12/27/2017 Vol 109, No 1 (2015)
Iso!avone content of soybean [Glycine max (L). Merr.] cultivars with different nitrogen sources and growing season under dry land conditions
Yaya Hasanah, Tengku Chairun Nisa, Hapsoh Armidin, Hamidah Hanum
PDF 5-17
Agricultural vulnerability in Bangladesh to climate change induced sea level rise and options for adaptation: a study of a coastal Upazila
Md. Anowarul Islam, Paul Kumar Shitangsu, Md. Zahidul Hassan
PDF 19-39
Econometric Analysis of the Demand for Pulses in Sri Lanka: An Almost Ideal Estimation with a Censored Regression
Lokuge Dona Manori Nimanthika Lokuge, Jagath Chaminda Edirisinghe
PDF 41-53
Variabilité morphologiques et conservation des morphotypes de Jatropha curcas Linn. (Euphoriaceae) au Benin.
Charlemagne Judes Gbemavo, Kisito Gandji, Cesaire Paul Gnangle, Achille Ephrem Assogbadjo, Romain Lucas Glèlè Kakaï
PDF 55-69
Determinants of Adoption of Improved Onion Variety in Bangladesh
Asif Reza Anik, Md. Abdus Salam
PDF 71-88
Composts de déchets urbains et dynamiques du carbone du sol à Donsin, Burkina Faso
Dasmané Bambara, Adjima Thiombiano, Victor Hien
PDF 89-108
Cotton price change and welfare in Togo
Anani Nourredine Mensah
PDF 109-122
Seasonal dynamic of herbaceous fodder production in the Sahelian pastures used by domestic ruminants
Oumou Sanon, F. Ouattara, Moumini Savadogo
PDF 123-138
Irrnet estimation for maize and cotton in Piracicaba, São Paulo, Brazil
Paolo Enrico Sertoli
PDF 139-162
Journal of Agriculture and Environment for International Development - JAEID 2015, 109 (1): 5 - 17
DOI: 10.12895/jaeid.20151.216
Isoflavone content of soybean [
Glycine max
(L). Merr.]
cultivars with different nitrogen souces and growing
season under dry land conditions
Y
AYAH
ASANAH1*, T
ENGKUC
HAIRUNN
ISA1, H
APSOHA
RMIDIN2, H
AMIDAHH
ANUM11
Faculty of Agriculture, University of Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia.
2Faculty of Agriculture, University of Riau, Pekanbaru, Indonesia.
*Corresponding author: [email protected]
Submitted on 2014, 3 March; accepted on 2015, 16 March. Section: Research Paper
Abstract
: The objective of the research was to determine the best N nutrient
management for isoflavone content in three soybean cultivars under dry land
conditions. Two experiments were experiment I (June to September 2012
growing season) and Experiment II (October to December 2012 growing
season). Experimental design was a randomized block design with 2 factors and
3 replications. The first factor was soybean cultivars (Anjasmoro, Wilis,
Sinabung). The second factor was N source, with Urea (50 kg/ha),
Bradyrhizobium
sp., farmyard manure (10 ton/ha), a combination of
Bradyrhizobium
sp. + farmyard manure (5 ton/ha) and a control with no N. A
combined analysis of variance was done to evaluate the production and the
content of isoflavone in the two different growing seasons as affected by N
source and cultivar. The parameters observed were the content of genistein,
daidzein, glycitein and total isoflavone content. Results showed that the October
to December growing season had higher genistein, daidzein, glycitein and total
of isoflavones than the June to September growing season. The treatment
cultivar Wilis plus
Bradyrhizobium
sp. grown at October to December growing
season increased total isoflavone content more than other treatments.
Keywords: isoflavone, nitrogen, soybean.
Introduction
which are beneficial to health. Soybean is the most common source of isoflavones in
human foods, especially in many Asian countries. Soybean isoflavones have a positive
impact on human health including prevention of chronic diseases such as cancer,
heart disease, osteoporosis and menopausal symptoms (Messina, 1995) and beneficial
effects on diabetes and renal diseases (Ranich et al., 2001). Genistein, daidzein and
glycitein, the known soybean isoflavones, are synthesized by a branch of the
phenylpropanoid pathway (Yu and McGonigle, 2005).
Isoflavone content in soybean depends on both genetic and environmental factors.
Influencing environmental factors consist of both biotic, such as wounding,
nodulation and pathogen attack, and abiotic elements such as temperature, water
regime, UV light, soil nutrient content and atmospheric carbon dioxide level (Dixon
and Paiva, 1995, Lozovaya et al., 2005, Subramanian et al., 2006, Naoumkina et al.,
2007, Subramanian et al., 2007). Planting location, crop year, planting dates within a
given crop year, and storage conditions can also affect isoflavone content (Zhu et al.,
2005; Hoeck et al., 2000; Lee et al., 2003; Seguin et al, 2004). Previous investigations
have shown that isoflavone concentrations in soybean seeds (Hoeck et al., 2000; Wang
and Murphy, 1994) are influenced significantly by location. Carrao-Panizzi
et al.
(1999) reported that the highest isoflavone concentrations were observed in seeds of
soybean plants grown in locations with high latitudes (cooler temperatures) when
compared to locations with low latitudes (warmer temperatures).
Demand for soybean in Indonesia continues to increase, along with increasing
public knowledge of the benefits of soy as a functional food. Production of soybean
is not keeping up with demand, so that efforts are necessary to improve national
soybean production. This can be achieved through increased production approaches
including expansion of soy cultivation in marginal (sub-optimal) lands. Among these
are sub-optimal dry lands. Soybean cultivation on dry land has problems such as low
soil fertility, low pH, higher amounts of Al, Fe and Mn, low organic matter as well as
water shortages, especially in dry season because of the limited water resources. Pests,
diseases and weeds along with the use of unimproved local varieties can also be
contributing factors (Arsyad and Purwantoro, 2010).
Increased productivity and content of soy isoflavones on dry land can be achieved
by the application of specific technologies according to the agroecology of dry land
agriculture. One area of dry land in North Sumatera that was once the centre of
soybean production is Sambirejo Village, District Binjei, Langkat. The dry land is
classified as lowland wet climate, experiencing problems such as drought stress during
the dry season (June to August), low pH, (pH 5.0), and low soil content of N, P and
K. Based on these problems, the management of dry land for optimum production
of soybean for yield and isoflavone characteristics can be accomplished using two
basic approaches; the selection of soybean cultivars adapted to dry land and
improvement of soil fertility through management of N and other nutrients.
Y. Hasanah et al.: Isoflavone content of soybean [Glycine max(L). Merr.] cultivars...growing season under dry land conditions
Nitrogen is one of the essential nutrients for plants. It is a key element in proteins
and nucleic acids, and is required in the synthesis of chlorophyll. Isoflavones are also
one of the important secondary metabolites in soybean plants formed through the
phenylpropanoid biosynthetic pathway precursor phenylalanine which is one of the
essential amino acids that requires N in its synthesis.
Differences in dry seasons in dry land areas affect soybean production and content
of isoflavones patterns of rainfall, humidity and temperature. It is therefore necessary
to study which growing season is best for production of soybean and seasonal effect
on isoflavones content and composition. Therefore, the objective of this research was
to determine the effect of growing season and N management on production and soy
isoflavone content in dry land.
Materials and Methods
Research was conducted in Sambirejo Village, Binjei District, Langkat, Sumatra
Utara (Indonesia), a dry land area, June to December 2012. The soil texture of the
experimental site was a sandy clay loam which had 11% coarse sand, 38% fine sand,
29% silt and 22% clay. Nitrogen content was low (0.14%), organic matter was 1.02%,
with a pH of 5.0.
Experimental design and crop management
Two planting times (seasons) were studied. Treatments were arranged in a
Randomized Block Design with two factors and three replications. The first factor
was three soybean cultivars (Anjasmoro, Wilis and Sinabung). The second factor was
(N) sources and consisted of urea at 50 kg/ha, innoculation of seed with
Bradyrhizobium sp., 10 t/ha farmyard manure, the combination Bradyrhizobium sp.
+
farmyard manure at 5 t/ha and a zero N control. The research consisted of two series
of experiments. The first was from June to September 2012 (dry season) and the
second was from October to December 2012 (rainy season). The dry season generally
goes from June to August, with the rainy season being from September to May. The
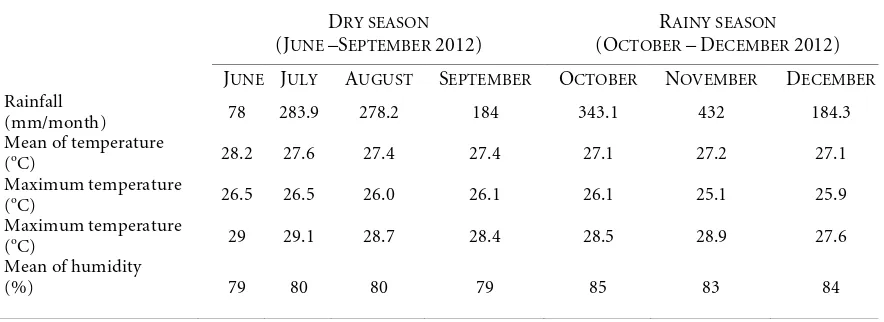
climatic characteristics of the two seasons are given in Table 1.
Isoflavone extraction and HPLC analyses
Following harvest, seeds were stored at room temperature and within one month,
isoflavones were extracted for determination of isoflavone composition and content.
Concentration of genistein, daidzein and glycitein were determined using a
high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) method from Vyn et al.
(2002). Finely
ground soybean seed was weighed in duplicate samples of 0.50 g each and dispersed
Journal of Agriculture and Environment for International Development - JAEID - 2015, 109 (1)
in 10 mL of ethanol plus 2 mL of concentrated HCl. The resulting solutions were
hydrolyzed by heating to 125 °C for 2 hours in a sand bath. After the samples were
cooled, they were centrifuged at 3000 rpm for 10 minutes. The clear aliquot was
filtered through a 0.45-µm PTFE filter. Individual hydrolyzed daidzein, genistein, and
glycitein were separated on a HPLC equipped with a photodiode array (PDA) detector
(200-300 nm). HPLC column, Waters Nove Pak C18 column (3.9 x 150 mm, 5-mm
particle size) with C18 guard column; HPLC mobile phases, solvent A was 4% aqueous
acetic acid and solvent B was 100% HPLC grade methanol; flow rate, 1.5 mL min-1;
and injection volume, 5 mL. HPLC mobile phases were solvent A (4% aq. acetic acid)
and solvent B (100% methanol), and the solvent system was as follows (%solvent A%
solvent B): 0 min (70/30), 12.5 min (65/35), 13 min (50/50), 15 min (30/70), 22.5 min
(25/75), and 23 min (70/30). Recovery was monitored by the addition of a recovery
standard, flavone, to the sample prior to hydrolysis.
Statistical data analysis
Data were subjected to analysis of variance (ANOVA) for comparison of means. A
combined analysis of variance was done to evaluate isoflavones affected by growing
season. Means were separated using Duncan’s Mutiple Range Test at the 0.05
probability level.
Results
Genistein
Mean comparisons for the effect of N sources in different growing seasons on
genistein content of soybean cultivars are shown in Table 2. Soybean grown during
the rainy season had higher genistein content (219.96 µg/g) than that grown during
Y. Hasanah et al.: Isoflavone content of soybean [Glycine max(L). Merr.] cultivars...growing season under dry land conditions
Journal of Agriculture and Environment for International Development - JAEID - 2015, 109 (1) 8
Table 1 - Climate characteristic factors of dry and rainy seasons at Sambirejo Village, Binjei District.
Source: Meteorology Climatology and Geophysics Agency, Medan (2012). DRY SEASON
(JUNE –SEPTEMBER 2012)
RAINY SEASON
(OCTOBER –DECEMBER 2012) JUNE JULY AUGUST SEPTEMBER OCTOBER NOVEMBER DECEMBER
Rainfall
(mm/month) 78 283.9 278.2 184 343.1 432 184.3
Mean of temperature
(oC) 28.2 27.6 27.4 27.4 27.1 27.2 27.1
Maximum temperature
(oC) 26.5 26.5 26.0 26.1 26.1 25.1 25.9
Maximum temperature
(oC) 29 29.1 28.7 28.4 28.5 28.9 27.6
Mean of humidity
Journal of Agriculture and Environment for International Development - JAEID - 2015, 109 (1)
Y. Hasanah et al.: Isoflavone content of soybean [Glycine max(L). Merr.] cultivars...growing season under dry land conditions 9
CULTIVAR
GROWING SEASON MEAN
N SOURCES
DRY SEASON RAINY SEASON
... µG/G SEED WEIGHT ...
Anjasmoro Without N application 220.16 208.71 214.43 (V1) Urea (50 kg/ha) 220.23 189.32 204.77
Bradyrhizobium sp. 206.53 246.80 226.66
Farmyard manure (10 t/ha) 218.38 231.74 225.06
Bradyrhizobium sp. + farmyard
manure (5 t/ha) 187.51 207.31 197.41 Mean of V1 x M 210.56i 216.77h
Mean of V1 213.67
Wilis Without N application 202.96 197.43 200.19 (V2) Urea (50 kg/ha) 213.01 221.16 217.08
Bradyrhizobium sp. 212.86 243.67 228.27
Farmyard manure (10 t/ha) 199.18 203.12 201.15
Bradyrhizobium sp. + Farmyard
manure (5 t/ha) 165.14 232.77 198.96 Mean of V2 x M 198.63j 219.63gh
Mean of V2 209.13
Sinabung Without N application 188.88 210.88 199.88 (V3) Urea (50 kg/ha) 186.14 226.26 206.20
Bradyrhizobium sp. 179.28 234.71 206.99 Farmyard manure (10 t/ha) 175.97 230.44 203.21
Bradyrhizobium sp. + Farmyard
manure (5 t/ha) 194.78 215.10 204.94 Mean of V3 x M 185.01k 223.48g
Mean of V3 204.24 Without N application 204.00ef 205.67def 204.84 Urea (50 kg/ha) 206.46de 212.25cd 209.35
Bradyrhizobium sp. 199.56ef 241.72a 220.64 Farmyard manure (10 t/ha) 197.84f 221.77b 209.81
Bradyrhizobium sp. + farmyard
manure (5 t/ha) 182.48g 218.39bc 200.44 Mean of M 198.07y 219.96x
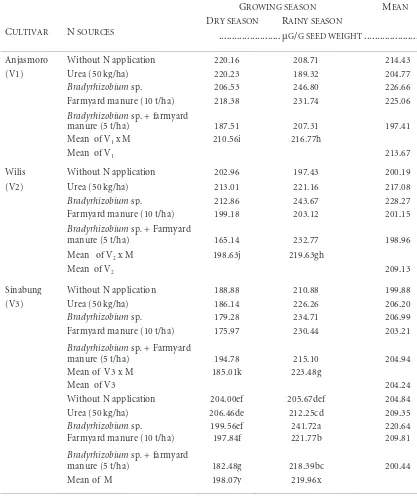
Table 2 - Genistein content of soybean cultivars with different of N. sources and growing seasons
under dry land conditions.
the dry season (198.07 µg/g). Cultivar Anjasmoro tended to have higher genistein
content (213.67 µg/g) than Willis (209.13 µg/g) and Sinabung (204.24 µg/g). Sinabung
cultivar grown during the rainy season had the highest genistein content (223.48 µg/g)
than Sinabung cultivar grown during the dry season which had the lowest genistein
content (185.01 µg/g). The treatment of Bradyrhizobium sp. during the dry season
had the highest genistein content (234.71 µg/g), than the treatment of Bradyrhizobium
sp.
+ farmyard manure (5 t/ha) during the dry season had the lowest genistein content
(182.48 µg/g).
Daidzein
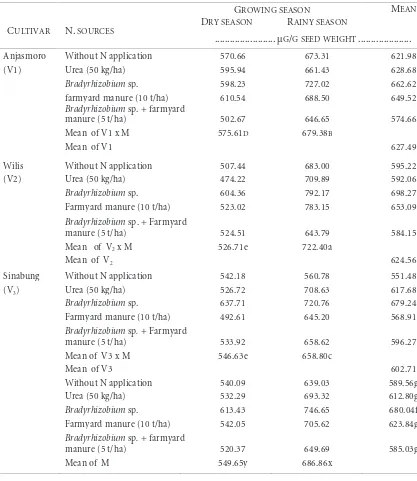
Mean comparisons for the effect of N sources at different growing seasons on
daidzein content of soybean cultivars are shown in Table 3. Soybean grown during
the rainy season had a higher daidzein content (686.86 µg/g) significantly than the
dry season (549.65 µg/g). Cultivar of Anjasmoro tended to have a higher daidzein
content (627.49 µg/g) than Willis (624.56 µg/g) and Sinabung (602.71 µg/g). Wilis
cultivar grown during the dry season had the lowest content of daidzein (526.71 µg/g),
while Wilis cultivar grown during the rainy season had the highest content of daidzein
(722.40 µg/g). Treatment of Bradyrhizobium sp.
had significantly higher content of
daidzein (680.04 µg/g) than all other N sources treatment. The interaction among N
source of Bradyrhizobium sp. and Wilis cultivar grown during the rainy season tended
to increase daidzein content (792.17 µg/g), while the interaction among Urea and
Wilis cultivar grown during the dry season tended to have the lowest content of
daidzein (474.22 µg/g).
Glycitein
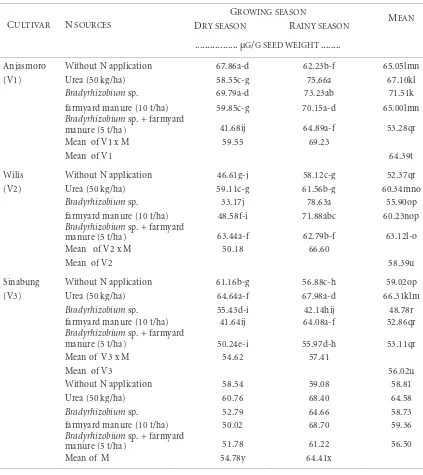
Mean comparisons for the effect of N sources at different of growing seasons on
glycitein content of soybean cultivars are shown in Table 4. Soybean grown during
the rainy season had a higher glycitein content (64.41 µg/g) significantly than the dry
season (54.78 µg/g). Anjasmoro cultivar had the highest glycitein content (64.39
µg/g) than Wilis (58.39 µg/g) and Sinabung (56.02 µg/g). The treatment of
Bradyrhizobium sp.
and Anjasmoro cultivar had the highest glycitein content (71.51
µg/g) than other treatments. The treatment of Urea (50 t/ha) and Anjasmoro cultivar
grown during the rainy season increased glycitein content(75.66 µg/g) significantly
than other combination treatments.
Y. Hasanah et al.: Isoflavone content of soybean [Glycine max(L). Merr.] cultivars...growing season under dry land conditions
Journal of Agriculture and Environment for International Development - JAEID - 2015, 109 (1)
Y. Hasanah et al.: Isoflavone content of soybean [Glycine max(L). Merr.] cultivars...growing season under dry land conditions 11
Table 3 - Daidzein content of soybean cultivars with different of N sources and growing seasons
under dry land conditions.
CULTIVAR
N. SOURCES
GROWING SEASON MEAN DRY SEASON RAINY SEASON
...µG/G SEED WEIGHT ...
Anjasmoro Without N application 570.66 673.31 621.98 (V1) Urea (50 kg/ha) 595.94 661.43 628.68
Bradyrhizobium sp. 598.23 727.02 662.62
farmyard manure (10 t/ha) 610.54 688.50 649.52
Bradyrhizobium sp. + farmyard
manure (5 t/ha) 502.67 646.65 574.66 Mean of V1 x M 575.61D 679.38B
Mean of V1 627.49
Wilis Without N application 507.44 683.00 595.22 (V2) Urea (50 kg/ha) 474.22 709.89 592.06
Bradyrhizobium sp. 604.36 792.17 698.27
Farmyard manure (10 t/ha) 523.02 783.15 653.09
Bradyrhizobium sp. + Farmyard
manure (5 t/ha) 524.51 643.79 584.15 Mean of V2 x M 526.71e 722.40a
Mean of V2 624.56
Sinabung Without N application 542.18 560.78 551.48 (V3) Urea (50 kg/ha) 526.72 708.63 617.68
Bradyrhizobium sp. 637.71 720.76 679.24
Farmyard manure (10 t/ha) 492.61 645.20 568.91
Bradyrhizobium sp. + Farmyard
manure (5 t/ha) 533.92 658.62 596.27 Mean of V3 x M 546.63e 658.80c
Mean of V3 602.71
Without N application 540.09 639.03 589.56g Urea (50 kg/ha) 532.29 693.32 612.80g
Bradyrhizobium sp. 613.43 746.65 680.04f
Farmyard manure (10 t/ha) 542.05 705.62 623.84g
Bradyrhizobium sp. + farmyard
manure (5 t/ha) 520.37 649.69 585.03g Mean of M 549.65y 686.86x
Y. Hasanah et al.: Isoflavone content of soybean [Glycine max(L). Merr.] cultivars...growing season under dry land conditions
Journal of Agriculture and Environment for International Development - JAEID - 2015, 109 (1) 12
Table 4 - Glycitein content of soybean cultivars with different of N sources and growing seasons under
dry land conditions.
Different letters at the same of group treatment represent significant differences at Duncan’s Multiple Range Test (p < 0.05).
CULTIVAR N SOURCES
GROWING SEASON
MEAN DRY SEASON RAINY SEASON
... µG/G SEED WEIGHT ...
Anjasmoro Without N application 67.86a-d 62.23b-f 65.05lmn (V1) Urea (50 kg/ha) 58.55c-g 75.66a 67.10kl
Bradyrhizobium sp. 69.79a-d 73.23ab 71.51k farmyard manure (10 t/ha) 59.85c-g 70.15a-d 65.00lmn
Bradyrhizobium sp. + farmyard
manure (5 t/ha) 41.68ij 64.89a-f 53.28qr Mean of V1 x M 59.55 69.23
Mean of V1 64.39t
Wilis Without N application 46.61g-j 58.12c-g 52.37qr (V2) Urea (50 kg/ha) 59.11c-g 61.56b-g 60.34mno
Bradyrhizobium sp. 33.17j 78.63a 55.90op
farmyard manure (10 t/ha) 48.58f-i 71.88abc 60.23nop
Bradyrhizobium sp. + farmyard
manure (5 t/ha) 63.44a-f 62.79b-f 63.12l-o Mean of V2 x M 50.18 66.60
Mean of V2 58.39u
Sinabung Without N application 61.16b-g 56.88c-h 59.02op (V3) Urea (50 kg/ha) 64.64a-f 67.98a-d 66.31klm
Bradyrhizobium sp. 55.43d-i 42.14hij 48.78r farmyard manure (10 t/ha) 41.64ij 64.08a-f 52.86qr
Bradyrhizobium sp. + farmyard
manure (5 t/ha) 50.24e-i 55.97d-h 53.11qr Mean of V3 x M 54.62 57.41
Mean of V3 56.02u
Without N application 58.54 59.08 58.81 Urea (50 kg/ha) 60.76 68.40 64.58
Bradyrhizobium sp. 52.79 64.66 58.73
farmyard manure (10 t/ha) 50.02 68.70 59.36
Bradyrhizobium sp. + farmyard
Journal of Agriculture and Environment for International Development - JAEID - 2015, 109 (1)
Y. Hasanah et al.: Isoflavone content of soybean [Glycine max(L). Merr.] cultivars...growing season under dry land conditions 13
Table 5 - Total isoflavones of soybean cultivars with different of N sources and growing seasons
under dry land conditions.
Different letters at the same of group treatment represent significant differences at Duncan’s Multiple Range Test (p < 0.05).
CULTIVAR N SOURCES
GROWING SEASON MEAN DRY SEASON RAINY SEASON
... µG/G SEED WEIGHT ...
Anjasmoro Without N application 67.86a-d 62.23b-f 65.05lmn (V1) Urea (50 kg/ha) 58.55c-g 75.66a 67.10kl
Bradyrhizobium sp. 69.79a-d 73.23ab 71.51k farmyard manure (10 t/ha) 59.85c-g 70.15a-d 65.00lmn
Bradyrhizobium sp. + farmyard
manure (5 t/ha) 41.68ij 64.89a-f 53.28qr Mean of V1 x M 59.55 69.23
Mean of V1 64.39t
Wilis Without N application 46.61g-j 58.12c-g 52.37qr (V2) Urea (50 kg/ha) 59.11c-g 61.56b-g 60.34mno
Bradyrhizobium sp. 33.17j 78.63a 55.90op
farmyard manure (10 t/ha) 48.58f-i 71.88abc 60.23nop
Bradyrhizobium sp. + farmyard
manure (5 t/ha) 63.44a-f 62.79b-f 63.12l-o Mean of V2 x M 50.18 66.60
Mean of V2 58.39u
Sinabung Without N application 61.16b-g 56.88c-h 59.02op (V3) Urea (50 kg/ha) 64.64a-f 67.98a-d 66.31klm
Bradyrhizobium sp. 55.43d-i 42.14hij 48.78r farmyard manure (10 t/ha) 41.64ij 64.08a-f 52.86qr
Bradyrhizobium sp. + farmyard
manure (5 t/ha) 50.24e-i 55.97d-h 53.11qr Mean of V3 x M 54.62 57.41
Mean of V3 56.02u
Without N application 58.54 59.08 58.81 Urea (50 kg/ha) 60.76 68.40 64.58
Bradyrhizobium sp. 52.79 64.66 58.73
farmyard manure (10 t/ha) 50.02 68.70 59.36
Bradyrhizobium sp. + farmyard
Total isoflavone
Mean comparisons for the effect of N sources at different of planting time on total
isoflavones content of soybean cultivars are shown in Table 5. Soybean grown during
the rainy season had a significantly higher isoflavones total content (971.23 µg/g) than
the dry season (803.61 µg/g). Anjasmoro cultivar had higher total isoflavone content
(907.21 µg/g) than Wilis or Sinabung. Wilis cultivar grown during the rainy season
had higher total isoflavone content (1008.63 µg/g) that other treatments, while Wilis
cultivar was grown during the dry season had the lowest total isoflavone content. The
treatment of Bradyrhizobium sp. and Wilis cultivar grown during the rainy season
tended to increase the total isoflavone than all other treatments.
Discussion and conclusion
The content all of soybean isoflavones (genistein, daidzein and glycitein) were
affected by growing season. In general, soybean grown during the rainy season had
higher content of genistein, daidzein, glycitein and higher total of isoflavone content
compared to soybean grown during the dry season. The rainy season had higher
rainfall and humidity but the temperature was lower compared to the dry season
(Table 1). This suggested that the climatic conditions during rainy season were more
suitable for isoflavone accumulation than in dry season. Kim and Yung (2007).
Dhaubhadel et al.
(2007) and Gonzalez et al. (2010) reported that accumulation of
isoflavones in soybean seeds takes place during the later stages of seed maturation
(R7). It suggests that their levels are greatly influenced by water availability during
this period. Nevertheless, little is known about the timing and magnitude of the water
deprivation required to exert a significant effect, and it is yet to be determined at which
stage of seed development drought might cause more variation. In this research, the
higher soil moisture due to higher of rainfall during the rainy season caused an
increase in the accumulation of genistein, daidzein, glycitein and isoflavones total.
This was in line with previous research by Lozovaya
et al.
(2005), who studied the
effect of temperature and soil moisture status during seed development under
controlled conditions and concluded that high soil moisture increased daidzein,
genistein and total isoflavones. In addition, Morrison
et al.
(2010) reported that
precipitation has been suggested as a potential factor influencing isoflavone
concentration. Seguin et al.
(2004) achieved the lowest total isoflavones concentration
in the driest year of a two-year study.
The high accumulation of isoflavone content (genistein, daidzein, glycitein and
isoflavones total) on Anjasmoro cultivar indicated that the accumulation of
isoflavones contents was highly influenced by genotype. Previously research (Wang
and Murphy, 1994; Hoeck et al.,
2000; Lee et al., 2003; Mebrahtu et al., 2004, Gonzalez
Y. Hasanah et al.: Isoflavone content of soybean [Glycine max(L). Merr.] cultivars...growing season under dry land conditions
et al., 2009; 2010) reported that accumulation of soybean isoflavones compounds
depend on the genetic factor (the cultivar) and the environmental factors. Influencing
environmental factors consist of both biotic, such as wounding, nodulation and
pathogen attack, and abiotic elements: temperature, water regime, UV light, soil
nutrient content and carbon dioxide (Dixon and Paiva, 1995, Lozovaya et al., 2005;
Subramanian et al.,
2006; Naoumkina et al.,
2007)
The high accumulation of genistein, daidzein and total isoflavones contents on
Bradyrhizobium sp. treatment may be related to the role of genistein and daidzein on
root nodulation. Nodulation is one of the environmental factors that can influence
accumulation of isoflavones (Lozovaya et al., 2005; Subramanian et al., 2005; Gonzalez
et al., 2010). In addition, it also showed the role of mutualism symbiosis between
Bradyrhizobium sp. and soybean root in nitrogen fixation as a biochemical process
that converts free N2 into N compounds that are available to plants. N is a primary
plant nutrient and a key element in proteins and nucleic acids (Wood et al., 1993;
Walker et al., 2001), and is required in the synthesis of chlorophyll. Isoflavones are
also one of the important secondary metabolites in soybean plants formed through
the phenylpropanoid biosynthetic pathway precursor phenylalanine which is one of
the essential amino acids that requires N in its synthesis. Genistein and daidzein are
the two principal isoflavones in soybean, while glycitein is present in much lesser
amounts, and is unique for soy plants. They are stored as glucosyl- and
malonyl-glucosyl conjugates in vacuoles (Yu and McGonigle, 2005). Although seed isoflavone
content is greatly dependent on the environment, the production is largely under
genetic control (Eldridge et al., 1983; Wang et al., 1994; Hoeck et al., 2000; Nelson et
al., 2002).
In this study, our results demonstrated that growing season was significantly
influenced isoflavone accumulation in soybean. Soybean grown during the rainy
season had a higher content of genistein, daidzein, glycitein and total isoflavones than
soybean grown during the dry season. Growing season of October to December had
the higher rainfall and humidity but the temperature was lower than the planting time
of June to September. Wilis cultivar grown from October to December increased total
isoflavone (1008.63 µg/g) more than other treatments, while Wilis cultivar was grown
from June to September gave the lowest of total isoflavone content. The treatment of
Bradyrhizobium
sp. and Wilis cultivar grown during the rainy season tended to
increase the total isoflavone.
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully thank Dr. David B. Weaver from Auburn University, Alabama US for
his criticism on this research. We also thank Yuda P. Surbakti and Irma Afriyanti for technical
assistance in planting and harvesting the research.
Journal of Agriculture and Environment for International Development - JAEID - 2015, 109 (1)
References
Arsyad D.M. dan Purwantoro, 2010. Kriteria seleksi dan toleransi galur kedelai pada
lahan kering masam. Penelitian Pertanian Tanaman Pangan 29(2): 98-104.
Brevedan R.E. and Egli D., 2003. Short periods of water stress during seed filling, leaf
senescence, and yield of soybean . Crop Sci. 43: 2083 - 2088 .
Carrão-Panizzi M., De Goes-Favoni S.P. and Kikuchi A., 2004. Hydrothermal
treatments in the development of isoflavone aglycones in soybean [Glycine
max(L.) Merrill] grains. Braz. arch. biol. technol. 47 (2): 225-232.
Dixon R.A. and Paiva N.L., 1995. Stress-induced phenylpropanoid metabolism. P lant
Cell 7: 1085 – 1097.
Eldridge A. and Kwolek W., 1983. Soybean isoflavones: Effect of the environment and
variety on composition. J. Agric. Food Chem. 31: 394-396.
Hoeck J.A., W.R. Fehr, P.A. Murphy and G.A. Welke, 2000. Influence of genotype and
environment on isoflavone contents of soybean. Crop Sci. 40: 48-51.
Lee S., J. Ahn, J. Kim, S. Han, M. Jung, I. Chung, 2003. Variation in isoflavone of
soybean cultivars with location and storage duration. J. Agric. Food Chem. 51:
3382 - 3389.
Liener I.E., 1994. Implications of antinutritional components in soybean foods. Crit.
Food Sci. Nutr. 34: 31 - 67.
Lozovaya V.V., Lygin A.V., Ulanov A.V., Nelson R.L., Dayde J. and Widholm A.M., 2005.
Effect of temperature and soil moisture status during seed development on soybean
seed isoflavone concentration and composition. Crop Sci. 45 : 1934 - 1940 .
Mebrahtu T., Mohamed A., Wang C.Y. and Andebrhan T., 2004. Analysis of isoflavone
contents in vegetable soybeans. Plant Food for Human Nutr. 59: 59 - 61.
Messina M., 1995. Modern applications for an ancient bean: soybeans and the
prevention and treatment of chronic disease. J. Nutr. 125: 567 - 569.
Morrison M.J., Cober E.R., Saleem M.F., McLaughlin N.B., Frégeau-Reid J., Woodrow
B.L., Ma L., 2010. Seasonal changes in temperature and precipitation influence
isoflavone concentration in short-season soybean. Field Crop Res. 117: 113 - 121.
Naoumkina M., Farag M.A., Sumner L.W., Tang Y., Liu C.J. and Dixon R.A., 2007.
Different mechanisms for phytoalexin induction by pathogen and wound
signals in Medicago truncatula. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104 : 17909 - 17915.
Nelson R.L., Lozovaya V., Lygin A. and Widholm J., 2001. Variation in isoflavones in
seeds of domestic and exotic soybean germplasma. In: 2001 Agronomy Abstracts
(CD-ROM). ASA. CSSA and SSSA. Madison. WI.
Ososki A.L. and Kennelly E.J., 2003. Phytoestrogens: a review of the present state of
research. Phytother. Res. 17: 845 - 869.
Ranich T., Bhathena S. J. and Velasquez M. T., 2001. Protective effects of dietary
Y. Hasanah et al.: Isoflavone content of soybean [Glycine max(L). Merr.] cultivars...growing season under dry land conditions
phytoestrogens in chronic renal disease. J. Ren. Nutr. 11: 183 - 93.
Rochfort S. and Panozzo J., 2007. Phytochemicals for health, the role of pulses. J.
Agric. Food Chem. 55: 7981 - 7994 .
Sakai T. and Kogiso M., 2008. Soy isoflavones and immunity. J. Med. Invest. 55: 167-173.
Seguin P., Zheng W., Smith D. L. and Deng W., 2004. Isoflavone content of soybean
cultivars grown in eastern Canada. J. Sci. Food Agric. 84: 1327-1332.
Subramanian S., Stacey G. and Yu O., 2006. Endogenous isoflavones are essential for
the establishment of symbiosis between soybean and
Bradyrhizobium
japonicum. Plant J. 48: 261 - 273 .
Subramanian S., Stacey G. and Yu O., 2000. Distinct, crucial roles of flavonoids during
legume nodulation . Trends Plant Sci. 12: 282 - 285
Tiller S. A. and Parry A. D., 1994. Isoflavonoid conjugates and their response to
developmental change and abiotic stress in alfalfa
(Medicago sativa L.) Acta
Hort. 381: 227 - 234
Tsukamoto C., Shimada S., Igita K., Kudou S., Kokubun M., Okubo K. and Kitamura
K., 1995. Factors affecting isoflavones content in soybean seeds: changes in
isoflavones, saponins, and composition of fatty acids at different temperatures
during seed development. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 43: 1184 -1192.
Walker R.L., Burns I.G. and Moorby J., 2001. Responses of plant growth rate to
nitrogen supply: a comparison of relative addition and N interruption
treatments. J. of Exp. Bot. 52(355):309-317.
Wang H. and Murphy P. A., 1994. Isoflavone composition of American and Japanese
soybeans in Iowa: Effects of variety, crop year and location. J. Agric. Food Chem.
42: 1674-1677.
Wood C.W., Torbert H. A. and Weaver D. B., 1993. Nitrogen fertilizer effects on
soybean growth, yield and seed composition. J. of Prod. Agric. 6(3): 354-360.
Yu O. and McGonigle B., 2005. Metabolic engineering of isoflavone biosynthesis. A
dv. Agron. 86: 147 - 190.
Zhu D. N., Hettiarachchy S., Horax R., and Chen P., 2005. Isoflavone contents in
germinated soybean seeds,” Plant Foods for Human Nutr. 60(3): 147-151.
Journal of Agriculture and Environment for International Development - JAEID - 2015, 109 (1)
12/27/2017 International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research - IJSTR.ORG
http://www.ijstr.org/research-paper-publishing.php?month=june2014 1/31
International Journal of
Scientific & Technology
Research
Home About Us Scope Editorial Board Blog/Latest
News Contact Us
IJSTR Volume 3- Issue 6, June 2014
Edition - ISSN 2277-8616
All listed papers are published after full consent of respective author or co-author(s).
For any discussion on research subject or research matter, the reader should directly contact to undersigned authors.
IJSTR Terms and Conditions
Geometric Modelling Of Complex Objects
Using Iterated Function System
Ankit Garg, Ashish Negi, Akshat Agrawal, Bhupendra Latwal
Abstract: In the field of computer graphics construction of complex objects is difficult process. Objects in nature are complex such as tree, plants, mountains and clouds. Traditional geometry is not adequate to describe these objects. Researchers are investigating different techniques to model such types of complex objects. Algorithms presented in this paper are deterministic algorithm and random iteration algorithm which comes under iterated function system. The fundamental property of any IFS is that image generated by it is also a fractal which is called attractor. Any set of affine transformation and associated set of probabilities determines an Iterated function system (IFS). This paper presents the role of iterated function system in geometric modeling of 2D and 3D fractal objects.
12/27/2017 International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research - IJSTR.ORG
http://www.ijstr.org/research-paper-publishing.php?month=june2014 2/31
behaviors, so it requires consuming a noticeable quantity of time and cost. prediction of system behavior and performance of processes after exertion of the given changes may be either a difficult task that is exposed to uncertainty and or requires taking time and waste of sources in order to characterize the results derived from employing the executed changes. The present essay is mainly intended to present an effective and reliable model by means of stimulation approach toward recognizing of bottleneck in manufacturing aerators (ventilation filters) and industrial valves in order to reduce time period for delivery of orders. The results of current investigation led to predict of reduced time for delivery of orders up to 49%.
Orina HezronNyamoko, Rimiru Richard, Abanti Cyrus Makori
12/27/2017 International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research - IJSTR.ORG
http://www.ijstr.org/research-paper-publishing.php?month=june2014 3/31
Bartholomew Dzudzor, Selikem Nuwormegbe, Richard H. Asmah, Naa A. Sodzi-Tettey, William Kudzi, Charles Brown
Abstract: Haptoglobin (HP), an acute phase glycoprotein with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and immune-modulatory functions may be an excellent candidate gene to investigate human longevity. The gene is polymorphic and the proteins expressed have different functional capacities due to their distinct biochemical and biophysical properties. The study aimed at determining the possible role of haptoglobin genotypes as genetic markers for longevity. One hundred and thirty three healthy elderly people above 50 years were recruited for the study. The average age of 37 (28%) males was 70.9 years and 96 (72%) females was 75.7 years. Blood samples were collected from participants for hematological analysis, HP genotyping and determination of oxidative stress. A positive correlation between superoxide dismutase activity and age (p = 0.002) was observed in this study population. A negative correlation was observed between age and total white blood cells (p = 0.020), age and neutrophil (p = 0.028), age and platelet counts (p = 0.006). HP1 and HP2 allelic frequencies were found to be 49.5% and 50.5%. Genotypic frequencies for HP2-2, HP2-1, and HP1-1 were 38%, 25% and 37% respectively, showing a departure from the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. The HP1 and HP2 genotypic polymorphisms did not appear to influence longevity in the Ghanaian population and none of the genotypes conferred a survival advantage.
[View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 18-22
Implementation Of RS Decoder Using
High-Speed UHD Architecture
Bhashipaka. Ashok, M. A. Himayath Shamshi
Abstract: Reed-Solomon (RS) codes are widely used as f orward correction codes (FEC) in digital com munication and storage systems.correcting ran random errors of RS codes have been extensiv ely studied in both academia and industry. Ho wever, for burst-error correction, the research is still quite limited due to its ultra high compu tation complexity. In this brief, starting from a recent theoretical work, a low-complexity refo rmulated inversionless burst-error correcting (RiBC) algorithm is developed for practical ap plications.Then, based on the proposed algorit hm, a unified VLSI architecture that is capabl e of correcting burst errors, as well as random errors and erasures, is firstly presented for mu lti-mode decoding requirements. This new arc hitecture is denoted as unified hybrid decoding (UHD)architecture. It will be shown that,being the first RS decoder owning enhanced burst er ror correcting capability, it can achieve signifi cantly improved error correcting
12/27/2017 International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research - IJSTR.ORG
http://www.ijstr.org/research-paper-publishing.php?month=june2014 4/31
capability th an traditional hard-decision decoding (HDD) design. A design of (7, 3) Reed Solomon encod er and Decoder are implemented using VHDL hardware description language (HDL) code, sim ulated and synthesized by XILINX ISE simulator. General Terms : Burst errors, Reed-Solomon codes,RiBC algorith m and UHD architecture.
[View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 23-29
Microturbine :Fabrication Forefficient
Power Generation
Rohit Shriyan, Saurabh Sande, Aniket Dolas, Siddhant Shinde, Madan Jagtap
Abstract : We all know that in India many of the village s still do not have electricity. But many a times it becomes difficult to transfer energy from its source/ plant up to its destination and as the distance increases cost of electricity also goes on increasing. Now to tackle this problem there are many ideas. One of those is to generate own energy from the resources available. But electricity generation can be very costly. No construction of hydro dams is necessary for such an application. As well as in hydro power plants, compact helical turbines can be used in Wind Farms instead of conventional propeller-type machines of huge diameter. So to solve these problems we are making a Microhydro turbine with less initial cost and maintainace cost. So that electricity is available to everyone also in areas where it is not able to reach. Also it` does not required much large land for its setup. The utilization of energy is an indication of the growth of a nation. For example, the per capita energy consumption in USA is 9000 KWh (Kilo Watt hour) per year, whereas the consumption in India is 1200 KWh (Kilo Watt hour). One might conclude that to be materially rich and prosperous, a human being needs to consume more and more energy. A recent survey on the energy consumption in India had published a pathetic report that 85,000 villages in India do not still have electricity. Supply of power in most part of the country is poor. Hence more research and development and commercialization of technologies are needed in this field.
[View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 30-33
Production Of 5 Clones Of Cassava Is
Applied Plant Regulator Growth, Microbial
Fertilizer, NPK And Harvested At Different
Age
12/27/2017 International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research - IJSTR.ORG
http://www.ijstr.org/research-paper-publishing.php?month=june2014 5/31
Abstract: Cassava is an important crop plants as a source of carbohydrate, raw materials for industrial, cosmetic, feed and energy. The study aims to determine the 5 clones of cassava production is applied Hormax regulator growth + Organox microbial fertilizer + NPK and harvested at different age. The experiment was conducted in the form of three-factor factorial experiement based on rendomized complete block design. Study result shows that the interaction between the clone MLG 0311and Hormax 20 mL.L-1 water + Organox 40 mL.L-1 water + NPK 150 kg.ha-1 and the age of 9 month when the cassava crop is harvested produced the highest weight of tuber yield per tree (4.870 kg), the highest of total wet weight of sugar level (0.65 %), conversion of fresh peeled tuber with the highest ethanol (155.00 ml.kg-1). clone of ADIRA-4 with Hormax 20 mL.L-1 water + Organox 40 mL.L-1 + water + NPK 150 kg.ha-1 and harvest age of 9 month resulted in the highest harvest index (94.261 %). Klon MAL-6 with Hormax 20 mL.L-1 water + Organox 40 mL.L-1 water + NPK 150 kg.ha-1 and harvest age of 9 month produced the highest of dry weght yield starch content (70,24 %).
[View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 34-37
Production Of Hydrogen By Anion
Exchange Membrane Using AWE
J. Donald Joe, D. B. Siva Kumar, P. SivakumarAbstract: This paper reports the performance of nickel oxide based electrode in alkaline anion exchange membrane water electrolysis. The membrane used is polystyrene based alkaline membrane and the electrode used is Nickel as cathode and Nickel oxide as anode. The electrochemical activity of the Nickel oxide is high compared to uncoated electrode. The AWE membrane electrode gave high current density at 300C with deionised water. The performance tends to increase by changing the temperature and alkaline solution. This results in increasing hydrogen production and be a promising technology in the future.
[View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 38-42
Arm Based Gas Monitoring System
Harshada Navale, Prof. B.V.Pawar12/27/2017 International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research - IJSTR.ORG
http://www.ijstr.org/research-paper-publishing.php?month=june2014 6/31
leakage of LPG using gas sensor and alerts the persons about the gas leakage using the buzzer and by sending the SMS. This system continuously monitors the level of the LPG present in the cylinder When the system detects the LPG concentration in the air exceeds the certain level it immediately alerts the persons by activating an alarm and sending message to the specified mobile phones. The Proposed system uses the GSM to alert the person about gas leakage via SMS .Simultaneously to take the necessary action it automatically switches on the exhaust fan and sprinkler to decrease the gas concentration in the air. [View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 43-45
An Alternative Synthetic Approach For
1,3-Benzoxazine Derivatives
A. U G/Gabbas, I. A Mohammed, M. B. Ahmad
ABSTRACT: 1,3-benzoxazine derivatives were synthesized in high yield using three-step synthetic technique by the condensation of 2-hydroxybenzaldehyde with aromatic amines, reducing the condensation products and replacing the usual formaldehyde with methylene bromide to achieve ring closure. The structures of the benzoxazines were confirmed by FTIR, 1H and 13C NMR spectra and Mass spectroscopy.
[View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 46-48
REUSE OF NATURAL WASTE MATERIAL FOR
MAKING LIGHT WEIGHT BRICKS
MOHAMMAD SHAHID ARSHAD, DR. P.Y. PAWADE
12/27/2017 International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research - IJSTR.ORG
http://www.ijstr.org/research-paper-publishing.php?month=june2014 7/31
1077:1992 (fifth revision) and ASTM C 67-03a standards. From experimentation it is observed that waste create bricks (WCB) prepared is light weight, shock absorbing and meets compressive strength requirements of ASTM C 67-03a and BIS. The brick making procedure being simple can be undertaken as rural entrepreneurship by unskilled labours of developing countries.
[View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 49-53
Photovoltaic Energy Asessment Using
Geospatial Technology
Deepak Kumar, Sulochana Shekhar
ABSTRACT: Now days, Geospatial Technology have become an important segment for evaluation and deployment of solar renewable energy systems, demanding close attention to issues of functionality, sustainability and usability. Whilst some research has begun to examine the functionality of Modelling & Assessment of systems but little attention has been paid. The work influences Solar Energy Modelling for Photovoltaic (PV) potential assessment for local energy management. An accurate assessment of projects requires a spatial analysis of resources, which can be most easily completed within a Geographic Information System (GIS). Methodology explains how the general Geospatial tools are used to identify and quantify these potential, constraints of these projects to enhance their efficiency. The methodology section of this paper offers insight to work the done and the ways in which other researchers can use GIS in the field of Solar Energy. When it comes to sound energy management, conservation is always top priority. At the Regional Peel, we recognize the reducing energy use helps to save money, decrease the need for additional power generation and best of all it helps to protect our environment. This paper describes for solar energy assessment modelling using GIS and its application to the regional scale. It also explains the value of GIS for renewable energy resources problems and suggests the use of the tool for energy supply demand matching.
[View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 54-60
Routing Planning As An Application Of
Graph Theory
Prof Boominathan P, Kanchan Arora
12/27/2017 International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research - IJSTR.ORG
http://www.ijstr.org/research-paper-publishing.php?month=june2014 8/31
searching a graph, starting at one point, and exploring adjacent nodes from there until the destination node is reached. Generally, the goal is of course to obtain the shortest route to the destination. The proposed Fuzzy Routing Algorithm (FRA) modifies the well-known Dijkstra s Single-source shortest path algorithm by using fuzzy-logic membership functions in the path-cost update process. The main objective of FRA is to reduce path-request blocking and increase overall utilization. The fuzzy weighted graphs, along with generalizations of algorithms for finding optimal paths within them, have emerged as an adequate modeling tool for prohibitively complex and/or inherently imprecise systems. These algorithms are reviewed and formulized with uncertainty which comes from weights on edges according to actual situation on the road such as weather conditions, and road capacity at the specified time. The two key issues need to be addressed in SPP(Shortest Path Algorithm) with fuzzy parameters are to determine the addition of two edges and to compare the distance between two different paths with their edge lengths represented by fuzzy numbers.
[View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 61-66
Intelligent Accident-Detection And
Ambulance- Rescue System
Bhandari Prachi, Dalvi Kasturi, Chopade Priyanka
Abstract: Road accidents and traffic congestion are the major problems in urban areas. Currently there is no technology for accident detection. Also due to the delay in reaching of the ambulance to the accident location and the traffic congestion in between accident location and hospital increases the chances of the death of victim. There is a need of introducing a system to reduce the loss of life due to accidents and the time taken by the ambulance to reach the hospital. To overcome the drawback of existing system we will implement the new system in which there is an automatic detection of accident through sensors provided in the vehicle. A main server unit houses the database of all hospitals in the city. A GPS and GSM module in the concerned vehicle will send the location of the accident to the main server which will rush an ambulance from a nearest hospital to the accident spot. Along with this there would be control of traffic light signals in the path of the ambulance using RF communication. This will minimize the time of ambulance to reach the hospital. A patient monitoring system in the ambulance will send the vital parameters of the patient to the concerned hospital. This system is fully automated, thus it finds the accident spot, controls the traffic lights, helping to reach the hospital in time
12/27/2017 International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research - IJSTR.ORG
http://www.ijstr.org/research-paper-publishing.php?month=june2014 9/31
[References]
Design Of 1.7 GHz Multiband Meandered
Planar Inverted F Antenna
Ankit P Dabhi, Shobhit K Patel
Abstract: Now-a-days, there is a tremendous demand for the antennas having multiband operation and wideband characteristics for wireless communications. This paper expresses the design of 1.7 GHz multiband Planar Inverted F Antenna which can be much useful in areas like terrestrial wireless communication, low earth satellites and sometimes as intermediate frequency for satellite television. The design exemplifies much better return loss at 3.9 GHz and 5.15 GHz which are more favorable band in WLAN and WIMAX applications. In this paper, the radiating patch is given the meandered shape in order to achieve the multiband operation of the antenna. The result shows that the antenna gives gain of 5.8 dB and also offer good impedance bandwidth. The antenna is of 22mm x 22mm in area.
[View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 71-74
System Development For Low Cost Data
Acquisition For Mobile Satellite Signal
Performance Measurement In Low-Latitude
I Abba, W A W Z Abidin, T Masri, K H Ping, M S Muhammad, B V PaiAbstract: Mobile Satellite (MS) Signal performance is affected by many factors such as ionospheric effect, multipath fading tree-shadowed and building-shadowed. These cause variations in the received signal quality. Although many studies have been carried out in order to improve the performance of MS signal, there are still many areas lacking data especially from the less-developed and developing countries. Furthermore, costly data acquisition method hinders more study to be carried out in these regions. This paper discusses the cost effective alternative method for MS data acquisition for satellite operating in the L-band by utilizing the GPS satellites data. Details methodology for doing the experimental works will be discussed. The measurements of the signal performance are performed for open space environment in Sarawak. The analysis of the signal performance under different MS environments is performed with respect to the information such as elevation and azimuth angles. The analysis produced forms an important part in the studies of the signal performance. From this research work, we characterized the MS received signal for Sarawak.
12/27/2017 International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research - IJSTR.ORG
http://www.ijstr.org/research-paper-publishing.php?month=june2014 10/31
[View Full Paper] [Download] [References]
Black Holes Algorithm With Fuzzy Hawking
Radiation
Mostafa Nemati, Hossein Momeni
Abstract: In this paper we improved efficiency of black holes algorithm with using of fuzzy Hawking radiation. A black hole is a region of space-time whose gravitational field is so strong that nothing which enters it, not even light, can escape. In the black holes algorithm there is a phase with name Hawking radiation. In this phase the position of the some black hole changes a little. This phase as equal mutation in genetic algorithm. We proposed a fuzzy Hawking radiation for these phase. The experimental results on different benchmarks show that the performance of the proposed algorithm is better than basic Black holes Algorithm (BLA) and firefly algorithm (FA).
[View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 85-88
Representations Of Ghanaian Tradition In
Sutherland
s The Marriage Of Anansewaa
And Fiawoo
s The Fifth Landing Stage
Annin Felicia, Abrefa Amma AdomaABSTRACT: Culture identifies people in a society, and a society without culture lacks focus and direction in the upbringing and nurturing of its youth. This paper seeks to explore Ghanaian tradition in two drama texts: The Marriage of Anansewaa and The Fifth Landing Stage written by Efua Sutherland and Kwesi Fiawoo respectively. It will juxtapose Ghanaian perspective of African culture as presented in the plays. The playwrights couch their languages beautifully so as to present the tradition of Ghana to the admiration of the outside world. Aspects of culture to be discussed include: traditional marriage, patriarchal system, storytelling/songs, funerals, puberty rites, chieftaincy, etc and their relevance in modern Ghana. It will conclude by discussing the influence of foreign cultures on Ghanaians and the way forward.
[View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 89-94
Radiations On Static Random Access
Memory Cell
12/27/2017 International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research - IJSTR.ORG
http://www.ijstr.org/research-paper-publishing.php?month=june2014 11/31
Abstract: With increased memory capacity usually comes increased bit line parasitice capacitance. This increased bit line capacitance in turn slows down voltage sensing and makes bit line voltage swing energy expensive resulting in slower more energy hungry memories. A full description of the various methods is beyond the scope of this article; instead, the focus is on providing primary developments that have taken place in the area of radiation effects on SRAM In this paper a comparision of different current mode sense amplifiers with flip flop structures using 0.35µm technology is presented with the effect of Radation effectv of 100 Krad exposures. Simulations results are given regarding sensing delay and power dissipation.
[View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 95-98
Self Guided Adhvik Humanoid Robot
Aditya Mishra, Ashutosh Shrivastav, Neha Maurya, S. Vamshi KrishnaAbstract: This paper describes the walking pattern of our humanoid robot namely Adhvik. The robot possesses the characteristic of cheapest bipedal motion and is primarily used for object detection and path finding. For this purpose we are using four servo motors operating on the principle of servomechanism which are controlled by an Arduino development board comprising of Atemga8 microcontroller of Atmel series. The supplementary MATLAB software is used for image processing of the red coloured object dividing it into frames using a camera mounted on its head. The humanoid is controlled by a computer through wireless module CC2500. The software controls the real time walking of the robot.
[View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 99-102
Preparation And Characterization Of
Ceramic Sponge For Water Filter
M. S. Sharmiwati, R. M. Mizan, A. B. Noorhelinahani12/27/2017 International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research - IJSTR.ORG
http://www.ijstr.org/research-paper-publishing.php?month=june2014 12/31
highest density and porosity are 0.83499 g/m³ and 69.965%. The maximum compressive strength that produces from ceramic sponge is 0.276324 MPa at 60 wt% solid loading.
[View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 103-106
A Survey Of 12th Grade Students' Errors In
Solving Calculus Problems
Nguyen Phu Loc, Tran Cong Thai Hoc
Abstract: Calculus in high schools is a discipline of advanced mathematics. Its intrinsic complexity is very high. Many researchers around the world have pointed out difficulties and obstacles that students have encountered when studying it. To understand a concept and a theorem of calculus is not easy; therefore, when solving calculus problems students cannot avoid errors. Find out the errors of students in mathematics learning have been a problem that several of mathematics educators around the world interested in. In this paper, we report the answers to the following two research questions: (1) In solving calculus problems, what errors have 12th grade -students committed? (2) What are the teachers' opinions about how often the errors of the students have occurred? The data collection was performed in high schools in Tan Chau town, An Giang province, Vietnam
[View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 107-108
Complex And Nano-Structured Amorphous
Carbon Films From Hydrocarbon Palm Oil
As A P-Type In Photovoltaic Heterojunction
Solar Cell Applications
A. Ishak, M. Rusop
12/27/2017 International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research - IJSTR.ORG
http://www.ijstr.org/research-paper-publishing.php?month=june2014 13/31
14.91723 mA/cm2, 0.33582, and 1.542622 %, respectively. The conversion efficiency was increased as the p-type a-C:B film in the nanostructured form. [View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 109-113
Efficacy Of Physiotherapy On Adhesive
Capsulitis Of Shoulder In Diabetic And
Non-Diabetic Patients
Ali Shawesh, Hesham Nashnoush
Abstract: Background and Purpose: Shoulder stiffness is one of the common clinical conditions which affect both diabetic and non diabetic of both genders as a primary or secondary problem. However the improvement varies between diabetic and non diabetic following physiotherapy. The purpose of this study was to compare the effectiveness physiotherapy (mobilization techniques and interferential therapy) in diabetic and non diabetic subjects with adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder. Subjects and Methods: Thirty patients (15 with diabetes mellitus, fasting blood glucose ≥127mg/dl, and 2hr blood glucose is ≥l80 mg/dl, and 15 with non-diabetes). They had unilateral adhesive capsulitis, lasting more than three months and ≥ 30% loss of passive movement of the shoulder joint compared to the non-affected side. Pain with motion with a minimum visual analogue scale (VAS) score of 5. Subjects assigned to the diabetic and non diabetic groups were treated with interferential therapy, mobilization techniques and home exercise programme. The duration of treatment was 10 days in both groups. Assessment of patients was at first and at 3, 5, 7 and 10 days by visual analogue scale (VAS), for pain intensity and goniometer for shoulder range of motion (abduction and external rotation). Results: The mean age, duration of symptoms, ratios of sex were similar in the two groups. Comparison of the initial pain scores and ROM values between the two groups revealed no statistical significance (P >0. 05). The mean changes in pain scores values and shoulder range of motion abduction and external rotation revealed highly statistical significant (P<0. 01), reduction. Improvement in pain, shoulder range of motion abduction and external rotation were, however; significantly better in the non diabetic group. Discussion and Conclusion: In subjects with adhesive capsulitis of the shoulder, physiotherapy appear to be more effective in improving shoulder joint mobility and pain in non-diabetic than diabetic during short period follow up.
[View Full Paper] [Download]
12/27/2017 International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research - IJSTR.ORG
http://www.ijstr.org/research-paper-publishing.php?month=june2014 14/31
A Survey Of K-Means And GA-KM The
Hybrid Clustering Algorithm
Yogita chauhan, Vaibhav Chaurasia, Chetan Agarwal
Abstract: In this paper we present application of hybrid clustering algorithm that combines partitioning clustering algorithm and heuristic search algorithm. Our method uses portioning method with Genetic algorithm . First we cluster the data using K-Means clustering algorithm with the value of K no. of clusters then we calculate the centroid of K cluster obtain from the previous step. Than we apply Genetic algorithm for centroids for the given value K clusters (GAKM). After applying the GAKM we compare the result of simple K-Means and GAKM algorithm .our experimental results shows that the cluster obtained from GAKM are provides more optimal result in comparison of simple K-Means algorithm cluster result.
[View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 119-122
Growth Analysis Of Soybean Varieties At
Dry Land With Application Of Nitrogen
Sources
Yaya Hasanah, Tengku Chairun Nisa, Hapsoh, Hamidah Hanum
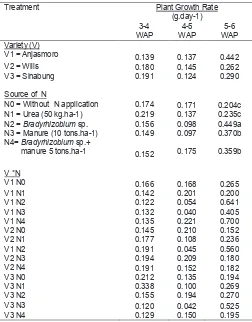
Abstract: Soybean is annual major crops in the world and important legumes in food security. Increased soybean production can achieve through increased in the intensity of soybean cultivation and expansion of soybean cultivation to marginal lands such as dry land. Nitrogen is a limited nutrient at dry land. The objective of this research was to determine the growth analysis of three soybean varieties on dry land with application of Nitrogen sources. Research using randomized block design with 2 factors and 3 replications. The first factor is soybean varieties (Anjasmoro, Wilis and Sinabung). The second factor is the sources of N consists of without application of N, Urea 50 kg/ha, Bradyrhizobium sp., manure 10 tons/ha and combinations of Bradyrhizobium sp. + manure 5 tons/ha. The research result shown that Anjasmoro variety significantly increased the relative growth rate and net assimilation rate 5-6 WAP compared with Sinabung and Wilis. Application of Bradyrhizobium sp. significantly increased the plant growth rate and relative growth rate 5-6 WAP compared with other N treatments. Combination of Bradyrhizobium sp. and manure 5 tons/ha on Anjasmoro variety tent to increase the net assimilation rate 5-6 WAP.
[View Full Paper] [Download]
12/27/2017 International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research - IJSTR.ORG
http://www.ijstr.org/research-paper-publishing.php?month=june2014 15/31
Performance Assessment Of An
Imperceptible And Robust Secured
E-Voting Model
Olaniyi Olayemi M, Arulogun Oladiran T, Omidiora Elijah O, Okediran Oladotun O
Abstract: In this paper, we present the performance assessment of an imperceptible and robust secured stegano-cryptographic model of electronic voting. The Performance analysis was achieved based on the degree to which the model meets the generic and functional requirements of secured e-voting system: authentication, integrity, confidentiality and verifiability as well as other functional security requirements of a secured voting using five-point psychometric analysis. The result of the quantitative evaluation of the model assert that the model possessed capacity to guarantee and validate voter s for who they said they are, guarantees the integrity of elections, ensures privacy of the voters, guarantees the confidentiality of the vote and provide mechanism for fraud detection after the electioneering process in developing country where digital divide is significant. [View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 127-132
Design Of Area And Speed Efficient Square
Root Carry Select Adder Using Fast Adders
K.Mariya Priyadarshini, N.V.N. Ravi Kiran, N. Tejasri, T.C. Venkat AnishAbstract: Area and speed are the most important design objectives in integrated circuits. As addition is the basic operation of all computer arithmetic, adders are one of the widely used components in digital integrated circuit design. Since propagation of carry is of major concern in designing efficient adders, this paper presents different fast adders and their performance analysis. Among all the adders discussed Square root Carry Select Adder (SQCSA) provides a good compromise between cost and performance. As, Conventional SQCSA is still area consuming due to dual Ripple Carry Adder(RCA)structures, modifications are done at gate level to reduce area. Modified SQCSA is designed using fast adders like Carry Skip Adder (CSA) and Carry Look-Ahead Adder (CLA) to increase the speed of operation.
[View Full Paper] [Download]
[References] 133-138