E13 - 1
Kinetic of Drying of Sliced Turmeric with Modified Direct Sun Drying by
Employing Greenhouse Effect
Hanim Z. Amanah1 Silvia Insan Muliawati2 and Sri Rahayoe1
1
Faculty of Agricultural Technology, Universitas Gadjah Mada, E-mail : [email protected]
Abstract
Drying of sliced turmeric generally carried out by direct sun drying. This Research was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of modified direct sun drying by employing greenhouse effect on the drying of sliced turmeric. The research also aimed to determine characteristics drying of sliced turmeric by finding the drying rate constant (k). In this research, turmeric was sliced with the thickness of 2 mm and then dried using direct sun drying and modified sun drying with employing greenhouse effect. The change of temperature and moisture content were observed every 30 minutes. Determining the drying rate constant (k) was done by using zero and first order kinetic equation.
Result showed that ambient temperature inside dryer was always higher than temperature outside the dryer. The drying rate constant (k) with modified sun drying using greenhouse effect was higher than direct sun drying, respectively and this parameter could be used to predict water content of sliced turmeric during drying process accurately.
Keywords: Kinetic, sun drying, greenhouse effect, turmeric
Introduction
Turmeric may have originated from South or South-East Asia, its center of domestication is certainly the Indian subcontinent. Currently, India is the major producer of turmeric, and it is also the major user of its own production. Other producers in Asia include Bangladesh, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Taiwan, China, Burma (Myanmar), and Indonesia. Turmeric is also produced in the Caribbean and Latin America: Jamaica, Haiti, Costa Rica, Peru, and Brazil
Turmeric ready for harvest approximately 7 to 10 months after planting. However its depend on the cultivar, soil and the growing condition. The bunches of the rhizome are dug out manually with a spade, or the soil is first loosen with a small digger, and clumps manually lifted. It is better to cut the leaves before lifting the rhizomes. Rhizomes are cleaned from soil by soaking in water, and long roots are removed as well as leaf scales.
Most agricultural commodities including turmeric require drying process in an effort to preserve the quality of the final product. The quality of the products depends on many factors including the drying temperature and duration of drying time (Fudholi et al, 2010). Recently, there have been many reports on drying kinetics of agricultural fruits and vegetables. Thin-layer drying models also have been widely used for analysis of drying of medical herbs.
E13 - 2 increase air temperature and then decrease humidity of air . Temperatures in the greenhouse can reach 50oC. The objective of this research is to evaluate the efectiveness of the greenhouse effect in increasing drying rate of sliced turmeric by determine the value of drying rate constant (k) using zero and firs order kinetic equation. This k parameter could be used to predict a decreasing moisture content of sliced turmeric during the drying process with the same method.
Materials and methods
Equipments and material
The dryer with employing greenhouse effect was manufactured in Yogyakarta. The experiment was conducted in the Laboratory of Postharvest and Food Engineering Faculty of Agricultural Technology, Universitas Gadjah Mada.
The design of dryer is shown in Figure 1. The dryer is a cabinet dryer that constructed by an iron and glass of thickness of 5 mm and consist of two tray. The cross sectional area of the dryer is 1000 mm x 2000 mm. The vertical distance beetween the second tray from the top of the roof is 1000 mm. The bottom of the dryer covered by aluminium sheet and the vertical distance from the groud is 40 cm. This dryer is completed by an air ventilator to allow proper air circulation.The distance between ventilator and ground is 2100 mm. There is hole beetween the roof and the wall for air circulation. The total dimention of dryer is 1000 mm x 2000 mm x 2100 mm. The inside of dryer was painted black to serve an absorber of dryer. This has capacity of 5 - 10 kg of raw material. During experiment, the digital thermocouple with four-channel was used to measure the product and ambient temperature, while thermo hygrometer was used to measure ambient relative humidity (RH).
The materials used are fresh turmeric with 80% - 90% (wb) moisture content and then dried to 12% moisture content. About 5 kg of turmeric was used in one running for each method of drying.
Experimental design
The experiments were conducted by two drying method, direct sun drying and modified sun drying by employing greenhouse effect. The two method was done at the same time to obtain a similar weather condition.
The turmeric were sliced of 2 mm thickness and spread into the tray of the dryer and then dried from 80% - 90% water content to about 12% water content. At the same time, sliced turmeric also dried by direct sun drying. Ambient temperature inside and outside dryer was measured by digital thermocouple. The data of temperature and water content was collected every 30 minutes during the drying process.
E13 - 3 Notes:
1. Ventilator 6. Aluminium sheet painted black 2. Glasses wall 7. 1st sampling point
3. First tray 8. 2nd sampling point 4. Second tray 9. 3rd sampling point 5. Covered chamber
Figure 1. The design of dryer by employing green house effect for sliced turmeric
Results and discussion
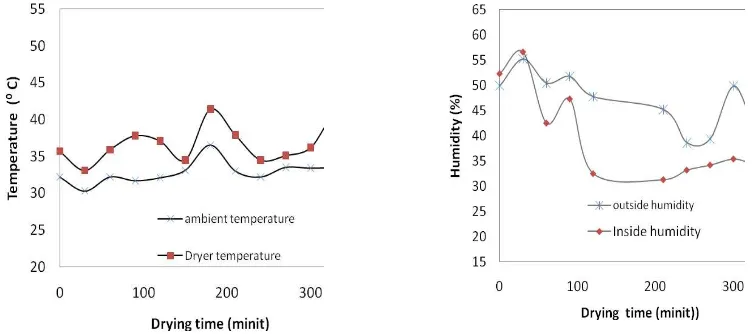
Figure 2 shows the typical of ambient and inside dryer temperature during drying process. It was quite clear that dryer temperature was higher than ambient temperature. The result shows that greenhouse effect (GE) can raise ambient to higher value for efective drying. The highest temperature inside dryer is about 44oC or almost 10oC higher than the highest ambient temperature. Figure 2 also shows that humidity in the dryer was lower than outside and became an important factor to increase drying rate.
.
Figure 2. Temperature and relative humidity history inside and outside dryer during drying
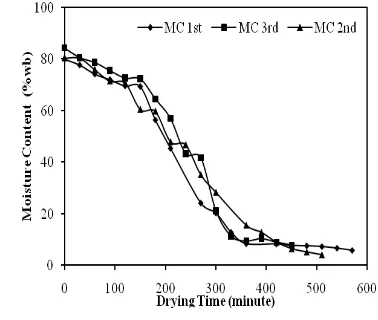
E13 - 4 1). In this research, the highest value of drying rate is obtained at the 3rd replication , i.e. 0.15%/min for constant periods and 0.038%/min for falling rate periods. All of them are for drying by employing greenhouse effect. It is clear that greenhouse effect increase ambient temperature and decrease humidity for effective drying.
a.Drying by employing greenhouse effect b. Direct Sun Drying
Figure 3. The moisture change of sliced turmeric during drying
Table 1. The drying rate of constant periods and falling periods
Number of replication
Drying with GE Direct Sun Drying
Constant rate (%/min)
Falling rate (%/min)
Constant rate
(%/min) Falling rate (%/min)
1 0.14 0.019 0.09 0.011
2 0.07 0.016 0.09 0.012
3 0.15 0.038 0.14 0.017
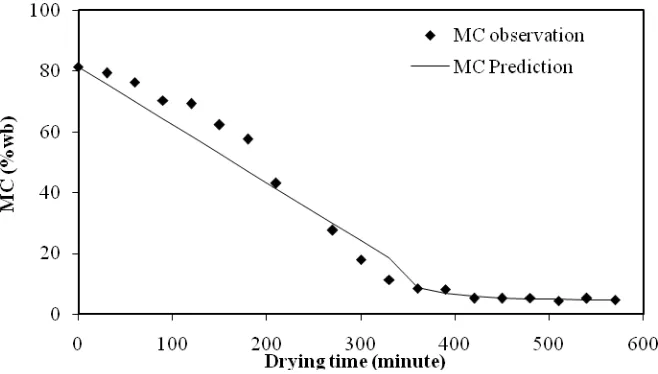
E13 - 5 Figure 4. The prediction and observation of moisture content (MC) on sliced turmeric by
employing greenhouse effect
Conclusion
It can be concluded that, the design of dryer with employing greenhouse effect can dry sliced turmeric into desired moisture content and more effective than direct sun drying. In particular, it also can be concluded that: 1) Modified sun dryer with employing greenhouse effect could increase ambient temperature inside dryer to 44oC or 10oC higher than the temperature outside of the dryer. 2)Drying rate at constant periods for dryer with employing greenhouse effect are ranged from 0.07%/min to 0.15%/min, while direct sun drying are ranged 0.09%/min to 0.14%/min. 3)Drying rate at falling rate periods for dryer with employing greenhouse effect are ranged from 0.019%/min to 0.38%/min, while direct sun drying are ranged 0.11%/min to 0.17%/min
References
1. Alonge, A.F. (1997). A Natural Convection Solar Crop Dryer. Proceeding of 19th Annual Conference of the Nigerian Society of Agricultural Engineering (NSAE) 19: 211-214 2. Anna, P., et al (2004). Turmeric : Post harvest Operation, Food and Agriculture
Organization of the United Nations (FAO), New York, USA
3. Brooker, D.B., et al. (1974). Drying Cereal Grains. The AVI publishing Company, Inc. Westport Connecticut. USA.
4. Brooker, D. B., F W. Baker-Arkema dan C. W. Hall. (1972). Drying and Storege of Grains and Oilseeds. Van Nostrand Reinhold. New York.
5. Desrosier, N. W. (2008). Teknologi Pengawetan Pangan. Penerbit Universitas Indonesia. 6. Earle,R.L. (1969). Unit Operations in Food Processing. Pergamon Press. United
Kingdom.