By:
Santi Noviyanti
108014000077
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TARBIYA AND TEACHERS TRAINING
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH
i
of SMPN 3 Tangerang Selatan. Skripsi of English Education Department at
Faculty of Tabiyah and Teacher’s Training of State Islamic University Syarif
Hidayatullah Jakarta, 2013.
Keywords: Error Analysis, Types of Error.
This study was carried out to analyze and to classify the types and the sources of student’s grammatical errors in writing descriptive paragraph. The error collected was classified based on Corder’s theory. Besides, the purpose of this study was to find out their frequency of in writing descriptive paragraph.
The method used in this study was qualitative. The qualitative design applied in this study was a case study. Furthermore, the subject of this study was second year students of 8.8. The writer took 30 students as the sample. The data were collected through test.
ii
of SMPN 3 Tangerang Selatan. Skripsi of English Education Department at
Faculty of Tabiyah and Teacher’s Training of State Islamic University Syarif
Hidayatullah Jakarta. 2013.
Keywords: Error Analysis, Types of Error.
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk menganalisis dan mengelompokkan kesalahan-kesalahan yang dilakukan oleh siswa dalam menulis paragraf deskriptif. Kesalahan-kesalahan tersebut dikelompokkan berdasarkan teori Corder. Penelitian ini bertujuan juga untuk memperoleh persentasi dari setiap jenis kesalahan yang dilakukan oleh siswa dalam menulis paragraf deskriptif.
Metode yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini adalah metodekualitatif, sedangkan pola umum atau rancangan penelitian yang digunakan oleh peneliti adalah studi kasus (case study). Selanjutnya, peneliti memilih siswakelas 8.8. Penulis mengambil 30 siswa sebagai subjek dalam penelitian ini. Data dalam penelitian ini diperoleh melalui tes.
Hasil dari penelitian error analysis menunjukan bahwa siswa melakukan empat jenis kesalahan yaitu omission, addition, selection, and misordering.
iii
finishing this research paper. Peace and blessing be upon our prophet Muhammad
SAW, his family, companions, and all his followers.
Alhamdulillah by the grace of Allah the Highest, the writer could finish
her research paper after long hard effort of writing. Thus, she would like to
express her greatest gratitude to her beloved parents (Nunu Erwin Siswanto and
Enok Ernawati) who always pray, support, and motivate her in every part of her
life especially in doing this study.
The writer would also like to address her gratitude to her advisors Dr.
Fahriany, M. Pd and Neneng Sunegsih M. Pd for their patient guidance, kindness,
valuable advice, and correction during the development of this research.
She would like to express her deep appreciation and gratitude to:
1. All lecturers of English Education Department who have taught her new
knowledge and have given her gorgeous experiences in study.
2. Drs. Syauki, M.Pd. and Zaharil Anasy, M.Hum. The head and secretary
of English Education Department.
3. Dra. Nurlena Rifa’i, Ph.D,the Dean of Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers
Training.
4. The principal and the English teacher of SMPN3 Tangerang Selatan for
permitting and helping the writer to conduct the research.
5. Her beloved best friends who have always been in the researcher side in
facing all the laughter and tears during her study, especially for Annis
Novitsania, Setya Ningrum, Nurma Hudaya, Hani Nur Hanifah and
iv
May Allah, the Almighty bless them all.Amin.
Finally, the writer realizes that this research paper still has some weakness
and shortage. Thus, she would be grateful to accept any suggestions and
corrections from anyone for better writing.
Jakarta, 20 August 2013
v
ABSTRAK ... ii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... iii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... v
LIST OF TABLES ... viii
LIST OF APPENDICES ... ix
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION A.The Background of the Study... 1
B.The Identification of the Problem ... 3
C.The Limitation of the Problem... 4
D.The Formulation of the Problem... 4
E. The Significance of the Study... 4
F. The Organization of Writing... 4
CHAPTER II: THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK A. Error and Error Analysis …. ... 5
1. The Definition of Error …………. ... 5
2. The Distinction Between Error and Mistake ... 5
3. The Types of Error... 6
B. The Error Analysis... 10
1. The Definition of Error Analysis... 13
2. The Procedure in Error Analysis... 14
3. Goal of Error Analysis... 14
C. Writing ... 14
1. The Definition of Writing ... 14
2. The Purpose of Writing ... 15
3. The Kinds of Writing ... 16
vi
E. The Previous Related to Study ... 24
CHAPTER III: REASERCH METHODOLOGY A. Research Design ... 26
B. Place and Time of the Study …………. ... 26
C. The Subject of the Study ... 27
D. Instrument of The Research ... 27
E. Techniques of Data Collecting ... 27
F. Techniques of Data Analysis ... 29
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH FINDING A. The Data Description ... 31
1. The Result of Test ... ... 31
B. The Data Analysis ... ... 33
1. The Description of Error ... 33
2. The Explanation of Error ... 42
3. The Evaluation of Error ... 43
C. The Interpretation of the Data ... 44
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION A. Conclusion ………. ... 45
B. Suggestion ……… .... 46
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... 47
vii
Table 2.2 Purposes for Descriptive ... 19
Table 3.1 Table of Specification of Test Instrument ... 28
Table 3.2 Table Description of Error ... 29
Table 4.1 The Recapitulation of Student Error ... 31
Table 4.2 The Description Error of Ommision, Addition, Selection andOrdering ... 34
1 A. Background of the Study
English as a foreign language in Indonesia has influenced many aspects
of life. Language has an important role on the intelect, improvement and society.
In Indonesian Schools, English is determined as a compulsory subject in the
national curriculum. It is taught at the beginning from Elementary School up to
the University. In English subject, there are four skill that are learnt by students.
They are Listening, Speaking, Reading and Writing. Beside four skills, the
students have to learn linguistics competence. Based on the 2004 English Curiculum; “Students have to be equipped with the linguistics competence in order they master the four language skills.”1
it is also supported by Jack and Rodgers that “one of dimensions of communicative competence is grammatical competence refers to what Chomsky call linguistic competence.”2
From that
statement, it is clear that the students have to learn linguistic competence to be
proficient in English and one of the linguistic competences is grammar.
Grammar is one of the sub-skills which support in writing. But, the
problem is, some of the students make an errors when they want to make a
sentence until its sentences become a good paragraph. It is known that English
grammar is different from Indonesian grammar. Consequently, it is difficult for
students to develop their English proficiency. The difference between the
grammar of native language and target language is one of the factors, which
induces the students to make many errors. It can affect the content of their
1
Direktorat Pendidikan Lanjutan Pertama, Pedoman Khusus Pengembangan Silabus Mata Pelajaran Bahasa Inggris, (Jakarta: Departement Pendidikan Nasional, 2003), h.2.
2
writing, as the result, their messages do not convey successfully to the reader.
For example; Grammar consists of tenses, word choice, spelling, etc. In tenses,
for example, I buyed a book yesterday. Which is supposed to be I bought a book.
And in word choice, like sentence she have black hair. It should be she has black
hair. And the last is spelling, for example my father stop smoking, whereas the
right sentence is my father stopped smoking.
Based on the explanation above, that grammar undoubtedly has important
role in writing especially in descriptive text that the writer is going to analyze.
Kind of writings which started to be taught at the beginning level as at first of
junior high schools are description and procedure. The problem which is often
found in writing descriptive text is the students forget about the generic
structures of descriptive text. They are straight to describe the thing that they
want to describe. But the crucial thing is in grammar. And there are still many
other errors that occur in writing English paragraph. That is why the students are
confused in writing grammatically and make some errors even though they have
studied English for many years and have learned the grammar until the university
level.
From the description above, the writer tries to classify the errors based on Corder’s theory, there are error of omission, error of addition, error of selection and error of missordering. Therefore, an error analysis has an important role to
reveal what kinds of error that the students do most. Finally, the writer is
interested in conducting an error analysis by proposing Skripsi under the title:
“An Analysis On Students’ Grammatical Errors in Writing Descriptive Paragraph by the Second Grade Students of Junior High School at SMPN 3
B. Identification of Problems
There are some problems faced by the students in writing descriptive
paragraph such as: The students often forget about the generic structure of
descriptive. However, the crucial problem is in grammar which consists of
verb-tenses, word choice, spelling, etc. So that the writer tries to identify the problem
related to the student’s errors in writing English paragraph based on Corder’s
theory, there are error of omission, error of addition, error of selection and error
of missordering.
C. Limitation of Problem
From the writer has explained above, there many problems faced by the
students in writing English paragraph. So that, In this study, the writer focused on analyzing the second grade students’ grammatical errors on writing descriptive paragraph at SMPN 3 Tangerang Selatan. To be more focused, the problem is
limited on analyzing the students’ grammatical errors on English writing through
descriptive paragraph that are based on Corder’s theory.
D. Formulation of Problem
Based on the background of study, the writer would like to seek the answer
by the following problem; what are the common grammatical errors that the
students do in writing descriptive paragraph?
E. Objective of the study
The main goal of the study is to know the most frequent errors that the
F. The Significance of Study
The result of the study will be benefit for English teachers to improve the
teaching techniques and to encourage students to be more cautious in using every
aspect of grammar in writing descriptive paragraph. For the students, this
research may assist them in writing descriptive paragraph correctly. For the
writer, this research becomes an input about the most typical grammatical errors
that the students do and the last benefit is for the other researchers, the result may
serve as guidelines for the future study related to the subject.
G. The Organization of Writing
To make this Skripsi is easy to read, the writer, proportionally, divides it
into five chapters:
Chapter I is an introduction which consists of background of the study,
identification of the study, limitation of the study, formulation of the study,
objective of the study, significance of the study, and the organization of writing.
Chapter II is theoretical framework which consists of theoretical
framework, study question, and relevant reference library.
Chapter III is research methodology which consists of place and time of
the research, the subject of the study, research design, instrument of the research,
techniques of data collecting, and techniques of data analysis.
Chapter IV is research finding which consists of data identification, data
description, and data explanation.
5 CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A. Error and Error Analysis
1. The Definitions of Error
To get clear understanding about the error, it is better for the
writerto consider several opinions given by some linguists. According to
Harmer as quoted by Brown, “Errors are part of the students‟ interlingua
that is the version of the language which a learner has at any one stage of
development, and which is continually reshaped as he or she aims toward
full mastery.1
While, according to Dullay, error is the flawed side of learner
speech or writing, those are part of conversation or composition that
deviates from some selected norm of nature language performance.2
Brown has different opinion. He gives more attention on the Interlingual
competence of the speaker. He defines an error as noticeable deviation
from the adult grammar of a native speaker reflecting the Interlingual
competence of the learner.3
From all definitions above, the writer can summarize that error is
flawed side of learner speech caused by the factor of competence. On the
other hand, they do not understand well the use of linguistics‟ system of
the target language; it will lead the students to make errors consistently.
2. The Distinction between Error and Mistake
Error and mistake are not the same thing. But most the people still
misunderstand about the definition of both. To be more clarified between
1
Jeremy Harmer, Principle of Language Learning and Teaching, (New York: Prentice Hall Regents, 1987), p. 170.
2
Heidi Dullay, et/al, Two (New York: Oxford University Press), p.139.
3
H. Douglas Brown, Principle of Language Learning and Teaching, 4th edition, (New
error and mistake. Julian Edge suggests that mistake can be devided into two
broad categories: “slips (that is mistakes which students can correct themselves and which therefore need explanation), and attempts (that is when
a student tries to say something but does not yet know the correct way to
From explanation above, it can be concluded that error is
systematic and the students cannot be self-corrected, because it reflects the
student‟s competence in the target language. On the contrary, a mistake is an
error that students can be self-corrected,because it is only the result of the
students‟ performance.
3. The Types of Error
Error may be viewed as being either global or local error.These errors are
divided into two kinds of error:6
a. Global errors
Global errors are errors that affect overall sentence organization
which possibly influence the flow of communication. For example the
wrong order of major constituents, “English language use many people.”
The sentence should be, “Many people use English language.” b. Local errors
Local errors are errors that affect one element or constituent in a
sentence which usually do not break the flow of communication. These
errors include errors in noun and verb inflections, articles, and
auxiliaries. For example, “Why you like him?” The listeners of the utterance will still understand the speaker‟s message although the
4
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English Language Teaching 3rd edition, (London: Longman,2001), p. 99.
5
Johanna Klassen, Using Student Error for Teaching, (English Teaching Forum, January 1991) Vol. 29, N. 1, p. 10.
6
sentence does not contain auxiliary. In addition, in classifying the
student‟s errors in writing descriptive paragraph the writer would like to use Corder theory. He stated five types error which will be explained
below. The types of errors are error of omission, error of addition, error
of selection, error of ordering.
a. Error of Ommision
Error of omission is the absence of an item that should appear.
“Errors of omission where some element is omitted which should be present.”7
The learner omits the item that should appear in the good
utterance. “Omission has two types of morphemes that are omitted more than others. They are content morphemes and grammatical morphemes.”8
Content morphemes are morphemes that have meaning like nouns, verbs,
adjectives, adverbs. Grammatical morphemes are little words that have
minor play in sentences like noun and verb inflections, articles,
auxiliaries, and preposition.Example: Angelina is an actress. From the
explanation and example above, the word Angelina and actress are
content morphemes because Angelina and actress is noun and has a
mayor meaning. The words is and an are grammatical morphemes
because they are verb auxiliaries and article, and they are also play a
minor meaning in that sentence.
“Omit grammatical morphemes are more frequently than content words.”9
It is caused by the grammatical morphemes are more complex,
for example in using tenses, the learner should be aware of the addition
of the ending of the verb (-ed,-ing,-s) correctly. Omit content morphemes
are typically made by the learner in the early stage. It happens because
Heidi Dulay, Marina Burt, and Stephen Krashen, Language Two, (New York: Oxford University Press, 1982), p. 150.
9
b. Error of Addition
Addition is the opposite of omission. Addition isthe presence of an
item that must not appear in well-formed utterences.10 In addition, the
learners add the utterance which is not needed in a sentence, or the
learners add some unnecessary element. For example: She didn’t studied
yesterday. From the example above, the learner want to tell that she
didn’t study yesterday. She knows that to tell the past event, she has to use the past verb, but she puts two items for the same features; didn’t and
studied.
c. Error of Selection
This error is made by the learner where the learner chooses the
wrong items in the right place. Different from omission where the items
are not supplied at all, in errors of selection, the learner supplies
something even though that is incorrect. For example; I buyed a novel
two days ago. A past tense marker is put by the learner, but it is incorrect.
d. Error of Ordering
Error of ordering is the error where the items presented are correct
but wrongly sequences. For example, I have pen blue. From the example
above, the items are correct, but the writer doesn‟t put the items in the
appropriate order.
B. Error Analysis
1. The Definition of Error Analysis
It is inevitable when students make an error inprocess of language
learning. Fundamentaly, learning is a process that involves the making of
mistakes, erors, misjudgment, etc. So, that is why students will make an error
in their process of acquiring new language because students find many
10
different characteristic of language which is different in their own mother
tongue. However, it is important for the teacher to recognize the errors. Thus,
for the students will not do the same errors.
The study of learner‟s error is called by the linguist as Error Analysis. It is away of looking at errors made by the learners of the target language. Error
analysis is an independent source of valid data. It provides information on
student‟s error and also improves the effectiveness of their teaching.
Apparently, errors give the sign to the teacher and researcher how target
learning is successfully achieved. According to Corder as quoted by Brown: “ A learner‟s error ... are significant in that they provide to the researcher and
the learner is employing in the discovery of the language.11The writer tries to
conclude that error analysis is a way of looking at errors that made by the
students because inevitably the students will make errors in the process of
acquiring new language system.
Error analysis was born as a response of Contrastive Analysis theory
which claimed that L1 is the source of errors made by students. Contrastive
Analysis is based on theory of behaviorism which assumes that language is a
set of habit formation. On the other hand, Error Analysis believes that
learner‟s errors are not only caused by L1 but alsodeal with the learning process in the classroom. Therefore, making mistakes is unavoidable in
learning process; it is natural. Errors indicate three important aspects of
language learning: the first aspect is show what the learner has acquired and
what remains to be learned, secondly, provide information on how language
is learned and acquired, and what strategies and procedures a language
learners is utilizing, the last aspect is serve as a guide to the language learners
with aspect to hypothesis about the nature of the target language.
11
To be more detail, Error Analysis was first introduced by W.R. Lee in
1957, and it gained popularity in the 1970s.12 Even though, the field of error
analysis in SLA (Second Language Acquisition) was established in the 1970
by Corder and collegues, error analysis was an alternative to contrastive
analysis.13According to Crystal, “Error analysis in language teaching and
learning is the study of the unacceptable forms produced by someone in
learning a language, especially foreign language.”14
So the writer tries to conclude that the errors analysis is a way of
looking at errors made by the learners of the target language, as a source of
information to the teachers, which in turns helps them correct the students‟
errors, and improves the effectiveness of their teaching.
2. Procedures in ErrorAnalysis
In analyzing students‟ errors, there are some steps to be followed. Many linguists have already discussed how to analyze students‟ errors in their book.
One of them is Corder; he suggests five steps in analyzing students‟ errors,
they are: collection of sample of learner language, identification of errors,
description of errors, explanation of errors and evaluation of errors.15
a. Collection of Sample of Learner Language
The first step of analyzing errors which suggested by Corder is
collection of sample. In this step, the researcher must decide a number of
students which is being sample for the research. Then, they will be given
regular examination in order to get data.
12
Nuril Huda, Language Learning and Teaching: Issues and Trends, (Malang : IKIP Malang Publisher, 1999), p. 5.
13
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/second language acquisition. 27 Agustus 2012. 14
David Crystal, An Encyclopedic Dictionary of Languages, (Oxford: Blackwell, 1992), p.125.
15
b. Identification of errors
In this step the researcher must identify error from data collection.
For identifying error, the researcher must compare the sentence that was
produced by students to the correct sentence in the target language. For
examples:
Sari watched TV, and Rudi sleeped in his room.
The correct form in target language is
Sari watched TV, and Rudi slept in his room.
By comparing two sentences it can be seen that the student
produced an error in constructing simple past tense sentence where she
used –ed after sleep instead of using irregular verb.
c. Description of Errros
After identifying errors, the next step is description of errors. In
this step, all errors that have been identified, then they would be classified
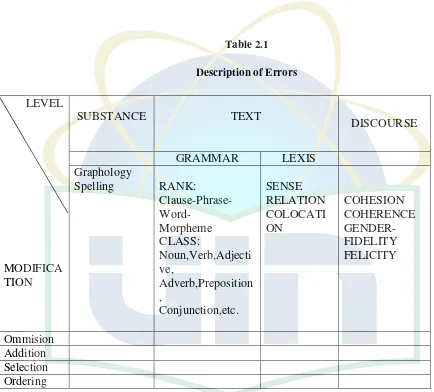
into the types of errors. In description of error James introduces a table to
make it easy. This table can be seen as below.16
16
Table 2.1
consist of omission, addition, Misformation/misselection, and misorder.
d. Explanation of Errors
This step will explain why errors occur. This explanation concerned
on the sources of errors. From example above, the researcher may consider
that the student above does an error in using –ed (regular verb) instead of
using irregular verb whether because of interlingual
transfer/overgeneralization, ignorance of the rule restriction, incomplete
e. Evaluation of Errors
In this step, the researcher must decide the criteria of errors which will
be corrected because some errors can be considered more serious than
other. The aim of evaluating errors is to distinct which errors will be
corrected so the learner, which made an error, will not be stress of getting
correction.
3. Goal of Error Analysis
According to Norrish, “Error analysis can give a picture of the type of difficulty that learners are experiencing. If carried out on a large scale such as
survey, it can be helpful in drawing up a curriculum.”17
Based on this opinion,
error analysis can be helpful for syllabus designers because errors found in
language learning can be data for them to determine which materials are
important to be included and which ones need to be improved.
While Corder makes a distinction between the theoretical and applied
goal of error analysis. They are:18
a. Applied goal aspect is, correcting and eradicating the learner's error at the
expense of the more important and logically prior task of evolving an
explanatory theory of learner's performance. In other word, the applied
goal serves to enable the students to learn more efficiently by exploiting
their knowledge.
b. Theoretical goal aspect is as worthy of study in and on itself as is that of
child language acquisition and can, in turn, provide insights into the
process of language acquisition in general.
17
John Norrish, Language Learners and their Errors, (London: The Macmillan Press Ltd., 1983), p.80
18
C. Writing
Writing is the most difficult skill among other language skills, Richards
stated that “Learning to write in either the first or second language is one of
the most difficult tasks, a student encounters and one that few people can be
said to fully master.19 Because of that, to make a good writing, the students
need a hard thinking and they must have an extent knowledge to get correct
writing.
1. Definition of Writing
There are several opinions about the definition of writing that have
been given by the experts: Ur said that: “writing is a learned skill”.20
From this statement the writer tries to identify that writing is a skill which
can be learned by anyone by practice intensively because writing is not an
automatic skill. Writing is used as a tool for communication by the people
who want to communicate with others. Remembering that writing is more
than the language is used to express and communicate with others.
According to Hairstone “writing is a tool for discovery. Writing generates new ideas by helping us to make a connection and see
relationships.21 This opinion is supported by Raymond on his book;
Writing is an unnatural Act, stated:
Writing is more than a medium of communication. It is a way of remembering and a way of thinking as well ..., writing has a private importance as a tool for clear thinking, for sharpening our awareness of the realities around us, for solving problems and shaping arguments, for developing that short of knowledge – clear, specific, detailed – that makes human consciousness different from every other form of consciousness on earth. Writing also a way of learning. It is a way of finding out what we know and what we need to learn.22
19
Jack C Richards,Language Teaching Matrix, (New York: Cambridge University Press, 1990),p. 101
20
Penny Ur, A Course in Language Teaching, (United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press, 1996),p. 161
21
Maxine Hairston, Contemporary Composition, (Boston: HoughtonMiffin Company, 1986), p. 2
22
From the definition above, it can be concluded that writing is more
than a language. Writing is a skill which can be learned by anyone who
want to express their thought, ideas, feeling, etc. In addition, it is a tool of
communication, so that writing is a hard skill becauseit is an unnatural
act which is need a hard thinking and it is a way of remembering and a
way of thinking as well.
2. Purpose of writing
In general, people write either because they are required to or
because they choose to write for their own reasons. If we ask ourselves
why we write at all, the first answer will be to get information to someone
we cannot presently talk to. Thus writing allows us to transcend time. The
second answer might be (especially when we needs of society as a whole.
To solve the problem of volume, of having to store more than the human
brain can remember. A less likely, but nevertheless important, the third
reason for writing might be to filter and shape our experience.23 The
purpose of writing is not only to teach someone to convey idea to the
readers but also to reinforce all aspect of languages that have been
learned by the students. There is some additional and very important
reason why writing is needed in teaching English. According to Ur in her
book, “A Course in Language Teaching, she explained that the purpose of writing, in principle is the expression of ideas, the conveying of a
message to the reader, so the ideas themselves should arguably be seen as
the most aspect of the writing.”24
Furthermore, Miller, on his book; Motives for Writing explained the
motives of writing. Purpose of writing is essentially the same as motive of
23
Arthur Brookes and Peter Grundy, Beginning to Write; Writing Activities for Elementary and Intermediate Learners, (New York: Cambridge University Press, 1991), p.3
24
writing; both terms are used to describe what a writer hopes to
accomplish. There are motives of writing such as:25
a. Writing to understand experiences.
b. Writing to report information.
c. Writing explain information.
d. Writing to evaluate something.
e. Writing to analyze images.
f. Writing to analyze texts.
g. Writing to persuade others.
h. Writing to inspire others.
i. Writing to amuse others.
j. Writing to experiment with form.
The writer tries to conclude that many reason when people want to
write somehing because the purpose of writing is the essentially the same
as the motive of writing. It depends on what the writer‟s need. It can be to
get the information, to explain information or to amuse others or etc like
what the writer mentioned above.
3. Kinds of Writing
There are a number of types of writing task that most of us will be
familiar with, both as teacher and from our own language learning
experienced simplifying for the moment, they can be listed under three
broad headings.26
a. Free writing
Free writing is writing without stopping. It means writing
comes to the mind without worry that everything they write is correct
or incorrect. The purpose is to free up the mind so that is can make
association and connection.
25
Robert Keith Miller, Motives for Writing, (New York: Mc Graw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2006), pp.47-69
26
Jo. McDonough and Christopher Shaw, Materials and Methods in ELT: A Teacher’s
Apparently, at the other end of the spectrum, a „free writing‟task requires learners to „create‟ an essay on a given topic,
often as part of a language examination. Sometimes students are
simply invited to write on a personal topic, their hobbies, what they
did on holiday, interesting experiences and the like. Other material
provide a readingpassage as stimulus for a piece of writing on a
pararel topic, usually with comprehention questions spread between
the two activities.
b. Controlled writing
If the focus of a language programme is on accuracy, then
schemes for controlling learners‟ writing output will obviously
predominate. The students will focus to practice on getting words
down on they paper and they have to concentrate one one or two
problems all the time. Controlled writing focuses the student‟s
attention on specific features of the written language. It is a good
method of reinforcing grammar, vocabulary, and syntax. The range of
activity types is considerable, and typical approaches include:
1) providing a model sentence and asking students to construct a
pararel sentence with different lexical items.
2) inserting a missing grammatical form.
3) composing sentenses from tabular information, with a model
provided.
4) joining sentences to make a short paragraph, inserting supplied
conjuctions (but, and however, because, although).
c. Guided Writing
It is an extension of controlled writing; it is less controlled
than controlled writing. In using this kind of writing to teach writing,
students are given a first sentence, a last sentence, an outline to fil out,
a series of question to respond to, or information to include in their
piece of writing, students should be able to discuss, make notes, and
the students will not make a serious errors if they follow the instrution
which are given by their teacher.
4. Descriptive Writing
a. Definition of Descriptive
Description reproduces the way things look, smell, taste, feel, or
sound; it may also evoke moods such as happiness, lonelines, or fear.
It is used to create visual image of people, place even units of
time-days, times of day, or a reason. It‟s maybe used also to ilustrate more
than outward appearance of people. And this kind of writing may tell
about the traits or character or personality.27A paragraph that
describes is called a descriptive paragraph, in a descriptive paragraph,
the writer describes.28 The purpose of writing is to give a picture or to
describe about something.
Futhermore, Hogins on his book; Contemporary Exposition
stated that description calls for specific details and accurate, fresh
ways of characterizing a particular object, setting it apart from all
others.29 However, Good descriptive writing can stimulate the
reader‟s imagination to form sensory responses from all five senses.
Frequently, the reader has no choice: many people cannot read an
article about taste of citrus fruits, for example, without having a
physical response to the imagined taste. And a passage about specific
food left out of the refrigerator too long will produce a shudder from
readers as they imagine the resulting smell.
Based on the explanation above, the writer tries to conclude that
description is the way things look, smell, taste, feel, or sound, it can
27
John E. Lincoln, Writing a Colledge Handbook, (New York: W. W. Norton & Company, 1986), p. 86
28
James A.W. Hefferman and John E. Lincoln, Writing A College Handbook(New York: W. W Norton A Company Inc, 1986), Second Edition, p. 83
29
stimulate the reader‟s imagination to form sensory responses from all
five senses.
b. Purpose of Descriptive Writing
Simon stated that description can serve several purposes as
follow:
1) it can ilustrate the basis on which you are making inferences, that
will allow readers to imagine the physical object involved in the
writer experience.
2) it can provide visual images to make the essay lively and concrete
3) it can reflect criteria for comparing two subjects.30
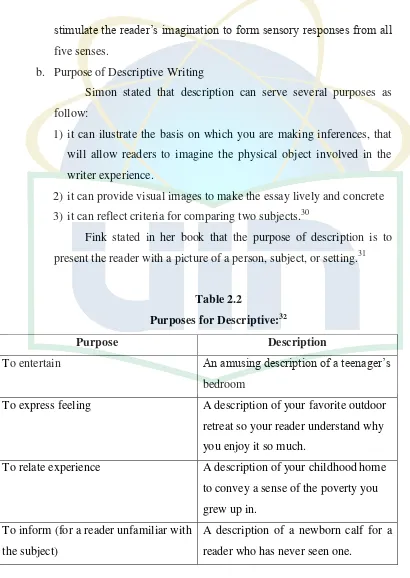
Fink stated in her book that the purpose of description is to
present the reader with a picture of a person, subject, or setting.31
Table 2.2
Purposes for Descriptive:32
30
Linda Simon, A Guide and Source Book for Writing Across The Curriculum, (New
York: St. Martin‟s Press, 1998), pp. 21-23.
31
Lila Fink, et al., A Text for Writing and Reading, (Boston: Little, Brown Company, 1983), p. 3.
32
Barbara Fine Clouse, The Student Writer, (New York: McGraw-Hill Companies, 2000), p. 143
Purpose Description
To entertain An amusing description of a teenager‟s
bedroom
To express feeling A description of your favorite outdoor
retreat so your reader understand why
you enjoy it so much.
To relate experience A description of your childhood home
to convey a sense of the poverty you
grew up in.
To inform (for a reader unfamiliar with
the subject)
A description of a newborn calf for a
D. Paragraph
1. Definition of Paragraph
In written form, English is divided into paragraph to distinguish one
main idea. According to Brown “A paragraph is a group of sentences that
work together as a team to discuss a single main idea.33Cowad said paragraph
is composed of a sentence or a chunk of sentences which the writer has
grouped together for some definite reason.34 In addition Oshima and Houge
said paragraph is a group of related statement that a writer develops about a
subject. Each paragraph is separate unit marked by indenting the first word
from the left-hand margin, or by living extra space above and below the
paragraph.
The definition above can be cloncluded that a paragraph is a basic unit
of organization in writing in which a group of related sentences develop one
main idea. And it can be seen as a group of sentences that work together as
team work.
2. Types of Paragraph
a. Description
A description iswriting about the way persons, animal, or things
appear.35In description, the writer takes a scene or an object captures it in
language. That is, he or she organizes the details of the object or scene
they wish to describe in the way that will most effectively convey the
sensual image.36 Therefore, the important thing in descriptive writing is to
combine three essential elements such as mood, dominant impression, and
logical development in writing. Language features of descriptive writing
are; it focuses on specific participants as I, you, animals, place, or people;
it uses atributive and identifying processes, and it uses the simple present
tense. Moreover, there are two schematic structures of description such as
identification and description. This structural form is the guidance for the
writer to write the description paragraphs.
Descriptions usually include the following grammatical features:37
a) verb in the present tense
b) adjectives to describe the features of the subject
c) topic sentences to begin paragraph and organize the various aspects
of the description.
d) proper nouns (e.g. Hana, my dog).
e) action verbs (e.g. dance , go)
Here is the model of the descriptive paragraph:
My apartment is a very small but comfortable. It has living room, a kitchen, a bedroom, and a bathroo. At the enterance, two doors lead into the bathromm and the bedroom. The bedroom is on the far left, and the bathroom is next to it.Directly in front of the entrance is the kitchen. Between the bedroom and the kitchen is a large storage closet. On the right side of the enterance is the living room. The living room is a quite large, for it also serves as a dining room. In the back wall of living room, a door leads to a narrow balcony. In nice weather, you can sit outside and enjoy the view. In summary, my apartment is a
Robert Scholes and Nancy R. Comley, The Practice of Writing 2nd edition, (New York:
St. Martin‟s Press), p. 11
37
Anderson, Mark and Kathy, Anderson. Text Type in English, (Melbourne: Macmillan Education Australia Ltd, 1998).
38
order that they happen. Moreover, Mark and Kathy Anderson propose
that narrative is a text that tells a story and, in doing so, entertains the
audience. The purpose of narrative, other than providing entertainment,
can be to make the audience think about an issue, teach them a lesson,
or excite emotions.39
Narrative can be presented as written or spoken texts. Written
narratives often take the form of novels. The story is usually told by
narrator. If the narrator is one of the the characters in the story, the
story is said to be told in the first person. If a person outside the story
is the narrator, then the story is being told in the third person.
Narrative text can be found in diaries journals, newspapers,
biographies, and autobiographies. The examples of narrative text are;
myths, fairytales, aboriginal dreaming stories, science fiction,
historical fiction, and romance novels.40 Moreover, the schematic
structures of narration are orientation, evaluation, complication,
resolution and reorientation. These structures make the readers easier
to read the text or the narrative writing. The language features are
focusing on specific participant, it uses past tense, it uses temporal
conjuctions and temporal circumtances, and also the material or action
processes.41
c. Recount
A recount is a piece of text that retells past event, usually in the
order in which they occured. Its purpose is to provide the audience
with a description of what occured and when it occurred. A recount
consits of the reconstruction of a past experience or event; usually one
sequence with appropriate language usage to link the events and to
show the passing of time. A recountmay involve the stating of
observations and the inclusion of a personal comment.42
A recount text usually has three main sections. The first
paragraph gives background information about who, what, and when
(called an orientation). This is followed by a series of paragraps that
retell the events in the order in which they happened (events). Some
recounts have a concluding paragraph. However, this is not always
necessary (re- orientation).
Recounts usually include the following grammatical features:
a) proper nouns to identify those involved in the text.
b) descriptive words to give details about who, what, when, where,
and how.
c) the use of past tense to retell the events.
d) words that show the order of events (for example, first, next, then).
e) the elimination of irrelevant details so that only the important
aspects of the event are included.
f) the use of personal pronouns in recounts in which the author was a
participant.
Below is the example of recount paragraph:43
Last Saturday I woke up early, but I didn‟t get up because there was no
school. Suddenly, my telephone was rung. It was my friend Fanny, she asked me to go out at 10.00 o clock. She wanted to buy something in traditional market. Finally, we were out. In the street, I saw a piece of pink coupon. Interested with its colour, I took it, then Fanny and I read this out. We were fully shocked, it was a receipt of a four nights tour to Lombok !! The expired date was that day. To our surprised, the name was Fanny Fenita and the birth date was exactly the same like Fanny my friend, and it was also valid for two persons. My God!! We were thinking that maybe the coupon just fell from the sky and it was there for us. We were in hurried to the address of the tour agency that issued
the coupon. The tour agency took care of everything. We went home and still could not believe what was going on. Two days later we were on the Senggigi Beach, lied in the warmth sun. Moreover, we had long
public holiday, so we could enjoy the “gift” happily. We also bought
some presents for our family and friends.
(Adapted from: English in Focus for Grade VIII Junior High School)
E. Previous Related Study
There are some studies related with the grammatical errors in writing.
Firstly, a research done by Emmaryana, Fajariani entitle “An Analysis on
Students Grammatical Errors in the Student’s writing (A Case study of the First Year Students of “SMA Negeri 1, Ciledug-Bogor)”, the writer used qualitative descriptive method with the purpose of the research wasto know
the most grammatical errors made by the students in writing recount text,
where the result was the highest grammatical errors was in tenses done by 19
students or 95% .
Another study researchwas a research done by Natalina Margawati,
entitle “Error on Students’ descriptive Writing (Case Study at the first grade
of SMP PGRI 2 Ciputat)”, the writer used descriptive analysis in form qualitative. The purpose of the reseach was to know out the most type of
common errors in descriptive writing. Where the causes of errors the students
made in descriptive writing was because of the influence in the mother tongue
with the highest error is in word-order is 28, 10%.
The last study research is a research done by Mawaddah Z. A, entitle
“An Analysis on Grammatical Errors in Student’s English Writing in
Argumentative text (A case study in the second year of XI of Madrasah Aliyah
Pembangunan UIN Jakarta)”. This study was carried out to identify what kinds of Grammatical errors were commonly made by the students. The
method used in this study was descriptive analysis or quantitative method,
classifying them into the grammatical errors based on Betty Azar. With the
result is the most error made by the students of XI Science I of Madrasah
Aliyah Pembangunan UIN is in verb tenses which caused by intralingual
Based on the previous researchers above, it is known that grammatical
factors in writing descriptive paragraph still become the most difficult
material. Thus, in this research, the writer intends to analyze what cause and
type of errors that made by the students in writing descriptive paragraph.
By understanding the source and types of students‟ errors, the writer
expects that she could give beneficial suggestions to solve students‟ problem.
26 CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Research Design
The method uses in this researchis qualitative method. As Bogdan and
Biklen state that qualitative is descriptive that data collected take the form of
words or pictures rather than a numbers.1So that the writer presented the data
collected in words rather than numbers. Furthermore, this research is
designed in a case study and she only examine a single subject like Bogdan
and Biklen state that a case study is a detailed examination of one setting or a
single subject.2To get the data the writer uses test.The test is done twice to
know whether it is a mistake or an error. Finally, the errors that have been
collected were analyzed to determine the types of errors after by following
Corder theory. In this term, error broken down into five categories: error of
omission, error of addition error of selection, and error of ordering. While the
analysis on error types are presented in tables by following James table.
Futhermore, to know the frequency of occurency of each error type the writer
used descriptive analysis technique (percentage).
B. Place and Time of The Research
The writer will conduct this research at SMPN 3 Tangerang Selatan
which is located on Jl. Ir. H. Juanda I No. 1 Ciputat, Tangerang Selatan,
Banten.She is conducting the research at the school from 19th of June to
26thof July 2013.
1
Robert C. Bogdan and Sari Knopp Biklen, Qualitative Research for Education an Introduction to Theories and Methods, (Boston: Pearson, 2007), p. 5
2
C. The Participant of The Research
The subject of the research is the eighth year students of SMPN 3
Tangsel which is devided into Eighth regular classes 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4, 8.5,
8.6, 8.7, 8.8. the writer uses purposive samplingto take the sample that is a
class 8.8.The writer only took 30 students.
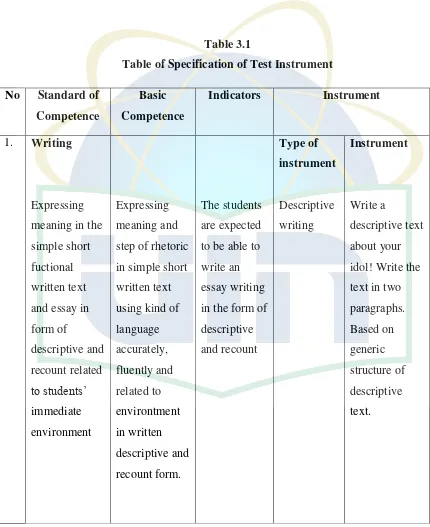
D. Instrument of The Research
The instrument of the research is test. The test is an essay writing test about ‘Describing your idol’ which is guided by four question. So that the students need to make a paragraph based on the insruction given.
E. Techniques of Data Collecting
To measure the ability of students, the writer takes essay writing in the
paper that is given as the test to the second grade student of SMPN 3
Tangerang Selatan.The writing test that students made indicates their
understanding in using grammatical in descriptive text.Before the students do
the test, the writer givesthe explanation and direction about what the students
Table 3.1
Table of Specification of Test Instrument
F. Technique of data analysis
The data collected will be analyzed by using procedures in doing error
analysis. The procedures consist of five steps based on Corder.It consists collecting of the sample, identification of error, describing student’s errors after that she explanation of the error.This step attempts to account for why
the errors occur. It means to determine the sources (causes) of the errors based
on Corder theory beside that the writer uses interview as supporting data.
Thus, the James table can be seen as below.
Finally, the last procedure is evaluation of the error which means to
distinct which errors will be corrected so the learner, which made an error,
will not be stress of getting correction. To do the last step which is
quantifying each percentage of error, the formula below is used:3
P =
Note:
P: Percentage;
f: Frequency of a type of error;
n: Number of total errors occur.
3
31
the class, but the writer only took 30 students as a sample. Actually the total
of the student was 46 and most of them did not attend the class. The test is an
essay writing test about „Describing your idol‟, which is guided by four
question. So that the students need to make a paragraph based on the
insruction given. After conducting the test, the writer analyzed the data from
the students‟ test to find out the errors that students made in his/her answer by circling each erroneous item. The result of this identification can be seen as
12 Student 12 1 - 3 -
13 Student 13 1 - 4 -
14 Student 14 3 - 2 -
15 Student 15 3 - 2 -
16 Student 16 2 - 6 1
17 Student 17 5 2 5 1
18 Student 18 2 - 7 -
19 Student 19 2 1 4 -
20 Student 20 - 1 5 1
21 Student 21 2 1 2 -
22 Student 22 1 - 4 1
23 Student 23 2 - 4 -
24 Student 24 1 - 4 -
25 Student 25 - 1 4 -
26 Student 26 1 - 4 -
27 Student 27 2 - 2 1
28 Student 28 1 - 1 -
29 Student 29 1 1 4 -
30 Student 30 1 - 8 -
TOTAL = 51 13 99 8
As the calculation above, the writer describes the examples and the causes
why the errors occur as follow:
1. The Error of Omission =
29.8%
2. The Error of Addition =
3. The Error of Selection =
4. The Error of Misordering =
B. Data Analysis
The procedure of error analysis has been explained clearly in the
preceding chapter and some of those procedures have been done well such as
collecting data and identifying students errors. Moreover, the other
procedures would be described clearly as follows:
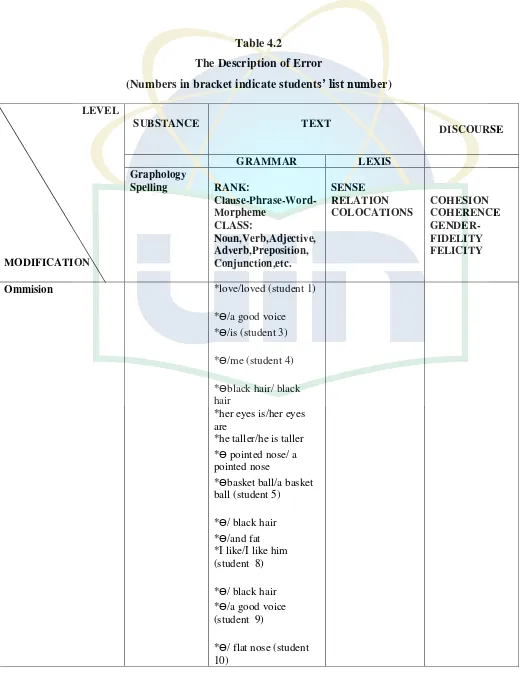
1. The Description of Error
After identifying the data, the writer analyzed the errors and
classified them based on the Surface Taxonomy Categories to know
whether these errors involve in omission, addition, selection, or
ordering. This is the following example is taken from the student‟s
answer sheet. (Students number 17).
a. Error of Ommision
*he have oval face. The correct sentence is he has an oval face.
Actually the student omit the article there must be exist before the
adjective in that sentence that is an oval face.
b. Error of Addition
*he is was born in Medan. The correct sentence is he was born in
Medan. The student add the verb „is‟ which does not need it in that
sentence.
c. Error of Selection
*he have black hair. The correct sentence is he has a black hair. In
this form the student is select the wrong verb, it must be „has‟ for third
singular person „he‟
d. Error of Ordering
*he is a idola cilik 2013 runner up. The correct form is he is a runner
up in idola cilik 2013.
Besides the examples above, the writer recognises the other
errors done by the students. This classification is presented in the table
Table 4.2
The Description of Error
(Numbers in bracket indicate students’ list number)
LEVEL
Ommision *love/loved (student 1)
*he smart/he is smart *he play/he plays *he smart/he is smart (student 11)
*Ɵ/ blue hair (student 12)
*Ɵ/his full name (student 13) *Ɵ/an
*he is old man/he is an old man
*flat Ɵ/flat nose (student 14) *Ɵ/an idol *Ɵ/an old man *flatƟ/flat nose (student 15) *Ɵ/a smart girl *Ɵ/her skin (student 16)
*Ɵ/his nick name *Ɵ/an oval face *Ɵ/are
*Ɵ/sharp-nose *Ɵ handsome/he is handsome (student 17) *Ɵ/in(2)
*Ɵ/his national team (student 18)
*he also singer/ he is also a singer
*Ɵ/his height (student 19)
*Ɵ/him
*Ɵ/an (student 22,27) *Ɵ/ black hair
*Ɵ/is playing (student 23)
*Ɵ/a (student no 24,26,28,29,30) *she Ɵ elegant/is (student 27)
Addition *dad and mom
*doing/Ɵ (student 1) *he is like/he likes (student 5)
*he is have/he has (sudent 7)
*someone idol/an idol *he is have/he has (3) (student 10)
*a idol/an idol *because (student 11) *a black/ black *he is was bown/he was born (student 17) *his tall/his height (student 19) *the finally/finally (student 20)
*he is born on 24 years old/he is 24 years old. (student 21)
After identifying the data, the writer analyzed the errors and classified
them based on the Surface Taxonomy Categories to know whether these errors
involve in omission, addition, selection, or ordering.
This calculation used the formula of descriptive analysis technique as can
be seen as below:
P =
Note:
P: Percentage;
body (student 8) *hair long/long hair
*hair
brown/brown hair (student 10) *dance good/good dancer(student 16) *he is a short to me/he is shorter than me.
*he is a idola cilik 2013 runner up/he is a runner up in idola cilik 2013 (student 17) *his short body tall body 169 cm/his height is 169cm (student 22)
f: Frequency of a type of error;
n: Number of total errors occur.
Furthermore, to make it easier to read, she presents it in the following
table below:
Table 4.3
The Recapitulation of Error Types, Frequency and its Percentage
No. Level /
Modification Substance
Text
Discourse Total Of Error
Grammar Lexis
1. Omission 51=29.8 51= 29.8
2. Addition 13=7.6 13= 7.6
3. Selection 7= 4.1 47=27.5 7= 4.1 38= 22.2 99= 57.9
4. Ordering 2= 1.2 6= 3.5 8= 4.7
TOTAL 171 = 100%
Based on the calculation above, it can be concluded that the total errors of
omission are 51 errors or 29,8% (error of omission in grammar text levelis 51
errors or 29,8%), the addition are 13 errors or 7,6% in grammar text level.the
error of selection are 99 errors or 57.9% (error in substance level are 7 errors or
4.1%, in grammar text level are 47 errors or 27.5%, in lexis text level are 7 errors
or 4,1%, and in discourse level is 38 errors or 22,2%), while the error of ordering
is 8 errors or 4,7% in substance level level are 2 errors or 1,2% and in discourse
level are 6 errors or 3,5% . From the calculation of the data, error of selection is
the most frequent errors done by the second grade students of SMP 3 Tangsel with
the percentage 57,9%. Moreover, it is followed by error of omission with
To be more clearly the writer explains each of the error below:
1) Ommision
The total error of ommision is 51 errors or 29,8%. Ommision error
occurs when the learner ommitted a necessary element of word.
Omission errors fell both in the substance and in the grammar level.
Most students committed errors by omitting a letter which must exist
within a morpheme. For examples:*he has black hair. While he is
supposed to write, he has a black hair.*he taller than me.While he is
supposed to write, he istaller than me.
From the example above it is clear that the students did not use an
article and a verb. The reason they made this error is in Indonesian
writing, they do not use the article and verb. The source of this error
comes from interlingual transfer. The students did not use the rule of
their target language well.
2) Addition
The total errors of addition is 13 or 7,6% in grammar text level. On
the writer‟s opinion, these errors occurred because the students had not
clearly understood of the structure of the sentence. So the source of this
error comes from the interlingual transfer. They add the unnecessary
word that does not needed in their sentence. For example, *his parents
is Scott dad and Lisa mom. The word „dad and mom‟ there must be
ommited because it is not needed. As we know that without the word
„dad’and „mom‟ we know that Scott is his/her father and Lisa is his/her
mom. So that the right answer is supposed to be his parents are Scott
and Lisa. Or another example is *his body tall. While the student is
supposed to write his height. So that the word body it is not needed in
that sentence.
3) Selection
The total error of selection that the writer found is 99 errors or
text level are 47 errors or 27.5%, in lexis text level are 7 errors or 4,1%,
and in discourse level is 38 errors or 22,2%). And this is the highest
error that the students do. These errors happened because the students
having lack of vocabulary and its use. The students were confused in
choosing the appropriate class of words. In this case, the example: *I
like Sule because he is have ability. While the answer is supposed to be
I like Sule because he is multitalented. From this sentence it can be seen
that the student is wrong to choose vocabulary so they misselection
about it.
4) Missordering
While the error of ordering that the writer found is 8 errors or 4,7%
in substance level are 2 errors or 1,2% and in discourse level are 6
errors or 3,5%. This error is sometimes as the result from interlingual
transfer. The students got the influence of the structure or order of their
native language which is Indonesian language. “I like album Justin Bieber.” The correct one is, “I like Justin Bieber album.
2. The Explanation Of Error
In this step, the writer would like to classify the errors based on their
source of error. she wanted to analyze these errors based on the differences
between Indonesian language system and English, and the target language
system itself (intralingual). So that the writer would not use the sources of
error base on context learning and communication strategies.
a. Interlingual Transfer
Interlingual transfer is an error which is caused by the students use
their own native language as a source. It means what they do are translate
Bahasa Indonesia into English directly. In fact, both Indonesian and
English have different structure. For exampe, *I have someone idol his
name “Entis Sutisna” the correct one is “I have an idol, his name is Entis
Sutisna. The other example is *I have a idol, he smart play foot ball. the
because handsome and elegant and he is a idola cilik 2013 runner up.
While he is supposed to write I like him because he is handsome and
elegant and he is a runner up in Idola Cilik 2013. These errors are happen
because the pattern of Both Bahasa – which is their mother tongue- and
English are totally different. The students ommited the verb, -is, -ing. And
the students misselection and ommited the article. As the writer compares
to the result of interview, the students did not really understand about the
rules which is mean the grammar and also they did not really understand
of structure of the sentence. And the teacher did not explain it clearly. So
that the source comes from interlingual transfer because they still
influenced by their own mother tongue.
b. Intralingual Transfer
This errors occur because the students are overgeneralization the
rules in wrong concepts. So that intralingual transfer is happen because of
partial learning. For example, *he is was born in Medan. In this sentences
the student only know to put the verb after the subject but he does not
know the correct one. So he uses the verb –is and –was at the same time.
While he is supposed to write “He was born in Medan.”The source of this error is intralingual transfer because they overgenerates the rules in wrong
concept.
3. The Evaluation of Error
If the purpose of the error analysis is to help students to study
second language, it is important to evaluate the errors. Some errors can be
considered more serious than others because they could hinder the
message of the communication. In this research, the writer considered that
the errors which are caused by partial learning, this error could hinder the
message to be understood because partial learning tends to have an impact
for the students such as they do not have deep understanding or