THE EFFECT OF PREDICTION AND INFERENCE STRATEGY
ON STUDENTS’ READ
ING COMPREHENSION
IN ANALYTICAL EXPOSITION TEXT
A THESIS
Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements For the degree of Sarjana Pendidikan
By:
ERA ENJELYNA LUMBANRAJA
REGISTER NUMBER: 2113121022
ENGLISH AND LITERATURE DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF LANGUAGES AND ARTS
i
ABSTRACT
Lumbanraja, Era Enjelyna. 2113121022. The Effect of Prediction and Inference Strategy on Students’ Reading Comprehension in Analytical Exposition Text. A Thesis. Faculty of Languages and Arts, State University of Medan. 2016.
This study aims at investigating the effect of prediction and inference strategy on
students’ reading comprehension in analytical exposition text. This study was
conducted by using experimental research design. The population of the study was the students of grade XI of SMA Negeri 14 Medan in the academic year 2015/2016; two classes were selected as the sample by applying random sampling. The sample was divided into two groups. The Experimental group (XI IPA 1) was taught by applying prediction and inference strategy, while the control group (XI IPA 3) was taught by using direct instructional teaching. The data of the study were obtained by using objectives test. To determine the reliability of the test, the writer used KR 20 formula. The data calculation showed that the coefficient of reliability of the test was 0.81. It showed that the test was reliable. The data were analyzed by applying t-test formula and the result of the study showed that t-observed (4.29) was higher than t-table (2.00) (t-observed > t-table) at the level of significance of α = 0.05 and at the degree of freedom (df) = 58. It
means that prediction and inference strategy significantly affects students’ reading
comprehension in analytical exposition text or in other word the alternative hypothesis is accepted.
ii give guidance, suggestions, advices, comments and moral supports. Therefore, the writer would like to express her thanks and sincere gratitude to:
Prof. Dr. Syawal Gultom., M.Pd., the Rector of State University of
Medan.
Dr. Isda Pramuniati, M.Hum., the Dean of Faculty of Languages
and Arts, State University of Medan.
Prof. Dr. Hj. Sumarsih, M.Pd., the Head of English Department. Dra. Meisuri, M.A., the Secretary of English Department and her academic years and has given guidance, support, and comments.
Prof. Dr. Busmin Gurning, M.Pd., her Reviewer and Examiner, who has given her precious time, guidance, suggestions, and comments.
All the Lecturers of English Department who have taught, guided,
and advised her throughout the academic years.
Eis Sri Wahyuningsih, M.Pd., as the Administration Staff of English
Department, for her attention, assistance, and information in completing this thesis.
Sofyan, S.Pd., the Headmaster of SMA Negeri 14 Medan, for his
permission in allowing the writer to do observation and to collect the data needed for the thesis.
Nurjannah, S.Pd., M.Hum., the English Teacher of SMA Negeri 3
iii
Her beloved parents, Barita Lumbanraja and Nurliana Harinja, her lovely brothers, Aji Lumbanraja and Carlos Lumbanraja, for their everlasting love, prayer, great motivation, courage and everything that that they have given to the writer during the study and in completing the thesis. This thesis is dedicated to you
Her beloved bestfriends, Fibie Liona, Irdawati Siagian, Dwi Suci
Indahswari Tarigan, Yessi Van Carmelia Simbolon, Lestaria Doloksaribu, Indah Pratama Prida, Intam Nilam Sari, Siti Khairin Nasroh, Novia, Aryadi M Gultom, Jelita Sitorus, Harni Gultom for the courage, support, help and spirit during the
completing of her thesis.
Her lovely family in R/N HKBP Binjai Amplas, especially Gr.
Klemens Situmeang, Bang Jubi Simanjuntak, Kak Ferty Hutajulu, Bang Richi Suhendra Manullang, Jenny Tobing, Ester Sinaga, Artha Tambunan, Ochien Tobing, Ricky Purba, Mangisi Sihombing, Mori Silitonga, Ester Siregar, for their prayer,
motivation, support, and spirit during completing this thesis.
Her lovely sisters, Yusnita Tamba, Jesika Puspita Sari, Ardhana
Sipahutar, Paskah Sitorus, Sadarni Damanik, for their time,
support and spirit.
Her friends in Regular Dik A 2011, for their togetherness throughout the four years
Her friends in PPLT 2014 SMK Soposurung, especially for Rohana
Tarawati, Angela Mutia, Debora Panjaitan, Ganda Sianipar, Ira Simamora, Rades Sianipar, Iwandi Sagala for the togetherness and
the experiences shared. And also for those who cannot mentioned on by one.
Last but not least, the writes realizes that this thesis still has the paucity and mistakes, she conveniently to accept suggestions, comments, critics and advices for the better writing.
Medan, February 2016 The Writer,
iv
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Pages
ABSTRACT ... i
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... ii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... iv
LIST OF TABLES ... vii
LIST OF FIGURES ... viii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... ix
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION ... 1
A.The Background of Study ... 1
B.The Problem of Study ... 5
C.The Objective of Study ... 5
D.The Scope of Study ... 6
E. The Significance of Study ... 6
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF LITERATURE ... 7
A.Theoretical Framework ... 7
1. The Nature of Reading Comprehension ... 7
2. Factors Affecting Reading Comprehension ... 11
3. Levels of Reading Comprehension ... 12
4. Measuring Reading Comprehension ... 14
5. Teaching Reading Comprehension ... 16
6. Analytical Exposition Text ... 18
7. Prediction and Inference Strategy... 20
v
b. The Procedures of Prediction and Inference Strategy in Reading
Comprehension ... 22
c. The Advantages and Disadvantages of Prediction and Inference Strategy ... 24
B.Conceptual Framework ... 25
C.Hypothesis ... 26
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 27
A.Research Design ... 27
B.Population and Sample ... 2 8 C.The Source of Data ... 28
D.The Instruments for Collecting Data ... 28
E. The Procedures of Research ... 29
1. Try Out ... 29
H.Homogeneity and Normality of the test ... 34
1. Homogeneity of Variance ... 34
2. Normality of the test ... 35
I. The Technique for Analyzing Data ... 35
J. Statistical Hypothesis ... 36
CHAPTER IV. DATA AND DATA ANALYSIS ... 37
A. Data Description... 37
B. Data Analysis ... 41
vi
2. Reliability of the test ... 42
3. Testing of Homogeneity of Variance ... 43
4. Testing Normality ... 44
5. Data Analysis by Using t-test formula ... 45
C. Testing Hypothesis ... 46
D. Research Findings ... 47
E. Discussion ... 47
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 51
A. Conclusion ... 51
B. Suggestion ... 51
vii
LISTS OF TABLE
Pages
Table 1.1 The Eleventh Grade Students’ Score of Reading Test ... 3
Table 3.1 Research Design ... 27
Table 3.2 Treatment in Experimental Group ... 30
Table 3.3 Conventional Teaching in Control Group ... 31
Table 4.1 Students’ Achievement Score in Pre-test and Post-test ... 38
viii
LIST OF FIGURE
Pages
Figure 2.1 The example of Analytical Exposition Text ... 19
Figure 4.1 Students’ achievement score in Pre-test ... 39
ix
LIST OF APPENDICES
Pages
Appendix A. Pre-Test And Post Test for Experimental And Control Group ... 56
Appendix B. Answer Key of Reading Test Pre-Test and Post-Test ... 64
Appendix C. The Scores of Pre-Test and Post-Test ... 65
Appendix D. The Scores of Validity ... 67
Appendix E. The Scores of Reliability ... 68
Appendix F. The Calculation of Reliability ... 70
Appendix G. The Table Calculation of t-Test ... 71
Appendix H. The Calculation of t-Test ... 74
Appendix I. Percentage Points of T Distribution ... 76
Appendix J. Test for Homogeneity of Variance of Pre-test in Experimental and Control Group ... 77
Appendix K. Test for Homogeneity of Variance of Post-test in Experimental and Control Group ... 79
Appendix L. Test for Distribution of Frequency in Experimental Group... 81
Appendix M. Test for Distribution of Frequency in Control Group ... 84
Appendix N. Testing Normality in Experimental Group ... 87
Appendix O. Testing Normality in Control Group ... 89
Appendix P. Table of Normality from 0 to Z... 91
Appendix Q. List of Testing Liliefors ... 92
Appendix R. F-Distribution (α = 0,05 in the Right Tail) ... 93
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A.
The Background of the StudyReading is one of the basic skills that should be mastered by the students in learning English. It has a significant contribution to be successful in learning.
Reading is the reader’s act to gain the information which is stated directly or
indirectly in the text. Through reading, students will be able to increase their knowledge. They will get useful information so that they can think critically because they have a wide insight.
According to Snowling and Hulme (2011) reading is primary goal of learning education, in which the goal of reading is to get the competence in understanding and comprehending the text. In reading skill, the students are not only expected to read the text in good pronunciation or to find out the meaning of each word within the text but also to understand, to evaluate and to recognize the
writer’s ideas of the reading text.
2
The internal factor comes from students themselves such as minimum vocabulary, lack of knowledge and reading interest. This situation makes the students having difficulties in getting the meaning in the text. Another factor is external factor which comes from out of the students, such as teaching strategy and materials that the teacher uses in teaching reading. The teacher still uses conventional teaching. The teacher only asks the students to read the text, find out the difficult words, and translate the words into Indonesian. Then, last activity is answering the questions in the textbook. The materials that the teacher provides is also unattractive, therefore the students feel that reading is boring activity and
they can’t improve their knowledge.
However, according to The Nation’s Report card: Reading 2013, there is only 33% of all eight graders which are in above a proficient level, while 42% at a basic level, and 23% at below-basic level. It means that more than 60% of students in eighth grade in 2013 were struggling to comprehend the text. It means that the ability of the students to comprehend is still lower; therefore, the students
can’t comprehend the text well.
The problem of students in comprehending a text was found in SMA Negeri 14 Medan while the writer did the observation. The writer asked the
students’ opinion about reading class. Most of the students said that reading text
3
structure of the text and answer the questions in the text book. These strategies made the students feel bored and do not have willingness in reading the text. The
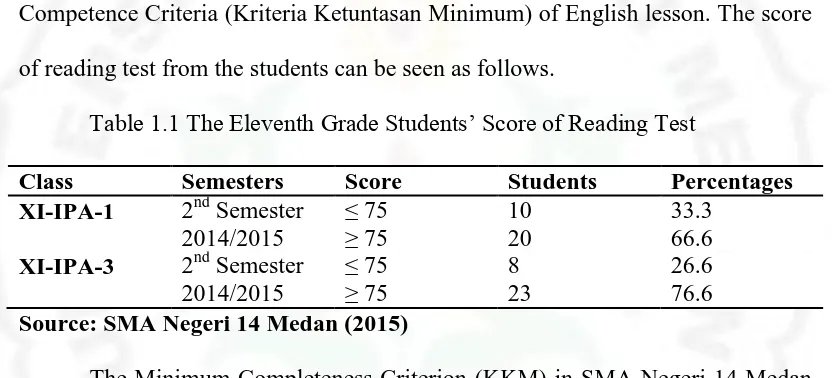
writer found the data of XI grade students’ score in the first semester at 2014/2015
academic year from English teacher. The students got the score below Minimum Competence Criteria (Kriteria Ketuntasan Minimum) of English lesson. The score of reading test from the students can be seen as follows.
Table 1.1 The Eleventh Grade Students’ Score of Reading Test
Class Semesters Score Students Percentages
XI-IPA-1 2nd Semester
Source: SMA Negeri 14 Medan (2015)
The Minimum Completeness Criterion (KKM) in SMA Negeri 14 Medan was 75. From the data above, it can be concluded that students’ reading comprehension is still low. From 60 students, there were only 18 Students got score of Minimum Competence Criteria and 42 students who did not get the score of Minimum Competence Criteria.
In addition, based on the writer’s experience at Teaching Practice in PPLT
2014 in Vocational high school, most of the students were not able to read and comprehend the text. It was caused by the lack of vocabulary and teaching
learning process isn’t effective. Most of the students were passive in the class. They also have minimum score in English Subject.
4
strategy. Prediction and Inference Strategy is one of the strategies that is useful to help the students to gain the meaning of the text.
Prediction and Inference strategy is an effective strategy to develop their mental models to combining the current text information with one’s own experience in order to create meaning that not directly states in the text. It means
creating connections and making educated guesses that go beyond the author’s
exact words or images.
Zwiers (2010: 99) states that the students use the text clues and our background knowledge to predict what will happen next in a text or what we will learn later in a text. Students then go through the text to confirm, discard, change, or make new predictions, based on new evidence that comes up. Prediction provides the students with motivation and purpose for reading. It also helps the mind preparing itself to understand the upcoming ideas in the text.
Through, Prediction and Inference strategy, the students would be effectively and automatically combine the text and their background knowledge to make good inferences and predictions. Prediction and Inference strategy facilitate the students to set up the purpose of reading and anticipate what the students will read. It can be concluded that Prediction and Inference strategy is an appropriate strategy to teach reading comprehension in order to help the students building their thinking process in comprehending the text.
The previous research by Thomas (2005) in ESL students’ classroom.
Prediction and inference used as a strategy to build the students’ comprehension
5
concept with their implicit or personal knowledge. Another research by Baretta et, al (2009) proved that students in University of Auckland, New Zealand who taught by using inference strategy significantly better in comprehending reading expository text than when reading narrative text. The students generally bridging inferences more easily and were better of judging the unsuitability of expository text. In addition Linda (2007) concluded that prediction and inference strategy has significantly affected the students in sixth-graders from two Canadian urban centers in reading comprehension by establishing textual coherence or embellishing meaning in the text.
Based on the explanation above, the researcher was interested in conducting a study by applying Prediction and Inference Strategy on students’ reading comprehension in analytical exposition text.
B. The Problems of the Study
Based on the background of the study, the research problem of this study was formulated as the following: “Is there any significant effect of prediction and inference strategy on students’ reading comprehension in analytical exposition text?”
C. The Objectives of the Study
The objective of this study was to investigate whether there is a significant
effect of Prediction and Inference strategy on students’ reading comprehension in
6
D. The Scope of the Study
There were several strategies that can be used to improve reading comprehension. In this study, the writer only focused on applying Prediction and Inference strategy on students’ reading comprehension in analytical exposition text.
E. The Significance of the Study
The findings of this study are expected to be useful as,
a. Theoretically, the findings of this study are expected to enhance the theories of reading comprehension.
b. Practically, the findings of this study is expected to give feedback to: 1. English teachers, they can use this strategy as a reference in
teaching reading to improve the students’ reading comprehension
especially analytical exposition text.
51
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
A. Conclusion
Based on the data analysis, it is concluded that applying prediction and
inference strategy significantly affects the students’ reading comprehension in
reading analytical exposition text. Thus, the students’ score in experimental group was higher than the students score in control group. The calculation of the data in the testing hypothesis showed that t-observed 4.29 was higher than t-table 2.000, it means that the alternative hypothesis (Ha) is acceptable.
B. Suggestions
This study showed that reading comprehension by using prediction and
inference strategy could improve students’ reading comprehension in analytical
exposition text. In relation above, some suggestions are offered as the following: 1. Since Prediction and Inference strategy is significantly effective, it is
suggested that the teacher should apply this strategy in teaching process in order to improve students’ reading comprehension in analytical exposition text.
52
REFERENCES
Antonacci, P & Callaghan, C. 2011. Strategies for Middle and Secondar
Classroom. California: Sage Publication, Inc.
Ary, D., Jacobs, L.C. & Sorensen, C. 2010. Introduction to Research in Education
(8th edition). Canada: Cengage Learning.
Attaprechakul, Damrong. 2013. Inference Strategy to Improve Reading Comprehension of Challenging Text. Canadian Center English Language
Teaching. 6 (3).
Azzizmohammadi, Fatemah. 2013. Investigating the Effect of Drawing Inference in EFL Learners Reading Comprehension Ability by Using Recall of short Stories. International Journal of Language and Linguistics. 1 (4), 155-159 Barreta, Luciane., Tomitch, Leda. 2009. Inference Making While Reading
Narrative and Expository Texts: An ERP Study. Psychology and
Neuroscience. 2 (2), 137-145
Best, J. W. & Kahn, J. V. 2006. Research in Education (10th edition). New Dehli: Prentice Hall.
Blachowicz, C. & O, Donna. 2008. Reading Comprehension: Strategies for
Independent (Second Edition). New York: The Guildford Press.
Bloom, B.S. 2000. Taxonomy of Educational Objectives: Classificationof
educational goals. New York: Longman
Brown, Douglas. 2004. Teaching Principle: An Interactive Approach to Language
Pedagogy. San Francisco University: Pearson Logman.
Brown, Douglas. 2004. Language assessment: A Principle and Classroom
Practices. New York: Pearson Education.
Carr, Ellien and Dewitz, Petter. 1983. The Effect of Inference training on
Children’s Reading Comprehension of Expository Text. Journal of Reading Behaviour. 15 (3)
Cunningham, G. K. 2005. Assessment in the Classroom: Constructing and
Interpreting Texts. Washington, D.C: The Falmer Press
53
Duffy, Gerald G. 2009. Explaining Reading: A Resource for Teaching Concepts,
Skills and Strategies ( Second Edition). New York: The Guildford Press.
Duffy, Gerald G. 2014. Explaining Reading: A resource for Explicit Teaching of
Common Core Standards. New York: The Guildford Press.
Grabe, William. 2009. Reading in Second Language: Moving from theory to
Practice. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Harmer, Jeremy. 2001. The Practice of English Language Teaching. New York: Logman
Hornby, A.S. 2000. Oxford Advanced Learners Dictionary of Current English. Oxford: Oxford University Press
Jiang, Yongmei. 2009. Predicting Strategy and Listening Comprehension. Asian
Social Science. 5 (1)
Johnson, Andrew P. 2008. Teaching Reading and Writing: A Guidebook for
Tutoring and Remediating Students. New York: Rowman & Littlefield
Education.
Kligner, Jannete K., Vaugh, Sharon & Boadman, Alison. 2007. Teaching Reading
Comprehension to Students with Learning Difficulties. New York: The
Guildford Press.
Knapp, Peter., Watkins, Megan. 2005. Genre, Text, Grammar: Technologies for teaching and assessing writing. Sydney. NSW Press Book.
Kurniasari, T., Wisnu, Andra. 2009. Jakarta as a Bad Working Place for
Expatriates. (Online). Retrieved from:
http://m.thejakartapost.com/news/2009/04/15/Jakarta-as-a-Bad-Working-Place-for-Expatriates.html (Accessed on July 2015)
Linda, Philips M. 2007. Inference Strategy in Reading Comprehension. 174
Children Research Center.
Lems, Kristin., Miller, L.D & Soro, T.M. 2010. Teaching Reading to English
Language Learners: Insight from Linguistic. New York: The Guildford
Press.
McNamara, Danille S. 2007. Reading Comprehension Strategies: Theories,
Inventons and Technologies. New Jersey: Lawrance Erlbrawn
54
Moreillon, Judi. 2007. Collaborative Strategies for Teaching Reading
Comprehension. Chicago: American Library Association.
Morgan, S. 2002. The Effect of Teaching Predicting and Visualizing Strategies on Upper Primary Students with Reading Difficulties. Reciprocal
Teaching-Teaching Education Centre.
Serravallo, Jeniffer. 2010. Teaching Reading in Small Group. Differentiated
Instruction for Building Strategic, Independent Reader: Portsmouth.
Heinnaman.
Snowling, J. Margaret & Hulme, Charles. 2011. Evidence Based Interventions for
Reading and Language Difficulties: Creating a Vistuous Circle. Victoria:
Blackwell Publishing.
Sudjana, Nana. 2005. Metode Statistika. Bandung. Tarsito
Thomas, Ursula. 2005. The Power of Prediction: Using Prediction Journal to Increase Comprehension. (Online). Retrieved from http://educationnext.org/the-educational-prediction-inference/ (Accessed on July 2015)
The Nation’s Report Card. Propotions of Students Groups are Reading
Proficiency at 2013. Retrieved from:
//http:www.nationsreportcard.gov/reading_math_2013/#Students-Groups/ Accessed on 8th May 2015.
Westwood, Peter. 2001. Reading and Learning Difficulties: Approaches to
Teaching and Assessment. Victoria: ACER Press.
Westwood, Peter. 2008. What Teacher Need to Know about Reading and Writing
Difficulties. Victoria: ACER Press.
Willis, Judi & D. M. 2008. Teaching The Brain to Read: Strategies for Improving
Fluency, Vocabulary, and Comprehension. Virginia: ASCD
Zwiers, Jeff. 2010. Building Reading Comprehension Habits in Grade 6-12: A
Toolkit Actives (Second Edition). New York: International Reading