THE 2
NDINTERNATIONLAL CONFERENCE ON COMMUNICATION,
MEDIA AND SOCIETY 2014
(iCOMES2014)
BANDUNG, INDONESIA
Proceeding
Theme : Media, Gender and Culture
Effect of Lectures’ Recruitment model, Work Satisfaction and Organizational Culture towards Turnover Intention of Lecturers
(Case Study: Female lectures at Indonesia Computer University)
Dr. Ir. Eddy Soeryanto Soegoto
Abstract
One of the main problems in Private Universities in Indonesia is turnover intention. In this
paper, the writer tries to reveal the underlying problems of it. In order to solve this problem,
the writer conducted a study among the female lecturers in Indonesian Computer
University Bandung. The method that the writer employed in this research is survey method,
namely descriptive survey. In testing the hypothesis, the writer uses a statistical procedure,
namely the structural equation modeling, with the help of the LISREL program used to
analyze the data. In this research, the writer employed 127 respondents. The result of the
research divulges some factors causing the turnover intention among the lecturers, namely
recruitment model employed by respective institution, work satisfaction and
organizational culture. Furthermore, there is significant correlation between the
recruitment model and the lecturer’s job satisfaction and between the recruitment model
and organizational culture as well as between the job satisfaction and the organizational
culture. Moreover, the recruitment model, job satisfaction and organizational culture both
simultaneously and partially have a significant effect on the turnover intention.
Keywords: Recruitment Model, Work Satisfaction, Organizational Culture, Turnover Intention
Background of the Research
Becoming a lecturer at private universities brings about several consequences in
relation to the life‟s future since history has proved that mostly the lecturers do not
obtain sufficient salary. That is why, working as a lecturer in private higher education
institution become uninteresting work in Indonesia. For those who have been in the system,
they cannot generate maximum capability and expertise due to the several reasons, one of
which is financial insufficiency because of small amount of salary.
their jobs, some of them are as follows:
Because of the small amount of salary, lecturers tend to leave the job to find other
higher education institutions in order to obtain higher salary or to terminate their jobs
as lecturers in order to find other jobs outside the education world
Bargaining power‟s position of private higher education institution‟s lecturers is
weaker compared to the lecturers at the state higher education institution.
Up to now, there is no any single legal institution yet for the private higher education institution‟s lecturers to share and solve their problems mentioned above, such as
KORPRI (legal organization of the government employees in Indonesia)
The existence of the private higher education institution‟ lecturers depends solely on the private higher education institution‟ s foundation that organize the institution. In other words, the owner of the institution plays an important role in recruiting lecturers
that will be employed in their institution.
The following are the formulation of the problems of the research:
a. How is the level of the recruitment model, work satisfaction, organizational culture
and turn over intention of the foundation‟s female lecturers in Indonesian Computer
University?
b. How is the correlation between recruitment model and work satisfaction of in he
foundation‟s female lecturers in Indonesian Computer University?
c. How is the correlation between recruitment model and organizational culture in the
foundation‟s lecturers in Indonesian Computer University?
d. How is the correlation between work satisfaction and organizational culture of in the
foundation‟s lecturers in Indonesian Computer University?
e. How much is the effect of recruitment model, work satisfaction, and organizational
culture towards the turn over intention of in the foundation‟s lecturers in Indonesian
Goals of the Research
The following are goals of the research:
a. To know the level of the recruitment model, work satisfaction, organizational culture
and turn over intention of the foundation‟s lecturers in Indonesian Computer
University.
b. To analyze the correlation between recruitment model and work satisfaction of in
the foundation‟s lecturers in Indonesian Computer University.
c. To analyze the correlation between recruitment model and organizational culture
in the foundation‟s lecturers in Indonesian Computer University.
d. To analyze the correlation between work satisfaction and organizational culture
in the foundation‟s lecturers in Indonesian Computer University.
e. To measure the effect of recruitment model, work satisfaction, and organizational
culture towards the turn over intention of in the foundation‟s lecturers in Indonesian
Computer University.
Contribution of the Research
The following are contribution of the research:
Contribution for the Knowledge Development
a. Theoretical benefit: the writer expect that these findings will contribute towards the
knowledge development of organizational culture, and educational management in
Indonesia. Furthermore, it is expected it can add reference in the field of
organizational culture and human resource management.
b. Practical benefit: the writer expect that these findings can inform beneficially to all
parties involved in the management of human resource, especially in managing
recruitment, work satisfaction, organizational culture and turn over intention.
c. Benefit for Researcher: the writer expect that these findings can encourage further
research on individual behavior, in managing human resource, especially in
overcoming turn over intention of the lecturers in the future considering other variables
affecting problems that have not been studied yet
Operational Benefits
Practically, this research‟s result will contribute benefits for the related parties as follows:
privateuniversities in handling the problems of turnover intention in the lecturers.
2) Contributing useful information for the management parties in educational service
sector, and as input to apply model of turnover occurring in educational field,
specifically private universities.
Study Literature
Based on the previous study, it has been known before that private universities, with
all potentiality and encumbered mission, are demanded to be able to place in fast changing
strategic contextual environment. In relation to that, Ria Ratna Ariawati (2003) stated that
“The present educational world is demanded to be capable to present educational service in accordance with the need of society directing into globalization. Furthermore, she said that
the educational service at the 21st era should be different with the previous periods. In the
past, educational provider was still simple and was not demanded fully by the users, namely
students. Accordingly, at present every educational provider possesses mission resulting
ready-to-work graduates instead of ready-to be-trained merely. Bearing the mind the
following considerations, the term of ready-to-work include: (1) There is harder competition
for the current graduates among state, private and overseas affiliation graduates who also find
jobs in the country; (2) The fact says that there are no 100% graduates who directly can
meet the demand of the end users. This occurs due to the limited budget to realize the
planned students‟ activities resulting insufficient capability of the students to work in a real
working world; and (3) The emerging need to internationalize the higher education
institution‟s accreditation system which, in fact, has not been fulfilled by the current National
Accreditation Board (BAN) as a matter of fact globalization and AFTA in 2003 has already
given an impact. Accordingly, the prospective BAN should refer to the ASEAN evaluation
higher education institution provider with the following main jobs: teaching, conducting
research and community service. Second, lecturers‟ professional competence portrayed in the
institution‟s mission. It conveys the meaning that the availability of various devices and
completing process of educational system will not guarantee if there are no qualified lecturers
yet.
More qualified capability in managing and developing the higher education institution
have become more and more important, including the usage of modern managerial
principles possessing high quality. In the point of view of the owner and provider of the
higher education institution, quality management system basically contains continuous
improvement for the system concerned.
Becoming lecturers should meet the necessary qualification in order to be able to
deliver their knowledge to their students. The existence of the competent and qualified
lecturers will enable more easily the process of transferring the science and technology to the
receivers so that the students can apply those in pursuant to their respective capability and
major. Because the lecturers‟ performance will have direct impact on the attitude,
behavior, and perception of the students as stated by Khoe Yau Tung (2002:126) that
“Lecturers will give direct impact on the development of intellectual exercise of the students” As the roles of lecturers are important in the process of education, the higher
education institution‟s provider should pay attention much on the existence of the lecturers.
Some of features that should be considered are job fit, work satisfaction, organizational
culture and turn over intention. Some theories reveal the correlation between the recruitment
model and work satisfaction and even show the causal influence among them.
Moreover, the recruitment model, as a matter of fact is a significant factor to achieve
the professionalism of the lecturers in implementing their jobs. Due to that reason, the
organization should pay attention seriously on the process of selection and recruitment of the
prospective lecturers. If there is no convenience between individual characteristics and the
profession within a certain lecturer, this will create the high tension and stress. Accordingly,
work dissatisfaction will emerge. This condition brings about the person concerned will
leave out the job. Goldstein & Rockart, 1991 (in Rasch, Ronald & Andrian Hareell
(1999: 15) that individual characteristics, namely work characteristics and individual ones
have correlation with the turnover intention as implemented in the actual assignment of the
job.
Beside that, the characteristics of the organization where the lecturers works will
affect them. If this happens, such condition is in fact those persons‟ choice. If lecturers
will tend to leave the job. On the contrary, if that person feel there is convenience with the
institution where they work; this will influence towards his or her motivation, work
satisfaction and effectiveness in the actual jobs. Research done by Caldwell and O‟Reilly
(1993:648) support that statement. Their research shows that the level of fit between the
individual and the work is a significant factor in estimating the trend of the workers to leave
out the organization concerned. Similarly, Premack & Wanous (1995:712) in a
experiment of meta analysis concludes that a person‟s choice of a certain job is affected by
the preliminary knowledge towards such job itself. Posner, Kouzes and Schmidt (in
Premack & Wanous, 1995:709) concludes that a manager that possess high fit with the
company where he works, he shows willingness to work in the same company for five years.
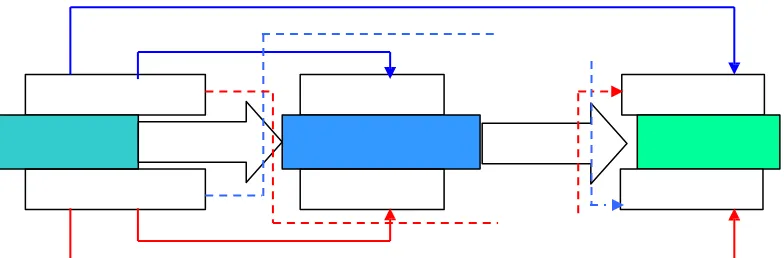
The following diagram delineates the expectation of effect of recruitment and
organizational culture towards turnover intention:
Figure 5.1 The Effect of The Recruitment model and Organizational Culture towards Turnover Intention
The relationship between organizational culture and turnover intention is another
significant matter. Organizational culture refers to the degree to which employees believe in
and accept organizational goals and desire to remain with the organization (Mathis and
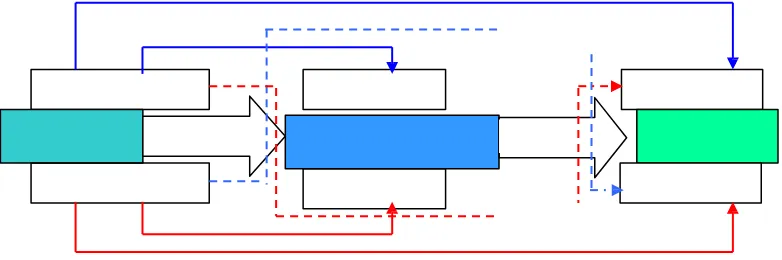
Jackson (2004:920). Based on the explanation above, the following diagram delineates the
expectation of the influence of work satisfaction and organizational commitment towards
Figure 5.2 The Effect of Work Satisfaction and Organizational Culture towards Turnover Intention
Research Methodology Method
This study employs economic sciences approach, focusing on human resources
management and organization behavior as well as educational management concerning
attitude and behavior of the lecturer and studying aspects of work fit, work satisfaction, and
organizational culture in the effect on the turnover intention. Survey and grounded research
is used. Unit of analysis in this research is female lecturers at Indonesian Computer
University Bandung.
Operationalization of Variables
In this research, there are four variables studied, namely 1) recruitment model, 2)
work satisfaction, 3) organizational culture, and 4) turnover intention . The
suitable recruitment model is convenience between individual characteristics and job ones
needed in order to obtain superior performance covering: knowledge, ability, skills,
personal needs, values, personality traits and interest. (Bowen, et. al.,1997: 37).
Work satisfaction means employees‟ perception towards how their work gives
something important as an expression of satisfactory feeling. There are five dimensions of
work satisfaction, namely satisfaction against work condition, salary, promotion,
supervision and partner Gibson, Ivancevich, Donnelly (1994: 121).
Organizational culture refers to the culture underlying behavior of the organization in
attempting to meet the goals of organization and intention to keep staying in that
organization.
work in other places and has not been implemented in a actual behavior. To measure this,
Pasewark and Strawser‟s opinion is used (1996:104), namely: (1) How much
interesting the current work is; (2) The availability of other alternative works in the near time
less than 3 months (3) The availability of other alternative works in the near future.
Sampling Technique
The writer uses both primary and secondary data which were collected from
respondents using the questionnaire and structured observation. Model testing developed in
this research is by using procedure of structural equation modeling (SEM).
Population
Population used in this study are female lecturers in Indonesian Computer
University, namely 127 lecturers.
Sample
Method of sampling employed in this study is census that is why all 127 lecturers
were selected as respondents.
Data Collection Technique
The writer used questionnaire, observation and interview guidance as the instruments
of data collection. The questionnaire are given to all respondents. Closed questions are used
in this questionnaire and the options are given using Likert scale model. Structured
observation is also conducted in the field.
Data Test of Validity and Reliability
Prior to the instruments used to gather the data, test of validity and reliability are
conducted . The test of validity uses Pearson correlation. The value of the correlation is then
compared to the critical value (value from the Pearson correlation table). The instruments are
valid when the value of the correlation from the research is positive and bigger than the
critical value. Result of the validity test of the instrument consisting 80 items exceeds the
lower limit of correlation coefficient 0.4140. This result shows that the instruments has
high validity, it proves that the data collected is valid.
Joreskog. The conclusion is that all items explaining recruitment model variable is valid
because the value of t of the question items is above than 1.68 and alpha coefficient is as
much as 0.8315, with standardized item alpha as much as 0.8289. The alpha value of
work satisfaction is as much as 0.9042; the organizational culture as much as 0.8612 and the
turnover intention as much as 0.8482. Accordingly, all items of the test is reliable since
the t value > 1.68 and coefficient of Cronbach’s Alpha > 0,70.
Method of Analysis
Primary data gathered from the questionnaire and the interview are processed
through four phases, namely coding, editing, processing data, and then analyzing. Data from
the questionnaire has ordinal value. Technique of analysis is descriptive analytic and
structural equation modeling (SEM).
Descriptive analysis is used to describe each variable so that the readers know about
high and low level of the recruitment model, work satisfaction, organizational culture and
turnover intention of the lecturers. Structural equation modeling (SEM) is used to analyze
relationship among one latent variable with another one known as structural equation. The
tool of analysis uses LISREL program (Linier Structural Relationship). To conduct analysis
using LISREL, the writer needs data whose scale is minimally interval. Therefore, for the
sake of the analysis, the data is then transformed from ordinal into interval using successive
intervals method (MSI).
Research Results
Result of Research Description
The following is the research description:
1. Recruitment model of the lecturers in the private universities is included into high
classification, meaning that the current jobs as lecturers have been in accordance with
their characteristics. The fit of capability, skill, and interest with the characteristics of the
job shows good. Moreover, the fit for knowledge and basic needs, such as affiliation,
power, achievement is sufficient. This can be explained because the majority of them are
S1 (bachelor) graduate. Furthermore, the indicator of the need fulfillment and values
followed by each individual with the organization‟s atmosphere is also sufficient.
This is understood because the need and values are factors difficult to predict by the
2. 2. Work satisfaction is classified sufficient. It means that the level of the lecturer‟s work
satisfaction functions as correspondence between expectation, aspiration, need, and how
far the organization can fulfill the need and adapt the expectation and aspiration.
3. 3. Organizational culture is classified high. It conveys the meaning that the
organizational culture is an important factor affecting the willingness of the lecturers to
work or join the organization concerned.
4. 4. The turnover is included in sufficient classification. This is proved with the high response towards the question asking them if there is other alternative work outside the
current institution. Generally, the turnover intention is more triggered by the availability
of other alternative works outside the current institution.
Hypothesis Testing
a. First Hypothesis Testing
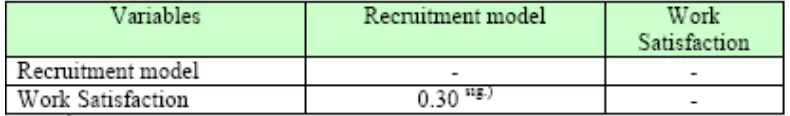
Result of statistic calculation using LISREL to conduct the first hypothesis testing
concerning the correlation between Recruitment model and Work Satisfaction is
presented in Table 7.2.1. below.
Tabel 7.2.1
The correlation between Recruitment model and Work Satisfaction
Note: sig.) Significant Level at alpha = 0.05
Table 7.2.1 shows the recruitment model has significant correlation with work
satisfaction. Accordingly, the degree of association between the two variables can be
measured using coefficient of correlation. Furthermore the correlation between
recruitment model and work satisfaction is as much as 0.30 showing positive correlation.
Thus it can be concluded that a lecturer who feel convenient with type of work and work
environment will reach work satisfaction. On the other side, lecturers who have got sufficient
work satisfaction will create convenience with the work as a for of self adjustment due to the
b. Second Hypothesis Testing
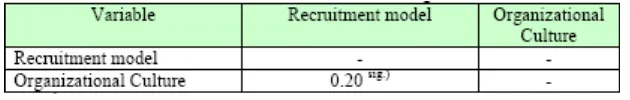
Result of statistic calculation using LISREL to conduct the second hypothesis
testing concerning the correlation between Recruitment model and Organizational Culture
is presented in Table 7.2.2. below
Table 7.2.2.
Correlation between Recruitment model and Organizational Culture
Note: sig.) Significant Level at alpha = 0.05
Table 7.2.2 shows the recruitment model has significant correlation with
organizational culture. Accordingly, the degree of association between the two variables can
be measured using coefficient of correlation. The second hypothesis testing show that there is
positive and significant correlation between recruitment model and organizational culture as
much as 0.20. This is suitable with the opinion with Sims & K Gaen Kroeck (1994) stating
that „When a person determines career that he or she will undergo, so the next thing to do is
to determine the organization as a place where to work in future.
c. Third Hypothesis Testing
Result of statistic calculation using LISREL to conduct the third hypothesis
testing concerning the correlation between Work Satisfaction and Organizational
Culture is presented in Table 7.2.3. below.
Table 7.2.3.
Correlation between Work Satisfaction and Organizational Culture
Note: sig.) Significant Level at alpha = 0.05
Table 7.2.3 shows work satisfaction has significant correlation with
organizational culture. Accordingly, the degree of association between the two variables
can be measured using coefficient of correlation. The third hypothesis testing show that there
much as 0.42.
d. Fourth Hypothesis Testing
This fourth hypothesis testing is done to conduct testing the effect of recruitment
model, work satisfaction, organizational culture simultaneously and partially towards the
turnover intention. The calculation result is shown in Table 7.2.4.
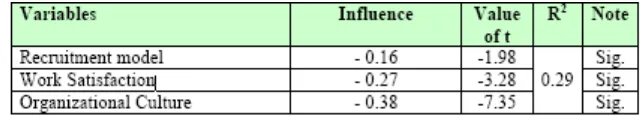
Table 7.2.4.
The Effect of Recruitment model, Work Satisfaction, and Organizational Culture Simultaneously and Partially towards the Turnover Intention
Note : sig. = Significant Level at alpha 0.05
Table 7.2.4 reveals that the path coefficient of the three variables show significant.
Recruitment model, Work Satisfaction, and Organizational Culture show negative effect and
significant towards the Turnover Intention simultaneously and partially at the level of
significance 0.05 (5%). Significance from those three path coefficient shows that value
of t for those three paths respectively as much as -1.98; -
3.28; and -7.35 is bigger than the critical value of t 1.942.
Result of the research shows that simultaneously the effect of recruitment model, work
satisfaction, and organizational culture towards turnover intention is 29%, while the
remainder is 71% due to other factors outside this study as well as partially organizational
culture shows effect on turnover intention is as much as 0.38, work satisfaction as much as
0.27, and the smallest effect is recruitment model as much as 0.16.
Conclusion and Recommendation Conclusion
From the previous analysis that has been conducted, the writer draws conclusion as
follows:
a. Descriptive Parts
The work satisfaction includes in the sufficient classification and indicators of
controling and promotion have been implemented by the institution well.
organizational culture shows significant to the turn over intention.
Turnover intention of the lecturers includes in sufficient classification. This is
known form the high response on item questioning the availability of alternative
works outside the current institution.
b. The correlation between recruitment model and work satisfaction is significant and
positive. It means that if the lecturers‟ recruitment is correct and convenient, the
person concerned will possess high work satisfaction as well.
c. The correlation between recruitment model and organizational culture is significant and
positive. It means that if a person has been selected correctly, the person concerned can
follow the organizational culture as well.
d. The correlation between work satisfaction and organizational culture is significant and
positive. It means that if a person has high work satisfaction, the person concerned
will shows high relevance to the organizational culture as well
e. The effect of recruitment model, work satisfaction and organizational culture towards
turnover intent is significant and negative. It means if a person possesses high job fit,
work satisfaction and organizational culture relevance, the person concerned will
have low turnover intention
Recommendation
Based on the above conclusion, the writer proposes the following recommendations.
Recommendation for Private University Management
1. Since there is correlation between the recruitment model, work satisfaction, and organizational culture; it proves that those three aspects complement each
other within the organization. To enhance the synergy of the organziation, the writer
suggests the following matters to the management as follows:
It is necesssary to pay attention to those three aspects because they are important aspects in relation to the management of the human resources, namely lecturers.
Conduct re-study of those three aspects periodically to view the effectivitenes of
the system concerning those three factors.
Those three aspects should be managed simultaneously.
2. Since the factors that affect the turnover intention has been proved hypothetically correct,
the management can use this study in order to comprehend those factors. Furthermore, in
Optimizing the application of all dimensions of job fit to every lecturer by means of : increasing the expertise of the lecturers thorugh further study;
participating in training activities; responding actively towards the lecturers‟
problems concerning the need of affiliation and their personal values; analyzing
factors influencing the lecturers‟ work satisfaction and minimizing the factors
influencing the dissatisfaction;
Optimizing the organizational culture relevance of the lecturers by motivating the
lecturers to be more involved in the organization.
References
Bowen, David. E; Ledford, Geral E. & Nathan, Barry R.,1997. Hiring For The Job, Not the
Organization. Academy of Management Executive, Vol 5. No.4, p. 35 – 51.
Caldwell, David F., and C, O‟Reilly, 1993, Measuring Person-Job Fit a Profile-
Comparison Process, Journal of Applied Psychology, 75, p. 648 – 657.
Khoe Yao Tung. 2002. Simphoni Sedih Pendidikan Nasional: Refleksi Dunia Pendidikan
Nasional. Kumpulan Artikel Tentang Ulasan Kritis Tentang Kepedihan,
Kegetiran dan Keprihatinan Atas Krisis Pendidikan Kita. Abdi Tandur, Jakarta.
Ria Ratna Ariawati. 2003. Link And Match di Dunia Pendidikan dan Dunia Kerja Dalam
Menghadapi Era Globalisasi, Seminar Sehari Himpunan Mahasiswa Manajemen
Fakultas Ekonomi UNIKOM.
Rasch, Ronald H. & Andrian Harrell, 1999. The Impact Of Individual Differences On MAS
Personnel Satisfaction and Turnover Intentions. Journal of Information Systems. 13 –
22.
Premack, S.L., & J.P. Wanous, 1995 „A Meta Analysis of Realistic Job Preview
Mathis, Robert L., & John H. Jackson. 2004. Human Resource Management.
International Student Edition. South-Western, a division of Thomson Learning,
Thomson Learning is a trademark used herein under license, In Singapore.
Gibson, James L., John M.Invancevich & J.M. Donnelly. 1994. Organization: Behavior,
Structure and Process. Seventh Edition, Homewood, Richard D.Irwin, Boston.
Pasewark, W.R. & Strawser,J.R.. 1996, The Determinants and Outcomes Associated
With Job Insecurity on Professional Accounting Environments. Behavior
Research in Accounting. Vol. 8, pp. 91 – 113.
Sims, Randi L, and K Galen Kroeck. 1994. The Influence of Ethical Fit on Employee
Satisfaction, Commitment and Turnover. Journal of Business Ethics. Vol. 13, p.