Vol7, No 1, January - March 1998 Anti Herpes Simplex Virus of Phyllanthus urinaria (L) 29
Anti
herpes simplex virus
property
of
Phyllanthus
urinaria
(L)
as
shown by
plaque
reduction
assay
Praseno
Abstrak
Obat tradisional telah popular di Indonesia. Banyak di antara obat tersebut yang efektif untuk menyembuhkan pelbagai penyakit,
termasuk penyakit infeksi. Berdasarkan hal tersebut, aktifitas anti Herpes Simplex Virus ekstrak Phyllanthus urinaria (L) diteliti secara
in vitro dengan metoda "plaque reduction assay". Hasil menunjukkan bahwaIDng dicapai oleh ekstrak pada konsentrasi 6Vo dan4Vo
vlv untuk HSV-2 dan HSV-I
Abstract
Traditional medicine has been popular in Indonesia. Many oIthem are effective fo curingvarious diseases. Based on that, antiviral activity to Herpes Simplex Virus
oian
aqueos phaseof exlnclof
Phillantus urinaria (L) plant was investigated in vitro by a plaquereduction assay. Result showed that lDtoo was achieved by the extract at concentration of 6Vo and 4Vo
v/v
for HSV-2 and HSV-Irespectively.
Keywords : Phyllanthus urinaria (L)-Herpes Symplex Virus-traditional medicine-plaque reduction assay
INTRODUCTION
Indonesian peoples has long been using
traditional
medication
in
daily
life. Many traditional
medicine
derived
from
plantsor
herbsproved
to beeffective
for
curing various
diseases,including
diabetes,hyperten-sion, renal
stone and someinfectious
diseases.At
last
145different
plants
have been documented andreported to
have
phàrmacological properties.l
Evenwith
the
introduction of
modern medicine
the practiceof using
traditional
medication
isstill
continuing.
Fur-thermore, several
centers
for
researchand
develop-nent
of traditional medicine
have been
established,such as "Pusat Pengembangan
Obat Tradisional"
atGadjah
Mada
University.
Phyllanthus
urinaria
(L), or "dawn
gendong
anell'
been usedeffectively
for treatment of hepatitis,urinary
tract infection, bacilary
dysentery,
ureteral colic,
toothache,
and asdiuretic.l'z
Sinceihe most common
cause
of
hepatitis
is viral origin, we
predicted
thatextract of this plants
may haveantiviral activity.
How-ever,
becauseof difficulties
in isolation
of
hepatitisDepartment of M icrobiology Faculty of Medicine Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia
viruses or
eventhey cannot
be adaptedin cell
culture
system,
we
used herpessimplex
virus to
evaluate
in
vitro antiviral
activity
of extract
of
Phyllanthus
urinaria (L).
METHODS
Preparation of the extract
One gram of
whole plant
was cutinto small
pieces andfinely
ground. This material
wastransferred
into
con-ical
tubeof
15ml
and addedwith
9ml
of
aquadest andmixed well by brief vortexing. The material
was
left
over night
atroom
temperatureto
allow
water soluble
substance todissolve.
On the next day themixture
wasspinned down, supernatant collected and filtered
through
a membraneof
0,45 Fm pore size.This
super-natantcontaining water soluble extract
of
theplant
isused
for
theexperiment.
Evaluation of
antiviral
activity by reduction
assaymethod3
30 Praseno
monolayer
growth
was achieved, medium
was
replaced
with 2 ml
of fresh
DMEM
containing
57o FCS. 0,2ml
suspensionof
103 plaqueforming
unit/ml
of
HSV
1 andHSV 2
were addedinto individual
flaks
and thecultures returned into incubator.
After
2 hoursincubation, flasks
were taken
out from
the incubator
and the medium decanted. The culture were rinsedwith
phophate-buffered saline
to
remove any
remaining
virus particles, after which 5 ml of DMEM
suple-mented with
57oFCS was added
into the
flasks. 400pl,
300pl,
20O 1t1,100pl,
50 pl, of the extract were addedto individual flasks. Two
flasks
of culture
in-fected
with HSV
1 andHSV
2, respectively were
notlreated with the exlract
and served as
controls.
Oneflasks
of
uninfected culture
was used as negativecon-trol.
These prosedureswere
donein
duplicate.
All
cultures were reincubated at
3/C
for
three days.At
the endof
incubation period medium
was decanted and thecultures
was stainedwith
crystal
violet
stain tovisualised the plaques. Number
of plaques
on
eachflasks
wascompared to
thatof
control.
Interprctation
of
the
result
Antiviral activity of
theextract
is expressedof
plaqueformation
andcalculated by
theformula
:No. ol plaque of control
-
No. of treated culÈure'x
tN%
No. of plaque of control
Table.1. Inhibitory effect of Phyllanthus Vero cell line
Med J Indones
The arnount
of extract
capable
of
reducing
plaquenumber
by
IOOTois
said
to
be
inhibitory
close 100(ID166).RESULT
Total inhibition
of plaque formation
(ID100)
wasachieved
by the extract
with
the concentration
of
67o
vlv
for HSV-2
and 47ofor
HSV-I, respectively
(table 1).
Concentration
of
0,5%ov/v
has noeffect
on
inhibition
of
plaque formation on HSV-1 and HSV-2
infected
Vero cell was enhauced
by addition
of the extract.This
growth
enhancement wasclearly
seenbefore
andafter
staining procedure; extract
-
treated cultures
weremore
deeply stained
than
those
of controls
(seefig-urel).
DISCUSSION
Our study
showed thatextract
of phyllanthus
urinaria
(L)
has in viJroactivity
against HerpesSimplex
Virus.
Inhibitory
Dose100
was achieved
by
the extract
atconcentration
of
67ov/v
and
47avlv
for HSV-2
andHSV-I,
respectively.
It
means
that lDroo will be
60pl/ml
and40
gilml
Since we used crudeextract in this
study,
we
estimated
much lower
concentration
is
re-quired to
getIDl00
if
we
usedpurified
extract
in
the assay.urinaria
(L)
extract on plaque formationof
HSV-1 and HSV-2 infectedAddition o[ extract (r.l)
Final concentration
ol
extract (Vov/v) Plaque on'
Number culturesof
infected with7o inhibition
o[
plaque formationHSV-I HSV-2
HSV.I
HSV.2400 300 200 100 50 25 0 (control) 8 6 4 2
I
0,5 0 0 0 0 31 52 67 63 0 0 36 42 55 82 78100
r00r00
100100
53,8050,70
46,14t7,40
29,6000
Vol 7, No 7, January - March 1QQ8 Anti Herpes Simplex Virus of Phyllanthus urinaria (L) 31
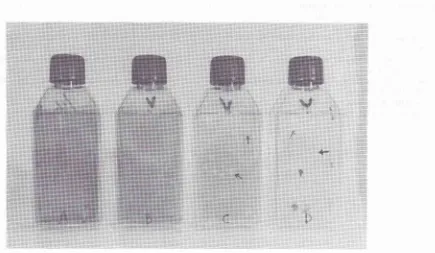
Figure 1. HSV-infected Vero cell line. A, B arul C: cullures treated with extract of Phyllanthus urinaria (L).
D:
untreated culture (control). Arrows indicate positions of the plaques. Note that treated are more densely stained than control.Enhaircernent
of the growth of Vero cell
lile
in extracf
treatedcultures indicate
that there wasllo
toxid
effect
of
this extract on the cell.
It
is
very
likely
that
theextract contains hight
concentration
of
vitarnins
andminerals
which
promote growth
of
the cells.Specific treatment
of
HSV
infectiou
is
usually
notrequired unless serious complication
involving
vis-ceral organs are
ailticipated.
This
is,in
part becauseof
relatively
expensive cornrnercially available synthetic
antiviral drugs
for
most
people
iu
Indonesia.
Unfor-tunately, untreated
cases
of
HSV
infection
will
bepotential sources
o f spreading the v irus to other people.In
addition,
several studies showed that
some strainsof
HSV
were resistance
to
antiviral
d.ugs.a's The
problems were also complicated
by
the
presenceof
asymtolnatic
caseswho
shed the virus persistently andby the
ability
of the disease to becorne lalerrt.o'/ Despitepossible
involvernent
of
the
brain
in
HSV
infection,
especially
in
imrnune compromised
patients, moreat-tention should
be paidto HSV infection
during
preg-nancy asit
rnay cause spontaueousabortion,
stillbirth,
and congenital rnalforrnation
or,
rnore
frequently,
mucocutaneous
infection
occuriug
at
the
tirne of
delivery.s
In
order
to
overcome
part of
these problern) we havebeen searching back
for
anti
HSV
agent derived frornplauts
readily
available
in our
environment. Our
pre-vious study
showed
that
another
plants,
Momordica
charantia or spring cucurnber, also hasin
vitro activity
agairst HSV-2.v
In
vivo activity
of
these
extract
arenow
under investigation. Further studies are
alsoneeded
to
elucidate other pharmacological
aspects,including
mechanisrnof action
andpossible
effect of
the extract
on
other viruses.
The
search
for
active substaucehaving
antiviral effect from
these plants isalso
importaut.
Nevertheless,
from practical point
of
view,
it
will
bernore
beneficial
if
the
whole plant
or
the crudeextract
can be used as an alternativeof
anti
HSV
agents asit
will
much
facilitate its
usein
treat-mentof HSV
infection.
Acknowledgement
We thank Dr. Nobert Ryan
of Fairfield Hospital,
Vic-toria, Australia
for
kindly
providing HSV-infected
Vero
cell line;
Ms.Nenes
Prastiwi
for
assistancein
preparing the rnanuscript.
REFERENCES
1.
Dharma AP. Indonesian Medicinal Plants. Jakarta. Balai Pustaka 1987: 160-1.-32 Praseno
Balows
A,
HauslerWJ, Herman
KL, etal.
Manual ofCllinical Microbiology. 5th e<1. Washington DC. American
Society for Microbiology
l99l
: ll84-90.Crumpacker CS, Schnipper LE, Marlowe SI, etal.
Resis-fance [o Antiviral Drugs of Herpes Simplex Virus Isolated
from
A
Patient Treatedwitb
Acyclovir.N
EnglJ Med
19821.3O6:343-6.
Whitley RJ, Gnann JW. Acyclovir: A decade later. N Engl J
Med 1992;327:782-8.
Field BN, Knipe DM, Clhanock RM, et
al.
Fielcls Virology.2ncl eÀ. New York. Raven Press. 1990:1843-88.
MedJ Indones
Jawetz E, Adelberg EA, Melnick JL, Brook GF. Medical
Microbiology.
l8th
ed. PrenticeHall International Inc.
1989:358-80.Stagno S, Whitley RJ. Current Concept: Herpes Virus
Infec-tions of Pregnancy. N Engl J Med I985;3I3:t327-9.
Praseno, Suparwoto S, Ning Rintiswati. Antiviral Activity
of Momordica Charantia:
A Preliminary Study on
in vitroanti Herpes Simplex Virus Berkala
llmu Kedokteran (in
press).
8.
9.
5