Laporan Penelitian
Global Warming and Its Effect
to the Characteristics and Productivities
of Volcanic Soils
By:
Dr. Rina Devnita, Ir., M.S., M.Sc Prof. Dr. Adjat Sudradjat, Ir., M.S., M.Sc.
Ridha Hudaya, Ir., M.S.
Abstract
The increasing of temperature globally is already happened worldwide and influences some aspects of the natural behavior and characteristic, include the characteristic of soils. Volcanic soil, one of the productive soils in the world, is influenced by the increasing temperature through its irreversible drying characteristics. Two locations of volcanic soils, in the intensive farming and under pine forest vegetation were studied to investigate the influence of increasing temperature to some soil characteristics related to the irreversible drying. Soils in the intensive farming receive the solar radiation maximally, followed by the increasing soil temperature, meanwhile soil under pine forest vegetation is protected from the solar heat trough the leaves canopy yearly, lowered the soil temperature. Aggregate stability, bulk density, soil consistency, available water, soil mineralogy, soil pH, and P-retention were the parameters investigated. The result showed that the increasing temperature due to global warming increasing the bulk density, decreasing the soil consistency, available water, aggregate stability. Meanwhile, the increasing of temperature have no influence to soil pH and P-retention.
Introduction
The annual average temperature in Indonesia showed an increasing as 0.3
0
C since 1990. United Nation Convention on Climate Change (2007) concluded that global temperature increase 0.74 0C during the twentieth century. The intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change have found out that, since 1900, temperatures have risen around the world by an average of 0.8 0C. In the Netherland for example, that is even 1.6 0C. The global warming could change various soil characteristics and decrease the soil productivity.
Volcanic soils cover 1 % of Earth’s surface, yet support 10 % of the
world‘s population, including some of the highest human population densities, attributed to their natural fertility. However, this is true only in part. This account addresses the specific features and genesis of volcanic soils, and how they are abused in various global environmental settings.
The aim of this research is to investigate the influence the global warming to irreversible drying, measured through soil physical and chemical properties and mineralogical characteristics.
The research was executed at volcanic soil developed on andesite parent material of Holocene age, erupted by Mt. Tangkuban Parahu. The method is the descriptive and comparative surveys and laboratory analyses.
Materials and Methods
Environmental setting and selected profile
The Mt. Tangkuban Parahu complex, located in West Java about 40 km northwest of Bandung, elevated on 1300 – 1400 m asl, consist of separate extrusion ranging from andesite. Erupted early in the sequence through successive eruption of augite-hypersthene-andesit, hornblende-andesite and biotite-andesite. Volcanic events of the last few thousand years consist of eruption associated with emission of suffocating gasses and hydrothermal activities, indicated by active hot spring, solfataras, and fumaroles. Rainfall for Mt. Tangkuban Perahu region is reported between 3000 – 4500 mm per year; it is 3725 mm around this study site. The soils are considering suitable for growing corn, tomato, and red chilly. The more rugged parts of the landscape are planted with pine trees.
Two locations were selected :
1. Intensive farming area at Balai Penelitian Tanaman Sayuran Balitsa, (BLS)
2. Pine forest vegetation at Cikole, (CKL)
Three profiles were selected in every location between 1300 – 1400 m asl on the volcano slopes. All the profiles studied have an isohypertermic temperature regime and udic soil moisture regime. The other environmental conditions of the selected profiles were observed for completing the information of the location.
stored at field moisture conditions with the remainder air-dried and crushed to pass a 2 mm sieve.
The analyses were done on air-dry fine earth, using techniques recommended for volcanic soils (van Reeuwijk, 1992), include organic carbon, soil pH, CEC, P retention, short range order constituent minerals and bulk density. The analyses were done in the Laboratory of Soil Science, Faculty of Agriculture and Laboratory of Geology, Padjadjaran University. The mineralogical analyses were done in the Faculty of Engineering, Kyushu University – Japan, and Laboratory of Quarternary Geology, The Centre of Geology Survey – Bandung.
Result and Discussion
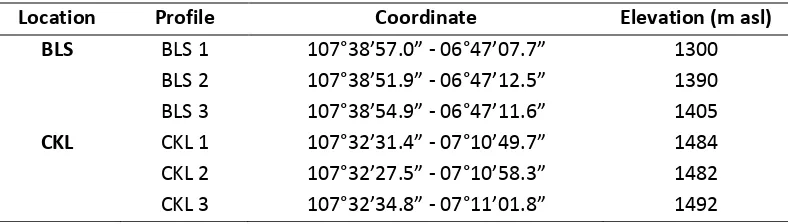
The geographical location of studied profile is presented in Table 1. Table 1. The geographical position of studied profiles.
Location Profile Coordinate Elevation (m asl)
BLS BLS 1 ° ’ . ” - ° ’ . ” 1300
The composition of heavy minerals in the soils can be seen in the Table 2. Table 2. The composition of heavy minerals.
Profil
Heavy Minerals/HM % Light Minerals/LM % Total
CKL Basalt - Pleistocene
Ap 6 2 9 2 3 2 21 25 4 26 100 22 78
Bw 6 2 10 4 4 5 16 21 3 29 100 26 74
Bt 2 9 12 4 2 2 15 27 4 23 100 29 71
BC 5 7 7 4 3 3 24 19 3 25 100 26 74
2 Ab 5 9 4 5 5 3 15 35 3 16 100 28 72
2 Bw 7 6 6 2 5 2 15 26 4 27 100 26 74
Conclusion
Global warming give the increasing of the bulk density, but still in the range of andic soil properties. The change of other characteristics can be seen in the increasing of irreversible drying and the decreasing of aggregate stability, soil consistency, and available water. The increasing having no influence to soil pH and P-retention.
Acknowledgement
REFERENCES
Arifin, M. (1994). Pedogenetic of Andisols Derived from Andesit and Basalt Volcanic Ash in Some Agroclimatic Zones of Tea Plantation in West Java. Ph.D. Thesis. Bogor Institute of Agriculture. 202 p (in Indonesian).
Bartoli, F. (2004). Shrinkage and Drainage in Undisturbed Soil Cores and Cape Hopkins, New Britain, Papua New Guinea. Geoderma, vol. 11:123-135
Broquen, P., Lobartini, J. C., Candan, F., and Falbo, G. (2005). Allophane, aluminum, and organic matter accumulation across a bioclimatic sequence of volcanic ash soils of Argentina. Geoderma, vol. 129, 167-177. E-Journal on-line. Retrieve 1st of September, 2006 from
http://www.elsevier.com/locate/geoderma
Devnita, R. 2010. Kajian Karakteristik Mineralogi dan Ameliorasi Andisol di Jawa Barat. Disertasi. Program PAscasarjana Universitas Padjadjaran. 192 hal.
Maeda, T., Takenaka, H., and Warkentin, B.P. (1984). Physical properties of allophanic soils. Adv. Agron., vol. 29, 229-264.
Mizota, C. (1981). Clay mineralogy of seven Dystrandepts developed from basalt in Northland, the French massive central, and western Oregon. Soil Sci. United State Departement of Agriculture. 219 p.
Qafoku, N. P., Van Ranst, E. Noble, A., and Baert, G. (2004). Variable charge soils, their mineralogy, chemistry and management. Advances in Agronomy, vol. 84, 157-213.
Shoji, S., and Saigusa, M. (1977). Amorphous clay materials of Towada Ando soils. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr., vol. 23, 437-455
Silitonga, P. H. (2003). Geological Map of Bandung, West Java. Geological Research and Development Centre. Indonesia
Soil Survey Staff. (2010). Keys to Soil Taxonomy. 11th ed. Natural Resources Conservation Service. 332 p.
Sudradjat, A. (2009). The Development of Volcanologic Investigation in Indonesia. Universitas Padjadjaran Press. Bandung. Indonesia. 239 p.
Uehara, G., and G. Gillman. 1981. The Mineralogy, Chemistry And Physics of Tropical Soils with Variable Charge Clays. Westview Press, Inc. Colorado. 170 p.
Utami, S. R. (1998). Properties and Rational Management Aspects of Volcanic Ash Soils from Java, Indonesia. Ph.D. Thesis. University of Ghent. Belgium. 388 p.
Van Bemmelen, R. W. (1949). The Geology of Indonesia. Vol. I A : General Geology of Indonesia and Adjacent Archipelagoes. The Hague. Jakarta. 732 p.
Van Ranst, E. (1991). Soils of the Tropics and Subtropics : Geography, Classification, Properties and Management. Ghent University. Belgium. 293 p.
Van Ranst, E., Utami, S. R., Verdoodt, A., and Qafoku, N. P. (2008). Mineralogy of perudic Andosol in Central Java, Indonesia. Geoderma, vol. 144, 379-386.
Van Ranst, E., De Conninck, F. and Debaveye, J. (1993). Implication of Charge Properties and Chemical Management of Volcanic Ash Soils in West Cameroon. Proceeding In 2nd African Soil Science Society Conference, p. 255-264.