The Teaching of Vocabulary by Using Game, Song and Story
Techniques to Young Learners Based on Teachers
’
Perspectives
(Descriptive Qualitative Study at Madrasah Ibtida’iyyah Pembangunan UIN Jakarta in the 2014/2015 Academic Year)
“Skripsi”
By
Ilham Aditiara Rahman
1110014000028
DEPARTMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
FACULTYOF TARBIYAH AND T
EACHERS’
TRAINING
SYARIFHIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
i
ABSTRAK
Ilham Aditiara Rahman, 1110014000028. Pengajaran Vocabulary dengan Menggunakan Teknik-Teknik kepada Murid Sekolah Dasar Berdasarkan Perspektif
Guru-Guru Bahasa Inggris (Studi Deskriptif di Madrasah Ibtida’iyyah Pembangunan
UIN Tahun Akademik 2014/2015)
Kata Kunci:Teknik-teknik dalam Mengajarkan Vocabulary, Frekuensi Penggunaan Teknik, dan KeEfektifan Teknik.
Penelitian ini dilakukan untuk menganalisis fenomena penggunaan teknik-teknik dalam pengajaran yang terjadi dalam pengajaran Bahasa Inggris di Madrasah Ibtida’iyyah Pembangunan UIN Jakarta. Tujuan dari penelitian ini adalah untuk menganalisis teknik-teknik yang sering digunakan dalam proses belajar mengajar Bahasa Inggris dan tingkat keseringan dari teknik-teknik yang digunakan berdasarkan perspektif guru-guru.
Metode yang digunakan dalam studi ini adalah metode kualitatif deskriptif. Peneliti mengamati tiga guru dalam pengajran Bahasa Inggris selama empat sampai lima pertemuan dengan tema pegajaran yang berbeda untuk mlihat keseringan penggunaan teknik yang digunakan dalam kelas. Peneliti juga mewawancarai tiga guru Bahasa Inggris dan membagikan angket untuk mengetahui teknik-teknik yang digunakan dan tingkat keseringan penggunaan teknik menurut para respondent. Kemudian peneliti menganalisis hasil observasi yang dilakukan selama kurang lebih empat sampai lima pertemuan. Setelah itu, peneliti menghitung hasil tersebut menggunakan rumus statistik sederhana. Lalu, data yang diperoleh dideskripsikan menggunakan analisis deskripsi. Peneliti menggunakan buku-buku dan bahan-bahan lainnya dari internet yang sesuai dengan topik yang diteliti untuk mendukung pembahasan. Subyek dari penelitian ini adalah tiga guru Bahasa Inggris yang mengajar di tingkat kelas yand berbeda di MI Pembangunan UIN Jakarta.
ii ABSTRACT
Ilham Aditiara Rahman, 1110014000028. The Teaching of Vocabulary by Using Game, Song and Story Techniques to Young Learners Based on Teachers’ Perspectives (Descriptive Qualitative Study at MI Pembangunan UIN in the 2014/2015 Academic Year)
Keywords: Techniques of Teaching Vocabulary, Frequency of the Technique Use, and the Effectiveness of the Technique.
This study was conducted to analyze the use of techniques phenomenon in teaching vocabulary to young learners in MI Pembangunan UIN Jakarta. The objective of this study is to analyze techniques that are frequently used in the learning and teaching English process and the frequency level of techniques which are used according to teachers’ perspectives.
The method designed in this study was a qualitative descriptive. Three teachers were observed during teaching and learning in the classroom for four meetings under the different themes to analyze the frequency of the use of the technique in the classroom. The three English teachers who are teaching in different grades were given the questionnaire and interviewed to find out the frequency level of techniques used by teachers. Then, the result of the observation that has been conducted for four meetings was analyzed. After that, the writer calculated the data result using simple statistic formula and the data was described in description analysis. Textbooks and other materials from internet which have topic related to this study were used to support the discussion. The subjects in this study are three English teachers who teach in different grades in MI Pembangunan UIN Jakarta.
The result of this study shows that from three respondents, the first and second used song technique frequently in the teaching process. Meanwhile the second respondent used frequently game. This observation result obviously supported the interview and questionnaire data collected. The first respondent use song for eleven times with the percentage of (61.18 %), meanwhile the second respondent used game for 7 times with the percentage of (63.64 %), and the third respondent use song as well for 6 times with the percentage of frequency of (85.72 %). From the result above, it can be concluded that the use of song technique is used by first respondent who teaches for 1st and 2nd grades and it is also used by the third respondent who
teaches in 3rd grade. Meanwhile, the use of game was used by the second respondent
who teaches in 4th grade of MI Pembangunan UIN Jakarta. Both techniques are often
used for some purposes like improving the students’ understanding of the vocabulary
iii
Acknowledgement
All praise be to Allah, Lord of the universe, who has given the writer His Mercies, Blesses, and Permission to accomplish this research paper “Skripsi”. Peace and salutation be upon the last prophet Muhammad, his family, his companions, and his followers.
This research paper is presented to the department of English Education, the
Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training State Islamic University Syarif
Hidayatullah Jakarta as a partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Strata 1 in English language education.
The writer would like to express his special great honor and the deepest gratitude to his beloved parents, his mother (Nurjanah binti Saman) and his father (Ahmad Marzuki bin Iing Suryadi) and his beloved sisters for their love which always warm his heart, then for their help, support, motivation, and moral encouragement to finish his study.
Next, the writer would like to express his gratitude an appreciation to her advisors, Drs. Nasifuddin Jalil, M.Ag. and Maya Defianty, M.Pd. for their valuable guidance, motivation, attention, correction, suggestion for the completion of this research.
His gratitude also goes to:
1. Nurlena Rifa’i, M.A., Ph.D. The Dean of Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training.
2. Drs. Syauki, M.Pd., The Head of English Education Department.
3. Zaharil Anasy, M.Hum., The Secretary of English Education Department.
4. All lecturers in English Education Department who have taught and
iv
5. KH. Syekh Misbahul Anam At-Tijani, the owner of Pondok Pesantren
Al-Umm and all the staff, teachers, and students who have given guidance, help, and support during the writer were studying and becoming the students in Pondok Pesantren Al-Umm.
6. Miss Aida Ainul Wardah, The Academic Staff of English Education
Department, for the help, advices, and support that have been given.
7. Sari Febriyanti, S.Pd. who helped the writer in making the statistical data
of the observation.
8. M. Syafri, S,Pd. who facilitated the writer in dong the research.
9. Drs. Sugiono, The Headmaster of MI Pembangunan UIN Jakarta, for the
support and permission for doing research in his school.
10.Mrs. Ai Yuliawati, S.Pd., Mrs. Upit Sarimanah, S.Pd, and Mrs. Khusnul
Khotimah, M.Pd. who have become the respondents during the research.
11.Muhammad Sofyan, S.Pd who gave more supports during to the last of the
making of the research.
12.All who have given their help in writing this skripsi that the writer could
not mention one by one.
The writer realizes that this skripsi is far from being perfect. Therefore, the
writer would highly welcome any suggestion or critiques to make this skripsi better.
Then, the writer hopes that this skripsi will give advantage for all.
Jakarta, 20th December 2014
v
TABLE OF CONTENTS
ABSTRACT……….i
ABSTRAK………...ii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS………...iii
TABLE OF CONTENTS………...iv
LIST OF TABLE………......v
LIST OF APPENDICES………...vii
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION………...1
A. Background of Study ………...1
B. Identification of the Problem ………...5
C. Limitation of the Problem ………..……...6
D. Formulation of Problem ………...6
E. Purpose of the Study ………... ……..6
F. Significance of the Study ………...6
G. Clarification of Terms ………...7
CHAPTER II THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK ………...9
A. Literature Review ………..9
1. Young Learners ……….9
2. Vocabulary ………...10
a. Definition of Vocabulary ………..10
b. Kinds of Vocabulary ……….11
3. Games ……….14
a. Definition of Game ………...14
b. Function of Game in Language Learning ……….14
vii
4. Song ………16
5. Story ………18
a. Definition of Story ………18
b. Purpose of Story ………19
c. Types of Story ………...20
d. Characteristics of Folktale ………21
B. Previous Study ………24
C. Theoretical Framework ………...26
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY……….28
A. Place and Time of the Research.………..28
B. Respondents of the Research ………..28
C. Method, Design and Procedure of the Research..………29
D. Technique of Collecting Data.……….30
E. Technique of Checking The Data Validity.……….31
F. Technique of Data Analysis.………32
G. Unit of Analysis.………..33
CHAPTER IV RESEARCH FINDINGS………...34
A. Findings………...34
1. Frequency of Technique Use...………...35
B. Discussion ………...75
CHAPTER V CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION.………..83
A. Conclusion.………..83
B. Suggestion.………...84
BIBLIOGRAPHY.………...85
viii
LIST OF TABLES
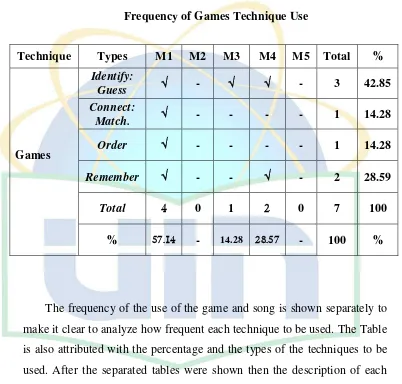
[image:11.612.98.543.176.597.2]Table 4.1 Frequency of Games Technique Use (Respondent 1)………..41
Table 4.2 Frequency of Song Technique Use (Respondent 1)……….42
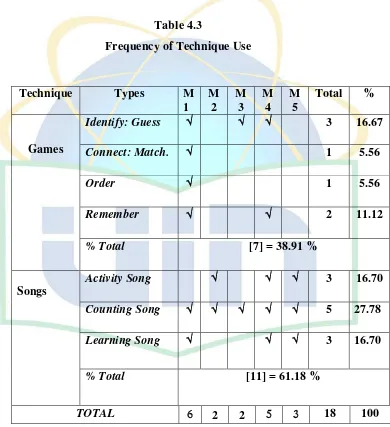
Table 4.3 Frequencies of Techniques use (Respondent 1)………...52
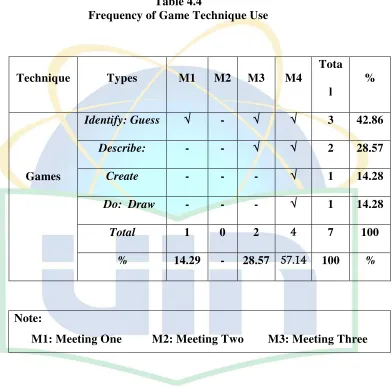
Table 4.4 Frequency of Games Technique Use (Respondent 2)………..59
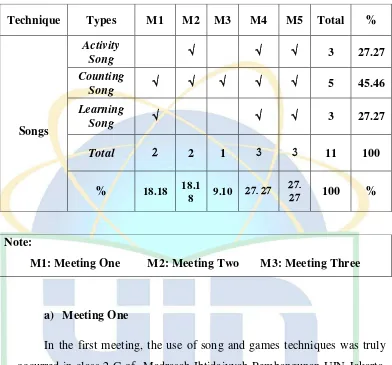
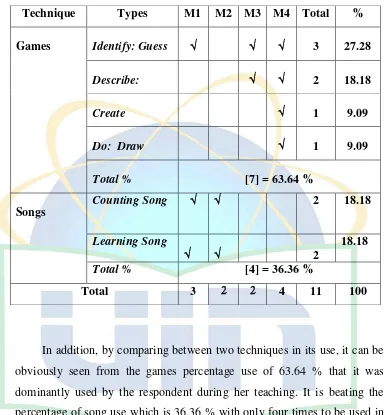
Table 4.5 Frequency of Games Technique Use (Respondent 2)……….61-62 Table 4.6 Frequency of Technique Use (Respondent 2)………...64
Table 4.7 Frequency of Song Technique Use (Respondent 3)………69-70 Table 4.8 Frequency of Techniques Use (Respondent 3)……….70
ix
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix 1: Permission letter for Doing Research ………..88
Appendix 2: Respondents’ Profiles………...91
Appendix 3: The Questionnaire ………98
Appendix 4: The Interview………..108
Appendix 5: The Observational Notes……….115
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background
English for Young Learners in Indonesia is well known as (MULOK) or Local Content in primary school since last decade. It is based on the government decision-making of decentralization of education that English should be taught as the local content to young learners.1 As the result of this decision-making, the enhancing of the public interest in English for young learners (EYL) has become overflowing and the increasing number of district governments all over the country which offer English classes at the primary school level has become the evidence.
Little has been known that teaching English to young learners in Indonesia
deal with problem of the teaching itself. This might be because while the decision
to teach English to primary school pupils have been made, requirements for teachers to be able to teach English well at this level are seldom discussed in public as crucial topic. As results, our knowledge about this important issue is very limited. In reality, the teaching of English to young learners is not accompanied with the specifically efforts for the training of teachers in primary school. Furthermore, there even teachers in primary schools who are from various educational background with the minimum knowledge of language teaching. Moreover, there is no any standardization for English teachers in primary school in Indonesia. Besides, the English department in any faculties of Teacher’s Training is designed to provide the professional teachers for the junior and senior high school students only. In the situation of being no such curriculum for English teaching in Indonesia for the primary level, English primary teachers
1 Bachrudin Musthafa, English to Young Learners in Indonesia: Essential Requirements,
2
are given freedom and unhampered to choose techniques in teaching English to Young Learners.
This might be a challenge to English teachers who teach in primary schools. Mustafa has synthesized the basic knowledge and skills from multiple sources
that become teachers’ requirements in teaching young learners. First teachers
should know who children are, how the children learn, how the children learn a language, how Indonesian children learn English as a foreign language, and how
teachers can facilitate children learning English as a foreign language.2 From this
explanation, it can be known that teachers should firstly get to know the field of teaching. It is a must for teachers to know it in order to get a good result of teaching. Then in this case, English teachers in primary school are not as figures that have the capability to teach only, but also to design the materials and choose the techniques which are appropriate in teaching Young Learners. As stated by Cameron, all the good skills of good primary teachers are required in teaching language to children, it is carried out to manage children and keep them on task,
plus knowledge of language teaching and of language learning.3 The managing
students on the task is not an easy task, teachers should be able to find a way to keep them in a good mood during learning and teaching process. Thus, the technique choice is considered as crucial aspect that should not be neglected by the teachers.
Techniques are considered as the crucial elements in delivering materials designed for young learners and will be effective if it is made according to circumstances of the class. Due to this fact, the English teachers in primary school need theoretical bases on teaching-learning English to young learners. Thus, teachers with good skills are needed to apply the technique of a meaningful teaching and learning.
2Ibid., p. 120
On its going as part of educational curriculum, the exact method of teaching English is a must and crucial. However, although English is considered as foreign language for Indonesians, the essence of English does not differ with other foreign languages such as Arabic and Germany in the way of handling and applying it. This kind of aspect has been completely recognized by government. What is so called as the essence here is the component of the language then what people know as the language component is about vocabulary, grammar and pronunciation which have become the elements of the priority especially for reading some simple text in daily life which requires more students’ mastery of vocabulary.
The function of this component is considered as important element of the language. According to Harmer, when the grammar or structures of one language plays the role to build up the skeleton of language, then it is vocabulary as the
component that provides the vital organ and the flesh.4 If this component has been
mastered, the language skill such as listening, reading, writing or even speaking will be supported. Students need to master some basic vocabularies to help them to understand doing some other real life activities related to language skills such as reading texts, writing essays, responding to exam questions, and participating in class discussion which by these some activities, students can practice their vocabularies from time to time.
In developing vocabulary regarding to what is written above, English teachers should have the initiative to motivate students to be more active in learning in order to make them comprehend more about basic vocabularies which crave to be mastered by students. Therefore, the techniques of teaching and learning English especially vocabulary also craves to be maximized to get students’ vocabulary achievement improved in the teaching.
4
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English Language Teaching, (New York: Longman
4
The next case is the students find it difficult in getting vocabularies in the teaching and learning, for commonly it is not intentionally delivered or it could be said that it is not based on real life teaching and learning. This problem commonly makes students stuck in expanding their English. They tend to be silent while being asked several questions in English rather than answering the questions. Based on the description mentioned, the writer assumed that the more vocabularies students achieved the more understandable the reading text will be in daily life lesson in case of reading skill as an example of how vocabulary comprehension could support English language skill.
In the reality, teaching vocabulary is not as easy as some people imagine. There could be barrier in delivering vocabularies. Some teachers may be successful in doing so, that students get a satisfying achievement in the end of the lesson. However, even if the teaching seemed to be successful on its going, the improvement of teaching techniques and methods use is still considered as a necessary aspect.
Starting from this point, it has been highlighted that the teaching of English especially when narrowed down to vocabulary, the teaching often tends to be boring and stressful. In finding the effective technique, here writer offers several techniques of English teaching which are commonly used in teaching vocabulary, comfortable and fit on students in order to push kind of teaching in conventional way away that in final the writer will only choose the most effective technique from the several techniques.
mastering the language components (vocabulary, grammar, and pronunciation). Furthermore, in order to get good results, the teachers should carefully plan teaching and learning activities based on the games that they want to use. This type of technique is quite joyful because some students tend to be happy in its applying but could take much time if it was not organized in applying it.
Telling story by some tools such as picture and other real tools would be the
next technique of English teaching. Teacher can take students’ attention during
the teaching by telling them an impressive story. All of these items had been
commonly used and they could become a good references to improve students’
vocabulary mastery in English teaching. However, it is not impossible that there are other techniques commonly used by English teachers but song, story and games.
Departing from the discussion above, it is assumed that techniques in teaching
English to in primary school will affect the students’ understanding to the lesson,
specifically vocabulary. Thus this research will find out or investigate the techniques used in teaching English to Young Learners at MI Pembangunan UIN
Jakarta according to teachers’ perspectives and the frequency level of the
techniques use during the learning and teaching process in classroom. Therefore the study will be conducted by qualitative descriptive study.
B. Identification of the problem
From the description above, there will be several problems that can be identified:
1) How the chosen techniques improve students comprehension in learning
in class.
2) There is a need for teachers to have appropriate technique in teaching
6
3) How English teachers’ perceptions in MI Pembangunan UIN Syarif
Hidayatullah among three common effective techniques is.
4) What techniques are commonly used by teachers during the English
teaching
5) How frequent the techniques are being used in the classroom activity.
C. Limitation of the Problem
This study will be limited only in techniques used in teaching English vocabulary by teachers in Madrasah Ibtidaiyyah Pembangunan which is in the scope of primary School.
D. Problem of Formulation
According to background above the writer formulates the research question as follows:
1. How do English Teachers in primary school use the techniques in teaching
EYL?
2. What is the most frequent technique based on English Young Learners
(EYL) teachers in teaching English in MI Pembangunan UIN Jakarta?
E. Purpose of the study
F. Significance of the study
This study is created in order to help all people interested in the study. However, it is also specially designed to:
1) Giving general explanation about the condition of English vocabulary
teaching in primary level.
2) As the references for people who are interested in doing the research related to Young Learners
3) For English teacher especially primary school teachers. Teachers will be
facilitated in teaching vocabulary to their students based on the considerations of techniques analyzed in this study. Teacher also can use this research to improve their knowledge about English vocabulary teaching.
4) Students can also use the result of this research to be a reference of their
techniques of learning vocabulary.
G. Clarification of Terms 1. Techniques
The techniques in this study refer to the frequent techniques that are used for teaching young learners in primary school.
a) Song
Song is categorized important technique in teaching and learning process of vocabulary for it can stimulate students to say words again and over again, because the song of course cannot be sung without words
b) Game
8
c) Story
When students are facing the fascinating of the storytelling, they are just waiting for the story to be told until the last telling to get the ending of the story. During the listening to the story, they absolutely listen every single word that tracks them to the way of the story. It is helpful for they will absorb the words naturally from listening.
2. Young Learners
9
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A.
Literature Review
1.Young Learner
According to Phillips, The Young Learner means the first year children of
formal schooling (five or six years old) to eleven or twelve years of age.1
Another thought about who young learners are comes from Caroline stated that young learners are children between ages of 5-12.2 However, the children’s ages do not define how mature they are. There could be some aspects of life that influence children maturity, such as their culture, environment (city or rural), sex, expectation of friends and parents.3
In educational world, it is well known that young learners are capable to learn everything gradually and continually. Piaget’s theory said that the knowledge that is produced from children is not from imitating activity process or in-born, but
children actively construct it.4 Therefore the educational modern program puts a
concern to the young learners especially in the primary school.
As people cannot predict how mature the students in classroom by their ages, whatever the type of activities and approach a teacher decides to use in classroom will be all influenced by teacher’s knowledge of students’ attitudes, circumstances, and interests.
Besides students’ maturity, teachers also need to concern on their basic physical and psychological needs. Therefore, thecare necessary and appropriate instruction to meet these needs should be provided by teacher so that young
1
Sarah Phillips, Young Learners: Resource Book for Teachers, (New York: Oxford University
Press, 1993), p. 3
2
Caroline T. Linse, Practical English Language Teaching: Young Learners, (New York:
McGraw-Hill, 2006) p. 2
3
Phillips, loc.cit
4
10
learners can thrive and focus on learning.5 In other words, both providing care and instructionare teachers’ jobs.
On the other side, young learners have both advantages and disadvantages because of their respond to language according to what it does and what they can do with it, rather than treating it as an abstract system. Thus, young learners will seem more familiar to the concrete aspects rather than the abstract ones.
It can be concluded that young learners have the moment when their ages are very promising in learning, because they acquire knowledge easily but still with limited materials based on their level of learning. Hence, it is important to know techniques in teaching language the more vocabulary aspect.
2.
Vocabulary
a.
Definition of Vocabulary
It is well known that vocabulary is the basic element of language, Harmer stated that the vocabulary holds the important role as provider of organs and
flesh while language structures make up the skeleton of language.6
Vocabulary is the basic component of language, vocabulary itself can be
defined as the total number of words that make up a language.7
It is also a language component that consists of information about
meaning and words use in language.8 Caroline said that vocabulary is words
that language consists of. It is words collection that is known by individual. 9
In short vocabulary is a language component which is words that hold up a language which make up language user competent in every single skill of target language. It is one of important aspects of language that cannot be neglected in learning language.
5T. Linse, op. cit., p. 2
6
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English Language Teaching, (New York: Longman Publishing,
1991), p. 153
7
A.S Hornby, Oxford advanced Learner’s Dictionary (Oxford University Press, 1985), P.956
8
Harimukti Kridalaksana, Kamus Linguistik, Edisi Ketiga (Jakarta:PT Gramedia Pustaka Utama,
1993), P. 127
9
Looking at how important vocabulary of one language is, the variety of vocabulary usage will tend to help someone in manipulating grammatical structures. In short, it can be said that someone’s ability in manipulating the grammar when expressing meaning does not have any potential unless words are used.10
b.
Kinds of Vocabulary
Harmer divided vocabulary into two kinds, Active and Passive Vocabulary.
1). Active Vocabulary
It is also called as the productive vocabulary. Learners more commonly
use it appropriately in speaking and writing. Although when in practice, it seems more difficult to be carried out, but at least learners must know how to pronounce it appropriately, able use the words with good structure in target
language. Vocabulary can be called as an Active Vocabulary when students
have already learnt it and they are expected to be able to use it properly.
2). Passive Vocabulary
It is called as receptive vocabulary as well. It is words that commonly are
uneasy to be recognized and understood in the context of listening and reading either by learners. The Passive Vocabulary refers to items that learners will probably find it difficult or even not able to produce it and they will only
recognize it when they meet them.11
In short active vocabulary is easier to use because probably someone has already learned it properly and practiced it a lot, while passive vocabulary will tend to be difficult to use after it is acquired but no more used because probably it is considered as an unimportant word to use. Then in avoiding this case, someone needs to practice and have more directional contact to words that are just found so that it will not go away easily.
10
Harmer, op. cit.,
11
12
On the other side, Margaret and Curtis stated there are two kinds of words: 1) Word recognition
It is the child’s searching for meaning that make him or her to recognize the words which are printed. According to its position, it will be best acquired when it is acquired naturally, as in speech. Thus, the word recognition is the moment when the child recognizes some words in the daily life.
2). Word meaning which are important for reading.
These kinds of vocabularies develop overtime, they relate to the reading
process and to the teaching and learning. 12
According to McLuhan, these two kinds of vocabularies called as the medium or the message. In this case the medium might be thought as the Word recognition in the reading process, it conveys the message, and Word meaning is the message itself.13
In the case of using the words of language, Fries has categorized words into
two classes, they are function and content words.
1) Function words
It is words that do not receive additional words such as preposition, auxiliaries, modals, or any structure words of language.
2). Content words
The words that can be added whenever it is to get new meaning of words,
words and necessarily invention in communication.14
The Content Words are divided into general classes according to Fries: 1. Nouns, words that interpret things, ideas, entitles, etc.
2. Verbs, words which express actions
12
Margaret G. Mc Keown and Mary E. Curtis, The Nature of Vocabulary Acquisition, (New York:
Pychology Press, 2009), p.7
13
Ibid., p.7
14
Finnochiaro Mary and Bonomo Michael, The Foreign Language Learner: A Guide For Teacher
3. Adverbs and adjective, these kinds of words are usually used to describe
action (verbs) or things (nouns). 15
In daily life, words are used differently depending on the context we see, because based on harmer in his book, he stated that words can change their shape and their value in grammar. In the teaching vocabulary, Harmer suggests that the students need to know some facts about word formation. Those facts are:
1)How to twist words to fit different grammatical contexts
As the example of this aspect, the verb „run’ has „running’ and „ran’ as the
participles. Run is a verb, but it also can be noun meanwhile running can be used
as adjective.
2) Knowing how suffixes and prefixes work
For example, students need to know why they preface one with “in-” and
the other with “im-”
3) Knowing how words are spelt and how they sound
Spoken form is the part of learning “s” word, in speaking aspect learners
need to be able to stress words, especially when words’ grammatical function is different.
4) Able to understand and use words in speech.16
Based on the description above, it can be simply concluded that Word formation means knowing how words are able to change their form and how they are written and spoken.
15
Charles C. Fries, Teaching and Learning English as a Foreign Language (USA: The University
of Michigan, 1945), p. 47
16
14
2)
Games
a.
Definition of Games
Wright defined games as an entertaining and engaging activity, it is often
challenging when being played and stimulate learners to interact with others.17
b.
Function of Games in Language Learning
The functions of games commonly depend on what kind of the circumstances occurs during the language learning. Here are several functions of Games made up by Andrew according to the problems encountered in language learning. These functions are appeared by the causes occurred in learning target language, those causes are:
1). Language learning is hard work
Games function is to make many learners to be encouraged and to help them to sustain their interest and work. This function exists because language learning is hard work. In understanding target language learners must struggle to make some efforts in repeating accurately, adapting, using newly understood language in conversation and written composition.
2). Experiencing language
In learning language, learners need to experience what language is. When the learners want to take part in understanding what others are saying or have written they must participate to speak or write words to express their information. Games provide one way of helping the learners to experience language rather than merely study it. Games also help the teacher to create contexts in which language is useful and meaningful.
17
3). Repeated use of language
Game is the technique which holds “Drill” as the key features provided.
4). Central to learning
When it is believed that games can provide intense and meaningful practice based on what is written above, then games must be regarded as
central to language teacher’s repertoire and not merely way of passing the
time.18
c.
Types of Games
Games are known widely with its variety. Each of these varieties has its own essential character and way which engages the learner that is helpful in the adaptation of games or the creation of new games.
Again Wright has categorized games into several types according to its family types. These are those several types of games in the following way:
1). Care and Share
This game type is all games in which the learner feels comfortable to share about their personal information with other learners
2). Do: Move, Mime, Draw, Obey
Here, the game will stimulate learners to physically respond to a read or a heard text because learners are expected to do something non-verbally
3). Identify: Discriminate, Guess, Speculate
The challenge of this game is that learners should identify something which is difficult to identify or to hypothesis about something which is then compared with the facts.
18
16
4). Describe
Differently to Care and Share type, this game type push learners to feel
challenged to describe something to other learners by speaking or writing, and in responding that speaking and writing other learners can do something, for example, draw a picture.
5). Connect: Compare, Match, Group
In this type learners will be involved in activities of connecting, comparing, matching and grouping various items of information. It could be picture or texts, objectively or subjectively. The language will be used by learners to describe or comment on the pairs or groups of information.
6). Order
Here, the activity will be putting various bits of information into an order of quality and importance, subjectively or objectively, or to put text, picture, objects, into a developmental sequence, also subjectively or objectively where learners feel challenged to do so.
7). Remember
The use of memory or remembering is essential in this game type. Learners try to remember something and then communicate what they remembered.
8). Create
The learners are challenged or invited to make their own story, poem, or other kinds of material.
3). Song
about their experiences: they reassure them in their moments of trouble. They are the art form which could satisfy and entertain its listener, the lyric fits the music and the music fits the lyrics and together they form a complete unit. Another reason might be the ability of songs and music in general to affect their emotions. Many people can be moved to tears or other strong emotions by music, and songs can acquire strong emotional associations with people, events and places.
Songs have personal quality that makes the listener react as the songs were
being sung for the listener personally.19
This might be because songs directly have music inside which makes it balanced in the melody. As stated before that the lyrics or words of the song fit the music and music fits the lyric back. It makes the listener feel joy while listening to it, because every fiber of their being is crawled by the music of the song, becoming one and affecting many aspects of our lives.
The first aspect is that Music affects shopping habits, the higher profitability is translated by the proper selection of music. When background music is present in the shopping situation, people feel less crowded and less stressed.
Secondly, Music in the use has some beneficial effects through our moods. It
can calm, relax, excite, motivate to action or in other words suggest appropriate emotions to people. For instance people become aroused; their blood pressure and heartbeat rise, their bodies focus, and their muscles tense when music excites them.
Thirdly, that music affects productivity. Someone’s doing some activities, in
other words all sorts of routine tasks, such as hiking, jogging, typing, sewing, and driving more successfully when music accompanies the these activities. This is because music makes assembly line efficiency improves when background music is linked to repeated motion at appropriate speeds.
The last, music is also beneficial in altering human’s physiology, making
people happier, or even healthier. It can help the body fight of viruses, reducing
stress hormone levels and affecting the heartbeat.20
19
Lenn Millbower, Training with a Beat: the Teaching Power of Music, (Canada: Stylus
18
Here, the writer tried to classify some songs which are frequently used in teaching English vocabulary. Some songs will accompany the teaching of vocabulary when it fits to the materials of the lesson. Songs are classified as follows:
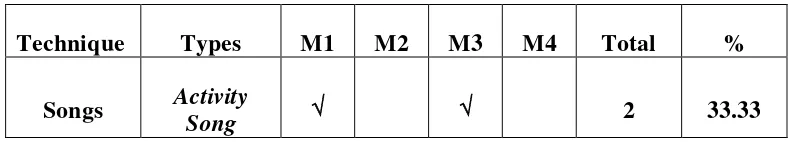
1) Activity song
Looking at its type, activity song is a song which full of action verbs vocabulary which makes the listener motivated to move and do what is written in the lyric. The song contains of the activities serve a variety of purposes: to introduce or reinforce vocabulary knowledge, to provide practice using prediction skills, to develop awareness of coherence, and to improve storytelling ability.21
2) Counting Song
It is a song type which will appropriately be used in the teaching of counting numbers. It is a popular in teaching basic mathematic subject in English.
3) Learning song
Every English song for children is actually for their learning activity, this song is just the song contains of vocabularies students need to know.
4). Story
a.
Definition of Story
Story is told in every nation, or even our cultures have its own stories to be told in hereditary or from generation to generation whether they are real or unreal.
20
Millbower, loc. cit., p. 6-9
21
According to Phillips in her book stated
“Story is a feature of all culture and have a universal appeal. Stories in the broadest sense (including anecdotes, jokes, „you’ll never guess what happened to me’ etc.) fascinate both children and adults-everybody loves a
story- and they can be used to great effect in the language classroom.”22
Stories are created and they don’t accidentally happen. There must be a story maker and teller if there is to be a story. The story maker is the controller of all what the story is going to be for he must know the details of his story. Therefore he has the control over who the characters are, what they do in the story etc. he also has a control over the way of the story to be told, and who should tell the story out.23
Highlighting one of the points of view which have been mentioned above the story maker has control over the way of the story to be told, and who should tell the story out. This point means that whoever touches the story and tell it by his ways will give quite different total story either from the aspect of the meaning, impression or any other aspects of the story.
Hence, in this case the man should be put on the right place, the one who is able to tell the story should be there then the story itself can be delivered to the listener.
In the educational area, deeply in language teaching story is one of the techniques commonly used to teach language, here teachers need to able to control the way of the story when it is being told.
b.
Purpose of Story
Story is meant for entertainment, a description of how something happened, that is intended to entertain people, and may be true of imaginary
Entertainment is one of several numerous reasons for why the stories are told beside many of them are used to teach a moral and life lesson. Although
22
Phillips, op. cit. p.16
23
20
some of the stories are fictional, they seemed still so popular. There is always mystery need to be told in the stories which is sometimes unexpected happens. Normally people usually predict what is going to happen in the story being told, but they seem cannot wait to hear it. This is the reason why story is liked by many people.
. Another thought why stories are told is because stories are written for
writers have something about human experience to say, and sometimes people tell the stories by showing human beings living differently from what they are now, that sometimes the characters of the story are treated as unique ones. If they are not, then few readers would show their interest in them at all for everyone should
not have the same desire of the character’s role in the story.
However, some stories which are entirely written just to teach about the life or even moral lesson are often told than not flat and bloodless stories. In this story type, the aspect of the lesson is highly emphasized, and then the characters will play the role of acting out the lesson.24
c.
Types of Story
There seemed to be many kinds of story during our life time to be told around us. They were unclassified and being told over and over again to generations.
The most common story to be told is folktales. The term Folktale was long time used for several related kind of stories. Most narrowly, it is a traditional story that has been told from parent to their children over many generations or passed on by countless storytellers.25 They are quite valuable as good story source, the expressions of social and stories, literature and moral teaching. The more, in the language teaching and learning they have many special characteristics that get them exceptionally used. They characteristic of frequent repetitions are excellent for reinforcing new vocabulary.
24
Robert W. Boynton and Maynard Mack, Introduction of the Short Story: Revised Second Edition, (New Jersey: Hayden Book Company, Inc, 1972).p 61.
25
In the beneficial aspect, folktales seemed easier to understand rather than any other types of literature, because they began as oral stories. Some of folktales are also accessible to learners with limited language abilities since they are often published as children’s book easy language and context that provides illustrations of the stories. However, nowadays there are also many more literary retellings of folktales which are difficult.
Therefore, folktales are not easy literature for children only but it is materials provided for every level from beginner to advanced learners. In addition with its varying levels of difficulty, it makes folktales very useful in multilevel classroom.26
d.
Characteristics of Folktales
As mentioned before in the previous sub-chapter that certain characteristics typical in folktales contribute to relatively easy reading.
This will keep happening though there are a lot of variations between one folktale and others or even when the same folktales told by two telling. Those characteristics are:
1) Time-ordered story structure
This means that all materials provided in the story are arranged in time order. Different cultures will have different ways of arranging material but when it comes about the time aspect the idea will be the same, tell
about events in the order they happened. The words first, then after this,
after that, then, finally, are time words structure provided for the story.
2) Repetition and redundancy
Stories that people listen from oral tradition tend to have much more repetition and redundancy than those that do not have. This is not similar when they are listening, they cannot slow down or go back and reread what they have listened or read if they miss something.
26
22
Therefore they can conclude that this aspect will help language learners in several ways such as helping students in acquiring new vocabulary to stick in their mind.
3) Predictability
Folktales have two aspects make them predictable when they are being told; the ethical quality that lies and exists behind many folktales and the repetitions of the main events and ideas.
4) Relatively simple grammar
The oral tales of folktales somewhat have the simple grammar that makes it easier for low-level learners to understand and comprehend. The more folktales in which they are closest to the oral tradition tend to have more simple grammar. This happens naturally because the sentences in the story tend to be short, the common tenses are simple past and present, subordinate clauses are not very common, the conjunction between sentences and ideas relatively simple such as “and” and “but.”
In the more literary forms of folktales, the grammar seemed to be more complex; for the various level of grammatical difficulty means more difficult materials of story, but are still less complex than language people found in essay or academic writing.
5) Concrete vocabulary
6) Concrete ideas
The concreteness of folktales helps learners to understand the content of the story more easily. Even when they are talking about their native language stories, the simple and concrete ideas seemed more acceptable and understandable.
The abstractness and difficulty levels of the ideas affect how hard the text to understand. When the idea presented is easy enough to understand, the learners have more attention to focus on the language used to communicate that idea and they do not spend much energy available for noticing the language and how it is used to convey the meaning.
7) Illustration that provide support and context for the next
Illustrations provide information to help the learners know and find out parts of the story that are difficult to understand. More common illustrations of the story are pictures which are considered as useful illustration for much more than this.
8) A unique reader-writer relationship
Reader and author in folktales are commonly put in the relationship between two peers. Because the storyteller of folktales regard it is not necessarily an authority on morality or the problems addressed in the story. Finally, stories are seemed subjective rather than factual. This helps learners interact with stories as should interact will all writing.27
27
24
B.
Previous Study
Many studies have been carried out related to this research which compares the techniques between song, games and story in teaching vocabulary.
Ruth l. Cathcart-strong has carried out the related study by the title „input
generation by young second language learners’. The purpose of the study was to determine the effectiveness of various types of communicative acts (e.g., requests for information, calls for attention, intention statements, and so on) for eliciting native-speaker input. The study examined some of the spontaneous communicative acts of a group of young second language learners and their native-speaker interlocutors' responses in three play situations. Results showed that while the response rate to some types of utterances was predictable (e.g., to requests for information), others (e.g., calls for, attention) did not generate the expected feedback. In addition, there was an unexpectedly high response rate to other communicative acts, such as statements of intention. These findings are discussed as evidence of superordinate strategies in child discourse. The implications of such behavior for language learning and teaching are discussed,
and classroom applications are suggested.28
Second related study is from Yau Hau Tse, he was conducting the study of Malaysian Teachers‟ Perspectives on Using Songs in English Language Teaching. The objective of this research is to survey the perspectives of English
as a Second Language (ESL) teachers (n= 60) in Malaysian state primary
schools on using songs to teach English to young learners (YLs). Data collection is by means of questionnaires and the findings revealed that teachers have concrete conceptions on the teaching values of songs and its potency in teaching ESL to young children. Yet, the result depicted that teachers had difficulties in selecting songs and the recommendation is to provide them with interesting and enjoyable song materials for their classes. To conclude, songs
28
Ruth L. Cathcart-Strong, Teachers of English to Speakers of Other Languages, Input
can become useful sources to assist language learning and acquisition if teachers
possess the strategies in using them.29
Thirdly, the study was carried out by Patricia on Music Vocabulary of
First-Grade Children: Words Listed for Instruction and Their Actual UseThese
research objectives were developed to provide useful information about what first-grade children already know in relation to what they are expected to learn, and to target the specific words or concepts that might need particular attention in the primary music curriculum. This study's four purposes were to: (1) determine which music vocabulary words were listed for study in first-grade basal music series textbooks; (2) compare the oral vocabulary of first graders with the vocabulary listed for music instruction; (3) look at the relationship between word frequency in the general oral vocabulary of first graders taken from a pre-existing source and the oral music vocabulary of 42first graders interviewed in the present study; and (4) compare the frequency of selected music terms with the frequency of those same terms used in general oral vocabulary. Little consistency was found in the music vocabulary listed in three basal music series text-books. Forty of a total 147 music words were listed in more than one of the textbooks, and 23 of the 40 terms were already within the general oral vocabulary of first grade children. A correlation of .82 was found between oral music vocabulary and general vocabulary, suggesting that children possess a lexicon that is used to describe their various life experiences, and that music words are not reserved specifically for discussions about music. Finally, 110 words were selected and compared on their frequency of use in music and
general vocabularies.30
29
Andrew Yau Hau Tse, Malaysian Teachers‟ Perspectives on Using Songs in English Language Teaching, Vol. 5, pp. 87-89
30
Patricia J. Flowers, Music Vocabulary of First-Grade Children: Words Listed for Instruction
26
C.
Theoretical Framework
Vocabulary is an important component of a language. This would be one condition to know language for learner of a target language, especially young learners. Teaching vocabulary is not an easy task, though in fact when teachers are teaching young learners they only teach the individual words of the language that they expect learners to acquire
.
Therefore, the appropriate techniques inteaching vocabulary play the important role for them to gain their mastery of
vocabulary which will be useful to understand many simple English texts written in daily life.
The selection of some appropriate techniques will affect learners’ ways of
learning when they are applied. One of factors affects learners’ motivation to be low when learning is that teachers tend to teach vocabulary by similar methods in
everyday, it has a tendency of appearing learners’ boring when learning.
Therefore, techniques of teaching vocabulary relates to vocabulary achievement, for their ways to learn will determine their comprehension. Learners’ comfort in acquiring, absorbing and processing knowledge can be said that it depends on what techniques selected in teaching and learning.
28
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A.
Place and Time of Research
This study takes a place at Madrasah Ibtidaiyyah Pembangunan UIN Jakarta in the First Semester of lesson year 2014/2015. Writer takes a study under the authority which the headmaster of the school has handed over. The study are
held from October 21st 2014 to December 5th 2014.
B.
Respondents of The Study
The respondents of this study are English teachers of Madrasah Ibtidaiyyah Pembangunan UIN Jakarta. Here are some respondents who will participate in the study, those are written as follows:
First of all is the first Respondent. English teacher of first and second grade of MI Pembangunan with NUPTK 4653-7606-6121-0122 and NRG (Teacher Registration Number) 121572198021, she was born in Sukabumi, on March 21st 1982. She has been teaching English since July 1st 2005, thus it has been 9 years and 3 months up to now since 2005. She was graduated from English Education Program of UIN Islamic State University Syarif Hidayatullah in 2005. Her teaching hour is 26 hours and now she lives in Gg. Bungur No. 36 D. Pisangan Ciputat.
Education Program in 2013. Now she lives in Jln. Rawa Kopi no. 101 Pangkalan Jatibaru - Kec. Limo Depok.
Finally, the last but not least is the third Respondent, English teacher with NUPTK: 7642 7586 5921 0122 and NRG: 111572157001. She was born in
Bekasi, March 10th 1980, she is now teaching for fourth and fifth grade with 26
hours of teaching. Her last educational background is English Education Program at UIN Syarif Hidayatullah which she graduated in 2013. She has been teaching
in MI Pembangunan since July 20th 2005. She now lives in PERUM Muslim
Al-Fallah 3 Blok EI No.1 RT.02/RW.21 Pondok Benda Pamulang.
C.
Method, Design and Procedure of The Research
This research is categorized as a qualitative study. Similar to other types of research, methods of the research are factors that determine how the research is going to run. Method is called a process, procedure which used to approach the problem and find the answer. In other words, methodology is a general approach to examine the research topic.
This study takes a qualitative descriptive method which will take teachers’ perspectives as the primary data. The form of qualitative descriptive in general is carried out in type of qualitative study research. Its form is concerning to one unit which is determined from some phenomena. This feature makes the study possible to reach the deeper information and this will be the consideration in this model of research.1
At last, obviously it is possible to conduct the deeper study about the
difference between three techniques commonly used to teach English in this case
vocabulary to young learners according to teachers’ perspectives. The respondent
of this study will be the teacher who has applied some techniques in teaching vocabulary to young learners and the focus is the difference of the Games, Song, Story and other techniques in teaching vocabulary.
30
D.
Technique of Collecting Data
In the qualitative research, the researcher is a live instrument to measure the focus of the research. One element should not be forgotten is instrument. This instrument latter on will be used for collecting data. In this case, observation, questionnaire, and interview are selected the as his instrument to be attributed with him.
1. Questionnaire
Questionnaire was designed based on the theory of the using song, story,
and games techniques to the teaching vocabulary. The questionnaire focuses on
Teachers’ perception of techniques used during lesson time.
2. Interview
Interview simply means some questions which have been provided for respondent in the study about research topic in face to face situation. The answers mentioned by the respondent are recorded and transcribed. Burhan Bungin stated that interview generally has type of subject and object that are put into some categories.2 One of those categories is the interview which is done to someone by one individual or the researcher. This category represented what is going to be carried out in his research that the researcher will interview teacher who applies common techniques in teaching vocabulary to young learners. Thus the teacher will be the individual interviewee.
Secondly, the interviewee is some individuals in a group which are interviewed by someone or researcher. In line with this category, the research plans to visit class where the teachers teach English vocabulary using common techniques.
3. Observation
The classroom observation is used to find out the practice of learning and teaching vocabulary and what techniques commonly used by teacher. The data collected from here (observation) will be only the primary data as well. Researcher observes directly to the object of the research to check closely the activity of teaching and learning which is being done. There are two types of observation; participatory observation and non participatory one. The non participatory observation type will be carried out in this research, which the writer as the researcher is not included as a participant in the activity.3
E.
Technique of Checking The Data Validity
It can be seen from the instrument made that the data collecting will be the primary information source. The primary data can be achieved through field study, in form of observation, interview with the questionnaire. To check the data to be valid, the triangulation technique is used.
1)
Triangulation
After all the data are collected, Triangulation is conducted to the data will
be carried out. In collecting the data, Triangulation means as a technique of data checking that tends to combine many data sources existed.
In defining what triangulation is, Susan Stainback stated that the aim is not to determine the truth about some social phenomenon, rather the purpose of the triangulation is to increase one’s understanding of whatever is being investigated. In line with Susan, Bogdan as cited in Sugiono also adds that:
3 Dr. Sudaryono, Educational Research Methodology, (Jakarta Pusat: Lentera Ilmu Cendikia,
32
“What the qualitative researcher is interested in is not truth perse, but rather perspectives. Thus, rather than trying to determine the “truth” of people’s perceptions, the purpose of corroboration (Triangulation) is to help researchers increase their understanding and the probability that their finding will be seen as credible or worthy of consideration by others”4
Thus, each respondent will be interviewed with the same techniques of interviewing and then the data are going to be combined until they complete each other.
2)
Technique of Data Analysis
The analyzing of the data is the process to find out and arrange systematically the acquired data from the interview which has been done, documentation, and field notes by organizing the data into some category, selecting the most crucial subject to be studied, and making the understandable conclusion for the reader or anyone else.5
Miles and Huberman give a concept of analyzing the data that seemed to be fitted on his research. The concept contains the meaning that the activity in the qualitative data analyzing is carried out interactively in each of phase of the research until it reached its limit.
There are some components that build up the model of analyzing the data:6
1. Data Reduction
If the acquired data report has a big amount of information, then the writer shall need to carefully write the detail information needed of the research. Reducing means to summary, select the fundamental aspects, concern to find the important factors, theme and its pattern.
4
Prof. Dr. Sugiyono, Metode Penelitian Pendidikan (Pendeketan Kuantitatif, Kualitatif, dan
R&D), (Bandung : Alfabeta, 2009), cet. IX, p. 241
5
Ibid., p. 329.
2. Data Display
After reducing the data, the next phase will be displaying the data. Displaying the data can be done in form of brief summary, draft, relation between category, flowchart and etc.
In this study, the result of the observation will be presented by words and table of calculation of simple statistic adapted from Statistika Untuk Analisis Data Penelitian by Susetyo.7 The statistic is used to calculate the the frequency of the techniques which are used by respondents. The adapted calculation result will be presented in the statistic Table as shown below.
Table
Frequency of Technique Use
3. Conclusion Drawing/Verification
The beginning conclusion stated characteristically temporary, and changeable if there found strong evidence that holds on to the next phase. But it would not be if the first stated conclusion is supported by some valid and consistent evidences when the researcher is back to the field study to collect the data, then it can be concluded that the conclusion is credible one.
3)
Unit of Analysis
In this study, the writer used the data of interview with the teacher as the major data which are analyzed to find out the most appropriate techniques used between three commonly techniques used in teaching English to students of primary school.
7
Dr. Budi Susetyo, M.Pd., Statistika Untuk Analisis Data Penelitian, (Bandung: PT Refika Aditama,
2010), p. 40-42
Technique Types M1-M4/M5 Total %
(-)
(-) (-) (-) (-)
[image:45.612.104.537.88.608.2]34
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS
A.
Findings
The presenting of findings in this section are based on the research questions which focus on the techniques commonly used by English Young
Learners (EYL) teacher in the classroom, the most frequent applicable
technique to be used in teaching EYL based on teachers’ perception. The
findings of the observation, interview and questionnaire are presented in separated description coordinated to each research question.
The questionnaire is answered by three English teachers of MI Pembangunan UIN Syarif Hidayatullah who have a role as the respondents to this study. In addition, the result of the teaching classroom observation is presented after the presenting of the interview is done. There are also list of aspects that should be noticed in the questionnaire given to respondents which is attached in Appendix 3. Some kinds and type of techniques are written down based on teaching activity done by teachers during the observation in the observation notes which is available in Appendix 5.
The function of the observation is to give more supporting information to the data obtained from the respondents in the interview. The first
respondent is the teacher who teaches 1st and 2nd grade, the second respondent
is available in fourth grade. And the last but not least is the third respondent who teaches the 3rd grade.
The complete question of the interview and the answer received during the question and answering are available and can be seen in the Appendix 4.
been carried out, and the observation of three respondents will be analyzed. Some tables are used as the result of the simple statistic calculation of the frequency of technique use.
1.
Frequency of Techniques Use
In this section, the acquired data from three techniques of data collecting will be described to show the effectiveness of the techniques based
on three respondents’ perspectives and used in the teaching English
vocabulary.
a. Classification of 1stRespondent’s Data
1) Questionnaire
From questionnaire that has been distributed to the first respondent, teacher of the first and second grade. She filled up the questionnaire based on her opinion and perspective of teaching English to Young Learners. Between three components of language provided to be chosen, she selected vocabulary and pronunciation, it is her response to the question of what language component of her students that she thinks she needs to improve and develop. In number two of questionnaire, it is question of what language skills of her students she thinks she needs to improve and develop. She selected only listening and speaking even though it is written in the instruction of the questionnaire that the respondent is able to fill more than one or more.
36
of questions in the questionnaire which is here the respondent is required
to rank the optional answers (# 1, 2, 3,…) started from the answer which
is considered as the most important. From the first question she ranked vocabulary as the first aspect of language component which is appropriate to be improved in teaching English to young learners. She then ranked pronunciation as the second and grammar as the third. In the question number five, the respondent is asked to also give numbers or rank the skills of language which is most important for young learners. It looks similar with the previous question.
As what she has already done to the previous question, here she ranked listening as the first and speaking as second skill which is important and need to be improved. From the four language skills provided for respondents to fill in with giving ranking to which one is most necessary to develop, the first respondent gave the first ranking to listening, the second to speaking, then to reading and the last is writing, she assumed that listening is the first ability of human. In the last question of questionnaire of among many techniques of teaching EYL the respondent put games in the first ranking as the most frequent technique to be used in teaching and learning English, then it is followed by song that she ranked as the second most frequent technique based on her perspective.
As the result of questionnaire has been interpreted, the writer then