THE USE OF TASK BASED LEARNING TO IMPROVE
STUDENTS’ WRITING
SKILLS
(A Classroom Action Research of the Eleventh Grade Students of MA Utsmaniyyah Ngroto, Grobogan in the Academic Year of 2017/2018)
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board of Examiner as a Partial Fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S. Pd.)
English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education faculty
State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
By:
Eva Nuryani
(11313073)
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
MOTTO
ِ إ
اًرْسُي ِرْسُعْلا َعَم َّن
﴿
٦
﴾
﴾
٥
﴿
اًرْسُي ِرْسُعْلا َعَم َّنِإَف
“For indeed, with hardship (will be) ease. Indeed, with hardship (will be) ease.”
(Al-Insyirah: 5-6)
“Education is not learning of fact, but the training of the mind to think”
“Never give up on what you really want to do. The person with big dream is
more powerful than the one with all facts”
DEDICATION
This graduating paper is dedicated to:
1. My lord, Allah SWT…Thank to Allah for gives me guidance and strength in my
life, especially to finish this graduating paper.
2. My beloved parent, my mother (Maspiyah) and my father (Wur Sriyanto) who
always prays guide and motivate me to become better person.
3. My big family that supported for my education and finishing this graduating
paper
4. My honorable consultant (Mrs. Maslihatul Umami, M.A) who always gives me
suggestion and patience throughout my graduating paper. Thank you very much!
5. Thank you for all lecturers of Education faculty State Institute for Islamic Studies
(IAIN) Salatiga, who always teach me brilliantly, give me the best advice. I will
never forgetting to you.
6. Thank you for my struggle friends Agustina Ridho Utami, Aning Sulistyaningsih,
Dwi Ratnasari, Istifarini, Puji Ningsih,
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Bismillahirrohmanirrohim,
In the name of Allah, the most gracious and merciful, the king of universe and
space. Thank you to Allah because the researcher can complete this graduating paper
as one of requirement to finish the study in English Department of States for Institute
Islamic Studies Salatiga.
This graduating paper would not have been completed without support, guidance
and help from individual and institution. Therefore, I would like to express special
thanks to:
1. Dr. Rahmad Haryadi, M. Pd. as the Rector of State Institute for Islamic Studies
(IAIN) Salatiga.
2. Suwardi, M. Pd, as a Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
3. Nor Malihah, Ph. D. as the Head of English Language Teaching Department of
State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga.
4. Maslihatul Umami, M. A. as counselor who has bring up, espoused, and given the
researcher advices, suggestion and recommendations for this graduating paper
from beginning until the end. Thank you for patience and care.
5. All the lecturers in the English Language Teaching Department who have given
much knowledge, the researcher deeply thank you all.
6. My beloved family, thanks for your spirit and patient.
7. All of staff who have helped the writer in processing of graduating paper
ABSTRACT
Nuryani, Eva. 2017. “The Use of Task Based Learning to Improve Students Writing Skills.” graduating paper. Teacher Training and Education Faculty. English Education Department. State Institute for Islamic Studies Salatiga.
Consultant: Maslihatul Umami, M.A
Key Words: Task Based Learning, Improvment, Writing Skills.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE ... i
DECLARATION ... ii
ATTENTIVE CONCELOR NOTES ... iii
CERTIVICATION PAGE ... iv
MOTTO ... v
DEDICATION ... vi
ACKNOWLEDMENT ... vii
ABSTRACT ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... x
LIST OF THE TABLES ... xiii
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Study ... 1
B. Statement of Problem ... 3
C. The Objective of the Study ... 3
D. Benefits of the Study ... 4
E. Limitation of the Problems ... 5
F. Definition of Key Term ... 5
G. The Outline of the Study ... 6
B. Literature Review ... 10
1. Task Based Learning ... 10
a. Definition of Task Based Learning ... 10
b. Task Based Learning Methodology ... 13
c. Teacher Rules in Task Based Learning ... 14
d. The Advantages of Task Based Learning ... 15
2. Writing Skill ... 16
a. Definition of Writing ... 16
b. Genres of Text ... 19
c. The Writing Process ... 21
d. Teacher Roles in Teaching Writing ... 22
e. Scoring of Writing ... 23
CHAPTER III: METHOD OF RESEARCH A. Research Setting ... 26
1. General Situation of MA Utsmaniyyah... 26
2. The Schedule of Research ... 27
3. The Subject of Research... 28
B. Method of Research ... 29
C. Procedure of Research... 30
D. Technique of Collecting Data ... 34
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH IMPLEMENTATION AND ANALYSIS
A. Research Implementation ... 40
B. Statistical Analysis ... 60
C. Analysis and Discussion ... 75
1. Analysis ... 75
2. Discussions ... 76
CHAPTER V: CLOSURE A. Conclusions ... 79
B. Suggestions ... 81
1. Teacher ... 81
2. Students ... 81
3. Other Researcher ... 82
REFFERENCES
APPENDICES
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2.1 Rubric scoring of writing ... 23
Table 3.1 The schedule of research ... 27
Table 3.2 List of XI IPS class ... 28
Table 3.3 Kemmis and MC Taggart’s model ... 31
Table 4.1 Teacher’s observation checklist cycle 1... 47
Table 4.2 Students’ observation Checklist cycle 1 ... 49
Table 4.3 Teacher’s observation checklist cycle 2... 56
Table 4.4 Students’ observation Checklist cycle 2 ... 58
Table 4.5 The students’ score in pre-test cycle 1 ... 60
Table 4.6 Count of passing grade pre-test cycle 1 ... 62
Table 4.7 The students’ score in post-test cycle 1 ... 63
Table 4.8 Count of passing grade post-test cycle 1 ... 64
Table 4.9 Difference square of pre and post-test score in cycle 1 ... 65
Table 4.10 The students’ score in pre-test cycle 2 ... 69
Table 4.11 Count of passing grade pre-test cycle 2 ... 70
Table 4.12 The students’ score in post-test cycle 2 ... 71
Table 4.13 Count of passing grade post-test cycle 2 ... 72
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Study
Language is a system or tool of communication. Communication means
act or process using words, sounds, signs or behaviour to express information or
to express your ideas, thoughts, feelings to someone else. According to Sapir
(1921, p. 8), language is a purely human and non instinctive method of
communicating ideas, emotions, and desires by means of a system of voluntarily
produced symbol. It means that people use it to communicate each other, to share
their ideas and to deliver the messages from the writer or speaker to the reader or
listener. According to Ahmed, R. Z & Bidin, S. J (2016) English language has
emerged as the most important and widely used language all over the world, so it
is required to learn English everywhere in all continents. In it fact that English
has become international language. It is familiar for people around the world.
Almost all of countries use it to communicate each other. Most of people learn
English to communicate and socialize with others in the world. English has four
basic skills; they are writing, speaking, reading and listening. In this section, the
researcher focuses on writing skill, because the researcher thinks that writing
skill is the most important skill among the others. According to Tillema, M
(2012, p.1) writing is one of the most important skills for educational success,
Writing is difficult to learn, because writing is a productive skill, so
students who are learning writing have to learn how to find ideas, and express
them into writing. However, writing should be learn. Writing has advantages,
such as it helps developing students’ crusial thinking, it gives information to the
reader.
Effective writing skills demand knowledge, discipline, effort and
organization (Mahmoud, 1992, p. 11). It means that good writing demand of
their knowledge and experience. Writing habit is good for students in expressing
their ideas and make them creative in writing paragraph.
The researcher observes in MA Utsmaniyyah Ngroto Grobogan. The
researcher meet one of the English teacher named Mr. Edi Christanto, S.Pd. and
interview him. In that interview, the researcher asks some questions to the
teacher related to students’ writing skill. From that interview, the researcher
finds some students’ difficulties in writing. The students are lack of vocabularies.
They do not know how to make an appropriate grammar work, and they have
less understanding with the contexts so these become the major problem for
students. These problems causes students can not write paragraphs well.
Based on the condition above, the researcher tries to apply Task Based
Learning to improve students’ writing skill. Task Based Learning is activities
that require the use of target language in order to complete a writing task. In
Task Based Learning, the students are learning by doing. The lesson is focused
Based Learning to Improve Students’ Writing Skills (A Classroom Action
Research of the Eleventh Grade Students of MA Utsmaniyyah Ngroto,
Grobogan in the Academic Year of 2017/2018).”
B. Statement of Problems
Based on the research above, this research is aimed at giving answer on
the following problems:
1. Can the implementation of Task Based Learning improve students’ writing
skills for the eleventh grade students of MA Utsmaniyyah Ngroto, Grobogan
in the academic year of 2017/2018?
2. How significant is the use of Task Based Learning to improve students’
writing skills for the eleventh grade students of MA Utsmaniyyah Ngroto,
Grobogan in the academic year of 2017/2018?
C. Objective of the Study
The general purposes of the study is to know the degree of Task Based
Learning that is suitable with class condition. The specific objectives of this
study are:
1. To find out whether the implementation of Task Based Learning can improve
the students’ writing skills for the eleventh grade students of MA
2. To find out how far the use of Task Based Learning can improve students’
writing skills for the eleventh grade students of MA Utsmaniyyah Ngroto,
Grobogan in the academic year of 2017/2018.
D. Benefit of the Study
The result of this research is expected to give benefit for:
1. For the Teacher
The expeceted of this research is help the teacher enrich about
approach of teaching English particularly in writing skill and to solve the
problem of students. This research not only gives additional contribution for
English teacher to develop language teaching, but also the teachers are able to
improve the quality of teaching learning process.
2. For the Students
For the students, this research can be used to solve their problems in
writing, so they can improve their writing ability.
3. For the Researcher
This research is hoped to be able to give a new knowledge for the
researcher in order to make a better research in teaching and learning cases.
Furthermore, it will help the further researcher to solve the students’ and
E. Limitation of the Problems
This research will be conducted at MA Utsmaniyyah Ngroto, Grobogan.
The population of this research is the eleventh grade students of MA
Utsmaniyyah Ngroto, Grobogan in the academic year of 2017/2018. The topic
must be limited in order to investigate and solve the problems more accurately,
clearly and correctly. Therefore, this research only focuses on improving
students’ writing skills by using Task Based Learning, especially in Report Text.
F. Definitions of Key Term
There are key terms of this research:
1. Task-Based Learning
According to Alsagheer A & A Hasan (2014, p. 254) Task-Based
Learning is an instruction in the field of language acquisition and learning. It
focuses on the students doing meaningful task using target language.
2. Improvement
Improve means become or make better, meanwhile improvement is
process of becoming or making better (Oxford dictionary 2011, p. 222). It
explains the students writing skill will be better if they use Task-Based
Learning.
3. Writing Skills
According to Sitepu, A. S. R., & Siregar, M. (2014, p. 2) Writing is
G. The Outline of the Study
In order to make systematic research, the researcher organizes this
research into five chapters, they are as follows:
Chapter I is Introduction. It contains of background of study, research
questions, objectives of study, significant of study, limitation of problems, the
definition of key term, previous research and the outline of the study. Chapter II
is Theoretical Framework. It contains of previous research result and literature
review. Literature review consists of the underlying theories that include the
definition of Task Based Learning and writing skill. Chapter III is Method of
Research. It contains of the setting of research, the method of research,
procedure of research, technigues of collecting data and the data analysis.
Chapter IV is Research Implementation and Analysis. It contains of the
implementation of using Task Based Learning to improve students’ writing
skills. It also contains the significant improvement of using Task Based Learning
to improve students’ writing skills. Chapter V is the Closure. It contains of
conclusion and suggestion. After that, it is followed by references and
CHAPTER II
THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK
In this chapter, the researcher presents Theoretical Framework. It is
aimed to give relevant of the study. Therefore, this chapter describes some
information involving: Previous Research Results and Literature Review.
A. Previous researches
In order to improve the understanding this research, the researcher
presents five relevant studies. The first research has been done by Ruso (1999)
entitled “The Influence of Task Based Learning on EFL Classroom”.
Increasing learners’ motivation and performance has always been primary
concern of language teacher. The present study adopt in Action Research
approach. A new approach, TBL, is applied to a traditional classroom
situation with the aim of finding solution to certain problems such as poor
learner motivation. 55 EFL students from two English classrooms and the
researcher, a Turkish teacher, participated in the study. In this study, learner’s
opinions about TBL are investigated through different data collection.
Method: as a questionnaire, diaries and semi structural interviews. The finding
of the study reveals that implementing of TBL approach in EFL classes
creates variety for the students. Moreover it enhances their learning, since
improvements regarding their language performance. The research
participants suggest that they do not like teacher-directed lessons where they
cannot find enough opportunities to express themselves in the target language.
The second research has been done by Charles. D. (2002) entitled
“Implementing Task‐Based learning with young learners”. This article
draws on qualitative classroom observation data from case studies of three
EFL classes in Hong Kong primary schools. It analyses four themes relevant
to the classroom implementation of task‐based learning with young learners,
namely, noise/indiscipline, the use of the mother tongue, the extent of pupil
involvement, and the role of drawing or coloring activities. For each of these
issues, strategies for classroom practice are discussed. It is suggested that the
paper carries implications for teachers carrying out activities or tasks with
young EFL learners in other contexts.
The third research has been done by Murphy. J. (2003) entitled
“Task‐based learning: the interaction between tasks and learners”.
Recent research into task‐based learning claims that manipulation of task
characteristics and processing conditions can focus a learner's attention on the
competing goals of accuracy, fluency, and complexity. However, it is also
necessary to consider the ways in which learners interact with tasks within the
classroom environment, and this small‐scale study investigates the
manipulation of task characteristics and conditions may not achieve the
intended pedagogic outcomes, and that new ways are needed to focus learners'
attention on form without sacrificing the meaning‐driven principles of
task‐based learning. Teachers are in a unique position with regard to their
understanding and knowledge of individual learners, and a closer partnership
between teachers and researchers would be beneficial to support this process.
The fourth research has been done by Septiarini (2011) entitled
“Improving Students’ Speaking skill Through Task-Based Learning by
using Creative Task of the Fifth Grade of MI Islamiyah Gumukrejo
Teras Boyolali in the Academic Year 2011/2012”. The students are
enthusiastic and interested to take part in the classroom activities. The result
of the analysis shows that students are able to pronoun the word well and their
vocabulary is also increase.
The last research has been done by Siska /11308096, entitled
“Improving Students Reading Ability by Using Task Based Learning
(TBL) for the Seventh Grade Students of SMPN I Boyolangu”. She says
that, implementing task based learning improve students’ writing ability
because the mean score of the students’ reading ability achieved the criteria of
success. By implementing TBL, the researcher can make students feel enjoy,
collaborator, she concludes that the students can understand about reading,
especially in descriptive text.
However, the fifth researches above investigate the use of Task Based
Learning. The first research investigates the influence of Task Based Learning
on EFL (English as a foreign language) classroom. The second research
investigates the implementation of Task Based Learning for young learners.
The third research investigates of interaction between task and learners in
Task Based Learning. The fourth research investigates the improvement of
Task Based Learning in students’ speaking skill. The last research investigates
the improvement students’ reading ability using Task Based Learning. In this
research, the researcher uses Task Based Learning to improve students’
writing skill.
B. Literature Review
1. Task Based Learning
a. Definition of Task Based Learning
According to Soni, M. & Yadav, D. (2015) task based learning is
an approach which offers students to actively engage in
communication in order to achieve a goal or complete a task using
language. According to Ganta, T. G. (2015, p. 2760) the prominence
of Task Based Learning in the present day context is evident from the
Teaching. Task based approach focuses on communication and
conveying message.
History of Task Based Learning goes to back to 1980s it
emerged out of the Communicative Language Teaching project in
India by Prabu, Prabu (1987) quoted by Ahmed, R. Z & Bidin, S. J
(2016). According to Prabhu (1987) as quoted by Harmer (2001, p.
86), he said that the idea of Task-Based Learning was greatly
popularized by N Prabhu who, working with school in Bangalore,
Southern India, speculated that students were just a likely to learn
language if they were thinking about a non-linguistic problem than if
they were concentrating on particular language form. Richards (2005,
p. 29) as quoted by Littlewood (2007, p. 243) said that includes both
task-based and control-based instruction as extension of the CLT
movement but which take different routes to achieve the goal
communicative language teaching-to develop learners’ communicative
competence. It means that task based learning is extension of CLT.
Task based learning (TBL) also is called task based language teaching
(TBLT). Based on Nunan (2003) as quoted by Littlewood (2007, p.
243) in several countries, teacher already being urged to move on from
earlier form of CLT (Communicative Language Teaching) and
instruction or task- based learning, henceforth referred to here as
TBLT).
According to Willis (1996, p. 34) defines that task based learning
is a goal-oriented communicative activity with a specific outcome,
where the emphasis on exchanging meanings not producing specific
language forms. It means that the task is a students’ activity which use
language to achieve a specific outcome.
Richard (1986: 289) quoted by Nunan (2004, p. 2) task
becomes pedagogical task. The definition of pedagogical task:
“Task is an activity or action which is carried out as the result of processing or understanding language (i.e. as a response).
For example, drawing a map while listening to a tape, listening
to an instruction and performing a command may be referred to
as task. Task may or may not involve the production of
language. A task usually requires the teacher to specify what
will be regarded as successful completion of task. The use of
variety of different kinds of task in language teaching is said to
make language teaching more communicative since it provides
a purpose for a classroom activity which goes beyond the practice of language for its own sake.”
Based on definition above, the researcher concludes that Task
Based Learning is an approach to teach language that is teaching and
given to the students to know the students achievement. Task Based
Learning is a study which learning by doing.
b. Task Based Learning Methodology
According to Willis (1996, p. 38) frameworks for Task-Based
Learning are:
Pre-task
Introduction to topic and task
Teacher explores the topic with the class, highlights useful words and phrases, helps students understand task instruxtions and prepare. Students may hear a recording of other doing a similar task.
c. Teacher Rules in Task Based Learning
According to Willis (1996, p. 40-41), there are some teacher
roles in Task Based Learning, they are:
1. Teacher as a facilitator
The teacher is generally a facilitator. They have responsible
to control the conditions for teaching and learning process.
Usually, they help students to understand the lesson.
2. The teacher is involved in setting task
The teacher is involved in setting task up, ensuring that
learners understand and get on with them, and drawing them to a
close.
3. The teacher as a controller
Although the learners doing task independently, the teacher
4. Teacher act language guide
The part the teacher plays during each component of the task
framework also varies according to its aim. At the end of the
framework, where the focus turns to language form, the teacher
acts as language guide.
d. The Advantages of Task Based Learning
According to Willis (1996, p.35) said that there are some
advantages of TBL like:
1. It gives learners confidence to try out whether language they
know, or think they know, in the relative privacy of a pair or small
group, without being wrong or of being corrected in front of the
class.
2. It gives learner experience of spontaneous interaction, which
involves composing what they want to say in real time,
formulating phrases and unit of meaning.
3. It gives learner a change to benefit from noticing how to express
similar meaning. Research show they are more likely to provide
corrective feedback to each other (when encouraged to do so) than
4. It engages learners in using language purposefully and
co-operatively, concentrating on building meaning, and not just using
language for display purposes.
5. It make learner participate in a complete interaction, not just
one-off sentences. Negotiating opening and closing, new stages of
change of direction are their responsibility. It is likely that
discourse skills such as these can only be acquired through
interaction.
6. It gives learners more changes to try out communication strategies
like checking understanding, paraphrasing to get round an
unknown word, reformulating other people’s ideas, and supplying
words and phrase for other speaker.
7. It help learners gradually gain confidence as they find they can on
co-operation with their follow students to achieve the goals of
these task mainly through use of the target language.
2. Writing skill
a. Definition of Writing
In the language learning, students learn some of language skill.
There are four language skills: speaking, writing, listening and
ideas or feeling to others in written form. In this study, the researcher
tries to explain the definition of writing:
There are a lot of definitions of writing. The first definition is
taken from Paker, T & Eraslan, A. (2015, p. 1) writing is one of the
most important skills to be developed for people learning a second
language, and this is more emphasized in academic world.
The second definition of writing is taken from Langan (2006, p.
13) a realistic attitude about writing must build on the idea that writing
is a skill. It is a skill like driving, typing or cooking and like any skill,
it can be learned.
The last definition is taken from Eric Lenneberg, (as quoted by
Brown, 2001, p. 334), he said that different from speaking in which
people learn language through a natural process or human behavior as
learning to ‘walk’, writing is a learned behavior as learning to ‘swim’,
people need someone to teach them.
It means that people learn to write if they are members of a
literate society and usually if they teach students.
The genres of writing this is slightly shorter, you should be
aware of surprising multiplicity of options of written genres that
second language learners need to acquire. (Brown, 2004, p. 219)
1. Academic writing
Essays, compositions
Academically focused journals
Short-answer test reports (e.g. lab reports)
Thesis, dissertations
2. Job-related writing
Messages (e.g. phone message)
Letters/emails
Memos (e.g. interoffice)
Reports (e.g. job evaluations, project reports)
Schedules, label, announcements
Manuals
3. Personal writing
Letters, email, greeting card, invitations
Message, notes
Calendar entries, shopping list, reminders
Financial documents (e.g. checks, tax forms, loan applications)
Forms, questionnaires, medical reports, immigration document,
diaries, personal and journal
b. Genres of Writing
According to Law (2013, p. 2-30), there are some genre of text,
they are:
1. Narrative
Narrative uses to entertain and engage the reader in an
imaginative experience.
2. Recount
Recount tells the reader what happened and this may involve
the author’s personal interpretation of events.
3. Procedure
Procedure is written text to explain how something is done,
in a series of sequenced steps.
4. Report
Report is written to describe or classify the way things are or
seem to be. The generic structures are general classification and
description.
5. Explanation
Explanation is written to explain how something works or the
6. Persuasive
Persuasive text is written to argue or persuade. Persuasive
texts are organized with: proposition to be argued, arguments in
logical order and reiteration.
7. Descriptive
Description is a type of text that describes a particular
person, place or thing detail. The generic structures are
identification and description.
8. Analytical Exposition
Analytical Exposition is text that uses to reveal the readers
that something is the importance case. The generic structures are
thesis, argument and reiteration or conclusion.
9. Hortatory Exposition
Analytical Exposition is a type of text that uses to persuade
the readers that something should or should not be the case or be
done. The generic structures are thesis, argument and
recommendation.
10.Procedure
Procedure is a type of text that uses to help readers how to do
or make something completely. The generic structures are goal or
c. The Writing Process
According to Rahayu and Prayitno (2015, p. 43) there are four
main stages in the writing process, they are:
1. Pre-writing
Choose and narrow the topic to a particular aspect of the
general one. For example if the topic is about environmental you
can narrow it from the environmental pollution to the pollution of
ocean and finally you can narrow it to the most specific topic.
2. Planning
Plan what to write, when to start, and how to end. Making
planning is important because from this point you will decide your
writing.
3. Writing and revising draft
As soon as you have planned, you directly execute writing with
all the techniques that you have learnt then practice it. After
writing the draft you have done, do not forget to revise it. Finally,
writing process should be accomplished.
4. Writing the final copy
Writing the final version takes some time, hence it should be
done very carefully. Then you are ready to hand in your lecturer
d. Teacher Roles in Teaching Writing
According to Harmer (2001, p. 261), he said that the teacher
needs usual process when the students are asked to write, the ones that
are especially important are as follows:
1. Teacher as a Motivator
One of our principle roles in writing task will be to motivate
the students, creating the right conditions for the generations of
ideas, persuading them of the usefulness of the activity and
encouraging them to make as much effort on our part for longer
process writing sequence.
2. Teacher as a Resource
In writing task, the teacher should be ready to supply
information and language where necessary. The teacher needs to
tell students in offering devices and suggestion to look their
progresses.
3. Feedback provider
The teacher needs to give feedback on writing task. The
teacher should correct the task and respond positively to the
e. Scoring of Writing
Assessing writing product divided into five components, they are
content, organization, grammar, vocabulary and mechanic (Brown
2007; as quoted file:///C:/Users/ASp%20E1-422/Downloads/rubrik%)
access on Monday 24th 2017.
TABLE 2.1
Scoring writing Rubric
Aspect Score Performance Description
Content
Topic
Details
4 The topic is complete and clear and the
details are relating to the topic
3 The topic is complete and clear but the
details are most relating to the topic
2 The topic is complete and clear but the
details are not relatingto the topic
1 The topic is not clear and the details are
description are arranged with proper
Description 3 General condition is almost complete
description are arranged with misuse of
connectives
inaccuracies but not affect on meaning
2 Numerous grammatical or agreement
inaccuracies
1 Frequent grammatical or agreement
inaccuracies
Vocabulary 4 Effective choice of words and word
forms
3 Few misuse of vocabularies, word
2 Limited range confusing words and
word form
1 Very poor knowledge of words, word
form and not understandable
Mechanics
Spelling
Punctuation
Capitalization
4 It uses correct spelling, punctuation and
capitalization
3 It has occasional errors of spelling,
punctuations and capitalization
2 It has frequent errors of spelling,
punctuations and capitalization
1 It is dominated by error of spelling,
CHAPTER III
METHOD OF RESEARCH
A. Research Setting
1. General Situation of MA Utsmaniyyah
The research is conducted at MA Utsmaniyyah Ngroto, Grobogan in
the academic year 2017/2018. MA Utsmaniyyah is an Islamic senior high
school which consists of 3th grade of the students. There are 3 classes.
Beside of the classroom, there are other room and facilities at MA
Utsmaniyyah, like library, computer room, teachers’ room, headmaster
room, toilet, parking area and field sport.
Name of school : MA Utsmmaniyyah
NSS : 131233150037
NPSN : 69894829
Address : Jl. Abdurrohman Ganjur NO. 01 Ngroto, Gubug,
Grobogan, Jawa Tengah, Indonesia.
Phone : 085740754780
E-mail : ma.utsmaniyyah@gmail.com
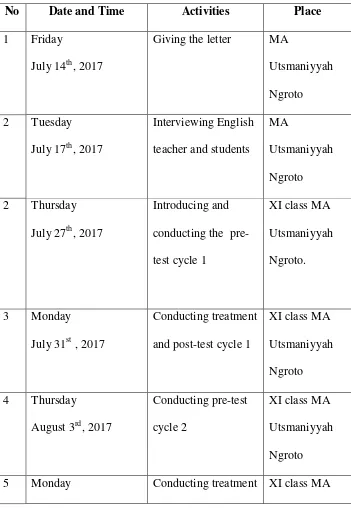
2. The schedule of research
The schedule of research can be drawn in the table below:
Table 3.1The schedule of research
August 7th, July 2017 and post-test cycle 2 Utsmaniyyah
Ngroto
3. The subject of research
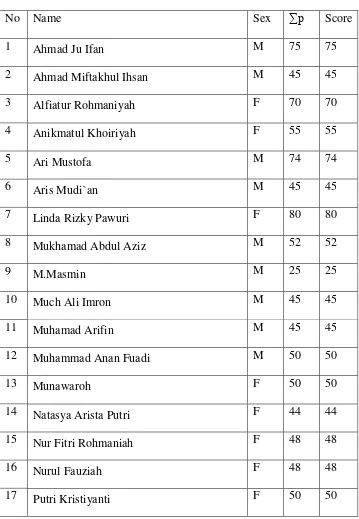
The subject of the study is XI class of MA Utsmaniyyah Ngroto,
Grobogan in academic year 2017/2018. The researcher takes XI class,
there are 20 students which consist of 11 females and 9 males. Based on
the researcher’ observation, this class has low score in English term,
especially in writing. Therefore, the researcher wants to apply Task Based
Learning approach in order to improve students’ writing skill. The
position of the researcher in this research is as an observer. Moreover, the
teacher of this research is the teacher from this school itself.
Table 3.2
List of the XI IPS class of MA Utsmaniyyah Ngroto, Grobogan in
the Academic Year 2017/2018
No Name Sex
1 Ahmad Ju Ifan Male
2 Ahmad Miftakhul Ihsan Male
3 Alfiatur Rohmaniyah Female
4 Anikmatul Khoiriyah Female
6 Aris Mudi`an Male
7 Linda Rizky Pawuri Female
8 Mukhamad Abdul Aziz Male
9 M.Masmin Male
10 Much Ali Imron Male
11 Muhamad Arifin Male
12 Muhammad Anan Fuadi Male
13 Munawaroh Female
14 Natasya Arista Putri Female
15 Nur Fitri Rohmaniah Female
16 Nurul Fauziah Female
17 Putri Kristiyanti Female
18 Ryan Munif Efendi Male
19 Sinta Sinambela Female
20 Umi Muryani Female
B. Method of Research
In this research, the researcher uses classroom action research. There
are some definitions of classroom action research.
According to McNiff (1998, p. 1) action research is the name given to
teacher to be reflective of his own practice in order to enhance the quality of
education for himself and his students.
According to Fraeknel, W & Hyun (2012, p. 589) action research is
conducted by one or more individuals or groups for the purpose of solving a
problem or obtaining information in order to inform local practice.
According to Elliot (1991, p. 54), he said that action research
integrates teaching and teacher development, curriculum development and
evaluation, research and philosophical reflection into a unified conception of a
reflective educational practice.
Based on definitions above, the researcher concludes that classroom
action research is research or practical interpretation is conducted by a person
in educational practice or teaching learning process to know the situation
when they are studying. The researcher identifies the problem which is found
in the class before applying Classroom Action Research.
C. Procedure of the Research
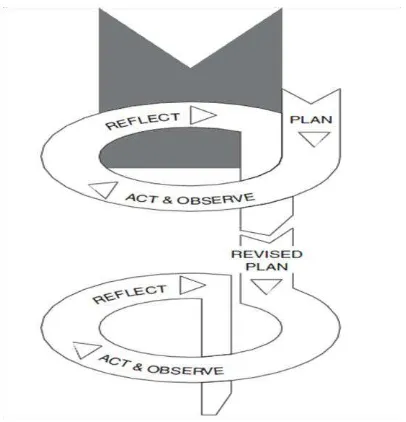
Kemmis, S. & McTaggart (2007, p. 278) makes a spiral model of
action research that has four steps. The spiral model is illustrated in the figure
TABLE 3.3
KEMMIS AND MC TAGGART’S MODEL (2007)
1. Planning
The activities in the planning are as follow:
a. Preparing syllabus, lesson-plan, rubric, pre-test, Post-test, media,
material.
b. Preparing validation sheet for lesson plan and syllabus
c. Preparing students’ worksheet
d. Preparing the teacher’s and students’ observational checklist
e. Preparing teaching aids of learning in the class (e.g. worksheet, power
2. Action
In action activities, as an implementation of the planning, the
researcher presented them in the following:
a. Providing some pictures that related with the material
b. Guiding students to identify the picture based on the characteristics
generally
c. Giving feedback of the picture
d. Giving a complete Report Text
e. Giving opportunity to the students by asking the difficulties problems
f. Asking the students to identify the generic structure of the text
g. Asking the students to write based on the instruction of the teacher
(students’ worksheet)
h. Asking the students to present their assignment
i. Summarizing and discussing the result of the presentation
j. Helping students to get main point of the lesson
3. Observation
In this research, the researcher is an observer and the teacher is the
teacher of the school itself. In this activity, the researcher observes the
teacher and students’ activity during the lesson. It is started from pre-test
until post-test. All of situation in the class are observed and written in an
observational checklist. The observational checklist for teacher is
a. Teacher enter the class and greeting students before the lesson.
b. Teacher ask the students to read praying.
c. Checking students’ attendance.
d. Giving ice breaking that related to the material.
e. Explaining the material fluency by using Task Based Learning
method.
f. Giving pictures in power point thet related with the material and ask
the students to describes generally.
g. Asking students to identify the text based on the generic structure.
h. Giving worksheet (picture) to the students.
i. Asking the students to write simple sentence based on worksheet
j. Asking the students to present their assigment
k. Asking one of students write the their sentence on the board
l. Evaluating students’ assignment and giving feedback for their work.
m. Asking students to summarize the lesson
n. Informing next material for nex meeting
o. Closure
Later on, the result of the students’ observation checklist are explained
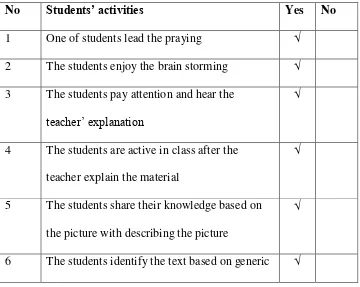
below:
a. One of students lead the praying
b. Students enjoy the ice breaker
d. Students active in class after the teacher explain the material
e. Students sharing their knowledge based on the picture with describing
the picture
f. Students identify the text based on generic structure
g. Students write simple sentence based on worksheet
h. Students present their assigment
i. One of tudents write their sentence on board
4. Reflection
The observer’s reflection discuss with the teacher to know the
changes happened toward students, classroom atmosphere. The researcher
would analyze the observation sheets and identify the problems to find the
alternative decision to solve the problem. Then the next cycle can be
decided or designed.
D. Techniques of Collecting Data
In this research, the researcher uses some technique to collect the data,
as follows:
1. Observation
According to Khosy (2005, p. 99), observation plays an important
part in any kind of data-gathering and most action research project this
instrument. Observation is a natural process to observe use this action and
2. Interview
According to Khosy (2005, p. 98) states that the main purposes of
interview is to gather responses which are richer informative than
questionnaire data. The researcher uses interview to know the problems
happening in the class. Before conducing class room action research, the
researcher interviews the teacher.
3. Test Instrument
Test is a set of question or exercise or other instrument used to
measure knowledge, intelligence, ability or attitude of groups or
individual.
a. Pre -Test
Pre test is used to know how far is the student’s ability in
writing skill before using Task Based Learning.
b. Post- Test
Post test is used to know how far the students writing skill
after the application Task Based Learning.
4. Documentation
The researcher would record visual data about learning process or
result of learning in the class. So, the researcher knows about the learning
activity of the students in the class. According to Hopkins (1993, p. 140)
stated that document surrounding curriculum or other educational concern
E. Techniques of Data Analysis
In this study, the researcher uses quantitative data. According to
Khosy (2005, p. 86) states that quantitative can be measured and represented
by numbers. The researcher analyses the numeric data by calculating the mean
of pre-test and post-test. The researcher uses statistical technique to know the
students’ score. A statistical technique is used to summarize the data using
number. This technique is used to know the students’ score of writing in each
cycle. Statistic is a body of mathematical techniques or processes for
gathering, organizing, analyzing and interpreting numerical data (Malvino &
Leach, 1981, p. 219). The researcher uses statistical techniques through some
ways, they are:
1. Mean calculation
Central tendency is a single value that attempt to describe a set of
data by identifying the central position within that set of data. There are
three commonly which is used central tendencies are mean, median and
the mode. Analyzing the data in this research, the researcher only uses one
central tendency, which is mean. Mean is formula to know the average of
the students score. The formula is:
(https://statistics.laerd.com/statistical-guides/measures-central-tendency-mean-mode-median.php) access On
M =
Explanation:
M : Mean of the student’s score
∑X : The sum of student’s score
N : The total of number of students
2. Calculate Mean of Difference
According to Sudijono (2009, p. 306), to calculate the t-test the
following formula should be used Calculate Mean of Difference. The
formula is:
MD =
Explanation:
MD : Mean of difference
∑D : Total of difference between pre-and post-test.
3. Standard Deviation Calculation
Standard Deviation is a statistic that tells you tightly all the various
examples are clustered around the mean in set of data (Robert Niles; quoted
from http://www.robertniles.com/stats/stdev.shtml access on Thursday 20th,
2017. The formula used for calculating standard deviation is as follow:
Explanation:
: Standard Deviation
D : Different between pre and post-test
N : The number of students
4. Standard Error Mean Difference
According to Sudijono (2009, p. 307) to calculate the t-test the
following formula should be used:
=
Explanation:
:Standard Error Mean Difference
: Standard Deviation
N : The number of students
5. T-test
After calculating SD, the researcher calculates t-test to know is
there any significant improvement or not between pre-test and post-test.
According to Sudijono (2009, p. 307) the formula is:
Explanation:
To : T-test
: Standard Error Mean Difference
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH IMPLEMENTATION AND ANALYSIS
This chapter focuses on analyzing the data collection. The researcher collects
the data from eleventh grade students of Utsmaniyyah Ngroto Islamic High School
academic year 2017/2018. It shows the finding of the data collected from the
beginning until the end of the research. The findings consist of the results of pre and
post-test of cycle 1 and cycle 2. In this study, the researcher arranges two cycles
which use Task Based Learning to improve students’ writing skill.
A. The implementation of Task Based Learning to improve students’ writing
skill for the eleventh grade students of MA Utsmaniyyah Ngroto, Grobogan
in the academic year of 2017/2018.
1. Cycle I
a. Planning
The activities in the planning were done by the researcher as follows:
1) Preparing the syllabus (Report Text)
2) Preparing the lesson plan (Report Text)
3) Preparing the pre-test and post-test based on indicator
4) Preparing rubric (scoring of students’ writing and score fill the blank)
5) Preparing the students’ worksheet
6) Preparing the students’ and teacher’s observational check list for cycle
7) Validating the lesson plan and syllabus with the teacher in order to
confirm its compability
8) Preparing teaching material (Report Text)
9) Preparing the media (Slides of Power Point Presentation)
10) Preparing the students’ attendance list
11) Preparing the tools of learning in the class(a projector and laptop)
12) Preparing the camera to take pictures and videos
b. Implementation of Action
The first cycle was done on July 27th, and 31st 2017. The researcher
gave the pre-test to the students on the first day on July 27th, 2017. For the
second day was on July 31st , 2017, the researcher gave treatment and
post-test to the students.
1) Pre-test
In the first day, the researcher gave pre-test and introduced
herself to the students. The researcher gave instruction how to do the
pre-test. The researcher gave two points of test. The theme of A point
was “Beach”, the students were asked to fill the blank space with the
given words. For B point, the students were asked to write 10
sentences generally about “Mobile Phone”. The researcher walked
around the class in order to check the students during the test.
In the pre-test, the students worked A point, but they did not
each blank in A point, it was caused that they did not know the
appropriate word. For A point, the researcher also asked the students
to write down again in order to know how the students’ writing ability.
On B point, the students did not write down their ideas yet. Actually,
the researcher provided some words that related to the topic in the
whiteboard. In addition, those words helped the students to write their
ideas. Unfortunately, the students were still confused to write what
they want to write. The students also got some difficulties to make a
simple sentence within correct grammar.
2) Treatment and post-test
a) Treatment
The second day of this cycle, the researcher gave the
treatment for the students. The teacher entered the class and
greeted the students. Starting the lesson, the teacher asked one
of the student to recite basmallah and pray together. Then, the
teacher checked students’ attendance list. The teacher gave an
brain storming to invite the students’ interaction. In the class,
the researcher helped the teacher to operate the computer. The
researcher also observed the students’ and the teacher’s
activities during the lesson. The researcher had a partner who
helped the researcher to take video or photos for
In this research, the researcher used Task Based
Learning to improve the students’ writing skill. In Task Based
Learning, there were 3 methodologies in the learning process.
The first stage was pre task activity, the teacher introduced and
explained the topic. The second stage was cycle task activity
which consists of three parts such as planning, task and report.
For the third stage was language focus which consists of 2
parts such as analysis and practice.
The first stage of the method was pre-task activity. The
teacher gave a brain storming the material. It helped the
students to understand the material. When the students enjoyed
it, the students understand what the teacher taught easily. In
this activity, the teacher explained the generic structure and
language function of the text. The teacher gave a complete
explanation about the report text on PowerPoint Presentation.
Besides, the teacher gave an example of report text about
“Teacher” in a piece of paper. After the teacher explained the
material, the students still paid attention, but there were no
question from the students. The teacher tried to build the
students’ interest by giving pictures that related to the topic.
Indeed, the students were interested in the lesson by giving
Task Based Learning focused on the learning by doing,
so the teacher gave some task of this cycle. The teacher asked
the students to analyze the generic structures of the text and
also looked for the verb of the text. The discussion could not
be success because the students were still confused to
determine the generic structure and verb on the text. Then, the
teacher reviewed the material. Finally, most of the students
were easy to understand the materials.
The second stage was cycle task activity. It consists of
3 parts; they were planning, task and report. In the planning
activity, the teacher gave a picture about school equipment
(Eraser). In the task activity, the teacher asked the students to
write down simple sentences based on the picture. They were
still confused to write simple sentences. However, the teacher
tried to give some clues to the students, so they could write
simple sentences even though they still making some mistakes.
In the report activity, the teacher asked students to present their
sentences.
The last stage was language focus activity. It consists of
analysis and practices. In the analysis activity, the students
examined and discussed the specific feature of their sentences.
assignment. Then, the teacher gave feedback to make the
students more understand the lesson. The teacher helped the
students to summarize the main point of the lesson, so the
student might remember the material. After that, the teacher
closed the lesson.
b) Post-test
After the treatment, the researcher gave post-test for the
students. The students were not ready because they were given
assignment for twice. Then the researcher explained it to them
to make the students understand. The researcher also said that
the question were almost same with the pre-test. The researcher
gave an instruction that the students were allowed to open their
dictionary.
In the post-test, the students’ improvement in analyzing
the incomplete sentences could be seen by answering the
questions of A point is better than pre-test. For B point, some
students tried to write simple sentences based on the
researcher’s instruction. They had some grammatical error, like
“Many people like they”, it should be written “Many people
like them”. Besides, the researcher had found the difficulties in
translating words, like “Rabbit is which very cute”, it should
researcher felt proud of them, because they were so responsible
with their assignment. The researcher concludes that the
students still adapted with the process of the study.
c. Observation
In the first cycle, the researcher observed the teaching and learning
process. The researcher made two observational checklist for the teacher
and students. The explanation of the result of the teacher’s observational
checklist are as follows:
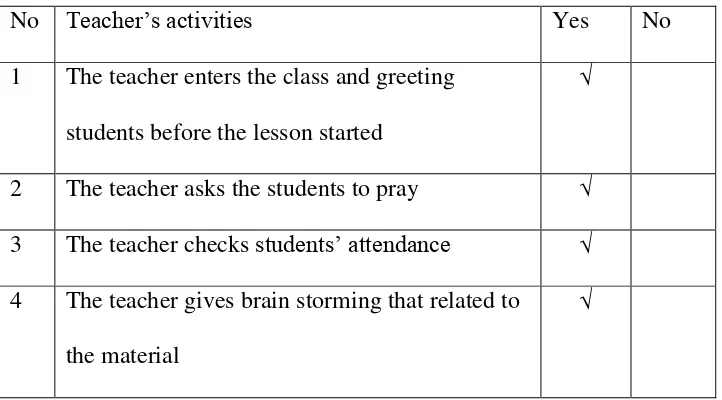
Table 4.1
Teacher’s Observation Checklist of Cycle 1
No Teacher’s activities Yes No
1 The teacher enters the class and greeting
students before starting the lesson
√
2 The teacher asks the students to pray √
3 The teacher checks students’ attendance √
4 The teacher gives brain storming related to the
material
√
5 The teacher explains the material by using Task
Based Learning method
√
related with the material and asks the students
to describe generally
7 The teacher asks the students to identify the text
based on the generic structure
√
8 The teacher gives worksheet (picture) to the
students
√
9 The teacher asks the students to write simple
sentence based on worksheet
√
10 The teacher asks the students to present their
assigment
√
11 The teacher asks one of students to write their
sentences on the board
√
12 The students evaluates and gives feedback for
students’ assignment
√
13 The teacher asks the students to summarize the
lesson
√
14 The teacher informs the next material for next
meeting
√
The teacher forgot to inform the next material. The students did
not present and write their assigment in front of the class because they were
shy to express their assignment and also they were afraid if their
assignment was wrong. In this research, the researcher used KTSP
curriculum which consists of 3 stages, there were Exploration, Elaborate
and confirmation.
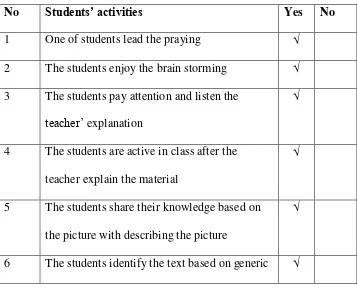
Later on, the result of the students’ observation checklist were
explained below:
Table 4.2
Students’ Observational Checklist of cycle 1
No Students’ activities Yes No
1 One of students lead the praying √
2 The students enjoy the brain storming √
3 The students pay attention and listen the
teacher’ explanation
√
4 The students are active in class after the
teacher explain the material
√
5 The students share their knowledge based on
the picture with describing the picture
√
structure
7 The students write simple sentence based on
worksheet
√
8 The students present their assigment √
9 One of tudents write their sentence on board √
For the table above, the researcher concluded that the students had
participated the class well. The students gave good responses and asked
what they did not understand. The students shared their knowledge based
on the picture and described it, some of students did not present and write
their assigment in front of the class because they were shy to express their
assignment and also they were afraid if their assignment was wrong. The
researcher thought that the students still adapted with that implememtation.
d. Reflection
Based on the analizing of the first cycle, the researcher concluded
that the apllication of Task Based Learning in this class was not effective
yet. The students still adapted with this approach. In the first cycle, the
researcher thought that there were 2 causes that made the students difficult
to understand the lesson. The first cause was the researcher gave 3
categories of task, so the students felt bored and difficult to understand the
Learning for the students individually was not effective, so the researcher
would replace of task in order to make the students more focus in
understanding the lesson. Then, the researcher also wanted to change the
lesson in pair. The researcher should be creative in giving explanation,
because the students did not like the learning writing especially to write
paragraph.
The passing grade of English lesson was 70. The researcher had
found low score from the passing grade. The students who had score more
70 there were 25% from 20 students. The students who had score 70 there
were 5% from 20 students. Then, there were 70% from 20 students who
got less score from the passing grade. In this cycle , the students did not
reach the passing grade so the researcher should conduct the cycle 2 to
achieve the target.
2. Cycle 2
a. Planning
The activities in the planning were done by the researcher as follows:
1) Preparing syllabus (Report Text)
2) Preparing the lesson plan (Report Text)
3) Preparing the pre-test and post-test based on indicator
4) Preparing rubric (scoring of students’ writing and score of incomplete
sentences)
6) Preparing the students’ and teacher’s observational check list for cycle
2
7) Validating the lesson plan and syllabus with the teacher in order to
confirm its compability
8) Preparing teaching material (Report Text)
9) Preparing media (Slides of Power Point Presentation)
10) Preparing students’ attendance list
11) Preparing tools of learning in the class(a projector and laptop)
12) Preparing the camera to take pictures and video.
b. Implementation of Action
The cycle 2 was done on August 3rd and 7th 2017. The researcher gave
the pre-test to the students on the first day on August 3rd , 2017. For the
second day was on August 7th ,2017, the researcher gave treatment and
post-test to the students.
1) Pre-test
In the first day, the researcher gave pre-test to the students. The
researcher also gave an instruction how to do the pre-test. The theme
of A point was “Elephant”. The students were asked to fill the blank
space with the given words. For B point, the students were asked to
write 10 sentences generally about “Rabbit”. The researcher walked
In the pre-test, most of the students worked A point well, but
there were some words inappropriate answer. In B point, the students
began to write down their ideas in short sentence. The researcher also
provided some words related to the topic in whiteboard. In this cycle,
students could write some simple sentences eventhough they got some
grammatical errors.
2) Treatment and post-test
a) Treatment
The second day of this cycle, the researcher gave the
treatment for students. The teacher entered the class and greeted
the students in the class. Before the lesson started, the teacher
asked one of student to recite basmallah and prayed together.
Then, the teacher checked the students’ attendance list. The teacher
gave a brain storming to invite the students’ interaction. In the
class, the researcher helped the teacher to operate the computer.
The researcher also observed the students’ and the teacher’s
activities during the lesson. The students were ready to follow the
lesson when the teacher asked them. The researcher’ partner was
also ready to take photos for documentation.
In this research, the resaercher used Task Based Learning
to improve the students’ writing skill. In Task Based Learning,
was pre task activity which the topic explained by the teacher. The
second stage was cycle task activity which consisted of three parts
such as planning, task and report. For the third was language focus
which consists of 2 parts such as analysis and practice.
The first stage was pre-task activity. The teacher gave a
brain storming related to the material. When the students enjoyed
the lesson, the students could understand what the teacher taught
easily. In this activity, the teacher explained the generic structure
and language function of the text. The teacher gave a complete
explanation about the report text on PowerPoint Presentation.
Besides that, the teacher gave an example of report text about
“Kangaroo” in a piece of paper. The teacher tried to build the
students’ interest by giving pictures related to the topic. Indeed, the
students gave good responses and asked what they did not
understand. The students were active in learning process. Some of
the students asked about grammar that could be used in report text.
They began to understand the lesson.
The second stage was cycle task activity. It consists of 3
parts: planning, task and report. In the planning activity, the
teacher divided the students in pair. The teacher determined their
pair based on their seat. The teacher gave pictures about animal
students to write down simple sentences based on the picture with
their pairs. The students could write simple sentences. In the report
activity, the teacher asked the students to present their sentences.
One of them wrote their sentences on the board. They discussed it
well. They also wanted to come forward to present their task.
The last part was language focus activity. It consists of
analysis and practices. In the analysis activity, the students
examined and discussed specific feature of their sentences. In the
practice activity, the teacher analyzed the students’ assignment.
Then, the teacher gave feedback to make the students more
understand and they fixed their mistake. It was done by discussing
the sentences with the students. The teacher helped the students to
summarize the main point of the lesson, so the students would
memorize the material. Then, the teacher closed the lesson and
greeted the students.
b) Post-test
After the treatment, the researcher gave post-test for the
students. There were two forms of the questions. Almost all of the
students answered the questions of A point better than pre-test. For
B point, some students wrote simple with correct grammar.
When the students did the post-test, the researcher saw the