(A case Study At the Second Year Students of Mts Muhammadiyah 1 Ciputat) The Skripsi
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiya and Teachers’ Training in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Strata One (S1)
Degree of English Language Education.
SUDIRMAN 105014000363
DEPARTEMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
THE FACULTY OF TARBIYA AND TEACHERS’ TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
(A case Study At the Second Year Students of Mts Muhammadiyah 1 Ciputat)
By:
SUDIRMAN NIM: 105014000363
Approved by: ADVISOR
DRS. NASIPUDDIN DJALIL,M.Ag NIP.195605601990031002
DEPARTEMENT OF ENGLISH EDUCATION
THE FACULTY OF TARBIYA AND TEACHERS’ TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
certified that the „Skripsi’ (Scientific) entitle “Analysis on students’ difficulties in learning Modal Auxiliaries ‘CAN’ and ‘COULD’ (A case Study At the Second Year Students of Mts Muhammadiyah 1 Ciputat)”, written by Sudirman, student’s registration number: 105014000363, was examined by the Committee on March 7th 2011 at examination session of state Islamic university (UIN) Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta. This “ Skripsi” has fulfilled one of the requirement for academic title of „S.Pd. (Bachelor of Art)’ in English Language Education at the Department of English Education.
Jakarta, March 07th, 2011
EXAMINATION COMMITTEE
CHAIRMAN : Drs. Syauki,M.Pd ( )
NIP:196412121991031002
SECRETARY : Neneng Sunengsih, M.Pd ( )
NIP:197306251999032001
EXAMINER I : Drs. Syauki,M.Pd ( )
NIP:196412121991031002
EXAMINER II : Dr. Fahriany, M.Pd ( )
NIP:197006111991012001
Acknowledged by;
Dean of Tarbiya and Teacher Training Faculty
Bismillahirrahmanirrahim I herein undersigned:
Name : Sudirman
Nim : 105014000363
Faculty : faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training
Title of skripsi : Analysis on students’ difficulties in learning Modal Auxiliaries „CAN’ and COULD’ (A case Study At the Second Year Students of Mts Muhammadiyah 1 Ciputat)
Hereto I declare that:
1. This “skripsi” constitutes my original opus result proposed for the partial fulfillment of the requirements for Strata One Degree(S1) at State Islamic University Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta.
2. Any source that I utilize in this paper writing has been attached by Me correspond to prevailing rule at state Islamic University Syarif
Hidayatullah Jakarta.
3. If once there is an evident proves that this paper is not my Original opus or an opus of other, I have the honor to accept sanction based on the
prevailing law at State Islamic University Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta.
Jakarta, October 16th ,2010 The writer
i „Can’ and „Could’
(A case Study At the Second Year Students of Mts Muhammadiyah 1 Ciputat)English Departement Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teacher Training Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University Jakarta.
Advisor : Drs. Nasipuddin Djalil, M.Ag
Key words : Students’ difficulties and Modal Auxiliaries.
The study is aimed to know the problem faced by the second grade students of MTs Muhammadiyah 1 Ciputat in learning modal Auxiliary, the writer wants to give a description in learning modal Auxiliary especially in Can and
Could, to make it easy for the students. The writer wants to know not only their reason in difficulties in using modal Auxiliaries but also the level of students’ comprehension in using modal Auxiliaries.
To collect data, the writer observes the second grade students of Mts Muhammadiyah 1 Ciputat by giving the test and interview the students who got low score. The writer uses a descriptive analysis technique with visiting the school to do research, the writer gives them the test about Modal Auxiliary in meaning, function and form.
ii
Auxiliary „Can’ dan „Could’. ( study kasus di di kelas Dua Mts Muhammadyh 1 Ciputat) Jurusan Bahasa Inggris, fakultas Ilmu Tarbiyah dan Keguruan Universitas Islam Negri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta .
Pembimbing : Drs. Nasipuddin Djalil, M.Ag
Kata Kunci : Kesulitan Siswa dan Modal Auxiliary
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengetahui permasalahan yang di hadapi siswa kelas dua Madrasah Tsanawiyah (Mts) Muhammadiyah 1 Ciputat dalam mempelajari Modal Auxiliary, penulis ingin memberikan penjelasan dalam mempelajari Modal Auxiliary khususnya „Can’ dan „Could’ agar bisa di pahami oleh pelajar. Penulis tidak hanya ingin mengetahui alasan mereka dalam mengalami kesulitan belajar Modal Auxiliary, tetapi juga tingkat pemahaman pelajar dalam Modal Auxiliary.
Dalam pengumpulan data, penulis mengamati pelajar kelas Dua madrasah Tsanawiyah (Mts) Muhammadiyah 1 Ciputat dengan memberikan tes dan melakukan wawancara terhadap siswa yang mendapatkan nilai rendah. Penulis menggunakan tehnik analis descriptive yang mana dengan mengunjungi sekolah untuk melakukan penelitian, yaitu penulis memberikan tes tentang modal Auxiliary pada arti, pungsi dan bentuk.
iii In the name of Allah the Beneficent the Merciful.
All praise be to Allah, Lord of the World, who has blessed and given the writer abundant mercies, helps and guidance so that he could complete this “skripsi” properly; peace and blessing be upon the prophet Muhammad (peace be upon him),his families, his companions, and his followers.
The writer is absolutely consious that he could not carry out this work without helping of others either in materiality or in spirituality.
On this great occasion, he would like to express his greatest honor to his beloved parents: H. Jubed, his father, Hj. Hasanah, his mother; who have given him the meaningful things and much love that never end so that he could finish his study,and also to his brother and his sister: H.Solehudin, Hj.Jumsi Ayu lestari and Ani FitriAni, who have prayed him and have given huge spirit and motivation, and the whole family who have given him the moral encouragment to finish this “skripsi”. He is proud to be part of all.
The writer does not forget to express his great appreciation and gratitude to his advisor, Drs Nasipuddin Djalil, M.Ag, for his huge motivation, spirit and sincerity in guiding him to carry out this work from the beginning to the end. The writer also wishes to express acknowledgement and deep gatitude to:
1. Prof. Dr. Dede Rosyada, MA, the dean of the Faculty of tarbiya and Teachers’ Training, Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic Univeristy, Jakarta. 2. Drs. Syauki, M.Pd, the head of English Departement.
3. Neneng Sunengsih, M.Pd, the Secretary of English Departement.
4. All lecturers of English Departement who have taught and educated the writer during his study in Syarif hidayatullah State Islamic University, jakarta.
5. Drs. Euis Amalia, the headmaster of Mts Muhammadiyah 1 Ciputat, who
has allowed him to observe the school.
6. Eni S.pd, and Marfuah S.Pd, the English teacher of Mts Muhammadiyah 1
iv
7. The librarians of Syarif Hidayatullah State Islamic University UIN Jakarta, IAIN Banten and ATMAJAYA who have him opportunity to overview the books and reference concerning with the topic discussed in this “skripsi”.
Finally, the words can not be enough to be expressed, except praise be to Allah the lord of the world, for his blessing and quidence. May this “skripsi” be useful to every one, particulary for the writer and the reader in general. Also the writer realizes that this “Skripsi” is far from being perfect. It is a pleasure for him to receive contructive critics and suggestion from everyone who read this “skripsi”. May Allah grant our wishes. Amien.
Ciputat, 03 Desember 2010
v
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... ii
TABLE OF CONTENT ... iv
LIST OF TABLE ... vii
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. Background of the study ... 1
B. Limitation of the study ... 4
C. Formulation of the study ... 4
D. Use of study ... 5
E. Organization of study ... 5
CHAPTER II THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK A. Modal Auxiliaries 1. Definition of modal ... 6
2. Kinds of modal Auxiliary... 7
3. Sentence pattence of Modal ... 9
B. Modal Auxiliaries: CAN and COULD 1. Usage Of CAN and COULD... 9
2. Meaning of Modal Auxiliaries; CAN and COULD .. 10
C. The students’ difficulties in using modal Auxiliary ... 14
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METODOLOGY A. Purpose of the Research ... 20
B. Place and Time of Research ... 20
C. Method of Research ... 20
D. Population and sample ... 21
E. Technique of Data Collection ... 21
vi
C. Data Interpretation ... 29
CHAPTER V CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
A. Conclusion ... 31 B. Suggestion ... 32
vii
Table 4.2 Modal auxiliaries area and each item ... 24
Table 4.3 The items of modal auxiliary form... 24
Table 4.4 Frequency of Error in Can ... 24
Table 4.5 Frequency of Error in Could ... 25
Table 4.6 Frequency of Error in Modal Auxiliaries Form ... 26
Table 4.7 The internal and external factors which caused the students’ difficulties ... 27
1 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Study
Nowadays, it is acknowledged that English is one of the well known languages in the world. It has become the most widely studied foreign language on the earth.1 English language is an international language that is mostly utilized by the word society to get interracial interaction and communication. One of the importhant thing for prefaring in that comunication is mastering the internasional language, English, whether it is in written form or in spoken form. As an internasional language, English is spoken by most of the people all over the world. It is getting more important. Many countries use English to communicate and convey message or idea to others.
One of the the language which is taught in the school of our country is English language. English is one of the internasional language that have an important role in the world. It is widely studied and used as a tool of communication among people all over the world. English becomes one of the important subject matter taught at school. In Indonesi,a English is considered at the first foreign language and becomes compulsary subject learned by all the student from the elemtery up to university level.
1
Jack C. Richards and Theodore S. Rodgers, Approaches and Methods in language
The students study English In the school or in the Course, they expect to learn some abilities, such as ability to listen of English sound, the ability to read and understand English Book, the ability to speak English, and ability to write English. Those are Abilities of “Language skills” (Listening, Speaking, reading and Writing). Beside the four skills, the students have to master language components. One of the language components is grammar and its components are such as morphology, syntax and so on. Grammar is also needed even in the communication because it can avoid misunderstanding. By mastering grammar, it is hoped that he/she can share the information and be proves that he or she is capable in English.
Grammar is an important element to be learned in learning a language because it is used to understand the language. Language without grammar can cause confusion in comprehending the ideas, opinions, feelings of the person who expresses oral or written. English person who is good at grammar can communicate with language better than person that is low at grammar.
Grammar is one of the language aspects which is taught to every language learner. It is as the basic knowledge and as important role in understanding the English language. “Grammar is partly the study of what forms (or structures) are possible in a language. Traditionally, grammar is a description of the rules that govern how language’s sentences are formed”.2
According to As Paul Robert:“grammar is a body of generalization about how people say things”.3
Students who learn a foreign language encounter a number of problems, especially with the grammar of the language which are complicated
2
Scott Thornburry, How to teach grammar, (England: Pearson Education Limited. 1999),p.1
and which make confusing. When the students learn English, they try to avoid the grammar because it is confusing and difficult to understand. For some students who have a lack of knowledge in grammar, of course they will get confused how many different meaning of the verb “in spoken or in writtent”, why the verb in sentence must change, etc. There for to make them not confused anymore, they have to master grammar. By mastering it they will understand the rules and how the sentences are constructed.
There are many aspects discussed in English grammar one of them is “modal Auxiliaries”. or “modal verb” are: can, could, will, would, shall, should, may, might, and must. These auxiliaries add to a special semantic component such as Ability, obligation, possibility. They have special grammatical features, have more than one meaning, and also complex. Some modal change meaning in the negative must be expressed with other auxiliaries. Eventhough the modals are used only with the simple form of the verb. And here the students still have difficulties to make the sentence using auxiliaries and to decide the meaning of the modal.
There are two factors that make learning difficulty. The first one is the internal factors which include physiology factors and psychology factors. And the second one is the internal factors which includes non social factors and social factors.4
Beside factors above, here the error of the students is for example: they have no infinitive and the third person singular no’s’. The modal verbs have not only a grammatical function, but also a dictionary meaning (must and can mean „be obligate to’),for example in sentence : we must study hard for English test. But in reality some student still makes mistakes and finds difficulty in identifying modal. Here are examples of wrong sentence that are often made by the student in using the form of modal.
- We must to study hard for English test
- He can to speak English
4
Abu Ahmadi & Widodo Supriyono, Psikologi Belajar, (Jakarta: PT. Rineke
- She could spoke English well, and soon
In this case, the writer is interested to analyze the student’s difficulty in learning some modal auxiliaries entitled “ Analysis on students’ difficulties in learning Modal Auxiliaries ‘CAN’ and ‘COULD’ “ (A case Study At the Second Year Students of Mts Muhammadiyah 1 Ciputat). It is because there are many students who still face difficulty in understanding the meaning, theorycal and the form of modal Auxiliaries. By observing the student’s difficulties, the writer tries to identify and analyze them. The writer hopes it can help the teachers in teaching and learning process.
B. Limitation of the Study
It is essential to limit the problem in order to avoid misunderstanding in interpreting the problem. The writer limits the problem in this writing only in the student’s difficulties in learning modal auxiliaries. They are: Both Can and could and the reasons why the students find difficulties in learning modal Auxiliaries.
C. Formulation of the Study
Based on the statement in the background of the study described above, it is necessary to analyze the students’ difficulties in learning modal auxiliaries at second year students of MTs Muhammadiyah 1 Ciputat. The general question of this study is “Do the second year students of MTs Muhammadiyah 1 find difficulties in learning modal auxiliaries?”
To specify this problem, the specific research questions are formulated as follows:
1. What difficulties are faced by the students in learning some modal auxiliaries?
D. Use of the Study
This paper is intended to find out the difficulties faced by the second year student of Mts Muhammadiyah 1 Ciputat, to analyze the reason why the students face the difficulties in learning modal auxiliaries, to enlarge the writer’s knowledge in their grammar especially in learning some modal auxiliaries.
E. Organization of the Study
In discussing the topic, the writer divides this study into five chapters as follows:
Chapter one is introduction, involving the background of study, the limitation of problem, the formulation of study, the use of study and the organization of study.
In Chapter two, the writer will discuss about Theoretical framework. This chapter will be divided into three sub chapters. The first is talking about Modal Auxiliaries, kinds of modal, form of modals and meaning of modals. The second is talking about Modal Auxiliaries: Can and Could, usage of Can and could, and similar expression of Can and Could. The third is talking about students difficulties in learning Modal Auxiliaries of Can and Could.
Chapter three presents the implementation of the research methodology which consists of the purpose of study, the place and time, the method of study, the population and sample, the technique of data collection, and the technique of data Analysis.
Chapter four present the implementation of research finding which comprises of data description, data analysis, and data interpretation.
6 CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
A. Modal Auxiliaries
1. Definition of Modal auxiliaries
Modal auxilary or called modal verbs may sound difficult but in fact they are easy. They are invariable (no conjuntion). And the main verb is always the “bare ifinitive” (without “to”). Modal auxiliaries generally express a speaker’s attitudes, or “mood”. For example, modal can express that a speaker feels something necessary, advisable, permissible, possible, or probable; and in addition, they can convey the strength of these attitudes.1 These are the modal verb can, could, may, might, must, will, would, shall, should, ought, and need. They are different from the other three auxiliary verbs (do, be and have) in two ways. Firstly, they have special grammatical features (for instance, they have no infinitive and the third person singular has no s). And secondly, most modal verbs have not only a grammatical function, but also a “dictionary meaning”: for instance, must can mean „be obliged to’.(do, be and have do not really have “meaning”) of this kind when they are used as auxiliary verbs).2
Modal verb is technical one of these verb form: can, could, may, might, shall, should, will, would, must, ought to, used to, need, had
1
Michael Swam, Practical English Usage, (Oxford: Oxford university press.1980),p.90 2
Betty Schramfer Azhar, Understanding and using English Grammar 2nd Edition, (New
better, and dare. They are all used with others verb to change their meaning by expressing ideas such as possibility, permission, or intension.3 And according to Irma Rosita Gloria Barus, et.al:“modal auxiliaries adalah suatu bentuk atau kategori dalam tata bahasa inggris yang berfungsi sebagai pembantu kata kerja (auxiliaries) yang salah satu pungsinya adalah untuk menunjukan kebenaran, prakiraan, atau kemungkinan”. (modal auxiliaries are kinds or categories in grammar which function as auxiliaries such as for showing the truth, prediction, or possibility). 4
And modal verb is different from auxiliary verb (or 'helping') verbs that are used together with other verbs to 'help' them particular grammatical functions or meanings (for instance, to make questions, or to form tenses). In English, a lot of important meanings are expressed by changes in the verb, for example: questioning, negation, time, completion, continuation, repetition, willingness, possibility, and obligation. But English verb do not have many different forms, (e.g. see, sees, seeing, saw, seen). So to express these meanings, a number of auxiliary verbs are used such as do, be, and have.
Do is used to make question and negative form of simple tenses, and for some other purposes. Be is used with participles (-ing and –ed form) to make progressive and passive verb-form. Have is used to make perfect verb forms. Do, be, and have also have other 'non-auxiliary' uses.5
In conclusion, modal auxiliaries are functional words that help verbs to express specific meaning such as ability, probability, possibility, obligatory, etc.
2. Kinds of Modal Auxiliary
In English, such verbs have largely replaced the subjunctive mood, and three kinds of modality can be distinguished for them: (1) epistemic modality, which expresses a judgment about the truth of a proposition
3Longman Dictionary,…p.916 4
Irma Rosita Gloria Barus dkk, Bahasa Inggris II, (Jakarta: Pusat Penerbitan Universitas Terbuka. 2004), p.24
5
(whether it is possible, probable, or necessarily true): John may be in his office. (2) Deontic modality, which involves the giving of directives (in terms of such notions as permission and obligation): You must leave immediately. (3) Dynamic modality, which describes such properties as ability and volition to the subject of the sentence: 6I can come. Often the same modal verb is used for more than one kind of modality: may for possibility (It may rain tomorrow) and permission (You may smoke now);
must for necessity (The plane must have landed by now) an obligation (I must go).
According to Betty Schramfer Azhar, the types of Modal Auxiliaries can be divided into two kinds. First, modal auxiliaries with different meaning such as: can, could, had better, may, might, must, ought to, shall, should, will, and would. Second, modal auxililaries with similar expression such as: be able to, be going to be supposed to, be to, have to, have got to, used to.7
Modal and semi modals can be grouped into three major categories according to their main meaning (excluding used to, which relates to past time).
a. Permission/possibility/ability: can, could, may, might
b. Obligation/ necessity: must, should, had better, Have (got)to, need to, ought to, be supposed to
c. Volition/prediction: will, would, shall, be going to.8
Can and could are modal auxiliaries that used to assist verb to express ability, possibility and permission. Like other modal auxiliaries Can and Could are usually placed before the predicates of the sentence in positive sentence, for example: I can swim, he could play guitar. In negative sentence, modal need "not" between modal and verb, for
6 http://www.encyclopedia.com/doc/1O29-MODALVERB.html
7
Betty Schramfer Azhar, Understanding and using English Grammar …,p.68
8
example: I cannot swim, he could not play guitar. In interrogative sentence, for example: Can I swim? Could he play guitar?
3. Sentence pattence of modal
Sentence is a group of word that contains at least object and one verb. A sentence expresses a complete thought.9
a. Positive sentence
The pattern of modal auxilaries in the positive sentence is:
e.g:Rifah can speak English well b. Negative sentence
The pattern of modal auxilaries in the negative sentence is:
e.g: Rifah can not speak English well c. Introgative sentence
The pattern of modal auxilaries in the introgative sentence is:
e.g: Can she speak english well?
B. Modal Auxiliaries : CAN and COULD
1. Usage of modal :Can and Could
Can is used informally to request permission, especially if the speaker is talking to someone he/she kows fairly well.10
The detail functions of Can are followed. a. To express the ability.
e.g: - I can speak three foreign language.
b. To express reguest or asking to someone else for doing sometning. e.g : Can you help me?
9
Alice Oshima Anna Oaline, Introduction to Academic Writting 3rd edition.(New York: pearson education,inc.2007).p,11
10
Betty Schramfer Azhar,...p.68
S + modal auxilaries + V (infinitive without „to’+o/c)
S + modal auxilaries +not+ V (infinitive without „to’+o/c)
c. To express asking or giving permission. e. To express offering something to someone else.
e.g: can I get you some tea?11
The detail functions of Could are followed.
a. Could expresses ability, subject to certain conditions which probably do not exist. In this use, could can refer to the present, the past, or the future.
e.g: I could go now, if I wanted to. (I do not want to)
b. Could is used to request permission. It is somewhat more formal and polite than can.
e.g: Could I borrow your money?
c. Could is used to expres the abbility in the fast. e.g: when I was younger, I could run fast.12 d. Could also expresses the possibility.
e.g: he could be very busy at that time.
2. Meaning of Modals Auxiliaries; Can and Could
According to Michael Swam, there are five meaning of can and could, namely to express ability, to show possibility, to indicate permission, offers, and to express request and order.13
11
a. Ability; Can and Could
To talk about future ability, can is often possible when people make present decisions about future ability.
- We can talk about that later
2) Conditional Could
Another meaning of could with expresses an ability, can also be found in conditional sentence such as:
- I could have a really good time if I had a flat of my own. - I could break your neck if I want!
b. Possibility: Can and Could.
Another meaning of can and could is to show possibility of something. Detailed explanations are as follows:
1) Theoretical possibility
Can is used to say that events and situations are possible (without taking about the chances of them actually happening)
- How many elephant can fit into a mini?
Sentence with can often give information about the characteristic behaviors of people or things.
- Scotland can be very warm in September. - Gold can't be dissolved in hydrochloric acid.
To talk about the past, could is used
- My mother could be very unpleasant at times.
14
Can also used to make suggestions about possible solutions to a problem, or possible actions.
- Here there are three choices: we can go to the police, we can talk to peter ourselves, or we can forget all about it.
- 'What shall we do?' – 'We can try asking Lucy for help. ' Can we meet again tomorrow?
In order to make suggestions more 'tentative' – less strong or definite, the writer used Could.
- We could try asking Lucy, if you think it's a good idea. - Could we meet again tomorrow?
'Suggestions' are sometimes really requests or orders. - You could give me a hand with the cooking.
2) Change
a) Future possibility. The writer don't use can to say that there is a change that something will happen.
b) Present possibility. Could are also used to say that something is possibly true at the moment of speaking.
- You couldbe right, but I don’t think you are
- This could be your big chance
Can is sometimes used to talk about present possibility, but only in question and negative sentences.
- Who can that be at the door?
- It can be true. She must be mistaken.15
15
c. Permission: Can and Could
Can and Could also have meaning to indicate permission. The following details are the use of can and could to express permission.16
1) Asking for permission
Can and could are all used in asking for permission. Can is probably the commenest of the two (though some people consider that can is „not correct’) given, may is not usually used.
- It’s not fair. Joey can stay up till ten and have to go to bed at
When I lived at home, I could watch TV whenever I wanted to.
But the writer don’t use could to talk about permission for one particular action in past.
16
- I was allowed to see her yesterday evening. (Not:* I could see her...)17
d. Offers; can and could
Can and Could are also often used to offer something to another people. To make offers more polite could is used more approprite than can. The following examples are some of the use when could and can express offers.
- I canlend you the money till tommorow, if you need it. - I could do shopping for you, if you are tired.
- Can I carry your luggage?
- Could I give You dinner tonight? e. Request and Order: can and could
Can and Could are also used to make someone to do something, or to
C. Students’ difficulties in using CAN and COULD
Modal auxilaries are among the more difficult structure ESL and English teacher have to deal with. One of the reasons for his is the form of modals. The students,who have been told time to time again that present-tense verb with third person singular subjects require an-s ending, overgeneralize this rule to modals this rule to modals- for example,* He cans play tennis.
17
And the main verb (modal auxilaries) is always the bare infinitive (infinitive without “to”). It is can not say: he can to play tennis or He could to play tennis but He can play tennis or He could play tennis. This overgeneralization results in error because in English modal Auxilaries (can, could,may,will,etc) are distinguished from other auxilariey verb (be, have, do) as well as from ordinary verbs by their lack of tense and their resultant lack of subject-verb agreement; that is, modals do not inflect.
In English, modals are derived from verb that did carry tense and take agreement markers during a much earlier stages of the language. It is thus important to emphasize to learners that English no longer inflects modals for tense and number. Another formal property of modals that may cause your students some trouble is that modal directly precede a verb without the intervening infinitive to that is required when two ordinary verbs follow each other in sequence.18
Modal+ verb verb +verb
I can go I want to go.
*I can to go *I want go.
Many of the students will treat modals like ordinary verbs and produce error by using a superfluous infinitive to: * Jack must to Study Harder.
The biggest problem of ESL students face with modals is their meaning. Each modal can have more than one meaning and each meaning is a member of an inter-related system. When a speaker chooses to use one modal, s/he is deciding not to use any of the other modals, thereby indicating the degree of emphasis."The problem lies not in the surface positioning of modals nor in their wide range of meanings, but in associating the right modal with the right meaning." The difficulties, in interpreting an already complex system, have often been compounded by teaching methods that present modals as a list. Students memorize the modals with their accompanying
18
Diane Larsen Freeman and Marianne Murcia ,THE GRAMMAR BOOK An ESL/EFL
meanings, but they may have no idea of the subtle social and cultural information each choice conveys.19
Modals can also appear in the perfect aspect with a have + -en construction. This can also be a difficult area for students. The problems students experience with the perfect modal construction can be attributed to the fact that they often believe the addition of the perfect construction adds "perfectiveness" to the meaning.
Beside that, the difficulties in learning modal auxiliaries were caused by internal factor; the factor comes from inside of the students, such as Interest, motivation, mental health and talent. As Muhibin Syah said “ The internal factor is divided into aspects; physiological aspect and psychological aspect”.20
1. Physiological Aspect
This aspect is about the conditions of the students’ body from every part of the body. For instance, when the students got headache, they could not study well. The condition of the body can influence students’ intensity and spirits in studying. So, if their bodies are healthy, they can study well; can receive the information about what they are learning and can get a good achievement. However, if they are not, it will influence too. The students become lazy and no spirit to study.
2. Psychological Aspect
This factor emphasize on the inside conditions of the students. It consists of the students’ intelligence, talent, interest, motivation, mental health and special types of learner.
a. Intelligence
they will face the difficulties, especially in their learning. The higher IQ that students have, the higher achievement they will get.
b. Talent
Talent is the basic potential or basic competence which is gotten from born.
Everyone has different talent. Someone will be easy learning something that is not suitable with their talent will get bored, give up and unhappy.
c. Interest
Interest is a tendency and high spirit or desire to something. The students’ interest can be seen by the way students follow the learning process, complete or incomplete their note and pay attention to the italic word in those learning. Without interesting to the learning process, they will get learning difficulties. So, for those who have high interest in learning process, they will study hard to get what they want happily. Nevertheless, for those who have less interest in learning process, they will study just as long as they want.
d. Motivation
Motivation is as inner factor that functions for making, basing and pointing to the learning. Students’ motivation can determine good or bad in their learning achievement. The higher motivation they have, the higher learning success they will get.
Furthermore, there are two kinds of motivation, intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. Intrinsic motivation is a motivation that comes from the inside students that can force them to study. Extrinsic motivation is motivation comes from outside students that give energy to study. It means the extrinsic motivation is the verse of intrinsic motivation.
e. Mental Health
mental health will make the good result in learning process. In addition, if the students get successful in their learning, they will have self-esteem. The appearance of someone’s self-esteem is the factor of mental health.
f. Special types of learner
As we know, there are three types of learning styles, those are: visual, motorist, and visual-motorist. If the learning process is suitable with their learning style, they will study happily.
Besides the internal factor, there is external factor that causes learning difficulties. In this case, the students did not concentrate to the material given because their friends disturbed them, or there is the parent did not support them to study. It is meant, the difficulties were caused by the external factors. The external factor includes social environment and non social environment.21
1. Social Environment
The social environment here is the human environment outside students who have contact directly with them such as family, in their school, neighbors and mass media.
Family is the first center of education. But it can be the cause of learning difficulties if the families give less attention to their children.
Social environment in school such as teachers, staff administration and classmates can influence the students. The teacher can be a cause for learning difficulties when:
a. Unqualified teacher
b. Bad relationship between the teacher and the student. c. The high learning standard from the teacher
d. Has no skill in diagnosing the students learning difficulties, and e. The unsuitable method.
Moreover, the neighbors or people surrounding them can also influence in their learning activities.
21
2. Nonsocial Environment
20 CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. Purpose of the Research
The writer wants to know the students’ difficulties in learning modal auxiliary especially of „Can’ and „Could’ in determining the meaning, function and form of Modal Auxiliary and then the writer wants to analyze why they face the difficulties in using Modal auxiliary.
B. Place and Time of the Research
The research was held at Mts Muhammadiyah 1 Ciputat, which is located on Jl.Nangka No. 21 Ciputat, Tangerang. It’s not far and only about 20 minutes from the writer’s lodging house. This research began by doing the observation at school and the research was carried on May 2010.
C. Method of the Research
D. Population and Sample
The population of this research is the eight grade students of Mts Muhammadiyah that divided into three classes, and the writer took VIII-2 class as the sample that consists of 35 students from 42 students. So the sample of this research is 35 students, because three students of class VIII-2 were sick and four students of class VIII-2 were absent.
The sample is taken by using cluster Sampling tehnique, because the writer took one class from three classes, and it is consists of 35 students and 17 students will be interviewed, the determaining of class that will be researched based on the policy and ease from the school.
E. Techniques of Data Collecting.
1. Written Test
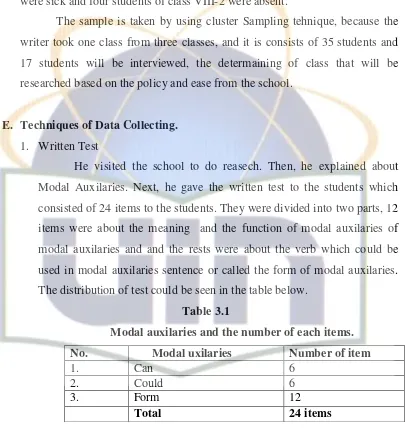
He visited the school to do reasech. Then, he explained about Modal Auxilaries. Next, he gave the written test to the students which consisted of 24 items to the students. They were divided into two parts, 12 items were about the meaning and the function of modal auxilaries of modal auxilaries and and the rests were about the verb which could be used in modal auxilaries sentence or called the form of modal auxilaries. The distribution of test could be seen in the table below.
Table 3.1
Modal auxilaries and the number of each items.
2. Interview
In this step, the writer interviewed some students who got bad and good score in order to know about thier difficulties in learning modal auxilaries espesially “Can and Could”. For reinforching the data, he also interviewed the English teacher.
F. Techniques of Data Analysis
The techniques of data anakysis that are used in this used in this research are descriptive analysis techniques (percentage), which is described in the table of percentage. In the table of percentage the writer used this
Drs. Anas Sudjiono, Pengantar statistik pendididkan, (Jakarta: PT.Raja Grapindo
23 CHAPTER IV
RESEACH FINDINGS
A. Data Description
In doing his research, the writer took class VIII-2 for his sample. The numbers of students in class VIII-2 are 42 students. When, the test is given, 7 students were sick and absent so the writer took 35 student in this reseach. And he took 17 student of class VIII-2 to unterview which are about 50% of the sample. The students’ name of class VIII-2 could be seen in the table below.
Having done the test, the writer can collect the data needed. The test covers the meaning, the fuction and the form of modal Auxilaries (Can and
Could) which consists of 24 items. Next, the writer will analyze the students’
Table 4.2
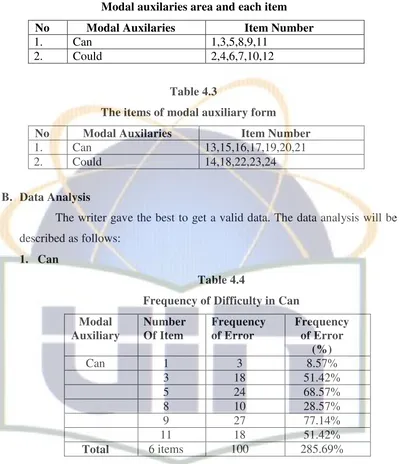
Modal auxilaries area and each item
No Modal Auxilaries Item Number
1. Can 1,3,5,8,9,11
2. Could 2,4,6,7,10,12
Table 4.3
The items of modal auxiliary form
No Modal Auxilaries Item Number
1. Can 13,15,16,17,19,20,21
2. Could 14,18,22,23,24
B. Data Analysis
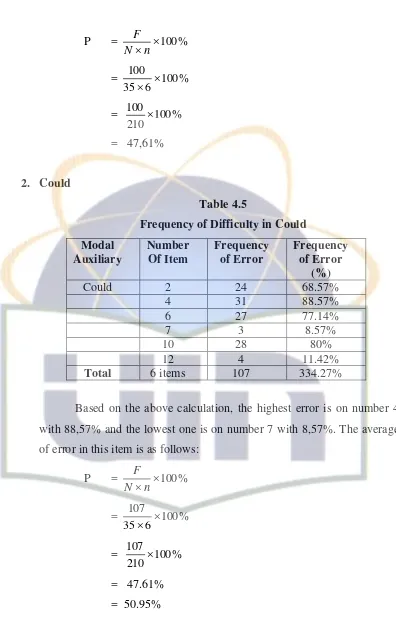
P = 100% with 88,57% and the lowest one is on number 7 with 8,57%. The average of error in this item is as follows:
3. The Form of Modal Auxilaries
Table 4.6
Frequency of Difficulty in Modal Auxiliaries Form
Number of students have to know the pattern of Modal Auxiliary in a sentence. From the calculation mentioned above, the highest frequency is on number 23 with 91,42% and the lowest frequency is on 16 with 14,28%. He can also see, there are two items which have the same frequencies. Those are on 20 and 22 with 85,71% student who chose the wrong answers. Then, the average of the students’ error in this item is as follows:
Based on the data which have been receive about the analysis of learning difficulties of modal auxilaries, the writer got the information that the learning difficulties were:
a. In written test
After the test given, the writer checked the data and got the information about the difficulties faced by the students in learning modal auxiliaries. Based on the data showed almost the student faced difficulties in the meaning and function of modal auxiliaries in the meaning and function of modal auxiliaries.
b. In interview
The writer did the interview to the students and to the English teacher for reiforcing the data. The interview consisted of 10 items. He took 17 students from class VIII-2 which he did the written test.
Table 4.7
The Internal factor and External factors which caused the
students’ difficulties
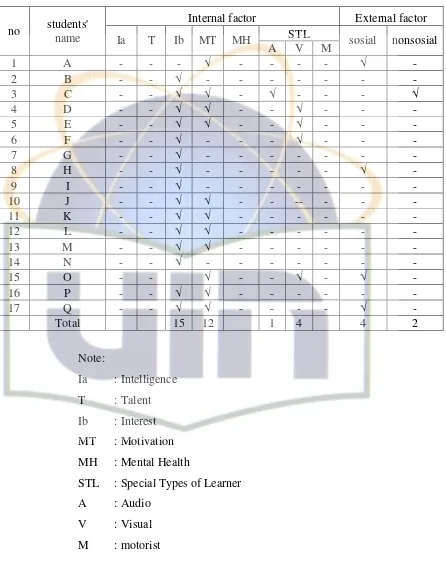
STL : Special Types of Learner
A : Audio
V : Visual
From the observant result explained above, that the cause of the students’ learning difficulties were came from the internal factor, that most of interviewee facing the difficulties caused by the interest, they do not attention to the teacher’s explanation, beside that the cause of difficulties are caused by their motivation in learning English subject with 12 students and their special types of learner with 5 students. The external factors, social environment is 4 students. They could not study well and bad-relationship between teacher and students. And non-social environment is 2 students. Which is the learning instrument and the class too hot.
C. Data Interpretation
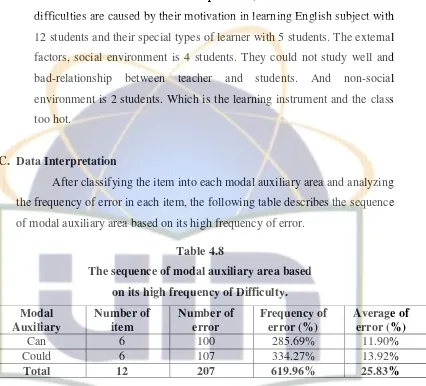
After classifying the item into each modal auxiliary area and analyzing the frequency of error in each item, the following table describes the sequence of modal auxiliary area based on its high frequency of error.
Table 4.8
The sequence of modal auxiliary area based
on its high frequency of Difficulty.
Modal frequency of error 334,27% and the average 13,92%. It is mean this frequency is the higher than frequency of “Can”.
Table 4.9
The sequence of meaning, function and form of modal auxiliaries
The table showed the average value of similar students in meaning and function of modal auxiliary, eventhough the meaning and function are higher than form, it is 25.83%.
31 CHAPTER V
CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION
A. Conclusion
Based on the data analysis and the discussion in the previous chapter, the writer would like to conclude that the mastery of second year students (class VIII-2) to modal auxiliary especially in determining the meaning and function and also the form of “Can” and “Could” is low. Here the causes of students’ difficulties in learning some modal auxiliaries of Can and could
came from internal and external factors.
1. The students were still confused to differentiate the meaning and function of modal Auxiliaries.
2. The students were still low in mastering form of modal Auxiliary especially Can and Could.
3. The students were low interest and motivation in learning English.
B. Suggestion
In order to reduce the error in Modal auxiliaries, the writer would like to present some suggestion to the English teacher and the students themselves. 1. The students should pay more attention to the teacher’s explanation. 2. They do not only have to listen to the teacher’s explanation but also to
practice materials they have already given.
3. The teachers to give more exercises either oral or written form and review before getting the new chapter or material
4. The teachers have to be more active in motivating the students to be more relaxed in learning English and tell them that English is easy and not to be afraid of making mistakes, because it is process to gain success.
33 Cipta,1991.
Azar, Betty Schramfer, Fundamentals English Grammar 2nd Edition. New Jersey: Precentice-Hall, In,.1992
_______. Understanding and Using English Grammar 2nd Edition. New
Jersey:Prentice Hall Regents,1989.
Barus, Irma Rosita Gloria dkk. Bahasa Inggris II. Jakarta: pusat Penerbitan Universitas Terbuka,2004.
Beaumount, Digby and Colin Granger, English Grammar, Heinemen first
published, 1989
Bibes, Douglas, et al, Grammar of Spoken and Written English, London: Longman pearson joranic, inc, 1983
Crosby, Harry H. The Commited Writer Mastering Non Fiction Genre. Boston; Mc.Graw Hill Book Company. 1986
E.Wishon George, M. Burks Julia. Let’s Write English, New York: Litton educational Publishing, inc. 1980
Frank, Marcella Modern English: A Practical Reference Guide, Englewood cliffs, New Jersey practice hall inc.1989
Freeman, Diana Larsen. Techniques and Principle in Language Teaching. New York : Oxford University press.1984
Hall, Engenej, Grammar for Use A Realistic Approach to grammar study for immediate practical Aplication, Bima Rupa Aksara, 1993
Harmer, Jeremy. English Language Teaching. Edinburg gate : Pearson education limited, 2001
Hartono, Rudi. Genre of Text. English Departement faculty of Language and art semarang University Semarang; 2005
LeTorneau, Mark S. English Grammar. United Stated of America: Harcourt College Publishers,2001
Margono, S. Metodologi Penelitian. Jakarta: PT.Rineka Cipta,2007
Mas’ud Fuad Drs. Essential of English grammar a practical Guide, BPFE-yogyakarta;edisi kedua juli 1992
Murcia-Maranne and Freeman- Diane larsen,THE GRAMMAR BOOK An
ESL/EFL Teacher’s Course second edition (United State of America,1999),
Roberts,Paul, Understanding Grammar, New York; 1954
Schmid, Helen Hoyt, Advance English Grammar, lowa: prentice Hall Regents, 1995
Sudjana, Nana, Dasar- Dasar Penilaian Hasil Belajar (Jakarta: CV Cera Jaya,1982)
Sudjiono,Anas, Pengantar Statistik Pendidikan. Jakarta: PT. Raja Grafindo Persada,2005.
Sukur, Silvester Goridus. Complete English Grammar for The TOEFL.
Yogyakarta: Indonesia Cerdas,2007
Swam, Michael, Basic English usage, London : oxford University pres, 1984 ______. Practical English Usage. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1980
Widjaja, Grace. Complete English Grammar and the exercises. Salatiga: PT.Bhuana ilmu populer,2002.
http://www.encyclopedia.com/doc/1O29
MODALVERB.htmlhttp://www.encyclopedia.com/doc/1O29
Name :
Class :
Date/ day :
A. Complete the following questions with the correct aswer of modal
auxilaries (Can and Could).
1. She... sing like an angel.
2. Our son...talk when he was two years old. 3. I’m sure you...get hight score if you study hard. 4. He... read arabic when he was a little Boy. 5. My sister ... sing very well.
6. My brothers ... speak arabic and english when they were in senior high school.
7. My grandfather...walk without any help last night. 8. ... you tell me what time it is, please?
9. According to Radio, it... rain this morning. 10.When My father was younger, he... run fast. 11... I borrow your pen (please)?
12.When I lived at grand mom’s house I... eat food whenever I wanted to.
B. Choose the best anwer a, b, c, or d !
13.I don’t have enough money. So I can not... on a picnic with them.
a. going b. to go
c. go d. goes
14.When she was young, she could... guitar very well.
a. plays b. play
c. played d. to play
15.Can you please... the salt?
a. Passing b. Pass
c. to sing d. singing 17.He can... very well.
a. drives b.drive
c. do drive d. driving
18.Ani could... a song when she was young.
a. to sing b. singing
c. sing d. sings
19.Can you... me with my homework?
a. helped b. helps
c. to help d. help
20.Sorry, I am busy today. But I can...you tomorrow.
a. help b. helps
c. helping d. to help
21.You can not smoke here, but you can... in the garden.
a. smoke b. smoking
c. to smoke d. smokes
22.Could I ... in this room?
a. ate b. eating
c. eat d. eats
23.My father could.... several language.
a. spoke b. Speaks
c. speak d. to speak
24.Could you... me where the bank is, please?
a. told b. tell
Section A
1. Can
2. Could
3. Can
4. Could
5. Can
6. Could
7. Could
8. Can
9. Can
10.Could 11.Can 12.Could
Section B
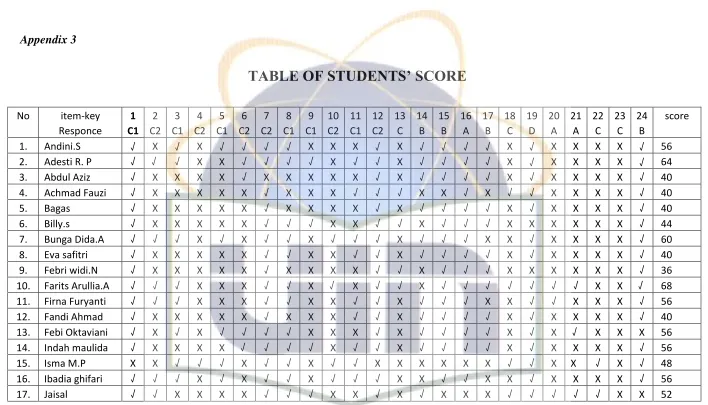
TABLE OF STUDENTS’ SCORE
No item-key 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 score
Responce C1 C2 C1 C2 C1 C2 C2 C1 C1 C2 C1 C2 C B B A B C D A A C C B
1. Andini.S √ Х √ Х √ √ √ √ Х Х Х √ Х √ √ √ √ Х √ Х Х Х Х √ 56
2. Adesti R. P √ √ √ Х Х √ √ √ √ Х √ √ Х √ √ √ √ Х √ Х Х Х Х √ 64
3. Abdul Aziz √ Х Х Х Х √ Х Х Х Х Х √ Х √ √ √ √ Х √ Х Х Х Х √ 40
4. Achmad Fauzi √ Х Х Х Х Х √ Х Х Х √ √ √ Х Х √ Х √ √ Х Х Х Х √ 40
5. Bagas √ Х Х Х Х Х √ Х Х Х Х √ Х √ √ √ √ Х √ Х Х Х Х √ 40
6. Billy.s √ Х Х Х Х Х √ √ √ Х Х √ √ Х √ √ √ Х Х Х Х Х Х √ 44
7. Bunga Dida.A √ √ √ Х √ Х √ √ Х √ √ √ Х √ √ √ Х Х √ Х Х Х Х √ 60
8. Eva safitri √ Х Х Х Х Х √ √ Х Х √ √ Х √ √ √ √ Х √ Х Х Х Х √ 40
9. Febri widi.N √ Х Х Х Х Х √ Х Х Х Х √ √ Х √ √ √ Х Х Х Х Х Х √ 36
10. Farits Arullia.A √ √ √ Х Х Х √ √ Х √ Х √ √ Х √ √ √ √ √ √ √ Х Х √ 68 11. Firna Furyanti √ √ √ Х Х Х √ √ Х Х √ √ Х √ √ √ Х Х √ √ Х Х Х √ 56
12. Fandi Ahmad √ Х Х Х Х Х √ Х Х Х √ √ Х √ √ √ √ Х √ Х Х Х Х √ 40
13. Febi Oktaviani √ Х √ Х √ √ √ √ Х Х Х √ Х √ √ √ √ Х √ Х √ Х Х Х 56 14. Indah maulida √ Х Х Х Х √ √ √ √ Х √ √ Х √ √ √ √ Х √ Х Х Х Х √ 56
15. Isma M.P Х Х √ √ √ Х √ √ Х √ √ Х Х Х Х Х Х √ √ Х Х √ Х √ 48
16. Ibadia ghifari √ √ √ Х √ Х √ √ Х √ √ √ Х Х √ √ Х Х √ Х Х Х Х √ 56
20. Mahfuddin √ Х Х Х Х Х √ Х Х Х Х √ √ Х Х √ √ Х √ Х Х Х √ √ 40
21. M.Nurkhozim √ Х Х Х Х Х √ Х Х Х Х √ Х √ √ √ √ Х √ Х Х Х Х √ 40
22. M.Rizky. R Х Х Х Х Х √ Х √ Х √ √ Х √ Х Х √ Х √ √ Х √ √ Х √ 48
23. M.Hafizh √ Х √ Х Х Х √ Х Х Х Х √ Х √ √ √ √ Х Х Х Х Х Х Х 36
24. M.Adam.k √ Х √ Х Х Х √ √ Х Х Х Х Х √ √ √ √ Х √ Х Х Х √ √ 48
25. Nora Novita √ Х √ Х √ √ √ √ √ √ √ √ Х Х √ √ √ Х √ Х Х Х Х √ 64 26. Prasetyo Ajie √ √ √ Х √ Х √ √ Х √ √ √ Х √ √ √ Х Х √ Х Х Х Х √ 60 27. Ratih Utami √ Х √ Х √ √ √ √ Х Х Х √ Х √ √ √ √ Х √ Х Х Х Х √ 60
28. Renata.F √ √ √ √ √ Х √ √ Х √ √ Х Х Х Х Х Х √ √ Х √ √ Х Х 56
29. Rian Saputra √ Х Х Х Х Х √ Х Х Х Х √ Х √ √ √ √ Х √ Х Х Х Х √ 40
30. Rizky .D √ Х Х Х Х Х √ Х Х Х Х √ Х √ √ √ √ Х √ Х Х Х Х √ 40
31. Siti Nurbaiti √ Х Х Х Х Х √ √ √ Х √ √ Х √ √ √ √ Х √ Х Х Х Х √ 52
32. siti Nurjanah Х Х Х Х Х Х √ √ Х Х √ Х Х Х Х Х Х √ √ Х √ √ Х √ 36
33. Vandi Sadam √ √ √ √ √ Х √ √ Х Х √ √ Х √ √ √ Х Х √ Х Х Х Х √ 60
34. Wenni.A √ √ √ Х Х Х √ √ Х Х Х √ √ Х √ √ √ √ √ √ √ Х Х Х 60
Interviewee : Eni Maryani , S.pd
Day/ Date : Wednesday , June 02,2010
Place :Mts Muhammadiyah 1 Ciputat
Position : English Teacher
1. Sejak kapan Ibu mengajar di Mts Muhammadiyah Ini, dan mata pelajaran
apa saja yang Ibu pegang?
Answer: Saya mengajar Bahasa inggris saja, sejak tahun 1997 sampai sekarang.
2. Bagaimana antusiasme siswa terhadap mata pelajaran bahasa inggris terutama di kelas VIII-2?
Anwer: kalau di kelas VIII-2 lumayan merespon terhadap pelajaran bahasa inggris.
3. Dalam pengajaran bahasa inggris, metode pengajaran apa yang ibu Gunakan selama ini?
Answer: saya menggunakan metode campuran saja, tergantung materi dan situasi di dalam kelas.
4. Fasilitas penunjang apa sajakah yang tersedia disekolah ini khususnya untuk mata pelajaran bahasa inggris?
Answer: Buku paket ( seize the day By Dwi Hesti Yuliani) dan LKS
6. Apakah ibu menggunakan sember lain dalam mengajarkan materi
tersebut?
Answer: ya, tergantung materi, terkadang dari Buku paket, Lks dan dari kumpulan soal-soal.
7. Dari mana biasanya ibu mengambil sumber materi untuk kelancaran proses belajar mengajar?
Answer: dari Buku paket, Buku Grammar dan LKS
8. Bagaimana Ibu menggajarkan materi grammar khususnya Modal
Auxiliary?
Answer: Dengan Ceramah, drama dan Coversation.
9. Kesulitan apakah yang biasa di hadapi siswa ketika Ibu mengajarkan Grammar terutama Modal Auxiliary?
Answer: latihan di kelas dan memberikan pekerjaan Rumah (PR)
Ciputat, 02 Juni 2010
Interviewee interviewer
Eni Maryani S.Pd Sudirman
105014000363
Interviewee : The students
Date/ Day : Wednesday,May 26, 2010
Place : Mts Muhammadiyah Ciputat 1
1. Bagaimana pandangan anda terhadap mata pelajaran bahasa inggris?
The answer of student A : kadang senang, kadang tidak
The answer of student B :terkadang gampang,ter kadang susah tapi
menyenangkan
The answer of student C : sedikit pusing
The answer of student D : sulit dan membingungkan
The answer of student E : kadang-kadang asyik,kadang-kadang
nyebelin
The answer of student F : pusing
The answer of student G : sulit, memusingkan
The answer of student H : sulit engga sulit, asyik engga asyik
The answer of student I : susah-susah gampang
The answer of student M : pusing tapi pengen bisa
The answer of student N : menyenangkan
The answer of student O : Butek tapi agak menyenangkan
The answer of student P : kadang susah dan kadang-kadang
gampang
The answer of student Q : puyeng
2. Apakah anda pernah mengikuti kegiatan yang berhubungan dengan
bahasa inggris(kursus)?
The answer of Student A : tidak pernah
The answer of student B :ya, pernah ikut lest
The answer of student C : tidak
The answer of student D : tidak pernah
The answer of student E : ga pernah
The answer of student F : tidak pernah
The answer of student G : pernah ikut lest
The answer of student K : engga pernah
The answer of student L : engga pernah
The answer of student M : tidak
The answer of student N : belajar dan bercanda sama kaka
The answer of student O : tidak pernah
The answer of student P :engga pernah
The answer of student Q : tidak
3. Dalam belajar bahasa inggris, cara belajar apa yang anda gunakan selama ini?
The answer of Student A : belajar sambil ngobrol
The answer of student B : belajar sambil ngobrol sama
temen-teman
The answer of student C : belajr sambil dengerin musik Mp3
The answer of student D : belajar sambil nonton Tv
The answer of student E : belajar sambil ngobrol dan Nonton TV
The answer of student I : insyallah bisa
The answer of student J : belajar sama kaka
The answer of student K : belajar sendiri
The answer of student L : belajar sendiri
The answer of student M : belajar sekalian bercanda
The answer of student N : ya, jadi gampang di ingat
The answer of student O : mendengarkan orang berbicara b.inggris
The answer of student P : belajar sambil ngobrol
The answer of student Q : belajar bersama
4. Apakah dengan cara belajar tersebut, anda dapat meningkatkan prestasi belajar anda?
The answer of Student A : mudah-mudahan bisa
The answer of student B : lumayan
The answer of student C : lumayan sedang
The answer of student D :ya, bisa sedikit
The answer of student H : Iya, tapi Cuma setengah tapi memuaskan
The answer of student I : cukup membantu
The answer of student J : lumaya bisa
The answer of student K : tidak
The answer of student L : tidak
The answer of student M : sedikit-sedikit
The answer of student N : ya, sedikit
The answer of student O : ya, kalau mendengarkan,terasa saya
faham
The answer of student P : insyaallah bisa
The answer of student Q : insyaallah bisa
5. Apakah fasilitas penunjang kebahasaan yang tersedia di sekolah ini dapat membantu meningkatkan prestasi belajar bahasa inggris anda?
The answer of Student A : sedikit
The answer of student B : sedikit
The answer of student F : tidak
The answer of student G : kurang
The answer of student H : iya, sedikit
The answer of student I : cukup
The answer of student J : iya sedikit
The answer of student K : kurang
The answer of student L : kurang
The answer of student M : ya
The answer of student N :ya, sedikit
The answer of student O : tidak terlalu
The answer of student P : kurang
The answer of student Q : ya, sedikit
6. Dalam bahasa inggris item manakah yang anda senangi(listening,
speaking, reading atau writing)?
The answer of Student A : listening
The answer of student E : writing
The answer of student F : listening
The answer of student G : mendengarkan
The answer of student H : listening dan writing
The answer of student I : sediki sulit
The answer of student J : listening
The answer of student K : reading
The answer of student L : reading
The answer of student M : speaking
The answer of student N : speaking
The answer of student O : listening dan speaking
The answer of student P : listening dan reading
The answer of student Q : listening
7. Bagaimana menurut anda tentang grammar?
The answer of Student A : gampang-gampang susah si
The answer of student E : gampang-gampang sulit
The answer of student F : sulit
The answer of student G : susah-susah gampang
The answer of student H : gampang-gampang sulit
The answer of student I : sedikit sulit
The answer of student J : gampang-gampang susah
The answer of student K : susah-susah gampang
The answer of student L : susah-susah gampang
The answer of student M : gampang-gampang susah sih
The answer of student N : biasa-biasa ajah, kadang susah dan
gampang
The answer of student O : lumayan sulit dan mudah
The answer of student P : ribet banget,susah dimengerti
The answer of student A : semuanya, apa lagi arti nya.
The answer of student B : penggunaan Verb
The answer of student C :menentukan arti
The answer of student D : dalam penggunaan modal auxilirary
The answer of student E : menggunakan arti
The answer of student F : menentukan arti kata
The answer of student G : semuanya, terutama kata kerja.
The answer of student H : membedakan arti dan membedakan
penggunaan
The answer of student I : penggunaan modal Auxiliaries
The answer of student J : menggunakan penggunaanya
The answer of student K : mencari ciri-cirinya
The answer of student L : belajar kurang konsentrasi
The answer of student M : menentukan artinya
The answer of student N : arti dan penggunaan
The answer of student O : menentukan penggunaanya
The answer of student P : menentukan arti
The answer of Student A : belajar tidak konsen dan Gurunya Kurang asyik
The answer of student B : Gurunya asyik, tapi pelajaran bahasa
inggris kurang suka
The answer of student C : tidak konsen
The answer of student D : saya belajar tapi tidak konsen
The answer of student E : Gurunya asyik, tapi pelajaranya sulit
The answer of student F : tidak konsen, berisik
The answer of student G : saya belajar tidak konsentrasi
The answer of student H : tidak konsen,dikelas sllu berisik dan Ribut
The answer of student I : tidak konsen
The answer of student J : saya belajar tapi tidak konsen
The answer of student K : lagi belajar tapi tidak konsen
The answer of student L : belajar kurang konsen
The answer of student M : saya tidak konsen
The answer of student N : belajar tidak konsen
The answer of student O : saya tidak suka b.inggris dan Gurunya
10.Apakah anda bisa mengikuti dan memahami penjelasan Guru anda tentang Modal auxiliary?
The answer of Student A : ya, tapi kurang
The answer of student B :ya, sekit. Lama-lama bisa memahami
The answer of student C : sedikit
The answer of student D : Bisa,tapi sedikit
The answer of student E : bisa tapi sedikit
The answer of student F : sedikit
The answer of student G : ya, tapi kurang
The answer of student H : iya, tapi sedikit
The answer of student I : ya, tapi sedikit
The answer of student J : ya,
The answer of student K : insyaallah
The answer of student L : insyaallh
The answer of student M : sedikit-sedikit
A = Abdul Aziz
B = Achmad Fauzy
C = Billy.S
D = Eva Safitri
E = Febri Wdi.N
F = Fandi Ahmad
G = Isma. M.P
H = M. Saifullah
I = M.Nurkhozim
J = Mahpudin
K = M. Hafizh
L = M.Adam
M = Rian Saputra
N = Rizky.D
O = M. Rizky