Vol7, No 4, October - December
1998
Effect ofverapamil onSTI
193Effect
of
verapamil
on systolic time
intervals
in
rabbits
K. Singh
Abstrak
Interval waktu sistolik merupakan indikator sensitif fungsi miokard. Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk menilai kinerja ventrikel
kiri
sebelum dan sesudah pemberian verapamil i.v. pada kelinci. Elektrokardiogram, fonokardiogram, denyut a.karotid, dan tekanan darah arteri dicatat. Penurunan sistolik elektromekanik, peningkntanwaktu curahventrikel kiri, penurunanwaktu pra-curah dan perbandingan PEP/LVET sesudah pembeian verapamil menunjukkan peningkatan kinerja ventrikel, walaupun terdapat penurunan denyut jantung dan penurunan tekanan darah. HaI ini merupakan dasar penggunaan penghambat kanal kalsium pada penyakit-penyakit jantung.Abstract
Systolic time interttals (STI) are sensitive indices of myocardial function. The present study was conducted to evaluate left
ventricular (LV) performance before and after administration
of
calcium channel blocker-verapamil (intravenously)in
rabbits. Electrocardiogram, phonocardiogram, carotid arterial pulse, and mean arterial blood pressure were recorded. Reduction in electro mechanical systole (QSz) rise in left yenticular ejection time (LVET), reduction in pre-ejection period (PEP) and ratio of PEP/LVET after verapamil administration showed enhanced ventricular performance, although it causes decrease in heart rate andfall
in blood pressure. Thatforms the basis ofuse ofthe calcium blockers in cardiac diseases.Keywords : myocardium, calcium blockers, systole
The
ability of
calcium antagonists
to
block calcium
mediated
electromechanical coupling in contractile
tis-sue canproduce arterial dilatation
in bothcorontuy
andperipheral vascular bed.
While inhibition
of
trans-membrane
cellular
flow
of
calcium during the slow
inward
current produces favorable electrophysiologic
effects.l Calcium
antagonists have been shown to have negativeinotropic
and negativechronotropic
effectbut
at
the
sametime they
are advocatedfor the treatment
of various cardiovascular
diseasesi.e. coronary
artery diseases,hypertension and cardiomyopathy. Systolic
time
intervals
(STIs)
is
sensitive and noninvasive
method
for
assessmentof
left ventricular
(LV)
func-tions.
It
was, therefore, decided
to
study the
time
course
of
STI
changes after administration
of
com-monly
used
calcium
channel
blocker (CCB)
i.e.
verapamil
in
anesthetizedrabbits.
MATERIAL
AND METHODS
The study was
carried out in rabbits (n=18) of either
sex weighing
one to two kilogram
(mean
1,96+
.6).Department
of
Physiology, Pt B.D. Sharma Post graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Rohtak, 124001, Haryana, IndiaAnimal
was anesthetizedwith
urethane (0.5to
I
gm/kg
body weight).
After
tracheal intubation, the right
femoral artery
wascannulated
andconnected to
pres-sure transduces
(Strain
gaugetype), which in turn
was connectedto two channel polyrite
to record the
meanarterial
blood
pressure
(MAP).
Electro
cardiogram
(ECG), carotid arterial pulse
(CAP)
and
phonocar-diogram (PCG)
wererecorded simultaneously
onfour
channel polyrite (INCO).
Heart rate (HR) was
calcu-lated from R-R interval of ECG. STIs were recorded
before and after intravenous
(I.V.)
administration
of
verapamil (0.1 mg/kg body weight).
Electromechani-cal
systole
(QSz),
left
ventricular ejection
time
(LVET), pre ejection period
(PEP) and ratio
of
PEPLVET
were calculated
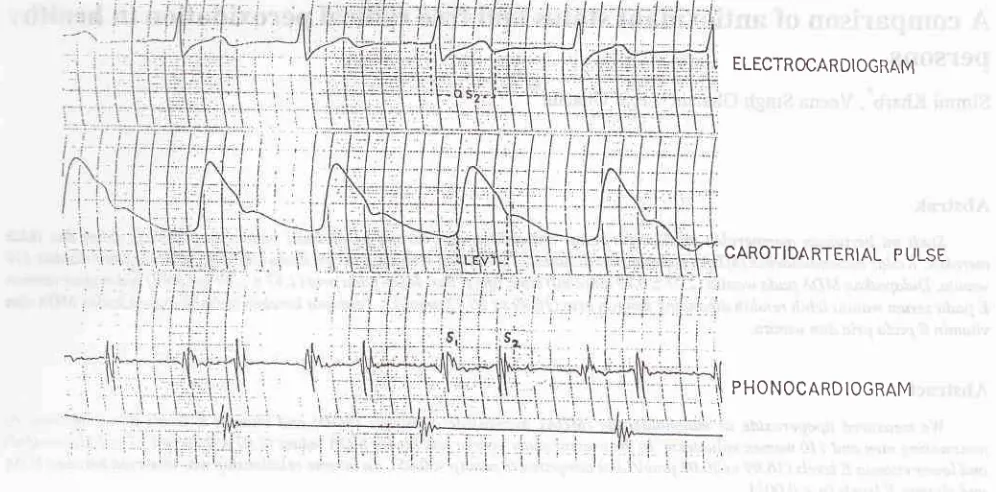
(Figure 1).
To
calculate STI
indices,
the
values were corrected
for HR
using
Weissler
original HR STI
regression.2The data were subjected
to
statistical analysis using
student
't'
test. P values of
lessthan 0.05 were
takenas
statistically
significant.
RESULT
There was
significant
fall
in
meanarterial
pressure and194 Singh
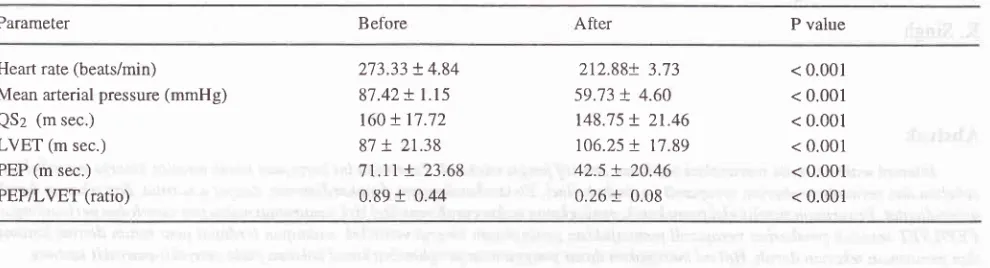
Table
l.
Effect of verapamil on systolic time intervalsMed
I
IndonesParameter Before After P value
Heart rate (beats/min)
Mean arterial pressure (mmHg) QS2 (m sec.)
LVET (m sec.) PEP (m sec.) PEP/LVET (ratio)
273.33 + 4.84
87.42+
l.l5
t60
t
17.72 87+
21.38'tl.tt
+
23.68 0.89+
0.442t2.88!
3.73 59.73+
4.60 148.75!
2t.46106.25
!
17.89 42.5+
20.46 0.26+
0.08< 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001 < 0.001
148.1 5
+
21.46 (p < 0.00 1 ) afterverapamil.
There wassignificant rise in
LVET
andfall
in
PEP
andratio
of
PEP
to LVET (p
<
0.001)
from
control values
onverapamil administration (Figure
2 andTable
1).DISCUSSION
STI is
anindirect
non-invasive
measureof myocardial
contractility. Effects
of
calcium
antagonists result
from
acomplex interplay of direct
andindirect
cardiacand
vascular
actions.
Bradycardia
after verapamil
in
present
study may be
adirect effect.
It
may
be due toreduction
in
the
frequency
of
sinoatrial
(SA)
depolarisatio.r.l
Itr
direct
effect
on SA
nodeis
shownverapamil into
ï,'::ï;:,î'o
Calcium
blocking
drugsinterfere with
electromechani-cal coupling
in contractile tissues.' This
explains
thereduction
in
QSzin
presentcommunication.
Prolonga-tion of LVET,
andindicator of contractility,
indicates
increase
in
strokevolume.r But inspite of
reducedHR,
LVET is found to
be elevated
in this
study
while
thehemodynamic
consequence
of
direct
negative
chronotropic effect
is
apotential
decreasein
cardiac
output.
So
either a
reduced
HR
with
consequent
in-creasein diastolic
filling
period
or decreasein
LV
after
load induced
by
vasodilatation
(fall in mAP)
aloneor
baroreceptor mediated reflexes increase
in
beta-adrenergii
tone
in
responseto vasodilationl
could
in-crease the
LEVT.
PEP and
ratio
of
PEP/LVE
are
good
measureof
in-otropic
stateof
heart.6 PEP hassignificant
correlation
with
LV
dp/dt.
Decrease
LV
performance results
in
increase
in
PEP/LVET
and PEP.
It
is
reported
thatverapamil exert negativc
inotropic effect
in
isolated
myocardial preparation.'
In
the
present
context
in-creased
contratility
as
evident
by
decreasePEP
andratio
of
PEPiLVET can be explained
by its
indirect
effect.
That is baroreceptor mediatedreflex
increasein
beta
adrenergic
toneelicited
by peripheral
vasodilata-tion
after verapamil. Further,
it
increases themyocar-dial oxygen supply (coronary arterial
vasodilatation)
as
well
as reduces
mvocardial oxvsen
demand
(reduced heart rate and
aiter
toad).1So, changes
in STIs
showed that
verapamil
enhancesthe
contractile
stateof ventricle. This is in
consistent
with
the findings
of
other
authors
who
stated
that
asiginificant
improvement
in
cardiac
function
wasob-served
with
increase
in
cardiac
index
and
meanvelocity
- ..of
fiber
shortening
after administration
of
I
verapamll.
REFERENCES
l.
Low RI, Takeda P, Mason DT, DeMaria AN. The effectsof
calcium channel blocking agents on cardiovascular function. Am J Cardiol 1982;49:537-53.
2. Weissler
AM,
Hanis WS, SchoenfeldCD.
Systolic time intervals in heart failurein
man. Circulation1968;37'.149-59.
3. Ono H, Himori N, Taira N. Chronotropic effects of coronary vasodilators as assessed
in
the isolated blood perfusedsinoatrial preparation
of
the
dog. TohokuJ
E,xp med 1977;121:383- 90.4. Mangiardi
LM,
Hariman RJ, McAllister RG, Bhargava V,Suravicz
B,
ShebataiR.
Electrophysiologic and hemo-dynamic effects of verapamil: correlation with plasma dntg concentration. Circulation 1978;57 :366-i 2.5. Tavel ME. Clinical phono cardiography and external pulse recording. 3'o ed.
Year book
medical publishers, Inc. Chicago, London 1978; 193.6. Weissler AM, Ganad CL Jr. Systolic time intervals in car-diac disease. Mod Conrc Cardiovasc Dis 1970;40:
l.
7. HenryPD.
Comparative pharmacologyof
calcium [image:2.595.50.545.99.233.2]VoI7, No 4, October - December 1998
QS2 LVET
Effect ofverapamil on STI r95
ELECTROCARDI0cRt\M
CAROTIDARTERIAL PULSE
PHONOCARDIOGRAM
PEP/LVET RATIO PEP
B
=
BEFORE
[image:3.595.44.542.82.328.2]A
=
AFTER VERAPAMIL
ADMTNTSTRATION