i
A CORRELATIONAL STUDY BETWEEN THE
STUDENTS’
EXPERIENCE AS ENGLISH TUTOR TO
THEIR ABILITIES IN TRANSLATING TEXT INTO
INDONESIAN
(A Study of Sixth Semester Students of English Education
Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
at IAIN Salatiga in the Academic Year of 2016/2017)
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board of Examiners as a partial fulfillment of
the requirements for the degree of
Sarjana Pendidikan
(
S.Pd.
) in
English Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
By:
SITI NUR HANIFAH
113 13 125
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
ii
iii
MINISTRY OF RELIGIOUS AFFAIRS
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
SALATIGA
Jl. Tentara Pelajar 2 Telp (0298) 323433 Fax 323433 Salatiga 50721
Website: www.iainsalatiga.ac.id email: [email protected] a
Salatiga, August 11th 2017
Hanung Triyoko, S.S., M. Hum., M.Ed.
The lecturer of English Education Department
State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR‟ NOTE Case: Siti Nur Hanifah
Dear,
Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty Assalamu‟alaikum wr. wb.
After reading and correcting Siti Nur Hanifah‟s graduating paper entitled “A
CORRELATIONAL STUDY BETWEEN THE STUDENTS’ EXPERIENCE
AS ENGLISH TUTOR TO THEIR ABILITIES IN TRANSLATING TEXT
INTO INDONESIAN”, I have decided and would like to propose that this paper
can be accepted by the Teacher Training and Education Faculty. I hope this paper
will be examined as soon as possible.
Wassalamu‟alaikum wr. wb.
Counselor
Hanung Triyoko, S.S.,M.Hum.M, M.Ed.
v
MOTTO
Everything will come to those who keep trying with
determination and patience
-Edison-
90% of the causes of human failure is submission to reality
vi
DEDICATION
This graduating paper especially dedicated for :
1. My dearest parents, Father (Lazim) and Mother (Diniah) for their never
ended prayers, resignation, love, struggle, sacrifice and everything are
precious for me.
2. My beloved sister Laily and Salsa, thanks for your help and motivation
which are really helpful for me.
3. My beloved partner, Edy Setiawan thanks for always staying beside me in
vii
ACKNOWLEDMENT
Alhamdulillahirobbil „alamin. All praises be to Allah Subhanahu wa
Ta‟ala, the Lord of Universe. Because of Him, the researcher could finish
this graduating paper as one of the requirements for getting Sarjana
Pendidikan (S.Pd) degree in English Education Department of Teacher
Training and Education Faculty of State Institute of Islamic Studies (IAIN)
Salatiga in 2017.
The completion of this graduating paper is not apart from the
supports, encouragement, guidance, advice, and help from individuals and
institution. Therefore, the researcher would like to express the deepest
gratitude to:
1. Dr. Rahmat Hariyadi, M.Pd, the Rector of State Institute of Islamic
Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
2. Suwardi, M. Pd., the Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
3. Noor Malihah, Ph.D., the Head of English Education Department
4. Hanung Triyoko, S.S., M.Hum., M. Ed., the counselor of this
graduating paper. Thank you very much for the suggestions, guidance,
and moreover, for time that was spent in guiding the researcher to
complete this graduating paper from the beginning until it is finished
5. All lecturers of English Education Department of IAIN Salatiga. The
researcher deeply appreciates the advices, knowledge, motivations,
viii 6. All the librarian of IAIN Salatiga
7. My beloved family
8. My beloved friends in “Jeneng Group”, thanks for beautiful days in
this campus
9. My beloved best friends, “Fifin, Ella, Risna, Betik, Fitri, Firda,
Elverda, Risa”
10. All students of English Education Department 2013
11. Everyone that the researcher cannot mention one by one. Thank you
very much for the encouragement, advice, and help
Salatiga, August 2017
The Reseacher
ix
F. Definition of the Key words………... 7
x
5. Principle, Procedure and and Method of Translation ...
a. Principles of translation ...
b. Procedures of translation ...
c. Method of translation ...
6. Translation Strategies ...
7. Form and Meaning of Translation ...
8. Process of Translation ...
9. Difficulties of Translation ...
xi
2. Profile of Institution ………...
33
D. Technique of Data Collection ………... 38
E. Data Analysis Technique ………... 42
F. Technique of Data Interpretation………... 44
xii APPENDICES
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 2.1 Translation Process by Larson ………... 24
xiii
LIST OF TABLES
Table 3.1 List of Subject of the Research ... 37
Table 3.2 Table Category of Assesment‟ Translating Text ... 41
Table 3.3 Grade of Students Experience ... 42
Table 3.4 Grade of Students Translation Abilities ... 43
Table 3.5 Pearson‟s Product-Moment Correlation Formula ... 43
Table 3.6 r Value Interpretation ... 44
Table 4.1 Points of Questionnaire ...…………... 46
Table 4.2 Score Translating Text ...………... 48
Table 4.3 Data Analysis ...…... 50
Table 4.4 Calculation Research of Required Data ………... 52
Table 4.5 SPSS Correlation Table ………... 54
Table 4.6 The Interpretation of Correlation “r” Product Moment ... 55
xiv ABSTRACT
Hanifah, Siti Nur. 2017. “A CORRELATIONAL STUDY BETWEEN THE
STUDENTS’ EXPERIENCE AS ENGLISH TUTOR TO THEIR
ABILITIES IN TRANSLATING TEXT INTO INDONESIAN (A Study of Sixth Semester Students of English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty at IAIN Salatiga in Academic Year of 2016/2017)”. (Counselor : Hanung Triyoko, S.S., M.Hum., M.Ed.)
Keywords : correlation, experience, tutor, translation
1 CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Study
Language is an instrument of social communication that is formed
by symbol of voice from human being (Gorys Keraf, 2010:1). Human is a
social creature who need to communicate with others. Through language
we can know the origins, education backgrounds, and characteristics of
someone. Language can show someone regarding their origins or their
personalities.
Nowadays, international language that is used in the whole world
is English. So, it is very important for us to learn it. This time, English has
been taught in all levels of educational institutions in Indonesia, from the
lowest until the highest level. We can see the curriculum that is used in
English has become an important necessity to support human‟s
education or career. So, some people consider that learning English in the
school isn‟t enough, they need more additional lessons from out of school.
Such as; they come to learn English in English Course or call a tutor to
2
A tutor is someone who gives private lessons to one student or a
small group of students. Nowadays, majority of tutors are university
students who are still learning in the college. Why do they become tutors?
They have many reasons, such as they want to practice to be a teacher, get
any experiences and get the fee from their result of teaching. However,
they will get many advantages from their experience as tutors, they can
increase their skill in teaching.
Experience as tutors can also increase their ability in teaching
English and broaden their knowledge. Such as; speaking, writing, reading,
translating and grammar. By teaching, the tutors will be doing practices of
teaching and learning subjects regarding English language that will be
taught to their students. Topping and Ehly (1998:26) note that tutors can
learn to be nurturing toward their learners, and in so doing, develop a
sense of pride and responsibility and that improved motivation and attitude
can lead to greater commitment, improved self-esteem, self-confidence,
and greater empathy with others. So, their knowledge will increase more
and more over time.
Translation is one of the skills that is needed to teach English.
When tutors teach English in Elementary School, Junior High School and
Senior High School, they will do many translating sentences activities
from the subjects that they teach or answer questions from their students
about the meaning of some vocabularies, sentences, and texts. So, tutor‟s
3
Translating is the process of replacing the meaning from the
Source Language into the Target Language. We must pay a close
attention in translating, because the form of the meaning may change. The
Language translated is called a Source Language (SL) and the language
used to translate is called Target Language (TL) (Larson, 1984:1).
Translation is sometimes referred to as the fifth language skill
alongside the other four basic skills of listening, speaking, reading,
writing. Translation holds a special importance at an intermediate and
advanced level: in the advanced or final stage of language teaching,
translation from L1 to L2 and from L2 to L1 is recognized as the fifth skill
and the most important social skill since it promotes communication and
understanding between strangers (Ross, 2000:2).
Translating is not something easy. People must practices
translating a lot to become a good translator. Reading lots of texts in the
target language is part of practices to be good translators. When people
become a tutor of English from Junior High School and Senior High
School students, people would be exposed to many English texts as
learning materials. In addition, in Elementary school people can meet
English texts in some materials, although they were still very simple texts.
Automatically, a tutor needs to help students to translate their texts and
explain the meaning of all contents of texts. So, texts that people read and
4
Leila Razmjou (2002:4) said that the role of language is closely
related with translation, because linguistic study is always related with the
processes of producing and interpreting texts. It is as approach toward
study of translation. She also explains that to make good translation we
should read from many different texts, because translator needs active
knowledges. We can read texts from different genres to get a
comprehensive knowledge from source language and target language.
Farahzad (2007:6) said that translators use content meaning in source texts
to create whole new text in target text.
Translation skill is important skill by learners, because that skill
can make them learning all knowledges in the world. So, translators must
translate target language without changing the source meaning.
Translation skill needs special thingking and practices (Sudarno, 2011:34).
According Moelyono in Ngadiso (1995:57) that as tutors the
translation skill is important skill, they are extend materils and knowledges
to students. Tutors must extend their translation well, in order to make
students easy to understand. A good translator is translator who can
translate text appropriate to levels students.
Based on the researcher‟s interest in analyzing the correlation
between students‟ experience as English tutors and their abilities in
translation, the researcher select the students in the sixth semester on
5
entities “A CORRELATIONAL STUDY BETWEEN THE STUDENTS‟
EXPERIENCE AS ENGLISH TUTORS TO THEIR ABILITIES IN
TRANSLATING TEXT INTO INDONESIAN (A Study of the Sixth
Semester Students of English Education Department of Teacher Training
and Education Faculty at IAIN Salatiga in Academic year of 2016/2017).”
B. Problem of the Study
Based on the background of the research, the researcher arranges
the problems as follows:
1. Is there any correlation between students‟ experience as English tutors
to their abilities in translating text into Indonesian at the sixth semester
students of English Education Department of Teacher Training and
Education Faculty at IAIN Salatiga in the academic year of
2016/2017?
2. Does the research result show a significant correlation at the sixth
semester students of English Education Department of Teacher
Training and Education Faculty at IAIN Salatiga in the academic year
of 2016/2017?
3. What factors influence the correlation between student experience as
English tutors to their abilities in translating text into Indonesian at the
sixth semester students of English Education Department of Teacher
Training and Education Faculty at IAIN Salatiga in the academic year
6 C. Objectives of the Study
Based on the problems as stated before, the researcher has some
hypotheses for the study, there are :
1. To know whether is a correlation between the students‟ experience as
English tutors to their abilities in translating text into Indonesian at the
sixth semester students of English Education Department of Teacher
Training and Education Faculty at IAIN Salatiga in the academic year
of 2016/2017 or not.
2. To find out the research result show a significant correlation at the
sixth semester students of English Education Department of Teacher
Training and Education Faculty at IAIN Salatiga in the academic year
of 2016/2017.
3. To know factors influence the correlation between student experience
as English tutors to their abilities in translating text into Indonesian at
the sixth semester students of English Education Department of
Teacher Training and Education Faculty at IAIN Salatiga in the
academic year of 2016/2017.
D. Significances of the Study
The researcher hopes that the result of this research can be useful
and it can give many informations for others practically and theoretically;
7
tutor and increase their abilities in translation.
c. For the other researcher
The result of this research can be used as an input or evaluation for
English learners, especially students of English Education
Department.
2. Theoretically
The result of the research can be used as reference material for another
research based on the similar topics.
E. Limitation of the Study
In order to focus on this research, there must be a limitation of the
problem. The topic must be limited in order to investigate the problem
more accurately, precisely and correctly. Therefore, the researcher must
limit to research the correlation between students‟ experience as English
tutors to their ability in translating text at the sixth semester students of
English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
8 F. Definition of Keywords
The researcher would define all of keywords used in this research, as
follow:
1. Definition of correlation
Correlation is the mutual relationship or connection between two
things in which one thing changes as the other does. (Oxford
Dictionary, 2011: 98). Correlation is this study means a correlation
study which describe terms the degree to which two variables are
related. (Gay, 1992:229)
2. Definition of experience
Experience is knowledge or skill gained by doing or seeing things.
(Oxford Dictionary, 2011:155). Experience can also defined the
knowledge or mastery of an event or subject gained through
involvement in or exposure to it.
3. Definition of tutor
Tutor is private teacher, especially of one pupil. (Oxford
Dictionary, 2011:480). Tutor is someone who gives private lessons to
one student or a small group of students.
4. Definition of translation
Wida in Ngadiso (1995:17) defined that translation consist in
reproducing in the receptor language the closest natural equivalent of
9
terms of style. In addition, (Catford, 1965:124) said that translation is
replacement of textual material in one language (SL) by equivalent
textual material in another language (TL).
G. Organization of the Graduating Paper
This research consist of five chapters. As follow :
Chapter I tells about introduction. This research consists about
general background of the study, statements of the study, objectives of the
study, significance of the study, limitation of the study, definition of
keywords, and organization of the graduating paper. Chapter II tells about
theoritical framework, consist of definition of keywords in this research
and supporting theories. The researcher takes some books written by many
expert as references which explain more about English tutors and
translation. Chapter III discusses about the research method. It consist of
research method, setting of the research, subject of research, technique of
data collection, and data analyse technique. Chapter IV is finding and
discussion. It is analysis to answers the problem of the research. Chapter V
is Closure. It consist of conclusion and suggestion. The last past is
10 CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
This chapter discusses about definition of correlation, definition of experience,
definition of tutor, general definition of translation, types of translation, kinds of
translation, pricinples, procedures and methods of translation, translation
strategies, form and meaning of translation, process of translation, difficulties of
translation, and criterians of good translation.
A. Correlation
Correlation is the mutual relationship or connection between two things in
which one thing changes as the other does. (Oxford Dictionary, 2011: 98).
Correlation of this study means a correlation study which describe terms the
degree to which two variables are related. (Gay, 2009:229)
Correlational research is a research study that involves collecting data in
order to determine whether and to what degree a relationship exists between two
or more quantifiable variables (Gay, 2009:430)
Correlational research is to investigate the extent to which variations in
one factor corresponde with variations in one or more other factors based on
11 B. Experience
In English Oxford Dictionaries (2011:112), definition of experience is the
knowledge or skill acquired by a period of practical experience of something,
especially that gained in a particular profession. Other definition in this dictionary
that experience is an event or occurence which leaves an impression on someone.
The meaning of experience in Cambridge Dictionay (2016), is the process
of getting knowledge or skill from doing, seeing, and feeling things. Whereas in
Merriam Webster Dictionary (1828), experience is direct observation of or
participation in events as a basis of knowledge. Other definition is the fact or
state of having been affected by or gained knowledge through direct observation
or participation.
C. Tutor
Tutor is private teacher, especially of one pupil. (Oxford Dictionary,
2011:480). Tutor is someone who gives private lessons to one student or a small
group of students.
It is important to be aware that, while this article focuses on a program that
was created to provide teaching experience to pre-service English teachers,
anyone can tutor and anyone can be tutored. Tutors can be almost any age, from
primary school up, and they can come from a variety of disciplines. Ten-year-olds
12 D. Translation
1. General definition of Translation
Wida in Ngadiso (1995:17) defined that translation consist in reproducing
in the receptor language the closest natural equivalent of the source language
message, first in terms of meaning and secondly in terms of style. In addition,
Catford,(1965:45) said that translation is replacement of textual material in
one language (SL) by equivalent textual material in another language (TL).
Translation is a craft consisting in the attemp to replace a written message
and/or statement in one language by the same message and/or statement in
another language (Newmark, 1973:7).
A translation can also defined as a presentation of a text in a language
other than that in which it was originally written. Translating is concerned
with conversion of the written word, interpreting with that of the spoken word
(Finlay, 1971:78).
Translation is considered as a work of a written or text form of message.
It concerns to the replacemet of written message without burden to transfer the
equivalent form in the target language form the source language. The most
significant matter of correct translation is about the consistence or closest
natural equivalence of the message transferred from SL to Tl. Thus a work can
be stated as the the work of translation when it has the following
requirements:
13
b. It concern with written message or textual material or text.
c. Transfer the content or thought or message; not the form of SL text.
d. It is also a kind of process or exercise.
e. The second text must have the same meaning or message with the first or
original.
f. The secont text uses idiomatic expression in the TL to retain the style or to
make it sounds like the original text.
g. The second text uses target language equivalent to the source language.
2. Types of translation
According Jacobson (2000:14), there are three types of translation :
a. Intralingual Translation
Intralingual translation, or rewording (an interpretation of verbal
signs by means of other signs in the same language).
For example; in a sentence “every celibate is a bachelor, but not every
bachelor is a celibate.” The sentece contains synonym or idimatic phrase
and can change that sentence become “every bachelor is unmarried man,
and every unmarried man is a bachelor”or “every celibate is bound not to
marry, and everyone who is bound not to marry is a celibate.”
b. Interlingual Translation
Interlingual translation or translation proper (an interpretation of
14
For example; “cheese” is a word about food that made by milk, but in
other country or in target language “cheese” can have other meaning,
because difference of culture or geographycal factors.
c. Intersimiotic Translation
Intersemiotic translation or transmutation (an interpretation of
verbal signs by means of signs of nonverbal sign systems).
According Roman Jacobson (2000:114) translators can omit all
rhymes or change a proverb to be a sentence that can understand by reader
in target language. For example; there is a proverb in Italian “Traduttore,
traditore”, if translated in English become “the translator is a betrayer”.
3. Kind of Translation
Catford (1965:21) divided the three aspects of translation differently, those
are : extent, level, and ranks.
Based on the extent, the types of translation are :
a. Full translation
It is a type of translation in which the entire SL text in reproduced by the
TL text materials.
b. Partial translation
There are only some parts of the SL text to be translated into the TL
text.
15 a. Total translation
The TL materials replaces all levels of the SL text.
b. Restricted translation
It is the replacement of SL textual material with equivalent TL material at
only one level; whether at the phonological level, graphonological levels,
or at the level of grammar and lexis.
In terms of rank, translation is divided into :
a. Rank-bound translation
It means that the selection of TL text equivalent is limited at only one
rank, such as word-for-word equivalence, morpheme-for-morpheme
equivalence, etc.
b. Unbounded tranlation
It can move freely up and down the rank scale.
Based on the purposes of translation, Brislin in Choliludin (2005:26)
categorized translation into four types, namely :
a. Pragmatic translation
It refers to the translation of a message with an interest in accuracy
of the information that was meant to be conveyed in the SL form and it is
not conveyed with other aspects of the original language version.
Example; the translation of the information about repairing a machine.
16
It refer to translation in which the translator takes into account the
affect, emotion, and feeling of an original version, the aesthetic form used
by the original author, as well as any information in the message.
Example; the translation of sonnet, rhyme, heroic couplet, dramatic
dialogue, and novel.
c. Ethnographic translation
Its purpose is to explicate the cultural context of the SL and TL
version. Tethbransalators have to be sensitive to the way words are used
and must know how the word fits into cultures.
Example; the use of word „yes‟ versus „yeah‟ in America.
d. Linguistic translation
Is concerned with equivalent meanings of the constituent
morphemes of the SL and grammatical form.
Example; language in a computer program and translation machine.
4. Principles, Procedures and Methods of Translation
Translation, as a process, is always uni-directional : it is always performed
in a given direction, “from” a source language “into” a target language. This
below are some general principles of translation (Savery, 1968:49) :
1. A translation must give the words of the original.
2. A translation must give the ideas of the original.
3. A translation should read like an original.
17
5. A translation should reflect the style of the original.
6. A translation should process the style of the translation.
7. A translation should read as a contemporary of the original.
8. A translation should read as a contemporary of the translation.
9. A translation may add to or omit from original.
10. A translation may never add to or omit from the original.
11. A translation of verse should be in verse.
12. A translation of verse should be in process.
Translation is the very broad sense of the term can be listed in terms of different
levels of complexity (Pinchuck, 1977:188). The procedures can be in the form of :
1. Transcription
another with a different alphabetical system. For example; from Arabic to
Latin or Russian Cyrillic alpabhets into Latin.
3. Borrowing
The procedure often used when the TL has no equivalent for the SL units
is to adopt them without change but sometimes with spelling or
18
This is replacing a grammatical structure in the TL in order to achieve the
some effect. e.g :
Indonesian : kopinya masih terlalu panas untuk diminum.
English : the coffee is still too to drink.
6. Modulation
Modulation entails a change in lexical elements, a shift in the point of
view. Transposition and modulation may take place at the some time. e.g :
Time is money = waktu itu sangat berharga
7. Adaptation
Adaptation is utilized when the others are not sufficient. It involves
modifying the concept, or using situation analogous to the SL situation
19
The levels of equivalent in ascending order are follows :
a. Substitution of printed letter for printed letter
Example : from Arabic into Roman
b. Substitution of morphem – for- morphem
Example : economics = ilmu ekonomi
c. Substitution of word –for- word
Example : principle = prinsip
d. Substitution of phrase – for- phrase
Example : the educated people = orag-orang terpelajar
e. Substitution of sentence for sentence
Example : you had better go home = sebaiknya kau pulang
According Newmark (1988:81) mentions the difference between
translation methods and translation procedures. He writes that while
translation methods relate to whole text, translation procedure are used for
sentence and the smaller units of language. He goes on to refer to the
following methods of translation :
a. Word for word translation
In which the SL word order is preserved and the words translated singly
by their most common meanings, out of the context.
20
within the constraints of the TL grammatical structures.
d. Semantic translation
Which differs from “faithful translation” only is far as it must take more
account of the aesthetic value of the SL text.
e. Adaptation
Which is the freest form of translation, and is used mainly for plays
(comedies) and poetry; the themes characters, plots are usually preserved,
the SL culture is converted to the TL culture and the text is rewritten.
f. Free translation
Is procedures the TL text without the style, form, or content of the
original.
g. Idiomatic translation
It reproduces the message of the original but tends to distord nuances of
meaning by preferring colloqualism and idioms where these do not exist in
the original.
21
It attemps to render the exact contextual meaning of the original in such
away that both content and language are readily acceptable and
comprehensible to the readership.
5. Translation Strategies
The term strategy is often said similar to the term technique. In some ways it
can be called similar because some experts use these terms with the same purpose.
For example, Mona Baker says that she proposes some strategies to translate
idiomatic expressions, whereas Andrejs Veisberg proposes some techniques to
translate idiomatic expressions. Both expressions aim at the same point.
According to Oxford Advanced Learner‟s Dictionary, technique is a method
of doing or performing something whereas strategy is a plan to accomplish a
specific goal. This research will use the term strategy related to Mona Baker‟s
theory of strategies to translate idiomatic translation. Mona Baker‟s view of
translation strategies are applied when a translation difficulty occurs and the
translator wishes to solve the problem and produce a good translation. Thus,
translation strategies are means which considers to be the best in order to reach
the goals.
Based on many experts in translation, there are many translation strategies to
translate a text. Every translator uses different strategies to translate a text since
different people may understand a word in different ways. Furthermore, there are
22
culture. Idioms in one language probably have different forms in other languages.
It may have distinctive form but the same meaning.
The way in which an idiom can be translated into another language depends
on many factors, such as the availability of an idiom with a similar meaning, the
significance of the specific lexical items which constitute the idiom, and the
appropriateness of using idiomatic language in a given register in the target
language.
6. Form and Meaning of Translation
Larson (1984: 3) states that translation is basically a change of form. These
forms are referred to as the surface structure of a language. It is the structural part
of language which is actually seen in print or heard in speech. Baker (1992: 24)
says that the form of the source language in translation is replaced by the
equivalent lexical item (form) of the receptor language. However, there is often no
equivalent in the target language for a particular form in the source text.
According to Larson (1984: 3), translation is done by going from the form of
the first language to the form of second language by way of semantic structure.
When a translator makes a translation, it means that he or she transfers meaning of
source text. What is necessary to consider is that the meaning must be maintained
23
be maintained. It is the characteristic of a language that the same meaning
component will occur in several surface structure lexical items (forms).
In the translation process, the first thing to do is understand the total meaning
of the source text. There are three types of “meaning” that can be determined in
the analysis of meaning of the source text (Nida and Taber, 1982: 34), namely (1)
grammatical meaning, (2) referential meaning, and (3) connotative meaning. In
grammatical meaning, when one thinks of meaning, it is almost inevitably in
terms of words or idioms. Generally grammar is taken for granted since it seems
to be merely a set of arbitrary rules about arrangement, rules that must be
Translation has been performed as a process which begins with the source
text, then the meaning of the text is analyzed, discovered, transferred, and
reexpressed in the receptor language. In actual practice, however, the translator
moves back and forward from the source text to the receptor text. Sometimes he
or she will analyze the source text in order to find the meaning, then restructure
this meaning in the receptor language, and move back once again to look at the
source text. In translation, the translators should know the types of meanings. By
24
be transferred well. Then, the well-transferred meaning will make easier to
understand for the readers.
7. Process of translation
According to Larson (1984: 3) when translating a text, the translator‟s goal is
an idiomatic translation which makes every effort to communicate their meaning
of the SL text into the natural forms of the receptor language. Furthermore, he
states that translation is concerned with a study of the lexicon, grammatical
structure, communication situation, and cultural context of the SL text, which is
analyzed in order to determine its meaning. The discovered meaning is then
re-expressed or reconstructed using the lexicon and grammatical structure which are
appropriate in the receptor language and its cultural context.
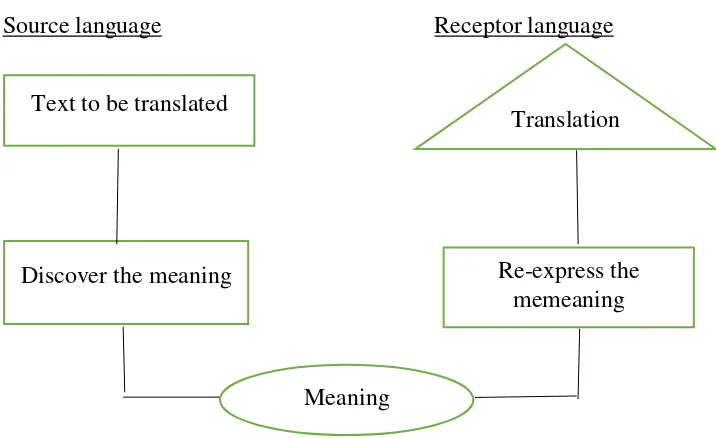
The following diagram is presented by Larson as the translation process.
Figure 2.1
Source language Receptor language
Text to be translated
Discover the meaning Re-express the
memeaning
Meaning
25
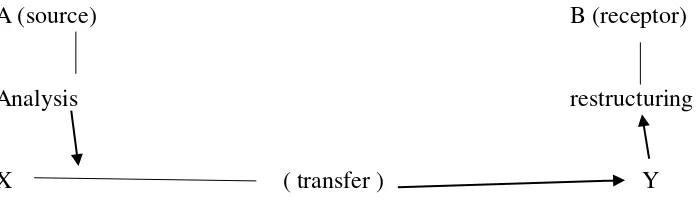
Nida and Taber (1982: 33) distinguish translation process into three stages: (1)
analysis, in which the surface structure is analyzed in terms of (a) the grammatical
relationships and (b) the meaning of the words and combinations of words, (2)
transfer, in which the analyzed material is transferred in the mind of the translator
from language A to language B, and (3) restructuring, in which the transferred
material is restructured in order to make the final message fully acceptable in the
receptor language.
Figure 2.2
The translation process can be illustrated in the following diagram :
A (source) B (receptor)
Analysis restructuring
X ( transfer ) Y
8. Difficulties of Translation
According Finlay (1971:80) in translating texts, translator sometimes find
difficulties. The kind of difficulties that often find by translators such as;
a. Word that have to be omitted from or added to the traslation
There are in most language a number of small words or particles
which belong to its correct usage, whereas they do not form part of the
standart English idiom under the same circumtances.
For example; in structure of Indonesian language do not have any definite
and indifinite article, however in English there are “mother”, “a mother”,
26 b. Faux amis
Is used to describe those words in various language which
resemble in appearance words in other language, but have a meaning quite
different from the words they resemble.
For example; the word “particular” in Dutch means “private”, but
“particular” in English means “special”.
c. Words that cannot be “translated”
There are in most languages words that refer to concepts so
specific to that language or the country in which it is spoken that they
cannot be “translated”, but have to be pharaphrased or described.
For example; the Dutch academic title Doctorandus abbreviation as Drs.,
suggests to English people either that the person has to doctorates or that
the proofreader has slipped up. Neither in this case, the title in fact
meaning that the person in question has carried out all preliminary
studies, etc. for obtaining a doctorate, but has not written and had accepted
the necessary thesis. Difficulties of this type also occur sometimes in
relation to the title of book.
d. Foreign words
There are no really pure languages, all containing a greater or
lesser number of words which has been borrowedfrom other language,
with or without complete formal assimilation, not necessarily with a
27
For example; the recent flood of British and American English words into
French has given rise to much concern and has led to the coining of the
term Franglais to designate the resultant brand of Franch peppered with
English words.
e. Regional differences
Worthy of attention is that in certain countries there is quite often a
distinct difference between the spoken and written language. Dialect and
slang also present the translator with great difficulties. Should these be
translated into what seem their counterparts in the target language or
should they be suppressed, thus altering the atmosphere and register and
possibly also dispensing with their function as indicators of social
differences.
For example; in Dutch several “book words” which have their “spoken”
counterparts. Such differences must, of course, be appreciated by
translators of texts which are intended to be spoken rather than read, such
as those of plays and works for television ad radio, as well as films.
f. Translation of proper names
Some languages need use but one letter to represent a sound
requiring two or three letters in another language. These two processes can
give rise to the appearance of proper names in forms in which they will not
28
For example; Russian and Japanese names require careful handling by
translators, as do those of merried women in the Netherlands in the case of
which the women‟s maiden name is coupled with that of her husband.
g. Trade marks and slogan
These offer difficulties to the translator in to main ways. Firstly,
he must be able to recognize a word as a trade mark and not as generic
word and, secondly, it does not by any means always follow that, because
a word is a trade mark in one country, it will also be in other countries in
which it is used.
For example; namely the wording used in conjunction with the Wool Mark
and the phrase used in conjunction with the launching of the new Ford
Capri.
h. Abbreviations
Abbreviations and acroniyms, that is to say words made up from
the initial letters. Abbreviations are often formed quite arbitraruly by
authorss to whom it never occurs to imagine that others may not be
members of their own private worlds.
For example; Oxfam, Unesco, Aslib, Adac, DAW, EFTA. TAS, etc.
i. Changes in orthography
This inevitably means that the translator will be confronted with
text exhibiting various spellings and that, if he is using old dictionaries, he
will in some cases have to make allowances for changes in spelling when
29
For examples; differences in spelling between British and American
English have increased in recent years, these affecting a number of
technical words. Such as sulfur and alumunium which are, in British
English, sulphur and aluminium.
j. Handwriting
The moral of this that a translators worthy on the name shoukd
make sure that he obtains practice in reading the handwriten forms of his
source language.
Translators maybe cannot translate a letter in German, Yiddish and
Hebrew handwriting merely becausethey cannot read it.
k. Bibliographycal references
These frequently occur at the end of articles in journals, and ways
of indicating them frequently differ from country to country. These
differences relate to such matters as volume number, year, issue within a
year and the like. For to sake of uniformity, it is desirable that the
translator should adopt the system current in the country of the target
language.
For example; bibliographical references and should form part of every
scientific translator‟s library. It covers books, periodicals and various
ancillary matters.
l. Conversions of units
Not all countries yet use the same units for the same quantities.
30
seconds. Units of length, area, volume and weight very often have to be
converted and such conversions can become quite complicated. They
contribute to creating the impression on the reader that he is not reading a
translation.
For example; when a double conversion is involved as in kilometers per
litre to miles per gallon. There are several system used for indicating the
thicness or weight of textile fibres and yarns, although a universal system,
using a unit called a tex, is gradually being adopted.
m. Tables
translation, while others do not object if they are all relegated to the end of
the translation.
n. Numbers
Translators should also know how to read numbers, squares, square
roots and the like in their source and target language, since they may well
be asked to do this from time to time.
For example; the German Milliarde means, in British English, a thousand
million whereas, in American English it is a billion.
31
It is real difficulties, so the translator to make himselfs familiar
with them. There are, of course, other matters, and no two translations will
ever be quite the same in the problems they post.
For example; sometimes differ in the naming of complex organic
compounds, but there are books describing the methods accepted in a
given country or used in given publication.
9. Criterian of Good Translation
Finlay (1971:8) argues that translation doomed to failure because : a) a
language are never sufficienly similiar to express the same realities, and b)
even worse, “reality” cannot be assumed to exist independently of language.
The criterions of good translation are :
a. The translation should be present an accurate account of the contents of the
original, omitting nothing and likewise adding nothing. This implies a
complete understanding of the original in every way coupled with a
corresponding knowledge of thr target language.
b. Having understood the text in target language, the translator must be able
to reconstitute it, as it were, in the target language, using all the facility
that he would if he were writing an original document in that language.
c. That it should capture the style and atmosphere of the original this is more
important and difficult in the case of literary texts which are very often not
contemporary and which, more often that not, are set in a cultural milieu
32
Whereas according Larson (1984:485) that there are three criterians of
good translation;
a. Accuracy
The means are that translators give all informations from source
language into target language without omitting or adding informations
in texts. Nida (1964:185) said that :
Utimately, however, the correctness of a translation must be determined not in terms of the corresponding sets of words, but on the basis of the extent to which the corresponding sets of semantic components are accurately represented in the restructuring. This is essential if the resulting form of the message in the receptor language is to represent the closest natural equivalent of the source language
without misunderstanding. According Larson (1984:485), ones of way
to check the translation is clear or not, we can give the tests or
questions for readers about that texts.
c. Naturalness
Translators must make the translation easy to understand by reader, so
the reader would feel that the texts as not translation texts. It is related
with how the translators choose vocabularies or dictions that generally
33
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
In this chapter the researcher will discuss about research method, setting of
the research, subject of the research, technique of data collection, and data
analysis technique.
34
The type of this research is Quantitative research. Quantitative research
methods are research methods dealing with numbers and anything that is
measurable in a systematic way of investigation of phenomena and their
relationships. It is used to answer questions on relationships within measurable
variables with an intention to explain, predict and control a phenomena (Leedy,
1993:137). Method of this research is Correlation. Correlation analysis studies the
combined variation of two or more variables in order to determine the amount of
correlation between those two or more variables (Kothari, 2004:25).
From the definition above, Correlation Research is said as a research
study that involves collectig data in order to determine whether, and to what
degree, a relationship exist between two or more quantifiable variables (Gay,
2009:430). The researcher will analyze the correlation between students‟
experience as English tutors toward their abilities in translation text into
Indonesia.
B. Setting of the Research
1. Research Location
This research conducted in State Institute for Islamic Studies
(IAIN) Salatiga, which is located in Jl. Lingkar Selatan Salatiga, Pulutan
District, Sidorejo Subdistrict, Salatiga, Central Java, Indonesia. IAIN
Salatiga is biggest Islamic University in Salatiga. The student come from
different schools. There are also foreign lecturers coming from United
35 2. Profile of Institution
IAIN Salatiga was established to carry out the science transformation
through educational framework. By upholding Islamic values, IAIN
Salatiga proves that religion is a dimension that should be preserved and
will be beneficial for the professional development. Furthermore, IAIN
Salatiga shows that learning religion does not even give a bad effect for
the science development at all. In fact, religion is the powerful motivator
for the development of the way of thingking and acting.
a. Vision
Become a Referral-Indonesia Islamic Studies for the Establishment
of Honorable Peaceful Society in 2030.
b. Mission
a) Education is various disciplines of Islam based on the
Indonesian values.
b) Conducting research in various disciplines for strengthen
Islamic values.
c) Organizing dedication to the community-based research for
streghtening the values of the nation.
d) Developing a culture of the campus community that reflects the
values of Islam in Indonesia.
e) Organizing a professional and accountable management of
higher education.
36
a) Developing students potential to become a man of faith and
piety to God Almighty and noble, healthy, knowledgeable,
skilled, creative, independent, competent, and appreciate the
culture of nation.
b) Produce graduates who master branch of Science and / or
Technology-based Islamic sciences to meet the national interests
and improving competiveness of the nation.
c) Produce Science and Technology through the research that
observes and implement Islamic values in order to give benefit
for the nation‟s progress, and the progress of civitazion and
welfare of mankind.
d) Realizing Community Service based Islamic science and
37
Population is all members of well defined class of people, events,
or objects (Ary, 1985:138). Kothari (2004: 55) defines the population
of research as all items in any field of a research study.
The population of this study are the students in sixth semester of
English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education
Faculty at IAIN Salatiga in academic year of 2016/2017. The
researcher selected the sixth semester as the subject of the research
because they were got Translation lesson in before semester, and
usually they have been teaching or become a tutor and have experience
so much.
b. Sample
A sample is selected participants taken from the population for the
research study. According to Kothari (2004:57) if the population is too
large, it is better to use a sample. Futhermore, the research can be
effective and wouldn‟t waste much time, cost and energy. Technique
design in choosing the sample, researcher used Purposive sampling
design. According Etikan (2015:2) purposive sample is a type of
non-probability sampling which means selecting a sample by judgement of
researcher rather than using mathematical probability for selecting a
sample. In purposive sampling researcher targets a group of people
among population under consideration based on research. Purposive
sampling is useful as it requires less time for selecting purposive
38
To find research sample, the researcher was asked some students in
sixth semester students of English Education Department of Teacher
Training and Education Faculty at IAIN Salatiga. Then, the researcher
found 30 students who had been tutors until the time the research was
conducted. They taught English lesson in English Courses as private
teacher who came to their students‟ house, which included Elementary
School, Junior High School, Senior High School, and University
Students. The researcher considered that 30 students were enough to
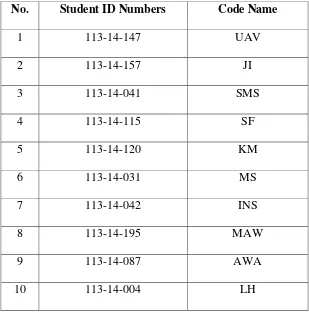
be research sample. The sample are below;
Table 3.1
TABLE List of Subject of the Research
40 D. Technique of Data Collection
In order to gain the sufficient data to be analyzed, the researcher uses :
1. Questionnaire
The researcher used questionnaire to measure students experience
as English tutor. The form of questionnaire is multiple choice. The
researcher gives 7 questions to respodents. The questions about some
activities that they do when respondents become an English tutor.
Each question has different points. The highest point is 4. The
scale is one up to four. This scale will be easier to determine the
students‟ experience as English tutor.
2. Test
Test can be defined as assesment to measure skills, ability, or
knowledge in certain aspects. In this research, the researcher used test
to measure students abilities in translation text into Indonesian. That
texts consists 5 paragraphs, which must translated by respondents.
To measure the translation are good or not, the researcher used
Priciple Assesment according Mounin in Durdureanu (2011:10) below:
1) Stucture (grammatical)
Stucture about morphology and syntax. It is very important
in grammatical/structure. Syntax about related words which is form
a phrase, clause, or sentence. Whereas, morphology is about
41
Syntax is very important in translation, because a mistake
in transfering structure would change the meaning. So, the
translators must can translate all texts without change the meaning.
2) Spelling
It all about spells of letters, words and punctuation. In
translation the all spells should to be true, so the reader would not
misunderstanding in read the translation texts.
3) Diction
The function of diction are to explain or express something
exactly. Diction must appropriate with situation and function of
using the words. There are 5 levels in choosing of diction; they are
Literal, Syntatical, Idiomatical, Aesthetical, and Ethical.
4) Idiom
Oxford Dictionary (2011:20) idiom is a group of words
whose meaning cannot be predicate from the meaning of the
constituent words. Idiom also defines a linguistic usage that is
grammatical and natural to native speakers of language.
Understanding the meaning of idioms is also very
important, in order to avoid the change of meaning in translation.
42
Effectiveness of sentence is sentence which have capability
to make the reader and writer comprehend the same ideas and
language. Translators must know and use language styles that used
by source writer.
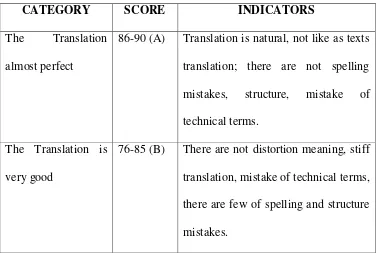
86-90 (A) Translation is natural, not like as texts
translation; there are not spelling
mistakes, structure, mistake of
technical terms.
The Translation is
very good
76-85 (B) There are not distortion meaning, stiff
translation, mistake of technical terms,
there are few of spelling and structure
43 The Translation is
good
61-75 (C) There are not distortion meaning,
there are stiff translation but not more
that 15% from text overall, mistake in
structure and idiom not more than
texts but not more that 25%, there are
mistake in structure and idiom but not
more than 25%, there few of stiff
technical terms/ unclear/ not
appropriate.
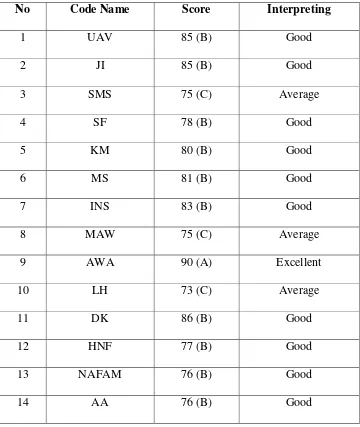
1. Interpreting how good are students‟ experience as English tutor based
44
Table 3.3
Score of Classification
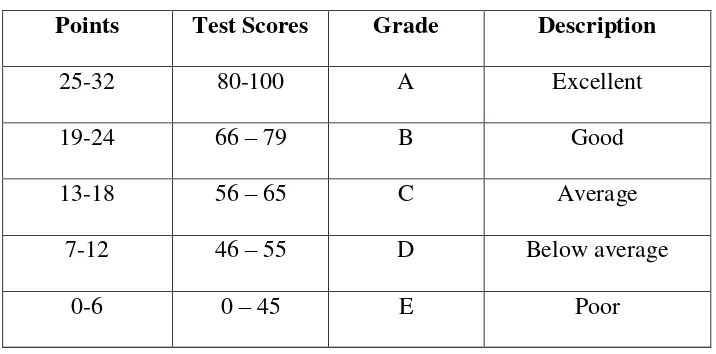
(Sudijono, 2011:35)
Points Test Scores Grade Description
25-32 80-100 A Excellent
Test Scores Grade Description
80-100 A Excellent
66 – 79 B Good
56 – 65 C Average
46 – 55 D Below average
45
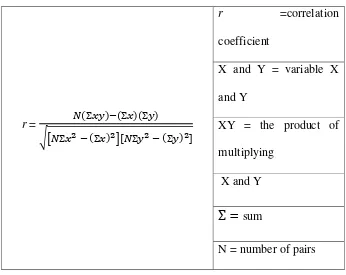
3. Calculating the correlation coefficient between the two variables using
Pearson‟s product-moment formula to find out of correlation
coefficient. The formula is as follows :
Table 3.5
4. Interpreting the r value by using the classification for interpreting the r
value (Arikunto, 2002:245)
Table 3.6
r Value Interpretation
r Value Interpretation
0.00-0.20 Very weak correlation
46
0.40-0.70 Medium correlation
0.70-0.90 High correlation
0.90-1.00 Very high correlation
5. Describing factors influence the correlation between variable X and
variable Y.
F. Technique of Data Interpretation
After analyzing the data, the researcher will interpret the result of the data
analysis by answering the questions that are presented in the problem of the
research regarding the extend of students‟ experience as English tutor and
students abilities in translation text, and deciding whether there is a correlation
between the two variables, whether there is a significant correlation or not, and
whether the correlation is positive or negative.
Based on direction, the correlation have two kinds. They are positive
correlation and negative correlation. Positive Correlation can be defined as
correlation in the same direction. If one variable increase other is also increase,
and if one variable decrease other is also decrease. Whereas the Negative
Correlation is the correlation in opposite direction. If one variable is increase the
47
researcher got from questionnaire and test. The participant of the test were
students sixth semester from English Education Department in IAIN
Salatiga. There are two kind of result, they are scores or points of students
49
Table 4.1 shows the points of Questionnaire that the researcher gave to the
participants. As the researcher discuss in CHAPTER III, the Questionnaire
consists 7 questions that each of answer from question has different point.
The result of this questionnaire, then will be analyze in the next section to
see if there is any correlation with the translating text scores that the
researcher shows in the table 4.2 below ;
50
Table 4.2 above demostrates the scores of test for translating text that the
researcher gave to the participants in sixth semester in English Education
Department of IAIN Salatiga. The test formed English text consist 5
paragraphs that must translate into Indonesia. And then, as the researcher
51
correlation or not with the students‟ experience as English tutor in the next
section.
Then, to do the analysis, the researcher calculating the scores of the
point of Questionnaire and translation test, where the point of
Questionnaire is the variable X and the score of translation text is the
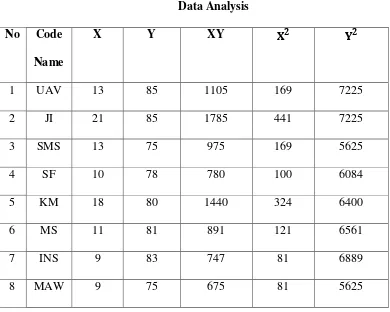
variable Y. The analysis of data is shown in the table 4.3 below ;
53
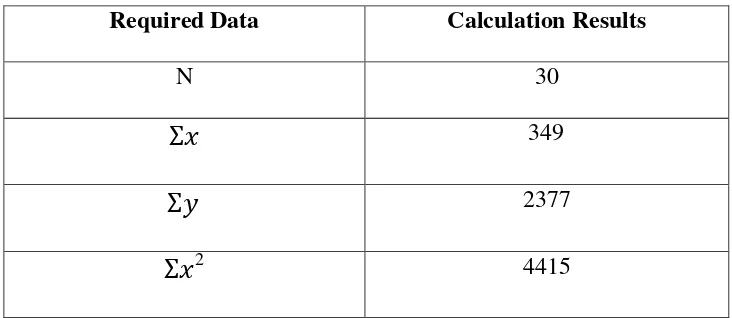
N = 30 ƩX=349 ƩY=2377 ƩXY=27853 Ʃ =4415 Ʃ =189231
The interpretation of the symbol in table 4.3 above is :
N : number of participants
X : students experience as English tutor point
Y : students ability in translating text score
ƩX : students experience as English tutor sum point
ƩY : students ability in translating text sum score
Ʃ : the sum of square points of students experience as English tutor
Ʃ : the sum of square scores of students ability in translating text
ƩXY : the sum of multiple scores between X and Y
From table 4.3 the researcher gets the following results than will be used
in calculating the correlation coefficient. The results are as follows:
54
2 189231
(
)
2 121801( )
2 5650129(
)
27853Then, those score will be calculated to find out the index of correlation “r”
between variable X and Y using this formula :
55 = 0.3561
From the calculate above, it is found that the index of correlation “r”
between variable X and Y is 0.3561
To make sure the result of the calculation above, the researcher
SPSS program. The using of SPSS is to know whether the calculation that
researcher did manually is correct or not and to make sure that there is not
mismatching calculation between score that the writer counted. The
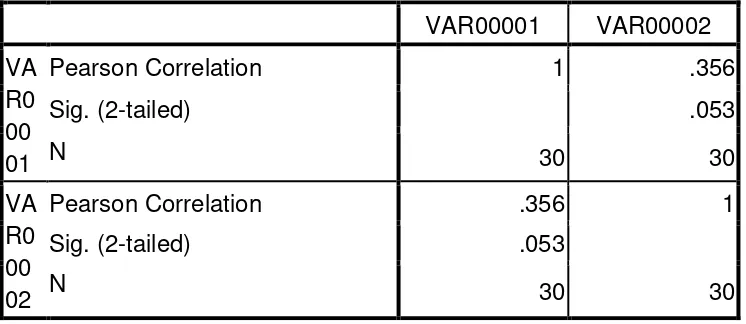
calculation of SPSS is describedsuch as follow ;
Table 4.5
SPSS Correlation Table
The result of those two calculation (manual calculation and SPSS
calculation) are same, in which show the value of correlation “r” between
variable X and Y is 0.356. It means there is no mismatch in the process of
calculating the data.
Pearson Correlation 1 .356
Sig. (2-tailed) .053
Pearson Correlation .356 1
Sig. (2-tailed) .053
56 C. Interpretation of Data
To interpret the score of correlation “r” between variable X and Y
that has found 0.356. The researcher used a way below ;
Based on the table guidelines of Pearson‟s correlation, the final
score of “r” is 0.356. This score is positive. This position is between 0.20
– 0.40, it shows the index correlation between two variables is weak. It
considers that there is positive signifigant correlation between students‟
experience as English tutor and students abilities in translating text into
Indonesian. The table of index correlation “r” interpretation is concluded
such as below;
Table 4.6
The Interpretation of Correlation “r” Product Moment
r Value Interpretation
0.00-0.20 Very weak correlation
0.20-0.40 Weak correlation
0.40-0.70 Medium correlation
0.70-0.90 High correlation
0.90-1.00 Very high correlation
This interpretation shows that the correlation between two
variables, in this case students‟ experience as English tutor and their
57
researcher found many of students or participants got below average points
in Questionnaire about students experience as English tutor, but they got
score good category in translation test. It can be conclude that students
experience as Eglish tutor can give effect to their abilitis in translating text
into Indonesian, although little or weak. From the data researcher find that
some students‟ or participants can translate text well, although their
experience as English tutor still less. For the data in Questionnaire the
researcher find that the students mostly was to be a tutor about one or two
years and translated text about one or two texts in a week. Whereas, for the
data translation test the researcher find worse performance in spell and
effectiveness of sentence when they are translated texts. In translating text,
there are many factors that influences them to make their translation better,
such as often practices by theirself.
To know the details of factors influence the correlation between
experience as English tutors to their abilities in translating text into
Indonesian at the sixth semester students of English Education Department
of Teacher Training and Education Faculty at IAIN Salatiga in the
academic year of 2016/2017 the researcher makes table below;
58
read texts many times before teaching,
so he was reached good score in
translation, although she got average
score.
good score in translation, although
average in experience as English tutor.
It is because she often read texts before
teaching.
6 MS 11 (D) 81 (B) Based on the questionnaire she reached