THE EFFECT OF VIDEO GAME TOWARDS STUDENTS’
READING COMPREHENSION OF NARRATIVE TEXT
(A Quasi-experimental Study at the Eighth Grade of SMP Negeri 96 Jakarta in theAcademic Year 2015/2016)
A ‘Skripsi’
Presented to the Faculty of Educational Sciences as a Partial Fulfillment of Requirements for Degree of S.Pd. (S-1) in English Education
By
AUDREY NINGTYAS
1111014000083
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION THE FACULTY OF EDUCATIONAL SCIENCES SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
iii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
In the name of Allah, The Beneficent and The Merciful
All praises be to Allah S.W.T., Lord of the worlds, for the blessing, the
guidance and the strength given to the writer in completion this research. Peace
and blessing be upon to Prophet Muhammad S.A.W., his family, his companion,
his adherence.
It is an honor the writer could finally accomplish a skripsi entitled “The Effect of Video Game towards Students’ Reading Comprehension of Narrative Text” (A Quasi-experimental Study at the Eighth Grade Students of SMP Negeri 96 Jakarta Selatan).This paper is submitted to fulfill one of the requirements for
the Degree of S.Pd. at the Department of English Education of Faculty of
Educational Sciences, State Islamic University Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta.
She dedicated this skripsi to her beloved parents, and brother, Dwi Atmodjo, Hariyanti S.Pd, and Aldo Ghani Atmodjo for eternal love, great support and
patience. Furthermore, the writer would particularly thank to her wonderful and
excellent advisors, Dr. Alek, M.Pd.and Zaharil Anasy, M.Hum., for the guidance,
knowledge, patience, and motivation in helping the writer to accomplish this
skripsi. In this occasion, the writer would like to give her deepest gratitude and salute to:
1. Prof. Dr. Ahmad Thib Raya, M.A., the Dean of Faculty of Educational
Sciences, Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta.
2. The Head of Department of English Education and the secretary of
Department of English Education, Dr. Alek, M.Pd. and Zaharil Anasy,
M.Hum.
iv
very brilliant and excellent.
5. H. Dwi Atmodjo (beloved father) and Hj. Hariyanti (beloved mother) who
always give their best motivation, everlasting love, wonderful patience, great
trust to the writer.
6. Families, especially the writer’s brother, Aldo Ghani Atmodjo who always
been the reason the writer bears every struggle.
7. The very close friends, Ernita Dewi K., M.M, Yulianti Sari, Nicky
Dwiningrum S.Pd., Putik Delima, Selinda Febriani S.Pd., Nadia Karimah
S.Pd., dan Novika Rahayu Ningtyas for their eternal support and help.
8. M. Hafidz Maulana, S.E. the writer’s partner. Thank you for his support and
keeping up with the writer’s hardships during writing this skripsi.
9. Rizka Muslimaini, S.Pd., Lulu Walidaini S.Pd., Nurita Wulandari S.Pd., Syifa
Fauziah S.Pd., and Gustav Firman for helping writer with patience during
writing skripsi.
10. English Education B Class family, for the great and bitter moments of writer’s university life.
11. The writer’s special warm for those one who have given such great help,
v
ABSTRACT
Ningtyas, Audrey (1111014000083). The Effect of Video Game towards Students’ Reading Comprehension on Narrative Text (A Quasi-experimental Study at the Eighth Grade Students of SMP Negeri 96 Jakarta Selatan). Skripsi, The Department of English Education, Faculty of Educational Sciences, Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University, 2016.
This research aimed to see the effect of video game towards students reading comprehension of narrative text. The sample was 30 students on the eighth grade students of SMP Negeri 96 Jakarta Selatan. The class samples were VIII-2 and VIII-3. The effect of video game can be seen from students’ multiple choice scores. The writer used a quantitative method and quasi experimental design as the research methodology with a purposive sampling technique. The research instrument was a multiple choice test.From the result of statistics calculation, it was obtained that the value of Tvalue was 1.10 and the degree of freedom (df) was
58. In the table of significance 5% the value of the significance was 1.67 (Ttable).
In comparison, the result was 1.10 < 1.67 which means Tvalue score was lower than
Ttable score. Therefore, the Null Hypothesis (H0) was accepted and the Alternative
Hypothesis (Ha) was rejected. This means, the video game has no effect towards
students’ reading comprehension of narrative text at the eighth grade students of SMP N 96 Jakarta Selatan. In conclusion, video game is not recommended as a media to learn reading comprehension of narrative text for Junior High School students.
vi
Siswa dalam Membaca Teks Narasi (Penelitian Kuasi Eksperimen terhadap Siswa Kelas Delapan di SMP Negeri 96 Jakarta Selatan). Skripsi jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Ilmu Pendidikan, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, 2016.
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk melihat apakah ada efek dari penggunaan video game terhadap kemampuan siswa dalam membaca teks narasi. Sampel penelitian ini adalah 30 siswa kelas 8 dari SMP Negeri 96 Jakarta Selatan. Kelas sampel adalah kelas VIII-2 dan VIII-3. Keefektifan siswa dapat dilihat berdasarkan nilai test pilihan ganda Bahasa Inggris siswa. Penulis menggunakan metode kuantitatif dan desain kuasi eksperimen sebagai metode penelitiannya dengan menggunakan teknik purposive sampling. Instrumen penelitian ini adalah tes soal pilihan ganda. Berdasarkan hasil dari hitungan statistic diperoleh hasil Tvalue yaitu 1.10 dan
derajat kebebasan (df) adalah 58. Dimana pada signifikansi 5% nilainya adalah 1.67 (Ttable). Dibandingkan dengan skornya, hasilnya adalah 1.10 < 1.67 yang
berarti Tvalue lebih kecil daripada Ttable. Kesimpulannya, Null Hypothesis (H0)
diterima dan alternative hipotesis (Ha) ditolak. Maka dari itu, tidak ada efek dari
penerapan video game terhadap kemampuan membaca siswa pada teks narasi terhadap siswa di SMP Negeri 96 Jakarta Selatan yang berarti bahwa permainan Video tidak di rekomendasikan untuk siswa SMP sebagai sarana mempelajari kemampuan membaca teks narrative.
vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
APPROVAL SHEET ... i
ENDORSEMENT SHEET ... ii
SURAT PERYATAAN KARYA ILMIAH ... iii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... iv
ABSTRACT ... vi
ABSTRAK ... vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... viii
LIST OF TABLES ... x
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xi
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Background of the Study ... 1
B. Identification of the Study ... 2
C. Limitation of the Problem ... 3
D. Formulation of the Problem ... 3
E. Objective of the Study ... 3
F. Significance of the Study ... 4
CHAPTER II. THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK ... 5
A. Reading ... 5
1. Definition of Reading ... 5
2. Reading Comprehension ... 6
3. Kinds of Reading ... 10
4. Models of Reading ... 11
5. Techniques of Reading ... 12
6. Purpose of Reading ... 12
7. Problems of Reading ... 14
B. Narrative Text ... 15
viii
1. What is a Video Game ... 18
2. Characteristics of Video Game ... 18
3. Motivation behind Playing Game ... 19
4. Narrative Devices in Video Game ... 19
D. Previous Study ... 20
E. Thinking Framework ... 23
F. Theoretical Hypothesis ... 23
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 24
A. Place and Time of the Research ... 24
B. Design of Research ... 24
C. Method of the Research ... 24
D. Population of the Research ... 25
E. Sample of the Research ... 25
F. Research Instrument ... 25
1. Instrument for Reading Comprehension of Narrative Text .... 26
G. Data Collection Technique ... 27
H. Data Analysis Technique ... 29
I. Statistical Hypotheses ... 32
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH FINDING AND INTERPRETATION ... 33
A. Research Findings ... 33
1. Data Description... 33
2. Data Analysis ... 37
3. Test of Hypotheses ... 39
ix
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTIONS ... 45
A. Conclusion ... 45
B. Suggestion ... 45
REFERENCES ... 47
x
Table 3.1 Test for Pre-test and Post-test ... 26
Table 4.1 Students’ Scores in Experimental Class ... 33
Table 4.2 Students’ Scores in Controlled Class ... 35
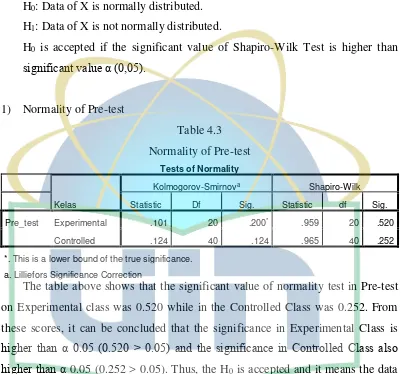
Table 4.3 Normality Pre-test ... 37
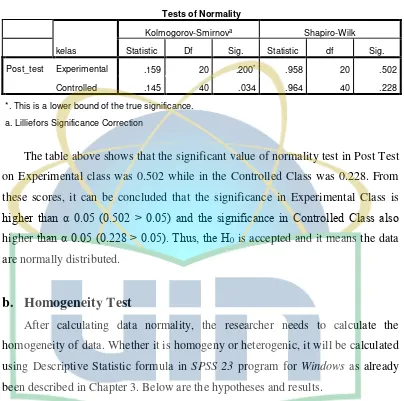
Table 4.4 Normality Post-test ... 38
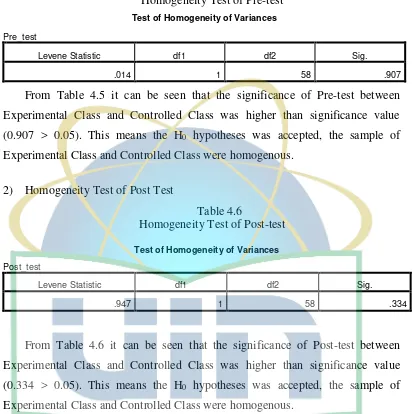
Table 4.5 Homogeneity Test of Pre-test ... 39
Table 4.6 Homogeneity Test of Post-test ... 39
xi
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix 1. Pre-test and Post-test Instrument ... 61
Appendix 2. Rencana Pelaksanaan Pembelajaran (RPP) Kelas Kontrol ... Appendix 3. Rencana Pelaksanaan Pembelajaran (RPP) Kelas Experimental ... 87
Appendix 4. Answer Key ... 88
Appendix 5. English Subject Syllabi of KTSP on 8th Grade Students in SMP N 96 Jakarta Selatan ... 89
Appendix 6. F-table ... 92
Appendix 7. t-table ... 93
Appendix 8. Surat Pengesahan Proposal Skripsi ... 94
Appendix 9. Surat Bimbingan Skripsi ... 95
Appendix 10. Surat Permohonan Izin Penelitian ... 96
Appendix 11. Surat Keterangan Penelitian dari Sekolah ... 97
Appendix 12. Foto-Foto Kegiatan Penelitian ... 98
1
A.
Background of the Study
In Indonesia, English is one of the subjects learned in school. It is learned
from elementary school up until college. The stage of learning English may vary
based on the school system and the curriculum. Mainly, there are four Basic
English skills that taught in school, listening, speaking, reading, and writing.
Listening, speaking and reading are taught since elementary school; only a little
part of writing skill is learned by the students. For example, writing a simple
sentence with the introduction of simple present tense.
For EFL students, each of those skills has its own problems and difficulties
when learned. The lack of knowledge about English language could be a problem
for listening and reading. Often, the lack of facility such as dictionary also affects students’ performance in learning English.
Based on the researcher experience in the school she teaches, many students
find it hard to learn English at school. It can be because of the lack of vocabulary
also because of teacher could not make the learning to be more fun and
interesting. Students are tired of monotonous learning which is full of task and
homework. Especially for reading sections, students feel tedious when they are
faced with long texts or story in exam; it is because they could not understand the
words they read. The researcher also experiences the feeling when she needs to
practice her reading comprehension. Not only that, students complained that
English is hard to learn and mostly, it is because they still could not grasp the
benefits they could get from learning English in the future. Therefore, the
researcher wants to prove that English could be learned in many different ways
and this time focused only on the fun and interesting way.
Students already learn English structure at school; each school have different
teacher, and therefore each teacher have their own method in teaching English. It
2
job to make all students understand what they have learned is hard. Teacher often
give them instruction to read their dictionary at home, but mostly they do not
listen. The purpose of this study is not only helping the students to learn English but also lessen teachers’ burden in case of vocabulary and reading comprehension.
Using video game as the method to learn English also has been used by researcher’s friends and relatives as prove that video game have positive effect too. The plot of the story made the player wanted to understand what they should
do or what is happening actually in the game, in order to get a good ending. Player
can be immersed in the world of simulated game, where they had to understand
the story to move on the next scene of the game.
That is not the only reason why the researcher wants to use video game as a
media to learn English. 8th grade students usually keen on playing video games,
by using video game; it might be the successful way to make students interested in
learning English more.
To get the idea or the plot story of the game, students need to understand the
conversations in the game. This is where Reading Comprehension skill is
important. Reading Comprehension is the ability to read process and understand
the meaning of a text.1 The researcher wants to see if video game could make the
students interested to learn English in order to understand the story. In other
words, the researcher wants to find out if this game does have effects on students
reading comprehension or not.
B.
Identification of the Problem
Based on the background of the study, it can be identified some problems as
follows:
1. Students find it boring when they have to read texts too much in order to
answer some text based questions.
2. The students have low motivation to comprehend stories or questions when
they do not really have mutual purpose of it.
3. Students have low interest in practicing to find words meaning in dictionary to
practice their comprehension.
C.
Limitation of the Problem
Based on the problems identified above, the problems of the research are
focused on as follows:
1. Using video game in learning English at the eighth grade students of SMP
Negeri 96 Jakarta.
2. Reading comprehension of Narrative text at the eighth grade students of SMP
Negeri 96 Jakarta.
D.
Formulation of the Problem
Based on the limitation of problems above, the problem of the research will
be formulated as follows: is there any different effect before and after using video
game on reading comprehension of narrative text at 8th grade students in SMP
Negeri 96 Jakarta?
E.
Objective of the Study
Based on the research questions, the objective of research is to obtain
empirical evidence about the effect of using video game on reading comprehension
4
F.
Significance of the Study
The results of this study are expected to give some clarity or significances not
only theoretically but also practically go to:
1. Students
The significance of this study, especially for students, is that it can give
students insight on methods of learning English. That English is not only learned
at school but also from other activities that they may enjoy in everyday life, for
example: playing video games.
2. Teachers
Through reading this research result, the teacher can grasp or promote their
understanding about some of the media used in teaching and learning EFL.
Besides, teacher also can apply any theories on best practices to their real teaching
situations.
3. Future Researchers
This study could be useful for future research on video games and its
relationship regarding the English language. It also can be a reference for future
5
A.
Reading
1.
Definition of Reading
Based on the research by National Reading Panel, reading is a complex
process that needs systematic instructional approach,1 while in Tiedeman,
Vygotsky and Wartofsky stated that there are two types of tools that can be used
in reading.2 It is the actual objects or instruments used to read, and the
visualization or symbols in picture and alphabetic.
From those statements it can be concluded that reading is a complex process
that will be systematically perceptible using a printed pages or multimedia
consisting of pictures and alphabets. This means reading is a process where the
brains systematically receive the information from the object used and based on
the prior knowledge of readers on the symbols and alphabet to understand what
the text is about.
Furthermore, reading also a process where symbols and alphabets combined to send the authors’ message to the reader, in this process the reader need to have a syntactic, semantic and pragmatic information to understand the authors’
message.3 Reading involves interaction between the readers’ thoughts, knowledge
and the texts being read. Thus, the results of one comprehension may differ from
each other because they may have different background knowledge and thoughts
in the text they read.
1 Cathy Healy, Reading: What the Experts Say: The Lowdown on the National Reading
Panel, PEATC, p. 1.
2 John Patrick Tiedemann, New Literacies, New Contexts? a Theoretical Definitions of
Reading Context, (Vanderbilt University, 2011), p. 4.
3 Donald Jr. J. Leu, Charles K. Kinzer, Effective Reading Instruction in the
6
2.
Reading Comprehension
Wooley stating on his journal that reading comprehension is a process to
make a meaning of a text but its goal is to understand the meaning of a whole text
not for each word or sentence.4 While Dutcher in Ulmer et al stating that reading
comprehension is a process which the reader background knowledge, the
information on the text and the situation when reading are interacted with each
other.5 From those points of view, the researcher concludes that a reading
comprehension is the complex process to understand what it is about by using our
prior knowledge and connecting with the information on the text.
Reading comprehension skill for EFL/ESL students is a little bit hard to
obtain. It could be because of the lack of memorizing the vocabulary, their method
of learning, their motivations or even the interventions from another subject that
can be considered more important than English.
a. Major Components of Reading Comprehension Process
1) Decoding KnowledgeDecoding knowledge is the knowledge used to determine a word with the
same meaning in the text. Decoding knowledge may be useful for reading
comprehension but it may not necessary too. It is useful when the reader identify
the meaning of word. Many readers know the spoken language form of words but
they do not know the written form. By using decoding knowledge, reader could
understand most of oral language in their written form. Decoding knowledge may
not be necessary if the words were scientific but, we could use the context clues in
order to understand the sentence.
4 Gary Woolley, Reading Comprehension: Assisting Children with Learning Difficulties,
Retrieved fromhttp://www.springer.com/us/book/9789400711730, p. 15.
5 Constance Ulmer et al, Creating Games as Reader Response and Comprehension
2) Vocabulary Knowledge
The ability to determine word meaning from context and determine oral
equivalent of words with their meaning are aspects of vocabulary knowledge. It is
vital for teacher to help their students improving the vocabulary knowledge, as
students will explore more unfamiliar subjects later in their lives. In the
vocabulary knowledge process, using context clues is handy, when students are
about to find the word meaning, they can look for it in the sentence after or before
the word.6
3) Syntactic Knowledge
In comprehension process, the knowledge of sentence syntax or word order is
important. It includes grammatical rules in a sentence and is useful to determine
meaning and pronunciations of words. Syntactic knowledge is learned by the
students from their early years with the help from their oral language ability.
4) Discourse Knowledge
Discourse knowledge includes the knowledge of structural organization of
many types of writing, for example, an argumentative essay will begin by thesis
statement and so on. It is useful for reading comprehension process, it fasten the
students ability to understand the story.
5) Readiness Aspects
Reading Readiness is the skill of students when they are about to read, it
means the benefits in comprehending text before reading a specific material.
Readiness includes knowledge of letter-names, left to right sequence of writing,
the ability to see similarities and differences in shapes, oral language proficiency,
ability to hear similarities and differences in sounds, ability to work cooperatively
in small groups and the ability to sustain independent works. Readiness consist of
pre reading activity such as developing background knowledge, learning new
vocabulary words, and so on.
8
6) Affective Aspects
Improving the students’ comprehension in reading would have a lot work to do. Making a comprehension learning session is often boring for students, and it is
encouraged to use as creative as possible in a way of learning comprehension in
reading.
b. Reading Comprehension Skill Characteristics
1) FluencyFluency is one of the required skills in comprehension. It is about the ability
to recognize the word meaning automatically in order to comprehend the
sentence. However, fluency appears to be a larger influence in developing reading
comprehension skills for younger readers compared to older ones. Yovanoff et al
in their study, proved that as text becomes more challenging with each grade
level, fluency becomes less predictive of reading comprehension and, instead,
gives way to vocabulary.
2) Vocabulary and Semantic Processing
Semantic processing is important in order to understand the meaning of the
text. It means, students must understand the word meaning before comprehending
the whole sentence. In one study of children from kindergarten through second
grade, Roth, Speece, and Cooper discovered that vocabulary skills, such as oral
definitions and word retrieval, were the best predictors of reading comprehension
development. A similar study conducted by Berninger et al at-risk second graders
revealed that verbal IQ was a statistically significant predictor of reading
comprehension in both the beginning and end of school year assessments
3) Visualization.
Another key component of reading comprehension is the active construction
reader understand the texts. The concept that readers process both visual
representations of verbal information and of objects to create meaning. Pressley
and National Reading Panel referred this mental imagery, that skill contributes to
comprehension and enhances memory of the text. In addition, Center et al and
Brown et al found statistically significant correlations between visualization
training and reading comprehension scores of students when used as part of a
multiple-strategy instruction intervention.
4) Working Memory
Working memory has also been identified as an important part of reading
comprehension. Rothlisberger et al stated that working memory is defined as an
executive function responsible for keeping and updating information in the mind.
Further, working memory is responsible for managing the process of extracting
information from text and integrating it with prior knowledge to create meaning.
Sequences of text-based information are held in working memory and integrated
with new incoming text and with prior knowledge held in long-term memory.
5) Reasoning and Inference.
Inferential reasoning is the ability to use information in the text to determine
additional information that implied by the text. National Foundation for
Educational Research discovered that the ability to draw inferences is directly
related to reading comprehension ability. The process of inferential reasoning
requires both short-term and long-term memory, as the provider of background
knowledge combined with the text to arrive at the implicit information from the
text7
7
10
3. Kinds of Reading
a. Intensive Reading
Intensive reading is an activity where the reader focused on the aims and
tasks of reading. Usually, intensive reading means to develop general reading
skill, such as vocabulary development, grammar learning, learning expressions in
the text, even translating the passage. Sometimes in the classroom, teacher asks
students to scan for specific information and skimming for main ideas as a part of
intensive reading activity.
However, intensive reading has several limitations. Students may not interest
with the text given by the teacher, also intensive reading activity using short text example which decrease the students’ chance to read fluently. The difference on students background knowledge is affecting on the goals in the activity, students
with low vocabulary knowledge might need teacher’s help in this part. In addition,
students are pacing with the time to meet the goals and the low level students
could be failed in meeting the goals of the activity.
b. Extensive Reading
Harmer states that extensive reading is a reading activity but with pleasure.8
Reading with pleasure means the activity of reading itself brings confidence and
enjoyment for the reader. For students, extensive reading includes reading novels,
newspaper, magazine or other materials. Students pick the materials themselves
and read at their own pace, they could read as much as possible. This activity
usually done outside the classroom, teacher only give the students
recommendations about what should they read or guiding the students what are
the goals after reading.
Though extensive reading is useful for students, it could be challenging for the teacher. It took a lot of time for teacher assessing students’ journal on their extensive reading activity, also extensive reading program is costly and time
consuming to set up if the materials are not enough for the students. Then,
8 Jeremy Harmer, How to Teach English: 2nd Edition, (England: Pearson Education
students who’s already experience intensive reading program may not believe in the extensive reading program way to learn language.
4. Models of Reading
These models of reading represent the process of general reading
comprehension based on their purpose, they are: 9
a.
Bottom-up Model
Bottom-up model indicates that the reader learning the text letter by letter or
word by word to get understanding of the whole text. According to Gough (1972),
it is begin by translating the parts of written language (letters) into speech sounds,
after that piece the sounds together to form individual words, and then piece the words together to arrive at an understanding of the author’s written message. Bottom up model uses only a little background knowledge from the reader.
b.
Top-down Model
This model represents type of reader who knows what they expect from the
text, and they mostly have their own goals when reading the text. The reader will
direct their eyes to the information they wanted to find in the text.
c.
Interactive Model
The interactive model is a combined model which it takes the word
recognition technique from bottom up model and background knowledge to
understand the text then look for the key ideas by using top down model.
9
12
5. Techniques of Reading
a.
Skimming
Skimming is a reading technique that involves the students reading the
material quickly to get a general understanding. According to Farrell skimming
assumes that readers know:
1) How the text is organized
2) Spotting the main point of the paragraph
3) Have the ability to infer the main idea of the paragraph10
There are many strategies that can be used when skimming. Some people read
the first and last paragraphs using headings, summarizes and other organizers as
they move down the page or screen. Skimming works well to find dates, names,
and places. It might be used to review graphs, tables, and charts.
b.
Scanning
Scanning is a reading technique when the students try to look for specific
information. When using this technique, students do not have to read every single
word in the passage to find the information they need.11 When scanning, look for
the author's use of organizers such as numbers, letters, steps, or the words, first,
second, or next. Look for words that are bold faced, italics, or in a different font
size, style, or color. Sometimes the author will put key ideas in the margin.
6.
Purpose of Reading
These are reading purposes that have been classified by Grabe and Stoller
which will be explained below:12
10 Thomas S. C. Farrel, Succeeding with English Language Learners: A Guide for
Beginning Teachers, (California: Corwin Press, 2006), p. 98.
11 Peter Mather, Rita McCarthy, The Art of Critical Reading, (New York: McGraw-Hill,
2012), p. 507.
12 William Grabe, Reading in Second Language: Moving from Theory to Practice,
a.
Reading to Search for Simple Information and to Skim
In reading to search, scanning for a specific word, or a specific piece of
information, or a few representative phrases is commonly used by reader. For
example, when we look for address or telephone number in Yellow Pages or when
we read a dictionary, looking for the word meaning. Skimming is also commonly
used by reader and it is a useful skill when we are about to read unfamiliar and
long text. We look for the important information then combine them with our
comprehension skill to generate the outline of the text.
b.
Reading to Learn from Text
Reading to learn from text means that the reader needs to learn significant
amount of information from a text. The reader have to remember main ideas and
supporting ideas of the text, then organize them to build understanding and
connect them to their base knowledge. Reading to learn allows reader to read the
text again and reflecting to help remember information because it needs deeper
comprehension to connect the information with base knowledge.
c.
Reading to Integrate Information, Write and Critique Texts
Reading to integrate information means that we make a new conclusion basedon the supporting and conflicting information we read, and then combine them
with other source of information. Reader can decide which information to
integrate and how they are going to integrate them for their own purpose. Reading
to write and reading to critique is a part of the reading to integrate because both of
them requires the skill to choose, critique and arrange information from a text.
d.
Reading for General Comprehension
Reading for general comprehension mostly known as the ability to understand
information of the text but the comprehension ability is much more complex than
that. It needs a quick and automated process of words then strong skills in making
14
7. Problems of Reading
Some students might fail at reading unlike other students. There are many
things that can cause this to happen. It could be physical or mental factor
furthermore it could be the situation or bad habits that develop unconsciously by
students in their early years. In this section, problems of reading will be divided
into six parts, common reading problems, physical factor reading disability,
intellectual factor, emotional factor, sociocultural factor, and school factor.13
a.
Physical factor reading disability
Students with low reading rates or lacking on certain understanding of text
could be having a physical condition called dyslexia. Dyslexia is a condition
where a person has difficulties in decoding alphabet and thus resulting in
difficulties when reading words. Children who suffer brain damage at birth will
find difficulties in reading word symbols too. They get confused with letters and
affect their perception on it which resulting in interference with word recognition.
Most of the case, children with brain damage are easily distracted and
hyperactive, only high skilled teachers can successfully teaching them to read.
b.
Intellectual Factors
In a group of children with high intellect, they tend to be a good reader. They
can do several tasks that require reading with no problem. While children with
average intellectual, they have some difficulties in reading task and have no
problem in task that requires no reading. The ability to remember sequence of
letters and words could be a factor in learning to read. Teacher can help students
improving their ability to manage visual symbols.
13 Robert Karlin. Teaching Elementary Reading: Third Edition. (New York: Harcourt
c. Emotional Factors
Children may experience failure in school because of their incapability to
handle emotions. Psychologists have studied that problematic children with
insecurity, hostility, dependency can resist and even hate reading. In this case,
children can be given treatment to relieve them from pressure and encourage them
to read. It has been proved that treatment not only helping students to read more
but also effective for children personal adjustment.
d.
Sociocultural Factors
There are enough evidences that student with higher socioeconomic classes
are far better readers than other. In this case, students with higher culture can read
proper English than students who speak dialects having hard time in written
Standard English. this can be helped with reading program from the school,
parents and teacher together they motivates students and provide them variety in
activities and books to read.
e.
School Factors
The school factors problem in reading is mainly from the teacher. If the
teacher could not provide special instruction for student with reading problems,
they can fail and it will become worse. School administration can be blamed too if
they could not provide support for teacher. They give teacher a large classroom
that is decreasing the teacher confidence to provide student in need.
B. Narrative Text
1. Definition of Narrative Text
Chatman in his book, state that narrative is a compiled series of events that
ends with conclusion.14 That means Narrative text is a compiled sequence of
problematic events, it always ends with resolution from the problems. In Narrative
text, plot became the main content, Gordon and Kuehner stated that plot could be
16
defined as an author’s careful array of events in narrative to achieve a desired effect.15 Plot in narrative text is important as it is necessary for narrative text to be
chronologically written.
2. Structure of Narrative Text
Narrative text focuses the text in chronological series of occurrence.16 Below
are the generic structure of narrative text:
a. Orientation (Introduction)
Orientation consists of setting in the story. It includes the introduction of characters, background story, time of the story etc. it usually answers “Who, When, and Where”. For example, Mr. Wolf went out hunting in the forest one dark gloomy night.
b. Complication or problem
Complication is a series of occurrences that happens in the story. It involves
the main characters problem or hardships in a story.
c. Resolution
There needs to be a resolution after the complication. The complication may
have happy ending or bad ending. Sometimes there are a number of complications
that have to be resolved. These complications will add and sustain interest and
suspense for the reader.
15 Jane Bachman Gordon and Karen Kuehner, Fiction: The Elements of Short Story,
(Ohio: McGraw-Hill, 1999), p. 1
16 Joko Priyana, Interlanguage: English for Senior High School XI, (Pusat Perbukuan
3. Sample of Narrative Text
Table 2.1
Narrative Text Sample and Structure
Generic Structure Text
Orientation In the town of Verona there lived two families, the
Capulets and the Montagues. They engaged in a bitter
feud. Among the Montagues was Romeo, a hot-blooded
young man with an eye for the ladies
Complication There, he was surprised to find Juliet on the balcony,
professing her love for him and wishing that he were not a “Montague”, a name behind his own. “What’s in a name? That which we call a rose by any other name would smell as sweet.” Romeo was ready to deny his name and professed his love. The two agree to meet at
nine o-clock the next morning to be married.
Resolution Unfortunately, the Friar’s letter failed to reach Romeo.
Under the cover of darkness, he broke into Juliet’s
tomb. Romeo kissed the lips of his Juliet one last time
and drank the poison. Meanwhile, the effects of the
sleeping potion wear off. Juliet woke up calling for
Romeo. She found her love next to her but was lying
dead, with a cup of poison in his hand.
Reorientation She tried to kiss the poison on his lips, but failed. Then
she died.
4. Types of Narrative Text
There are many types of Narrative text, mostly, students were introduced
fable, legend, myth, fairy tales and folk tales story. Fables where the characters
are animals and usually ends with moral value. Legend is one of the narrative
story that was told from one person to another person and is usually tells about
18
real; it was spread from one person to another person without a real evidence of
the story. Next is fairy tale, it is a folktale that usually tells about a magic in the
characters and at the end of the story may consist of moral value. Last is folktale it
is a tales that has been spread for generations and become a tradition for its
society. 17
C. Video Game
1.
What is a Video Game
A video games term is still uncommon for the study. However, Tavinor
having research towards the definition of video game and he concludes that he
doubts if a video game can be defined.18 Though, Tavinor presenting some
people’s point of view of what a video game is. For example, Juul explains about games but not exactly a video game. He refers the definition as a “Classic game model”. While, Tavinor argue that video games are a technologically designed entertainment object that will develop as long as the technology improvement still
going on.
The researcher concludes that it is hard to term the video game but based on
what Tavinor states, a video game is a tool to have fun and its technologies made
it more interesting to try on.
2.
Characteristics of Video Game
Video games according to Saulter has certain common characteristics, there
are 5 characteristics: 19
a. One or more players, a condition can be called a game when a player or
players identified.
b. Set of rules, a game must have rules; the rules will cover the consequences of
every action made by the player.
17
Joko Priyana, Interlanguage: English for Senior High School XI, (Pusat Perbukuan Departemen Pendidikan Nasional, 2008)
18 Grant Tavinor, The Definition of Video games Revisited, (The Philosophy of Computer
Games Conference: Oslo, 2009).
19
c. Player interaction with an opposing force, a game must have a conflict in it
which player must face and interact with.
d. Organized method of play, a game must be playable and the sequence should
be logical and balanced. A game that require strategy to play will make the
player became aware of the game and it results in better player.
e. Desirable goals or outcome, a game must have a goal, also one or more
possible endings according to the option the players take.
People play games basically because it is entertaining in its own way,
meaning, by playing the game, the player could be relieved or it might boost the
player mood. Research by Entertainment Software Association (ESA) found that
50 percent of Americans who play computer and video games are looking for
entertainment (Essential facts, 2005).
3.
Motivation behind Playing Game
This part will explain the motivations behind playing games focusing on
Education. Saulter stated that most of children’s first year learning through play.
For example, a game like Peek-a-Boo help children to learn that separation is not
always permanent. As for children nearing their adulthood, games trying to
educate children about important life lessons, such as trust, cooperation, conflict
resolution, communication and ethics.20
4.
Narrative Devices in Video Game
In order to keep the story goes, video games tend to have these devices:
a. Cut Scenes, is a mini clip or scene to make the players feel that they are
involved in the game. Mostly, it was just a non-interactive scene and usually
it contains information about the next action that the players should do.
b. Scripted Event, these scripted events are maintained by AI (Artificial
Intelligence). Usually an AI will determine the events based on the choices
made by the players.
20
20
There are many studies that using video games as a way to improve students’ English learning. Squire argues that video games have many factors on why it is
popular and influential for children:
a. Video games trigger strong emotional reactions to the players like fear,
happiness, or sadness.
b. Those emotions created through the plot, character traits, game achievement
and rewards, and competition or collaboration with other player.
c. Video game appears to be rich in socio-cultural which provides ‘raw material’
in youth culture.21
D. Previous Study
Ting-Yu Yang & Chen conducted a study of a group of 60 Taiwanese EFL learners’ perceptions of a commercial adventure video game for second/foreign language learning. This study wants to determine the effects of a commercial
adventure video game on foreign language learning and learners' perceptions
toward an adventure game. About twenty two college students in Taiwan were
asked to play an English adventure game titled BONE. The analysis results that
students learned some new words, however both groups are not improving on
their performance in learning. The researchers then conducting another research to
understand the strength and weakness of using adventure games in learning
foreign language, there are 35 college students tested on their perception towards
the game. This study resulting that the students consider playing video game is
helping them to make learning foreign language as interesting and motivating. It is
proved that this game is improving students listening, reading and vocabulary skill along with students’ motivation too. The research results identified both strengths and weaknesses of adventure games for EFL/ESL based on learners’ perceptions,
21
and should encourage more studies on the investigation of using adventure games
in language learning.22
The study above only investigating the students perception, while the study
the researcher wanted to investigate the implications towards reading
comprehensive and the motivations that emerge during playing the game.
However, it is not easy to do such research, it is mainly because playing video
games are still considered not educating and sometimes they were considered as ‘violent’. This fact made the researcher eager to prove that video games are not as what most people said.
The second study is the Effect of Video Games on Iranian EFL Learner’s
Vocabulary Learning by Sedigeh Vahdat from Shahid Chamran University and
Amin Rasti Behbahani from Islamic Azad University. In this study, the
researchers pick about 40 participants through TOEFL proficiency test; male and
female. The participants then divided into a control group and experimental group
consist of 10 males and 10 females each. The control group studied vocabulary
via traditional classes while the experimental group plays a video game titled
Runaway: A Road Adventure. The Researchers using three instruments where the
first instrument is simulated TOEFL test, second is an achievement test consist of
40 multiple choice test and the third is a Likert scale to determine the experimental group’s view and experience when learning through video games. This study proves that video games are useful for students’ vocabulary learning
and the male participants are more interested in learning through video games
than the female participants.23
The third study is the Effect of using Narrative Comprehension Cards
Strategy toward reading comprehension on narrative text from UIN Sultan Syarief
Kasim Riau researched by Erika. This study conducted for a senior high school
students and it is using quasi experiment where pre-test, treatment and post-test
22
Howard Hao-Jan Chen and Christine Ting-Yu Yang, the Impact of Adventure Video Games on Foreign Language Learning and the Perceptions of Learners, (Philadelphia: Taylor & Francis Ltd., 2013).
23
Sedigheh Vehdat and Amin Rasti B., the Effect of Video Games on Iranian EFL
22
are conducted. The treatment only directed once by the researcher then the
experimental group tried the strategy themselves. The result is that there is a
significant effect of the strategy used in the test. It is proved by the test result that the students’ comprehensions are increased after using the strategy.24
The fourth study is conducted by Romli with the title ‘Improving Students’ Reading Comprehension of Narrative Text through Story Mapping’ from UIN Syarief Hidayatullah Jakarta. The purpose of this study is to get the empirical prove in improving the students’ reading comprehension of narrative text through story mapping. The researcher using a Classroom Action Research method, where
he conducts observations, interviews, questionnaires and tests. The result for this study is that the story mapping method brings an improvement to the students’ comprehension in narrative texts.25
The results of the studies above are involving many kinds of methods in
language learning, which can inspire many teachers in teaching narrative texts. It
is proved that there are many ways to learn to comprehend English narrative texts.
That is why researcher wants to try another method. In this study, role playing game is going to be used and expected to have effects on students’ reading comprehension skills.
There are many differences and similarities from the study above with the
researcher study. From the first and second study, both using video games as the
tool for learning which the writer will use for this study. Meanwhile the third and
fourth study using a story mapping and narrative comprehension cards strategy as
the method of learning. The participants are varies from all of the study above, the
researchers mostly pick intermediate level students while the writer will choose
from Junior High School students in Jakarta Selatan.
24
Puspa Erika, The Effect of Using Narrative Comprehension Cards Strategy toward Reading Comprehension on Narrative Text of the Second Grade Students at SMAN 2 Bagan Sinembah Rohil Regency, Skripsi for undergraduate Sultan Syarif Kasim Riau State Islamic University, 2015.
25 Muhamad Romli, Improving the Students’ Reading Comprehension of Narrative Text
E. Thinking Framework
In learning second language, reading skill is one of the skill that learner must
have. It is because in order to understand a text in the target language one has to
understand the meaning of each words then connecting all the information with
the prior knowledge.
The researcher feels it herself when she was learning English for the first
time, find it hard to understand what is the meaning of each word and what it is
about. The urge to look for the meaning of the word is not enough for a child her
age and this is proved by her friends too. The lack of teachers’ creativity is a crucial matter to the students in teenage. How to attract the students’ attention is important in order to motivate them to learn second language.
This is why the researcher tries to find a way by using the modern technology
that actually intriguing to children these days and children at teenage love to play games and trying something new. This study is hoping to be useful for teachers’ creativity in engaging students while not in the class. While homework seems to
be scary back then, this time the researcher assume that it will be more exciting
and interesting.
F. Theoretical Hypothesis
Based on the problem formulation, the hypothesis of this research is “Video game has positive effect on students’ reading comprehension of narrative text at
24
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Place and Time of the Research
This research was conducted at SMP N 96 Jakarta Selatan on Jl. Margasatwa
RT 001/RW 03 Pondok Labu, Cilandak, South Jakarta, DKI Jakarta, 12450. The
research held from 27 April until 25 May on 2016.
B. Design of the Research
This research using an experimental research design in order to answers the
problems presented on the background. Experimental research is a research that
test the hypotheses cause and effect relationship about.1 For this study, as an
educational study where the variables are controlled and manipulated, this study is
a quasi-experimental research. Quasi Experiment itself is experimental situations
in which the researcher assigns, but not randomly, participants to groups because
the experimenter cannot artificially create groups for experiment.2
C. Method of the Research
In this study, Pre-test was given before the procedure applied on the samples.
After that, experimental class samples were given treatment by playing a role
playing game for some time and the last, both experimental and controlled class
were given a post-test which was the same kind of narrative text. The researcher
held one meeting for pre-test and one meeting for post-test. Treatment held for
four days a week for 80 minutes, and it lasted for two weeks. The experimental
group brought a dictionary while playing the game and only allowed to look up
for vocabulary when playing game.
1 Margeurite G. Lodico, Dean T. Spaulding, Katherine H. Voegtle, Method in
Educational Research, (US America: Jossey-Bass, 2006), p. 12.
2 John W. Cresswell, Educational Research Planning, (US America: Pearson Education
25
D. Population of the Research
The population of this study was eight grade students of SMP N 96 Jakarta
Selatan which from class VIII-1 until VIII-6. Purposive sampling used to
determine the sample of this study.
E. Sample of the Research
Purposive sampling is a technique to determine the sample by a specific
consideration.3 It means the sample will be special and suitable for the research.
For example, if the research is about political condition in one region, then the
sample will be people who have specialty in Politic. In this study, the students
who own a laptop or computer at home and have an average score of English
subject on their last report. Approximately 30 students for experimental class and
30 students for controlled class.
F. Research Instrument
In this study, the researcher using tests for instrument, first the researcher was
conducting pre-test, pre-test will give the researcher a view to assess the
participants before treatment,4 and in this case, the researcher made 10 narrative
texts and 5 questions for each text (50 in total) for the participants and then,
providing treatment afterwards. The treatment in experimental class was playing
video game for 30 minutes after that the participants in experimental class answer
about ten questions regarding the narrative in the game. In the control class, they
were also given pretest but the treatment is only reading narrative texts about the
game and answering the questions. Last, post-test was given to the sample with
same contents only differ in some parts. Post-test provides the researcher
evaluation after the treatment was given to the participants.5 The post-test also
3 Sugiyono. Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif, Kualitatif dan R&D. cetakan ke 8. 2009
Alfabeta, Bandung
4 John W. Cresswell, Educational Research Planning, (US America: Pearson Education
Limited, 2012), p. 297.
5 John W. Cresswell, Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Method
26
26
consists of 10 short narrative text with each text contains 5 questions related to the
text.
1. Instrument for Reading Comprehension of Narrative Text
a. Concept and Operational Definition
1)
Concept Definition
a) Dutcher in Ulmer et al stating that reading comprehension is a process which
the reader background knowledge, the information on the text and the
situation when reading are interacted with each other.
b) Chatman in his book, state that narrative is a compiled series of events that
ends with conclusion.
2)
Operational Definition
While the operational definition of reading comprehension on narrative text
includes students understanding in sentences, this includes their understanding of
[image:39.595.107.518.210.744.2]characters, plot, setting, moral of the story and classifying the text organization.
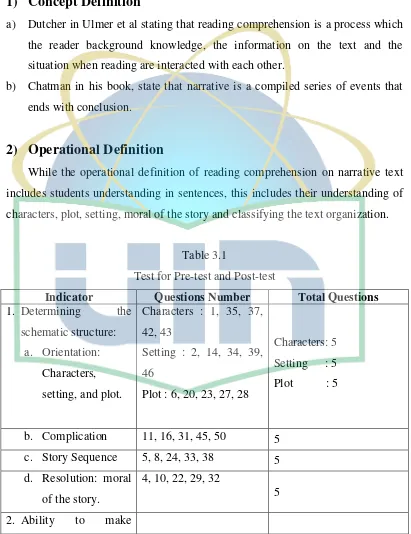
Table 3.1
Test for Pre-test and Post-test
Indicator Questions Number Total Questions
1. Determining the
schematic structure:
a. Orientation:
Characters,
setting, and plot.
Characters : 1, 35, 37,
42, 43
Setting : 2, 14, 34, 39,
46
Plot : 6, 20, 23, 27, 28
Characters: 5
Setting : 5
Plot : 5
b. Complication 11, 16, 31, 45, 50 5
c. Story Sequence 5, 8, 24, 33, 38 5
d. Resolution: moral
of the story.
4, 10, 22, 29, 32
5
27
Indicator Questions Number Total Questions
inferences of events in
the story and finding
the synonym and
antonym.
Inference: 9, 12, 18, 25,
48
Synonym: 3, 7, 13, 17,
21
Antonym: 26, 30, 40, 41,
44
Inference: 5
Synonym : 5
Antonym : 5
3. Determining the story
organization.
15, 19, 36, 47, 49
5
Total Questions 50
G. Data Collection Technique
In this research, there are three steps on the experiment. The pre-test where
the students read some narrative texts and answer sets of question regarding the
texts. Then, the class had a treatment that is playing the video game and taking
notes about their feelings on learning English through the game. Last, the post-test
is a narrative text too with its set of question and same level as the pre-test.
Before conducting pre-test and post-test, the researcher needed to determine
which questions is valid and reliable. Therefore, the researcher conducting
validity test and reliability test on the same school but in four different classes.
The researcher using class VIII-1, VIII-4, VIII-5, and VIII-6 to determine the
validity and reliability of the test, by providing 70 questions of multiple choices.
To analyze the test, there are four steps to determine the validity and reliability,
they were:
1. Validity Test
The researcher used anatest software version 4.0.9 developed by Drs. Karnoto, M.Pd. and Yudi Wibisono, ST., to test the validity of the instrument. A
valid test is a test that measures accurately on what it is intended to measure.6
6 Athur Hughes, Testing for Language Teachers, (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press,
28
28
The criteria of validity:7
r_xy = 0.91—1.00 = very high
r_xy = 0.71—0.90 = high
r_xy = 0.41—0.70 = enough
r_xy = 0.21—0.40 = low
r_xy = < 0.21 = very low
After calculating, the validity value of the instrument was 0.75. This means
that the test had high validity, from 70 questions there are 63 questions were valid
and the other questions are not valid.
2. Reliability Test
Reliability test used to measure the consistency of the test result. According to
Arikunto, reliability used to measure instrument that provides consistency of the
indicators in the research.8
Then, the researcher using anatest software version 4.0.9 developed by Drs. Karnoto, M.Pd. and Yudi Wibisono, ST. to determine the reliability value of the
instrument.
From the calculation using anatest, the reliability value r was 0.87 and 0.67. Then, r should be compared with the rt le (rt) of product moment. The students participated on this test was about 144 students, and based on the rt le
(rt) of product moment, it showed rt 5% is 0.16.
An instrument is reliable if the reliability value is higher than rt le 9. From
the calculation, it can be concluded that the reliability value (0.87 and.0.67) were
7 Suharsimi Arikunto, Dasar-Dasar Evaluasi Pendidikan, (Jakarta: Bumi Aksara, 2012), p.
89.
8 Ibid., p. 101.
9 Suharsimi Arikunto, Prosedur Penelitian Suatu Pendekatan Praktik, (Jakarta: Rineka Cipta,
29
higher than the rt le with 5% significance (0.16), therefore the test were reliable
(0.87 and 0.67 > 0.16).
H. Data Analysis Technique
In technique of analyzing data, comparative t-test statistical analysis was
used. The function was to compare the results of the students’ scores in pre-test
and post-test between the experimental group and control group.
These are the statistical formulas for t-test :
�
�= �−� ��−�
Below is the process of t-test
1. Determining mean of variable X (Experiment Class):
�
�=
∑ �2. Determining mean of variable Y (Control Class):
� =
∑ �3. Determining standard deviation of variable X:
�
= √
∑ � 2−
∑ �4. Determining standard deviation of variable Y:
�
= √
∑ � 2− (
∑ �)
5. Determining standard error of mean variable X:
�
=
√ −�6. Determining standard error of mean variable Y:
30
30
7. Determining standard error of different mean of variable x and mean of
variable Y:
� − = √� + �
M
x = mean of students' post-test score in experiment classM
y = mean of students’ post-test score in control class∑ fx
= sum of students’ post-test score of experiment class∑ fy
= sum of students’ post-test score of control classN
x = number of students’ in experiment classN
y = number of students in control classSD
x = standard deviation of mean in experiment classSD
y = standard deviation of mean in control classSE
Mx = standard error of mean in experiment classSE
My = standard error of mean in control classSE
Mx-My = standard error difference between Mx and Myt
0 = value of hypothesis testingAfter all of the data calculated, determine the degree of freedom with formula:
df = Nx + Ny – 2
8. Normality Test
Normality test used to know whether the data collected are normal on the
distribution or not. The researcher will use IBM SPSS Program version 23 to
find out the normality of the data.
Steps:
a) Open IBM SPSS 23 program, to find out the normality data, the researcher
31
b) First, write the variable view with Score for pretest or posttest score and Class
for experimental or control class
c) Then, click Analyze→Descriptive Statistics→Explore
d) Drag the Score to the Dependent List and Class to the Factor List
e) Click Plot→checklist Normality Plots with Test→OK
The criteria of determining the normality of the data was:
a) If Lvalue is smaller than Ltable (Lvalue < Ltable), it means that the data were
distributed normally.
b) If Lvalue is bigger than Ltable (Lvalue > Ltable), it means that the data were not
distributed normally.
2. Homogeneity Test
Homogeneity test is used to determine whether the data is in homogeneity
variance or not. Below are the steps to calculate the homogeneity data:
a) Open IBM SPSS 23 program, for homogeneity test, the researcher used
one-way ANOVA formula.
b) First, write the variable view with Score for pretest or posttest score and Class
for experimental or control class
c) Click Analyze→Compare Means → One-way ANOVA
d) Drag the Score to the Dependent List and Class to the Factor List
32
32
I. Statistical Hypotheses
Ho: β ≤ 0H1: β > 0
Description :
H0: Video Game has no positive effect on Students’ Reading Comprehension
of Narrative Text
H1: Video Game has a positive effect on students’ Reading Comprehension of
33
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND INTERPRETATION
A.
Research Findings
1.
Data Description
This chapter presents data collection of experimental class and controlled
class on SMP N 96 Jakarta Selatan where pre-test and post-test given. The
researcher chose class VIII-2 as the controlled class and class VIII-3 as the
experimental class. Both classes consist of 36 students each and the researcher
chose only 30 students as the sample. In this section, there are 2 tables presenting
test scores of experimental class and test scores of controlled class. Each table
consist of 3 columns, they are pre-test score, post-test score and gained score.
a.
Data of Experimental Class
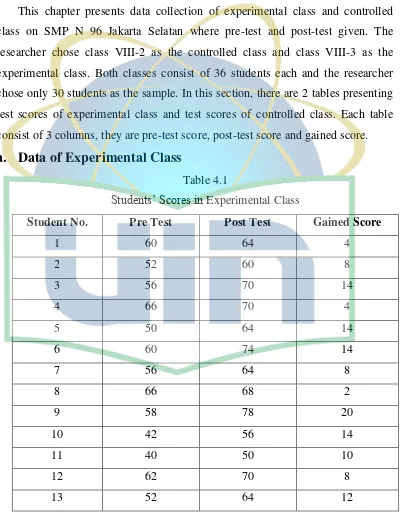
[image:46.595.117.517.230.747.2]Table 4.1
Students’ Scores in Experimental Class
Student No. Pre Test Post Test Gained Score
1 60 64 4
2 52 60 8
3 56 70 14
4 66 70 4
5 50 64 14
6 60 74 14
7 56 64 8
8 66 68 2
9 58 78 20
10 42 56 14
11 40 50 10
12 62 70 8
34
Student No. Pre Test Post Test Gained Score
14 42 58 16
15 60 72 12
16 50 68 18
17 52 74 22
18 48 50 2
19 56 64 8
20 54 58 4
21 50 60 10
22 56 68 12
23 54 68 14
24 50 66 16
25 62 70 8
26 54 70 16
27 48 70 22
28 54 64 10
29 58 70 12
30 52 60 8
∑ 1620 1962 342
Average Score 54 65.4 11.4
From Table 4.1, it was shown that the highest score on pre-test of
Experimental Class was 66 and the lowest score was 42, while in the post test of
Experimental Class, the highest score was 78 and the lowest was 58. In the Table
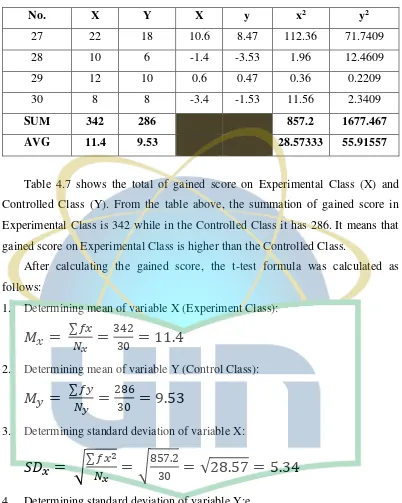
4.1, it also revealed that the total of gained score was 342 and the average score
between pre-test and post-test are different. The post test score was slightly higher
Table 4.2
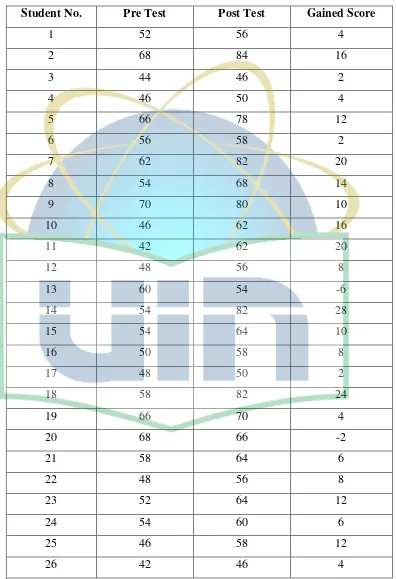
Students’ Scores in Controlled Class
Student No. Pre Test Post Test Gained Score
1 52 56 4
2 68 84 16
3 44 46 2
4 46 50 4
5 66 78 12
6 56 58 2
7 62 82 20
8 54 68 14
9 70 80 10
10 46 62 16
11 42 62 20
12 48 56 8
13 60 54 -6