Informasi Dokumen
- Penulis:
- TB Didi Supriadi
- Pengajar:
- Dr. Eng. Suripto Dwi Yuwono, M.T.
- Kamisah D. Pandiangan, M.Si.
- Prof. Dr. John Hendri, M.S.
- Dr. Yandri AS, M.Si.
- Andi Setiawan, Ph.D.
- Prof. Suharso, Ph.D.
- Sekolah: Universitas Lampung
- Mata Pelajaran: Kimia
- Topik: Preparation And Characterization Of Mixed Plastic Polypropylene (PP) / Poly Lactic Acid (PLA) With Addition Plasticizer Using Non Solution Casting
- Tipe: thesis
- Tahun: 2013
- Kota: Bandar Lampung
Ringkasan Dokumen
I. INTRODUCTION
The introduction discusses the increasing reliance on plastics due to their advantageous properties such as low cost, availability, and practicality. It highlights the environmental concerns associated with conventional plastics, particularly polypropylene (PP), which is widely used but poses significant degradation challenges. The need for biodegradable alternatives, such as poly lactic acid (PLA), is emphasized, along with the potential for blending these materials to enhance mechanical properties and biodegradability. This section sets the stage for understanding the importance of developing eco-friendly plastic solutions.
1.1 Background
This subsection elaborates on the environmental impact of conventional plastics, particularly PP, which contributes to pollution due to its non-biodegradable nature. It discusses the growing awareness of biodegradable plastics and the potential for using renewable materials like PLA to address these issues. The necessity for research into the blending of PP and PLA, along with plasticizers such as glycerol, is underscored to enhance the properties of the resultant materials.
1.2 Research Objectives
The objectives of the research are clearly defined, focusing on optimizing the conditions for creating biodegradable plastics from PP and PLA with the addition of plasticizers. The goals include characterizing the thermal and mechanical properties of the blends and assessing their biodegradability over time. This section is crucial for guiding the experimental design and ensuring that the research addresses pertinent environmental concerns.
1.3 Research Benefits
This subsection outlines the potential benefits of the research, emphasizing its contribution to reducing reliance on conventional plastics and promoting the use of environmentally friendly materials. By providing insights into the production and characterization of biodegradable plastics, the research aims to inform future developments in sustainable materials science, ultimately benefiting both industry and the environment.
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
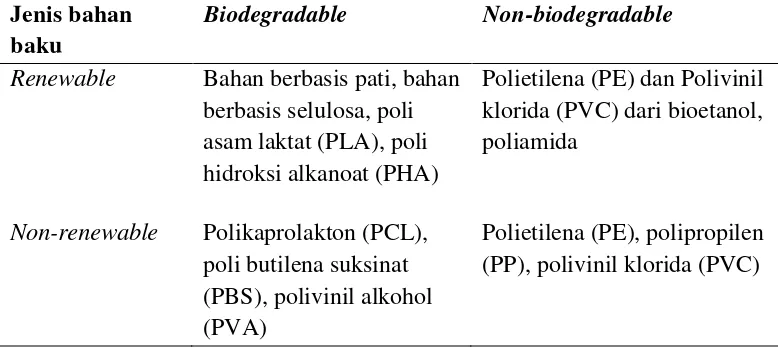
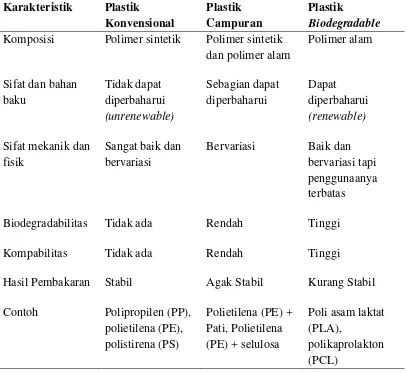
The literature review provides a comprehensive overview of plastics, focusing on their classifications, properties, and environmental impacts. It discusses conventional and biodegradable plastics, highlighting the advantages and limitations of each type. The review also covers the properties of PP and PLA, the role of plasticizers, and the techniques used for characterization, such as FT-IR and SEM. This section serves as a foundational understanding for the research, situating it within the broader context of materials science.
2.1 Plastics
This subsection defines plastics and their applications across various sectors, emphasizing their lightweight, strong, and waterproof properties. It categorizes plastics based on their raw materials and degradability, providing a comparative analysis of conventional and biodegradable options. This foundational knowledge is essential for understanding the implications of using different types of plastics in various applications.
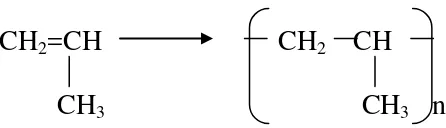
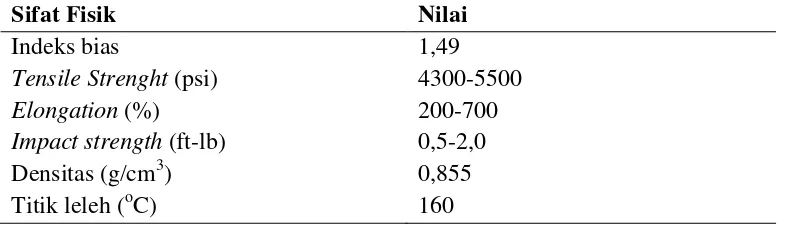
2.2 Polypropylene (PP)
The properties of PP are examined in detail, including its mechanical and thermal characteristics. The subsection discusses the production methods and applications of PP, as well as its environmental impact due to its non-biodegradable nature. Understanding PP's properties is crucial for evaluating its compatibility with PLA and the potential for creating effective blends.
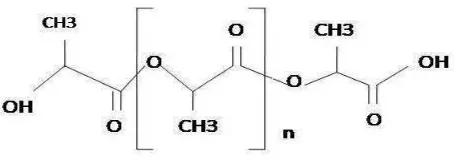
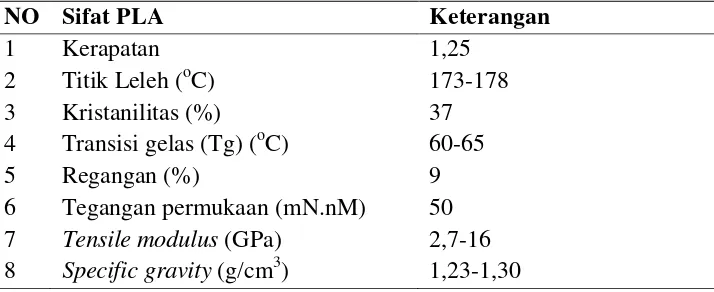
2.3 Poly Lactic Acid (PLA)
This subsection focuses on PLA, discussing its production from renewable resources and its biodegradable properties. It highlights PLA's mechanical strength and potential applications as an alternative to conventional plastics. The information presented here is vital for understanding how PLA can be effectively blended with PP to enhance biodegradability.
2.4 Plasticizers
The role of plasticizers in modifying the properties of plastics is discussed, with a focus on glycerol as a commonly used plasticizer. This subsection explains how plasticizers improve flexibility and reduce brittleness in plastic films. Knowledge of plasticizers is essential for the experimental design, particularly in optimizing the properties of PP/PLA blends.
2.5 Characterization Techniques
Various characterization techniques, including FT-IR, SEM, DSC, and TGA, are outlined in this subsection. Each method's principles and applications in analyzing the properties of polymer blends are explained. This information is crucial for selecting appropriate methods for evaluating the properties of the developed biodegradable plastics in the research.
III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The research methodology section details the experimental design, materials used, and procedures followed in the study. It outlines the process for blending PP and PLA with glycerol as a plasticizer, as well as the characterization methods employed to assess the physical and thermal properties of the resulting materials. This section is fundamental for replicating the study and validating the results.
3.1 Research Design
This subsection describes the overall research design, including the selection of materials, the blending process, and the rationale behind the chosen experimental methods. It emphasizes the importance of optimizing the composition ratios of PP and PLA to achieve desired properties in the final product. Understanding the design is essential for contextualizing the research findings.
3.2 Materials and Equipment
The materials used in the research, including PP, PLA, glycerol, and the equipment for blending and characterization, are listed in this subsection. Detailed descriptions of the equipment and their functions are provided, ensuring clarity on the tools necessary for conducting the experiments. This information is crucial for ensuring the reproducibility of the research.
3.3 Procedures
The procedures for creating the PP/PLA blends and conducting the characterization tests are outlined in this subsection. Step-by-step instructions are provided for each stage of the research, from blending to testing for biodegradability. Clear procedures are vital for allowing other researchers to replicate the study and validate its findings.
IV. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
This section presents the results of the experiments, including the physical and thermal properties of the PP/PLA blends and their biodegradability. The findings are discussed in relation to the research objectives and existing literature, providing insights into the effectiveness of the blends and the role of plasticizers. This section is critical for interpreting the data and understanding the implications of the research.
4.1 Characterization of Blends
The characterization results of the PP/PLA blends are presented in this subsection, including data from FT-IR, SEM, DSC, and TGA analyses. The findings are analyzed to determine how the addition of glycerol affects the properties of the blends. This analysis is essential for understanding the material's potential applications and performance.
4.2 Biodegradability Testing
The results of the biodegradability tests conducted over three months are discussed in this subsection. The weight loss percentages are analyzed to evaluate the effectiveness of the blends in degrading over time. This information is crucial for assessing the environmental impact of the developed materials and their potential as sustainable alternatives to conventional plastics.
4.3 Comparison with Existing Literature
This subsection compares the research findings with existing literature on biodegradable plastics and their properties. The discussion highlights how the results align with or differ from previous studies, providing a broader context for the research. Understanding these comparisons is important for situating the study within the field of materials science.
V. CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
The conclusion summarizes the key findings of the research, emphasizing the successful development of biodegradable PP/PLA blends with enhanced properties due to the addition of plasticizers. Recommendations for future research directions are also provided, highlighting areas for further exploration and potential improvements in the blending process. This section is vital for encapsulating the research's contributions and suggesting pathways for continued investigation.
5.1 Conclusion
This subsection encapsulates the main findings of the research, affirming the effectiveness of blending PP and PLA with glycerol to enhance biodegradability and mechanical properties. The conclusion reinforces the significance of the study in contributing to the development of sustainable materials.
5.2 Recommendations
Future research directions are suggested in this subsection, including exploring different plasticizers, varying blend ratios, and investigating the long-term environmental impacts of the developed materials. These recommendations are essential for guiding subsequent studies and advancing the field of biodegradable plastics.
Referensi Dokumen
- Bioengineering for Pollution Prevention through Development of Biobased Energy and Materials State of the Science Report ( Ahmann, D & Dorgan J. R. )
- Poly(Lactic Acid) Film as Food Packaging Materials ( Auras, R. )
- Polylactic Acid: Synthesis, Properties and Applications ( Avérous, L. )
- Basic Aspect of Food Extrusion ( Baianu, I.C. )
- Biodegradable Materials Present Situation and Future Perspectives ( Bastioli, C. )