CORRELATION BETWEEN STUDENTS’ LEARNING
STYLE AND ACHIEVEMENT IN CRITICAL
READING CLASS OF ENGLISH TEACHER
EDUCATION DEPARTMENT AT SUNAN AMPEL
STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY SURABAYA
THESIS
Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of
Sarjana Pendidikan (S.Pd) in Teaching English
By
Umi Malihah
NIM D95211091
ENGLISH TEACHER EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHERS TRAINING
SUNAN AMPEL STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
ABSTRACT
Malihah, Umi. (2015). Correlation between Students’ Learning Style and
Achievement in Critical Reading Class of English Teacher Education Department at Sunan Ampel State Islamic University Surabaya. A Thesis English Teacher Education Department, Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers Training Sunan Ampel State Islamic University Surabaya. Advisor: Muhammad Salik
TABLE OF CONTENT
TITLE SHEET ... i
ADVISOR APPROVAL SHEET ... ii
EXAMINER APPROVAL SHEET ... iii
MOTTO ... iv
DEDICATION SHEET ... v
ABSTRACT ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ... vii
PERNYATAAN KEASLIAN TULISAN ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENT ... x
LIST OF TABLE ... xii
LIST OF CHARTS ... xiii
LIST OF APPENDIX ... xiv
CHAPTER I ... 1
INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Research Background ... 1
B. Research Question ... 4
C. Objective of the Research ... 5
D. Hypothesis ... 5
E. Significance of the Research ... 6
F. Scope and Limits of the Research ... 7
G. Definition of Key Terms ... 7
CHAPTER II ... 10
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ... 10
A. Review of Related Literature ... 10
1. Definition of Learning Style ... 10
2. Various Learning Style Perspectives ... 11
3. Students’ Achievement ... 16
4. Critical Reading Class ... 17
5. Correlation between learning style and achievement ... 22
B. Review of Previous Studies... 23
CHAPTER III ... 29
RESEARCH METHOD ... 29
A. Research Design ... 29
B. Population and Sample ... 30
C. Research Instrument ... 31
D. Data Collection Technique ... 32
E. Data Analysis Technique ... 34
CHAPTER IV ... 38
RESEARCH FINDING ... 38
A. Students’ Learning Style Preference in Critical Reading Class ... 38
LIST OF TABLES
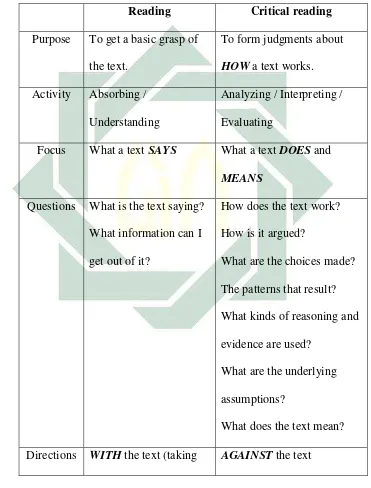
Table 2.1 : Differences between Reading and Critical Reading ... 20
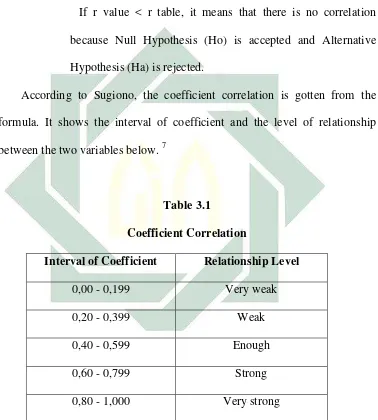
Table 3.1 : Coefficient Correlation ... 36
Table 4.1 : The Result of Students’ Total Score from Questionnaire ... 39
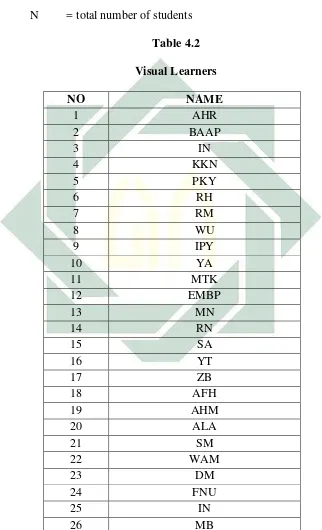
Table 4.2 : Visual Learners... 42
Table 4.3 : Auditory Learners... 44
Table 4.4 : Kinesthetic Learners ... 45
Table 4.5 : Students’ Critical Reading Score ... 50
Table 4.6 : Students’ Score Range of Critical Reading ... 52
Table 4.7 : Computation of Correlation between Students’ Visual Learning Style and Achievement in Critical Reading Class ... 54
Table 4.8 : Computation of Correlation between Students’ Auditory Learning Style and Achievement in Critical Reading Class ... 55
Table 4.9 : Computation of Correlation between Students’ Kinesthetic Learning Style and Achievement in Critical Reading Class ... 56
LIST OF CHARTS
Chart 4.1 : The Graph of Students’ Learning Style of 4th Semester at
Critical Reading Class ... 46
Chart 4.2 : Percentage of Visual Learners ... 47
Chart 4.3 : Percentage of Auditory Learners ... 48
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix 1 : Questionnaire of Learning Style
Appendix 2 : Students’ Learning Style Score
Appendix 3 : Students’ Critical Reading Score
Appendix 4 : The Computation of Correlation between Students’ Learning
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter presents a research background followed by research questions
objectives of the research, hypothesis and significance of research. Then scope and
limits of the research are presented along with the definitions of key terms.
A. Research Background
Learning is a relatively permanent change in a behavioral tendency and is the
result of reinforced practice.1 This means that learning is a process of
development through the process of actualizing the potential of human knowledge
that has existed within him. Someone’s natural abilities will be existed.
There are two factors that influence students’ learning, namely internal and
external factors. Internal factor is the factors which come from students
themselves. Meanwhile, external factor is the factor which is outside of students.2
The examples of internal factors are the physical condition, skill, interest,
intelligent and learning style. Meanwhile, the examples of external factors are
family, friends, school, environment and learning strategy.3
Learning style is one of internal factor that affects students’ learning. There
are different styles of learning owned by each student. Every person has a
1
Douglas Brown, Principle of Language Learning and Teaching, 4th ed. (New York: San Fransisco State University, 2000), 7.
2
Slameto, Belajar Dan Faktor- Faktor Yang Mempengaruhinya (Jakarta: Rineka Cipta, 2010), 54.
3
2
learning style that is natural and comfortable for them, when they are forced to
use another. Especially for learning process each student has different learning
style from a student to another student. Different pond, different fish, so it is also
different people, different learning styles as well. Teachers should pay attention to
students' learning styles because in every teaching the effectiveness will depend
on the manner or style other than the student's learning attitude and intellectual
ability. Therefore, students who have different learning style preference would
behave differently in the way they perceive, interact with and respond to the
learning environment.
Generally, students’ learning styles might cause specific effects on lectures
such as on reading for example; visual learners tend to like to read for pleasure.
But they will have trouble in an environment with noise and distraction, auditory
learner tend to like to plays and dialogues. But they will have trouble in reading
silently and with speed when not allowed to vocalize, then kinesthetic learners
tend to like to read how-to books and action oriented books. But they will get
problem in reading or listening for more than four minutes.4
Reading is one of language skills that cannot be separated from other
language skills because the students’ ability in one aspect will support their ability
in mastering the others. It is an important educational goal, because without
reading other language skills would not be improved. The ability of students in
4
3
reading is important because by having the ability to read, they will be able to
improve general language skills in English; reading can enlarge the students’
English vocabulary and it can help to improve the students’ writing or speaking
abilities. So, it can be concluded that reading is one of the keys to success for
everyone who wants to be an educated person.
According to Nation, ―Reading is a source of learning and source of
enjoyment‖.5
This means that reading can enlarge the students’ knowledge. As a
source of learning, reading can recall previously learned vocabulary and
grammar. It can help the students learn new vocabulary and grammar and through
success in language use. Reading can be source of enjoyment. If the students gain
skill and fluency in reading, their enjoyment can increase. By reading, students
can go around the world although just stay at home. They also can easily get the
scholarship and the job. Therefore, reading can help their life and learning to be
easily.
This research will be conducted at Sunan Ampel State Islamic University
Surabaya. There are some underlying points why the researcher does the research
in such university. Based on the preliminary research taken in critical reading
class at Sunan Ampel State Islamic University Surabaya, reading is the most
difficult course especially the last reading course-Critical reading, it can seen
from the final score of students. This means that reading comprehension for
academic reading is important to be considered. Critical reading is reading
5
4
activities that focus on what the students have understood from the text. Journal,
article, thesis, etc. are kinds of critical reading text. Additionally, the reading
objectives invite the students to understand what being presented by the writer.
Understanding will not only know what being delivered by focusing only on
intended meaning delivered, but also the deep inference of specific meaning and
message. Inference or decoding what being read is important in reading to
understand the text.
The research on the students’ learning styles and their achievement has
been widely studied. It is important to be considered it wisely. As described
above, the effect of learning style can bring big influence of students to get high
score in reading. That’s why the researcher will conduct the research on critical
reading class because it is commonly encountered students’ learning styles. So, in
this research the researcher decides a problem to be researched with the title
“CORRELATION BETWEEN STUDENTS’ LEARNING STYLES AND
ACHIEVEMENT IN CRITICAL READING CLASS OF ENGLISH TEACHER
EDUCATION DEPARTMENT AT SUNAN AMPEL STATE ISLAMIC
UNIVERSITY (UIN) SURABAYA”.
B. Research Question
Based on the research background above, here the researcher think it is
required answering some questions as the purpose of this research. The research
5
1. What are the learning style preferences of students in critical reading class?
2. Is there any significant correlation between students learning style and their
achievement in critical reading class?
C. Objective of the Research
Based on the research question elaborated above, the research purposes are:
1. To know what are specific learning style preferences of each student.
2. To find out whether the students’ learning style has significant correlation
with their achievement in critical reading class or not.
D. Hypothesis
The research is formulated to show the effect of the variable relationship.
Those are the alternative hypothesis (Ha) and null hypothesis (Ho). The
hypothesis is stated as follow:
Ha (alternative hypothesis) : there is significant correlation between students’
learning styles and their achievement in critical
reading class
Ho (Null hypothesis) : there is no significant correlation between students’
learning styles and their achievement in critical
6
E. Significance of the Research
To know more how the research gets significances, here the researchers states
below:
1. Theoretical benefit
Theoretically, this research results are expected to contribute the
development of education, especially in learning style and its correlation to
achievement in critical reading class.
2. Practical benefit
This research is expected to give benefit for students and lecturers in
English teacher education department and also for the next researchers.
a. For students, the result of this study provides information to understand
more that their learning styles and their achievement in critical reading
class is related. So they will be motivated to become used to learn in
different styles to improve their ability and also get good achievement in
critical reading class.
b. For the lecturers, the result can be used to help them understand better
about problems faced by students so they can provide more meaningful
feedback to their students and can provide students with better ways or
methods to help students being motivated in attending critical reading
class to get good achievement.
c. For the reference for next researchers who wants to conduct a research on
7
F. Scope and Limits of the Research
This study is limited to investigate critical reading class to find the correlation
between students’ learning styles and their achievement in that class. It shows that
the difference of students’ learning style brings the impact for their achievement
whether in all the lectures or in specific lectures such as critical reading.
G. Definition of Key Terms
The researcher writes down some definitions of key terms in order to support
the readers understands this study easily and have the same interpretation as the
writer.
1. Learning style
Learning style: It is habit, strategies, or regular behaviors concerning learning,
particularly deliberate educational learning that an individual displays 6
Learning style in this study is focused on the students’ learning styles
preference; it’s according to the perceptual side of Gardner’s theory. Those
are Visual, Auditory, and kinesthetic learning styles.
2. Students’ Achievement
According to Oxford dictionary, achievement is a thing done
successfully with effort, skill or courage.7 In this study students’ achievement
6
8
is focused on students’ accomplishment in critical reading class during one
semester which is in the 4th semester. It is investigated through students’
midterm examination score.
3. Critical Reading Class
Critical reading is an analytic activity. The reader rereads a text to
identify patterns of elements -- information, values, assumptions, and
language usage-- throughout the discussion. These elements are tied together
in an interpretation, an assertion of an underlying meaning of the text as a
whole.8 Critical reading class in this research is the last level of reading class
in English teacher education department. Students have to take this lecture in
4th semester.
H. Research Report Organization
This thesis is composed of five chapters. The first chapter is about introduction
including research background, research question, objective of the research,
hypothesis, significance of the research, scope and limits of the research and
definition of key terms.
The second chapter presents review of related literature and review of
previous studies. Review of related literature discusses about definition of
7 ―Oxford Dictionaries Language Matters,‖
accessed August 8, 2015, http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/learner/achievement.
8 Dan Karland, ―Reading and Writing Ideas As Well As Words,‖ accessed March 22, 2015,
9
learning style, various learning style perspectives, students achievement, critical
reading class and correlation between learning style and achievement.
The research method is presented in the third chapter; including research
design, population and sample, research instrument, data collection technique
and data analysis technique.
The four chapter presents finding and discussion.
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter consists of the two main discussions. They are review of related
literature and review of previous studies.
A. Review of Related Literature
1. Definition of Learning Style
There are some of definitions come up from the scientist. They are:
a. Kolb, Honey and Mumfrod describe learning style as an individual
preferred in habitual ways of processing and transforming knowledge.1
b. According to Keefe, learning style is as cognitive, affective and
psychological features that provide as quite stable indicators of how
the learners recognize, interact with and respond to the learning
environment.2
c. Haar, Hall, Schoepp and Smith also define learning style as
individuals’ differences in which information is perceived, processed
and communicated. 3
From those explanations above about the definition of learning style,
the researcher concludes that learning style is students’ different ways in
1
D. A. Kolb, Experiential Learning: Experience as a Source of Learning and Development, 1984.
11
learning, including the best and easiest way students learn about certain
subject.
2. Various Learning Style Perspectives
There are some perspective theories about learning style. Each person has
preferred ways of learning that is determined by their cultural and
educational background and personalities.4
a. Information Processing
Learning style distinguishes between the way learners sense, think,
solve problems, and remember information. According to Kolb's
Learning Styles inventory in Tatyana Putintseva’s article, entitled The
Importance of Learning Style in EFL/ ESL, some kinds of learning
style are:
1. Diverging (feeling and watching)
People with diverging styles are able to look at things from
different perspectives. They are sensitive. They prefer to watch
rather than do, tend to gather information and use imagination to
solve problems. They are best at viewing concrete situations from
several different viewpoints. Kolb called this style 'Diverging'
because these people perform better in situations that require
ideas-generation, for example, brainstorming. They have broad cultural
4
12
interests and like to gather information. They are interested in
people, tend to be imaginative and emotional, and tend to be strong
in the arts. They prefer to work in groups, to listen with an open
mind and to receive personal feedback.
2. Assimilating (watching and thinking)
The Assimilating learning preference is for a concise, logical
approach. Ideas and concepts are more important than people.
These people require good clear explanation rather than practical
opportunity. They excel at understanding wide-
14 ranging information and organizing it in a clear logical format.
They are less focused on people and more interested in ideas.
People with this style are more attracted to theories than practice. In
formal learning situations, people with this style prefer readings,
lectures, exploring analytical models, and having time to think.
3. Converging (doing and thinking)
People with a Converging learning style use their learning to find
solutions to practical issues. They prefer technical tasks, and are
less concerned with people. They can solve problems and make
decisions. A Converging learning style enables specialist and
technology abilities. People with a Converging style like to
experiment with new ideas, to simulate, and to work with practical
13
4. Accommodating (doing and feeling)
The Accommodating learning style is 'hands-on', and relies on
intuition rather than logic. These people use other people's analyses,
and prefer to take a practical, experiential approach. They are
attracted to new challenges and experiences, and to carrying out
plans. They commonly act on ' good instinct rather than logical
analysis. Also, they tend to rely on others for information. This
learning style is prevalent and useful in roles requiring action and
initiative. People with this learning style prefer to work in teams to
complete tasks. They set targets and actively works in the field
trying different ways to achieve an objective.5
b.Personality Pattern
This part is focused on attention, emotion, and values.
Understanding these differences allows predicting the way learners
react and feel about different situations. The Myers-Briggs Type
Indicator and the Keirsey Temperament Sorter are two of the most
well-known personality pattern evaluations. They are classified
according to their preference for:
1. Introversion (I) (Interest flowing mainly to the inner world of
concepts and ideas)
5Tatyana Putintseva. ―
14
2. Extroversion (E) (Interest flowing mainly to the outer world of
actions, objects, and persons);
3. Sensing (S) (Tending to perceive immediate, real, practical facts of
experience and life);
4. Intuition (N) (Tending to perceive possibilities, relationships, and
meanings of experiences);
5. Thinking (T)(Tending to make judgments or decisions objectively
and impersonally);
6. Feeling (F) (Tending to make judgments subjectively and
personally);
7. Judging (J)(Tending to act in a planned and decisive way);
8. Perceiving (P)(Tending to act in a spontaneous and flexible way).
c. Perceptual Learning Style
Gardner’s concept of multiple intelligences is commonly
viewed as, in fact, a model of learning styles such as Visual, Auditory
and Kinesthetic or also known as visual, auditory and kinesthetic
VAK.
- Visual learner is people who are visual-linguistic like to learn
through written language, such as reading and writing tasks. These
learners need to see the teacher's body language and facial
expression to fully understand the content of a lesson. They tend to
15
obstructions. They may think in pictures and learn best from visual
displays. They often prefer to take detailed notes to absorb the
information.6 They remember what has been written down, even if
they do not read it more than once.
- Auditory learner is people often do better talking to a colleague or
a tape recorder and hearing what was said. They like sequence,
repetition and summary, and when recalling memories tend to tilt
their head and use level eye movements.7
- Kinesthetic learner is people who do the best while touching and
moving. They tend to lose concentration if there is little or no
external stimulation or movement. They may find it hard to sit still
for long periods and may become distracted.8
d. Social Interaction
This part is focused on student attitudes toward learning, classroom
activities, teachers, and peers. This model identifies the following
types and their characteristics:
- Avoidant students tend to be at the lower end of the grade
distribution. They tend to have high absenteeism; they organize
their work poorly, and take little responsibility for their learning.
6Tatyana Putintseva. ―
The Importance of Learning Style…., 3
7
Pritchard Alan, Ways Of Learning Second Edition (New York: Routledge, 2009), 43.
8Tatyana Putintseva. ―
16
- Participative students are characterized as willing to accept
responsibility for self-learning and relate well to their peers.
- Competitive students are described as suspicious of their peers
leading to competition for rewards and recognition.
- Collaborative students enjoy working in harmony with their
peers.
- Dependent students typically become frustrated when facing new
challenges not directly addressed in the classroom.
- Independent students, as the name implies, prefer to work alone
and require little direction from the teacher. 9
3. Students’ Achievement
In today’s education era, students’ achievement is almost everything.
Academic achievement or (academic) performance is the outcome
of education — the extent to which a student, teacher or institution has
achieved their educational goals.10 Students’ achievement here means the
academic achievement that students can reach after attending the course.
How the teacher measure the ability or the understanding of the students
about what they have learned.
According to Cizek academic achievement is defined as ―Knowledge
gained or skills developed in the school subjects, usually designated by
9Tatyana Putintseva. ―
The Importance of Learning Style…., 4
10
17
test scores or by marks assigned by teachers, or by both.11 In addition,
Nurhidayah also states that academic achievement is the students’ result
that has been achieved after following certain subject at school.12
Furthermore, Cizek takes the definition of achievement from the
Dictionary of Education which is defined as ―Accomplishment or
proficiency of performance in a given skill or body of knowledge, and
progress in school.‖13
In this research the students’ achievement is students’ accomplishment
in teaching and learning in critical reading class during one semester
which is in the fourth semester 2014/2015 academic year. It is investigated
the students’ midterm test score.
level of comprehension involves what the author is actually saying.
The readers need to understand the ideas or information that is
11
Cizek Gregory J, Learning, Achievement, and Assessment: Construct at a Crossroads”. In Gary D. Phye (Ed.). Handbook of Classroom Assessment: Learning, Achievement, and Adjustment (California: Academic Press, 1997). 4.
12
Afit Nurhidayah, “The Influence of Students’ Attitude to English Teaching on Their English
Achievement at SMPN 1 Bancak of Semarang Regency”(Muhammadiyah University of Surakarta,
2008).
18
explicitly stated in the reading text. Basic questions on literal
comprehension involve who, what, when and where. Dates, names
and descriptions are all literal information easily understandable
from a text.
b. Inferential level
At this level, the readers are able to go beyond what is written on
the page and add meaning or drawing a conclusion. In addition, in
this level, the readers are attempting to read
between the lines. A reader is demanded to understand what the
author means (implied) not just what authors say in the written
words.
c. Critical level
The purpose of this level is the reader can asses the good sense of
what they are reading, its clarity, accuracy and truthfulness.
d. Creative level
The last, at this level the readers can take the information or ideas
from what have been read. The creative level stimulates the readers
to new and original thinking. It involves making personal
responses based on full of understanding of the expressed
messages.14
14
19
From those four levels, English teacher education department requires
the student to take the linier courses such as literal reading, interpretive
reading and the last is critical reading.
Critical reading is also called as academic reading because it is very
different from everyday reading. Academic reading introduces the new
ideas and enables thinking about them in a different way and because it is
all about being selective, there is no need to read every text on a subject.
In addition, critical reading is a more active way of reading. It is a deeper
and more complex engagement with a text. Critical reading is a process of
analyzing, interpreting and, sometimes, evaluating. When we read
critically, we use our critical thinking skills to question both the text and
our own reading of it. Different disciplines may have distinctive modes of
critical reading (scientific, philosophical, literary, etc).15 So that, critical
reading can be defined as an analytical activity because the readers have to
reread the text to find information, values, assumptions, and language
usage as the patterns of elements.
15Karland, Dan
20
Table 2.1
There are some differences between reading and critical reading
according to Karland.16
Questions What is the text saying?
What information can I
Directions WITH the text (taking AGAINST the text
16Karland, Dan
21
for granted it is right) (questioning its assumptions
and argument, interpreting
meaning in context
Response Restatement, Summary Description, Interpretation,
Evaluation
From the differences above we know that usual reading and critical
reading are different as well. Students need more preparations to practice
critical reading inside or outside the class in order to understand the text
and also to get good achievement. There are two steps to preparing to read
critically:
1. Self-Reflect: What experiences, assumptions, knowledge and
perspectives do you bring to the text? What the biases might you have?
Are you able to keep and open mind and consider other point of view?
2. Read to understand:
a. Examine the text and context:
Who is the author? Who is the publisher? Where and when
was it written? What kind of text is it?
b. Skim the text: What is the topic? What are the main ideas?
22
Look up unfamiliar words or terms in dictionaries or glossaries.
Go over difficult passages to clarify them.17
5. Correlation between learning style and achievement
The research on the students’ learning styles and their achievement has
been widely studied. Learning styles are found to affect the students’
learning behaviors. Students who have different learning style preferences
would behave differently in the way they perceive, interact with, and
respond to the learning environment. Since the learners differ in their
preferences to the certain learning styles, it will be important for an
educator to know the variations of students on the features of their
learning styles because the information about students’ learning style
preference can help the teachers or lecturers become aware of the
students’ differences bring to the classroom.18
According to Barbe and Swassing, the reading process is primarily
visual because a student must look at a word and understand all of the
meanings within the use of that word.19 So, when comparing learning style
and the students’ achievement in some courses, the result indicated that
there was relationship between VAK learning style and the achievement
of students in some courses especially in reading. Here, the research will
17Karland, Dan
. Reading and Writing Ideas...1
18 L Wang, ―Variation in Learning Styles in a Group of Chinese English as a Foreign Language Learners.‖ 8 (2007).
19
Judy Williams, “Doctoral Dissertation: “Reading Comprehension, Learning Styles, and Seventh
23
focus on critical reading to find specific result that there will an effect of
different learning style to their achievement.
B. Review of Previous Studies
In this part the researcher wants to show about the previous studies to find
the difference with this research.
The Relationship among Learning Styles, Language Learning Strategies
and the Academic Achievement among the English Majors at Al-Aqsa
University.
This research was conducted by Ashour Jhaish to identify the learning
styles and learning strategies of students, to check whether there are
significant differences in the learning style, and strategy preferences
between male and female learners and to investigate whether there is a
relationship between students’ learning style, strategy preference, and the
academic achievement among the third year English major at Al Aqsa
University. From the analysis of the results of the achievement test and
their correlation with the students' learning styles, it was found that there
are statistically significant correlation coefficient between achievement
24
significant correlation coefficient between achievement and visual,
kinesthetic, tactile, group learning, and individual learning. 20
Learning Styles and Overall Academic Achievement in A Specific
Educational System.
Zainol Abidin also did the research dealing with learning styles. He
employed the research to investigate the relationship between learning
styles and overall academic achievement. The analysis of the data
indicated a significant relationship between overall academic
achievements and learning styles. It was also found that the high,
moderate and low achievers have a similar preference pattern of learning
in all learning styles.21
An Analysis of Students’ VAK (Visual, Auditory, and Kinesthetic)
Learning Style and Strategies in English Speaking of Second Grade At
SMA Unggalan Sidoarjo
This research was dealt by Yuliyani. The research discussed two major
concerns. First, to find out students’ learning style, they are visual,
auditory, and kinesthetic. Second, to find out strategies used students who
have visual, auditory, and kinesthetic learners in English Speaking. The
method that is used in this research was Questionnaire, Observation, and
20
Ashour Jhaish. Mohamed, Thesis: “The Relationship among Learning Styles, Language Learning Strategies, and the Academic Achievement among the English Majors at Al-Aqsa University” (Al-Aqsa University, 2009).
21
25
Interview.22 It is different with this research because the researcher
focuses on the student’s achievement in critical reading class.
An analysis of English teachers’ strategies in accommodating the seventh
graders’ learning styles at MTsN 1 Munjungan, Trenggalek.
The research was conducted to find out some major goals. The first is
the students’ VAK learning style. The second goal from this research was
going to find out the strategies applied by teacher in order to
accommodate the students’ visual, auditory and kinesthetic and the third
reveals the students’ responses toward the English teachers’ strategies. In
this research the researcher collected the data to find out about the
correlation between students’ learning styles and their achievement.
Descriptive qualitative was applied by the researcher.23 This is different
with this study because the researcher uses descriptive quantitative as the
design of research.
Strategies of Learning Vocabulary for Students with Different Learning
Styles At SMP Bangsa Surabaya
The researcher wanted to know kind of strategies used by teacher in
teaching vocabulary, reason of the teacher in using certain strategies, and
22
Hajar Yuliani, Thesis:“An Analysis of Students’ VAK (Visual, Auditory, and Kinesthetic) Learning Style and Strategies in English Speaking of Second Grade at SMA Unggalan Sidoarjo.‖ (Surabaya: State Institute of Islamic Studies Sunan Ampel, 2012).
23
Rufaidah Kusumawati, “Thesis: “An Analysis of English Teachers’ Strategies in Accommodating
26
response of the students when their teacher used those strategies. This
research used descriptive design to analyze the result.24
A Study Relationship between Interest in Watching English Films and
English Achievement of The Second Year Students’ At SMK Gondang
Legi Malang 2006
This thesis was done by Larasati. The result of this research shows that
there is a correlation between interests in watching English movie with
students’ achievement in English subject. It can be seen from the result of
computation of the student’ score on interest in watching English films.
Concerning the main purpose of this study, it was concluded that there is
low correlation between interest in watching English films and English
achievement of the second year students‟ at SMK NU Gondang Legi of
Malang.25
The Students’ Learning Style and Their Problems Faced in The Process
of English Listening Activity at SMK Raden Rahmat Mojosari-Mojokerto
In accordance with students’ learning style, this research discussed
four major concerns. Accomplished by Tamjis, This research shown the
positive payoff. Students’ have different types of learning styles; those
are visual, auditory and kinesthetic. And visual learners are more
24
Nadlifah Hidayatun, Thesis: “Strategies of Learning Vocabulary for Students with Different
Learning Styles at SMP Bangsa Surabaya” (Surabaya: IAIN Sunan Ampel, 2012).
25Tri Ayu Larasati, ―A Study Relationship between Int
erest in Watching English Films and English
Achievement of The Second Year Students’ At SMK Gondang Legi Malang 2006‖ (Unpublished
27
dominant than auditory and kinesthetic learners. The researcher used
some method to find out the strategies of students; learning style in
English speaking. The result of this research shows some problem that
students are faced in English listening activity based on their own
preference learning style. 26
The correlation between interest in watching English movie and
students’ speaking achievement at the fourth semester of English
Departmentof Islamic University of Malang
This research is taken from Najahah. In this study, the instrument
used by the researcher was questionnaire to measure students‟ interest in
watching English movie. Based on the instrument used, the result of this
research indicates that there is a significant correlation between students’
interest in watching English movie and student speaking achievement.
The computation of the data was 0, 56. It means that the interest of
students’ in watching English movie is not too high. Finally it can be
conclude that there is positive correlation between students’ interest in
watching English movie and student speaking achievement.27
26
Akhmada Qadafi Tamjis, “The Students’ Learning Style And Their Problems Faced In The Process Of English Listening Activity At Smk Raden Rahmat Mojosari-Mojokerto” (Sunan Ampel State Islamic UniversitySurabaya, 2014).
27
Nailatun Najahah, “The Correlation between Interest in Watching English Movie and Students’ Speaking Achievement at the Fourth Semester of English Department of Islamic University of
28
Those examples of previous study above are different with this
research. There are some researchers who correlate students’ learning
style and teacher creativity as independent variables. Besides, here are a
lot of methods that other researchers used correlation, analysis, and also
the role many kinds of variables, such as strategies and students’ overall
achievement. However, in this research the researcher only focuses on
students’ VAK (Visual, Auditory and Kinesthetic) learning style and its
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHOD
This chapter presents the method of the research. It covers: research design,
population and sample, research instrument, data collection technique and data
analysis technique. The research method has an important role in guiding the research
because the method can determine the success of research. Beside that the result of
the research depend on the method which is used by the researcher.
A. Research Design
The research design of this research is correlation. This is useful to
find out the significance correlation between those two variables, variable X
and variable Y. Correlation studies are concerned with determining the extent
of relationship between variables. They enable one to measure the extent to
which variations in one variable are associated with variations in determined
through the use of the coefficient of correlation.1 In this case the researcher
wanted to correlate between students’ learning styles and their achievement in
critical reading class.
1
30
B. Population and Sample
A population can be defined as the total number of possible units or
elements that are included in the study.2 The population of this research is
comprised of 4th semester of English Teacher Education Department because
students in this level have to take Critical Reading Class as the linier lecture in
reading. The total of population is about 119 students. It is taken from four
classes of critical reading class.
It would be impossible for the researcher to investigate all population.
Arikunto says that if the number of subjects is more than 100 persons, we can
take 10%, 20%, 25% or more of them. Meanwhile, if the number of subjects
is less than 100 persons, we can take all population.3 Based on the statements,
the researcher decided to obtain students’ learning styles and their critical
reading achievement by purposive sampling and chose two classes to be
voluntary exposed to the critical reading score and their learning styles were
analyzed. Those two classes are class A about 34 students and class B about
28 students with the same lecture but different time allocation. The number of
sample is adequate to get information. The researcher would take all of the
sample size from the two classes of critical reading. Quantitative research
generally needs a large sample size. The larger sample was taken, the more
accurate the data is also acquired.
2
D. E Gray, Doing Research in The Real World (London: SAGE Publications Ltd, 2004), 82.
3
31
C. Research Instrument
Research instrument plays the important role in collecting the data.
The appropriate instrument of data collecting is very important to gain the
objective outcome of this research. The researcher chose an indirect
communication technique through questionnaire in order to get the data of
students’ learning style preferences. Moreover, the researcher also used
document study in order to measure the students’ achievement in critical
reading class.
1. Questionnaire
The type questionnaire that the researcher used is closed-ended
question. It limits respondents’ answer to the survey. It can help the
respondents to answer quickly and also to make the easiest way for
researcher to analyze the data. There are some options to answer
closed-ended questionnaire such as yes/no, true/false, or multiple choice with an
option for “other” to be filled in, or ranking scale such as strongly agree,
agree, undecided, disagree, strongly disagree. Closed-ended questionnaire
is about learning style questionnaire. It is about learning style
questionnaire. It consists of 30 questions about student’s learning style. It
32
2. Document Study
The researcher needed another data to help her run this research.
Arikunto says documentary aims to find out data about something in the
form of notes, transcript, newspaper, magazine, etc.4The data was
collected through document study of the students’ midterm test score in
critical reading class. It was used to validate the sample. The instrument
used for inferential critical reading as a mean of measuring the student’s
critical reading achievement. Seeing from the type of the test, test is given
by the lecturer of the course.
D. Data Collection Technique
The first step to collect the data is choosing the participants. The
participants of this research is the fourth semester students of critical reading
class. The next step is choosing the instruments. The instruments were used in
this research are questionnaire and documentation.
The researcher collected the data from the fourth semester students by
giving the questionnaire for obtaining the students’ learning style. For the
collecting the data of critical reading score, the researcher chose
documentation as the technique. This technique helped the researcher to study
the critical reading score of the students after obtaining the score of students’
final exam from the lecturer.
4
33
Answering the first research question, what is the learning style
preference of students in critical reading class? The researcher obtained the
answer by distributing the questionnaires to the students of two classes were
selected of critical reading class. After answering the first question, the
researcher collected the data from the students’ critical reading score; the
researcher obtained it from the lecturer of critical reading class, and then used
documentation technique to analyze the critical reading score.
To determine which are the variables for calculating the data, the
researcher defines the theory of Ary who states that Variable is the concept
that has various values. This research consists of two variables. First variable
is independent variable symbolized by “X” and second variable is dependent
variable symbolized by “Y”.
1. Independent variable
Independent variable is assumed as variable that affects the dependent
variable.5Students’ learning style is taken as an independent variable. 2. Dependent variable
Dependent variable is a variable affected by independent variable.6
Students’ achievement is taken as dependent variable.
Finally the second research question which is about the correlation
between students’ learning styles and their achievement in critical reading
5
Ary. Donald, Introduction to Research in Education….. 35.
6
34
class automatically will be answered. Consequently, the correlation of two
variables will be found.
E. Data Analysis Technique
The technique of data analysis was used by the writer is the formula of
Person’s product moment correlation to examine whether there is correlation
between students’ learning style and achievement or not. The researcher used
person’s product moment formula. The data about the students’ learning style
and critical reading achievement were analyzed in the following procedures:
- Preparation
a. Checking the student’s name and identity.
b. Checking the data completeness.
c. Checking the data content.
- Tabulating
a. Distributing the questionnaire to the students
b. Scoring the result of questionnaire
c. Collecting the documentation of students’ critical reading score.
d. The coefficient of correlation between the students’ EQ (X) and the
students’ English achievement (Y) had been determined.
Correlation coefficient usually represented by r indicates indicating
both the direction of the correlation (either positive or negative) and
35
The method used Person’s product moment to find the correlation
significant. The formula is as follows:
R : Correlation coefficient of variable X and Y
∑XY :
The sum of the product of X and Y scores for each students.
∑X : The sum of X scores
∑Y : The sum of Y scores
∑X2 : The sum of square of students learning style scores
∑Y2 : The sum of square of students’ achievement in critical
reading score
computation indicates whether there is any correlation between the two
36
Criteria : If r value > r table, it means that there is correlation because
Null Hypothesis (Ho) is rejected and Alternative Hypothesis
(Ha) is accepted.
If r value < r table, it means that there is no correlation
because Null Hypothesis (Ho) is accepted and Alternative
Hypothesis (Ha) is rejected.
According to Sugiono, the coefficient correlation is gotten from the
formula. It shows the interval of coefficient and the level of relationship
between the two variables below. 7
Table 3.1
Coefficient Correlation
Interval of Coefficient Relationship Level
0,00 - 0,199 Very weak
0,20 - 0,399 Weak
0,40 - 0,599 Enough
0,60 - 0,799 Strong
0,80 - 1,000 Very strong
The correlation coefficient has some important properties. Mark Belnaves
and Peter Caputi explains that the magnitude of the correlation coefficient
7
37
indicates the strength of the relationship between the variables. The values of
the correlation coefficient can range from -1 to +1. A coefficient close to +1
or to -1 indicates a strong relationship between two variables. Scores closes to
zero indicated the absence of a relationship between the two variables. The
variables are positively related, if the coefficient has positive sign. 8
Furthermore, in order to make calculating the data of research easier and
valid, the researcher used application SPSS 16.0 from windows computer
program. The value of sig from the output of SPSS with the level of
significance 0, 05 is compared. If the value of sig is higher than the level of
significance, the null hypothesis is rejected and the alternative hyphothesis is
accepted, it means that there is significant correlation and “vice versa” If the
value of sig is lower than the level of significance, the null hyphothesis is
accepted and the alternative hyphothesis is rejected, it means that there is no
significant correlation.
8
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDING
In this chapter the researcher describes the findings and the discussion which is
covered during the research. The data obtained is expected to be able to answer the
research questions mentioned in the first chapter. The descriptions of finding are
students’ preference learning style and students’ critical reading achievement. The
researcher presents them based on the data collected and the procedures presented in
the chapter III.
A. Students’ Learning Style Preference in Critical Reading Class
In the first research of this study the researcher has distributedlearning style
questionnaire to students. It was done on May 11st, 2015 and May 13rd, 2015 .
In this section the researcher distributed learning style questionnaires to the 62
students (the students from class A and class B of critical reading class) as the
sample of this research. It contains 30 questions. Students can answer by circling
the options that they prefer. One question only has one answer. The format of
answer as follow:
0 = Never
1 = Rarely
2 = Sometimes
3 = Often
39
The researcher gathers the data from questionnaire as follows:
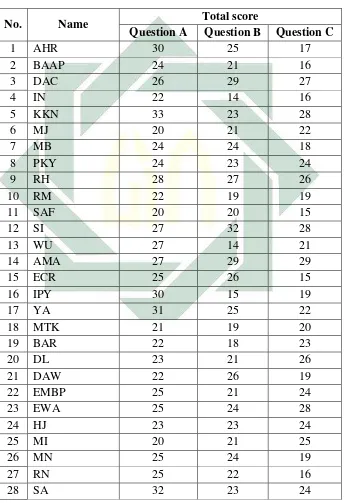
Table 4.1
The Result of Students’ Total Score from Questionnaire
No. Name Total score
Question A Question B Question C
41
The researcher makes the percentage from 30 items that consist of 10
questions for visual learner categories, 10 questions for auditory learner
categories and 10 questions for kinesthetic learner categories. The researcher
categorizes students’ learning style based on their score from each question.
Visual learners get highest score in question A, Auditory learners get highest
score in question B, and Kinesthetic learners get highest score in question C. But,
from the data the researcher finds some students have the same high score in
different learning style. It means that a student can prefer to have more than one
learning style, it is also known as mix of learning style or multiple learning
styles. Everyone has a mix of learning styles. Some people may find that they
have a dominant style of learning, with far less use of the other styles. Others
may find that they use different styles in different circumstances.1 Because of the
explanation above the researcher adds the total of respondent becomes 70
respondents (N = 70). In the table the researcher categorizes the type of learners
and makes percentages.
The researcher breaks down the data into percentage to make it easy for the
readers to understand the result of the observation. The formula to count the
percentage as follows:
1 “Overview of Learning Styles,” accessed June 25, 2015, http://www.learning
43
27 SAF
28 HS
29 IN
30 NAS
31 MD
32 AL
33 BRH
34 DAP
35 EAP
36 ENW
37 FYA
38 HK
39 IMA
40 MM
41 AM
42 MZ
P
=
x 100%
=
x 100%
= 0, 6 x 100%
44
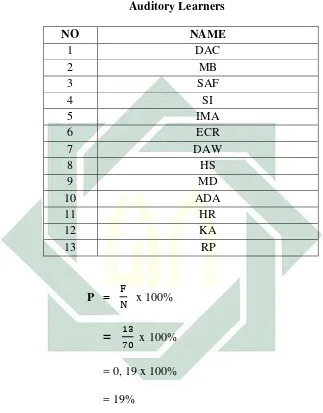
Table 4.3
Auditory Learners
NO NAME
1 DAC
2 MB
3 SAF
4 SI
5 IMA
6 ECR
7 DAW
8 HS
9 MD
10 ADA
11 HR
12 KA
13 RP
P =
x 100%
=
x 100%
= 0, 19 x 100%
45
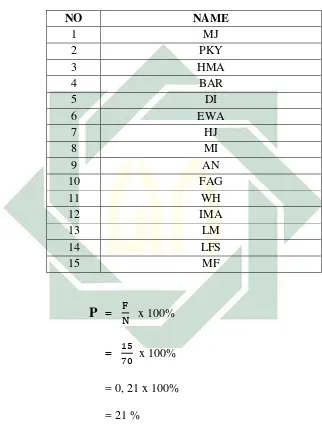
Table 4.4
Kinesthetic Learners
NO NAME
1 MJ
2 PKY
3 HMA
4 BAR
5 DI
6 EWA
7 HJ
8 MI
9 AN
10 FAG
11 WH
12 IMA
13 LM
14 LFS
15 MF
P
=x 100%
=
x 100%
= 0, 21 x 100%
46
60% 19%
21%
Percentage of Students' Learning Style
Visual
Auditory
Kinesthetic Chart 4.1
The Graph of Students’ Learning Style of 4th Semester
At Critical Reading Class
Based on the result above the researcher find the type of visual learners are
36 students (60%), auditory learners are 13 students (19%) and kinesthetic
learners are 15 students (21%). It shows that visual learners are more dominant
than auditory and kinesthetic learners in critical reading class. Yet, there are 14
students who have multiple learning styles.
The preeminent of students for each learning style is shown in table above.
For more detail about the score of students’ preeminent in each learning style is
47
0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60%
20,0-25,0 26,0-30,0 31,0-35,0
Percentage of Visual Learners
Students Chart 4.2
Based on the data obtained, the result the first question (visual preference)
of questionnaire shows that among 62 students, there are 7 students who got
highest score, their scores range from 31, 0 – 35, 0, there are 21 students who
got the scores range from 26, 0 – 30, 0 and there are 34 students who got the
scores range 20, 0 – 25, 0. This means that 55% students have tendencies in
48
0% 20% 40% 60% 80%
20,0-25,0 26,0-30,0 31,0-35,0
Percentage of Auditory Learners
Students
0% 20% 40% 60% 80%
20,0-25,0 26,0-30,0 31,0-35,0
Percentage of Kinesthetic Learners
Students Chart 4.3
For auditory learning style, the result of the data shows that there are only
4 students who get highest score, 13 students get the scores range from 26, 0 –
30, 0 and there are 47 students who get the scores range 20, 0 – 25, 0.
Chart 4.4
49
For kinesthetic learning style, there are only 1 student who get preeminent
or highest score in scores range from 31, 0 – 35, 0, there are 18 students who
get the scores range from 26, 0 – 30, 0 and there are 43 students who get the
scores range 20, 0 – 25, 0 this means the students majority have low
kinesthetic learning style.
Note for the table 4.5 – table 4.7:
20, 0 – 25, 0 = Negligible (Low)
26, 0 – 30, 0 = Minor learning style preference (Strength)
31, 0 – 35, 0 = Major learning style preference (Very Strength)
The note above means that every student has learning style preference that
reaches the higher point in an aspect of learning style than the other. In order to
make the reader easy to read, the researcher classify the data into 3 groups
including Negligible (Low), Minor learning style preference (Strength) and
Major learning style preference (Very Strength).
In addition, there are some students who get more than one highest score in
the sheet. It means that she/he has more than one majority learning style
50
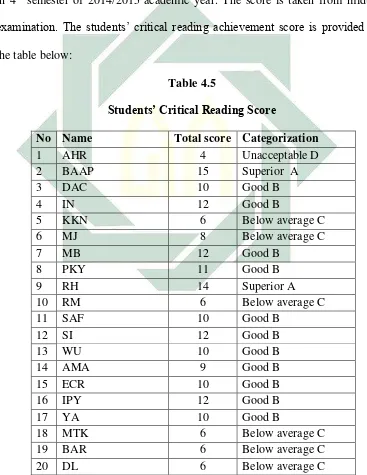
B. Correlation between Students’ Learning Style and Achievement in Critical
Reading Class
The second variable of this research is students’ achievement in critical
reading class. This variable is collected from the students’ critical reading score
in 4th semester of 2014/2015 academic year. The score is taken from midterm
examination. The students’ critical reading achievement score is provided into
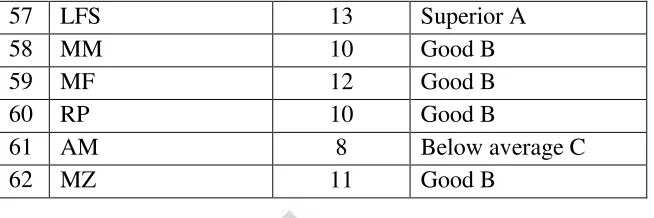
52
57 LFS 13 Superior A
58 MM 10 Good B
59 MF 12 Good B
60 RP 10 Good B
61 AM 8 Below average C
62 MZ 11 Good B
Based on the table above the higher score of the students is 15 and the lowest
score is 4. The categories of total score are:
Superior : 13 – 16 (A)
Good : 9 – 12 (B)
Below Average : 5 – 8 (C)
Unacceptable : 1 — 4 (D)
Based on the table above, among 62 students there are 3 students get the
lowest score (4) of critical reading middle test. It makes them fail the
examination because (4) is unacceptable.
The summary of critical reading score is presented by thefollowing table:
Table 4.6
Students’ Score Range of Critical Reading
No Score range Number of students
1 13-15 (Superior) 11
2 9-12 (Good) 31
3 5-8 (Below Average) 17
53
The table above shows that there are 11 students who get superior predicate
and the score is between 13-14 and 15-31students who get good predicate and the
average score is 9 to 12, 17 students who get below average predicate and the
score is between 6 and 8 and there are 3 students who unacceptable because their
score are 4. After the data is collected, the researcher calculates the data using
Pearson Product Moment Correlation to find the significant correlation between
students’ learning style and critical reading achievement. Based on the data
analysis technique on chapter III, the researcher uses application SPSS 16.0 to
calculate and to know the correlation between students’ learning style and
achievement in critical reading class. The result of computation is shown more
detail by making correlation between each learning style and the score of critical
54
The correlation is presented as below:
Table 4.7
The Computation of Correlation between Students’ Visual Learning
Style and Achievement in Critical Reading Class
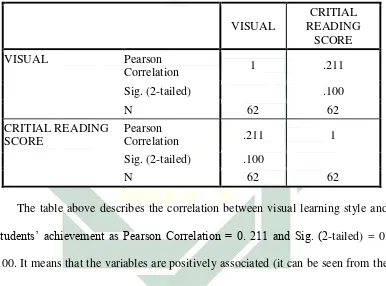
VISUAL
The table above describes the correlation between visual learning style and
students’ achievement as Pearson Correlation = 0. 211 and Sig. (2-tailed) = 0.
100. It means that the variables are positively associated (it can be seen from the
coefficient correlation) but there is a week correlation between two variables.
According to the statistical theory that is mentioned in chapter III, the standard
level of significant is 0. 05. The table above shows the value of Sig. is higher
than 0. 05. Accordingly, this shows there is no significant correlation between
55
Table 4.8
The Computation of Correlation between Students’ Auditory Learning
Style and Achievement in Critical Reading Class
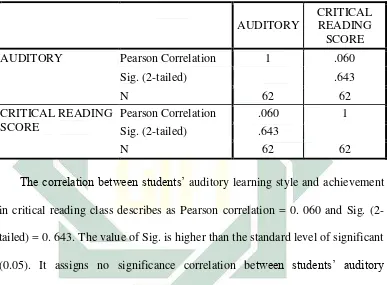
AUDITORY
CRITICAL READING SCORE
AUDITORY Pearson Correlation 1 .060
Sig. (2-tailed) .643
N 62 62
CRITICAL READING SCORE
Pearson Correlation .060 1
Sig. (2-tailed) .643
N 62 62
The correlation between students’ auditory learning style and achievement
in critical reading class describes as Pearson correlation = 0. 060 and Sig. (2-
tailed) = 0. 643. The value of Sig. is higher than the standard level of significant
(0.05). It assigns no significance correlation between students’ auditory
learning style and achievement in critical reading class. It also can be seen from
the coefficient correlation that shows the variables are positively associated but
56
Table 4.9
The Computation of Correlations between Students’ Kinesthetic Learning
Style and Achievement in Critical Reading Class
KINESTHETIC
CRITICAL READING
SCORE
KINESTHETIC Pearson Correlation 1 .024
Sig. (2-tailed) .853
N 62 62
CRITICAL READING SCORE
Pearson Correlation .024 1
Sig. (2-tailed) .853
N 62 62
The correlation between students’ kinesthetic learning style and achievement
in critical reading class describes as Pearson correlation = 0. 024 and Sig. (2-
tailed) = 0. 853. The value of Sig. is higher than the standard level of significant
(0.05). It presents no significance correlation between two variables students’
kinesthetic learning style and achievement in critical reading class. It also can be
seen from the coefficient correlation that shows the variables are positively
associated but there is a very weak correlation between two variables.
Besides calculating each learning style, the researcher also tries to find
overall result of correlation between students’ learning style and achievement in
57
Table 4.10
The Result of Correlation between Students’ Learning Style and
Achievement in Critical Reading Class