Parung Panjang-Bogor)
By:
Sheira Ayu Indrayani
109014000107
THE DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS
’
TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
v
Quasi Experimental Study at the Second Grade of SMA Mathla’ul Huda Parung Panjang-Bogor. Skripsi of English Education at Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training of State Islamic University Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, 2014.
The objective of this study is to find the effectiveness of mind mapping in improving students’ reading comprehension achievement, especially for narrative text at the second grade students of SMA Mathla’ul Huda Parung Panjang Bogor academic year 2013/2014. The subjects of this study were 70 students.
Experimental research was used as a method in this study. The study was carried out in two classes, they are the controlled class and the experimental class. The data were gathered through tests which were delivered into the pre-test and the post-test.
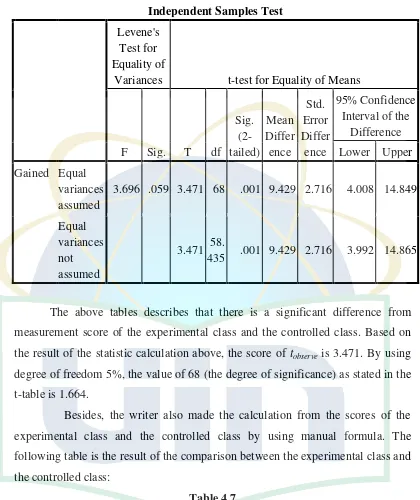
The result of the study showed that the mind mapping technique is effective to use in teaching reading comprehension of narrative text. Gained score of the experimental class (27.14) is higher than the controlled class (17.71). From the result of statistic calculation, it is obtained that the value of t-observation (to) is 3.47 and degree of freedom (df) is 68. In the table of significance 5%, the value of degree of significance is 1.66. Comparing those values, the result is 3.47 > 1.66 which means t-observation (to) score is higher than t-table (tt) score. In other word, the Alternative Hypothesis (Ha) is accepted and the Null Hypothesis (Ho) is rejected. Therefore, teaching reading comprehension of narrative text by using mind mapping technique is effective.
Keywords: Mind Mapping Technique, Reading Comprehension, Narrative Text, Experimental Study.
vi
Quasi Experimental Study at the Second Grade of SMA Mathla’ul Huda Parung Panjang-Bogor. Skripsi of English Education at Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training of State Islamic University Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta, 2014.
Penelitian ini dilakukan untuk mengetahui keefektifan tehnik mind mapping dalam meningkatkan prestasi belajar siswa dalam memahami bacaan dari teks narasi pada siswa kelas 2 SMA Mathla’ulhuda tahun akademik 2013/2014. Subjek penelitian ini terdiri dari 70 siswa.
Penelitian eksperimen adalah metode yang digunakan di dalam penelitian ini. Penelitian ini diadakan di dalam dua kelas, yaitu kelas kontrol dan kelas eksperimen. Data dikumpulkan melalui tes yang diberikan melalui pre-test dan post-test.
Hasil dari penelitian menunjukkan bahwa tehnik mind mapping efektif digunakan dalam pengajaran memahami bacaan dari teks narasi. Gained score yang diperoleh kelas eksperimen (27.14) lebih tinggi daripada kelas control (17.71). Dari hasil kalkulasi statistik, dapat diperoleh bahwa nilai dari t-observasi (to)adalah 3.47 dan degree of freedom (df) adalah 1.66. Dalam table signifikan 5%, nilai degree of freedom adalah 1.66. Dengan membandingkan nilai-nilai tersebut, hasilnya adalah 3.47 > 1.66 yang berarti skor t-observasi (to) lebih besar dari skor t-tabel (tt). Dengan kata lain, Hipotesis Alternatif (Ha) diterima dan Hipotesis Null (Ho) ditolak. Oleh karena itu, pengajaran memahami bacaan dari teks narasi menggunakan tehnik mind mapping efektif.
Kata kunci: Tehnik Mind Mapping, Memahami Bacaan, Teks Narasi, Penelitian Eksperimental.
vii
Praised be to Allah, Lord of the world, who has given mercy and blessing to the writer in finishing this skripsi. Peace and salutation be upon to the prophet Muhammad SAW, his family, his companion, and his adherence.
In this occasion, the writer would like to thank to her beloved family, Tonny Soelistyo Wahyudi and Suarni as her parents, and her brother Muhammad Fadel Azhari for their prayers, understanding, support, and motivation.
The writer also would like to address her great honor and attitude to her advisors, St. Nurul Azkiyah, M.Sc, Ph.D and Yenny Rahmawati, M.Ed for their guidance and valuable advices during the writer did this skripsi.
The writer’s sincere gratitude also goes to:
1. Drs. Syauki, M.Pd., the Head of English Education Departement.
2. All lecturers of English Education for the useful knowledge and skills given.
3. Ratu Nurul Ulfah, S.Sos.I.MM., the Headmaster of SMA Mathla’ul Huda Parung Panjang Bogor for giving permission to the writer to do observation and research.
4. Ferry Setiawan, S.Pd., and Sita Yulia as the English Teachers at SMA Mathla’ul Huda Parung Panjang Bogor.
5. All of the teachers and the second year students at SMA Mathla’ul Huda Parung Panjang Bogor.
6. All of her friends in English Education Department, especially C Class for academic year 2009 and the members of Bloom Project.
7. All of her friends in PPKT at SMAN 1 Parung Bogor.
viii
Jakarta, 12 Mei 2014
ix
PAGE OF APPROVAL ... ii
ENDORSEMENT SHEET ... iii
SURAT PERNYATAAN KARYA SENDIRI ... iv
ABSTRACT ... v
ABSTRAK ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... vii
TABLE OF CONTENT ... ix
LIST OF TABLES ... xi
LIST OF PICTURE ... xii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... xiii
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. The Background of The Study ... 1
B. The Problem of The Study ... 4
C. The Limitation of The Problem ... 5
D. The Formulation of The Problem ... 5
E. The Objective of The Study ... 5
F. The Significance of The Study ... 5
CHAPTER II. LITERATURE REVIEW ... 6
A. Reading ... 6
B. Reading Comprehension ... 7
1. The Definition of Reading Comprehension ... 7
2. The Factors Influencing Reading Comprehension ... 9
C. The Purposes of Reading ... 11
D. Narrative Text ... 12
E. Mind Mapping ... 14
x
Mapping ... 19
F. Teaching Reading Comprehension of Narrative Text Through Mind Mapping ... 21
G. Previous Studies ... 22
H. Conceptual Framework ... 24
I. Hypotheses ... 25
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 27
A. The Research Design ... 27
B. The Place and Time of The Research ... 27
C. The Population and Sample of The Research ... 28
D. The Data Collection Technique ... 28
E. The Content of The Intervention ... 29
F. The Data Analysis Technique ... 30
G. The Statistical Hypotheses ... 31
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH FINDING ... 33
A. The Data Description ... 33
1. The Pre-test Scores ... 33
2. The Post-test Scores... 35
3. The Gained Scores ... 37
B. The Data Analysis ... 38
C. The Data Interpretation ... 46
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 48
A. Conclusion ... 48
B. Suggestion ... 48
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... 49
xi
Table 4.1 The Students’ Pre-test Scores ... 33 Table 4.2 The Students’ Post-test Scores ... 35 Table 4.3 The Gained Scores of The Experimental Class and
The Controlled Class ... 37 Table 4.4 The t-test of Pre-test in The Experimental Class and
The Controlled Class ... 39 Table 4.5 The t-test of Post-test in The Experimental Class and
The Controlled Class ... 40 Table 4.6 The t-test of Gained Score in The Experimental Class
and The Controlled Class ... 41 Table 4.7 The Comparison Scores of Each Student in
xiii Appendix 2 : The Instrument
Appendix 3 : The Blueprint Test of Pre-Test and Post-Test Appendix 4 : The Instrument of Pre-Test and Post-Test Appendix 5 : The Answer Keys
Appendix 6 : Lesson Planning
Appendix 7 : Students’ Exercises Scores Appendix 8 : Student’s Mind Mapping
Appendix 9 : Surat Keterangan Telah Melakukan Penelitian Appendix 10 : Surat Pengesahan Proposal Skripsi
1
This chapter explains about the background of the study, the problem of the study, the limitation of the problem, the formulation of the problem, the purpose of the study, and the significance of the study.
A.
The Background of the Study
English as an international language has been used for all over the world in recent years. Jeremy Harmer states that today English is the world’s most widely studied foreign language.1 In other words, English has important role in
people’s communication. In Indonesia, English is taught in schools as a foreign
language. This subject is tested in the national exam which shows the importance of this subject.
In teaching and learning process of English, there are four skills taught: listening, speaking, reading, and writing. In foreign language learning, reading is a skill that teachers expect learners to acquire. It argues as the most essential skill for success in all education context.2 No wonder, the students can learn many things through reading. In other words, the more they read, the more knowledge they get; hence, a strong correlation between reading and academic success is shown.
The act of reading cannot be separated from comprehension. The students cannot achieve their academic success without comprehending what they read. In comprehending the text, the students should be monitored by their teachers, hence the way to teach comprehension should be well understood by the teachers. Teaching comprehension is an activity through some steps: selecting a text, explaining the strategy, modelling the strategy, guided support, practicing
1
Jeremy Harmer, Approaches and Methods in Language Teaching-8th Ed, (New York: Cambridge University Press, 1992), p.1
2
H. Douglas Brown, Language Assessment-Principles and Classroom Practices,
independently, and reflecting.3 Therefore, it can be concluded that reading comprehension is a long process.
In addition, having a good comprehension in reading can be facilitated by many strategies. McNamara whose thinking is adopted by the College Board underlines growing recognition that the use of reading strategies is essential; high ability students who use reading strategies are getting successful not only in comprehending reading, but also in overcoming reading problems and becoming a better reader and comprehender.4 In summary, the students should have better strategies for their good comprehension.
Nowadays, the need of reading comprehension requires teachers to facilitate students through interesting strategies in learning process. Harmer states that students are better to be impulsed in responding the context and gaining their feeling about it than only focussing them on the text construction.5 The teachers usually ask the students to read without giving the solution about how to read with pleasure and comprehend through interesting strategies. The students are used to comprehend the text only by reading normally, as what their habits in learning process. In conclusion, students are stated having no problems in learning reading comprehension because of their habits -reading normally.
At the senior high school level, the students are expected to master some types of text like narrative, discussion, and hortatory exposition. Narrative as one of those types become a common text used in students teaching and learning process, moreover used in national exam. Narrative is a text that tells a story to entertain the audience, let the audience think about an issue, teach them a lesson, or excite their emoticons.6 Based on the theories, it can be assumed that
3
NSW Department of Education and Training, Teaching Comprehension Strategies,
2010, p. 7.
4McNamara, Ozuru, Best, & O’Reilly, “
Reading Strategies strand in English Language Arts College Board Standards for College Success™” as cited by the College Board College Board Standards, 2006.
5
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English Language Teaching-Forth Ed (Oxford: Pearson Longman, 2007), pp.101.
6
narrative text can be studied easily, because it lets the students interested to read the text; as its purpose is to entertain people.
Based on the writer’s observation, there are many students of the
second grade at SMA Mathla’ul Huda Parung Panjang Bogor who have difficulties in comprehending a narrative text; they could not find the major elements of the narrative text including setting, character, conflict or problem, the goal and resolution in the text based on the writer’s observation. Moreover, they could not get the main idea and supporting details of the text. Consequently, most of the students think that reading comprehension is a hard activity to do. Panatda states that students who faced English as a foreign language have low ability in reading comprehension; they cannot reorganize and connect the new information from the text with their own knowledge.7
Moreover, most of the students think twice to read comprehendly the text given. It can be seen when they prefer to answer the question given suddenly, without read the text deeper. In addition, commonly the students are taught through conventional method like delivering the material without any interesting action in teaching and learning process of reading comprehension. Therefore, students are getting low in their achievements.
In summary, the students face some problems in reading comprehension activities. First, students have difficulties in getting information from the text, in this case is narrative text. Then, this situation brings the students have low achievements in reading activity. In addition, the teaching and learning process of reading comprehension runs conventionally in class. It makes the students think twice to do reading activity, moreover reading is a long activity.
Considering that facts, the writer suggests mind mapping as the technique for teaching reading comprehension. Drawing mind mapping is an activity which makes the brain easier to accept and remember visually stimulating, multi-coloured mind maps, rather than monotonous, boring linear
7
Panatda Siriphanich, Using Mind Mapping Technique to Improve Students’ Reading
notes.8Theoritically, it can be concluded that mind mapping is a creative technique which let the students to get success in remembering ideas or comprehending written information. Moreover, this technique enables students to associate story through pattern, keyword, or symbol.
The writer considers that mind mapping can be an alternative technique for students when doing reading comprehension in achieving their academic success later. The writer takes a quasi-experimental research design to get the evidence about whether mind mapping technique can improve students’ reading comprehension of narrative text. Mind-mapping is supposed to be an interesting alternative technique that will help the students to organize their ideas about the text they have read by their own schema, so that they can comprehend the text easily. This study focuses on students’ mind-mapping in interpreting the text, not on their creativity.
Finally, based on the explanation above, the writer entitles this study
“The Effectiveness of Using Mind Mapping in Students’ Reading Comprehension
of Narrative Text (Quasi-Experimental Study at the Second Grade of SMAMathla’ul Huda Parung Panjang Bogor).”
B.
The Problem of the Study
Based on the background above, there are some identified problems: 1. Reading comprehension of English text still becomes a hard activity to
do for students, because they still have difficulties in getting information from text, especially narrative text.
2. Students’ reading comprehension achievements are low.
3. The teaching and learning process of reading comprehension runs conventionally in class.
8
C.
The Limitation of the Problem
This study spesifically deals with teaching and learning process of reading comprehension in narrative text at the second grade of SMA Mathla’ul Huda Parung Panjang Bogor. This study intends to measure whether or not mind mapping technique is effective in improving students’ reading comprehension achievement of narrative text.
D.
The Formulation of the Problem
Based on the background above, the writer formulates the problem question: “Is mind mapping effective to improve students’ reading comprehension achievement at the second grade of SMA Mathla’ul Huda Parung Panjang Bogor?”
E.
The Objective of the Study
The study is intended to find the empirical evidence of mind mapping’s effectiveness in improving students’ reading comprehension, especially for narrative text.
F.
The Significance of the Study
6
This chapter explains about reading, reading comprehension, purposes of reading, narrative text, mind mapping, teaching reading comprehension through mind mapping, previous studies, conceptual framework, and hypotheses. Specifically, reading comprehension theories deliver into some points: the definition of reading comprehension and the factor influencing reading comprehension. While mind mapping theories state into some points: the concept of mind mapping, the purposes of mind mapping, the procedure of mind mapping, and the advantages and disadvantages of mind mapping.
A. Reading
Reading is the skill or activity of getting information from books. It is an important skill for students to learn. Hence, a student who is not engaged in reading activity, he/she will miss new information. Harmer states that reading is useful for language acquisition; the more the students read, the better they get at
it. In addition, reading also has positive effect on students’ vocabulary knowledge, on their spelling, and on their writing.1 Mc Donough supports by stating reading is clearly one of the most important.2
In order to know correctly what reading is, there are some definitions of reading below based on some experts.
Grabe states that reading is the ability to draw meaning from the printed page and interpret this information appropriately.3
McLaughin as cited by Barbara Hawkins points out that reading is the most complex and difficult skills than others that the child must acquire in
1
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English Language Teaching-4thEd., (Oxford: Pearson Longman, 2007), p.99.
2
Jo Mc Donough and Christopher Shaw, Materials and Methods in ELT: A Teacher’s Guide-2nd, (Malden: Blackwell Publishing, 2003), p.89.
3
school.4 In addition, based on Goodman, reading is a selective process which involves partial use of available minimal language cues selected from perceptual
input on the basis of the reader’s expectation. As this partial information is
processed, tentative decisions are made to be confirmed, rejected or refined as reading progresses.5
In summary, reading is the way to get some ideas and information from written text through continously process in which the reader can make a decision to confirm, reject, or refine the ideas itself. In line with Grabe’s statement before, the writer do agree that reading is a kind of activity that people need to interpret the printed page through drawing the meaning of that page. Based on the writer research, drawing the meaning helps readers to easily understand what they interpret from the text. Here, the writer interprets „drawing the meaning’ by linking these words with drawing the readers interpretation of the text through mind mapping. For visual readers and especially students, it really helps them to understand the text well.
B. Reading Comprehension
1. The Definition of Reading Comprehension
Comprehension is the ability to understand completely and be familiar with a situation, facts, etc. Comprehension is not a single unitary process. It starts from the moving of words on the page to meaning in the mind, the recognizing of individual words by using memory and knowledge of letter and sound patterns, matching the resulting pronunciations to meaning, and finally connects these words into idea units.6
4
Barbara Hawkins, Teaching Children to Read in a Second Language,Teaching English as A Second or Foreign Language, 2nd Ed. Marianne Celce-Murcia, (Boston: Heinle & Heinle, 1991), p. 169.
5
Goodman, K. (1970). Reading as a psychologistic guessing game. In H. Singer and R. b. Ruddell . (Eds). Theoretical models and Processes of Reading. Newark, (N.J.: International reading Association), p.260 as be cited by Parviz Ajideh, Schema Theory-Based Pre-Reading Tasks: A Neglected Essential in The ESL Reading Class (The Reading Matrix Vol.3. No.1, April 2003), p.1.
6
In line with the statements above, Wiggens and McTighe concludes six facets of understanding or comprehension. The first is explanation or understanding of why and how. The second facet is interpretation. The third facet is application or the ability to use knowledge in new situations and contexts. The fourth facet is perspective. The fifth facet is empathy for the feelings and views of others. The sixth facet is self-knowledge.7 Thus, it can be concluded that comprehension is the ability to get enlightenment on something through several steps in process.
Snow cited by Kurniawan states reading comprehension as the process
to get a precise understanding of the writer’s message through simultaneously extracting and constructing meaning by collaborating reader’s background
knowledge and interaction and involvement.8 In line with this, Grabe explains that reading comprehension is the interaction of information between the reader’s
drawing information from a text and the reader’s expectations or information
about the text that already has.9
Lems concludes that reading comprehension is not a static competency.
It depends on reader’s purpose to read and reader’s basic knowledge with the text
in used. In addition, the role of strategies helps the reading comprehension achieved.10
Wilhelm cited in Kurniawan’s writing defines that reading comprehension is the degree to which the readers understand what the readers read. It is the ultimate end-goal of reading that if the readers do not read to understand, the readers will read for nothing; Comprehension requires the reader to be an active constructor of meaning.11
7Ibid.,
p. 36-37.
8
Ashadi Kurniawan, Improving Students’ Reading Comprehension on Narrative Text Through Story Mapping Strategy (skripsi, teacher training and education faculty, Tanjungpura University, Pontianak, 2013), p.4.
9
William Grabe and Fredricka L. Stoller, Reading for Academic Purposes: Guidelines for the ESL/EFL Teacher, Teaching English as A Second or Foreign Language, 3rd Ed. Marianne Celce-Murcia (Boston: Heinle & Heinle, 2001), p.188.
10
Kristin Lems, et.al.,Teaching Reading to English Languager Learners: Insight from Linguistics, (New York: The Guildford Press, 2010), p.170.
11
Based on those definitions above, reading is an important activity used in learning process, but it becomes more useful when the readers can comprehend what they read. Overall, reading comprehension can be concluded as the ability to understand the meaning or idea in the written text completely and chronically. Eventhough reading comprehension has long process, what the readers get are comparable with the process itself.
In line with those theories, the writer concludes that reading comprehension ability is a must for people to have it. Based on the writer’s research, students need to comprehend what they read in order to get academic success. Of course, reading comprehension is a long activity, but with the appropriate technique for each student/reader, it is not possible that the long activity becomes an interesting long activity that makes the students/readers enjoy and can easily comprehend what they rea.
2. The Factors Influencing Reading Comprehension
It is undeniable that students’ ability to comprehend the print that they
meet in the class depend on their ability to understand both what a writer says and what they do not say, except between the lines.12 Comprehension is an active
process which engages the interaction between the reader’s construct meaning and
the information of the text itself.13 Therefore, comprehending depends on the ability:
a) to evaluate and make a judgment,
b) to distinguish between what an author offers as facts and the author’s opinions about those facts,
c) to recognize the difference between what is fact and what is assumed to be fact,
d) to compare, e) to categorize,
f) to grasp the explanation of a process,
12
Dorothy Piercey, Reading Activities in Content Area-2nd Ed (Boston: Allyn and Bacon, 1982) p. 26.
13
g) to identify an author’s theme, h) to know characters,
i) to recognize a main idea and the data that support it, j) to distiguish between cause and effect.
In doing comprehension, it cannot be denied that there are several factors which influencing the reader to become good or poor comprehender. Perfetti as in Jane V. Oakhill’s writing suggests that comprehension difficulties arise mainly because certain processes that can potentially become relatively automatic fail to become so.14
Paris states five foundations of comprehension:15 a) Conceptual knowledge.
In developing the students’ comprehension, they need to be familiar with the
concept of the text like the plot and the character’s thought of the story.
b) Language skills.
The mastery of language skills prove the better comprehension of students later. It means that a student who at least had mastered one skill, he/she can easily comprehend the text. As example, the students who good in vocabulary can easily do reading comprehension.
c) Text features.
In line with the conceptual knowledge, the students need to know how the concepts of genres, the schematic structures of texts, the titles, and many terms that related to the meaning of texts. It is used to help the students to construct the meaning from any types of texts.
d) Strategies.
14
Jane V. Oakhill and Kate Cain, Assessment of comprehension in reading, The Psychological Assessment of Reading, John R. Beech and Chris Singleton (London: Routledge, 1997), p. 178.
15
Dr. Scott Paris, Developing Comprehension Skills,
It is undeniable that students need a variety of strategies in helping them learning reading comprehension. The appropriate strategies will make them easier to comprehend the text, such as summarizing and paraphrasing important information or asking and aswering questions.
e) Fluent decoding.
Comprehension is difficult when the students only focused on how the words in a text pronounce correctly. In fact, it is easier when the students learn how to automatically decoding and recognizing the words quickly and accurately.
In conclusion, the comprehension process is a long activity that has influencing factors in its process. The plus or the minus of influencing factors
depend on the students’ decision, whether or not they want to maximize the
information gotten from what they read. When they want to take the benefit from the reading comprehension, they can improve their reading skill through some points of views above. If they are not, they will just get the information without the experience.
C.
The Purposes of Reading
When people decide to read, it means that they have a purpose. Even when they read novel for pleasure, at least they want to get information about the story. Like Nuttall’s statement, people read because they wanted to get something from the writing; whatever it was, people wanted to get the message that the writer had expressed.16
There are many experts define about the purpose of reading. Generally, their definition state that reading has two main purposes: reading for pleasure and reading for getting information. Here are some reasons below.
Rivers and Temperley list the reason for reading as below17:
1. to obtain information for some purpose or because curious about some topic, 2. to obtain instructions on how to perform some task for work or daily life,
16
Christine Nuttall, Teaching Reading Skills in a Foreign Language, (Portsmouth: Heinemann, 1989), p.3.
17
3. to keep in touch with friends by correspondence or to understand bussiness letters,
4. to know when or where something will take place or what is available,
5. to know what is happening or has happened (as reported in newspapers, magazines, reports),
6. for enjoyment or excitement.
Grabe on his books concludes the purpose of reading into some point, they are:18
1. Reading to search for simple information and reading to skim quickly. 2. Reading to learn from texts.
3. Reading to integrate information, write, and critique texts. 4. Reading for general comprehension.
To sum up, when the students have purpose in reading materials, it will let the students to be more focus on what they want to get. Whatever the purpose, the students will have new information and will be useful for their needs when the purpose has decided. Moreover, through the suitable technique in comprehending their reading materials, the students will be more focus in the learning process and maximize the information gotten.
D.
Narrative Text
There are some kind of texts which are learnt at school by the second grade students of senior high school and narrative takes a part. Narration is any written English text in which the writer wants to amuse, entertain people, and to deal with actual or vicarious experience in different ways.19 Narrative uses conflicts among the participants, either natural conflict, social conflict or psychological conflict. In some ways, a narrative text combines all these conflicts. Thus, commonly narrative text is found in story book.20
18
William Grabe and Fredricka L.Stoller, Op.Cit., p.13-15.
19
Sanggam Siahaan and Kisno Shinoda, Generic Text Structure (Yogyakarta: Graha Ilmu, 2008), p.73.
20
In addition, there are steps for constructing a narrative text: orientation, complication, sequence of events, resolution, and coda (an optional step).
1. Orientation includes who is in the story, when the story is taking place, and where the action is happening.
2. Complication sets off a chain of events that influences what will happen in the story.
3. Sequence of events tells how the characters react to the complication.
4. Resolution shows how the characters solve the problem created in the complication.
5. Coda provides a comment or moral based on what has been learned from the story (an optional step).21
In order to make the generic structure explanation becomes clear, here the example of narrative text includes its generic structure.22
Once upon a time, there was once a guy who was very much in love with this girl. This romantic guy folded 1,000 pieces of papercranes as a gift to his girl. Although, at that time he was just a
small executive in his company, his future doesn’t seem too bright,
they were very happy together. Until one day, his girl told him she was going to Paris and will never come back. She also told him that
she cannot visualise any future for the both of them, so let’s go
their own ways there and then... heartbroken, the guy agreed. When he regained his confidence, he worked hard day and night, just to make something out of himself. Finally with all these hard work and with the help of friends, this guy had set up his own company.
“You never fail until you stop trying.” He always told himself. “I must make it in life!” One rainy day, while this guy was
driving, he saw an elderly couple sharing an umbrella in the rain walking to some destination. Even with the umbrella, they were
21
Mark Anderson and Kathy Anderson, Text Types in English 3 (Melbourne: MacMillan,2003), p.3.
22
Joko Priyono, Interlanguage: English for Senior Hifh School Students XI Science and Social Study Programme (Jakarta: Pusat Perbukuan, Departemen Pendidikan Nasional, 2008), p.110-111.
Orientation
Complication
still drenched. It didn’t take him long to realise those were his ex
-girlfriend’s parents. With a heart in getting back at them, he drove
slowly beside the couple, wanting them to spot him in his luxury
car. He wanted them to know that he wasn’t the same anymore, he had his own company, car, condo, etc. He had made it in life!
Before the guy can realise, the couple was walking towards a cemetery, and he got out of his car and followed them and he saw his ex-girlfriend, a photograph of her smiling sweetly as ever at him from her tombstone. He saw his precious papercranes in a bottle placed beside her tomb. Her parents saw him. He walked over and asked them why this had happened. They explained that she did not leave for France at all. She was stricken ill with cancer. In her heart, she had believed that he will make it someday, but she did not want her illness to be his obstacle. Therefore she had chosen to leave him.
She had wanted her parents to put his papercranes beside her, because, if the day comes when fate brings him to her again he can take some of those back with him. The guy just wept.
To sum up, narrative can be concluded as a text which is used to amuse and entertain the readers through its story. In addition, some steps to make a narrative text should be paid attention for better construction. Narrative sounds an interesting kind of text. In line with reading comprehension, it must be easy for students to understand and comprehend narrative text. Although reading comprehension is the ability that is not easy to do, but by doing this activity continously in every single leisure time and adding by appropriate technique for students, it is not possible for them to comprehend narrative text easily.
E.
Mind Mapping
1. The Concept of Mind Mapping
The mind map is an expression of radiant thinking which includes on a nature function of brain.23 A mind map is a diagram used to visually outline
23
Tony Buzan, Barry Buzan, The Mind Map Book: How to Use Radiant Thinking to Maximize Your Brain’s Untapped Potential (New York: Penguin Group, 1994), p.57;59. Radiant
Resolution
information which often created around a single word or text, placed in the center, to which associated ideas, words, and concepts are added. Major categories radiate from a central node and lesser categories are sub-branches of larger branches. Categories can represent words, ideas, tasks, or other items related to a central key word or idea.
Based on the definition above, it can be concluded that a mind-map is a creative way to represent idea or information through diagram.
Mind mapping is a method to optimize learning capacities and understanding of how the elements of complex structures are connected. Buzan cited by Maier, “Mind-mapping was designed to use both sides to increase
memory retention and productivity.”24
It is because the brain works in different ways; different people think in different ways. However, while students thinking and reasoning follow a structure that is personal to theirselves, they still use a number of techniques that apply to most people. There are four essential characteristics of mind mapping:25
a) The subject of attention is crystallised on a central image.
b) The main theme of the subject radiate from the sentral image as branches. c) Branches comprise a key image or key word printed on an associated line.
Topic of lesser are also represented as branches attached to higher level branches.
d) The branches form are a connected modal structures.
Mind map may be enhanced and enriched through colour, pictures, codes, and dimension to add interest, beauty, and individuality. This is used to help in increasing creativity, memory and specifically the recall of information.26 There are several principles in making mind mapping, as states below:27
a) Use emphasis
Thinking refers to associative thought processes that proceed from or connect to central point; burst of thought.
24
P.S. Meier, Mind-mapping-a tool for eliciting and representing knowledge held by diverse informants (Guildford: University of Surrey, 2007), p.1.
25
Tony Buzan, TheMind Map Book: How to Use....Op.Cit., p.59.
26Ibid.,
p.60.
27
1) Always use a central image.
2) Use images throughout personal mind map. 3) Use three or more colours per central image. 4) Use dimension in images and around words.
5) Use synaesthesia (the blending of the physical senses). 6) Use variations of size of printing, line, and image. 7) Use organised spacing.
8) Use appropriate spacing. b) Use association
1) Use arrows when want to make connections within and across the branch pattern.
2) Use colours. 3) Use codes. c) Be clear
1) Use only one key word per line. 2) Print all words.
3) Print key words on lines.
4) Make line length equal to word length.
5) Make major branches connect to central image. 6) Connect lines to other lines.
7) Make the central lines thicker.
8) Make the boundaries „embrace’ the branch outline. 9) Make the images as clear as possible.
10)Keep the paper placed horizontally. 11)Keep the printing as upright as possible. d) Develop a personal style
Picture 2.1
The Sample of Mind Mapping28
28
Jennifer Goddard, Fun Activities on Holidays During School Holidays, http://www.braintraining4kids.com/fun-activities-on-rainy-days-during-school-holidays/
2. The Purposes of Mind Mapping
Everything happens for a purpose. As the way to help the students easier in reading comprehension, using mind mapping also has purpose. Generally, the purpose of mind mapping is to associate between ideas, topics or things.29 Besides, there are several specific purposes of mind mapping below:30
a) Mind mapping activates whole brain. b) Mind mapping fixes the mental tangled.
c) Mind mapping lets the students focus on main explanation.
d) Mind mapping helps to show the relationship between the separated information parts.
e) Mind mapping gives clear description wholly and specifically. f) Mind mapping lets the students to group the concept and compare it.
Based on the explanation above, mind mapping is hoped to help the students in getting better learning process. By activating the whole brain activities, it can be concluded that mind mapping is expected to make the students easier in comprehending the text or written information.
3. The Procedure of Mind Mapping
Making mind mapping is easy. The students can remember many information through this way. Here are several steps to make mind mapping:31
a) Starting from the center of the blank paper. It is better to rotate the paper, so you can use it horizontally (it helps the brain feels free to spread the ideas). b) Using picture or photo as the central of the idea. A picture has thousand
meanings and help the students to use their imagination. A central picture makes the students focus, concentrate, and feel interested in what they are mapping.
29
Martin Davies, Concept Mapping, MindMapping and ArgumentMapping: What are The Differences and Do They Matter?(Springer Science+Business Media B.V, 2010), p.11.
30
Tony Buzan, Buku Pintar Mind Map, terj. Susi Purwoko (Jakarta: Gramedia Pustaka Utama, 2013), p.6.
31
c) Using colors. Colors have same role as pictures, brain will stimulate an idea through colorful form. It gives mind map more alive and adds creative thinking energy for the students.
d) Linking the main branches with the central picture and linking within the supporting branches. An association has important role in brain activity, by linking two or more things will make the students easier to understand and remember.
e) Making curved line, not straight line. The straight line will only make the brain bored.
f) Using only a keyword to every single line. This is used to give flexibility in making the mind map.
g) Using pictures. Every single picture has thousand meanings as same as central picture.
4. The Advantages and Disadvantages of Mind Mapping
Mind mapping as a technique to help the students in learning reading comprehension cannot be separated with the advantages and disadvantages in its use. Facilitating these problems, the writer states several views below for these terms.
Those few headlines shows the advantages of using mind maps whenever students want to get things done faster, more effectively, and with better end results. Here are some advantages:32
a) Mind map helps the students to speed up their think rapidity. b) Mind map takes the students to develop new ideas quickly.
c) Mind map gives easy way for the students to plan, communicate, be creative, arrange, and explain the ideas fastly and efficiently when they want to work with others.
d) Mind map facilitates the students to understand a complicated system or structure because mind map delivers the students to be focused on the ideas.
32
Clelford states the advantages and disadvantages of using mind mapping as below:33
Advantages:
a) Easily add ideas or links later.
b) Helps to concentrate on information structure and relationships between ideas rather than disconnected facts.
c) Mind map may help people to see other connections and similarities in the information they receive.
d) Add sketches in making mind map is more memorable than conventional notes.
e) Mind maps can incorporate a mass of material (For example, a jet’s maintenance manual was reduced from 1000s of pages to a room-length mind map. A year's subject notes became an easily reviewed poster).
f) Mind mappings can help revision, even if the course notes are conventional. They condense material into a concise, memorable format.
Disadvantages:
a) People may want to redraw the maps later-but that will help them remember the material.
b) Someone’s map may be so personal and it could be difficult for others to understand. Mind maps are a great help when preparing essays and presentations, but they may be inappropriate as the final piece of work.
Instead of those views above, Casco explains the advantages of mind mapping into some points. The first is the flexibility to useby learners with different levels of proficiency in the target language. Next, mind mapping empowers the learners by allowing them to decide where to start and what to leave out. This possibility of making decisions develops a sense of self-efficacy and fosters autonomy. The last advantage is stimulating the learners’ creativity.34
33
Tony Clelford, Taking Notes with Mind Maps,
http://ebooks.uosiu.info/eBooki/Umys%C5%82/tony%20buzan%20-%20taking%20notes%20with%20mind%20maps.pdf (Accessed on February 9th, 2014).
34
From those explanation above, it can be concluded that mind mapping naturally just a technique which has both positive and negative things inside. Oftentimes, the learners can take the advantages through this technique, meanwhile the disadvantages cannot be separated from its use. Hence, it depends on the user to maximize the advantages of using mind mapping.
F.
Teaching Reading Comprehension of Narrative Text Through
Mind Mapping
The explanation below is the procedures of teaching narrative text through mind mapping:
First : introduce the procedure of making mind mapping and review about narrative text. Later, tells the students about the advantage of using mind mapping in learning text, especially narrative text.
Second : at the first meeting, divides the students into some groups which consist of 3-4 members in each. It is used to let the students learn first about making mind mapping together. For the second meeting, the students are asked to make their mind mapping individually.
Third : give students instruction to read and comprehend the text first. After comprehending the story, they have to write and draw their comprehension through mind mapping.
Fourth : the students tell their mind mapping in front of the class, then some others give their opinion; whether they have similar thinking about the text. For the second meeting, there are only some students present their mind mapping. It is used to maximalize the used of time.
Fifth : the students have to answer some questions related to the text, in order to make sure whether their reading comprehension are helped by mind mapping. The questions are given after the students present their mind map in front of the class.
to draw their own mind mapping. After that, they are asked to comprehend narrative text in group which later they are asked to draw its mind mapping based on what they comprehend about the text. Then, they have to present their mind mapping in front of the class. at the end of the presentation, the students discuss whether or not each group of students have similar idea about the text. Finally, the students have to answer the questions about the text. It is used to know their comprehension. In this case, the teacher has role as facilitator.
G.
Previous Studies
The first previous study is taken from Panatda Sirriphanich’s study
about the improvement of reading comprehension by using mind-mapping as
written on his article “Using Mind Mapping Technique to Improve Reading Comprehension Ability of Thai EFL University Students”.35 Heconducted the research by using one group pre-post test experimental research design to 35 1styear students at Songkhla Rajabhat University, Muang Songkhla who were
learning “English for communication and reading skills” as a compulsory subject. He found that mind mapping improved students’ English reading comprehension as in the post test mean score of students was higher than the pre test mean score at the 0.05 level of significance. Moreover, most students were satisfied with their own reading comprehension ability, and the last, they enjoyed working in group and agreed that mind mapping technique was a useful technique and can be applied to non-English subjects. Findings and implications for further research are discussion. To support his research, there are fifteen students (5 highly successful, 5 who did not show any improvement, and 5 unsuccessful) were selected for retrospective interviews after getting the score in post test.
The study above has more differences than similarity with the writer’s study. The differences are on the place, population and sample, method, and
35
design of the study. The only similarity with the writer’s study is on the use of mind mapping as the way to know the effectiveness in reading comprehension.
The second related study is The Effectiveness of Mind Map Technique in Learning Reading Comprehension of Narrative Text (A Quasi-Experimental Study at The Second Year Students of SMPN 13 Kota Tangerang Selatan) by Ika Yuli Astuti.36 The objective of this research is to find out the effectiveness of mind map technique in learning reading comprehension of narrative text. It is an experimental study which was conducted in two classes by using non-equivalent control group design, thus there was different treatment in each. The writer conducted the observation, interview, and test to gather the data. Later, the data was analysed through t-test. The result shows that mind map is effective to use in teaching and learning process of narrative text. It can be seen from the t-test value is higher than t-test table (to > tt = 6.43 > 2.68).
The study above has both the similarities and the differences with the
writer’s study. The similarities are having the same technique (mind map), using test as the instrument, and choosing narrative text as the material. The differences are on the place, sampling technique, and the use of observation and interview as the collecting data techniques of the study.
The last related study is Teaching Reading Comprehension Through Mind Mapping: A Case of The Eleventh Grade Students of SMA N 2 Demak in the academic year 2008/2009 by Ana Amalia.37 The objective of this study is to find
out the effectiveness of using mind mapping in improving students’ reading
comprehension achievement. It is a pre-experimental study which use random sampling in getting the sample. The collecting data is only through the test. The result indicates that using mind mapping in teaching reading comprehension is
effective to improve student’s reading comprehension achievement. It can be seen
36
Ika Yuli Astuti, The Effectiveness in Learning Reading Comprehension of Narrative Text (A Quasi-Experimental Study at The Second Year of SMPN 13 Kota Tangerang Selatan),
(Skripsi, Faculty of Tarbiya’ and Teachers’ Training, Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University,
Jakarta, 2012).
37
from the result of pre-test and post-test; the average score of pre-test = 12,6 and the standard deviation = 8,88. Meanwhile, the average score of post-test = 21,7 and the standard deviation = 9.
The study above has both the similarities and differences with the
writer’s study. Mind mapping as the technique studied and test as the instrument
are the similarities in this case, while the differences are on the place, sampling technique, and the research design.
H.
Conceptual Framework
Reading comprehension is one of important English aspects which should be mastered by students. The fact states, especially in Indonesia, students can answer the questions correctly when they can comprehend the text in national exam. In fact, some students are still getting difficult to comprehend the text, so do in SMA Mathla’ul Huda Parung Panjang Bogor. They have low achievements in facing text questions, like getting main idea, supporting details, and even deciding the schematic structure of the text (narrative). Undeniable, there are many aspects engage in this problem. Mostly, the problems faced are getting the main idea and the information stated. This situation is adding up by students’ reading habit that low; they think that reading is bored activity to do. Jeremy Harmer states that students need to be engaged with what they are reading. In other words, the students should be involved in joyful reading.38
Using mind mapping as a technique will help students comprehend what they read joyfully. As stated before, reading comprehension is important to
be learned to increase students’ comprehension especially in the target language text form. By arising students’ interest in comprehending the text through mind mapping, students can explore their knowledge and vocabulary in the target language materials.
Helping students in comprehending what they read, especially narrative text, is good as long as the technique used be able to increase students’
38
achievement in reading comprehension materials. In line with this, mind mapping becomes an alternative way in teaching reading comprehension. This technique is choosen because it can stimulate the students’ pleasure in teaching and learning process of reading comprehension; they are free to write and draw what they comprehend about the materials.
If students get in used with this technique, the writer assumes that students get better achievement in reading comprehension. Moreover, it can be effective in teaching and learning process of reading comprehension in classroom. Therefore, the writer wants to teach reading comprehension, especially narrative text, by using mind mapping.
I.
Hypotheses
In line with the question of the study, the writer formulates two hypotheses that be tested by “t” test. According to Creswell, there are two kinds of hypothesis which have to be made before the researchers do their experimental research.39 Hypotheses are formulated to draw a connection between two variables.40 The two hypotheses are null hypothesis (Ho) and alternative hypothesis (Ha) that described as follows:
1. The Null Hypothesis (Ho)
This hypothesis states that there is no difference mean between the two groups as population. If the null hypothesis is false, it means that there is a high probability effectiveness of mind mapping technique. The writer formulates the null hypothesis (Ho) as follow:
“Using mind mapping technique is not effective in improving students’ reading comprehension achievement at the second grade students of SMA
Mathla’ul Huda Parung Panjang Bogor.”
39
John W. Creswell, Educational Research (3rd ed.), (New Jersey: Pearson Prentice Hall, 2008), p. 137.
40
2. The Alternative Hypothesis (Ha)
This hypothesis is the null hypothesis opposite. It is examined statistically. The writer uses this hypothesis as follows:
27
This chapter discusses the research design and method, the place and time of the research, the population and sample of the research, the data collection technique, the content of the intervention, the data analysis technique, and the statistical hypotheses.
A.
The Research Design
This research was conducted quantitavely through quasi-experimental design. McMillan and Schumacher state that quasi-experimental research is a good design of the research because although it is not true experiments, it provides reasonable controlled over most sources of invalidity and it is usually stronger than the pre-experimental design.1 Quasi-experimental design focuses on treatment and outcome, hence the data was taken from pre-test and post-test in order to know whether or not mind mapping is effective than expository technique
in improving students’ reading comprehension achievement. In this research
design, there are two kinds of classes used. There are the experimental class which used mind mapping technique and the controlled class by expository technique.
B.
The Place and Time of The Research
The research was held in SMA Mathla’ul Huda which is located on Jl. Raya Mohammad Toha No.10, Parung Panjang Bogor 16360. This research was carried out for a month, start from February 4th, 2014 to March 4th, 2014 in the even semester 2013/2014.
1
C.
The Population and Sample of The Research
A population is a group of elements or cases, whether individuals, objects, or events, that conform to specific criteria and to which the results of the research are generalized.2 In this case, the population of this research is the second grade students of SMA Mathla’ul Huda Parung Panjang Bogor. There are only two classes of the second class, therefore the technique of sampling that used by the writer is quota sampling. Quota sampling is used when the researcher is unable to take a probability sample but is still able to select subjects on the basis of characteristics of the population.3
In this research, the population were 80 second grade students in two classes. The writer took XI IPS as the experimental class that has 40 students and XI IPA as the controlled class that has 40 students. XI IPS was chosen as the experimental class because it had lower mean score in pre-test than XI IPA; XI IPS was 52,71 and XI IPA was 54,29. The experimental class was taught reading comprehension through mind mapping technique, while the other was taught through expository technique. The teaching and learning process was carried out for four meetings.
In the last, the writer only got 35 students’ data as sample in each class.
This condition happened because there were some students who did not come in each meeting, either in pre-test, treatment, or post-test. Hence, the writer decided to take only 35 students as sample in each class based on their attendance.
D.
The Data Collection Technique
To know the effectiveness of mind mapping technique in this quantitative research, the writer used test as the instruments to get the data through multiple choice questions. There were two kinds of test used:
2Ibid.,
p.119.
3
1. Pre-test
Pre-test was delivered at the first time before the writer applied the treatment in both experimental and controlled class. The pre-test was held on February 14th, 2014.
2. Post-test
Post-test was held as the final test after the writer applied the treatment. It is used to see whether or not mind mapping effective to improve students’ reading comprehension achievement. The post-test was held on March 4th, 2014.
Each test was arranged into 20 items of multiple choices taken from
some students’ English books. The tests were given both to the experimental and controlled classes’ students.
Before giving the tests to the sample, the writer had tested the tests to the second grade students of SMA PGRI 4 Bogor. It was held to know the validity and reliability of pre-test and post-test. The validity and reliability of the instrument were analyzed by using ANATEST software.
The result shows that the instrument were reliable. The reliability score is 0.74 while the standard of reliable is 0.60. Hence, it can be concluded that is is reliable. At last, the writer limited the questions into 20 from 30 questions that were tested, with 6 questions were eliminated and some others were choosen as the questions after edited. (for further data, see appendix 1)
E.
The Content of The Intervention
higher improvement in their reading comprehension achievement after using mind mapping than using expository. In the last meeting, the post-test was given to check whether students’ achievement of reading comprehension in narrative text increased or not.
F.
The Data Analysis Technique
The gathered data are used to find out the differences of students’achievement in experimental class and controlled class. In line with this, the writer uses statistic calculation through t-test formula in manual calculation and SPSS (Statistic Product and Statistic Solution). It is used to examine the significance difference of students’ reading comprehension achievement between experimental class and controlled class. The formula of t-test as follow:4
Notes:
M1 = Mean of Variable X (experimental class)
M2 = Mean of variable Y (controlled class)
SE = Standard Error
There are several stages taken to get the calculation of t-test, it can be seen as follow:
1. Determining Mean of variable X, with formula: ∑
2. Determining Mean of variable Y, with formula:
∑
4
3. Determining Standard of Deviation Score of Variable X, with formula:
√∑
4. Determining Standard of Deviation Score of Variable Y, with formula:
√∑
5. Determining Standard Error Mean of Variable X, with formula:
√
6. Determining Standard Error Mean of Variable Y, with formula:
√
7. Determining Standard Error of different Mean of Variable X and Mean of Variable Y, with formula:
√
8. Determining to with formula:
9. Determining Degrees of Freedom (df), with formula:
G.
The Statistical Hypotheses
Before deciding the result of hypothesis, there are statistical research hypotheses as follows:
Notes:
Ho = Null hypothesis Ha = Alternative hypothesis
μ1= students’ reading comprehension achievement, who are taught through mind
mapping.
μ2 = students’ reading comprehension achievement, who are taught without mind
mapping.
The writer’s assumption of those hypotheses are as follow:
1. If to > ttable, the Null Hypothesis (Ho) is rejected and alternative hypothesis
(Ha) is accepted. It means there is a significant difference of students’ reading comprehension achievement between students who are taught through mind mapping and students who are taught without mind mapping.
2. If to < ttable, the Null hypothesis (Ho) is accepted and alternative hypothesis
33
This chapter presents findings of the study. The findings describe into the data description, the data analysis, and the data interpretation.
A.
The Data Description
This part shows the general description of students’ scores in both the
experimental class and the control class. The description is divided into some sections: the pre-test scores, the post-test scores, and the gained scores.
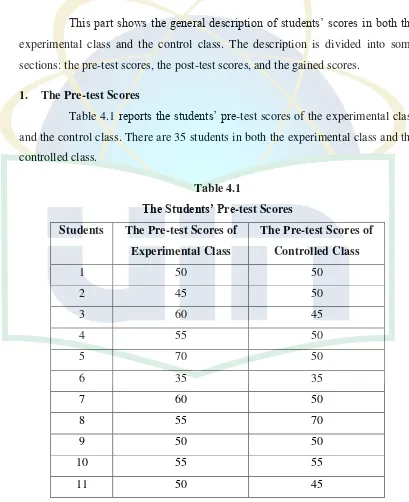
[image:46.595.94.503.251.753.2]1. The Pre-test Scores
Table 4.1 reports the students’ pre-test scores of the experimental class and the control class. There are 35 students in both the experimental class and the controlled class.
Table 4.1
The Students’ Pre-test Scores Students The Pre-test Scores of
Experimental Class
The Pre-test Scores of
Controlled Class
1 50 50
2 45 50
3 60 45
4 55 50
5 70 50
6 35 35
7 60 50
8 55 70
9 50 50
10 55 55
12 50 70
13 45 50
14 50 55
15 65 50
16 45 45
17 50 65
18 55 55
19 60 55
20 50 55
21 45 55
22 40 70
23 50 55
24 65 50
25 60 55
26 45 70
27 40 50
28 50 55
29 60 70
30 55 50
31 50 45
32 40 50
33 60 50
34 70 55
35 60 70
1845 1900
Mean 52.71 54.29
lowest score of pre-test, 50 as the median score, and 70 as the highest score. Besides, the mean score of experimental class is 52.71 and the controlled class is 54.29. Hence, it can be concluded that the pre-test scores of the experimental class and the controlled class seemed to be equivalent.
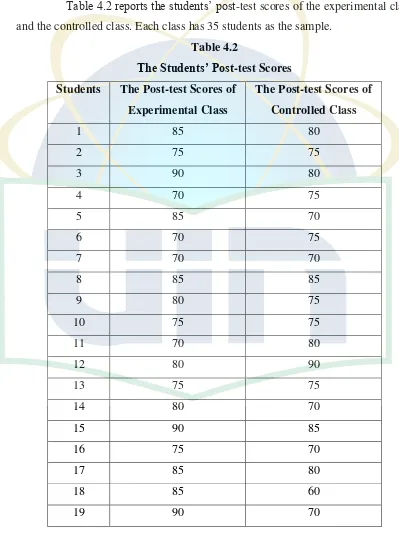
[image:48.595.97.496.228.761.2]2. The Post-test Scores
Table 4.2 reports the students’ post-test scores of the experimental class and the controlled class. Each class has 35 students as the sample.
Table 4.2
The Students’ Post-test Scores Students The Post-test Scores of
Experimental Class
The Post-test Scores of
Controlled Class
1 85 80
2 75 75
3 90 80
4 70 75
5 85 70
6 70 75
7 70 70
8 85 85
9 80 75
10 75 75
11 70 80
12 80 90
13 75 75
14 80 70
15 90 85
16 75 70
17 85 80
18 85 60
20 80 55
21 85 50
22 75 55
23 80 60
24 75 50
25 70 80
26 85 85
27 85 70
28 70 75
29 80 55
30 75 80
31 85 70
32 75 85
33 85 65
34 95 65
35 80 80
2795 2520
Mean 79.86 72.00
3. The Gained Scores
[image:50.595.95.497.222.751.2]Table 4.3 below reports the gained scores of the experimental class and the controlled class. Both the experimental class and the controlled class have 35 students.
Table 4.3
The Gained Scores of The Experimental Class and The Controlled Class
Students The Gained Scores of
Experimental Class
The Gained Scores of
Controlled Class
1 35 30
2 30 25
3 30 35
4 15 25
5 15 20
6 35 40
7 10 20
8 30 15
9 30 25
10 20 20
11 20 35
12 30 20
13 30 25
14 30 15
15 25 35
16 30 25
17 35 15
18 30 5
19 30 15
20 30 0
21 40 -5
23 30 5
24 10 0
25 10 25
26 40 15
27 45 20
28 20 20
29 20 -15
30 20 30
31 35 25
32 35 35
33 25 15
34 25 10
35 20 10
950 620
Mean 27.14 17.71
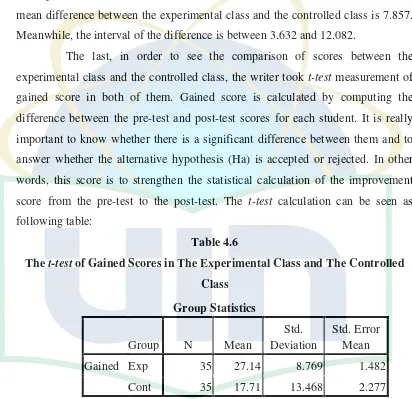
The table data above describes that the gained score for the experimental class is higher than the controlled class. The lowest gained score of the experimental class is 10 and the controlled class is -15, while the highest gained score of the experimental class is 45 and the controlled class is 40. Meanwhile, the median of the experimental class is 30 and the controlled class is 20. In addition, the mean of gained score in the experimental class is 27.14 and the controlled class is 17.71.
B.
The Data Analysis
This section is intended to answer the research question whether mind mapping is effective to improve students’ reading comprehension achievement at
Table 4.4
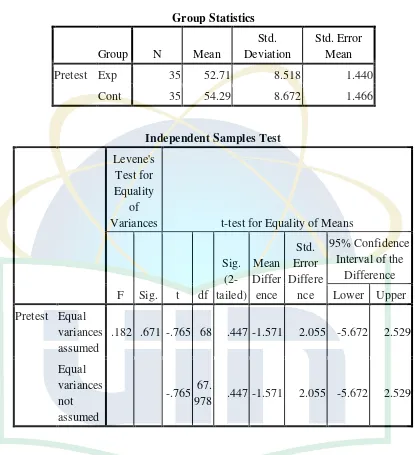
The t-test of Pre-test in The Experimental Class and The Controlled Class
Group Statistics
Group N Mean
Std. Deviation
Std. Error Mean Pretest Exp 35 52.71 8.518 1.440
Cont 35 54.29 8.672 1.466
Independent Samples Test
Levene's Test for Equality
of
Variances t-test for Equality of Means
F Sig. t df Sig. (2-tailed) Mean Differ ence Std. Error Differe nce 95% Confidence Interval of the
Difference Lower Upper Pretest Equal
variances assumed
.182 .671 -.765 68 .447 -1.571 2.055 -5.672 2.529
Equal variances not assumed
-.765 67.
978 .447 -1.571 2.055 -5.672 2.529
controlled class is 54.29. Meanwhile, the mean difference both the experimental class and the controlled class is -1.571. Besides, the interval of the difference is between -5.672 and 2.529.
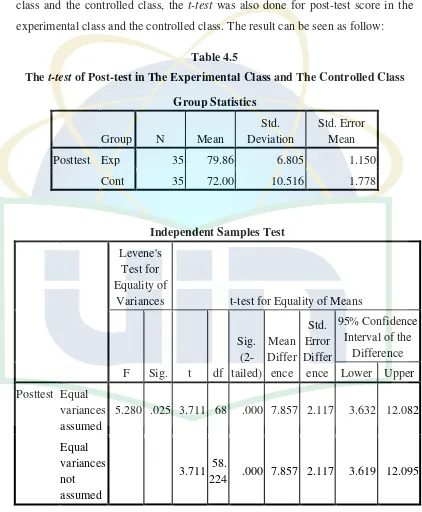
Secondly, after analyzing the t-test score of pre-test in the experimental class and the controlled class, the t-test was also done for post-test score in the experimental class and the controlled class. The result can be seen as follow:
Table 4.5
The t-test of Post-test in The Experimental Class and The Controlled Class
Group Statistics
Group N Mean
Std. Deviation