SPEAKING MATERIALS USING TASK-BASED LEARNING FOR THE SEVENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF ENGLISH EXTRACURRICULAR
ACTIVITY AT SMPPANGUDI LUHUR YOGYAKARTA
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By Ika Tyas Intani Student Number: 101214110
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
i
SPEAKING MATERIALS USING TASK-BASED LEARNING FOR THE SEVENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF ENGLISH EXTRACURRICULAR
ACTIVITY AT SMPPANGUDI LUHUR YOGYAKARTA
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By Ika Tyas Intani Student Number: 101214110
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY YOGYAKARTA
iv
DEDICATION PAGE
“If you can’t fly, then run, if you can’t run, then walk, if you can’t walk, then crawl, but, whatever you do, you have to keep moving forward.”
Martin Luther King Jr.
“Then give the world the best you have. And the best will come back to you.”
Madeline Bridges
I dedicate this thesis to:
v
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that this thesis, which I have written, does not contain the work of other people, except those cited in the quotations and the references, as a scientific paper should.
Yogyakarta, March 12th, 2015 The writer
vi
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN
PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswi Universitas Sanata Dharma: Nama : Ika Tyas Intani
Nomor Mahasiswa : 101214110
Demi kepentingan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
SPEAKING MATERIALS USING TASK-BASED LEARNING FOR THE SEVENTH GRADE STUDENTS OF ENGLISH EXTRACURRICULAR
ACTIVITY AT SMP PANGUDI LUHUR YOGYAKARTA
Beserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan demikian, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk lain, mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistribusikan secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikannya di Internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin dari saya maupun memberikan royalty kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini saya buat dengan sebenarnya.
Dibuat di Yogyakarta
Pada tanggal: 17 Februari 2015
Yang menyatakan
vii
ABSTRACT
Tyas Intani, Ika. (2014). Speaking Materials Using Task-Based Learning for the Seventh Grade Students of English Extracurricular Activity at SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
English is one of the compulsory lessons in the junior high school. As the one of the compulsory lessons, there are four skills that should be developed by the learners. One of those four skills is speaking skill, speaking skill is one of the important things to do in life. Therefore, there is an activity which helps the students to develop the speaking skill in the school. English extracurricular activity is one of the additional activities which are often offered to students. English Extracurricular is an activity that supports the regular time school.
Pangudi Luhur was one of the schools which offers their students to join the English extracurricular activity. Therefore, SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta started to cooperate with Sanata Dharma University in holding the English Extracurricular for their students. Sanata Dharma prepared some of their students to be the English extracurricular activity’s teachers at SMP Pangudi Luhur
Yogyakarta.
This research belonged to an Educational Research and Development research because it produced an educational product in the form of module. It had five steps of R&D namely, Information Collecting; Planning; Material Development; Material Validation; and Material Revision. Questionnaire, class observation and interview as the instruments employed in this research. Task-based learning is used to develop the section in each unit. There were 5 sections in
the module. The first section was “Do You Remember?”, this section belonged to the pre-task phase in task-based learning. “Let’s Prepare” and “It’s Your Turn”
were the second and third section which belonged to whilst phase. “Let’s Learn” and “What Did You Learn?” were the fourth and fifth section which belonged to language focus phase.
There was only one research problem of this study “what do speaking materials using task-based learning for the seventh grade students of English Extracurricular Activity at SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta look like?” The module consisted of four units, namely Good Morning, Mega; My Name is Aldo; What Time is It?; Is He Tall?. The module was divided into two namely Teacher’s
Book and Student’s Book.
viii
ABSTRAK
Tyas Intani, Ika. (2014). Speaking Materials Using Task-Based Learning for the Seventh Grade Students of English Extracurricular Activity at SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Bahasa Inggris adalah salah satu pelajaran wajib di Sekolah Menengah Pertama. Sebagai salah satu pelajaran wajib, keempat ketrampilan berbahasa haruslah ditingkatkan oleh para siswa. Salah satunya adalah ketrampilan berbicara. Ketrampilan berbicara adalah salah satu hal penting yang harus ditingkatkan di dalam hidup. Oleh karena itu, ada aktivitas yang membantu para siswa untuk meningkatkan ketrampilan berbicara di sekolah. Ekstrakurikuler Bahasa Inggris adalah salah satu aktifitas tambahan yang ditawarkan kepada para siswa. Aktifitas ini mendukung kegiatan belajar mengajar di sekolah.
SMP Pangudi Luhur adalah salah satu sekolah yang mewajibkan adanya keikutsertaan siswanya dalam kegiatan Ekstrakurikuler Bahasa Inggris. Oleh karena itu SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta memulai kerja sama dengan Sanata Dharma dalam pengajaran Ekstrakurikuler Bahasa Inggris. Universitas Sanata Dharma menyiapkan beberapa mahasiswanya untuk menjadi guru Ekstrakurikuler Bahasa Inggris di SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta.
Penelitian ini termasuk dalam Penelitian dan Pengembangan karena menghasilkan produk pendidikan berupa modul. Ada lima tahap dalam penelitian ini yaitu pengumpulan informasi, perencanaan, pengembangan materi, pengujian materi dan revisi materi. Kuesioner, observasi kelas dan wawancara adalah alat yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini. Task-based learning digunakan untuk menyusun bagian pembelajaran dalam setiap unit. Bagian pertama adalah “Do You Remember?” yang termasuk dalam the pre-task phase di task-based learning.
“Let’s Prepare” dan “It’s Your Turn” adalah bagian kedua dan ketiga yang termasuk dalam the whilst phase. “Let’s Learn” dan “What Did You Learn?” adalah bagian keempat dan kelima yang termasuk dalam the language focus phase.
Modul dalam penelitian ini merupakan hasil dari rumusan masalah yang
ada di penelitian ini “Seperti apakah materi berbicara menggunakan metode
penugasan untuk siswa kelas tujuh pada aktifitas Ekstrakurikuler Bahasa Inggris di SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta?” Di dalam modul ini terdapat empat unit yaitu “Good Morning, Mega”, “My Name is Aldo”, “What Time is It?”, dan “Is He Tall?”. Ada dua bagian di dalam modul ini yaitu Buku Guru dan Buku Siswa.
ix
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First, I would like to express my gratefulness to God. He always finds a way to bring me back to finish this thesis. God is good. With God all things are possible. He becomes the most beautiful one in my life.
My greatest gratitude is addressed to my thesis advisor, Christina Kristiyani S.Pd., M.Pd., for her patience, support, encouragement, guidance, and contribution of ideas in guiding me to accomplish this thesis. My greatest gratitude also goes to all of my lecturers in the ELESP of Sanata Dharma University for many precious chances to learn English and life values together in these four years, especially Drs. Barli Bram, M.Ed., Ph.D., Truly Almendo Pasaribu S.S., M.A., Made Frida Yulia S.Pd., M.Pd., and Pius Nurwidasa Prihatin, M.Ed., Ed,D., for willingly spending their time evaluating the designed materials and this thesis. I also thank Mbak Danik and Mas Yudo for always helping me with the administrative matters.
x
I am also grateful to my beloved parents, my father Nugroho Tyas Utomo and my mother Sunarni. Without their love, care, support and guidance I never have an opportunity to study. My gratitude is also addressed to my beloved brother Satya Dwi Nugroho. He teaches me how to stay strong even when I was down. My sincere thanks go to my grandmother Eyang Ti, my aunts Anik, Ita, Nining and Denny, my uncles Aik, Anto and Sapto and my cousins Lintang, Bagus, Citra, Kendra, Mbak Heni, Mas Danang and Wiwin for always supporting and motivating me during my thesis writing.
I warmly thank my best friends: Chika, Epi, Pritha, Ayu, Diah, Badra, Eka, Clara and Mbak Icha for their precious friendship. I thank them for willingly sharing the joy and spirit through the good and bad times. My gratefulness is also addressed to all of my friends: Gistha, Ratih, Vina, Narima, Ria, Tere, Heni, Gaby, Sandra, Nisa, Asti, Evi, Tory, Abi, Marino, Anus, Jason, Thomas, Satya, Ega and those who are always there for me.
I would like to give my deepest love and special thank to my beloved man, Reinardus Aldo Agassi. I thank him for his love, care, patience and guidance during my thesis writing.
xi
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Page
TITLE PAGE ……… i
APPROVAL PAGES ……… ii
DEDICATION PAGE ……… iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY ……… v
PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI ……… vi
ABSTRACT ………. vii
ABSTRAK ………. viii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ………. ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS ………. xi
LIST OF TABLES ………. xiv
LIST OF FIGURES ………. xv
LIST OF APPENDICES ………. CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION ……… 1
A. Research Background ……… 1
B. Research Problem ……… 3
C. Problem Limitation ……… 3
D. Research Objective ……… 4
E. Research Benefits ……… 4
xii
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ……… 7
A. Theoretical Description ……… 7
1. Speaking ……… 7
2. Task-based Learning ……… 9
3. 2013 Curriculum ……… 16
4. Material Adaptation ……… 18
B. Theoretical Framework ……… 20
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ……… 23
A. Research Method ……… 23
B. Research Setting ……… 26
C. Research Participants ………... 26
D. Instruments and Data Gathering Technique …………... 27
E. Data Analysis Technique ……… 29
F. Research Procedure ……… 31
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION …… 43
A. The Description of Instructional Goal ………. 43
B. The Description of Instructional Analysis ……….. 44
C. Learners’ Characteristics ………. 45
D. Performance Objectives and the Instructional Materials …… 47
xiii
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS …… 58
A. Conclusions ………. 58
B. Recommendations ………. 59
REFERENCES ………. 61
xiv
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
2.1. Nunan’s Task Classification (Nunan, 2004:59) ……… 13
3.1. The Description of Materials Validation Subjects ……… 27
3.2. The Researcher’s Data Collection ……… 28
3.3. The Basic Competence of Grade Seventh ……… 35
3.4. The Learning Topics of the Materials ………... 36
3.5. The General Purposes ………... 36
3.6. The Learning Indicators of the Materials ……… 36
3.7 The Organization of Subject Contents ……… 37
4.1. The Core Competence and Basic Competence ……… 44
4.2. The Learning Topics and Materials ……… 47
4.3. The General Purposes ……… 49
4.4. The Organization of Subject Contents ………. 49
4.5. The Description of Learning Indicators and Selected Materials.. 50
xv
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure Page
2.1. Willis Task-based Learning Framework (Willis, 1996:38) ……. 15
2.2. The Researcher’s Theoretical Framework ………. 22
4.1. The Example of “Do You Remember?” Section ………. 53
4.2. The Example of “Let’s Prepare” Section ………. 54
4.3. The Example of “It’s Your Turn” Section .………. 55
4.4. The Example of “Let’s Learn” Section ………. 56
xvi
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix Page
A. Letter for Permission ………. 63
B. Questionnaire for Need Analysis ………. 65
C. The Result of the Questionnaire for Need Analysis ………. 67
D. Interview Protocol for the English Teacher ………. 70
E. Questionnaire for Material Evaluation ………. 72
F. The Result of the Questionnaire for Material Evaluation ……. 75
G. The Example of Questionnaire for Need Analysis ……… 78
H. The Example of Questionnaire for Material Evaluation …… 80
I. Teacher’s Book ………. 83
1 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This study is intended to design speaking materials using task-based learning for the seventh grade students of English Extracurricular Activity at SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta. This chapter consists of six parts. The first part discusses the background of the study and why this study is conducted. The second part shows the problem which is going to be discussed in this research. The third part will give the clear boundary for the researcher in discussing the problem. The fourth part points out the objective of the study. The fifth part reveals the research benefits. The sixth part of this chapter will give clarification of terms used in this study. The details of the discussion would be presented below.
A. Research Background
help us understand what speaking is actually. Based on that reason, it will be good for the junior high school students if they are given English lesson which focuses on speaking.
In the teaching and learning process at the school, SMP students get more activities in reading, writing and listening rather than speaking. It occurs in almost of SMP. Because of that reason, the researcher will focus on the activity outside the regular-school time. It means that the activity after the regular-school time will be in a form English Extracurricular Activity.
Learning English in the Extracurricular Activity is not the same as the learning English in the regular school time. English in the Extracurricular Activity should facilitate the students to be able to speak English. Based on that reason, the learning process in the Extracurricular Activity should contain the interesting materials which will develop the speaking skill of the students. Without any interesting materials, the students will get bored in learning English.
Considering the need analysis from the observation of the 36 students in the seventh grade of SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta on May 16th, 2014, it can be concluded that the students need the materials during the teaching-learning process of English Extracurricular Activity especially in speaking. Based on the interview result obtained from the teacher who teaches English Extracurricular Activity, the researcher found that the speaking materials should be encouraged by the teachers to help the students in mastering the speaking skill.
have good facilities in learning process, the motivation of the students to learn something is high, and the important thing that there were no permanent materials for the students. As the compulsory Extracurricular Activity, English Extracurricular Activity is held to help the students develop the speaking skill.
B. Research Problem
The problem of this study is stated in the following question:
What do speaking materials using task-based learning for the seventh grade students of English Extracurricular Activity at SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta look like?
C. Problem Limitation
As what has been mentioned in the research background, this research is aimed at designing speaking materials using task-based learning for the seventh grade students of English Extracurricular Activity at SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta. The researcher chooses SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta as the subject of this study because SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta is one of the well-known schools in Yogyakarta which has a purpose to prepare the students to have the skill in speaking English. The researcher selects the seventh grade students because they need to have basic English speaking skill to support their next level of education.
Extracurricular Activity supports the regular-school time activity, thus, the researcher needs to consider the use of the 2013 Curriculum. The 2013 Curriculum itself is used to support the topic selection of the designed materials. This research is also only used for the seventh grade students of SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta in their English Extracurricular Activity.
D. Research Objective
As this research is intended to find out the answer of the problem, the researcher has an objective. The researcher expects that there would be speaking materials using task-based learning for the seventh grade students of English Extracurricular Activity at SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta at the end of the research.
E. Research Benefits
This research is expected to bring the benefits that can reflect on the students, the teacher, and future researchers who conduct the same research. 1. For the students
2. For the teacher
The teacher is given a set of English speaking materials that is expected to be a solution in facilitating the students’ need in learning English. This material provides references for the teacher to give new ways of learning speaking skill. 3. For the school
The school will obtain the speaking materials for the English Extracurricular Activity which supports the learning process in the regular-school time. The designed materials will help the school to increase the students’ competence in speaking through learning other skills of English.
4. For future researchers
This research can be used by the other researchers to be the basic of evaluating, programming and reconstructing the same study. The researcher tries to share the idea and knowledge in designing a new educational product which provides a new concept for the other researchers who have the same concern.
F. Definition of Terms 1. Speaking
2. English Extracurricular Activity
English extracurricular is an activity in the school which supports the learning process in the school. There are so many kinds of extracurricular activities. One of those kinds is English Extracurricular Activity. This activity accommodates the learners to develop the language skill. In this research, English Extracurricular Activity will be the process in which the students use the speaking materials.
3. Task-based Learning
According to Nunan (2004), task-based learning represents a realization of this philosophy at the levels of syllabus design and methodology. In this research, task-based learning is a method that uses tasks for learning.
4. SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta
7
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter discusses the theories which support this research. It consists of two sections: theoretical description and theoretical framework. The first part focuses on the related theories used in this research. While in the second part, the discussion focuses on a synthesis of related theories and research procedure which become a theoretical framework of this research.
A. Theoretical Description
In this section, there will be four related theories which are discussed as guidelines for the researcher to design the speaking materials using task-based learning. The presented theories in this section are (1) Theory of Speaking, (2) Task-Based Learning, (3) the 2013 Curriculum and (4) Material Adaptation. 1. Speaking
Speaking is the main skill that will be learned in this research. It is important for the researcher to know about speaking in depth.
a. Nature of Speaking
the classroom, speaking can over a wide range of oral activities, from genuine interaction to repetition drills (p.12). The learners do an activity which is included as an active skill and they will try to give an interaction of each other. If it happens continually, the learners will repeat the activity and they are doing oral activity.
According to Nunan (2003), in learning language, “speaking is the hardest
skill among the other skills for two reasons.” There are two reasons which explain
why speaking is the hardest skill: first, the person whom we are talking to is waiting for our response right then and the second, we cannot edit and cannot revise what we wish to say. By looking at those two reasons, the researcher should be aware in looking at the characteristics of speaking in designing the materials. The researcher chooses the appropriate activities to help the learners enhance their ability of speaking in their activity at the school.
b. Principles of Teaching Speaking
Hughes (2002) states that teaching speaking, is not easily separated from other objectives (p.32). A further complicating factor is that when the spoken language is the focus of classroom activity, there are another aims which the teacher might have. Those aims are to practice some aspects of linguistic knowledge, to develop production skills and to raise awareness of some socio-linguistic or pragmatic point.
Nunan (2003) states that there are five principles of teaching speaking: 1) Be aware of the differences between second language and foreign
2) Give learners practice with both fluency and accuracy.
3) Provide opportunities for learners to talk by using group or pair work, and limiting the teacher talk.
4) Plan speaking tasks that involve negotiation for meaning.
5) Design classroom activities that involve guidance and practice in both transactional and interactional speaking.
The researcher considers those five principles as the basic in designing the materials for the learners.
2. Task-Based Learning
Task-based learning is selected by the researcher as an approach in applying the designed materials. This research is aimed at designing English speaking materials to provide the students with a lot of exposure in learning English and task-based learning approach can give the students some tasks that facilitate the students in learning English naturally through English Extracurricular Activity. This section will explain the definition of task-based learning, types of task and the procedure of task-based learning.
a. Definition of Task-Based Learning
Nunan (2004) also supports the statement by saying intellectual growth occurs when learners engage in and reflect on sequence of tasks. Tasks which are given to the learners are aimed at facilitating them in learning language. Thus, the learners are free to choose whatever language forms they wish to express what they mean in order to achieve the task goal (Willis, 2003). The task goals are the vague and general intentions behind any learning task. They provide a link between the task and the broader curriculum (Nunan, 2004).
According to Willis (2003: 77) in task-based learning, “communication tasks (where language forms are not controlled) involve learners in an entirely different mental process as they compose what they want to say, expressing what
they think or feel.” It means that the teachers give the freedom for the students to
express anything they want. Still focus on giving the task to accommodate the learners want, the teacher should recognize the needs of the learners.
Willis (2003) delineates seven characteristics of the task-based learning framework that are different from other approaches:
1) In task-based learning framework, the learners use the target language naturally and frequently, so that the target language is already familiar when the learners get the language focus phase. The designed tasks in task-based learning have established the context.
3) Listening and reading have more varied exposure to natural language. The tasks allow the learners to read and listen naturally during the teaching learning process. The learners do not only listen to and read some examples made-up to illustrate a single language term.
4) In learning language using task-based learning framework, the learners will understand that language is more than verb tenses and new vocabularies. Task-based learning framework includes all the language elements as the exposure.
5) The learning activities are flexible. The learners may ask about any aspect of language at the analysis stage.
6) Fluency that may be the most important thing in learning the target language
is expected to establish the learners’ accuracy.
7) In task-based learning, the activities integrate all from skills – listen, speak, write and read – in natural way.
Then, the explanation of what task-based learning is has explained and it continues with the type of tasks in task-based learning.
b. Types of Task
Willis (2003) defines six types of task as follow: 1) Listing
Listing tasks tend to generate a lot of opportunities for language use, as learners explain their ideas. The processes involved in this type are brainstorming and fact-finding. The outcome would be the completed list, or possibly a draft mind map.
2) Ordering and Sorting
These tasks involve four main processes. They are sequencing items, actions or events in logical or chronological order, ranking items based on the personal values or specified criteria, categorizing items in given groups or grouping them under given headings, and classifying items in different ways, which its categories are not given.
3) Comparing
These tasks involve comparing information from two or more sources to identify common points. The processes involved are: matching to identify specific points and relate them to each other, finding the similarities and things in common, and finding differences.
4) Problem Solving
5) Sharing Personal Experiences
This type of task is goal-oriented as in other tasks. The learners are free to talk everything about themselves or their experiences. The sharing personal experiences activity can be used as the simulation for the learners. Thus, they are more familiar with the similar kind of conversation in a real life.
6) Creative Tasks
Creative task are often the combination of the other task types: listing, ordering and sorting, comparing and problem solving. Creative works are usually done in pairs or groups because the learners must do several task types in one activity. Sometimes, they also need an out-of-class research. Creative tasks also need organizational skills and teamwork.
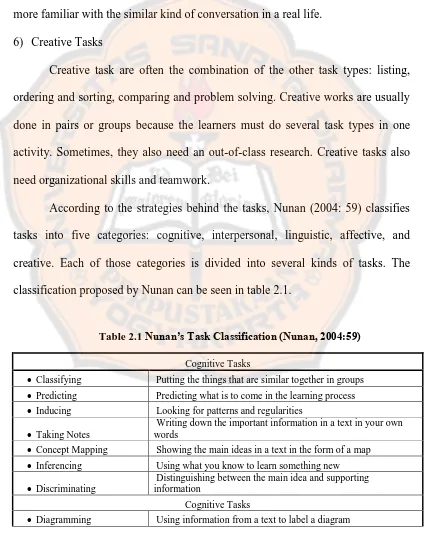
According to the strategies behind the tasks, Nunan (2004: 59) classifies tasks into five categories: cognitive, interpersonal, linguistic, affective, and creative. Each of those categories is divided into several kinds of tasks. The classification proposed by Nunan can be seen in table 2.1.
Table 2.1 Nunan’s Task Classification (Nunan, 2004:59)
Cognitive Tasks
Classifying Putting the things that are similar together in groups
Predicting Predicting what is to come in the learning process
Inducing Looking for patterns and regularities
Taking Notes
Writing down the important information in a text in your own words
Concept Mapping Showing the main ideas in a text in the form of a map
Inferencing Using what you know to learn something new
Discriminating
Distinguishing between the main idea and supporting information
Cognitive Tasks
Interpersonal Tasks
Co-operating Sharing ideas and learning with other students
Role Playing
Pretending to be somebody else and using the language for the situation you are in
Linguistic Tasks
Conversational Patterns Using expressions to start conversations and keep them going
Practicing Doing controlled exercises to improve knowledge and skills
Using Context
Using the surrounding context to guess the meaning of an unknown word, phrase, or concept
Summarizing
Picking out and presenting the major points in a text in summary form
Selective Listening
Listening for key information without trying to understand every word.
Skimming Reading quickly to get a general idea of a text Affective Tasks
Personalizing
Learners share their own opinions, feelings, and ideas about a subject
Self-evaluating
Thinking about how well you did on a learning task, and rating yourself on a scale
Reflecting Thinking about ways you learn beat Creative Tasks
Brainstorming Thinking of as many new words and ideas as one can.
Richards and Rodgers (2001) classify tasks into the following categories: 1) Jigsaw task: in this task, the learners combine different pieces of information
to form a whole, such as arranging the some parts of parts of a story into a good order.
2) Information-gap task: this task requires the learners to have a negotiation to find out what the task should be. In this task, there must be at least two students who have a set of information.
3) Problem-solving task: the learners are given a problem and a set of information then they must find out the way out of that problem.
5) Opinion-exchange task: in this task, the learners engage in discussion and exchange of ideas. They do not need to reach an agreement.
c. The Procedure of Task-based Learning
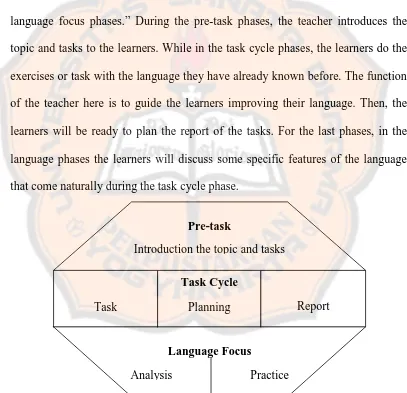
In applying task-based learning, we need to see the procedure in order to make the implementation easier. Willis (2003) states that “task-based learning consists of three phases, namely the pre-task phases, the task cycle phases and the language focus phases.” During the pre-task phases, the teacher introduces the topic and tasks to the learners. While in the task cycle phases, the learners do the exercises or task with the language they have already known before. The function of the teacher here is to guide the learners improving their language. Then, the learners will be ready to plan the report of the tasks. For the last phases, in the language phases the learners will discuss some specific features of the language that come naturally during the task cycle phase.
Figure 2.1: Willis Task-based Learning Framework (Willis, 1996:38)
Pre-task
Introduction the topic and tasks
Language Focus
Analysis Practice Task
Task Cycle
3. The 2013 Curriculum
SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta used the 2013 Curriculum which is the newest Curriculum in Indonesia. The 2013 Curriculum according to landasan yuridis kurikulum 2013 Kementrian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan is a design of education which gives enough space for the students to develop themselves based on their competences and potency. The 2013 Curriculum focuses on the character
building of the students besides the construction of the students’ competences
through several subjects in every level of education. The expectation of the 2013 Curriculum is to develop not only the students’ competences but also the
development of the students’ personality.
a. Background of the 2013 Curriculum
Richards (2001) states that curriculum is the process of a learning cycle that is started from determining the needs of the learner and then deciding the objectives then conducting the process of learning and finally it is evaluated to see whether the objective is achieved already. Furthermore, curriculum becomes the source as well as the destination for education. The process of teaching learning as an education field will be developed based on the curriculum and the result of the learning process will be evaluated based on the curriculum which is designed to develop the education.
has different paradigm and also different objectives regarding both the students and the teachers.
The development of each curriculum based on the evaluation and need analysis of the latest curriculum implemented. According to Permendikbud No. 70
(2013) in this new curriculum there are factors that become the background why this Curriculum should be developed. The factors are internal challenges, external challenges, development of the perspectives, development of the Curriculum management, and the development of the materials.
The development is also related with the existence of World Trade Organization (WTO), Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), and ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA). Those four associations influence the development of the economy in Indonesia. Based on the importance of those associations in Indonesia, the Curriculum in Indonesia could not be separated from the economical perspective.
b. The 2013 Curriculum Characteristic
The characteristic of the 2013 Curriculum is leading the students to produce meaning of the lesson rather than focusing on the materials given. The students have to deal with the meaning of the lesson in the teaching-learning process. Activities in the teaching-learning process will lead the students in the speaking time to be more active. Therefore, speaking process meant a process to relate the social purpose and produce it into speaking.
were expected to concern the correctness of the language’s rule. The Communicative Learning Approach renewed the view of language approach. The change makes the different perspective of the language. By this change, the students were expected to produce meaning rather than focusing on the grammar. c. Implementation of the 2013 Curriculum
The 2013 Curriculum has been constructed from several basic competences as same as the previous curriculum. The difference between the 2006 Curriculum and the 2013 Curriculum is the new standard that has been becoming the basic standard. This new standard is called Core Competences
(Kompetensi Inti). In the 2013 Curriculum there are four core competences that have been served to become the main sources of the basic competence and also the objective as well as the indicators. The Core Competences are specified into Basic Competences (Kompetensi Dasar) and also the Indicators.
4. Material Adaptation
The researcher conducted material adaptation in designing the materials. Adapting the materials is aimed in applying the existing materials, yet still
considering the learners’ characteristics. According to Tomlinson and Masuhara
(2004, p. 10) define “materials adaptation is adjusting and/ or changing the existing materials into suitable one which depends on the need of the learners, students, and the situation”.
Tomlinson and Masuhara (2004, p. 11) recommend “teachers may decide to use only part of a unit, add or delete texts or activities, and replace or supplement texts or activities with ones from other sources”.
According to Tomlinson and Masuhara (2004, p. 13) there are two principles of material adaptation. The first principle, “deep processing of language is required for effective and durable learning” means that the learners’ focus
should normally be on the meaning. The second principle, “the learners’ attention
should be drawn to linguistic features of the input” means that the teacher in the teaching-learning process can use kind of activities like listen to or read a text such as story and joke in order to obtain the attention from the learners before deriving the materials given.
In material adaptation, there are three main techniques according to Tomlinson and Masuhara (2004, p. 16), those are namely “Plus (+), Minus (-) and Zero (0) Category. Plus Category consists of two techniques, namely addition and expansion. The addition technique means that teachers may add different texts and/ or activities, meanwhile in the expansion technique, the teachers may expand the texts and activities by increasing the length, difficulty, and depth.
Zero Category consists of five techniques, namely, modification, replacement, reorganization, resequencing, and conversation. In the modification technique the teachers made the changes to instructions. In the replacement technique the teachers swapped one activity with another. In the reorganization technique the teachers changed the positions of texts and illustrations. In the resequencing technique the teachers changed the sequence of the activities. In the conversion technique the teachers changed the genre of a text or move the content from one medium to another.
B. Theoretical Framework
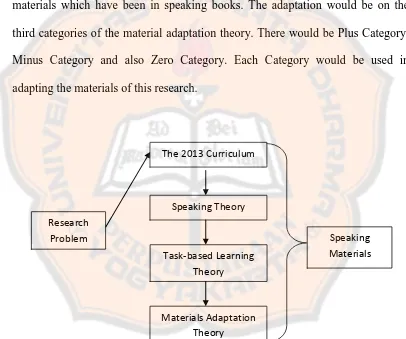
Referring to the theoretical descriptions that have been discussed in the previous section, the researcher discussed the synthesis of those theoretical descriptions. Designing materials for language teaching required a lot of considerations. Starting from the designing the curriculum, then designing the syllabus, and the lesson plan, then designing the content of the materials. Therefore, the researcher start the design from understanding the 2013 Curriculum to make an appropriate materials design for the students.
to accommodate the students’ needs. The 2013 Curriculum supported the active skill such as speaking skill. Since this research was conducted to develop speaking materials, the researcher also explained the use of speaking in this research.
Speaking as the main activity in this research would be designed by the researcher in a form of module. The researcher used the speaking theory of Nunan (2003). In order to obtain the material design, the researcher should design classroom activities that provide the chance for the students to speak. The researcher also wanted to limit the teacher talk in the activity. It meant that the activities would lead the students to use their opportunities to speak. The goal was the students would be able to speak as fluently as possible. The speaking skill could be learnt by doing some tasks. In this research, the researcher used task-based learning as the basic in developing the tasks in the material designed.
The theory of task-based learning by Richards and Rodgers (2001) and Willis (2003) were used by the researcher to choose the kinds of task in the designed materials. Task-based learning had its framework which consists of three components: pre-task phases, task-cycle phases and language focus phases. Each component had their functions. The researcher proposed to develop the design by referring to the components of task-based learning framework. The use of journal also as the form of task-based learning which would help the students more aware on their learning goals, learning strategies, learning difficulties, achievements, and
in developing the designed materials, the researcher also used material adaptation to support the development of the designed materials.
The material adaptation theory of Tomlinson and Masuhara (2004) is used to adapt the materials from several kinds of book which have the same learning goals with the designed materials of the researcher. The researcher adapted some materials which have been in speaking books. The adaptation would be on the third categories of the material adaptation theory. There would be Plus Category, Minus Category and also Zero Category. Each Category would be used in adapting the materials of this research.
Figure 2.2: the Researcher’s Theoretical Framework
Research Problem
Task-based Learning Theory Speaking Theory
Materials Adaptation Theory The 2013 Curriculum
23
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter discusses the research method used in this research. This chapter consists of six important points in conducting the research. They are research method, research setting, research participants, research instruments and data gathering technique, data analysis technique, research procedure.
A. Research Method
This research was conducted to obtain the relevant data needed in order to reach the research objective of this research. The researcher gathered and analyzed the data to answer the question in the research problem of this research. There was one question to be answered, that was ‘what do speaking materials using task-based learning for the seventh grade students of English Extracurricular Activity at SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta look like?’.
standards.” The goal of R&D is to take this research knowledge and incorporate it
into a product that can be used in the schools (Borg & Gall, 1983, p. 771)
In Educational Research and Development, there are several steps which are usually referred to R&D cycle. According to Borg, Gall and Gall (2007), there are ten major steps in the R&D cycle, namely:
1. Identification of the goal for the instructional activities or product which can be done by having need analysis.
2. Analysis of the instruction which is undertaken to specify the specific skills, procedure, learning task that are involved in reaching the goals of instruction. 3. Identification of the learner’s entry level and instructional setting.
4. Translating the needs and goals of instructions into specific performance objectives.
5. Developing the instructional assessments which are related directly to the knowledge of the students and the specific skills performed in the objectives. 6. Developing a specific instructional strategy for assisting learners with their
efforts to achieve each performance objective. 7. Developing the instructional materials.
8. Designing and conducting formative validation of instruction. 9. Revising the instruction.
10.Designing and conducting summative validation.
limitation of money. Moreover this research would be conducted in undergraduate level so the difficulty of conducting the ten steps would be very high. Therefore this research would be adopted from the research and development cycle into five steps.
Therefore, the steps which would be used in this research could be explained as follows:
1. Information Collecting: the first step will be the combination of the first three steps in the R&D cycle. This step consisted of the goals of the material design and the learners’ level.
2. Planning: this step is the adoption of fourth step of the original R&D cycle. The researcher will translate the needs and goals of instructions into specific performance objectives. The objectives will be the basic of the design materials.
3. Material development: the researcher adopted the fifth, sixth, and seventh step in the R&D cycle as the third step in this research. This step will be the main step in developing the materials. After developing the materials, the next step will be explained below.
4. Material validation: the ninth and the tenth step in the R&D cycle will be summarized as the fourth step in this research. The step will is material validation. The validation will be conducted by the experts.
of the new product in meeting its objectives and also to collect information that can be used to improve the product.
B. Research Setting
This research was conducted in 2014. It was started from May 2014, it was started by distributing the questionnaire to the learners and also conducting the interview to the teacher. After that the researcher developing the designed materials by analyzing the result of the questionnaire for need analysis and also the interview result. In finishing the material design, the researcher also distributed the questionnaire to the experts in order to obtain the validation of the material design. The researcher conducted the research at SMP Pangudi Luhur
Yogyakarta. This school is located at Jalan Timoho II/ 29, Yogyakarta.
C. Research Participants
In this research, there were two groups of research participants. The first group was the participants of the information collecting, and the second was the participants of the material validation.
1. Participants of the Information Collecting
information collecting of this research. The researcher distributed questionnaire to
the students in order to understand the students’ lacks, needs, and wants.
2. Participants of the Material Validation
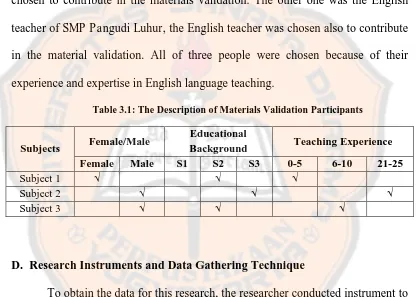
The participants of the material validation were two lecturers of English Language Educational Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. They were chosen to contribute in the materials validation. The other one was the English teacher of SMP Pangudi Luhur, the English teacher was chosen also to contribute in the material validation. All of three people were chosen because of their experience and expertise in English language teaching.
Table 3.1: The Description of Materials Validation Participants
Subjects Female/Male
Educational
Background Teaching Experience Female Male S1 S2 S3 0-5 6-10 21-25
Subject 1 √ √ √
Subject 2 √ √ √
Subject 3 √ √ √
D. Research Instruments and Data Gathering Technique
To obtain the data for this research, the researcher conducted instrument to collect the data of information collecting and material validation. The instruments were questionnaire and interview.
1. Questionnaire
Brown and Rodger (2002) stated that “a questionnaire is a list of questions asking about the opinion of people”. There are two kinds of questionnaire, namely
allowed the respondents to give free responses on what were asked in the questionnaire.
There were two kinds of questionnaires which were distributed in this research. The first one was the questionnaire for the students to collect the
information of the students’ lacks, needs and also wants. It helped the researcher
in designing the materials because it was the basic information. The second questionnaire was the material validation for the experts in order to obtain the appropriate design. The first questionnaire was given to the students in the beginning of May 2014. The second questionnaire was given to the experts in the beginning of December 2014.
In order to gather the data needed in this research, some techniques were applied in information collecting and material validation. In information collecting, the researcher distributed the questionnaire to the 36 students at SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta in order to obtain the students’ lacks, needs and
wants. In material validation, the researcher distributed the questionnaire and the designed materials to the experts in order to obtain the feedback to revise the designed materials.
Table 3.2 the Researcher’s Data Collection
Instruments Participants Times Data Obtained
Questionnaire for Needs Analysis
The students of SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta May 2014, before designing the materials Learners’ characteristics, learners’ educational background, learners’
difficulties in learning English,
available facilities, learners’
needs and interests. Questionnaire
for Expert Validation
Two English Lectures of English Education Research Activity of Sanata Dharma University December 2014, after designing the materials.
Instruments Participants Times Data Obtained
Questionnaire for Expert Users
One English
Extracurricular Teacher of SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta
December 2014, after designing the materials
Review, comments, and suggestions to the design materials.
2. Interview
The interview conducted in this research was for supporting the need analysis to develop the designed materials. Through interview, the participant could give actual information that individual probably would not reveal by any other data-collection method (Borg, Gall & Gall 2007). In the interview, there was a list of questions related to the data and information expected for the research. The researcher did the interview to the English teacher once.
E. Data Analysis Technique
In this research, the researcher analyzed the data after gathering the data from the questionnaire and the interview in the research instruments and gathering technique. The researcher adopted qualitative and quantitative data analysis. The questionnaire analysis utilized a quantitative approach, whereas the interview analysis utilized a qualitative approach through the rich description given.
1. Data for Questionnaire Analysis
The data obtained through the first questionnaire were calculated to find
out the percentage of participants’ opinion and other factual data needed for the
n
x 100 %
∑n
Note :
n : the number of participants who choose certain statements
∑n : the total number of participants
The second questionnaire was distributed in the material validation. The questionnaire was distributed to the two lectures of English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University Yogyakarta and one teacher of English Extracurricular Activity of SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta. In order to measure the opinion of the experts, the researcher delivered the questionnaire using open-ended questions.
The analysis of the second questionnaire would be in a form of descriptive analysis. Considering the open-ended questions, the researcher analyzed the result in order to get the appropriateness of the designed materials. The researcher analyzed the result based on the answers of the provided questions. After finishing the analysis, the researcher revised the designed materials.
2. Data for Interview Analysis
The researcher analyzed the interview result by utilizing qualitative approach. The analysis of the interview was stated in the descriptive form. The researcher recorded the discussion from the English teacher of SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta. The analysis will be in the form of coding analysis. Patton
coding data, finding patterns, labeling themes, and developing category systems”
(p.462).
In this research, coding was conducted in order to get coding scheme and coding categorization. The researcher read the interview scripts many times to find the clues. Bogdan and Biklen (2003) stated that “as you read through your
data, certain words, phrases, patterns of behavior, subjects’ ways of thinking, and
events repeat and stand out” (p. 161). The results of the analysis would be used to
the basis in designing the materials
F. Research Procedure
The researcher used five steps as the procedures of conducting this research. Those steps were:
1. Information Collecting
Information collecting was the step of collecting the data background and information for the researcher in designing the materials. The researcher collected the data by distributing the questionnaire to the students in SMP Pangudi Luhur
on May 16th, 2014 and interviewing the English teacher of SMP Pangudi Luhur
Yogyakarta on September 12th, 2014. By having the data information, the researcher decided and started to determine the objectives of the designed materials.
In this step, the researcher gathered information of the questionnaire and the result of the interview to the teacher. The information consisted of the
students’ perception of the importance of English, the students’ opinion of the
English Extracurricular Activity, the variation activity in English Extracurricular Activity, the students’ perception of the learning media and the class activity, the learning method for the material development and the learning materials. The result of the questionnaire would be shown in Appendix C.
The researcher conducted the interview with the English teacher of SMP Pangudi Luhur Yogyakarta. After conducting the interview, the researcher transcribed the interview results. After reading transcript regularly, the researcher did coding categorization. There were two categorizations were described as follows: (1) learning method and (2) learning materials. Furthermore, the researcher generated themes based on the categorization. Those themes are:
1) Task-based Learning as the Learning Method
The designed materials conducted task-based learning as the learning method. In task-based learning, the students do some tasks in achieving the goals of every topic. As what the teacher said:
The method in teaching English Extracurricular Activity is giving task to the students. The form of the task would be work in pair; work in groups; or even work individually. The task is more closely to the retell, speech, and conversation.
communicating with others, the task-based method would be appropriate to help the students learned more. Another quotation to support the first quotation was:
In a week, there are 90 minutes each meeting. It is an obligatory extracurricular so the attendance and the process in learning English
become the important thing. It is not only the good level of students’
competence but it is the process of learning. (English Extracurricular Activity’ teacher)
The existence of learning process in the English Extracurricular Activity was an important thing. The process consisted of the method in learning English through the task given. The task given was used to communicate with others. The opinion of the teacher about based had the same understanding with
task-based learning method. Richards and Rodgers (2001) quoted that “tasks are useful
vehicles for applying real communication activities for the learner to support the
learning process” (p.223). The same understanding between the teacher’s opinion
2) The Materials of Regular Class Grade 7 as the Learning Materials
In defining the materials, the researcher adapted the materials from regular grade 7. The following is a part of the interview transcript which showed the learning materials should be:
The material for English Extracurricular Activity depends on the 2013 Curriculum. The reason is English Extracurricular Activity supports the teaching learning activities in the school. (English Extracurricular Activity’ teacher)
The materials for teaching English Extracurricular Activity depended on the learning objectives and competences of regular class grade 7. It purposed to correlate the morning activity in the class with the activity in English Extracurricular Activity. The activity in the regular school-time focused on writing, reading, structure and vocabulary. Speaking was not really had enough time to be practiced.
In this research, the researcher defined the goal of the designed materials to facilitate the seventh grade students in the teaching-learning process of English Extracurricular Activity. By finishing this activity the students are expected to have skills in speaking English. Since English Extracurricular Activity is designed to support the teaching-learning activities in the regular school time, the researcher would develop the designed materials based on the curriculum employed by the school.
seventh grade students in English Extracurricular Activity would be shown in Table 3.3.
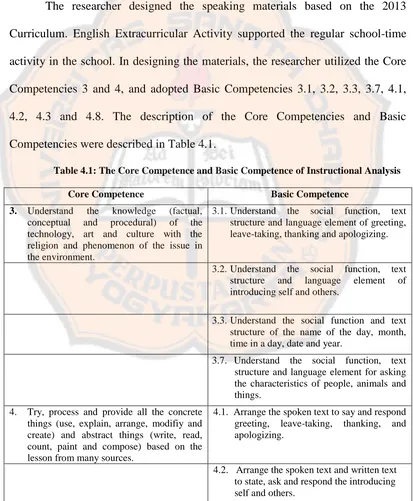
Table 3.3: The Basic Competences of Grade Seventh
Basic Competences
4.1. Arrange the spoken text to say and respond to greeting, leave-taking, thanking, and apologizing.
4.2. Arrange the spoken text and written text to state, ask and respond the introducing self and others.
4.3. Arrange the spoken text and written text to state and ask the name of day, month and time in a day.
4.4. Arrange the spoken text and written text to describe and ask the name of animal, things, and buildings.
4.5. Arrange the spoken text and written text to state and ask the characteristics of people, animals and things.
4.6. Arrange the spoken text and written text to state and ask the behavior of people, animals and things.
4.7. Arrange the spoken text and written text about instruction, short notice and warning. 4.8. Arrange the descriptive spoken text and written text about people, animals and things.
2. Planning
In this step, the researcher determined the objectives of learning, identification of the learners, and also the topics selection. This step was important since in this step the researcher made the direction of the design would be. The researcher also considered the 2013 Curriculum to be the main consideration besides considering the needs analysis result.
The researcher selected the topics of the materials based on the 2013 Curriculum. Since the school used the 2013 Curriculum, the topics selection
would be based on the students’ needs. The topics selection would present the
goals of the designed materials which could help the students to speak English. The researcher chose the topic which accommodated the students to be more active in speaking English. The topics were stated in Table 3.4.
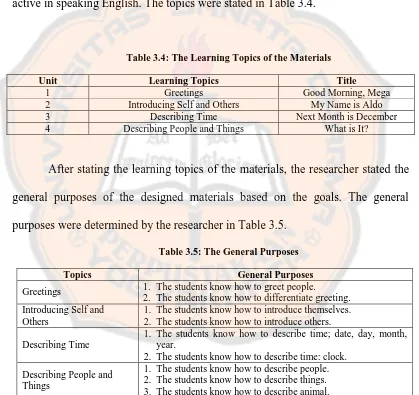
Table 3.4: The Learning Topics of the Materials
Unit Learning Topics Title
1 Greetings Good Morning, Mega 2 Introducing Self and Others My Name is Aldo 3 Describing Time Next Month is December 4 Describing People and Things What is It?
After stating the learning topics of the materials, the researcher stated the general purposes of the designed materials based on the goals. The general purposes were determined by the researcher in Table 3.5.
Table 3.5: The General Purposes
Topics General Purposes
Greetings 1. The students know how to greet people.
2. The students know how to differentiate greeting. Introducing Self and
Others
1. The students know how to introduce themselves. 2. The students know how to introduce others. Describing Time
1. The students know how to describe time; date, day, month, year.
2. The students know how to describe time: clock. Describing People and
Things
1. The students know how to describe people. 2. The students know how to describe things. 3. The students know how to describe animal.
competences as the main basic of the designed materials should be. The learning indicators would be presented in Table 3.6.
Table 3.6: The Learning Indicators of the Materials
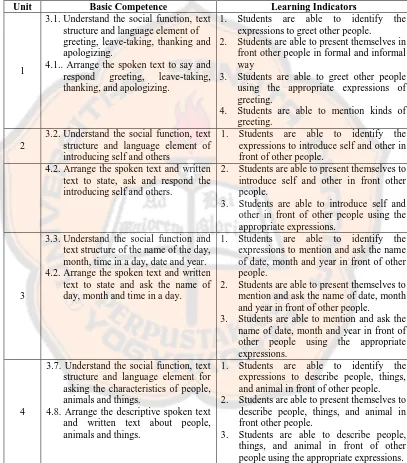
Unit Basic Competence Learning Indicators
1
3.1.Understand the social function, text structure and language element of greeting, leave-taking, thanking and apologizing.
4.1.. Arrange the spoken text to say and respond greeting, leave-taking, thanking, and apologizing.
1. Students are able to identify the expressions to greet other people.
2. Students are able to present themselves in front other people in formal and informal way
3. Students are able to greet other people using the appropriate expressions of greeting.
4. Students are able to mention kinds of greeting.
2
3.2.Understand the social function, text structure and language element of introducing self and others
1. Students are able to identify the expressions to introduce self and other in front of other people.
4.2.Arrange the spoken text and written text to state, ask and respond the introducing self and others.
2. Students are able to present themselves to introduce self and other in front other people.
3. Students are able to introduce self and other in front of other people using the appropriate expressions.
3
3.3.Understand the social function and text structure of the name of the day, month, time in a day, date and year. 4.2.Arrange the spoken text and written
text to state and ask the name of day, month and time in a day.
1. Students are able to identify the expressions to mention and ask the name of date, month and year in front of other people.
2. Students are able to present themselves to mention and ask the name of date, month and year in front of other people.
3. Students are able to mention and ask the name of date, month and year in front of other people using the appropriate expressions.
4
3.7. Understand the social function, text structure and language element for asking the characteristics of people, animals and things.
4.8. Arrange the descriptive spoken text and written text about people, animals and things.
1. Students are able to identify the expressions to describe people, things, and animal in front of other people. 2. Students are able to present themselves to
describe people, things, and animal in front other people.
3. Students are able to describe people, things, and animal in front of other people using the appropriate expressions.
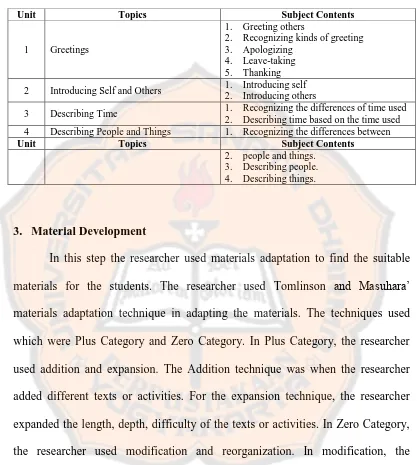
Table 3.7: The Organization of Subject Contents
Unit Topics Subject Contents
1 Greetings
1. Greeting others
2. Recognizing kinds of greeting 3. Apologizing
4. Leave-taking 5. Thanking 2 Introducing Self and Others 1. Introducing self
2. Introducing others
3 Describing Time 1. Recognizing the differences of time used 2. Describing time based on the time used 4 Describing People and Things 1. Recognizing the differences between
Unit Topics Subject Contents
2. people and things. 3. Describing people. 4. Describing things.
3. Material Development
In this step the researcher used materials adaptation to find the suitable materials for the students. The researcher used Tomlinson and Masuhara’ materials adaptation technique in adapting the materials. The techniques used which were Plus Category and Zero Category. In Plus Category, the researcher used addition and expansion. The Addition technique was when the researcher added different texts or activities. For the expansion technique, the researcher expanded the length, depth, difficulty of the texts or activities. In Zero Category, the researcher used modification and reorganization. In modification, the researcher changed the instruction of the materials. The researcher changed the position of the texts in the reorganizing technique.
students should follow. In each phase, the researcher also divided it into some sections. The sections in designed materials would help the students to learn English in a systematic way. It was because the sections provided some activities which had correlation each other.
The researcher classified the pre-task phase into “Do You Remember?” section, the task cycle phase into “Let’s Prepare” and “It’s Your Turn”, the language focus phase into “Let’s Learn“ and “What Did You Learn?”. Those five sections in the designed materials would help the learners in English Extracurricular Activity. The sections were made in order to provide the learning step in the teaching-learning activity in English Extracurricular Activity.
4. Material Validation
The researcher conducted the validation by looking at the result of the validation questionnaire from the experts. There were some questions related to the designed materials. The researcher did not use the degree of agreements in the statements, the open-ended questions was used in order to get more explanation of the validation.
After analyzing the data, the result of the validation questionnaire from the experts was satisfying. The researcher made the designed materials well-organized based on the lesson plan. The designed materials were also suitable to the core competence and basic competence. The basic in developing the materials were in the 2013 Curriculum. The researcher chose several Basic Competences which could be applied in speaking. The materials in the designed materials were also met their indicators. The indicators were made by the researcher in a form of lesson plan.
The activities in the designed materials also gave the variety to speak. It helped the learners to be more active in speaking. The activities provided some games, group work, pair work and dialogue. There were five sections in the
designed materials. Those sections were “Do You Remember?”, “Let’s Prepare”, “It’s Your Turn”, “Let’s Learn” and “What Did You Learn?”. Based on the
validation questionnaire, the result of those five sections were appropriate for teaching speaking. Each section has its own functions in the teaching-learning process.
The main section which was “It’s Your Turn” gave the opportunity for the
be more active in speaking. The result showed that the designed materials had some strengths and weaknesses. The strengths of the designed materials were the well-organized layout, lesson plans and guidelines, many interesting pictures, examples of the topic in each unit, the pleasant topic and the speaking activities. Based on the result, the researcher found that the designed materials were applicable for the speaking.
The weaknesses of the designed materials were some grammatical mistakes and unclear instructions. Based on the result, the researcher realized some mistakes that never be realized before. There were also opinions from the experts of the designed materials. The opinions from the experts were positive. The designed materials were fun for learning. There were some practical item, lesson plans and also guidelines. Those instruments helped the teacher in teaching speaking.
In terms of suggestions for revising the designed materials, there were some helpful suggestions. First of all, the expe