THE EFFECTIVENESSOF 3D ALKENE ISOMERISME COURSEWARE (3D-AI) AT MRSM TERENDAK, MELAKA
Norasiken Bakar1, Zilawati Roslinda Mat Zain2, Syariffanor Hisham3 Faculty of Information and Communication Technology
Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka (UTeM) Melaka, Malaysia1,2,3
[email protected], [email protected]2
Abstract-The usage of multimedia courseware in education field is one of the methods that can be used to increase the motivation and interest of student towards the subject that being taught. This research is about the development and effectiveness of courseware title 3 dimensional (3D) Alkenes Isomerism. This courseware is specifically developed for a topic in chemistry subject for form five students in Malaysia. The topic chosen are Alkenes and Isomerism which is a part of hydrocarbon topic in chemistry secondary syllabus. The research was done at Maktab Rendah Sains MARA Terendak Melaka involving Form five Students who took Sijil Pelajaran Malaysia (SPM) in year 2010.The questionnaires is the instrument used in this research to determine the problem statement. Based on the questionnaires, Alkenes and Isomerism are identify as the most difficult topic and suggested a courseware is developed and then tested for its effectiveness. The courseware used MAYA software version 2010 to develop the 3D molecules of Alkenes structure. Two group of students called Experimental group (EC) and Control group (CG) involved in this process and a set of questionnaires is used during pre-test and post test for this purpose. A pilot study is running to determine the effectiveness of the courseware before post test is carried out. From this research the researcher finds out that courseware titled 3 dimensional (3D) Alkenes Isomerism(3D AI) is suitable to used during teaching and learning process as teaching aid. This is also because it can help to increase student’s performance for topic Alkenes Isomerism.
Keywords-component; Courseware, 3D AI, Alkene Isomerisme, Chemistry
I. Introduction
Teaching and learning is an important process that happens in a classroom. Many studies have been carried out to identify the learning strategies and learning technique that is suitable to be implemented in classroom. This is to ensure that teaching and learning process reach its goal which is student get the knowledge and student is inspired to find the knowledge even they are not in the classroom.
Teaching and learning become more adventurous in 21st century. The progressing in ICT field expresses the big impact towards education process. Many researches show that ICT give positive effect to the teaching and learning process whether for the student or the process itself. ICT help to fasten the government agenda in education long term plan.
The science education become more important in Vision 2020 through it sixth challenges Rose Amnah et al. 2004. The sixth challenge of Vision 2020 is the challenge of establishing a scientific and progressive society, a society that is innovative and forward-looking, and one that is not only a consumer of technology but also a contributor to the scientific and technological civilization of the future. Teacher’s role is vital in implementing ICT literature to students. Teacher becomes facilitator or instructor that not only preparing the suitable environment for learning process but also help and instil good value in students for their future. Teacher play important role to guide students to surf internet, finds website, chose the right courseware also collect and review information (Norrizan, 2011). Based on Mateer (2011), instructor can engage students and produce more meaningful and deep learning experiences by using films, television shows, popular music, new stories, literature, documentaries and videos from sources such as YouTube.
II. Problem Statement
Chemistry has been regarded as a difficult subject for young students by chemistry teachers, researchers, and educators (Kirkwood & Symington, 1996; Lorenzo, 2005; Nakhleh, 1992). Students view chemistry as one of the most difficult subjects to study at all levels of schooling (Özmen, 2005). Many students reported to have trouble with the conceptual nature of chemistry (Rhoda, 2011).
atoms and molecule. It is true that one of the most difficult challenges in teaching and learning chemistry at secondary level involves conveying to students the three dimensional structures and dynamics interaction of atoms and molecules (Abdoolatiff & Narod, 2009). The main problem in Chemistry is the abstraction of facts in order to understand the 3D arrangements and properties of the molecules, Alonso et al. 2011.
Many studies all level of schooling to determine student’s ideas about basic chemistry concepts suggest that students who did not acquire satisfactory understanding of scientific concepts occurred because of traditional teaching method. In traditional teacher-centred classroom the students become listeners and the teachers gives out the facts and defines important ideas. Traditional teaching method in science means students may understand the subject but only at a ‘knowledge level’-memorizing the fact (Lewis, 2006).
One of the problems when student learn chemistry is students do not understand the topic well because it needs students to imagine the formation of the structure and their arrangement (Sun, 1997). By developing this courseware, it is use to stimulate student’s interest in some content of the learning and as a supplement to classroom teaching, the graphics and animation make the subject come alive, so that learning the subject is much easier, animation and voice are used to implement various teaching strategies such as tutorials, activities and games. Besides that, the simple animation can be use in this courseware to make the learning of content in the class more interactive. With the development of computer technology, multimedia methods are been increasingly used in teaching practice. A multimedia courseware can combine sound and pictures with knowledge. This reinforces the fact that students retain 50% of what they see and hear, as the use of multimedia technology gives students more information than just writing on the blackboard and increase the chance of active learning (Huo, 2006).
III. Multimedia in Chemistry Education
The well-known aim of science education is to teach the science concepts meaningfully and make students become aware of how these concepts can be used in their daily lives (Çepni, 2004).With the rapid development in science and technology, chemistry which is the fundamental to many disciplines, it becomes increasingly important (Saeed et al. 2011). Chemistry is often regarded as a difficult subject for students (Johnstone, 2000; Rhoda, et al. 2011). Chemistry subject at secondary level contain various topics, some of these are considered as difficult by various students (Rhoda, et al. 2001). The conceptual understanding in chemistry includes the ability to represent and translate chemical problems using macroscopic (observable), molecular (particulate) and symbolic forms of representation. Students are required to think at the molecular level and explain changes at macroscopic level in terms of interaction between individual atoms and molecules (Abdoolatiff & Narod, 2009). Visualization skills or the skills necessary to describe microscopic phenomena need to be developed as an integral part of chemistry teaching and learning (Steenberg & Bradley, 2009). Student learning and understanding has the potential to improve with the use of computer-based multimedia environments (Akili, 208). ICT-integrated environmental learning in experimental chemistry show positive and scientific perspective for academic research (Su, 2011).Students agreed to a larger extent that integrating ICT in teaching and learning of Chemistry enhances conceptual understanding of Organic Chemistry (Bhukuvhani, 2011). Thus, the Chemistry multimedia courseware prepared by the Ministry of Education is most welcome and right at the time. The materials were in the form of browser-based courseware, teachers’ guides, student worksheets, and sample lesson plans to guide the teachers in integrating the courseware in their lessons. 87.5% of the respondents felt that the multimedia courseware supplied by the Ministry to teach science and mathematics is well planned and effective in terms of content (Ong, 2008). This shows that multimedia courseware is one of the right tools to use in teaching and learning.
IV. Implication of multimedia in education for 3D AI courseware
Teachers today are encouraged to use technology-driven teaching and learning aids to enhance students learning (Rahimi et al. 2007). They need to ensure that, the educational software used as part of their classroom instructions is appropriate and effective in producing the intended outcome and achieving educational goals (Lim & Tay, 2003; Rahimi et al. 2007).This research is about to develop a multimedia courseware for secondary school students. The courseware choose a topic from form five chemistry syllabus as the topic has been chosen as one of the difficult topic among the students. Multimedia element is embedded in the courseware is in lined with the current technology pattern in education that approve the usage of ICT facilities in education. Text, graphic, animation and audio are used to make the 3D AI courseware is accepted as one of the adequate teaching aid. It also attracts student’s attention and use maximally to understand the content effectively. The presence of multimedia technology is an important for distributing information in teaching and learning process thus the teachers are the key factor for the success of multimedia application technology in the classroom (Arsat & Hasnisham, 2011).
V. Reasults and Analysis
questions before learning the topic to get their pre understanding before they learn in class. Both subtopics are continuous and related to each other. Hydrocarbon topic consist of subtopic Alkanes, Alkenes, Isomerism, Alcohols, Ester and Carboxylic Acids. The pre-test consisted of 20 objective questions with four choices of answer covering topic Alkene and Isomerism and 3 subjective questions with total mark 20.
The post-test questions consisted of the similar number of questions from the same topic. After both experimental and control group finish with pre-test, they start learning the topic. For experimental group, they learn both topics using the 3D AI courseware. From observation of the researcher, students are able to use the courseware and study on their own with minimum help form the teacher. After finish learning the topics using 3D AI, they answer the post test questions. For control group, they learn the topic in class as usual and answer the post test questions on question paper that distributed to them. The effectiveness of 3D AI courseware is measured by the performance of students in pre and post testing. Students were labeled from S1-S50 which is S1 to S25 is from control group while S26 to S50 is from experimental group.
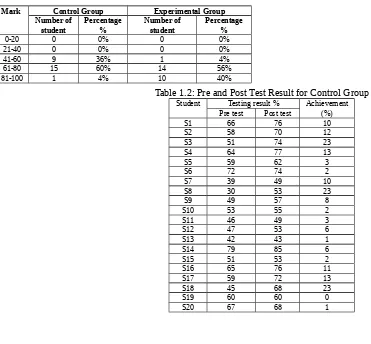
According to the Table 1.1, the result shows that for the control group, the highest percentage of the mark distributions is 60% in which the mark range is 61-80. It can be concluded that majority students in conventional method scored around 61-80. On the other hand, the highest percentage of the mark distributions using 3D AI courseware is 56% in which the range of the mark is also around 61-80.However, the number of students who score higher marks is greater in experimental group compared to control group. There is increment of 40% for marks range 81-100 for experimental group. This shows that 3D AI courseware effective to increase student performance in term of the achievement of student during test. It means that the students from experimental group tend to understand much better compared to students who takes conventional method. Figures 1.1 and Figure 1.2 shows the frequency histogram for control group and experimental group during post test.
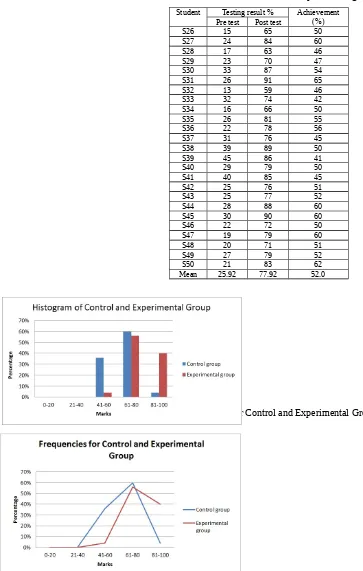
Regarding to the Table 1.2, the highest score for the pre-test is achieved by the student by S6 and with the score 72% and the lowest is gained by the 2 students, S7 and S8 with30%. Post-test is done after they learn Alkene and isomerism topics in class. The highest score is S14 with 85% and the lowest is by S13 with score 43%. The table proves that all of the students have achievement in their result with the lowest achievement is 1% and the highest achievement is 34%. Table 1.3 shows the achievement of pre and post-test for the experimental group.
Table 1.1: Marks Distributions for Control and Experimental Group in the Post Test
Table 1.2: Pre and Post Test Result for Control Group Student Testing result % Achievement
(%) Pre test Post test
S1 66 76 10
S2 58 70 12
S3 51 74 23
S4 64 77 13
S5 59 62 3
S6 72 74 2
S7 39 49 10
S8 30 53 23
S9 49 57 8
S10 53 55 2
S11 46 49 3
S12 47 53 6
S13 42 43 1
S14 79 85 6
S15 51 53 2
S16 65 76 11
S17 59 72 13
S18 45 68 23
S19 60 60 0
S20 67 68 1
Mark Control Group Experimental Group Number of student Percentage % Number of student Percentage %
0-20 0 0% 0 0%
21-40 0 0% 0 0%
41-60 9 36% 1 4%
61-80 15 60% 14 56%
S21 69 72 3
S22 66 74 8
S23 68 70 2
S24 65 72 7
S25 59 64 5
Mean 57.16 65.04 7.88
Table 1.3: Pre and Post Test Result for experimental group Student Testing result % Achievement
(%) Pre test Post test
S26 15 65 50
S27 24 84 60
S28 17 63 46
S29 23 70 47
S30 33 87 54
S31 26 91 65
S32 13 59 46
S33 32 74 42
S34 16 66 50
S35 26 81 55
S36 22 78 56
S37 31 76 45
S38 39 89 50
S39 45 86 41
S40 29 79 50
S41 40 85 45
S42 25 76 51
S43 25 77 52
S44 28 88 60
S45 30 90 60
S46 22 72 50
S47 19 79 60
S48 20 71 51
S49 27 79 52
S50 21 83 62
Mean 25.92 77.92 52.0
Figure 1.2: Frequencies for Control and Experimental Group
Based on the result of students’ achievements, researcher found that experimental group performance get higher mean compared to control group. Hence, learning using 3D AI courseware is more effective to learn Alkene Isomerism topic.
T-test is used to prove the null hypothesis H01, H02 and
H03.T-test has been carried out to evaluate if there is any significant
difference in term of student’s performance between student who use 3D
AI courseware which is Experimental group(G) and student who study
using text book which is Control group(C). The data is analyzing using
SPSS version 16. Table 5.8, Table 5.9 and Table 5.10 shows all the data
collected.
H01: There is no significance different in term of achievement in pre and post-test for Control group.
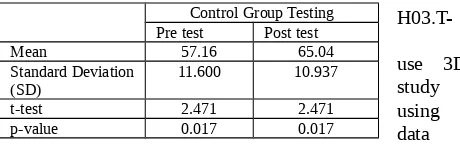
Table 1.4 shows the result of t-test and p-value for the Control group based on pre and post test result. Based on the result, it shows that t-value is 7.160 and the significant of two tailed value, p is 0.00. Because of the p <0.05, thus the null hypothesis H01 is rejected.
Table 1.4: Mean, SD and t-test for pre-test and post-test for Control Group
There is a significant difference in the result (t=2.471, df=48, p<.05). Null hypothesis is rejected because there is different in term of student’ marks between test and post-test group. The different mean value score (7.88) between both pre-test and post-pre-test is enough to reject the null hypothesis.
H02: There is no significance different in term of achievement in pre and post-test for experimental group.
Table 1.5 shows the result of t-test and p-value for the
Experimental Group based on pre and post test result. The testing is using
paired sample t-test since the same group has been used for two times (two
variables). Based on the performance of the students in t-test using pre and
post-test, the t-value is 21.949 and the significant of two tailed value, p is 0.00.
The result shows p<0.05, thus there is a significant difference between pre and
post-test. Hence the null hypothesis H01 is rejected.
Table 1.5: Mean, SD and t-test for pre and post-test for experimental group
The research result show a significance (t=21.949, df=48, p<.05). There is a different mark obtained by students between pre-test and post-test result for Experimental group. Null hypothesis is rejected because there is difference of student’s performance in pre-test and post-test. The difference’s mean value, 52.00 shows that Experimental group post-test result has greater performance in term of marks obtained by the student compared to the marks that they get during pre-test.
Control Group Testing Pre test Post test
Mean 57.16 65.04
Standard Deviation (SD)
11.600 10.937
t-test 2.471 2.471
p-value 0.017 0.017
Experimental Group Testing Pre Test Post test
Mean 25.92 77.92
Standard Deviation (SD)
7.889 8.836
t-test 21.949 21.949
H03: There is no significance different in term of achievement in post-test between Experimental group who use 3D AI courseware and controlled group who learn using text book.
Based on the result of student’s achievement, researcher found that post-test perform higher mean compared to pre-test result. Hence, it shows that Experimental group that using 3D AI courseware in their teaching and learning session in had achieved higher marks during post-test.
Table 1.6: Mean, SD and t-test for post-test for Control and Experimental Group
The result is significant (t=4.580, df=48, p< .05). Null hypothesis is rejected because there is different in term of the marks for Control and Experimental group result in the post-test. The different mean score value (12.880) for both group is sufficient to reject null hypothesis. This is caused by the standard error mean (2.812) that exist in the research data.
VI. Conclusion
This research covers the development and effectiveness of 3 dimensional (3D) Alkene Isomerism (3D AI) to achieve the objectives of the research. The starting of the research covers the background of study that explains the focus of the research and the use of ICT in education. This research is focus on secondary school which case study is at Maktab Rendah Sains MARA Terendak Melaka. The research focuses on the 3D AI courseware and its effectiveness in chemistry subject at secondary school. It is suggested to be an alternative of teaching material to be used in classroom. The study evaluates student’s achievements in both conventional and experimental method in the same topic which is Alkene and Isomerism topics. A courseware named 3D AI has been developing using ADDIE model. A systematic framework is being used to investigate the effectiveness of the courseware. The testing has been done with the involvement of 50 students who in Science stream that taken Chemistry subject.
REFERENCES
1) Rose Amnah Abdul Rauf, Abd Rashid Johar, Lilia Halim & Siti Rahayah Ariffin (2004) “Pemupukan Kemahiran Proses Sains di Kalangan Pelajar Tingkatan Dua di Sekolah Bestari”. Jurnal Teknologi, Jun.2004:19–32 Universiti Teknologi Malaysia.
2) Norrizan Razali (2011). I”CT Pupuk Kemahiran Abad ke-21”. Portal Pendidikan Utusan Malaysia.
3) Mateer G. Dirk, Ghent Linda S, Porter Tod & Purdom Ray (2011), “Using Media to Enhance Teaching and Learning”.
4) Kirkwood, V. and Symington, D. (1996). Lecturer Perceptions of Student Difficulties in a First-Year Chemistry Course. Journal of Chemical Education 73(4), 339 – 343.
5) Ozmen Haluk.(2005).” The Influence of computer-assisted instruction on students’ conceptual understanding of chemical bonding and attitude towards chemistry: A case for Turkey”. Karadeniz Technical University, Turkey.
6) Rhoda D. Beskeni, Muhammad Imran Yousuf, Mohd Mahzan Awang & Asif Naveed Ranjha (2011). “The Effect of Prior Knowledge in Understanding Chemistry Concepts by Senior Secondary School Students”. International Journal of Academic Research. Vol 3 (2) Part II. Mac 2011.
7) Johnstone, A.H., (2000). Teaching of Chemistry—Logical or Psychological?. Chemistry Education: Research and Practice in Europe, 1(1), 9-15.
8) Lewis, G.T (2006). “Evaluation Criterion for Computer-Based Training Courseware.” Journal of informatics. 4. 22-23.
9) Sun, T. T and Lian, K.T (1997). “CHEMMAT: Addaptive Multimedia Courseware for Chemistry.” Journal of Science and Technology. 6. 71.
10) Cepni Salih, Tas Erol &Kose Sacit (2003). The effects of computer-assisted material on students’ cognitivelevels, misconceptions and attitudes towards science. Karadeniz Technical University, Turkey.
11) S. Abdoolatiff, F.B. Narod (2009). Investigating the effectiveness of computer simulation in the teaching of “atomic Structure and Bonding”, Springer Science and Business Media.
12) Steenberg & Bradley, 2009. Chemistry Education in the ICT Age, Springer Science + Business Media B.V, 2009, ISBN:978-1-4020-9731-7
13) Su King-Dow (2011). “An intensive ICT-integrated Environmental learning strategy for enhancing student performance”. International Journal of Environmental & Science Education Vol. 6,No. 1,January2011, 39-58.
14) Akıllı, H. İ. (2008). “The effect of the computer in science and technology ınstruction on the students’ achievements level, the retention of the achievements and their attitude toward the lesson”. Unpublished Doctoral Dissertation University of Hacettepe, Ankara, Turkey.
Testing – Post Test Control Group Experimental
Group
Mean 65.04 77.92
Standard Deviation (SD)
10.937 8.836
t-test 4.580 4.580
15) Bhukuvhani C. E., Zezekwa Nicholas & Sunzuma Gladys (2011). Students’ preparedness to integrate Information and Communication Technology tools and resources for the learning of Organic Chemistry concepts in the District of Masvingo, Zimbabwe. International Journal of Education and Development using ICT. Vol 7(2).
16) Rahimi Md Saad, Noraini Idris, Loh Sau Cheong, Ahmad Zabidi Abdul Razak &Norjoharuddeen Mohd Nor (2007). “Evaluation of Courseware for teaching and learning of Form One Mathematics and Science”. MEDC Volume 1, December2007
17) Lim, C. P., & Tay, L. Y. (2003). Information and communication technologies (ICT) in an elementary school: Students’ engagement in higher-order