I. Introduction
This research investigates the influence of curing time on the bearing capacity of sandy clay soil stabilized with TX-300. The introduction establishes the context by highlighting the importance of road construction and the challenges posed by soils with poor bearing capacity. It emphasizes the need for soil stabilization techniques to enhance the load-bearing properties of unsuitable subgrade materials. The study focuses on sandy clay soil from Dusun Kali Ayu, Desa Jati Baru, Lampung Selatan, and employs TX-300 as a stabilizer. The research question centers on determining the optimal curing time for achieving maximum bearing capacity improvement using TX-300 in this specific soil type. This introduction provides essential background information and clearly defines the scope of the research, making it relevant for educating students on the practical applications of soil mechanics.
1.1 Background
The background section sets the stage by discussing the significance of road construction in development and the variability of soil properties affecting bearing capacity. It introduces the challenges posed by sandy clay soils, their susceptibility to changes in moisture content, and the necessity for soil stabilization techniques. The selection of TX-300 as a stabilizer is justified based on its properties and suitability for various soil types. This section lays the groundwork for understanding the practical problem addressed by the research, which is crucial for students learning about real-world engineering challenges.
1.2 Problem Statement
This section formally states the research problem: the lack of knowledge regarding the optimal curing time for TX-300 stabilized sandy clay soil. It highlights the need to determine the impact of varying curing durations (0, 7, 14, and 28 days) on the bearing capacity, as measured by the California Bearing Ratio (CBR) test. This precise articulation of the research problem is essential for students to understand the focused nature of the investigation and the specific variables being studied. This section also frames the research objectives, ensuring that students understand the goals that the study hopes to achieve.
1.3 Research Objectives
The objectives clearly outline the goals of the research. The primary aim is to quantify the increase in bearing capacity achieved through TX-300 stabilization compared to the original soil, using the CBR test as the key metric. A secondary objective is to ascertain the influence of different curing times on this bearing capacity enhancement. These precisely defined objectives are essential for a structured research approach and provide clear learning outcomes for students in terms of research design and methodology. This section emphasizes the importance of quantifiable results, which is a valuable lesson for students learning to conduct research.
II. Literature Review
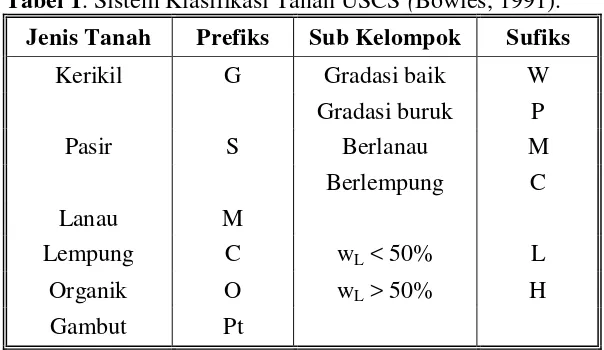
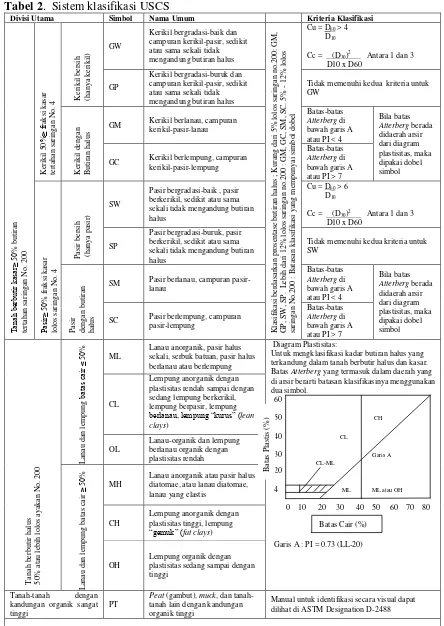
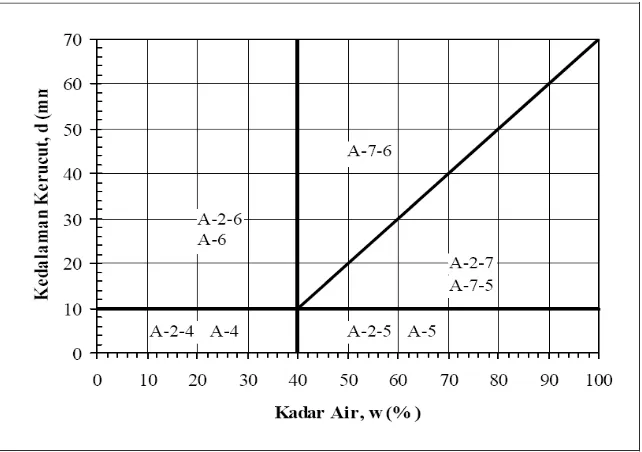
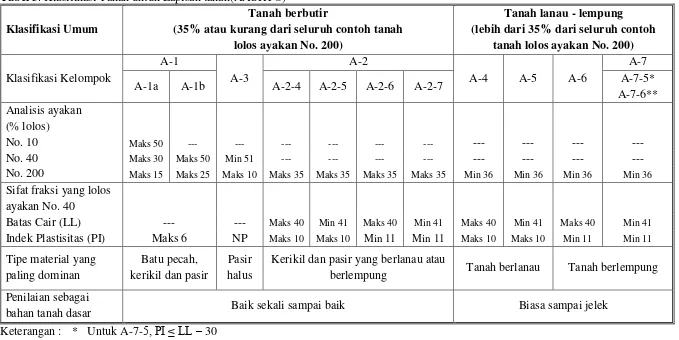
This section delves into existing knowledge regarding soil mechanics, soil classification systems (USCS and AASHTO), soil stabilization techniques, and the specific properties of TX-300 as a soil stabilizer. It reviews previous research on the use of TX-300 for soil stabilization and its effect on bearing capacity. The review of relevant theories and principles helps to establish a theoretical framework for the study. The inclusion of relevant soil classifications (like USCS and AASHTO) provides students with essential background knowledge on soil properties and behavior.
2.1 Soil Properties and Classification
This subsection covers fundamental soil properties like grain size distribution, Atterberg limits (liquid limit, plastic limit, plasticity index), and the role of these properties in determining soil behavior. It also details common soil classification systems like the USCS and AASHTO, explaining their criteria and application in geotechnical engineering. This foundational knowledge is crucial for students understanding the context of the research and the characteristics of the sandy clay soil under investigation.
2.2 Soil Stabilization Techniques
This subsection discusses various methods of soil stabilization, emphasizing the use of chemical additives. It explains the mechanisms by which these additives improve soil strength and bearing capacity. The discussion of mechanical stabilization methods provides a contrast and a broader understanding of engineering approaches. This broader perspective is crucial for students to fully grasp the specific techniques used in this research and their place within the larger field of geotechnical engineering.
2.3 TX-300 Stabilizer
This subsection provides detailed information on the chemical composition and properties of TX-300. It explains the mechanism of action of TX-300 in soil stabilization, focusing on its role in improving soil strength, reducing plasticity, and enhancing water resistance. This detailed examination helps students understand the specific material used in the research and its impact on the soil properties. The environmental friendliness of TX-300 is also a valuable point to include, providing a perspective on sustainable engineering practices.
2.4 Previous Research
This subsection reviews existing literature on the application of TX-300 as a soil stabilizer and its effects on the bearing capacity of various soil types. It analyzes the findings of previous studies to establish a baseline for comparison with the current research, highlighting similarities and differences in methodologies and results. This critical review is essential for students to understand how the current research contributes to the existing body of knowledge and the overall advancement of the field. It also teaches them how to synthesize information from various sources to draw meaningful conclusions.
III. Research Methodology
This section describes the experimental design and procedures followed in the study. It outlines the sample collection, preparation, and testing methods employed. It explains the variables investigated (curing time and TX-300 concentration) and the methodologies for data analysis. The detailed description of the research methodology is vital for students to understand the scientific rigor of the study and the reproducibility of its results. This section serves as a practical example of scientific methodology and data collection for students.
3.1 Sample Collection and Preparation
This subsection details the process of collecting soil samples from the chosen site, including the methods used to ensure representative sampling. It describes the preparation of the samples for testing, including the mixing of the soil with TX-300 at the optimized concentration, and the curing process under controlled conditions. This section provides a step-by-step guide to the experimental procedures, which is invaluable for students learning about experimental design and sample handling.
3.2 Experimental Procedures
This subsection outlines the laboratory tests performed, including the specifics of each test (e.g., Atterberg limits, CBR). It explains the equipment and procedures used for each test, including the controlled conditions maintained during the experiments. This section is important because it emphasizes the meticulousness required for accurate and reliable data acquisition. It shows students the importance of standard operating procedures and error minimization in laboratory experiments.
3.3 Data Analysis
This subsection describes the statistical methods employed for analyzing the collected data. It explains how the changes in bearing capacity with varying curing times are quantified and compared. This section emphasizes the importance of proper data analysis techniques for drawing valid conclusions. It provides students with an opportunity to learn about appropriate statistical approaches to analyze scientific data.
IV. Results and Discussion
This section presents the findings of the experimental work and interprets the results within the context of the literature review. It discusses the observed relationships between curing time, TX-300 concentration, and bearing capacity. It compares the results with those of previous studies and identifies any discrepancies or unexpected outcomes. This section is key to showing students how to synthesize and interpret experimental data, using statistical analysis to support their arguments. It allows for critical thinking skills to be honed, as students are challenged to find explanations for both expected and unexpected results.
4.1 Results of Soil Characterization
This subsection presents the results of the initial soil characterization tests (grain size distribution, Atterberg limits, etc.) for the undisturbed and stabilized soils. This baseline data is critical for comparing the before-and-after effects of TX-300 stabilization. This section highlights the importance of accurately characterizing materials prior to commencing experimental work – a critical skill for any engineer or researcher.
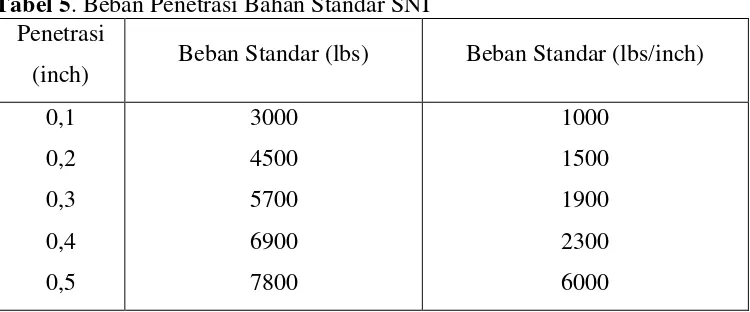
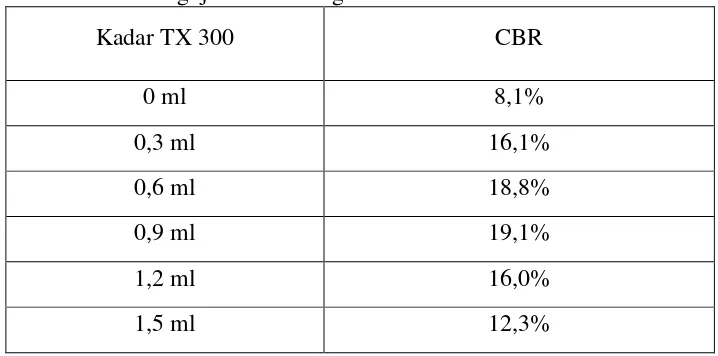
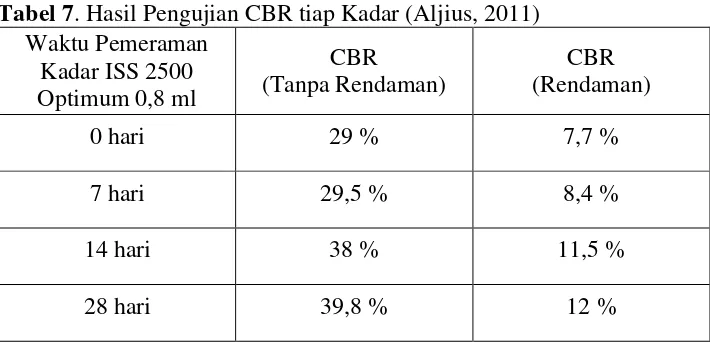
4.2 Results of CBR Tests
This subsection presents the key results of the CBR tests for both the untreated and TX-300 treated soils at various curing times. It should include tables and figures that clearly illustrate the relationship between curing time and CBR values. This is a crucial part, as the CBR value is the primary indicator of the success of the stabilization process. The ability to present and analyze data in a clear and concise manner is a significant learning outcome for students.
4.3 Discussion of Results
This subsection interprets the CBR test results, correlating them with the curing time and explaining the observed trends. It discusses the implications of the findings in terms of the effectiveness of TX-300 as a stabilizer and the optimal curing time for achieving the desired bearing capacity. This section allows for the application of engineering judgment and the development of critical thinking skills. The ability to draw conclusions and make recommendations based on experimental data is a valuable lesson for students.
V. Conclusion and Recommendations
This section summarizes the key findings of the research and draws conclusions based on the results and their interpretation. It provides recommendations for future research and practical applications of the findings, including suggestions for optimizing the use of TX-300 as a soil stabilizer. This final section is crucial because it shows students how to synthesize the research process and effectively communicate their findings. It teaches them to look forward and propose future research directions, as well as to draw practical conclusions from their work.
5.1 Conclusion
This subsection provides a concise summary of the main findings of the research. It restates the primary conclusions about the effect of curing time and TX-300 on the bearing capacity of sandy clay soil. This is a critical skill for students in terms of effective communication of research findings and summarizing core insights.
5.2 Recommendations
This subsection provides recommendations based on the research findings. This includes recommendations for practical application of the optimized curing time in real-world soil stabilization projects and suggestions for future research to investigate other aspects of TX-300's performance or its application in different soil types. This section is important as it demonstrates the value of research in contributing to practical solutions and prompting further investigation.