Proceeding International Conference
Current Breakthrough in Pharmacy Materials and Analyses / Nurwaini et al., (ed) Surakarta : Muhammadiyah University Press, 2015
xxi, 153 pages
ISBN: 978-602-70429-9-5
Pharmacy
Chairman of Editors : Setyo Nurwaini, M.Sc.
Team of Pharmaceutical Technology : Anita Sukmawati, Ph.D., Apt. Suprapto, M.Sc., Apt.
Erindyah Retno Wikantyasning, Ph.D., Apt.
Setyo Nurwaini, M.Sc.
Team of Chemical Analyses : Dedi Hanwar, M.Si., Apt. Dr. Muhammad Da’i, M.Si., Apt.
Broto Santoso, M.Sc., Apt.
Team of Pharmacy Community and Clinic : Dra. Nurul Mutma’inah, M.Si., Apt.
Zakky Cholisoh, M.Clin. Pharm., Ph.D., Apt. Arifah Sri Wahyuni, M.Sc., Apt.
Team of Pharmacological Study : Tanti Azizah Sujono, M.Sc., Apt.
Zakky Cholisoh, M.Clin. Pharm., Ph.D., Apt. Arifah Sri Wahyuni, M.Sc., Apt.
Dra. Nurul Mutma’inah, M.Si., Apt. Team of Herbal Medicine : Ratna Yuliani, M.Biotech.St.
Azis, Saifudin, Ph.D., Apt. Team of Microbiology Pharmacy : Ratna Yuliani, M.Biotech.St.
Azis, Saifudin, Ph.D., Apt.
Copyright ©2015
Copyright in compilers and reserved
Design cover: Publication and Documentation Team Layout: Secretaris and IT Team
Published by:
Muhammadiyah University Press Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta
PREFACE
It’s my great pleasure to welcome you to the st International Current Breakthrough (ICB)-Pharma Symposium 2015 in Solo Indonesia which will be held on 10 January, 2015 under the auspices of Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta.
ICB-Pharma 5 will feature a theme of Current Breakthrough in Pharmacy Material and Analyses and will consist of morning and afternoon sessions. There will be plenary lectures and session lectures given by several invited speakers from Japan, South Korea, Taiwan as well as from Indonesia, and also selected oral presentations of the submitted papers. The poster session from various fields of pharmaceutical sciences will take place nearby.
The ICB-Pharma will be directed for a tradition and in the future will be nurtured as a well-known scientific symposium in disseminating the breakthrough and novel technology in pharmacy materials. This purpose will be able to achieve by encouragement of national and international academic institution partners and supports from the industrial partners, Indonesian Pharmacist Association (Ikatan Apoteker Indonesia, IAI), colleagues and from the organizing committee. Moreover, I do hope and believe that, the 1st ICB-Pharma will offer great opportunities for the scientists to meet and discuss recent topics in the field of material and pharmaceutical science and bring the academics, health professionals and industries together for sharing their experiences to solve current problems and challenges in practice.
Warm regards,
Anita Sukmawati, PhD
PREFACE
This conference is held to disseminate current methods which provide advanced
materials and methods in pharmacy. This a good media for those who are engaged in
academic, industrial, regulatory fields to conduct social interactions, to share their
findings, to communicate bottle neck surrogates, and to seek the possibilities for
collaborations. Since it is our initial moment, we are quite humble to recognize our
weakness in running all agendas. Hence, from bottom of our heart we ask apologizes from
all participants for any service, lack facilities, low response, etc.. However, we must be
persistent and ensuring our positive contribution toward scientific society especially at
the attempt to develop capacity building of pharmaceutical sciences in Indonesia. Thus, we
will run ICB Pharmacy II in 2015/2016.
To all participants, I wish an inspiring moment in Solo city, a city where was born a
national leader and city of heritage !
Azis Saifudin, PhD
LIST OF COMMITTEES
Host Organizer : Pharmacy Faculty University of Muhammadiyah Surakarta
Steering Committee : Rectorate board of UMS, Dean of Faculty of Pharmacy UMS
Organizing Committee
Chair : Anita Sukmawati, Ph.D., Apt.
Email : [email protected] Mobile : +62 8122607928
Andi Suhendi, M.Sc., Apt.
Email : [email protected] Mobile : +62 85226494607
Secretary : 1. Erindyah Retno Wikantyasning, Ph.D., Apt. 2. Normaidah
3. Rani Utami Widyaningrum Treasurer : 1. Diah Sulistyowati
Administration : 1. Atika Yahdiyani Ikhsani, S.TP. 2. Rimaning Hastungkoro Primadani 3. Lita Rahima Oensjar
4. Sanggita Ayu Ikasari 5. Alifah Anastya Dini 6. Rafa Embun Religia 7. Rifqi Satrio Utomo Ceremony 1. Titis Putri, S.Farm, Apt
2. Cita Hanif, S.Farm., Apt.
3. Pembayun Putranti Putri, S.Farm., Apt. 4. Nita Irlya, S.Farm., Apt.
5. Ekhwan Tris Wanto 6. Desy Nurmalitasari 7. Hestu Putri Mitayani 8. Indah Hairunisa Publication and
Documentation
: 1. Yunita Ebrilianti Oktaria, S.Farm., Apt. 2. Andika Dwi Mahendra
3. Fahmi Azhari 4. Doni Wibowo
5. Arista Rizki Oktaviani 6. Amira
7. Yeni Cristiana
8. Faridha Cynthia Dhewanti Sponsorship : 1. Andhika Rizky Gilang Mahaputra
2. Choirul Ma’arif 3. Annie Rahmatillah
IT : 1. Drajat Tri Wahyudi
2. Fajar Kholikul Amri 3. Marhamah Nur Azizah 4. Westi Fajrin Bayu Nugrahaini Equipment : 1. Hadi Cahyo, S.Farm., Apt.
2. Iwan Setya Nugroho, S.Farm., Apt. 3. Amin Suryaningrum
4. Dyah Riswari Pitaloka Subagyo 5. Nunik Kurniasih
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PREFACE ... iii
LIST OF COMMETTEES ... v
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... vi
LIST OF PARTICIPANT NON PRESENTERS ... ix
LIST OF ORAL PRESENTERS ... xv
LIST OF POSTER PRESENTERS ... xviii
B-PHARMACEUTICAL TECHNOLOGY ... 1
B-002 DEVELOPMENT OF PARTICULATE FORMULATION, LOADING PROCEDURE AND NANO-SCALE CHARACTERIZATION OF PLGA NANOPARTICLES INCOORPORATING ROOT EXTRACT OF Pueraria lobata (Wild) Ohwl Mardiyanto1* , Neuèrt Achim2 ... 1
B-005 FORMULATION OF Jatropha Multifida Linn. LATEX AS TOPICAL DOSAGE FORM AND WOUND HEALING STUDY IN SWISS WEBSTER MICE Amila1, Fetri Lestari1, Abdul Rahman1 ... 8
B-008 EFFECT OF USE VIRGIN COCONUT OIL (VCO) AS EMOLIENT ON PHYSICAL PROPERTIES AND STABILITY OF VITAMIN C IN TRANSPARENT SOAP Ms. Fatimah Kasor1*, Anita Sukmawati1 ... 16
B-010 INCREASING SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION OF GLIMEPIRIDE THROUGH CO-CRYSTALLIZATION METHOD Fitrianti Darusman1*, Sundani N Soewandhi2, Rachmat Mauludin3 ... 25
B-012 SYNTHESIS OF POLY(METHACRYLIC ACID) CROSS-LINKED BY SILVER NANOPARTICLES FOR pH-RESPONSIVE NANOSENSOR Erindyah R. Wikantyasning1*, Bunga Savitri1, BrotoSantoso1, Suprapto1 ... 33
C-CHEMICAL ANALYSES ... 42
C-001 ELECTROCHEMICAL DETECTION OF ZANAMIVIR USING GOLD AND GOLD-MODIFIED BORON DOPED DIAMOND ELECTRODE Wulan Tri Wahyuni1,2*, Ivandini Tribidasari A1, Endang Saepudin1 ... 42
C-003 SYNTHESIS, CHARACTERIZATION AND IN VITRO TEST OF 1-(2,4-DICHLOROBENZOYL)-3-METHYL THIOUREA ON HeLa CELLS
Ruswanto1, 2*, Amir M. Miftah1, Daryono H. Tjahjono1, Siswandono3 ... 55
C-009 ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY OF ETANOLIC EXTRAC AND FRACTIONS OF LEMPUYANG EMPRIT (Zingiber amaricans Bl.) LEAVES BY DPPH METHOD AND DETERMINATION OF TOTAL PHENOLIC CONTENT
Afnan Madeng1* and Dedi Hanwar1 ... 62
C-010 ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY OF FRACTIONS AND ETHANOL EXTRACT OF LEMPUYANG WANGI LEAF (Zingiber aromaticum. Val) WITH DPPH METHOD AND DETERMINATION OF TOTAL PHENOLIC CONTENT
Nisreen Cheleng1* and Dedi Hanwar1 ... 70
C-014 METHOD DEVELOPMENT AND VALIDATION FOR THE SIMULTANEOUS ESTIMATION OF ASPARTAME AND ACESULFAME-K IN BAVARAGES BY RP-HPLC M. Hatta Prabowo1*, Ari Wibowo1, Mufida1, Ilham Taufiqurrahman1 ... 77
D-PHARMACY COMMUNITY AND CLINIC ... 85 D-001 THE ROLE OF ZINC ON REMISSION OF DIARRHEA IN HIV-INFECTED CHILDREN Rasmaya Niruri1*, N.P. Oka Mahayani1, K. Dewi Kumara Wati2 ... 85
D-002 CLINICAL RECOVERY TIME FROM TYPHOID FEVER AFTER RECEIVING CEPHALOSPORIN OR FLUOROQUINOLONE
Rasmaya Niruri1*, G.A.Eka Pertiwi1, Julius D.Tansale2, I. B .Eka Erlangga3 ... 94
D-003 COMPLIANCE LEVEL OF ANTIHYPERTENSIVE DRUG USE INHYPERTENSION PATIENTS IN OUT PATIENT INSTALLATION HOSPITAL X IN 2014
Chayanee Smantummkul, E. M. Sutrisna, and Suharsono ... 103
D-004 ANALYSIS USE OF ANTIBIOTICS IN URINARY TRACT INFECTION DISEASE BASED OF EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE (EBM) IN HOSPITAL "X" PERIOD JANUARY -JUNE 2013
Asmah Useng1, E. M. Sutrisna1, Suharsono1 ... 112
D-007 COST ANALYSIS OF OSTEOARTHRITIS IN RSUP SARDJITO YOGYAKARTA JANUARY 1 - JUNE 30, 2012
Dedi Hartanto1*, Tri Murti Andayani2, Satibi2 ... 131
E-PHARMACOLOGICAL STUDY ... 141
E-001 EFFECT OF HISTAMIN-2 RECEPTOR ANTAGONIST (RANITIDINE) ON THE ANTIPLATELET FUNCTION OF CLOPIDOGREL IN ACUTE CORONARY SYNDROME (ACS) PATIENTS
Vinci Mizranita1*, Dhian Novita2, Heru Sasongko1, Wisnu Kundarto1 ... 141
E-012 EFFECTIVENESS OF ETHANOLIC EXTRACT OF SARANG SEMUT (Myrmecodia tuberosa (non Jack) BI.) TO DECREASE BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVELS IN DIABETIC RATS INDUCED BY ALLOXAN
Tanti Azizah Sujono1*, Sartika Nurhaini1, E. M. Sutrisna1, Sri Setiyani1, Erwin Susanti1 .... 147
E-014 THE EFFECT OF LONG TERM ADMINISTRATION OF ETHANOLIC EXTRACT OF Persea americana Mill. PEEL TOWARDS ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE CONCENTRATION IN WISTAR MALE RATS INDUCED BY CARBON TETRACHLORIDE
Lusia Drikti Nini Gorantokan1*, Phebe Hendra1 ... 154
G-MICROBILOGY PHARMACY ... 162
G-002 ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF THREE EXTRACTS OF Litsea angulata SEED Joko Priyanto Wibowo1*, Sukrasno2, Rika Hartati2 ... 162
G-003 COMPARISON OF ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF ETHANOLIC EXTRACTS OF SEED AND STEM PAPAYA (Carica papaya L.) AGAINST Shigella dysenteriae AND Streptococcus pyogenes
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors are grateful for financial support by Lembaga Pengelola Dana Pendidikan (LPDP) Republic of Indonesia.
PP G003
COMPARISON OF ANTIBACTERIAL ACTIVITY OF ETHANOLIC EXTRACTS OF SEED AND STEM PAPAYA (Carica papaya L.) AGAINST Shigella dysenteriae AND
Streptococcus pyogenes
Yeni Cristiana1* and Ratna Yuliani1
1Faculty of Pharmacy, Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta, Surakarta, Indonesia
*E-mail: [email protected]
Abstract
Generally, seed and stem of papaya (Carica papaya L.) are not used. In a previous study, seed and stem of papaya inhibit growth of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. The aim of this study was to compare antibacterial activity of ethanolic extract of papaya seed to stem extract against Shigella dysenteriae and Streptococcus pyogenes. Papaya seed and stem were extracted using 70% ethanol by maceration method. The antibacterial activity tests were carried out using Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion method. Chemical compounds in the extracts were identified using thin layer chromatography (TLC) with silica GF254 asstationary phase and a mobile phase of ethyl acetate : methanol : water (100 : 13 : 17)v/v for papaya seed extract and methanol:chloroform (8:2)v/v for papaya stem extract. The results showed that ethanolic extract of papaya seed and stem have same antibacterial activity against Shigella dysenteriae and Streptococcus pyogenes. Based on TLC analysis, papaya seed contain alkaloid, steroid, and tannin, while papaya stem contain tannin.
Keywords: papaya (Carica papaya L.), antibacterial, Shigella dysenteriae, Streptococcus pyogenes.
INTRODUCTION
Papaya (Carica papaya L.) has many useful parts but not all of them are used. Seed and stem are usually discarded, though both of them contain a variety of compounds. Papaya seed contains alkaloid such as carpain, and glycosides such as glucotropaelin and benzyl-isothiocyanate (Nayak, 2012). Papaya stem contains alkaloid, tannin, saponin, steroid (Stephen et al., 2013) and anthraquinone (Setiawan, 2009).
and Escherichia coli with inhibition zone diameter of 13 and 17 mm, respectively (Okoye, 2011). Ethanolic extract of papaya stem with concentration of 0.5 g/mL inhibit Escherichia coli with inhibition zone diameter of 20 mm (Khan et al., 2014).
Active compounds in the seed and stem of papaya may solve the problem of resistance in the treatment of infections. The presence of infection in the body causes a variety of diseases (Tambayong, 2000). Shigella dysenteriae is a Gram-negative bacterium of genus Shigella that commonly causes gastrointestinal infection (Radji, 2009). Shigella
cause bloody mucoid diarrhea that is transmitted directly through food and drinking water (Sears et al., 2011). Diarrhea caused death of 5 million people each year, especially children (Shulman et al., 1994). Streptococcus pyogenes is a Gram-positive bacterium of genus Streptococcus that can spread infection by releasing a toxin. The bacteriacause skin, circulatory and respiratory system infections (Radji, 2009). This study was carried out to compare antibacterial activity of ethanolic extract of seed to stem extract of papaya (Carica papaya L.) against Shigella dysenteriae and Streptococcus pyogenes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Materials
Papaya seed and stem were obtained from Ringinsari, Randusari Village, District Teras, Boyolali, Shigella dysenteriae and Streptococcus pyogenes were obtained from Center of Health Laboratory of Yogyakarta, 70% ethanol, Mueller Hinton (MH) medium, Brain Heart Infussion (BHI), tetracycline, erythromycin, silica gel GF254, chloroform, methanol, ethyl acetate, distilled water, FeCl3, Dragendorff, ethanolic-KOH, Liebermann-Burchard (LB), and ammonia vapour.
Methods
Preparation of extract
White papaya seeds were taken from unripe papaya fruits which were about 2 to 5 months old. Papaya stem were taken from papaya trees that bear fruit. Briefly, 310 g of seed powder was extracted using 2.8 L 70% ethanol and 450 g of stem powder was extracted using 3.5 L of 70% ethanol in different maceration jar for 3-5 days and stirred manually every day. Papaya seed and stem extracts were filtered and concentrated using rotary evaporator and water bath.
Three or five pure colonies of Shigella dysenteriae and Streptococcus pyogenes
were touched with a sterile wire loop, suspended in 3 mL of Brain Heart Infussion and shook until reached the turbidity of McFarland’s standard.
Antibacterial activity test
Papaya seed and stem extracts were dissolved in 1.5 mL 70% ethanol to give a series concentration of 50%, 25%, 12.5%, and 6.25%. 20 µL of the extracts with concentrations of 50%, 25%, 12.5%, and 6.25% were loaded on sterile discs to give concentration of 10000 µg, 5000 µg, 2500 µg, and 1250 µg, respectively. Papaya seed and stem extracts were tested for antibacterial activity using the Kirby-Bauer disc diffusion method. Mueller Hinton agar plates were inoculated with 300 µL of Shigella dysenteriae
(1.5x108 CFU/mL) and 200 µL Streptococcus pyogenes (1.5x108 CFU/mL). After 20 min, 4 extract-loaded discs, 1 antibiotic disc (30 µg tetracycline disc as positive control for
Shigella dysenteriae and 30 µg erythromycin disc for Streptococcus pyogenes), and 1 70% ethanol-loaded disc (as a negative control) were transferred onto the agar surface of each plate using sterile forceps. The plates were then incubated at 37C for 24 hours. The activity of the papaya seed and stem extract as antibacterial against Shigella dysenteriae
and Streptococcus pyogenes was determined by measuring the diameter of inhibition zones.
Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
Chemical compounds in the papaya seed and stem extracts were identified using thin layer chromatography (TLC) with silica GF254 asstationary phase and a mobile phase of ethyl acetate:methanol:water (100:13:17) v/v for papaya seed extract and methanol:chloroform (8:2)v/v for papaya stem extract. 20 uL of extract solution with concentration of 50% were spotted on silica GF254 plates that had been activated by heating at 110C for 1 hour. When the sample has dried up, elution was carried out and the plate were removed when it reached the upper part of the silica plate. The spots on the silica plate were detected using visible light, UV 254 nm, 366 nm, ammonia vapour, and spray reagents such as FeCl3 Dragendorff, ethanolic- KOH, Liebermann-Burchard (LB).
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Antibacterial activity test
The antibacterial activity of ethanolic extract of papaya seed and stem against
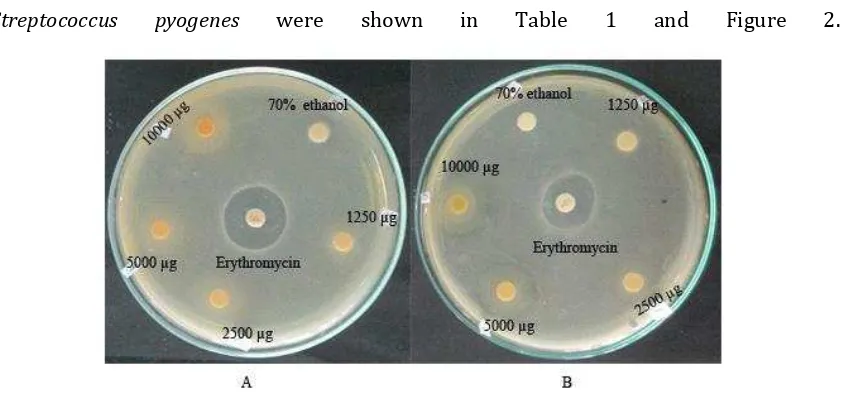
Table 1. Antibacterial activity of ethanolic extract of papaya seed and stem against Shigella dysenteriae and Streptococcus pyogenes
Samples Diameter of inhibition zones (mm)
Shigella dysenteriae Streptococcus pyogenes
Papaya seed extract
10000 µg 7,66±0,57* 7±0*
5000 µg 7,33±0,57* 7±0*
2500 µg 6±0 6±0
1250 µg 6±0 6±0
70% ethanol 14000 µg 6±0 6±0
Tetracycline 30 µg 18,33±0,57 -
Erythromycin 30 µg - 18,33±1,52
Papaya stem extract
10000 µg 8±0* 7,33±0,57*
5000 µg 7±0* 7±0*
2500 µg 6,33±0,57* 6±0
1250 µg 6±0 6±0
70% ethanol 14000 µg 6±0 6±0
Tetracycline 30 µg 16±1,73 -
Erythromycin 30 µg - 16,66±0,57
*irradical zone
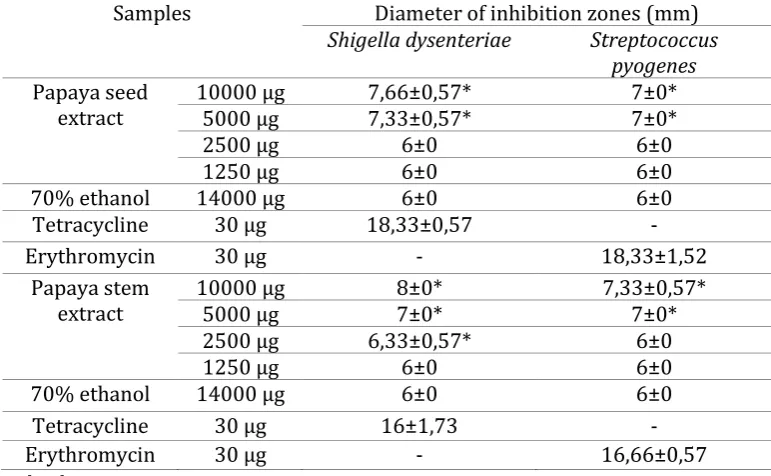
[image:13.595.143.454.443.606.2]Diameter of inhibition zone include disc diameter (6 mm)
Figure 1. Antibacterial activity of ethanolic extract of papaya seed (A) and stem (B) against Shigella dysenteriae
Proceeding International Conference
Current Breakthrough in Pharmacy Materials and Analyses ISBN : 978-602-70429-9-5
169 | P a g e papaya stem extract at concentration of 10000 µg, 5000 µg and 2500 µg have antibacterial activity against Shigella dysenteriae with inhibition zone diameter of 8±0, 7±0 and 6,33±0,57 mm, respectively. Papaya stem extract at concentration of 1250 µg have no antibacterial activity. Ethanolic extract of papaya seed and stem have same antibacterial activity against Shigella dysenteriae.
The antibacterial activity of ethanolic extract of papaya seed and stem against
Streptococcus pyogenes were shown in Table 1 and Figure 2.
[image:14.595.90.513.198.396.2]Irradical zones with diameter of 7±0 mm were observed around discs containing papaya seed extract with concentration of 10000 µg and 5000 µg. It indicated that the seed extracts have antibacterial activity against Streptococcus pyogenes. Papaya seed extract at concentration of 2500 µg and 1250 µg did not have antibacterial activity against
Streptococcus pyogenes. Papaya stem extract at concentration of 10000 µg and 5000 µg gave inhibition zone with diameter of 7.33±0.57 and 7±0 mm, respectively. Papaya stem extract at concentration of 2500 µg and 1250 µg did not inhibit the growth of
Streptococcus pyogenes. Ethanolic extract of papaya seed and stem have same antibacterial activity against Streptococcus pyogenes. The ethanolic extract of papaya stem have inhibition zone of 28 mm while the papaya seed did not have inhibition zone against
Staphylococcus aureus (Khan et al., 2012). Based on the results of antibacterial tests against Streptococcus pyogenes, papaya stem extract inhibit Gram-positive bacteria better than papaya seed.
Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
TLC results showed that the ethanolic extract of papaya seed contains alkaloid, steroid, and tannin. Alkaloid was shown as brownish color with Rf value of 0.08 after it has been sprayed with Dragendorff. Steroid showed blue fluorescence under UV 366 nm with Rf values of 0.16 and 0.95 after being sprayed with LB. Tannin showed black colour with Rf value of 0.26 after it has been sprayed with FeCl3. TLC results showed that the ethanolic extract of papaya stem contains tannin. Tannin shows black colour after FeCl3 sprayed with Rf value of 0.53. In theory, steroid give a blue fluorescence after being sprayed with LB, alkaloids showed red orange yellow background gray, brown/orange brown after being sprayed with Dragendorff, and tannins show blue, red, purple, green, or black after spraying with FeCl3 (Wagner and Bladt, 1996).
CONCLUSION
The ethanolic extracts of papaya seed and stem have same antibacterial activity against Shigella dysenteriae and Streptococcus pyogenes. The ethanolic extract of papaya seed contains alkaloid, steroid, and tannin, while the ethanolic extract of papaya stem contains tannin.
REFERENCES
Khan, J. A., Yadav, J., Srivastava, Y. & Pal, P. K., 2012, In Vitro Evaluation Of Antimicrobial Properties Of Carica papaya L., International Journal of Biology, Pharmacy and Allied Sciences, 1 (7), 933-945.
Nayak, B. S., Ramdeen, R., Adogwa, A., Ramsubhag, A., & Marshall, J. R., 2012, Wound-Healing Potential of an Ethanol Extract of Carica Papaya (Caricaceae) Seeds, International Wound Journal, 1-6.
Okoye, E. I., 2011, Preliminary Phytochemical Analysis And Antimicrobial Activity Of Seeds Of Carica papaya, Journal of Basic Physical Research, 2 (1), 66-69.
Radji, M., 2009, Buku Ajar Mikrobiologi: Panduan Mahasiswa Farmasi dan Kedokteran, 139, 156, Jakarta, EGC.
Saidu, A. N., & Nweri, C. G., 2013, Phytochemical Screening and Effects of Methanol Extract of Carica papaya Stem bark in alloxan induced Diabetic Rats, Journal of Emerging Trends in Engineering and Applied Sciences, 4 (6), 819-822
Sears, B. W., Spear, L. & Saenz, R., 2011, Intisari Mikrobiologi & Imunologi, diterjemahkan oleh Hartono, A., 120, Jakarta, EGC.
Setyawan, W., 2009, Aktivitas Antibakteri Ekstrak Etanol Batang Pepaya (Carica papaya L.) terhadap Staphylococcus aureus dan Escherichia coli Multiresisten Antibiotik, Skripsi, Fakultas Farmasi Universitas Muhammadiyah Surakarta.
Stephen, C., Ukpabi, C., EsiheTochukwu, E., Brown, N., 2013, Chemical Composition Of
Carica papaya Stem (Paw-Paw), American Open Food Science Journal, 1 (1), 1-5. Sears, B. W., Spear, L. & Saenz, R., 2011, Intisari Mikrobiologi & Imunologi, diterjemahkan
oleh Hartono, A., 120, Jakarta, EGC.
Tambayong, J., 2000, Mikrobiologi untuk Keperawatan, 3, 26, 45, Jakarta, Widya Medika. Wagner, H. & Bladt, S., 1996, PlantDrug Analysis: A Thin Layer Chromatography Atlas, 2nd