THE EFFECT
OF THE STUDENTS’ ATTENDANCE IN
ENGLISH LANGUAGE COURSE ON THEIR
ACHIEVEMENT
(Causal Comparative and Correlational Study at the Second Grade of SMP YPI Bintaro)
By:
Nian Chairani
107014000240
DEPARTEMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TA
RBIYA AND TEACHERS’ TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
i
ABSTRACT
NIAN CHAIRANI. 2014, The Effect of the Students’ Attendance In English Language Course on Their Achievement (A Case Study at The Second Year Students of SMP YPI Bintaro), Skripsi, English Department, The Faculty of
Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training, Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta.
Key word: Students’ Attendance, English Language Course, Achievement.
The objective of this study was to know the empirical evidence about the effect of the students’ attendance in English language course on the students’ achievement in English language learning in the classroom. The limitation of the problem was focusing on the difference between the student who always attend the English language course and the students who rarely attend, and after that the writer also analyzed the correlation between the students’ attendance in English
language course and the students’ achievement in English language learning. The object of this research is all students at second grade of SMP YPI Bintaro academic year 2013-2014 with the total students sample is 40 students. She used observation and documentation to get the data, and to know the differentiation of the variables she used t-formula and to know the correlation of the variables she used product moment formula.
The result showed that t-result is 2.952, means that t-result > t-table = 2.952 > 2.70 in significance level 5%, means that the difference between the students who always attend and the students who rarely attend are significantly different. And the result of the product moment formula is 0.40, means rxy >
r-table = 0.40 > 0.32 in significance level 5%, so in this level Ha (hypothesis alternative) is accepted and Ho (null hypothesis) is rejected, means that between students attendance in English language course and students achievement in English language learning, but in significance level 1% rxy < r-table = 0.40 <
ii
Students of SMP YPI Bintaro), Skripsi, Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Ilmu Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, UIN Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta.
Key word: Kehadiran, Kursus Bahasa Inggris, Prestasi, Pembelajaran.
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui bukti empiris tentang efek kehadiran siswa di kursus bahasa Inggris terhadap prestasi belajar di dalam kelas. Pembatasan dalam permasalahan ini adalah pada perbedaan antara siswa yang selalu hadir di kursus bahasa Inggris dan siswa yang jarang hadir, tidak hanya itu penulis juga menganalisa apakah kehadiran siswa di kursus bahasa Inggris berpengaruh terhadap prestasi belajar siswa di dalam kelas. Objek dari penelitian ini adalah siswa kelas II (VIII) SMP YPI Bintaro tahun pelajaran 2013-2014 dengan total sampel yang di ambil adalah 40 siswa dari jumlah keseluruhan siswa 286. Untuk mendapatkan data yang dibutuhkan, penulis melakukan observasi dan dokumentasi. Dan untuk mengetahui apakah ada perbedaan atau tidaknya penulis menggunakan rumus tformula dan untuk mengetahui apakah ada korelasi antara
variable X dan variable Y penulis menggunakan rumus product moment.
Hasilnya menunjukan bahwa hasil perhitungan t adalah 2.952, dengan demikian bahwa hasil t > t-table = 2.952 > 2.70 pada taraf signifikan 5%, berarti bahwa ada perbedaan prestasi bahasa Inggris yang signifikan antara siswa yang rajin hadir di kursus bahasa Inggris dengan siswa yang jarang hadir. Kemudian hasil dari perhitungan korelasi menggunakan rumus product moment adalah 0.40, berarti bahwa di level signifikan 5% rxy > r-table = 0.40 > 0.32, menunjukan
bahwa Ha (hipotesis alternatif) diterima dan Ho (hipotesis nol) ditolak, yang berarti ada hubungan antara kehadiran siswa di kursus bahasa Inggris dengan prestasi belajar bahasa Inggris mereka di dalam kelas. Akan tetapi di level signifikan 1% menunjukan bahwa rxy < r-table = 0.40 < 0.412, dan pada level ini
iii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Alhamdulillah, Praise and gratitude be to Allah, Lord of the worlds Who
has given the Mercy and Blessing to the writer, so that this “Skripsi” can be
finished completely. Sholawat and Salambe upon our prophet Muhammad
“Shollahu ‘alaihiwasallam”, his families, companions, and his followers.
The writer would like to express his greatest appreciation, honor, gratitude and love to her beloved mother who has been a great motivator and inspiration in
every condition, also to her father who has given her many inspirations and supports and her big family. She thanks to them for their pray, guidance, patience, and encouragement to motivate the writer to finish her study.
Also, on this occasion,the writer would like to express his gratitude to Mr.Dr. Atiq Susilo, M. A. as the writer’s advisor who had kindly spent his time to give his valuable advice, guidance, corrections, and suggestions in composing this
“Skripsi.”
Furthermore, her greatest gratitude also goes to:
1. Alllecturers of English Education Department, for teaching the precious knowledge, sharing the values of life and giving the unforgettable study experiences.
2. Mr. Drs. Syauki, M.Pd., as the chairman of English Education Department.
3. Mr. ZaharilAnasy, M.Hum., as the Secretary of English Education Department. Also, her thanks is given to the staffs of English Education Department, especially for Mrs. Aida AinulWardah, S.Pd. who always gives excellent service and contribution to the writer.
4. Mrs. Nurlena Rifa’i, M.A., Ph.D., the Dean of Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers Training.
iv
6. Her friends in LDK UIN Syahid and Department of English Education. 7. The people in BPZISand LP3M2-YPI Bank Mandiri for the support and
motivation to finish this “Skripsi”.
Finally, the writer realizes that this “Skripsi” is still far from being perfect.
Constructive criticism and suggestion would be welcomed to make it better. I hope that this Skripsi could be useful to other people, especially to people in education area.
Jakarta, August24th, 2013
v
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ABSTRACT... i
ABSTRAK... ii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT... iii
TABLE OF CONTENTS... v
LIST OF TABLES... vii
CHAPTER I : INTRODUCTION... 1
A. Background of the Study... 1
B. Formulation of the Problem ………... 4
C. Objective of the Study... 4
D. Method of the Study……... 4
E. Significance of the Study... 5
CHAPTER II : THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK... 6
A. English Language Learning ... 6
1. Theories of Learning... 6
2. English Language Skills………... 11
B. English Language Course... 14
General Concept of English Language course…….... 14
C. Students’ Learning Achievement ... 18
D. Framework of Thinking ………. 20
E. Hypothesis of the Research ……… 21
CHAPTER III : RESEARCH METHODOLOGY... 22
A. The Place and Time of the Research... 22
B. The Method of the Study ……….. 22
C. The Population and Sampling ……… 23
D. The technique of Collecting Data ……….. 24
E. The Technique of Data Analysis ………24
CHAPTER IV : RESEARCH FINDING ……… 28
vi
B. Suggestions... 39
vii
LIST OF TABLES
[image:11.595.115.514.205.596.2]Table 3.1 Class Data of VII SMP YPI Bintaro …………... 23
Table 3.2 Observation Sheet of English language course activity ……….. 25
Table 3.3 Interpretation number of correlation index “r” Product Moment ... 29
Table 4.1 Score of students’ attendance in English language course…………. 31
Table 4.2 Students’ score at Final test………. 33
Table 4.3 List of Students’ score classification in English language course
attendance ……… 35
1
A. Background of the Study
English language has the important role as a subject in Indonesian school. The Ministry of National Education (MUNE) has adopted English in Indonesia as the first foreign language, meaning that if an international communication is needed the first priority and choice therefore will fall on English, not French, Arabic, or Dutch.1 So that, from the MUNE’s rule English become the compulsory subject in the curriculum, it is thought from junior high school up to university level. English in Indonesian school become one of the important
subjects, and it is implied that English included in “UN (Ujian Nasional)”.
However, teachers now are responsible to give the students a quality instruction not only for academic proficiency but also for the attainment of progress in
English language acquisition. Students have to be skilled for the use of English language for not only in grammar or structure, or in the passive way, but also for reading, speaking, writing and listening in academics contents areas. As Harmer says English has four basic language skills to improve; those are speaking, writing, listening, and reading2. Those skills are the basic for the students; teacher can see the improvement of the students according those skills. Those also
support the development of students’ second language proficiency in general.
It means that there will be many school get strive to improve their
students’ ability in English language learning not only in class activity but also in out of class activity. Teaching English effectively that mean teacher teach the subject that motivates the students and provides the useful and relevant language
1
Mulyanto Soemardi (Professor in Applied Linguistic), “English for specific purposes (ESP) is it really?”, Paper Abstracts in The 55th TEFLIN International Conference, Jakarta, December 5th, 2007, p. 8 (tidak dipublikasikan)
2
2
practice, and helps the learners gain confidence in using English.3 Teaching English may not only focus on the book instructions but also on the situation of the students and also on the reality of the students until then students have confidence when practicing English language in their real life.
Today, some students also learn English may not because they like English, probably the greatest number of language student in the world do it because it is in the school curriculum whether they like or not.4 Feeling also play the major role in learning the language and need to be taken seriously in planning
the successful language learning campaign.5 From that situation Indonesian school must do extra way to make their students master in English language, not only in the learning class condition but also in out of the class. We can do this by creating a positive attitude to the language and its speakers, and we can try to be certain that we are supportive and encouraging to our students rather than critical and destructive.6 Fun learning is needed to make the student feeling happy when learn it. But many school in Indonesia still use conventional method, teacher teach then
go, some of them don’t pay attention on the students’ development in knowledge
or another aspects.
According to Ilza Mulyani, english teacher should have a good competences in order to be able to improve their students’ competency on the stages of literacy of performative, functional, informational, and epistemic (as
appropriate as the students’ class). In the stage of performative, student is able to
read, write, speak, and listen to the symbols that used. And on the functional stage, a student is able to use the language to fulfill their daily needs, such as read the newspaper, manual book. And on the informational stage a student is able to access the knowledge by using his own language skill. And the last is epistemic,
3
Jack C. Richard and David Bohlke, Creating Effective Language Lesson, (New York: Cambridge University Press, 2011), p. 1.
4
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English Language Teaching, (New York: Longman Publishing, 1996), p. 1.
5
Don Snow, From Language Learner to Language Teacher, (Michigan: McNoughton & Gunn, Inc., 2007), p. 23.
6
which a student is able to apply the language to explain the knowledge he has.7 It means that student has his own age in mastering the language. In the same book Mulyani explains that at SD/MI (elementary school) the teacher guides the student to a performative stage, and in more specific they are guided to the situation or interaction that happened in the classroom, and also preparing to study in SMP/MTs. Then at SMP/MTs they should have the target to achieve the functional stage, student can communicate both written and oral to solve their daily problem. And at SMA/MA, students are hoped to get informational stage,
and they are prepared to continue to university because at university student must have achieved the literacy of epistemic.8 To see that purposes, studying the
language, teachers in Indonesia have to work hard in improving the students’ skill.
Based on this phenomenon, YPI Bintaro tries to support the students in improving their English competence through English language course. YPI Bintaro creates this course as the additional subject beside of the English learning
in the classroom. Students must enter this course even they don’t like this subject.
As the result students joining the course just because the school regulations that student should involved to that activity. And the impact, this activity may be the
useless thing for some students who don’t have willingness on English language
subject. Because in learning the language students who have the strong desire to learn and who feel good about their progress are far more likely to continue working hard in the learning language.9 The other impact of this case is the students who have the desire in English language learning will have the good and fast improvement than the students who don’t have; they will be slower in catching the subject and understand it.
The writer is interested to do the research in that school to know whether English course influence the students’ achievement in English language learning.
7
Ilza Mayuni, Peningkatan Mutu Guru Bahasa Inggris-Melalui Pendidikan dalam Jabatan, (Bandun:, Lubuk Agung, 2007), p. 27-28.
8Ibid., p. 28 9
4
And the outcome of student achievement was selected because the ultimate goal of effective instruction is increased student achievement.
B. Formulation of the Problem
Based on the problem presented above, the writer is interested in analyzing how effective English Language Course is, and its influence to the students' interest in learning English language.
The problems of this research can be formulated into specific questions below:
“Is there any difference between students who always attend the English language course and the students who rarely attend the course?
“Does English language course attendance influence the students’ achievement in English language learning?”
C. Objective of the Study
The objective of this study is to know the empirical evidence about the difference students who always attend the English language course and the students who rarely attend the course, and to know the empirical evidence about
English Language Course attendance influences the students’ achievement in English language learning.
E. Significance of the Study
The findings of this study are expected to contribute to: 1.Committee of English Language Course
To give them reference for more information and to improve the awareness of the students in the course activity.
2.English language Teacher
Motivated the student to learn English language and motivated the students to have the active role in their activity both in the English
3.Students
The writer hopes this study motivates the students to improve their English skill and their interest in English language learning. And also motivate them to attend the course continuously.
4.Readers and further researcher
6
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
This chapter discusses the theoretical framework explaining English language learning, English language course, students' achievement, framework of thinking and hypothesis of the study.
A.
English Language Learning
1. The Theories of learning
The word of learning is familiar with us; learning is such an activity to get
something new, learning is a process and the subject of it is learner. We may interpret the word learning freely, because there will be any definitions about learning itself; in learning not only one process was involved.
People use the word "learn" loosely, to mean that they have discovered something new about someone or something, or have acquired a new point of view.1 Although learning is important for people, but still many of them say it is undesirable and boring activity. Mostly for the young learner, they sometime feel boring with this activity.
By learning, actually people can change everything; in the other book learning is an enduring change in behavior, or in the capacity to behave in a given fashion, which results from practice or other forms of experience. (Shuell, cite in Schunk, 1991, p. 2)2. Someone who learn, they should be more mature, as they can applied what they have learned.
Learning takes place whenever and individual finds himself in a situation to which he cannot adjust through the utilization of customary mode of response, or whenever he must overcome obstacle that interfere with desired activities. The process of adjusting to or overcoming obstacles may take place more or less
1
Lester D. Crow & Alice Crow, Human development and learning (New York: American Book Company, 1956), p. 211.
2
unconsciously, without thinking much about what he is doing, the learner tries out one or another already formed habit of behavior until he hits upon satisfactory response. Much of what is called "school learning", however, is engaged in with more or less awareness of the reason for the learning, what is being learned, and how the learning is taking place.3 It mean that in school learner is adjusted in the one situation or condition, with a curriculum, place condition, and roles of study. Learners at school should be known why he goes to school and learns there.
In the same book, Lester D. Crow & Alice Crow wrote, learning is complex.
At one and the same time, an individual is (1) learning new skills or improving those that already are operating, (2) building a store information or knowledge, and (3) developing interests, attitudes, and ways of thinking.4 Those kinds of learning is happened to the people for what they actually do learning. When they learn, they have any purposes and ways.
Meanwhile Barry and King write in their book that Learning has some categories; there are cognitive learning, psychomotor learning, and affective learning.5 Cognitive learning refers to learning that is primarily concern with mental or intellectual process. Psychomotor learning refers to learning concerned with the development of bodily movement. And affective learning refers to learning that is concerned with personal and social matters.
As we see today that learning in the past has different way with learning today, as Alferd H. Gorman writes in his book that learning process is always changed. In the past, students knew nothing, then teacher gave them the knowledge because the teacher knew. The communication between them was one way at a time with the odd heavily weighted on the side of the teacher. The teacher teach by lecturing and demonstrating; then the learner would recite orally or on the paper so that the teacher could determine whether understanding had
take place.6 Then today, students are encouraged to question ideas in the now
3
Lester D. Crow & Alice Crow, Human development and learning, (New York: American Book Company, 1956), p. 212.
4
Ibid.,
5
Kevin Barry & Len King, op. cit., p. 19.
6
8
generally approved quest for “critical thinking”. Teachers are expected to have
good senses of humor, respect of, and for students, well develop habits of pair play, and approaches that are perceived as reasonable in students’ terms.7 In the next era, it will be to carry on activities that will cut through overformal, distrustful relationship. The whole child and the whole teacher come into the classroom. Each has individual values, attitudes, and characteristic ways of behaving and perceiving others.8
Learning, however, applies to a more conscious process of accumulating
knowledge of the features, such as vocabulary and grammar, of the language, typically in an institutional setting.9
In sum up, Learning is the long process in changing there are two activities in learning those are transferring the knowledge and accepting it. In its process learning should make the students get the new point of view of something, because learning condition is always changed so teacher have to aware on it. In learning often related to the method, time, students, condition and sometimes teachers’ role in the class also changes, teachers today not always as the main resources for the students. Student is more critical.
Learning is not only build the knowledge but also attitude and mentality. As a result of learning students are strived not only in improving knowledge but also they should have good attitude and strong mentality.
If we see the definition about learning, we can conclude that learner is someone or the group of the people who has the desires and the needs of knowing something in the some places in certain purposes.
Afterwards, after we knew the definition of learning, then we see about the definition of English language learners; it’s a subgroup of these students, who have been identified, through assessment, as having levels of English language
7
Ibid., p. 10.
8Ibid.
, p. 17.
9
proficiency and academic achievement that preclude them from assessing, processing, and acquiring unmodified grade-level material in English.10
A second language learner is different from a very young child acquiring a first language.11 Young children learn their first language in their daily activities, they listen to the language when they were a baby, and they listen it with a pleasure, they learn the language through the acquisition process. And it is different with the second language learners. Mostly in Indonesia, students learn language in their own country, as Lightbown and Spada write that the older
learners have to solve the problem and engage in discussion of the language.12 Learning related to the education. There is a relation among education,
learning and training, as Crow and Crow write on his book, “the terms education
may be interpreted to connote the process through which experience or information is gained, or it may be use to indicate the result of such training, or
the product of the learning process.”13
Abdurrahman writes Education is “transfer pengetahuan dan nilai.”
(Transfer knowledge and value). From both transfers can be achieved through learning and teaching process to get the whole of the materials aspect.
According to a definition formulated by a group expert for the dictionary of Education, education is,
“(1) the aggregate of all the process by which a person develops ability, attitudes, and other forms of behavior of practical value, in the society in which he lives; (2) the social process by which people are subjected to the influence of a selected and controlled environment (especially that of the school) so that they
may obtain social competence and optimum individual development.” (Reprinted
10
Margo Gottlieb, Assessing English Language Learners: Bridge from Language Proficiency to Academic Achievement, (Thousand Oaks: Corwin Press. Inc., 2006), p. 3.
11
Patsy M. Lightbown and Nina Spada, How Language are Learned,3rd Edition, (New York: Oxford University Fress, 2010). p. 29.
12Ibid., p. 30. 13
10
from Dictionary of Education, edited by Carter V. Good, copyright, 1945, by the McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc., New York.)14
From the entirely statement about learning, in summary, learning has the complex meaning, it also has the purposes, methods and ways. In learning
someone must have a new point and an evaluation, about what, why, and how it’s
happened or done. Learning can change everything; it can be he or another that impact should be prepared, in the behavior changing, for instance if he has a bad
thing in something, he should be better after he learn. People learn in a conscious way, so he knows the improvement after he learn.
Furthermore, the most fundamental realities of language learning is that
language is a tool of communication. Because most of the teacher doesn’t
encourage the students to see that English is a communication tools, they only focus on the memorizing vocabularies, grammar rules, and preparation for the test and never involves the language as a communication tools. Studying English may be exciting if the students are introduced to make the communication with a new world possible, allow the student to face-to-face with someone from the foreign country, read the books, world magazines and news, or even watch films and listen to the song in English. Learning English is mean the developing the ability to understand and interact with the world.15
2. English Language Skills
The language skills itself define to the productive skills and receptive skills.
a. Productive Skills
The word productive is an adjective form of word produce, produce has a
same meaning as create or make. If this is related to this language context, productive skills can be defined as language that produced. The productive skills are speaking and writing, because learners doing these need to produce language.
14
Ibid.,
15
They are also known as active skills. They can be compared with the receptive skills of listening and reading.16 In summary, why it is called as active skills, because when someone uses the language people can see the result of these activities.
And here are some definition about speaking and writing.
1) Speaking
According to Jones, “speaking is a form of communication, so it is important that what you say is conveyed in the most effective way. How you say
something can be as important as what you say in getting meaning across.”17 It’s
called speaking if people produce the sound with the meaning, if someone can understand about what the people say, so that it can be called as speaking.
Speaking is an interactive process of constructing meaning that involves producing and receiving and processing information (Brown, 1994; Burns & Joyce, 1997).18 Because it has a meaning, speaking should be an interactive way in communication, because in this process people can understand the meaning each other.
2) Writing
Lewin write on his book that writing is constructing the meaning through
the text.19 In the same book also he write that wring enable the students to think about, to process, to grow ideas about the topic we are teaching them, then writing enable the students to gain proficiency in a critically importanty skill; writing itself, which is obviously a key communication tool.
As we see that writing produce the word, not like as speaking, writing is
expressed the ideas inside the writers’ mind into written form.
White (editor) writes on the introduction of the book New Ways in Teaching writing, that “writing can be viewed as involving a number of thinking process
16
http://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/knowledge-database/productive-skills
17
Rhodry Jones, Speaking and Listening, (London: John Murray Publisher Ltd., 1989), p. 14.
18
http://www.cal.org/caela/esl_resources/digests/Speak.html
19
12
which are drawn upon in varied and complex ways as an individual composes, transcribes, evaluates and revises (Arndt, 1987; Raimes, 1985).”20 Like speaking, writing also produces the word, if speaking through the sound, writing explain it through the written form.
b. Receptive Skills
The receptive is receiving something then save it. In the language context, receptive skills are like we receive the information from the outside or the other
and after that we process it passively. And the activity that include in receptive skills are listening and reading, because learners do not need to produce language to do these, they receive and understand it. These skills are sometimes known as passive skills. They can be contrasted with the productive or active skills of speaking and writing.21
And below are a short definition about listening and reading.
1) Listening
Listening is assuming greater and greater importance in many foreign language context, which have until relatively recently focused their efforts on the development of writing skills.22 Listening is essential in teaching language; it’s not only as a receptive skill but also to the development of the spoken language proficiency. In listening student should get the idea from what/the information they listen to. Listening also can help the students in improvement of the vocabularies. In language learning for example, through listening students can improve their competence in pronounce the word, produce the word when they speak, and also listening skill make the communication between the people or students more effective and understandable.
20
Ronald V. White (Editor), New Ways in Teaching Writing, (Illinois: Teachers of English to Speakers of Other Languages. Inc. (TESOL), 1995), p. v. (an Introduction).
21
http://www.teachingenglish.org.uk/knowledge-database/receptive-skills
22
2) Reading
Reading is an interactive process that takes places between the text and the
reader’s processing strategies and background knowledge.23
Reading comprehension is a very complex activity. Like the eyes glance or move at the printed words, it is also happened in the readers mind, there will be so many words should be processed in the readers mind. Good in reading can be achieved through practice the lifetime. Reading is difficult, because one must work, one must accomplish multiple thing simultaneously. But good readers
actually have a strategy because their good skill on it.24
The simple view of reading proposed by Hoover and Gough is that reading is the product of decoding and comprehension. 25
Reading = decoding x comprehension
Language is both knowledge and skill. A second important truth of language learning is that it is mastery of a skill as much as acquisition of knowledge.26 That
means that students don’t enough to know the vocabulary and the grammatical
only, they also have to apply that knowledge in speech or writing, or comprehend the language with the speaker, and read the text. Language skills have the important roles in language learning. And it is a big part of language besides of language components. Students use those skills when they learn a language.
B.
English Language Course
1.
General concept of English language course
In the Barnhart Concise Dictionary of Etymology, course is;
“(n) probably before 1300 cours onward movement; borrowed from Old French cours, curs, from Latin cursus (genitive cursūs), a running race or course, from past participle stem curs- of curere to run. The sense of planned or
23
Kristin Lems etc. Teaching Reading to English Language Learners. 2010, p. 33.
24
Larry Lewin, Paving the Wayin Reading and Writing, (San Francisco: Jossey-Bass, 2003), pp. 2-3.
25
Naomi Flynn and Rhona Stainthorp. The Learning and Teaching of Reading and Writing.
(England:Wiley, 2006), p. 8.
26
14
prescribed series of classes, lectures, etc. is first recorded in English in 1605;
probably from French, found in the 1300’s and earlier. Earlier instances of the
phrase of course (literally, of or in the ordinary course) are from 1541, replacing earlier be cours with the same meaning (probably before 1300). –v. 1466, to pursue; from the noun.”
The term course somehow connects to the terms of curriculum and syllabus. Hutchinson and Waters (1987:65) have defined a course as “an integrated series of teaching-learning experiences, whose ultimate aim is to lead
the learners to a particular state of knowledge”.27
Course should have the specific objective of their students to what kind of skill the students will be brought, and also should know about what the students really need in their daily life. There are many students in the course activities, so that in teaching-learning process the teacher should be as smart as possible to handle the students to get its aims of the course.
In the course, student has specific subject to be learned, in English language context for example, in this condition student who join the English course they have the motivation on to be the good user of English language or another part of English language. There is a course because there is a syllabus; a syllabus design is a part of course development, and a course is part of curriculum. A courses or a course content is order by the syllabus also its specification.28 As mentioned before that course should have the ultimate aims, so that syllabus becomes the important role to achieve the aims. The syllabus can help the teacher as the guidelines in teaching-learning activities.
After we see the definition of the course then we continue to the course process, it is begun by planning, the planning include the considering the students, thinking of the contents, materials and the activity that included into the courses,
or everything that help the teacher to construct the good in teaching course.29 in
27
Kathleen Graves (ed.), Teachers as Course Development, (Cambridge: The Press Syndicate of the University of Cambridge, 1996), p. 3.
28Ibid., 29
constructing the course teacher should have the good planning of the teaching-learning activity, teachers plan in every aspect in the course process, not only the material that they will be taught but also plan in everything about the students condition and need.
In the courses, curriculum and syllabus may be the guide for the teacher to plan the materials, contents and activities. Beside of the syllabus, teacher also can plan by considering the past learning experiences, using the course books, and learning as teacher teach.30 It can be a suggestion for the teachers to reflect on the kind of experiences they are offering students and to consider how these relate to
the students’ general educational development. If particular kinds of classroom
roles, mental processes and types of content are continually being offered to students in the course.
Course process development is similar to that of curriculum development. Course development include planning a course, teaching it, and modifying the plan, both while the course is in the progress and after the course is over.31
The same book, Kathleen Graves writes that when teacher who is about to design a new course then asks whether there are any guidelines, whether there is any procedure to follow, and the answers hope is yes. No teacher wants to reinvent the wheel, if there is a procedure to follow, they will ask what it is. In the
course practice the answer of the question may be “yes” or “no”: yes, because
there is a guidelines, procedures, models, and principles to help the teacher to know the situation and the condition of the course itself or the students, those are also can help the teacher as a resources for their teaching and organizing the progress of the students, and no, because the guidelines is not a recommendation, because there no a procedure can guarantee the successful of the course. The situation can be different for each teacher, and also the teacher itself.
Courses program should have framework components. The framework components that suggested by Kathleen Graves are:32
30
Ibid., p. 4-6
31
Kathleen Graves (ed.), Teachers as Course Development, (Cambridge: The Press Syndicate of the University of Cambridge, 1996), p. 3
32Ibid.,
16
1) Needs assessment
The term need assessment involves find out what the learners know and can do and what they need to learn and do so that course can bridge the gap. It is not the value-free process, the teacher’s view influence to what the course is about,
the institutional constraints, and the students’ perceptions of what of what is being
asked of them.
2) Determining goals and objectives
Sometime we use the term goals and objective in or writing. But what they
are, and what the relationship between them is. Goals are the general statements of the overall, long terms purposes of the courses. And the objectives are a specific ways in which the goals will be achieved. The goals of course represent the destination; the objectives, the various points that chart the course toward the destination.
Setting the goals and the objective provides a sense of a direction and a coherent framework for the teacher in planning the course.
Teacher may ask what the appropriate goals and objectives are, but to know
it, teacher can see to the students. Teacher can analyze the students’ needs, the
policies of the institution, and the way of the teacher conceptualizes the content, among other factor.
There are for types of goals for language learners that proposed by Stem (1992), those are proficiency goals, cognitive goals, affective goals, and transfers goals. Proficiency goals include general competency, mastery og the four skills (listening, speaking, reading, writing), or mastery of specific behaviors. Cognitive goals include mastery of linguistic knowledge and cultural knowledge. Affective goals include achieving positive attitudes and feelings about the target language achieving confidence as a user of the language in one self as a learner. Transfers
goals involve learning how to learn so that one can call upon learning skills gained in one situation to meet future learning challenges.
But the main issues today are that many teachers do not formulate the goals and objectives at all or do only after having thought about what they will teach
and how. And another issue involves clarity with respect to students’ needs. If the
need is clear it may make the set goals is easier. 3) Conceptualizing content
Conceptualizing the contents is teacher figure out which aspect of the language and language learning she will include, emphasize, and integrate in her course. Many teachers still conceptualize the contents traditionally, that may be
experienced in their own learning, that content is grammar, vocabulary, and sentence pattern, it also supported by Richards and Rodgers (1986), two decades ago, language teaching was still heavily influenced by a structural view of language.
4) Selecting and developing materials and activities.
For the teacher, think about the material they will use, activities that their students will do, and techniques they will employ become the ideas to start the course not by determining the objectives or conceptualizing the content. Choosing material may mean they develop the new material for which there are no suitable materials, collecting variety materials, or adapting existing materials.
There are varieties of factors in choosing, developing or adapting materials considered by the teachers. And two of the most important are effectiveness in achieving the purposes of the course and the appropriateness for the students and the teachers.
Because of the lack of time that teacher has, most of teacher often prefer to choose the existing materials. Developing the materials and the activities for using them requires time and a clear sense of why they will be used, how and by whom. Developing materials requires time before, during, and after the course – for
preparing, using, and modifying them, respectively. 5) Organization of content and activities.
18
sequencing material and then at the overall organization of the course. The complementary of the sequencing is building and recycling. In deciding how to sequence the material, one considers building from the simple to the complex. And the principle of recycling materials means that students encounter previous material in new ways: in a new skill area, in a different type activity, or with a new focus.
6) Evaluation
For most teacher, evaluation means evaluation within the course: assessing
students’ proficiency, progress, or achievement.
How proficient student in listening is, whether student improve their writing skill, whether student has learned the English for their work place. Those are the evaluation. Evaluation in course also includes the evaluation the course itself. Whether the course is effective, and in what way. Evaluation not only linked to
the students’ assessment and progress, even though the student has good achievement after the course or the feedback on the effectiveness of the course.
If the students got the test well and has a progress then we said that the
course had been effective. And if the students didn’t have any progress they didn’t
do the test well, then we questioned the effectiveness of the course. Here the function of the evaluation, we evaluate the entire elements of the course, why the
student doesn’t achieve the target achievement of the course, why the student
doesn’t make the progress expected.
The course is evaluated to promote and improve its effectiveness and also to provide documentation for policy reasons, such as continued funding or retention in the curriculum.
Any part of course development can be evaluated. 7) Consideration of resources and constraints.
Resources and constraints are two ways of looking at the same thing.
the classroom activity. The second is knowing the students’ learning style because every students has different way in learning, they may have different interest and
abilities, so that it’s very important for the teachers to know the nature of the
language learning. The third make the communication as the major of learning process not a grammar, teacher as co-participant not dominant in the course. The fourth is motivation. The fifth is the subject that the students learn; students who involved more in the course make the course more effective and make the material increased.33
C.
Students' Learning Achievement
There are many definitions about achievement. People can freely interpret
what achievement is. In athlete’s competition achievement can be the status of the
winning, if he wins that is the achievement. In cooking, if someone cook and have a good taste then many people like his cooking it can be said that it is his achievement. In academic context achievement may be things that has achieved up the standard score. In Longman Dictionary, achievement is something important that you success in doing by your own efforts. In Oxford dictionary, learning achievement means as a thing that somebody has done successfully, especially using their own effort and skill.
Norman stated that achievement is something that students have learned.34 It means that it is the result of the learning process from the students, students need process to get the achievement, and it is not the instant. After they have done their learning they will get their achievement.
In Thoha’s book Achievement is the extents to which a person has achieved
something acquired certain information or mastered certain skills, usually as a
result of specific information or mastered certain skills, usually as a result of
33
Anderew Peter Littlejohn, Increasing Learner Involvement in Course Management,
TESOL QUARTERLY, Vol. 17, 1983, p. 595-598.
34
20
specific instruction.35 Achievement something can be gotten after the process of the learning.
Meanwhile Myra Pollack S. and David Miller S writes on their book that
learning achievement is students’ action that they have disciplined mines and
adhere to traditional morals and behavior. It can be shown from their competency in academic subjects and traditional skill while they are demonstrating through test and writing.36 Achievement can be seen from the students after following the test or examination after the process of teaching-learning.
Achievement is something that students are going to achieve when they are learning. Every school has a standard of the study. There is a correlation between achievement and standard, as Torsten Husen write on his book, standard is the average of achievement, and it is the minimum of requirement to pass.37 That mean that standard in learning is very important, if there is no standard, teacher will not know what the students have achieved.
Teacher can decide the standards for the students, in language for example, teacher decided that student have understand and interpret written and spoken language in a variety of the topics, or students can use the language both within and beyond the school setting,38 if students can do or through that standard, mean students have gotten their achievement. It also supported by Stanley, that achievement in education means result of the test designed to determine a
students’ mastery of a given academic area.39
D.
Framework of Thinking
Learning language may be a boring activity for some students, but school and teacher should have the alternative way to encourage the student in order to
35
M. Chabib Thoha, Teknik Evaluasi Pendidikan, (Jakarta: Raja Grafindo Persada, 1996), p. 44.
36
Myra Pollack S. and David Miller S., Teachers, Schools, and Society, (new York: Mc Graw Hill, 2005), p. 330.
37
Torsten Husen, The Learning Society, translated by P. Surono Hargosewoyo, Yusuf Hadi Miarso with the title: Masyarakat belajar, (Jakarta: PT. Raja Grafindo, 1995), p. 42.
38
Alice Omaggio Hadley, Teaching Language in Contex, 3th edition, (Boston: Wendy Nelson, 2001), p. 37.
39
learn the language more interactive and fun. The writer sees that English language course can be the alternative way to improve the students need beside their activity in the classroom.
Teacher in the English language course can create the different atmosphere. Because the student seem studying the formal way in the classroom, in the English language course teacher can take it more freely, students can express themselves without any curriculum stressing. But somehow, curriculum is very important. As Don Snow writes that learning language is how the students involve
to the real communication, if in the classroom students didn’t focus on the communication skill, so the English language course can take it role. English language course can be the addition of English learning process in the classroom.
In other way, school create the English language course is to help the student to master the English language, they hope that the student will get to the good attitude in English language learning, they will be motivated in classroom and the last they will get good on the test.
Thus, if the school and the teacher work on it seriously and continuously, the English language course may be the effective way in improving the student competence in English language learning, even in the first the student only has the interest, but it can be the first thing that they want to learn English language seriously.
As we know that in English language course student will get new knowledge of English, then the writer assume that the students who always attend the English language course will have different achievement with the student who rarely attend the course.
From the statement above, the writer thinks that there will be correlation between the English language course students’ attendance and the students’
achievement in English language learning. If the students intensive in following English language course they should be motivated in learning English language and finally they have a positive grade in English language learning in the classroom.
22
E.
Theoretical Hypothesis
Based on the theories which are discussed above English language course can help the student in English language learning, means that it has the positive impact to the student. If the students follow it continuously they would have the
23
method of the research, the population and sample, the technique of data collecting, the research instruments, and the technique of data analysis.
A.
The Place and Time of the Research
The writerconducted the research at YPI CempakaPutihBintaro. The writer do the research on June 2014. She did the research at second grade of YPI CempakaPutihBintaroatsecond semester academic year 2013/2014 to be analyzed.
B.
The Method of the Research
In doing the research, the writer used the quantitative qualitative studyand then usedcomparative and correlational study as its methods. In this research shetries to find outthe difference between the students who always attend the English language course and the students who rarely attend. And also she tries to find out whether English language course is influence tothe students’ achievement in English language learning. After she findthe difference between them, then she correlatedthetwo variables, based on its correlation coefficient value. The two variables are independent variable (X variable) and dependent variable (Y variable). The independent variable is English language course attendance (X variable) and the dependent variable is the students’ achievement in English language learning (Y variable).
She used the documentationto get the data. After she got the score of the
students’ attendance, then she took the students’ English score. Both of
variable;students’ attendance in English language course and students’ English
24
C.
The population and Sampling
1.
Population
Population is the group to which a researcher would like the results of a
study to be generalizable.1
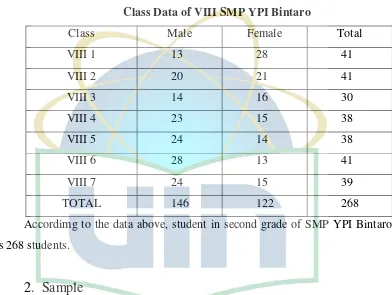
[image:35.595.118.510.260.555.2]Population this research is the whole students in second grade of SMP YPI Bintaro.
Table 3.1
Class Data of VIII SMP YPI Bintaro
Class Male Female Total
VIII 1 13 28 41
VIII 2 20 21 41
VIII 3 14 16 30
VIII 4 23 15 38
VIII 5 24 14 38
VIII 6 28 13 41
VIII 7 24 15 39
TOTAL 146 122 268
Accordimg to the data above, student in second grade of SMP YPI Bintaro is 268 students.
2.
Sample
SuharsimiArikunto writes on his that sampling is a part of population of the research2, and L. R. Gay writes that Sampling is the process of selecting a numbers of individuals for a study of such a way that the individual is represent the larger group from which they were selected.3 And according to Sukardi,
1
L. R. Gay, EDUCATIONAL REASEARCH, Competencies for Analysis and Application,
(Columbus: Merril Publishing Company, 1976), 3rd Edition, p. 18.
2
Prof. Dr. SuharsimiArikunto, PROSEDUR PENELITIAN, SuatuPendekatanPraktik,
(Jakarta: PT. RinekaCipta, 2006), 6th Ed., p. 131.
3
sampling is a part of population that chosen as a data research.4 If the subjects are less than 100 the researcher is better take the entire subject, and it is called as population research. But if the subject is broader, the researcher can take 10-15% or 20-25% or more.5The writer decided take 15% of the population of second grade of SMP YPI Bintaroon this research. And the total students become the sample of this research is 40 students.
D.
Instrument of the Study
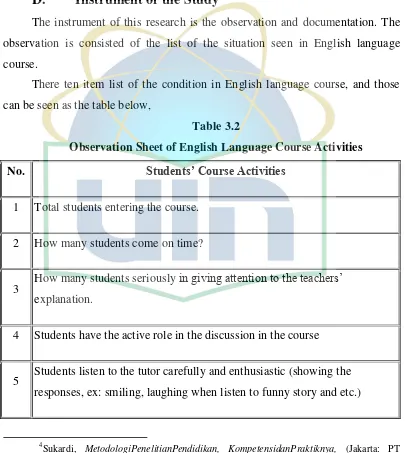
The instrument of this research is the observation and documentation. The observation is consisted of the list of the situation seen in English language course.
[image:36.595.110.515.267.720.2]There ten item list of the condition in English language course, and those can be seen as the table below,
Table 3.2
Observation Sheet of English Language Course Activities
No. Students’ Course Activities
1 Total students entering the course.
2 How many students come on time?
3 How many students seriously in giving attention to the teachers’ explanation.
4 Students have the active role in the discussion in the course
5 Students listen to the tutor carefully and enthusiastic (showing the responses, ex: smiling, laughing when listen to funny story and etc.)
4
Sukardi, MetodologiPenelitianPendidikan, KompetensidanPraktiknya, (Jakarta: PT BumiAksara, 2003), 1st Ed., p. 54.
5
Prof. Dr. SuharsimiArikunto, PROSEDUR PENELITIAN, SuatuPendekatanPraktik,
26
6 Students do the task that given by the tutor.
7 Students deliver their ideas when teaching-learning activity.
8 Students think critically in the course.
9 Students correct the mistake in course process.
10 Students make a conclusion of the course material using their own language.
Beside observation, this research also conducted by using documentation, it
conducted by collected the list of students’ score in even semester of 2013-2014
and also the students’ attendance list in English language course.
E.
The Technique of Collecting Data
The techniques of collecting the data used in this research are:
1. Observation, Observation is a technique of data collecting through the way of monitoring every case that happened and writing down on the observation tools about what the researcher want to monitor or do the research.6
In this context, she visited the school to observe the condition
of the school, teachers, students, employers, and school facilitations. The writer entered the class then saw the condition of the course
process, such as students’ attitude, students’ roles, and how many
students were coming to course.
2. Documentation study, Suharsimi write in his book that,
“ dalammelaksanakanmetodedokumentasipenelitimenyelidikibenda-bendasepertibuku, majalah, dokumen, peraturan, notulen,
catatanhariandan lain-lain”.7
In this research the writer take the
6
WinaSanjaya, PenelitianTindakanKelas, (Jakarta: Kencana, 2009), p. 86. 7
documentation such as students’ name list, students’ score in English
language test, the list of students who join English language course, and etc.
F.
The Technique of Data Analysis
Data analysis is the technique that used to explain the information or the datum which is gotten by the writer. It is used to help the reader understand what the writer mean.
Here are some steps that the writer used.
1. Editing
Editing is the first step that used to process the data. It is mean that the
writer check the list of the students’ attendance that given by the teacher. After
that she classified it.
2. Classifying
After got the data from the teacher and edited it, the next step is classifying. In this step, the writer divide the students into two groups according to the students their attendance in English language course, the first group is the students who have the score under 70 and the second group is the students who have the
score up to 70. To get the score of the students’ attendance she used the formula:
Score =
3. Tabulating
After classified the students according to their attendances’ score, the writer put them into the table. Because she used 2 method in this research, the tabulating of the data was put into the table of comparative and correlational table formula.
4. Analyzing
For the next step, the writer processed and analyzed the data. The first, the writer analyzed the scores between the students who always attend the course and
28
achievement, she used the technique of data analysis in this research is statistical analysis with t-Formula, and the formula is as follow:
t
̅ ̅√( )( )
And to know the significant of the value of the t then she compared with t-table.
After the writer know the result of difference between them, the she
correlate the students’ attendance score with students’ achievement in English
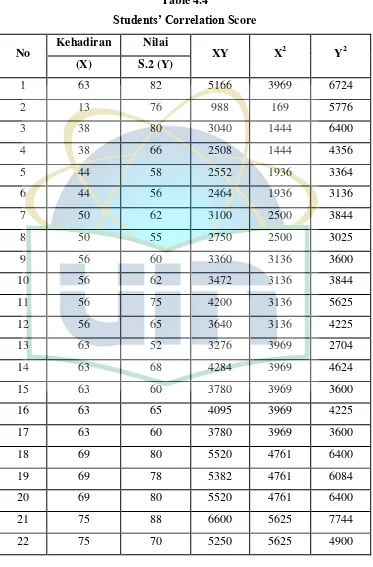
language learning. The writer used the product moment correlation coefficient formula.
The formula is:
rxy=
∑ ∑ ∑
√ ∑ ∑ ∑ ∑
rxy = Correlation coefficient between X and Y
∑XY = sum of cross products of deviation scores for X and Y
∑X = total score of X
∑Y = total score of Y N = Number of Cases
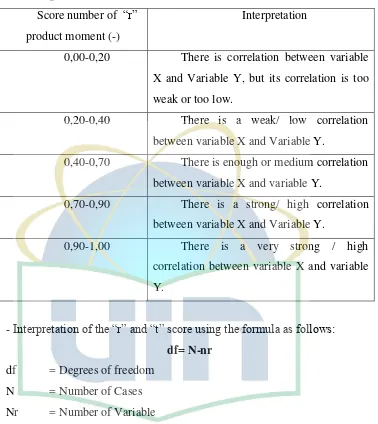
After she found the correlation or the “r” score, there are two ways to interpret it:
-Simple interpretation, it compares the result of the calculation of the
Tabel3.4
Interpretation number of correlation index “r” Product Moment8
Score number of “r”
product moment (-)
Interpretation
0,00-0,20 There is correlation between variable X and Variable Y, but its correlation is too weak or too low.
0,20-0,40 There is a weak/ low correlation between variable X and Variable Y.
0,40-0,70 There is enough or medium correlation between variable X and variable Y.
0,70-0,90 There is a strong/ high correlation between variable X and Variable Y.
0,90-1,00 There is a very strong / high correlation between variable X and variable Y.
-Interpretation of the “r” and “t” score using the formula as follows: df= N-nr
df = Degrees of freedom N = Number of Cases Nr = Number of Variable
After that the result of the interpretation is compares with the table of
coefficient “r” roduct moment Pearson on the standard of significant 1 % or 5%.
To search and know the contribution of variable X to variable Y use the formulas as follows:
8
30
KD= r2x100%
KD = coefficient of Determination
R =coefficient correlation between X and Y
G.
Statistical Hypothesis
To find out the answer of the problem, the writer should propose Alternative hypothesis (Ha) and Null hypothesis (Ho) as a follow:
1. Alternative hypothesis (Ha):
- There is a difference between students who always attend the English language course and the students who rarely attend the course.
- English language Course students’ attendance influence the students’ achievement in English Language Learning.
2. Null hypothesis (Ho):
- There is no difference between students who always attend the English language course and the students who rarely attend the course.
- English language Course students’ attendance doesn’t influence the
31
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDING AND INTERPRETATION
A.
Research Finding
1.
Description of the Data
The writer conducted the research about the difference between student who always attend the English language course and the students who rarely attend the English language course.
To know that that she used the documents of both variables, she asked the
list of students’ attendance to the English language committee and asked the result
of final test score in the forth semester 2013-2014 academic year.
After that she recapitulated the students’ attendance and gave the score
according to their attendance. Then, she divided the students into two; the students who always attend the course up to 70% and the students who attend no more than 70%. The total of the meeting is 16 times.
After she find the difference between two group then she also correlated the data, to know whether the students’ attendance in English language course influence the students achievement in English language learning or not.
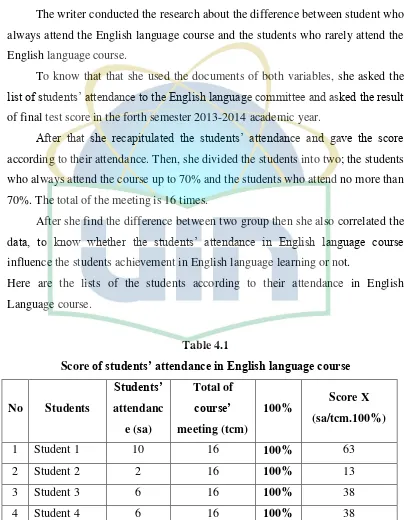
Here are the lists of the students according to their attendance in English Language course.
Table 4.1
Score of students’ attendance in English language course
No Students
Students’
attendanc
e (sa)
Total of
course’
meeting (tcm)
100% Score X
(sa/tcm.100%)
1 Student 1 10 16 100% 63
2 Student 2 2 16 100% 13
3 Student 3 6 16 100% 38
[image:42.595.106.516.227.747.2]32
5 Student 5 7 16 100% 44
6 Student 6 7 16 100% 44
7 Student 7 8 16 100% 50
8 Student 8 8 16 100% 50
9 Student 9 9 16 100% 56
10 Student 10 9 16 100% 56
11 Student 11 9 16 100% 56
12 Student 12 9 16 100% 56
13 Student 13 10 16 100% 63
14 Student 14 10 16 100% 63
15 Student 15 10 16 100% 63
16 Student 16 10 16 100% 63
17 Student 17 10 16 100% 63
18 Student 18 11 16 100% 69
19 Student 19 11 16 100% 69
20 Student 20 11 16 100% 69
21 Student 21 12 16 100% 75
22 Student 22 12 16 100% 75
23 Student 23 12 16 100% 75
24 Student 24 12 16 100% 75
25 Student 25 13 16 100% 81
26 Student 26 13 16 100% 81
27 Student 27 13 16 100% 81
28 Student 28 13 16 100% 81
29 Student 29 13 16 100% 81
30 Student 30 14 16 100% 88
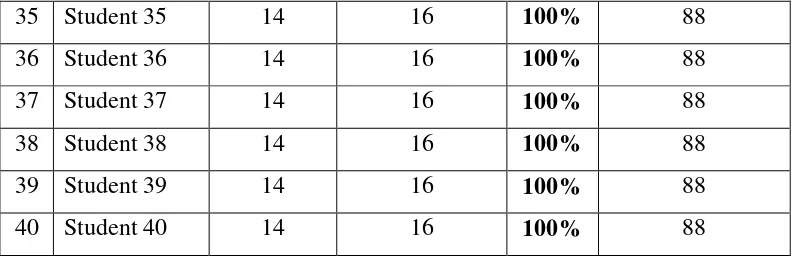
31 Student 31 14 16 100% 88
32 Student 32 14 16 100% 88
33 Student 33 14 16 100% 88
35 Student 35 14 16 100% 88
36 Student 36 14 16 100% 88
37 Student 37 14 16 100% 88
38 Student 38 14 16 100% 88
39 Student 39 14 16 100% 88
40 Student 40 14 16 100% 88
To find the students’ achievement in English language learning in the
[image:44.595.108.506.113.243.2]classroom, then the writer took the documentation of final test score to analyze the data. And here are the lists of students’ score in their final test.
Table 4.2
Students’ score at Final test
No Students Score Y
1 Student 1 82
2 Student 2 76
3 Student 3 80
4 Student 4 66
5 Student 5 58
6 Student 6 56
7 Student 7 62
8 Student 8 55
9 Student 9 60
10 Student 10 62
11 Student 11 75
12 Student 12 65
13 Student 13 52
14 Student 14 68
15 Student 15 60
34
17 Student 17 60
18 Student 18 80
19 Student 19 78
20 Student 20 80
21 Student 21 88
22 Student 22 70
23 Student 23 85
24 Student 24 76
25 Student 25 50
26 Student 26 68
27 Student 27 60
28 Student 28 80
29 Student 29 75
30 Student 30 76
31 Student 31 85
32 Student 32 80
33 Student 33 60
34 Student 34 72
35 Student 35 82
36 Student 36 85
37 Student 37 85
38 Student 38 82
39 Student 39 85
40 Student 40 82
2.
The Analysis of Data
The next steps after scoring each variable, the write calculate the data using
t-test formula.
Table 4.3
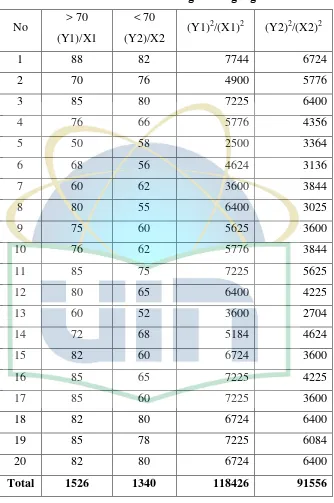
List of Students’ score classification in English language course attendance
No > 70 (Y1)/X1
< 70
(Y2)/X2 (Y1)
2
/(X1)2 (Y2)2/(X2)2
1 88 82 7744 6724
2 70 76 4900 5776
3 85 80 7225 6400
4 76 66 5776 4356
5 50 58 2500 3364
6 68 56 4624 3136
7 60 62 3600 3844
8 80 55 6400 3025
9 75 60 5625 3600
10 76 62 5776 3844
11 85 75 7225 5625
12 80 65 6400 4225
13 60 52 3600 2704
14 72 68 5184 4624
15 82 60 6724 3600
16 85 65 7225 4225
17 85 60 7225 3600
18 82 80 6724 6400
19 85 78 7225 6084
20 82 80 6724 6400
36
From the table above we can get some number to gain the formula of t-est.
t
̅ ̅√( )( )
Before we calculated the t formula, we have to find the SS score, to find the score of SS, we used the formula as follow;
SS1
∑
∑
or
SS2∑
∑Firstly we find the SS1 according to formula as follow.
SS1 ∑
∑
= 118426 – 86433,8
= 1992.2
After that we find the SS2 according to formula as follow.
SS2 ∑
∑
= 915566 – 89780
= 1776
And now we have everything to fill out on the formula to find the t-score.
t √