i
Submitted to the Faculty of Language Education as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan
Author:
Didit Nur Yulianto
20120540052
English Education Department Faculty of Language Education Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta
vii
Approval Sheet……… ii
Statement of Authenticity……….. iii
Motto ……….. iv
Acknowledgment ……… v
Abstract……… vi
Table of Contents …………..………. vii Chapter one Introduction ………. 1
Background of the Research ……… 1
Statement and Limitation of the Problem ……… 2
Research Questions ………. 3
Objectives of the Study ……… 3
Significances of the Study …………… 3
Chapter Two Literature Review ……… 4
Reading Comprehension ……… 4
Process of Reading Comprehension ……….. 5
Difficulties of Reading Comprehension ……… 5
Metacognitive strategies in reading ………... 7
Advantages of reading comprehension ………. 9
viii
Setting of Research ………. 14
Population and Sample ……… 14
Data Gathering Techniques ……….. 15
Data Analysis Method ………... 19
Chapter Four Results and Discussion .….………,……….. 20
Result ……….. 20
Discussion ……….. 29
Chapter Five Conclusion and suggestion ……….. 32
Conclusion ………. 32
Suggestion ………. 33
References ……… 34
vi
fulfilling this requirement the students face difficulties in reading comprehension. The students also use strategies in reading. This research aimed to find out the students’ difficulties and strategies in reading. The research used quantitative method using questioner as the instrument distributed to 64 participants. The participants were EED of UMY students batch 2014. They were chosen based on their availability and willingness. The data gathered were analyzed using SPSS. Related to the difficulties the students faced in reading, the result showed that the mean average of the category of phonological processing was 2.80 followed by complex sentences 2.75, meaning of word / vocabulary 2.61, lack of concentration during reading 2.51, language processing 2.41, inability to connect ideas in a passage 2.36, and meaning of sentences 2.11. This means the students only ‘sometimes’ faced these category of difficulties. From seven categories, the highest difficulty the students of EED of UMY batch 2014 faced when reading was related to phonological processing, while the lowest difficulty was related to meaning of sentences. In addition, the result related to the strategies used by the students showed that the mean average of the category of predicting was 3.06 followed by monitoring / clarifying / and fix up 3.04,
visualizing 2.91, summarizing / retelling 2.88, drawing inferences 2.67, and questioning 2.47. This means the students only ‘sometimes’ used these strategies. From the six categories of
strategies, the most strategy used by the students was predicting and the least strategy used by the students was questioning.
Chapter One Introduction
In this chapter, the researcher discusses the background of the research, the statement of problem, limitation of problem, research question, objective of the research, and significances of this research.
Background of the Research
Reading is a process determined by what the reader’s brain, emotions and
beliefs have brought to the reading such as the knowledge/information, strategies for processing text, moods, fears and joys (Weaver, 2009). Because the result of reading is comprehension or reading comprehension, people can improve their knowledge and get inspiration from reading. For students, reading activity can make them understand the materials that they want to learn better. They can improve their information and knowledge through reading.
In reading, usually students have many problems. They have difficulties to understand the main point of the text. They do not only need time to understand the main idea in the text, but they also have to know the purpose of reading and the benefit of reading. Students may have reading difficulties in understanding the main idea, vocabulary, structure, and grammar in the texts. The problems on reading will give influence to the students’ reading comprehension in the learning process.
phonological problems. The strategies are solution for students to improve their skills in reading. The skills of reading will improve the strategies in reading.
As a student of English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta (EED of UMY), the researcher believes that many activities in English Education Department of UMY given by the lecturers will improve students’ reading ability. However, reading activity is not easy for the students. The students, including the researcher, have difficulties in reading. Based on the researcher’s experience, the difficulties in reading comprehension often deal with vocabulary and getting the main ideas. The structure and grammar in the text books also sometimes make the students confused.
Considering the problems in reading comprehension faced by EED of UMY students and the strategies used by the students, the researcher would like to
investigate students difficulties in reading comprehension and strategies of students at EED of UMY.
Statement and Limitation of the Problem
In this research, the researcher wanted to focus the study on the students’ difficulties in reading comprehension. In addition, the researcher wanted to know about the students’ strategies in reading as the next concern of this research. This current research was limited to students of English Education Department of Universitas Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta students, Batch 2014.
Research Questions
To administer this research, based on the background, the researcher formulates the research questions. The formulated research questions are:
1. What are the students’ difficulties in reading comprehension at EED of UMY? 2. What are the students’ strategies in reading at EED of UMY?
Objectives of the Study
Based on the formulated research question, this research has two purposes. They are:
1. To find out the students’ difficulties in reading comprehension at EED of UMY.
2. To find out the students’ strategies in reading at EED of UMY. Significances of the Study
There are some significances that can be achieved from this research. The significances are addressed to the teachers, students, and other researcher.
Chapter Two
Literature Review
This chapter presents several points related to the topic of this study. Several theories are needed to support the study. The points will explain a review on reading
comprehension, the difficulties of reading comprehension, and the strategies in reading. The researcher also presents conceptual framework of this study in this
chapter.
Reading Comprehension
Reading comprehension is a complex process that involves many different variables and factors (McKee, 2012). “We define reading comprehension as the
process of simultaneously extracting and constructing meaning through interaction and involvement with written language” (Snow, 2002, p. 11). The definition shows
that many aspects have relations with reading comprehension. The students might
have significant difficulties comprehending written text (Zein, Solis, Vaughn, McCulley, 2012). The lack of vocabulary can be the source of the problem. According to Nosratinia, Gaurabsari, and Sarabchian (2014), vocabulary learning
strategies and autonomy significantly predict reading comprehension.
Reading, and specifically comprehension, is a complex endeavor that requires
a variety of skills (Nayton, 2013). Further, Nayton asserts that comprehension is fundamentally the goal of both reading and listening. He mentioned that numerous theorists have sought to explain the specific skills that are most essential to reading
Process of Reading Comprehension
According to Griffiths, Sohlberg, and Biancarosa, (2011) comprehension proses is the result from three levels in representation of the text`s meaning. The first level is the sentence level representation. This level is sometimes called surface level.
In this level words are literally written to make a text being read. The second level is the proposition level of representation. In this level, the reader takes the main ideas
from the literal text. The third is the level of situation model. This is the highest level. In this level, the readers construct their understanding of the text and integrate and update what they already know about the topic into more complex and holistic
conceptualization of the text.
Meanwhile, according to Perfetti and Stafura (2014), the components of
comprehension involve the role of memory, the use of inferences, and the updating of
mental models. Related to the comprehension process, Kulesz (2014) asserted that
creating a coherent mental representation of the text and employment of
comprehension processes depend on limited attentional as well as working memory resources.
Difficulties of Reading Comprehension
Reading comprehension difficulties can be identified early in students’ school
improving the reading activities of the students and making the practices more
appealing to the students (Erfanpour, 2013).
Nathan, Laurent, Sarah, Lee, Adam, and Nathasa, (February, 2016) said that “Comprehension relies on mastery of decoding; children who struggle to decode find
it difficult to understand and remember what has been read. Because their efforts to grasp individual words are so exhausting, they have no resources left for
understanding”. The following are the signs of difficulties in reading comprehension.
Confusion about the meaning of words and sentences. Some aspects can be the sources of confusion. They are as follow:
Word. The readers might have difficulties with words that have similar lexical forms, and they might mix between the meanings of pairs of words because they seem to be the same (Mehjadi, 2015).
Sentences.“Many students have comprehension problems because they have
difficulty interpreting the meaning in sentences” (Boroughs, 2012, p.3
). “Sentence complexity can create comprehension problems for struggling readers”
(Scott, 2009, p.185). Many children spell to read with silent process, but after read they do not understand the meaning of the new sentence in the reading (Supriasmoro, 2013).
Inability to connect ideas in a passage, “Personal need for structure and
Lack of concentration during reading, Students have weaknesses to pay
attention to many controls, when they approach a reading task very passively (Boroughs, 2012).
The other difficulties that the readers have when reading text is they do not
understand new sentences when reading the text. According to Boroughs (2012, p.6), “One reason they might have difficulty is because they are unfamiliar with the
complex sentence structures that occur in written language that do not occur in oral language”. According to Sanahan, Mejer, Salvadore (2015) said that “Some students
might have difficulties in reading comprehension such as phonological, and/or language processing”.
Phonological processing. Many poor readers have a specific weakness in
phonological processing even through their other processing skills (auditory and language processing) are strong.
Language processing. Language processing includes a variety of language abilities including reading and writing. It is a broader term than phonological processing.
Metacognitive Strategies in Reading
Reading strategies improve reading (Karami, 2008). According to Texas Reading Agency (2004, p.9), “A strategy is a general set of steps used to solve
problems”. In beginning reading and literacy, problems can include learning how to
decode unfamiliar words, how to read with sufficient fluency to maximize
students usually use metacognitive strategies. Metacognitive strategies refers to the
process of considering and regulating one`s own learning (Reading with
metacognition). The strategies can be used when they face problem in reading. They can use strategies to overcome better with the information to interact and assess
which ones for use in the most appropriate times (Garcia, Ramayan, Sepe & Silor, 2014).
According to Timothy Shanahan (2010) there are metacognitive strategies that can help the students learn from the text. The strategies are:
Activating prior knowledge/ predicting. Students thinkabout what they already know and use that knowledge in conjunction with other clues to construct meaning from what they read or to hypothesize what will happen next in the text. Activities related to the strategy are:
Pulling out main ideas. Pull out a main idea from the text and relates the idea to their experience. Students` predict whether a similar experience might occur in the text.
Halfway through the story. The Students predict what will happen at the end of the story. The students` explain how they decided on their prediction, which encourages them to make inferences about what they are reading and to look at the
Questioning. Students develop and attempt to answer questions about the
important ideas in the text while reading, using words such as where or why to develop their questions.
A technique of practices for questioning strategies are for example, by putting
words that are used to formulate questions (e.g., where, why) on index cards. The students` answer questions using these words.
Visualizing. Students develop a mental image of what is described in the text.
A practice for visualizing is, first, students visualize what is described in the text and remember what they read. Second, the students examine objects placed in front of
them, and later a picture depicting a scene. The students visualize and describe what they saw.
Monitoring, clarifying, and fix up. Students pay attention to whether they
understand what they are reading, and when they do not, they reread or use strategies
that will help them understand what they have read.
A practice for doing strategies are first, relate each strategy to a traffic sign (e.g., stop sign—stop reading and try to restate in your own words what is
happening in the text; U-turn—reread parts of the text that do not make sense). Reading comprehension strategies on cards with their signs, and have students work
in pairs to apply the strategies to text they do not understand.
Activities to make students to practice these strategies are, looking for key
words that help them understand text, and drawing inferences from such words. For example, a passage mentions “clowns” and “acrobats” is probably taking place in a
circus. Second, students’` identify key words in a sample passage of text and learn
about the passage from those words.
Summarizing/ Retelling. Students briefly describe, orally or in writing, the
main points of what they read. The strategy to practice summarizing is, the student describe the text in his or her own wordsto a partner or a teacher.
Advantages of Reading Comprehension
“Positive associations formed from being read to be able lead to an increasing
interest in books” (Crook, 2010, p.3). it was told that the system of education is not
ready for employing other strategies and in the present condition intensive reading is more effective, because the final goal for the students` was getting a good mark and
to be prepared for university entrance exam (Erfapour, 2013).Reading also helps to build concentration and attention skills
Reading builds vocabulary. In elementary school the students learned how
to infer the meaning of one word by reading the context of the other words in the sentence. The students get the same benefits from reading a book. While reading
books, especially challenging ones, the students will find themself exposed to many new words e.
Reading helps self-esteem. The key reading benefits is that the more the
more confidence. More confidence builds self-esteem. So it’s a chain reaction. Since the students are so well read, people look to them for answers. The student’s feelings
about themselves get better.
Reading improves creativity. Readingabout the diversity of life and expose
the students to new ideas and more information helps to develop the creative side of the brain as it imbibes innovation into reader thinking process, perhaps the best
reading benefit of all.
Review of Related Studies
There are some researches similar to the current research. Garcia, Ramayan,
Sepe and Silor (2014) studied the students’ difficulties in reading comprehension and
their metacognitive strategies in analyzing the lesson in technology and livelihood education in the college of education. The method of the research used random survey to 30 respondents who were identified by putting their names on the bowl and
were chosen by picking up. The Findings revealed that comprehension is very important to the Technology Livelihood Education students (TLE students). Reading comprehension is incredibly complex and multifaceted and TLE students used of
metacognitive strategies to be aware of their thinking processes in reading comprehension.
The second study was conducted by Sideridis, Mouzaki, Simos, and Protopapas (2006) who deliberated the classification of students with reading comprehension difficulties: the roles of motivation, affect, and psychopatholgy. The
participants. The researcher used liner discriminant analyses. The results of this study
is the students with reading comprehension difficulties could be accurately predicted by low cognitive skills and high competiveness. The conclusion of the study is that motivation, emotions, and psychopathology play a pivotal role in explaining the
achievement tendencies of students with reading comprehension difficulties. The third study was conducted by Wise, Sevcik, Morris (2010) who studied
the relationship between different measures of oral reading fluency and reading comprehension in second-grade students who evidence different oral reading fluency difficulties. The participants were second-grade students who were recruited for
participation in different reading intervention studies. Data analyzed were from
measures of nonsense-word oral reading fluency, real-word oral reading fluency, oral reading fluency of connected text, and reading comprehension that were collected at the pre-intervention time point. The result of the study is correlational and path
analyses indicated that real-word oral reading fluency was the strongest predictor of reading comprehension performance in both samples and across average and poor reading comprehension abilities.
The fourth, Febriani (2011) carried out a study on improving reading comprehension through reciprocal teaching technique. It was conducted through
action research. The instruments used in this research involved the English test sheet, observation sheets, and interview guidelines. The result shows the comprehension of the students in the text through reciprocal teaching technique has been improved, the
the KKM or 81.08% students and derived mean score is 75.57. This means learning is
generally positive.
Several previous related studies above were conducted in reading
comprehension scope that show that reading comprehension bring many difficulties.
The current research in EED of UMY also studied reading comprehension which focused on difficulties and strategies in reading. Similar method was applied in the
current research which used quantitative design. The one with qualitative method added the wider scope in reading comprehension.
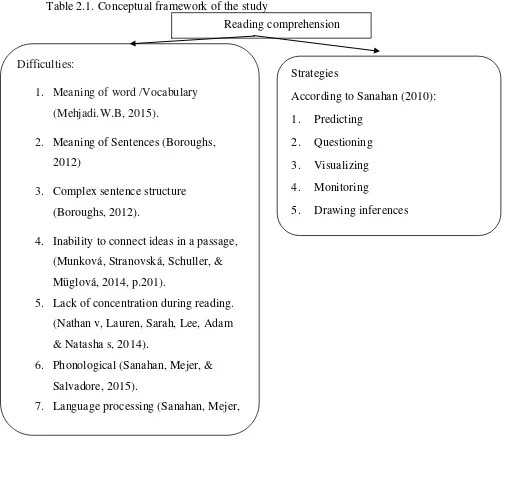
Conceptual framework
Reading comprehension is process to understand about main idea in text
which is read by someone. Reading comprehension needs concentration to understand idea, opinion, and theory from textbooks. This process is very important for
increasing the level of reader, because reading is one part in English language
learning. Reading comprehension needs strategies to overcome the problem. Many people have difficulties in reading comprehension. The difficulties in reading comprehension probably deal with confusion of the meaning of words and
sentences, inability to connect ideas in a passage, and lack of concentration during reading. Moreover, the other difficulties in reading comprehension are complex
sentence structure, phonological, and language processing.
Strategies are solution for reader when they face difficulties in reading activities. The readers needs some methods to solve their problem in reading. The
activating prior knowledge/predicting, questioning, visualizing, monitoring, drawing
inferences, and summarizing/retelling. The conceptual framework is presented in the following chart.
Table 2.1. Conceptual framework of the study
Reading comprehension
4. Inability to connect ideas in a passage, (Munková, Stranovská, Schuller, & Müglová, 2014, p.201).
Chapter Three
Research Methodology
This chapter discusses the research design research setting, population and sample of the research, data gathering technique, and data analysis method.
Research Design
This research was designed by using quantitative research design.
According to Creswell (2012), quantitative research is a research in which
investigators manage a survey to a sample or to the entire population of people to describe the attitudes, opinions, behaviors, or characteristics of the population. In
this research, the researcher conducted the research using descriptive quantitative. The researcher used quantitative research, because the researcher conducted the
research to describe the difficulties that were faced by the students and the strategies that they used in reading as generalization.
Setting of Research
The study was carried out at EED of UMY as the setting of this research. The researcher chooses EED of UMY as the setting because EED of UMY
requires the students to read textbooks a lot. When the students read textbooks, they face difficulties and they use various reading strategies. Therefore, EED of
UMY is suitable for the setting of this research because this research deals with students’ reading difficulties and strategies.
Population and Sample
The population of this research were the students of batch 2014. The students of this batch were chosen since they had enough reading experience and
students of batch 2014 was 160 students. According to Saleh (2011) the minimum
number use of sample is presented in the following guideline:
Table 3.1 Number of sample
Population Sample
UP to 100 50%
101 to 500 30% to 50%
501 - 1000 20% – 30%
Above 15% – 20 %
Source: Saleh (2011)
The population of participant was 160 students at EED of UMY batch
2014. The sample taken was 64 students or it was about 40% of the population. So, the number of population is appropriate with the theory by Saleh (2011).
Data Gathering Techniques
In this study, the researcher used questionnaire as the instrument to collect the data. The questionnaire was used to measure difficulties in reading
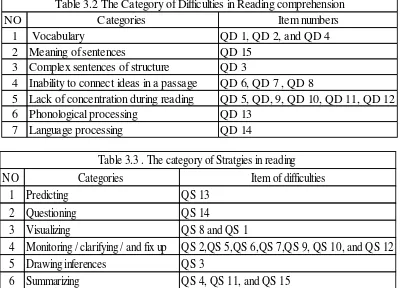
, lack of concentration during reading (Nathan v, Lauren, Sarah, Lee, Adam & Natasha s, 2014), phonological processing (Sanahan, Mejer, & Salvadore, 2015)., and language processing (Sanahan, Mejer, & Salvadore, 2015). These categories consisted of fifteen items. Besides that, there were six categories of strategies in reading. They were predicting, questioning, visualizing, monitoring / clarifying / and fix up, drawing inferences, and summarizing / retelling. These categories consisted of fifteen items and related with theory by Sanahan et al (2010). The categories and item numbers of difficulties and strategies in reading are shown in Table 3.2 and 3.3.
The researcher distributed questionnaires to EED of UMY students batch
2014 at the classroom. Students spent ten minutes to answer thirty items questionnaire. After students finished answering questionnaire, the researcher
took the result. The researcher used 65 questionnaires was distributed to
participant of EED of UMY students batch 2014 in three class. 64 questionnaires was collected from participant in class of EED of UMY students batch 2014. The
NO Categories Item numbers
1 Vocabulary QD 1, QD 2, and QD 4
2 Meaning of sentences QD 15
3 Complex sentences of structure QD 3
4 Inability to connect ideas in a passage QD 6, QD 7 , QD 8
5 Lack of concentration during reading QD 5, QD, 9, QD 10, QD 11, QD 12
6 Phonological processing QD 13
7 Language processing QD 14
Table 3.2 The Category of Difficulties in Reading comprehension
NO Categories Item of difficulties
1 Predicting QS 13
questionnaire item and guidelines of questionnaire item are attached in Appendix
1.
Validity
Validity is the measurement to indicate the level of certain instrument
(Arikunto, 2002). “Validity is the most important characteristic to consider when constructing or selecting a test or measurement technique” (Postlethwaite, 2005,
p.39). The instrument is called valid when the instrument measures what the researcher wants to measure and can reveal the data of the variables. The researcher used construct validity. According to Cohen, Manion, and Morrison
(2011, p. 188) construct validity “concerns the extent to which a particular measure or instrument for data collection conforms to the theoretical context in which it is located”. Expert judgment from two lecturers of EED was used to
ensure the validity of the instrument.
Reliability
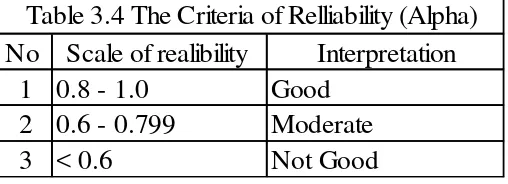
General Education Development testing service (2009) mentioned that reliability is inversely related to the amount of measurement error in test scores.
That is, the more measurement error present in test scores, the less reliable the test. In this study, the reliability performed used Cronbach`s Alpha Formula
techniques in SPSS 22.0 for Windows.
The range of reliability criteria is presented in the following table.
No Scale of realibility
Interpretation
1 0.8 - 1.0
Good
2 0.6 - 0.799
Moderate
3 < 0.6
Not Good
The item reliability of Difficulties was 0.6. It means the reliability of
Difficulties was in moderate level. The result of item reliability test of Strategies was 0.6. This means that the reliability of Strategies was in moderate level too.
Data Analysis Method
The data analysis method is a process to clarify the specific result of research with particular technique. This is to answer the research questions. This
includes determining how to assign numeric scores to the data, assessing the types of scores to use, selecting a statistical program, and inputting the data into a program, and then cleaning up the database for analysis (Creswell, 2012). As this
research uses quantitative method, the researcher make the results into a writing form that is easy to be understood and interpreted.
The researcher computed the data using electronic software for analysis (SPSS 22 program). The researcher calculated the level of student`s difficulties in
reading comprehension and reading strategies using by the students at EED of UMY. Moreover, the researcher used scale referenced grading to measure the difficulties in reading comprehension and strategies that were used by students
EED of UMY batch 2014. According to Sheridan (2016) the scale scores can be divided into several intervals. The Scale reference grading in this research is
presented in figure 4 below:
Chapter Four Results and Discussion
This chapter describes the results of the research. As this study used descriptive quantitative, the researcher described the results of the research
completely by using tables. The results essentially answered the research question. This chapter also shows the researcher’s discussion on the results.
Results
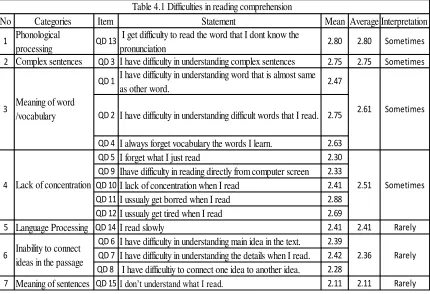
The table below shows the categories of difficulties in reading comprehension and describes the result of data analysis from categories of difficulties in reading comprehension. The table also describes the result of data analysis from fifteen items. The interpretation written on this table was based on scale referenced grading
presented in chapter three.
No Categories Item Statement Mean Average Interpretation
2 Complex sentences QD 3 I have difficulty in understanding complex sentences 2.75 2.75 Sometimes
QD 4 I always forget vocabulary the words I learn. 2.63 QD 5 I forget what I just read 2.30 QD 9 Ihave difficulty in reading directly from computer screen 2.33 QD 10I lack of concentration when I read 2.41 QD 11I ussualy get borred when I read 2.88 QD 12I ussualy get tired when I read 2.69
5 Language Processing QD 14 I read slowly 2.41 2.41 Rarely QD 6 I have difficulty in understanding main idea in the text. 2.39
QD 7 I have difficulty in understanding the details when I read. 2.42 QD 8 I have difficultiy to connect one idea to another idea. 2.28
7 Meaning of sentences QD 15I don’t understand what I read. 2.11 2.11 Rarely
Table 4.1 Difficulties in reading comprehension
I get difficulty to read the word that I dont know the
pronunciation 2.80 2.80 Sometimes
I have difficulty in understanding word that is almost same as other word.
QD 2 I have difficulty in understanding difficult words that I read.
The table 4.2 below shows the result of data analysis of metacognitive strategies used by the students in reading comprehension.
This table shows the categories of metacognitive strategies in reading used the EED students of UMY batch on 2014 and describe the result of data analysis of the mean point from categories of metacognitive strategies. Also, this table describe the result analysis of fifteen question. Also, the interpretation was written on this table. The result of this table is suitable with scale on chapter three.
Difficulties in reading comprehension
There are seven categories of difficulties in reading comprehension. The result of seven categories of difficulties in reading comprehension based on the range from
No Categories Item Statement Mean Average Interpretation
1 Predicting QS 13I use previous knowledge when I read. 3.06 3.06 Sometimes QS 2 I underline or highlight main idea what I read. 3.25
QS 5 Before I read, I decide the purpose for read. 2.64 QS 6 I read slowly and carefully to understand what I read.3.08 QS 7 I re-read when I lack of concentration. 3.30
QS 9 When I read, sometimes I stop and think what I
read. 3.13
QS 10When the reading is difficult, I pay more attention. 2.83 QS 12I re- read again, if I don’t understand. 3.13
QS1
I believe that it is easier to understand a reading passage if we memorize some of the information in it.
2.75
QS 8 To remember what I read, I try to imagine or
visualize the information what I read. 3.08
QS 4 I summarize main idea when I read. 2.78
QS 11I conclude what I read orally. 2.89 QS 15I use key word to summarize what I read. 2.98
6 Questioning QS 14I use question words (what, who, when, where,
why and how) for understanding what I read. 2.47 2.47 Rarely
Sometimes
I complete my reading with other references, when
the highest to the lowest score shown in table 4.1 are phonological processing
followed by complex sentences, meaning of word / vocabulary, lack of concentration during reading, language processing, Inability to connect ideas in a passage, and meaning of sentences. The result of each category of difficulties in reading comprehension is described below.
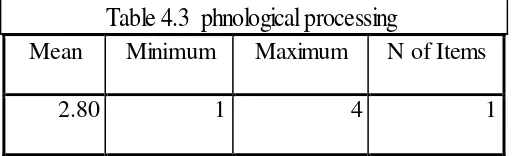
Phonological processing
The students have difficulties in phonological processing in reading
comprehension. The data description of phonological processing category is shown in table 4.3.
Mean Minimum Maximum N of Items
2.80 1 4 1
The item of difficulties related to phonological processing was shown by the mean score of 2.80. This score is in the category of “sometimes” as presented in table 4, page 18. This means the students ‘sometimes’ face difficulties related to
phonological processing when they read. Complex Sentences.
The result shows that the students have difficulties related to complex sentences in reading comprehension. Table 4.4 shows the statistic description of Complex sentence difficulties.
Mean Minimum Maximum N of Items
2.75 2 4 1
The mean of complex sentence difficulties in reading comprehension was 2.75 that was in category of “sometimes”. Therefore, the EED of UMY students batch 2014 sometimes face the complex sentences as difficulties in reading comprehension. Meaning of word / vocabulary.
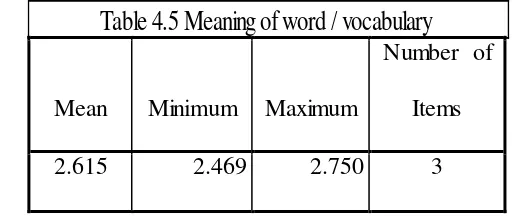
The result shows that the students have difficulties related to meaning of word or vocabulary in reading comprehension. Table 4.5 shows the statistic description of Meaning of word / vocabulary difficulties.
Mean Minimum Maximum
Number of Items
2.615 2.469 2.750 3
The mean average of the difficulties related to meaning of word or vocabulary was 2. 61 that was in the category of ‘sometimes’. This means that the EED of UMY students batch 2014 ‘sometimes’ face the difficulties related to meaning of word / vocabulary in reading comprehension.
Table 4.4 complex sentences
Lack of concentration during reading
The result shows that students have difficulties in reading comprehension because they lack of concentration during reading. The result can be seen in the table below.
Mean Minimum Maximum N of Items
2.519 2.297 2.875 5
The mean average of lack of concentration was 2.51 that was in the category of ‘sometimes’. This means that the students ‘sometimes’ lack of concentration when
they read.
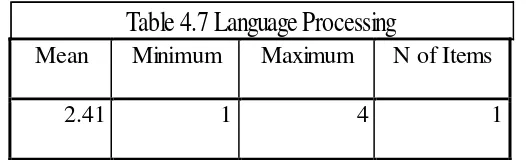
Language processing
The result in table 4.7 shows the score of language processing as difficulties in reading comprehension.
Mean Minimum Maximum N of Items
2.41 1 4 1
The mean average of language processing was 2.41 that was in category of “rarely”. This shows that the EED of UMY students rarely face language
processing as difficulties in reading comprehension. Table 4.6 Lack of concentration
Inability to connect ideas in a passage
The result shows the score of inability to connect ideas in a passage as difficulties in reading comprehension. The result as seen in table below.
Mean Minimum Maximum N of Items
2.365 2.281 2.422 3
The mean average of inability to connect ideas in passage was 2.36 that was in category of “rarely”. Therefore, the students` of EED of UMY ‘rarely’ face inability
to connect ideas in passage as difficulties in reading comprehension. Meaning of sentences.
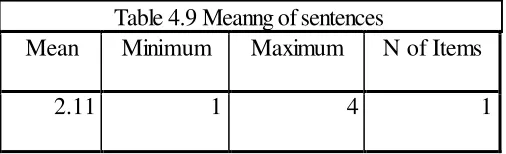
The result shows the score of meaning of sentences as difficulties in reading comprehension. The result can be seen in the table below.
Mean Minimum Maximum N of Items
2.11 1 4 1
The mean average of meaning of sentences was 2.11 that was in the category of “rarely”. This shows the students of EED of UMY rarely face the difficulties
related to meaning of sentences in reading comprehension. Table 4.8 Inability to connect ideas in passage
Metacognitive strategies in reading comprehension
The metacognitive strategies present some reading strategies that were used by students. There were six categories of metacognitive strategies in reading. The result of data analysis of the categories was ordered from the highest to the lowest as presented in table 4.2 page 18. They are predicting followed by monitoring,
clarifying, and fixing up, visualizing, summarizing, drawing inferences, and questioning. The result of each category of metacognitive strategies is described below.
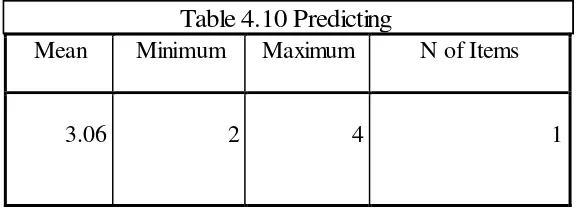
Predicting. The Result of description of predicting as a reading strategy used by the students is shown in table 4.10.
Mean Minimum Maximum N of Items
3.06 2 4 1
The mean average of predicting was 3.06 that was in category of ‘sometimes’, so the EED of UMY students batch 2014 ‘sometimes’ use predicting as one of the strategies in reading.
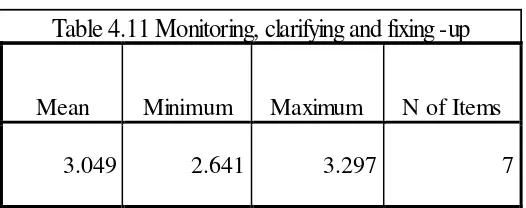
Monitoring, clarifying, and fixing up. The result of the data analysis on metacognitive strategies such as monitoring, clarifying, and fixing up can be seen in the table below.
The mean average of monitoring, clarifying, and fixing- up was 3.04 that was in category of ‘sometimes’, so the EED of UMY students batch 2014 ‘sometimes’
use monitoring, clarifying, and fixing-up as strategies in reading.
Visualizing. The result of data analysis on the visualizing strategy is shown in the table below.
Mean Minimum Maximum N of Items
2.914 2.750 3.078 2
The mean average of visualizing was 2.91 that was in the category of
‘sometimes’, so the EED of UMY student ‘sometimes’ use visualizing as strategies in
reading.
Summarizing / retelling. The result of summarizing / retelling can be seen in table below
Mean Minimum Maximum N of Items
2.885 2.781 2.984 3
Mean Minimum Maximum N of Items
3.049 2.641 3.297 7
Table 4.11 Monitoring, clarifying and fixing -up
Table 4.11 Visualizing
The mean average of summarizing / retelling was 2.88 that was in the category of ‘sometimes’. Therefore, the EED of UMY students ‘sometimes’ use
summarizing / retelling as their strategies in reading.
Drawing Inference. The result of data analysis on drawing inference is shown in table 4.13.
The mean average of drawing inference was 2.67 that was in the category of ‘sometimes’. Therefore, the EED of UMY students ‘sometimes’ use drawing
inference as their strategies in reading.
Questioning. The result of the data analysis on using questioning as reading strategy can be seen in table 4.14.
Mean Minimum Maximum N of Items
2.47 1 4 1
The mean average of questioning was 2.47 that was in the category of ‘rarely’. It means that EED of UMY students batch 2014 ‘rarely’ use questioning as
their reading strategies.
Mean Minimum Maximum N of Items
2.67 1 4 1
Table 4.13 Drawing inferences
Discussion
The result shows the description of the students` difficulties in reading comprehension. The difficulties in reading comprehension were sometimes faced by the students when they read. They were phonological processing, complex sentences, meaning of word / vocabulary, lack of concentration during reading, language
processing, inability to connect ideas in a passage, and meaning of sentences. In addition, the students used six metacognitive strategies when they read. They were predicting, monitoring, clarifying, and fix up, visualizing, summarizing, drawing inferences, and questioning.
Difficulties of reading comprehension. The data analysis shows that out of
seven difficulties in reading comprehension, the highest difficulty was related to the category of phonology processing. The mean of phonological processing was 2.80. This means the students sometimes face phonological processing. This result is appropriate with Sanahan et al. (2015) who mentioned that readers have a specific weakness in phonological processing. They might fail understanding phonetic coding. In this research, the statement on number thirteen “I get difficulty reading the words
that I didn’t know the pronunciation”represented the students’ difficulties in reading
related to the phonological processing especially the phonetic coding.
occur in written language that usually do not occur in oral language. This difficulty was shown in the statement ‘I have difficulty understanding complex sentences’.
On the contrary, the students ‘rarely’ face difficulties related to the meaning
of sentences as shown by the lowest score of mean 2.11. This means that that students rarely misunderstand the meaning of sentences when they read. The category of this difficulty is shown in item ‘I do not understand what I read’. Therefore, Boroughs’
(2012) statement which stated that many students have comprehension problems because they have difficulty interpreting the meaning in sentences is not highly reflected in EED of UMY students.
Metacognitive strategies in reading comprehension. In reading, the students apply some metacognitive strategies. The data analysis shows that from seven difficulties in reading comprehension, the highest strategy was related to the category of predicting. The mean of predicting was 3.06. It means the students sometimes use predicting when they do not understand to read text. The category of predicting is shown in item ‘I use previous knowledge when I read’. This is
appropriate with statement by Sanahan (2010). He said that the students think about what they already know and use that knowledge in conjunction with other clues to construct meaning from what they read or to hypothesize what will happen next n the text.
statement is ‘I believe that it is easier to understand a reading passage if we
memorize some of the information in it’. The second is ‘To remember what I read, I
try to imagine or visualize the information what I read’. The mean average of two
statements was 2.91. It means the students of EED of UMY sometimes use visualizing as their strategy when they read.
The result of data analysis showed that questioning was the lowest strategy in reading used by the EED students of UMY batch 2014. The mean was 2.47. It means the students rarely use questioning when they read. This strategy is represented in the item ‘I use question words (what, who, when, where, why, and how) for
understanding what I read’. Sahanan (2010) stated that students develop and attempt
Conclusion and suggestion
This chapter describes the summary or conclusion of the research and suggestion to overcome the problems in reading comprehension. The conclusion explains the result of this research after the description of data analysis was presented in the previous chapter. The suggestions in this study can be used to solve the problem of reading comprehension.
Conclusion
The final conclusion can be described as follows. The result on this research shows the mean of seven categories of difficulties in reading comprehension and six categories of strategies in reading.
The mean of categories of difficulties in reading comprehension of EED students of UMY batch 2014 was calculated from the means of the categories of phonological processing, complex sentences, meaning of word / vocabulary, lack of concentration during reading, language processing, inability to connect ideas in a passage, and meaning of sentences. The mean of categories of strategies in reading comprehension of the EED students of UMY batch 2014 was calculated from the means of categories of predicting, monitoring, clarifying, and fix up, visualizing, summarizing, drawing inferences, and questioning.
strategy. Suggestion
Based on the result of the research, the researcher provides suggestion to the lecturer and to the students. The suggestion is the opinion from researcher to give solution of the difficulties in reading comprehension.
The lecturers. The basic of reading is better introduced to the EED of UMY students as early as possible. The theory of reading comprehension is important for students. The reading comprehension is important to improve ability and creativity for EED of UMY students. The lecturers is suggested to guide the students to use suitable strategies in reading comprehension.
The students. In reading comprehension, the students should learn about the definition of reading comprehension. They should read more. Reading more books in one week can improve their ability on reading comprehension and they will be aware about the difficulties in reading comprehension. As a result students are suggested to apply more strategies in reading.
BOROUGHS, K. (2012). LANGUAGE & READING.
Catherine Snow. (2002). Reading for understanding : toward a research and development program in. Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, Pittsburgh: Rand. Retrieved from
http://www.rand.org/
Charles Perfetti and Joseph Stafura. (2014). Word Knowledge in a Theory of Reading Comprehension. Scientific Studies of Reading. doi:10.1080/10888438.2013.827687
county, d. o. (2016). Standards - referenced gathering. Ranchester, WY: sheridan county district 1.
Creswell, J. W. (2012). EDUCATION RESEARCH. nebraska .
Crook, D. (2010). Benefits and guidelines for reading to young children.
Erfanpour, M. A. (2013). The Effect of Intensive and Extensive Reading Strategies on
ReadingComprehension: A Case of Iranian High School Students. English for Specific Purposes World, 14(41). Retrieved from http://www.esp-world.info
Farah El Zein • Michael Solis • Sharon Vaughn •Lisa McCulley. (2013, november 12). Reading
Comprehension Interventions for Students with Autism. doi:DOI 10.1007/s10803-013-1989-2
Literature at Al-Zaytoonah Private University of Jordan. Asian Social Science, 8. doi:10.5539/ass.v8n4p237
Kristen D, beach and Rollanda O`connor . (2014 ). Developing and Strengthening Reading Fluency and Comprehension of poor readers in elementary school : a focused review of research . Perspectives on Language and Literacy.
Kulesz, P. A. (2014, May). THE EFFECTS OF READER CHARACTERISTICS, TEXT FEATURES, AND COMPREHENSION PROCESSES ON READING
COMPREHENSION.
Mania Nosratinia, Rosa Salehi Gourabsari and Elnaz Sarabchian. (2014). TOWARD
LEARNER-CENTERED READING: LINKING EFL LEARNERS’ AUTONOMY, VOCABULARY LEARNING STRATEGIES, AND READING COMPREHENSION. Modern Journal of Language Teaching Methods (MJLTM), 4(3).
McKee, S. (2012, February ). Reading Comprehension, What We Know: A Review of Research 1995 to 2011. Language Testing in Asia, volume.2, issue.1 ).
MEDJAHDI, W. B. (2015). Reading Comprehension Difficulties among EFLLearners: The Case of Third-Year Learners at Nehali Mohamed Secondary School.
http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/misunderstoodminds/readingdiffs.html
nayton, m. (2013). factors that contribut to successful reading comprehension .
Nixon, G. (n.d.). Benefits of Reading. Retrieved from gemm learning:
www.gemmlearning.com/blog/reading_and_dyslexia/benefits-reading
Ruth Schoenbach, Cynthia Greenleaf, Lynn Murphy. (2012). Reading for understanding . WESTED.
Saleh, M. (2012). Begining research in english language teaching. (h. waluyo, Ed.) semarang: Widya karya.
Scott, C. M. (2009, April ). A Case for the Sentence in reading comprehension. LANGUAGE, SPEECH, AND HEARING SERVICES IN SCHOOLS, volume.41, 184 -191 .
Supriasmoro. (2013 , maret ). MENANGANI ANAK KESULITAN BELAJAR MEMBACA. 1.
weaver, C. (2009). Reading Process. Brief Edition of Reading Process and Practice.
YOGYAKARTA
Nama Peneliti: Didit Nur Yulianto / 20120540052 PENELITI MENJAMIN KERAHASIAAN RESPONDEN Nama :__________________________________
No. Mhs./Class: ___________________________
Questionaire ini dibuat untuk tujuan penelitian. Informasi yang diberikan tidak akan digunakan untuk kepentingan yang lain. Tidak ada jawaban yang benar dan salah. Jawaban Anda sangat berarti untuk penelitian ini. Terima kasih atas bantuan dan kerjasamanya.
Petunjuk: Jawablah setiap pertanyaan dengan memilih salah satu angka diantara 4 sampai 1 untuk menunjukkan hal-hal yang pernah Anda alami. Angka-angka tersebut mempunyai makna seperti berikut:
4 = Sangat Sering 2. Jarang
3 = Sering 1. Sangat Jarang
Kesulitan dalam memahami bacaan berbahasa Inggris
No. INDIKATOR 4 1. Saya kesulitan memahami kata yang tulisannya hampir
sama dengan kata yang lain. 8. Saya sulit menghubungkan ide pokok dengan ide-ide
yang lain dalam bacaan.
9. Saya sulit membaca langsung dari layar computer. 10. Saya kurang konsentrasi ketika membaca.
11. Saya mudah bosan ketika membaca. 12. Saya mudah lelah ketika membaca.
13. Saya sulit memahami kata yang cara pengucapannya belum saya ketahui.
No. INDIKATOR 4
dengan menghafalkan informasi dalam bacaan. 2. Saya menggaris bawahi atau menstabilo ide-ide
utama.
3. Saya juga melengkapi dengan membaca referensi lain ketika membaca sebuah topik.
4. Saya menulis ringkas ide utama dalam bacaan. 5. Sebelum membaca, saya menetapkan dulu tujuannya
membaca.
6. Saya membaca secara perlahan dan hati-hati agar paham.
7. Saya membaca ulang ketika kehilangan konsentrasi. 8. Agar ingat apa yang saya baca, saya mencoba
membayangkan atau memvisualisasikan informasinya.
9. Ketika membaca, saya kadang-kadang berhenti dan berpikir tentang apa yang saya baca.
10. Ketika bacaannya sulit, saya lebih memperhatikan apa yang saya baca.
11. Saya menyimpulkan bacaan secara lisan.
12. Saya membaca ulang ketika saya belum paham. 13. Saya menggunakan pengetahuan saya sebelumnya
ketika membaca.
14. Saya menggunakan kata tanya (what, who, when, where, why dan how) untuk memahami bacaan. 15. Saya menggunakan kata kunci dalam bacaan untuk
menyimpulkan bacaan