification,
description, and Language Feature focus on specific participants, use of attribute
and identifying processes, frequent use of epithets and classifier in nominal
groups, and use of simple present.
B.Reading
1. The General Concept of Reading
As one of English language skills, reading plays an important role in our
daily life. It could be seen that we cannot separate ourselves from printed
materials. We read many fictions and non-fictions to get meaning and to get the
information. There are some linguists who defined what reading is. In the
following is the definition given by Jeremy Harmer:
Reading is working of eyes and brain, the eyes look the reading and receive the message and then the message is transferred to the brain to work out the message. An exercise dominated by the eyes and the brain. The eyes receive message and the brain then has to work out the significance of these messages.25
Here, he pointed out that reading is a working of eyes and brain, the eyes
look the reading and received the message and then the message is transferred to
the brain to work out the messages.
In accordance with Jeremey Harmer‟s statement, Christine Nuttal in her book “Teaching Reading Skill in A Foreign Language” also pointed out that
reading is a meaning, specifically with the transfer of meaning from mind to
mind; the transfer of message from writer to reader.26 Therefore, reading can be
described as a meaning-getting process where the recognition of important
elements of the meaning in their essential relation transferring meaning from the
printed written to the mind. In short, the two linguists above said that to get the
25 Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English Language Teaching, (New York: Longman, 1993),
p.153.
26Christine Nuttall, Teaching Reading Skills in a Foreign Language, (Bangkok: Macmillan, 1996),
meaning, the readers have to focus their eyes and brain to the printed material as
they are reading.
Meanwhile, According to Richard Allington and Michael Strange reading
is an active cognitive process that does indeed require using graphic (letters) and
phonic (sounds) information.27
This is in line with what John F Savage and Jean F
Mooney stated in their book that reading is a cognitive activity, an activity that
involves the use of higher mental process.28
The cognitive process here means that
the reader gets the knowledge from printed material. Cognitive process covers the
ability to retell the printed material and intelligence abilities such as implementing
the principle or the concept, analyzing, understanding etc.29Some linguistics said
that a cognitive process is the most important of reading act because the main goal
of reading is understanding.
Generally, it can be concluded that reading as cognitive process is the
process when the reader gets the knowledge from printed material. Furthermore,
reading is a complex cognitive process; where the reader comprehends the ideas
via medium of text. Reading is the process to understand, to get the knowledge, and to involve reader‟s mind.
However, in comprehending a printed language, it is quite difficult for the
reader to accomplish multiple things simultaneously in constructing the meaning
from a text. Learning to read involves learning to deal with secondary language
symbol system. Human invented language to represent or symbolize the objects,
experiences, ideas, emotions, etc.Here, Penny Ur explained that:
Our aims in (real-life) reading usually go beyond mere understanding. We may wish to understand something in order to learn from it (in a course of study), in order to find out how to act (instructions, directions), in order to express an opinion about it (a letter requesting advice), or for many other purposes. Other pieces of writing, into which the writer has invested thought and care, demand a personal response from the reader to the ideas in the text,
27
Richard Allington, and Michael Strange, Learning through Reading, (Massachusetts: D.C Health, 1990), p.16.
28John F Savage & Jean F Mooney, Teaching Reading to Children with Special Needs, (New York:
Allyn and Bacon, 1999), p.22.
29Suharsimi, Arikunto, Dasar-dasar Evaluasi Pendidikan, (Jakarta: Bumi Aksara, 2007), pp. 117—
such as interpretation, application to other contexts, criticism, or evaluation.30
From the definitions given by linguists above, the writer concluded that
reading is a process of getting meaning. Reading is not just process of decoding,
deciphering, identifying the words but it is a process of getting meaning from the
messages or written text and it is a process of transferring the meaning from the
writer to the reader.
2. The Purposes of Reading
In the real life, people read and listen to the language because they want to
know and grasp the information in written text and because they have a purpose
for doing so. According to Rivers and Tempely, they list the following examples
of the reason that students may need or want to read because they need:
To obtain information for some purposes or because we are curious about some topic, to obtain instruction on how to perform some task for our work or daily life, to keep in touch with friends by correspondence or to understand business letters, to know when o where something will take place or what is available, to know what is happening or has happened (as reported in newspaper, magazine, reports), and for enjoyment or excitement.31
From the explanation above, reading has some purposes to look for the
information in many kinds of printed materials. In addition, reading for pleasure is
considered as for enjoyment activities. In this sense, the readers read the text to
get the knowledge. It means that they learn something from a text. Actually, it
needs abilities to remember the main idea, recognize and build rhetorical in the
text, and correlate the prior knowledge to the text that has been read.
Another linguist such as Jeremy Harmer, he divided the reasons why
people like to read and to listen. Those are categorized into two broad areas: First
is, Instrumental; where people want to get some clear aim.32 It means that a large
amount of the reader integrate all the information that be found in the text to get
30
Penny Ur, A Course in Language Teaching; Practice and Theory, (New York, Cambridge University Press, 1996), p. 150.
31Jo McDonough and Christopher Shaw, Material and Method in ELT; Teacher’s Guide,
(Oxford: Blackwell Publishers, 1993), pp. 102—103.
32
the reader‟s goal, it is to get the information or the pleasure. Meanwhile, reading to write and reading to critique texts is the ability to build and critique information
from text, and they represent common academic tasks that call upon the reading
abilities needed to integrate information.
Second, as a pleasurable; thus people read magazines or spend hours
buried in the Sunday paper.33
Its assumption is in line with Francoise who also stated that, “there are two main reasons of reading: reading for pleasure and reading for information (in order to find out something or in order to do something with information you got”.34
Meanwhile Larry A. Harris figured out the purposes of reading as follows:
Just as the reader must adapt his reading to meet various purposes, he must also adjust his reading rate. The answer to a specific question concerning supporting detail will require the reader to skim for the right section and then read that section carefully for the correct answer. Following directions calls for slow, careful reading, as does reading an account of a scientific experiment. Recreational reading and newspaper reading often call for a rapid rate, but usually not as fast as skimming.35
Based on that, it is a common reading that usually held by the reader, they
usually use scanning technique in reading to search for simple information such as
looking for the time, name, place, etc. Not only scanning, but also skimming is
used to search the information for instance, getting the writer‟s purpose of the passage. Shortly, people read for many purposes. Some of them read for pleasure
and some read for getting information in which different purposes gain different
technique used. In addition, it is essential that reading for general comprehension
is the main goal of reading where most of the reader read the text to get general
comprehension of it. They do not need to analyze the structure or to know the
exact meaning of the words only get what the message of the writer.
Moreover, the different purposes of reading are also mentioned by William
Grabe and Federicka L. Stoller divided into seven purposes those are: reading to
33
Ibid. p. 201.33
34 Francoise Grellet, Developing Reading Skill: A Practical Guide to Reading Comprehension
Exercise, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1996), p. 4.
35Larry A. Harris, Reading Instruction; Diagnostic Teaching in the Classroom, (New York: Richard
search for simple information, reading to learn from texts, reading to integrate
information, write and critique texts, and reading for general comprehension.36
In conclusion, related to the purposes stated by many experts in language
above the conclusion the purposes of reading are as the essential purpose is to get
new information. Again, it has a purpose that reading is for enjoyment. Such as
someone reads the magazine, novel, newspaper and so on. Generally, reading
purposes as mentioned above is to comprehend and understand the printed
material, either getting information or pleasure. For instance, when the reader
reads the passage for pleasure they do not need to know the exact meaning of
certain word in order to get the message from the text.
3. The Kinds of Reading
There are some explanations about kinds of reading. According to
Huebener, he classified reading into intensive or extensive, it may be a classroom
activity or a supplementary exercise, and it may be done aloud or silently.
Then he adds that Intensive reading, whether silent or oral, is a controlled activity, carried on under the guidance of the teacher. It involves focusing upon new words and expressions, so that comprehension of the content may be facilitated. Extensive reading, on the other hand, is not concerned with the detailed study of words and structures.37
Moreover, another linguist Christine Nuttal divided reading into two
kinds: intensive reading and extensive reading:38
a. Intensive Reading
Intensive reading involves approaching in text under the close guidance of
teacher or under the guidance of a task, which forces the students to pay great
attention to the text.39
Hence, it is used to gain a deep understanding of a text, which is important for readers. “The aim of intensive reading is to arrive at a profound and detailed understanding of the text: not only of what it means, but
36
As quoted by Michael Grabe and Federicka L. Stoller in Nida Husna, Step by Step to Reading Skill Step 1, (Jakarta: Englsih Department, 2000), pp.9—10.
37Theodore Huebener, How to Teach Foreign Languages Effectively, (NY: New York University
Press, 1999) p. 49.
38Christine Nuttal, Teaching Reading Skill in a Foreign Language, 1998 p.38. 39
also how the meaning is produced.”40
For this kind of purpose it is better to teach
the students from a shorten text and develop step by step to a longer one. This
called also reading for accuracy.
b. Extensive Reading
“An extensive reading is suitable for reading to have a general idea of a text. The skimming process takes a prominent role.”41
Usually skimming relates to
longer text, where there are words that need special attention. It is appropriate in
reading a novel, magazine, or another text, which does not need full attention to a
word or a sentence.
Intensive reading and extensive reading are complementary and both are
necessary, as well as other strategies, which perhaps fit into neither category. The
labels indicate a difference in classroom procedures as well as a difference
purpose.42
Thus, in mastering the kind of reading including intensive reading and
extensive reading the reader should exercise their reading more and more. In order
to exercise their reading they should know the technique in reading. These
techniques help them to get better comprehension of the passage.
Meanwhile, A.H. Urquhart and C.J Weir distinguish reading became five
kinds. They are Search reading, Skimming, Scanning, Careful reading (at the
global level) and Browsing.43
1. Search reading.
2. Skimming.
3. Scanning.
4. Careful reading.
5. Browsing.
In the following, the writer would like to explain concerning the five
reading differences above; First, is search reading. It is used to locate information
40
Ibid. p.38.
41Ibid. p.38. 42
Ibid. p.23.
43 A.H Urquhart and C.J Weir, Reading in a Second Language: Process, Product and Practice,
on predetermined topic.44
to grasp the meaning of the text, a reader is sought to
gain the ability in interpreting the text meaningfully where he needs prior knowledge to assist him in making sense of the author‟s message.
Second, is skimming. Skimming is viewed as “the ability to process large
quantities of materials very rapidly in order to read for a specific purpose, the location of the main idea.”45
Skimming is a quick reading for the general drift of a
passage. It is an activity which is appropriate when there is no time to read
something carefully or when trying to decide it careful reading is merited. It is
also a great way to review material that the reader read before.
Third, is scanning. “Scanning is an excellent technique for reviewing to
make sure that you have mastered and understood the relevant supporting details.”46
For example, in finding out the supporting details of a text, we need to
focus on the facts we want and locate them quickly with a minimum effort.
Fourth, is careful reading. This is the kind of reading favored by many
educationalists and psychologists to the exclusion of all other types.47
Actually, it
is involved non-fixion reading types to select the printed materials to gain specific
knowledge or study. And the last but not least is browsing in which it is to
describe the sort reading where goals are not well defined and parts of text may be
skipped fairly randomly.48
In the reality, browsing can be carried out through
internet just by inserting the keywords and just looking the highlights then it can
be found many kinds of reading text.
In conclusion, the kinds of and purposes of reading will ease the readers in
reading appropriate text. That is why they have to decide and know exactly what
kinds of reading text they would like to read because in one reading text may have
multiple purposes in which for each purpose has its own reading technique.
Indeed, the kinds of reading texts have close relationship with its purposes to
encounter variety of reading technique.
44
Ibid. pp. 101—103.
45
Martha J. Maxwell, Skimming and Scanning Improvement: Section 2 Exercises, (Berkeley: McGraw-Hill Book Company, 2000), p. 1.
46Ibid. p. 2. 47
A.H Urquhart and C.J Weir, Reading in a Second Language: Process, Product and Practice, pp. 101—103.
48
C.Mind Mapping
1. The General Concept of Mind Mapping
There are many ways to teach genres. Mind mapping is one of good
techniques for students or the readers to grasp easily the meaning of the text or
would like to recall the information about the text.
Actually there are some definitions about mind mapping. But before that, we have to know previously what the “min mapping” terminology. Based on Oxford dictionary, mind is the thoughts, interest, etc.49
In other words, mind is
defined as the ideas or opinions. Map is a drawing to describe or give information
about something especially the way it is arranged or organized.50 Furthermore,
A.S. Hornby said that:
Mind mapping involves the left and the right brain which is in the left brain mind mapping involves some aspects that should be mastered such as word, number, logic, detail, etc. In the right brain mind mapping involves imagination, daydreaming, rhythm, etc.51
So that, the writer concludes that mind mapping can be ensured as a
creative note taking that draws the correlation ideas which make one united
through picture, symbol, keyword, and color. Indeed, mind mapping can solve the
learning problems that sourced from the ineffectiveness of the use both brains. It involves student‟s brain to identify the keyword and to recall what have been written.
Meanwhile, Tony Buzan says that Mind Mapping is a creative note taking, effective, basically it means map someone‟s ideas.52
Its form is a diagram to
represent the ideas, words, or other items which are correlated and arranged around a central keyword. Tony Buzan‟s statement is in line with the linguist Sutanto Windura who said that mind mapping, is a graphic technique which
allows the writer to explore the whole brain ability for the needs of thinking and
49
A.S Hornby, Oxford Advanced Learner’s Dictionary of Current English, (New York: Oxford University Press, 2003), p.844.
50
Ibid. pp. 815 & 844.
51Sutanto Windura, BLI, Mind Map (Langkah Demi Langkah), (Jakarta: Elex Media Komputindo,
2008), p. 5.
52 Tony Buzan, Buku Pintar Mind Map, Translt. From The Ultimate Book of Mind Maps by Susi
studying.53It this sense, mind mapping is a technique used to increase the reader‟s
thinking. It is not only for educational need but also for other business, work, fun,
and so on.
In accordance with those statements above, mind mapping is a
revolutionary new note taking;54
where many educational experts use it in
teaching learning activity. Mind mapping can help students to plan, to
communicate, to be more creative, to economize the time, to center the attention,
to arrange and to classify the ideas.55
Based on that fact, mind mapping would be
effective for the students to comprehend the texts including descriptive text.
Next, according to Windura, mind mapping is also considered as a technique that enables us to explore all our brain‟s skill for thinking and studying.56 It means that mind mapping can make our brain active, not only the
left hemisphere but also the right hemisphere. Consequently, mind mapping can overcome all the problems of study that appear from the unbalance of brain‟s usage.
Mind mapping is a diagram used to represent words, ideas, tasks, or other items linked to and arranged around a central key word or idea.
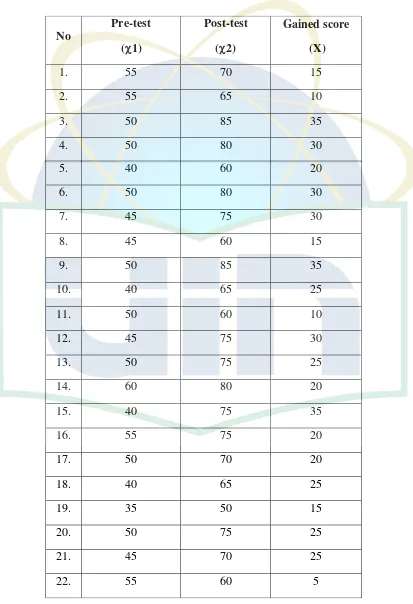
Buzan views that Mind Mapping involves visualizing an issue, problem, subject etc. The subject of the Mind Map is dropped into the centre, thick branches are drawn to denote key themes and secondary branches are added to indicate subthemes. Branches and sub branches are clearly labeled either with key words or with graphic representations. Linkages and relationships are indicated graphically, and use of color and pictures is encouraged.57
Based on that explanation, mind mapping may also aid recall of existing
memories because mind maps‟ elements arrange intuitively according to the
importance of the concepts, and are classified into groupings, branches, or areas,
with the goal of representing connections between portions of information. The
example of mind mapping as following:
53Sutanto Windura, “Mind Map Langkah Demi Langkah”, 2008, p.16. 54
Tony Buzan, The Speed Reading Book,2010, p.145
55Susi Purwoko, “
Buku Pintar Mind Map”, (Jakarta: Gramedia Pustaka Utama, 2010). P.6.
56Sutanto Windura, BLI, Mind Map (Langkah Demi Langkah), 2008, p. 16. 57
Figure 2.1
Mind Mapping
All mind mappings have some things in common. They have a natural
organizational structure that radiates from the center and use lines, symbols,
words, color and images according to simple, brain-friendly concepts.58 The figure
above can be further explained that there are some essential characteristics of
mind mapping.
Those are The main idea, subject or focus is crystallized in a central image. The main themes radiate from the central image as 'branches'. The branches comprise a key image or key word drawn or printed on its associated line. Topics of lesser importance are represented as 'twigs' of the relevant branch. The branches form a connected nodal structure.59
In sum up, a mind mapping is often created around a single word or text,
placed in the center, to which associated ideas, words and concepts are added.
They generally take a hierarchical or tree branch format, with ideas branching into
their subsections. Besides, mind mapping as a useful technique improves the way
you take notes, and supports and enhances your creative problem solving. It
means that mind mapping can quickly identify and understand the structure of a
subject, and the way that pieces of information fit together, and it can encourage
58Ibid. p.5. 59
[image:31.595.106.527.120.388.2]creative problem solving, and hold information in a format that your mind finds easy to remember and quick to review.
2. The Techniques of Using Mind Mapping
In this part is what are needed and how to implement the mind mapping.
According to SutantoWindura, he suggested to prepare the materials used to
implement the mind mapping such as following:
a. Paper
White
Empty Paper
Minimum size A4 (21 x 29.7 cm) b. Crayon or colored marker
Minimum color is three color
Use color variation like thick or thin. c. Imagination
d. The brain itself.60
The leading authority on mind mapping is Tony Buzan who further
illustrated toward the following basic rules for creating mind mapping
1) Read the story, and make a keyword for each schematic structure includes orientation, sequence of events and reorientation of recount text.
2) Start in the center with an image of the topic on a piece of paper. 3) Use images, symbols, codes, and color to complete the keyword.
4) Make the lines are connected each other, begin from the central image. The central lines are thicker, organic and flowing, becoming thinner as they radiate out from the centre.
5) Use one keyword for each line.
6) Make the connection lines are arched not straight.
7) Make the lines the same length as the word/image they support.61
Besides, we can improve our mind maps through developing our own
conventions to take them further. The following suggestions may help to increase
the effectiveness of mind mapping by adding the single words or simple phrases
for information, using color to separate different ideas, using symbols and images,
60
Sutanto Windura, BLI, Mind Map (Langkah Demi Langkah) 2008, p. 33.
61 Tony Buzan, Buku Pintar Mind Map, Translt. fromThe Ultimate Book of Mind Maps by Susi
and using cross-linkages.62We may use single words or simple phrases for
information where the single strong words and meaningful phrases can convey the
same meaning more potently. Print word, Joined up or indistinct writing can be
more difficult to read. Use color to separate different ideas in which this will help
you to separate ideas where necessary. It also makes your mind mapping easier to
remember. Color also helps to show the organization of the subject. Use symbols
and images, where a symbol or picture means something to you, use it. Pictures
can help you to remember information more effectively than words. Using
cross-linkages: information in one part of the mind mapping may relate to another part.
Here we can draw in lines to show the cross-linkages. This helps us to see how
one part of the subject connects with another.
In conclusion, mind mapping is really suitable to memorize and
understand the materials though picture, symbol, color, and keyword. Besides, we
can use all the suggestions above about creating and improving o produce the
effective mind mapping. Further, we can develop our mind mapping based on our
creativity as well.
D. Previous Studies
1. Studies on Descriptive Text
The first study, „Teaching descriptive text by using communicative language teaching (CLT) compared with the grammar translation method
(GTM)’.63 The method of this study was experimental research. For experiment class was taught by using CLT, and control class was taught by using GTM. The
data is taken and analyzed quantitatively to find the effectiveness of teaching
methods. At last, the result of the study was experiment class which taught by
using Communicative Language Teaching simply as know with Communicative
Approach was more effective than control class taught by using Grammar
Translation Method. The calculation of score experiment class was higher than
control class. From the explanation, the writer concluded that the application of
62Ibid. p.15—16. 63
CLT in teaching descriptive text was more effective than GTM. According the
processing data, the writer also got conclusion that to (test) is higher than tt
(table). In other words, there was a significant difference between teaching
descriptive text by using CLT and GTM.
The second study, „The Effectiveness of Teaching Descriptive by Using
Group Work’.64
Here, the writer tried to implement the technique of group work in
teaching descriptive text compared with the explanatory method. The method used
in this study was the experimental method which had the objective of finding out
whether group work as a strategy of teaching was effective in teaching reading or
not. In this research, the writer also tried to find out whether the students who
learned reading through group work showed better achievement than the students
who learned reading through explanatory method. In the other words, the using of
group work in teaching reading was more effective than using of explanatory
method in teaching reading (control class) to the students' achievement in the
second year students of MAN Batujaya, Karawang.
The third study, “The Effectiveness of Learning Reading through
Collaborative Learning”65
The design of this study was pre-experimental research
because it is intended to describe the effectiveness of learning descriptive text
through collaborative learning. Besides, this study was included in quantitative
research; the researcher used some numerical data which analyzed statistically.
After the writer did the research at the second grade students of SMAN 8 South
Tangerang, she got the result of the research; they are (1) the implementation of
collaborative learning in learning descriptive texts was applied well. It could be
known from the result that to score was higher than tt score obtained from the
result of calculating, the alternative hypothesis (Ha) was accepted and the null
hypothesis (Ho) rejected. It meant that Collaborative Learning was effective in
learning descriptive text at the second grade students of SMAN 8 South
64
Neneng Suraeha, The Effectiveness of Teaching Descriptive by Using Group Work; An Experiemental Study in the First Year of MAN Batu Jaya Karawang, (Jakarta: Perpustakaan Utama UIN Jakarta, 2009), p. vii.
65
Tangerang, (2) The improvement of students‟ achievement in learning reading before and after using collaborative learning was significance enough.
2. Studies on Mind Mapping
The first study, “The Implementation of Mind Mapping in Improving
Students’ Reading Comprehension of Recount Text”.66
This research was based on
the last observation result that the students still hard to comprehend a recount text.
This research was categorized as Classroom Action Research (CAR). It was carried out to solve students‟ problem in comprehending a recount text. The CAR design that used in this research is Kurt Lewin‟s design; it consisted of two cycles those were: cycle 1 and cycle 2. Every cycle consisted of four phases those were:
planning, acting, observing, and reflecting. The subject of this research was the
students of class VIII-II of MTs Al-Muhtadin Bekasi. In collecting the data, this
research used observation, interview and test. Based on the result and the
discussion of this research, it could be said that the implementation of mind
mapping in teaching reading comprehension of recount text was success since the
criteria of success were achieved.
The second study, “Improving Students’ Reading Comprehension through
Mind Mapping”67
This research was conducted to 35 students of class VIIID of
MTs Manaratul Islam Jakarta. The researcher used Classroom Action Research (CAR) to solve students‟ problem in understanding narrative text. The Kurt Lewin‟s model which consisted of four phases, planning, acting, observing and reflecting was implemented in this study. The findings of this study showed that
the students improved their understanding of narrative text during teaching and
learning process by using mind mapping technique. It was proven by the data
which derived from this study. First, from the observation, it could be seen that
the students were more active and interested in learning narrative text and could
answer the questions than has been given. Then data from interview result showed
66
Siti habibah Egiyantinah, The Implementation of Mind Mapping in Improving Students’ Reading Comprehension of Recount Text; A Classroom Action Research in the 8th Grade Students at MTs Al-Muhtadin Bekasi, (Jakarta: Perpustakaan Utama UIN Jakarta, 2010), p. xi.
67
that students‟ understanding of narrative text has improved. Last, from the test result. There were three tests conducted, those are pre-test, test 1 and post-test 2. The improvement of students‟ understanding of narrative text can be seen clearly in the improvement of their achievement in pre-test and post-test.
The third study, “Teaching Narrative Text by Using Mind Mapping
Technique”68
In this study, the writer acted as the only researches on teaching
reading narrative using mind mapping technique in the second grade SMP Lab
school Kebayoran Jakarta. The purpose of the research was to find whether and
how mind mapping motivates students in narrative text. The result of the study
was the students seemed to be interactive in learning narrative text by using mind
mapping technique. It could be proven from their improvement score from the
pre-test to post-test. Besides, through this technique, the teacher became more
creative and found a new strategy to teach reading texts.
3. Studies on Descriptive Text by Using Mind Mapping
The first study, “Improving Students’ Descriptive Writing through Mind
Mapping”69 This study was carried out to solve the students‟ problem in reading
comprehension. The method used in this study was Classroom Action Research
(CAR). The classroom action research design applied in this study was a
collaborative classroom action research. This study was conducted following
Kemmis and Taggart model with the following procedures of the action research:
planning, acting, observing, and reflecting. The study carried out in two cycles.
Each cycle consisted of three meetings. The data gathering in this study through
interview, observation checklist, field notes questionnaire and test. The results of the study showed that there was improvement of the students‟ ability in writing descriptive paragraph. Most of the students gradually gained good scores at the
end of each cycle. The score of Minimum Mastery Criterion- Kriteria Ketuntasan
Minimal (KKM) of English lesson was 70 (seventy). Furthermore, the class
condition during teaching learning process was also quite good. In addition there
68
Siti Ulfah, Teaching Narrative Text by Using Mind Mapping Technique; A Case Study in the Second Grade of SMP Labschool Jakarta, (Jakarta: Perpustakaan Utama UIN Jakarta, 2011), p. vii.
69
was a positive response from the students and the English teacher about implementing the action. In conclusion Mind Mapping can improve students‟ descriptive writing ability and it can increase students‟ participation.
The second study, “The Implementation of Mind Mapping in Teaching
Descriptive Text”70
This study was categorized as the Classroom Action Research (CAR) method in which to identify and to solve the problem on students‟ reading comprehension. The writer implemented the Kurt Lewin‟s design which consisted of four phases. Those are planning, acting, observing, and reflecting. Meanwhile,
the data were derived among from the test (pretest and posttest), interview, and
observation. The findings of this study were: related to the test result, there was
significant improvement of students‟ reading score after using mind mapping; where almost eighty percents of students who passed the KKM (2) related to the
observation result showed that the students were more active and interested in
learning reading activity in the classroom. Indeed, they could analyze the
schematic structures of descriptive text into mind mapping. (3) related to the interview result, it could be known that the students‟ reading comprehension in term of descriptive text improved and also assisted the teacher in finding the
appropriate strategy in teaching reading descriptive text.
The third study, “Teaching Descriptive Texts Through Mind Mapping”71
In this study, the writer was interested in describing the condition of the teaching
descriptive text through mind mapping at First Grade of SMP Islam Al-Fajar
Pamulang. It includes the teaching preparations, the instructional material used by
the English teacher, and the evaluation made by the English teacher. The purpose
of this study is to find the empirical evidence of the effectiveness of teaching
descriptive text using mind mapping compared with the use of Grammar
Translation Method. The design of this research was experimental study. In
selecting the sample is used purposive random sampling. The data collecting was
done by the observation and collecting the documentation. Based on the analysis,
70
Siti Khoerunnisa, The Implementation of Mind Mapping in Teaching Descriptive Text; A Classroom Action Research in the First Year of SMA Bina Harapan Cirebon, (Jakarta: Perpustakaan Utama UIN Jakarta, 2011), p. ix.
71Robiatul Adawiyah, Teaching Descriptive Texts Through Mind Mapping; An Experimental Study
the researcher found that to >tt = 47.4 > 1.99 in significance level 5% and to >tt =
47.4 > 2.65 in significance level 1%. It meant there was obvious difference
between average score from the result of teaching descriptive text in experiment
class and controlled class. It could be inferred that teaching descriptive text was
more effective by using mind mapping than GTM.