BAGAN ALIR BAHASAN
BAGAN ALIR BAHASAN
DISTRIBUSI TEGANGAN (8) GAYA ANGKAT DIBAWAH BANGUNAN AIR (6) PERENCANAAN PEMAMPATAN TANAH (9) TEGANGAN EFEKTIF (7) PONDASI DAYA DUKUNG TANAH STABILITAS DAN KEKUATAN TANAH KLASIFIKASI REMBESAN AIR DALAM TANAH (5) PERENCANAAN BANGUNAN PEMADATAN (4) KLASIFIKASI TANAH (3) KOMPOSISI TANAH (1) BANGUNAN TANAH TANAH (2)
BAGAN ALIR BAHASAN
BAGAN ALIR BAHASAN
POKOK BAHASANPOKOK BAHASAN DISTRIBUSI TEGANGAN (8) GAYA ANGKAT DIBAWAH BANGUNAN AIR (6) BAHASAN BAHASAN A. Komposisi Tanah B Parameter Fisik PEMAMPATAN TANAH (9) TEGANGAN EFEKTIF (7) B. Parameter Fisik Tanah 1. Hubungan Volume 2. Hubungan Berat Dan STABILITAS DAN KEKUATAN TANAH KLASIFIKASI REMBESAN AIR DALAM TANAH (5) Berat Dan Volume 3. Hubungan γ, E, Wc, Gs 4. Kerapatan Relatif PEMADATAN (4) KLASIFIKASI TANAH (3) KOMPOSISI TANAH (1) Relatif 5. Konsistensi Tanah 6. Aktivitas (A) C. Struktur Tanah TANAH (2)
POKOK BAHASANPOKOK BAHASAN
A. Komposisi tanah
BAHASAN BAHASANTanah terdiri dari :
• Butiran tanah yang padat (solid) • Air (water) A. Komposisi Tanah B Parameter Fisik ( ) • Udara (air)
MENGHITUNG VOLUME TANAH
B. Parameter Fisik Tanah 1. Hubungan Volume 2. Hubungan Berat Dan
BILA VOLUME TANAH
=
V
→ Vs = Volume Solid
V
V l
W t
V
V
V
V
Berat Dan Volume 3. Hubungan γ, E, Wc, Gs 4. Kerapatan Relatif→ Vw = Volume Water
→ Va = Volume Air
V = V
s + Vw + Va
5. Konsistensi Relatif Tanah 6. Aktivitas (A) C. Struktur Tanah→ Vv = Volume Pori
V
v = Vw + Va
POKOK BAHASANPOKOK BAHASAN Air VA BAHASAN BAHASAN Total volume (= V) Total weight (= W) Water W Ww
V
VV
Vw A. Komposisi Tanah B Parameter Fisik ( V) ( W) (a) solid Ws V s (b) B. Parameter Fisik Tanah 1. Hubungan Volume 2. Hubungan Berat Dan Soil element in natural state.(a) (b)
Three phases of the soil element
Berat Dan Volume 3. Hubungan γ, E, Wc, Gs 4. Kerapatan Relatif Gambar 2.1
Sketsa butiran tanah (solid) dan rongga (pori) dalam tanah
Relatif 5. Konsistensi Tanah 6. Aktivitas (A) C. Struktur Tanah gg (p )
POKOK BAHASANPOKOK BAHASAN
B. PARAMETER FISIK TANAH
BAHASAN BAHASAN
V
1.
Hubungan volume yang umum dipakai
A. Komposisi Tanah B Parameter Fisik
V
s vV
V
e
=
• Angka pori ( void ratio) =
e
B. Parameter Fisik Tanah 1. Hubungan Volume 2. Hubungan Berat Dan
%
100
×
=
V
V
n
vV
• Porositas ( porosity) =n
• Derajat kejenuhan Berat Dan Volume 3. Hubungan γ, E, Wc, Gs 4. Kerapatan Relatif%
100
×
=
v w RV
V
S
j j (degree of saturation) =S
Rn
e
Relatif 5. Konsistensi Tanah 6. Aktivitas (A) C. Struktur Tanah • Hubungane
dann
n
e
−
=
1
n
=
1
+
e
POKOK BAHASANPOKOK BAHASAN
2. Hubungan berat dan volume
BAHASAN BAHASAN a. Kadar air (water content)
= Wc
=
×
100
%
s w c
W
W
w
W
A. Komposisi Tanah B Parameter Fisikb. Berat volume (unit weight
)=
γ
V
W
=
γ
W ⎤
⎡
B. Parameter Fisik Tanah 1. Hubungan Volume 2. Hubungan Berat DanW
(
)
V
w
W
V
W
W
W
V
W
W
V
W
s s c w s w s=
+
⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎣
⎡
+
=
+
=
=
1
1
γ
Berat Dan Volume 3. Hubungan γ, E, Wc, Gs 4. Kerapatan RelatifBila :
s dV
W
γ
=
→
γ
d=
DRY UNIT WEIGHT(
)
γ
Relatif 5. Konsistensi Tanah 6. Aktivitas (A) C. Struktur Tanah(
)
(
)
c d c dw
w
+
=
→
+
=
1
1
γ
γ
γ
γ
Maka :
POKOK BAHASANPOKOK BAHASAN BAHASAN BAHASAN
water
air
Ww= V w= w.Gs Vv= e A. Komposisi Tanah B Parameter Fisiksolid
W w.Gs.γw Ws = w s Vs= 1 V = 1 + e B. Parameter Fisik Tanah 1. Hubungan Volume 2. Hubungan Berat Dan sGs.γw Berat Dan Volume
3. Hubungan γ, E, Wc, Gs 4. Kerapatan
Relatif
Fig. 2.2.
Three separate phases of a soil element with
volume of soil solid equal to 1.
Relatif 5. Konsistensi Tanah 6. Aktivitas (A) C. Struktur Tanah
q
POKOK BAHASANPOKOK BAHASAN BAHASAN BAHASAN
water
= ewVolume
Weight
e. γw A. Komposisi Tanah B Parameter Fisikwater
V = 1 + e Vv = V w 1 Ww = γw B. Parameter Fisik Tanah 1. Hubungan Volume 2. Hubungan Berat Dansolid
Vs = 1 Ws = G s .γ Berat Dan Volume 3. Hubungan γ, E, Wc, Gs 4. Kerapatan RelatifFig. 2.3.
Saturated soil element with
Relatif 5. Konsistensi
Tanah 6. Aktivitas (A) C. Struktur Tanah
POKOK BAHASANPOKOK BAHASAN
3. Hubungan
γ, e, w
c, G
s a. SPESIFIC GRAVITY= G
S A. Komposisi Tanah B Parameter Fisik a. SPESIFIC GRAVITYG
S w s sG
γ
γ
=
B. Parameter Fisik Tanah 1. Hubungan Volume 2. Hubungan Berat Dan w w w w w wW
V
V
W
=
→
=
γ
γ
...(
1
)
Berat Dan Volume 3. Hubungan γ, E, Wc, Gs 4. Kerapatan Relatifk
s s sV
W
=
γ
Relatif 5. Konsistensi Tanah 6. Aktivitas (A) C. Struktur TanahUntuk V
s= 1
→ γ
s= W
s ,POKOK BAHASANPOKOK BAHASAN
Jadi :
W s s w s sW
G
W
W
G
γ
γ
→
=
×
=
A. Komposisi Tanah B Parameter FisikBila :
W s c s c w s w cW
w
W
w
G
W
W
w
=
→
=
×
=
×
×
γ
B. Parameter Fisik Tanah 1. Hubungan Volume 2. Hubungan Berat DanBila :
)
2
(
...
...
s c w w s c ww
G
V
W
G
w
W
=
γ
→
=
Berat Dan Volume 3. Hubungan γ, E, Wc, Gs 4. Kerapatan Relatif1 dan 2 → V
w= w
cG
sBILA : V
s= 1
→ e = V
V Relatif 5. Konsistensi Tanah 6. Aktivitas (A) C. Struktur TanahV = V
s+ V
v→ V = 1+e
POKOK BAHASANPOKOK BAHASAN
b. BERAT VOLUME =
γ
c. BERAT V KERING =γ
d BAHASANBAHASANV
W
W
V
W
=
w+
s=
γ
γ
dG
W
γ
A. Komposisi Tanah B Parameter Fisik(
w
)
G
e
G
G
w
c w s w s w s c+
=
+
+
=
1
1
1
γ
γ
γ
γ
γ
e
G
V
W
s s w d+
=
=
1
γ
γ
B. Parameter Fisik Tanah 1. Hubungan Volume 2. Hubungan Berat Dane
+
1
γ
d. DERAJAT KEJENUHAN= S
R Berat Dan Volume 3. Hubungan γ, E, Wc, Gs 4. Kerapatan Relatif R s c R s c w RS
e
w
G
e
G
w
V
V
S
=
=
→
×
=
×
Relatif 5. Konsistensi Tanah 6. Aktivitas (A) C. Struktur Tanah ve
V
POKOK BAHASANPOKOK BAHASAN
e. BERAT VOLUME TANAH JENUH =
γ
SAT(
)
+
+
=
+
+
=
=
e
w
G
e
G
G
w
V
W
c s w s w s w c SAT1
1
1
γ
γ
γ
γ
A. Komposisi Tanah B Parameter Fisik⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
+
+
=
+
+
e
w
e
e
V
c d SAT1
1
1
1
γ
γ
B. Parameter Fisik Tanah 1. Hubungan Volume 2. Hubungan Berat Dan ATAUjuga dapat ditulis sebagai berikut :
Berat Dan Volume 3. Hubungan γ, E, Wc, Gs 4. Kerapatan Relatif
→ S
R= 1
→ e = W
cG
s(
s)
w s wG
e
G
e
γ
γ
γ
γ
=
.
+
=
+
Relatif 5. Konsistensi Tanah 6. Aktivitas (A) C. Struktur Tanah w SATe
e
γ
γ
+
=
+
=
1
1
POKOK BAHASANPOKOK BAHASAN
4. Kerapatan relative
a. Kerapatan relative ( DR) digunakan untuk
menentukan kerapatan tanah berbutir kasar di lapangan A. Komposisi Tanah B Parameter Fisik lapangan.
%
100
max−
×
=
e
e
D
R B. Parameter Fisik Tanah 1. Hubungan Volume 2. Hubungan Berat Dani---i---i
min max− e
e
Berat Dan Volume 3. Hubungan γ, E, Wc, Gs 4. Kerapatan Relatife
=
Angka pori tanah di lapangank h k d l l
e
=
Angka pori tanah di lapangank h k d l l
e
maxe e
min 5. Konsistensi Relatif Tanah 6. Aktivitas (A) C. Struktur Tanahe
max=
Angka pori tanah kondisi paling lepase
min=
Angka pori tanah kondisi paling padate
max=
Angka pori tanah kondisi paling lepasPOKOK BAHASANPOKOK BAHASAN
b. Hubungan antara
D
Rdengan
kondisi tanah di lapangan
BAHASAN BAHASAN A. Komposisi
Tanah
B Parameter Fisik
D
R(%)
Keadaan Tanah Di Lapangan
0 - 15 Sangat Lepas ( Very Loose)
B. Parameter Fisik Tanah 1. Hubungan Volume 2. Hubungan Berat Dan g p ( y ) 15 - 50 Lepas ( Loose) 50 - 70 Tengah ( Medium) Berat Dan Volume 3. Hubungan γ, E, Wc, Gs 4. Kerapatan Relatif 70 - 85 Padat (dense)
85 - 100 Sangat padat ( very dense)
Relatif 5. Konsistensi
Tanah 6. Aktivitas (A) C. Struktur Tanah
POKOK BAHASANPOKOK BAHASAN
5. Konsistensi tanah
a. Sifat kohesive tanah dibagi dalam 4 keadaan pokok :
- Padat (solid)
A. Komposisi Tanah
B Parameter Fisik
- Semi padat (semi solid) - Plastis (plastic)
- Cair (liquid)
Keadaan-keadaan tersebut terjadi karena adanya perubahan
B. Parameter Fisik Tanah 1. Hubungan Volume 2. Hubungan Berat Dan
Keadaan keadaan tersebut terjadi karena adanya perubahan
kadar air
( w
c)
PADAT SEMI PADAT PLASTIS CAIR
Berat Dan Volume 3. Hubungan γ, E, Wc, Gs 4. Kerapatan Relatif BATAS CAIR BATAS PLASTIS BATAS SUSUT Relatif 5. Konsistensi Tanah 6. Aktivitas (A) C. Struktur Tanah CAIR (LL) PLASTIS (PL) SUSUT (SL)
POKOK BAHASANPOKOK BAHASAN
5. Konsistensi tanah
b
.
BATAS CAIR ( LIQUID LIMIT = LL)LL = kadar air tanah dimana apabila dibuat goresan pada
A. Komposisi Tanah
B Parameter Fisik
tanah tersebut dengan spatula standard akan menutup pada 25 kali pukulan.
B. Parameter Fisik Tanah 1. Hubungan Volume 2. Hubungan Berat Dan Berat Dan Volume 3. Hubungan γ, E, Wc, Gs 4. Kerapatan Relatif Relatif 5. Konsistensi Tanah 6. Aktivitas (A) C. Struktur Tanah
Apparatus and grooving
tool Groove cut in sample prior to the test
Groove closed over 12.5 mm – soil at wLif this
POKOK POKOK
c. BATAS PLASTIS ( PLASTIC LIMIT = PL)
PL = Kadar air tanah dimana apabila tanah
BAHASAN BAHASAN
PL = Kadar air tanah dimana apabila tanah
tersebut digulung sampai dengan diameter 3.0 mm mulai terjadi retak-retak.
A. Komposisi T h Tanah B. Parameter Fisik Tanah 1. Hubungan Volume 2. Hubungan Berat Dan Volume 3. Hubungan γ, E, Wc, Gs 4 Kerapatan 4. Kerapatan Relatif 5. Konsistensi Tanah 6. Aktivitas (A) C Struktur Tanah C. Struktur Tanah
POKOK BAHASANPOKOK BAHASAN
d. INDEKS PLASTIS (PLASTICITY INDEX = IP)
PI = IP = LL - PL
e. INDEKS KECAIRAN (LIQUIDITY INDEX= LI)
PL
w
A. Komposisi Tanah
B Parameter Fisik
0 < LI < 1 → Tanah berada dalam daerah plastis
IP
PL
w
LI
=
C−
B. Parameter Fisik Tanah1. Hubungan Volume 2. Hubungan Berat Dan LL PL SL
SOLID SEMI SOLID PLASTIS CAIR
0
LI > 1 → Tanah dalam keadaan cair/hampir cair Berat Dan Volume
3. Hubungan γ, E, Wc, Gs 4. Kerapatan Relatif Relatif 5. Konsistensi Tanah 6. Aktivitas (A) C. Struktur Tanah
−
=
LI
0
1
POKOK BAHASANPOKOK BAHASAN
6. Aktivitas (A)
6. Aktivitas (A)
A =
IP A. Komposisi Tanah B Parameter FisikNAMA MINERAL LEMPUNG AKTIVITAS (A)
%
BUTIRAN YANG LEBIH KECIL 2μ
B. Parameter Fisik Tanah1. Hubungan Volume 2. Hubungan Berat Dan ( ) MONTMORILLONITE ( BENTONITE) 1 – 7 ILLITE 0.5 – 1 Berat Dan Volume 3. Hubungan γ, E, Wc, Gs 4. Kerapatan Relatif KAOLINITE 0.5 HALLOYSTE 0.5 ATTAPULGITE 0 5 – 1 2 Relatif 5. Konsistensi Tanah 6. Aktivitas (A) C. Struktur Tanah ATTAPULGITE 0.5 1.2 ALLPHANE 0.5 – 1.2
POKOK BAHASANPOKOK BAHASAN
C. STRUKTUR TANAH
1. STRUKTUR TANAH :
- SUSUNAN GEOMETRIK PARTIKEL TANAH A. Komposisi Tanah
B Parameter Fisik
- GAYA ANTAR PARTIKEL
2. TANAH BERBUTIR KASAR ( GRANULAR SOIL)
→ GAYA ANTAR PARTIKEL SANGAT KECIL → DIABAIKAN ,
B. Parameter Fisik Tanah 1. Hubungan Volume 2. Hubungan Berat Dan → G S G C → , JADI :
STRUKTUR TANAH = SUSUNAN GEOMETRIK PARTIKEL
3. TANAH BERBUTIR HALUS YANG KOHESIVE
Berat Dan Volume 3. Hubungan γ, E, Wc, Gs 4. Kerapatan Relatif
(COHESIVE SOIL; MIS. LEMPUNG)
→ GAYA ANTAR PARTIKEL → SANGAT DOMINAN
JADI : STRUKTUR TANAH KOHESIVE = SUSUNAN
Relatif 5. Konsistensi
Tanah 6. Aktivitas (A)
C. Struktur Tanah GEOMETRIK PARTIKEL TANAH + GAYA ANTAR
DISTRIBUSI TEGANGAN (8) GAYA ANGKAT DIBAWAH BANGUNAN AIR (6) PERENCANAAN PEMAMPATAN TANAH (9) TEGANGAN EFEKTIF (7) PONDASI DAYA DUKUNG TANAH STABILITAS DAN KEKUATAN TANAH KLASIFIKASI REMBESAN AIR DALAM TANAH (5) PERENCANAAN BANGUNAN PEMADATAN (4) KLASIFIKASI TANAH (3) KOMPOSISI TANAH (1) BANGUNAN TANAH TANAH (2)
POKOK BAHASANPOKOK BAHASAN DISTRIBUSI TEGANGAN (8) GAYA ANGKAT DIBAWAH BANGUNAN AIR (6) BAHASAN BAHASAN A. Umum. B T j an PEMAMPATAN TANAH (9) TEGANGAN EFEKTIF (7) B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test. 1 A li STABILITAS DAN KEKUATAN TANAH KLASIFIKASI REMBESAN AIR DALAM TANAH (5) 1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa Hidrometer 3. Kurva PEMADATAN (4) KLASIFIKASI TANAH (3) KOMPOSISI TANAH (1) Distribusi D. Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah. TANAH (2)
POKOK BAHASAN POKOK BAHASAN
A. Umum
BAHASAN BAHASAN A. Umum. B T j an B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test. 1 A li 1. WHY DO WE NEED TO CLASSIFY SOILS ???????To describe various soil types encountered in the nature in a systematic way and gathering soils that
have distinct physical properties in groups and units 1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa
Hidrometer 3. Kurva have distinct physical properties in groups and units.
2. GENERAL REQUIREMENTS OF A SOIL CLASSIFICATION SYSTEM:
a- Based on a scientific method
Distribusi
D. Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah.
a Based on a scientific method b- Simple
c- Permit classification by visual and manual tests. d- Describe certain engineering properties
e- Should be accepted to all engineers e Should be accepted to all engineers.
POKOK BAHASAN POKOK BAHASAN
A. Umum (lanjutan)
BAHASAN BAHASAN A. Umum. B T j an3 VARIOUS SOIL CLASSIFICATION SYSTEMS
(
j
)
B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test. 1 A li 3. VARIOUS SOIL CLASSIFICATION SYSTEMS:a- Geologic Soil Classification System b- Agronomic Soil Classification System
T t l S il Cl ifi ti S t (USDA) 1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa
Hidrometer 3. Kurva c- Textural Soil Classification System (USDA)
d- American Association of State Highway Transportation Officials System (AASHTO) e- Unified Soil Classification System (USCS)
f A i S i t f T ti d M t i l Distribusi
D. Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah.
f- American Society for Testing and Materials System (ASTM)
POKOK BAHASANPOKOK BAHASAN
B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah
BAHASANBAHASANA U
B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah
A. Umum. B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C J i T t Klasifikasi Tanah :
mengelompokkan tanah yang berbeda-beda tapi mempunyai sifat serupa kedalam group-group dan sub group. C. Jenis Test. 1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa Hidrometer g p Tujuannya :
untuk mendapatkan gambaran umum mengenai
perilaku suatu tanah Hidrometer
3. Kurva Distribusi
D. Sistem Klasifikasi
perilaku suatu tanah.
Dasar Klasifikasi Tanah :
1. Plastisitas tanah.
2 Ukuran butiran
Tanah.
POKOK BAHASAN POKOK BAHASAN
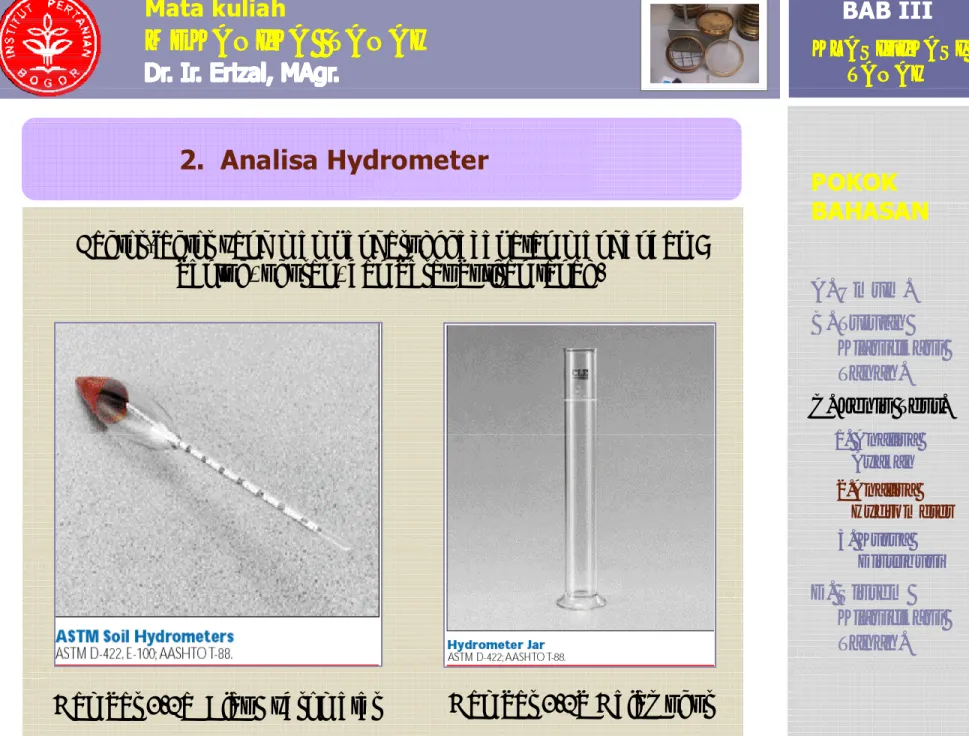
C. Jenis Test
BAHASAN BAHASAN A. Umum. B T j anJenis test untuk mendapatkan ukuran Butiran :
B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test. 1 A li p
1. Analisa / Test Ayakan (Gambar 3.1). 2. Analisa / Test Hydrometer (Gambar 3.2)
1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa Hidrometer 3 K Analisa ayakan :
1. Ayakan Yang Dikapai : Ayakan US-Standard. 2. Dasar : Ukuran Lubang Ayakan.
3. Kurva Distribusi D. Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah Analisa hydrometer
1. Menggunakan alat hydrometer
Tanah.
POKOK BAHASAN POKOK BAHASAN NO. AYAKAN AYAKAN (mm)
1. Analisa ayakan
BAHASAN BAHASAN A. Umum. B T j an 4 4.75 6 3.35 8 2.36 B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test. 1 A li 10 2.00 20 0.85 30 0.60 1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa Hidrometer 3 K 40 0.425 50 0.30 60 0.25 CATATAN :NO. 4 BERARTI DALAM 1 INCI PERSEGI ADA
3. Kurva Distribusi D. Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah 80 0.18 100 0.15 140 0.106 4 LUBANG. Tanah. 170 0.088 200 0.075
POKOK BAHASAN POKOK BAHASAN BAHASAN BAHASAN A. Umum. B T j an B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test. 1 A li 1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa Hidrometer 3 K 3. Kurva Distribusi D. Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah
Gambar 3.1.
Ayakan
US-Standard
Tanah.POKOK BAHASAN POKOK BAHASAN
2. Analisa Hydrometer
BAHASAN BAHASAN A. Umum. B T j anFaktor-faktor yang mempengaruhi kecepatan mengendap : bentuk, ukuran, dan berat butiran tanah.
B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test. 1 A li 1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa Hydrometer 3. Kurva Distribusi D. Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah.
Gambar 3.2b Gelas ukur Gambar 3.2a Alat Hydrometer
POKOK BAHASAN POKOK BAHASAN Gambar 3.2c BAHASAN BAHASAN A. Umum. B T j an
Sketsa alat Hydrometer dan alat Hydrometer didalam gelas ukur yang
berisi tanah yang sudah
B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test.
1 A li
dicampur dengan cairan standard. 1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa Hidrometer 3. Kurva Gambar 3.2d Percobaan Distribusi D. Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah. Percobaan Hydrometer di laboratorium Mekanika Tanah
POKOK BAHASAN POKOK BAHASAN
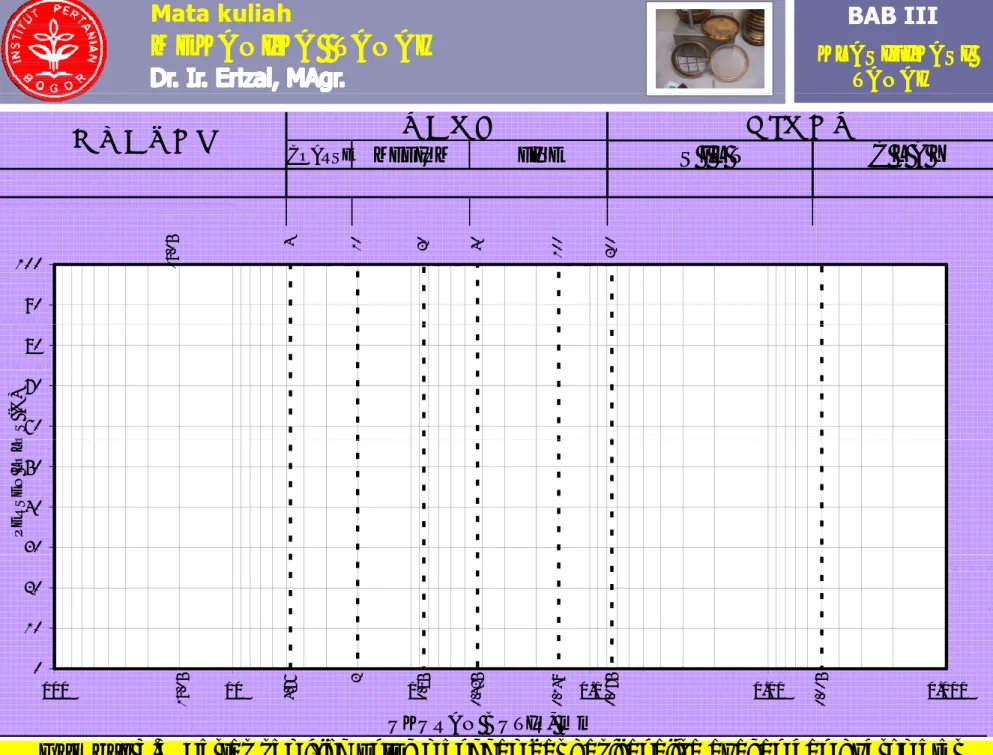
3. Kurva distribusi ukiran butiran
BAHASAN BAHASAN
A. Umum. B T j an
(grain size distribution)
B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test.
1 A li
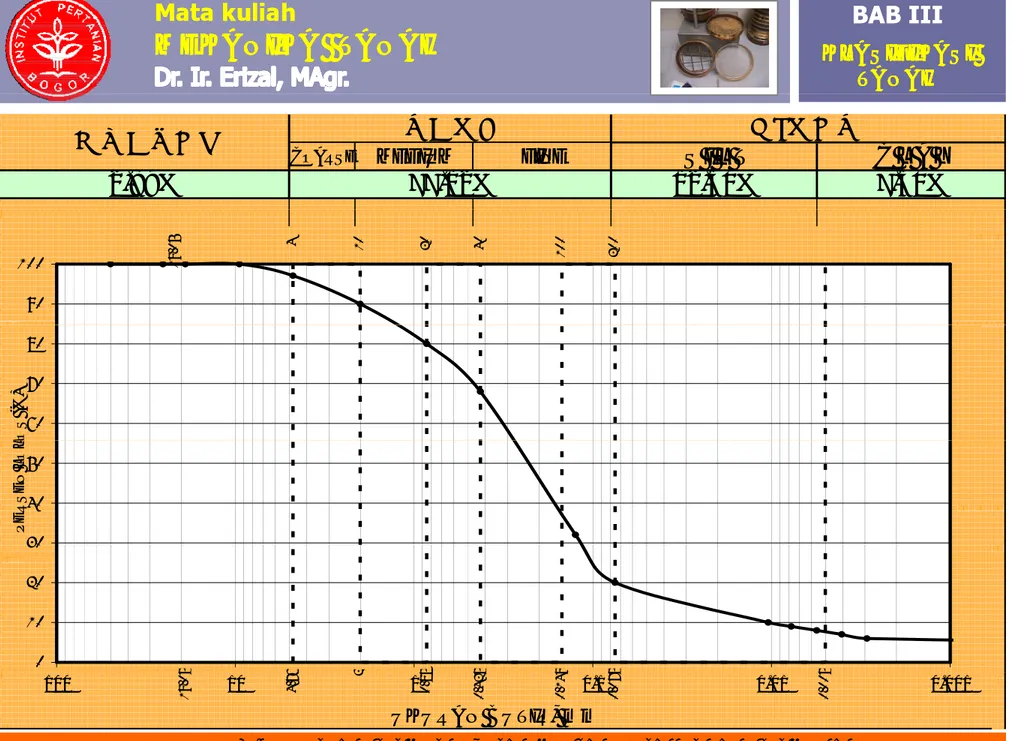
a. Hasil analisa ayakan dan analisa Hydrometer digambarkan dalam kertas semi-log (Gambar 3.3);
1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa
Hidrometer
3 K
b. Kurva hasil test diberikan dalam Gambar 3.4
c. Kurva pada Gambar 3.4 dinamakan:
KURVA DISTRIBUSI UKURAN BUTIRAN
(G S S O ) 3.Kurva
Distribusi
D. Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah (GRAIN SIZE DISTRIBUTION)
COARSE MEDIUM FINE S I L T C L A Y # 2 0 # 4 0 # 1 0 0 # 2 0 0 # 4 # 10 19 .0 5 90 100 60 70 80 O S ( % ) 30 40 50 PE RSE N LO L O 0 10 20 UKURAN BUTIR, mm 4. 76 2 0. 85 0. 42 5 0. 14 9 0. 07 5 0. 00 5 19 .0 5 0 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 100
COARSE MEDIUM FINE S I L T 12.50% C L A Y 77.12% 2.89% 7.50% # 10 # 4 # 2 0 0 # 1 0 0 # 40 # 20 19 .0 5 90 100 60 70 80 L OS ( % ) 30 40 50 PER S E N LO L 6 2 5 5 9 5 5 5 0 10 20 UKURAN BUTIR, mm 4. 7 6 2 0. 8 5 0. 42 5 0. 14 9 0. 07 5 0. 00 5 19. 0 5 0.001 0.01 0.1 1 10 100
POKOK BAHASAN POKOK BAHASAN
3. Kurva distribusi ukiran butiran (lanjutan)
BAHASAN BAHASAN
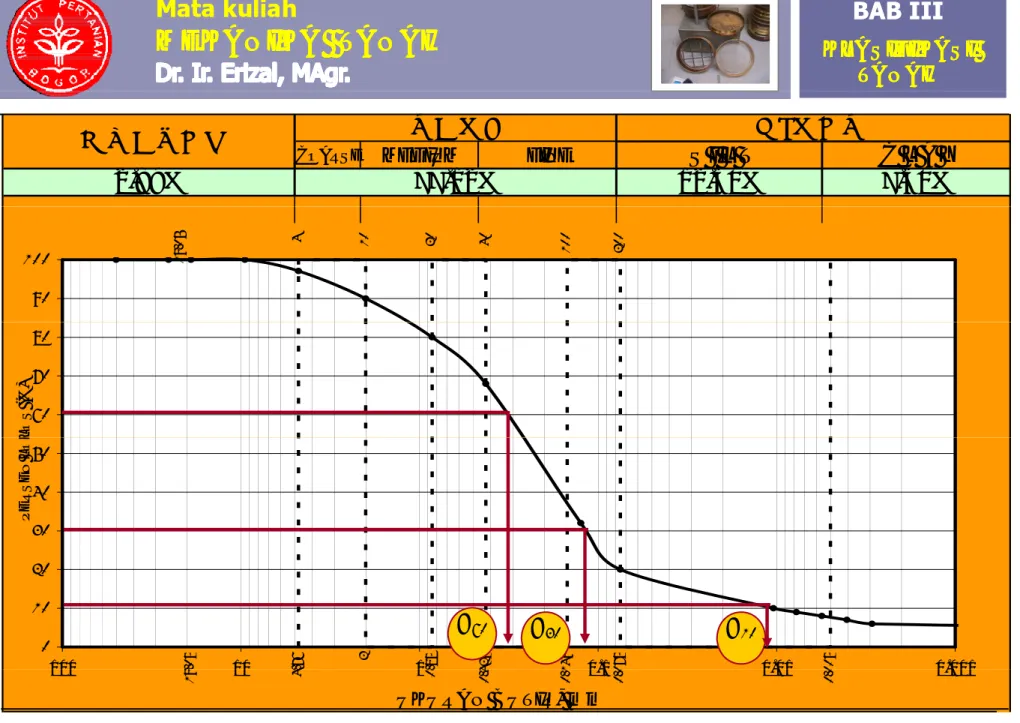
d. Tiga parameter dapat ditentukan dari kurva grain size distribution (lihat Gambar 3.5):
- UKURAN EFEKTIF (EFFECTIVE SIZE)
A. Umum. B T j an
UKURAN EFEKTIF (EFFECTIVE SIZE)
D10 : Diameter butiran dimana 10% dari Total butiran
lolos lebih kecil dari diameter tersebut.
- KOEFISIEN KESERAGAMAN (UNIFORMITY COEF.) =
C
uB. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test. 1 A li 60
D
C
u=
- KOEFISIEN GRADASI (GRADATION COEF.) =
C
c2 30
D
C
=
1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa Hidrometer 3 K 10D
uD
30 : Diameter butiran dimana 30% dari total butiran lolos /lebih kecil dari diameter tersebut.
10 60
x
D
D
C
c 3.Kurva Distribusi D. Sistem Klasifikasi TanahD
60 : Diameter butiran dimana 60% dari total butiran lolos /lebih kecil dari diameter tersebut.
COARSE MEDIUM FINE S I L T 12.50% C L A Y 77.12% 2.89% 7.50% # 10 # 4 # 2 0 0 # 1 0 0 # 40 # 20 19 .0 5 90 100 60 70 80 L OS ( % ) 30 40 50 PE RSE N L O L .76 2 .85 425 149 075 005 .0 5 0 10 20 0 001 0 01 0 1 1 10 100 D10 D30 D60 UKURAN BUTIR, mm 4 . 0. 0. 4 0. 1 0. 0 0. 0 19 10 1 0.1 0.01 0.001 100
POKOK BAHASAN POKOK BAHASAN
3. Kurva distribusi ukiran butiran (lanjutan)
BAHASAN BAHASAN
A. Umum. B T j an
e. Bentuk Kurva dapat dikelompokkan dalam 3 group
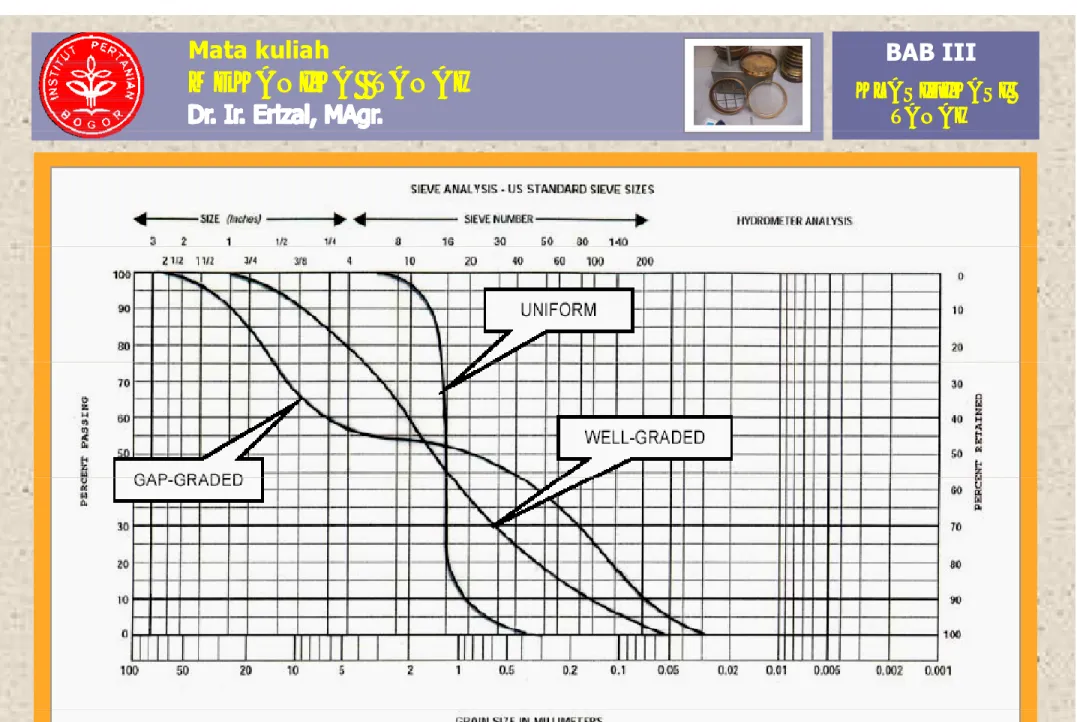
B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test. 1 A li p p g p (lihat Gambar 3.6):
- GAP GRADED (CURVA A) :
Tanah dimana 1 atau lebih ukuran butir tidak ada.
1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa
Hidrometer
3 K - WELL GRADED (CURVA B) :
Tanah dimana ukuran butirannya terbagi merata dalam suatu batasan yang luas (hampir semua
3.Kurva Distribusi D. Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah y g ( p
ukuran butir ada).
- UNIFORM GRADED (CURVA C) :
POKOK BAHASAN POKOK BAHASAN BAHASAN BAHASAN A. Umum. B T j an B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test. 1 A li 1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa Hidrometer 3 K 3.Kurva Distribusi D. Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah Gambar 3 6b Tanah. Gambar 3.6b.
• Ukuran partikel tanah: halus kasar
Ukuran partikel tanah: halus kasar
• Klasifikasi partikel tanah:
•
Segi-tiga tekstur Æ untuk pertanian
1. International Society of Soil Science (ISSS)
2. US Department of Agriculture (USDA)
Contoh:
• Determined by the relative
Determined by the relative
proportion of sand, silt and clay
Surface Area
Surface Area
Charge
Charge
Sand
Sand
50 cm
50 cm
2
2
/g
/g
none
none
Silt
Silt
500 cm
500 cm
2
2
/g
/g
none
none
Silt
Silt
500 cm
500 cm
2
2
/g
/g
none
none
Clay
Clay
5,000,000 cm
5,000,000 cm
2
2
/g
/g
negative
negative
barrel
plate
coin
Silt
- feels floury
(< 0.002 mm)Clay
- feels sticky
Sand
- feels gritty
(2 00 - 0 05 mm) (0.05 - 0.002 mm) (< 0.002 mm) 43 (2.00 0.05 mm)Clay
Percent
Silty Clay Silty Clay Clay Sandy ClayClay
Percent
Silt
S ty C ay Loam C ay Loam Sandy Clay Loam Loam Silt Loam SandySilt
Silt Sandy Loam Sand 44Percent Sand
Loamy
Sand
POKOK BAHASAN POKOK BAHASAN
D. Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah
BAHASAN BAHASAN
A. Umum. B T j an
Sistem klasifikasi yang di pakai :
B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test.
1 A li
1. USCS( Unified Soil Classification System)
Gambar 3.7 & Tabel 3.1
2. AASHTO ( American Association of State
Highway and Transportation Officials)
1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa
Hidrometer 3 K
Gambar 3.9 & Tabel 3.2.
Persamaan USCS & AASHTO
1 Kl ifik i t h d i ti USCS d 3.Kurva
Distribusi D. Sistem
Klasifikasi Tanah
1. Klasifikasi tanah dengan sistim USCS dan AASHTO
menggunakan dasar yang sama yaitu:
- ukuran butir, dan - plastisitas tanah
2. USCS dan AASHTO memisahkan tanah kedalam 2 kategori :g Tanah.
- tanah berbutir kasar ( coarse grained) - tanah berbutir halus ( fine grained)
POKOK BAHASAN POKOK BAHASAN
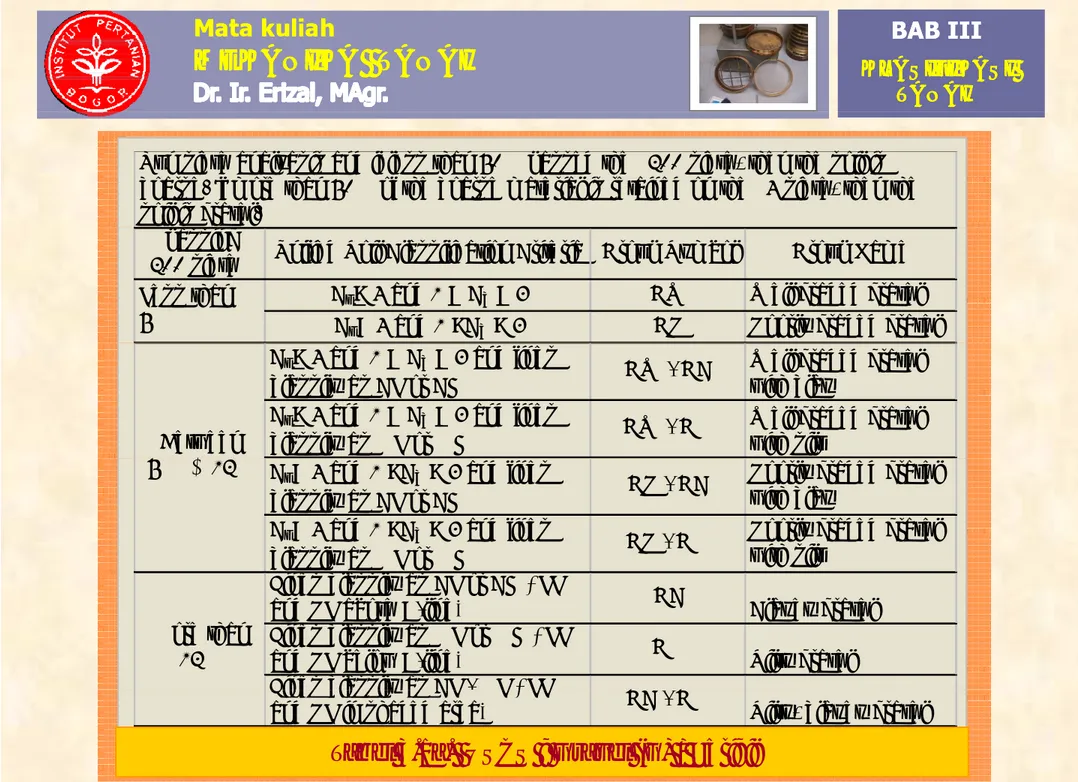
D. Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah (Lanjutan)
BAHASANBAHASAN A. Umum. B T j anPERBEDAAN USCS & AASHTO
(
j
)
B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test. 1 A liURAIAN PERBEDAAN USCS AASHTO
1. Tanah dikatakan berbutir kasar bila Lolos ayakan no 200 ≤ 50% Lolos ayakan no 200 ≤ 35% 1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa Hidrometer 3 K 200 ≤ 50% no 200 ≤ 35% 2. Ayakan yang dipakai untuk
memisahkan pasir dan kerikil
Ayakan no 4 Ayakan no 10
3. Perbedaan tanah-2 yang gravelly, Dibedakan Tidak
3.Kurva Distribusi D. Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah y g g y
sandy, silty, dan clayey soil secara jelas dibedakan 4. Klasifikasi untuk tanah organik OL, OH, Pt Tidak diberikan
5. Arti dari simbol tanah Lihat penjelasan Tidak ada Tanah. 5. Arti dari simbol tanah Lihat penjelasan Tidak ada
POKOK BAHASAN POKOK BAHASAN
Penjelasan 2 simbol huruf pada USCS
BAHASAN BAHASAN
A. Umum. B T j an
1. Huruf PERTAMA menggambarkan komponen utama dari tanah, yaitu:
a. Tanah berbutir kasar: G = Gravel / Kerikil
B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test. 1 A li S = Sand / Pasir
b. Tanah berbutir halus M = Silt / Lanau
C = Clay/ Lempung
c. Tanah organik O = Organik
1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa Hidrometer 3 K Pt = Peat .
2. Huruf KEDUA menggambarkan keadaan tanah:
3.Kurva Distribusi D. Sistem
Klasifikasi Tanah
a. Bergradasi baik / well graded (W) b. Bergradasi jelek / poorly graded (P) c. Tercampur lanau / kelanauan / silty (M)
d. Tercampur lempung / kelempungan / clayey (C)
Tanah.
e. Mempunyai plastisitas rendah / low plasticity (L) f. Mempunyai plastisitas tinggi / high plasticity (H)
POKOK BAHASAN POKOK BAHASAN
1. SISTIM KLASIFIKASI TANAH USCS
BAHASAN BAHASAN
A. Umum. B T j an
Run sieve analysis
B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test. 1 A li < 50% pass #200 > 50% pass #200 1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa Hidrometer 3 K > 50% of coarse fraction retained on #4 < 50% of coarse fraction retained on #4
Use plasticity chart (Fig. 3.14) 3.Kurva Distribusi D. Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah
Gravel Sand Silt, organic,or clay
Tanah.
POKOK BAHASAN POKOK BAHASAN
G
BAHASAN BAHASAN A. Umum. B T j an > 12 % pass #200 <5% pass #200 5-12% pass #200 B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test. 1 A li pass #200 GC GM pass #200 G W G P pass #200 GW-GC GW-GM 1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa Hidrometer 3 K GM GC-GM U d ti G P GW GM GP-GC GP-GM 3.Kurva Distribusi D. Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah Use gradation curve and plasticitychart to designate (Gb.3.8) Use gradation curve to designate Use gradation curve to designate Tanah.
coarse. If more than 50% of the coarse material is retained on the #4 sieve, then the soil is gravel.
Cu> 4 and 1 < Cc < 3 GW Well graded gravel Cu< 4 and 1 >Cc > 3 GP Poorly graded gravel % passing
#200 sieve Unified Soil Classification Criteria Group Symbol Group Name Less than
5%
Cu> 4 and 1 < Cc < 3 and fines
classify as CL or CH GW - GC
Well graded gravel with clay
Cu> 4 and 1 < Cc < 3 and fines
classify as ML or MH GW - GM
Well graded gravel with silt
Between
Cu< 4 and 1 >Cc > 3 and fines
classify as CL or CH GP - GC
Poorly graded gravel with clay
Cu< 4 and 1 >Cc > 3 and fines
classify as ML or MH GP - GM
Poorly graded gravel with silt
5 % & 12%
Fines classify as CL or CH ( LL
and PL above A-line) GC Clayey gravel
Fines classify as ML or MH ( LL
and PL below A-line) GM Silty gravel
Fines classify as CL - ML ( LL More than
12%
Fines classify as CL ML ( LL
and PL in shaded area) GC - GM Silty, clayey gravel
POKOK BAHASAN POKOK BAHASAN
S
BAHASAN BAHASAN A. Umum. B T j an > 12 % pass #200 <5% pass #200 5-12% pass #200 B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test. 1 A li SC SM SW SP SW-SC SW-SM 1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa Hidrometer 3 K SC-SM SP-SC SP-SM 3.Kurva Distribusi D. Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah Use gradation curve and plasticity chart to designate Use gradation curve to designate Use gradation curve to designate Tanah.coarse. If less than 50% of the coarse material is retained on the #4 sieve, then the soil is sand
Cu> 6 and 1 < Cc < 3 SW Well graded sand Cu< 6 and 1 >Cc > 3 SP Poorly graded sand
Group Symbol Group Name Less than
5%
% passing
#200 sieve Unified Soil Classification Criteria
Cu> 6 and 1 < Cc < 3 and fines
classify as CL or CH SW - SC
Well graded sand with clay
Cu> 6 and 1 < Cc < 3 and fines
classify as ML or MH SW - SM
Well graded sand with silt
Between
Cu< 6 and 1 >Cc > 3 and fines
classify as CL or CH SP - SC
Poorly graded sand with clay
Cu< 6 and 1 >Cc > 3 and fines
classify as ML or MH SP - SM
Poorly graded sand with silt
5 % & 12%
y
Fines classify as CL or CH ( LL
and PL above A-line) SC Clayey sand Fines classify as ML or MH ( LL
and PL below A-line) SM Silty sand Fi l if CL ML ( LL
More than 12%
Fines classify as CL - ML ( LL
and PL in shaded area) SC - SM Silty, clayey sand
Silt, organic, POKOK BAHASAN POKOK BAHASAN g , or clay LL < 50% LL > 50% BAHASAN BAHASAN A. Umum. B T j an LLR>0.75 LLR<0.75 LLR<0.75 LLR>0.75 B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test. 1 A li LL and PI plot below A-line LL and PI plot in shaded area LL and PI plot above A-line LL and PI plot below A-line LL and PI plot above A-line 1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa Hidrometer 3 K ML CL-ML CL OL OH MH CH 3.Kurva Distribusi D. Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah Gambar 3.7d.
Sistem Klasifikasi USCS untuk lanau, organik, dan lempung
Run sieve analyasis and if less than 50% passed the #200 sieve, then the soil is fine.Run liquid limit and plastic limit tests on materials passing #40 sieve. Note that ASTM requires that the liquid limit be determined using oven dried and undried samples The ratio of the
LLR < 0.75 OL Organic silt or clay LLR > 0 75 and PI < 4 or plots
that the liquid limit be determined using oven dried and undried samples . The ratio of the dried to the undried value is called the liquid limit ratio LLR.
Liquid Limit Unified Soil Classification Criteria Group Symbol Group Name LLR > 0.75 and PI < 4 or plots
below A-line in Fig. ML Inorganic silt LLR > 0.75 and PI > 7 or plots
above A-line in Fig. CL Lean clay LLR > 0.75 and PI > 7 and LL and
PI in shaded area of Fig CL-ML Silty clay Less than
50%
PI in shaded area of Fig. Silty clay
LLR < 0.75 OH Organic silt or clay LLR > 0.75 and PI plots below
A-line in Fig. MH Elastic silt LLR > 0.75 and PI plots on or
b A li i Fi CH F t l More than
50%
above A-line in Fig. Fat clay
PEAT
Highly organic soils. Normally more than 20% by weight is organic
Primary organic matter, dark in Pt P t
Primary organic matter, dark in
color and organic odor Pt Peat
POKOK BAHASAN POKOK BAHASAN BAHASAN BAHASAN A. Umum. B T j an B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test. 1 A li 1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa Hidrometer 3 K 3.Kurva Distribusi D. Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah Tanah.
Gambar 3.8. Plasicity Chart
POKOK POKOK 2. SISTIM KLASIFIKASI TANAH AASHTO <50% <30% pass # 40 <50% pass #10 PI is less than 6 A-1-a BAHASAN BAHASAN A. Umum. B T j an Pass #40 >51%
Pass <10% pass #200 A-3 PI is less than 6 <25% pass #200 <50% pass # 40 PI is less than 6 A-1-b <25% #200 Run LL and PL on material passing # 40 ≤ 35% B. Tujuan Klasifikasi Tanah. C. Jenis Test. 1 A li Pass #40 <10% pass #200 A-3 Run LL and PL on material ≤ 35% pass PI<10 A-2-4 LL<40 LL>41 A-2-5 pass #200 implies granular 1. Analisa Ayakan 2.Analisa Hidrometer 3 K material passing # 40 pass #200 PI>11 LL<40 A-2-6 LL>41 A-2-7 Run sieve analysis PI<10 LL<40 A-4 3.Kurva Distribusi D. Sistem Klasifikasi Tanah > 36% pass #200 implies silt-clay PI>11 PI<10 LL>41 A-5 LL<40 A-6 PI ≤ LL-30 A-7-5 Run LL and PL on material passing # 40 Tanah. LL>41 or PL ≥ 30 A 7 5 PI > LL-30 or PL < 30 A-7-6
Figure 3.9. Flow chart showing
General classification
A 2
Granular materials (35% or less of total sample passing No.200) A 1
A-1-a A-1-b A-2-4 A-2-5 A-2-6 A-2-7
Sieve analysis (percent passing)
A-3 A-2
Group classification A-1
No.10 50 max
No.40 30 max 50 max 51 min
No.200 15 max 25 max 10 max 35 max 35 max 35 max 35 max
Characteristic of fraction passing No.40
Liquid Limit 40 max 41 min 40 max 41 min
Plasticity Index NP 10 max 10 max 11 min 11 min
Usual types of significant
6 max Stone fragment Usual types of significant
constituent materials Fine sand
General subgrade rating
Silty or clayey gravel and sand Stone fragment,
gravel and sand
Excellent to good
General classification
A 7
Silt-clay materials (More than 35% of total sample passing No.200)
A-7 A-7-5* A-7-6^ Sieve analysis (percent
)
Group classification A-4 A-5 A-6
passing) No.10 No.40
No.200 36 min 36 min 36 min 36 min
Characteristic of fraction passing No.40
Liquid Limit 40 max 41 min 40 max 41 min
Plasticity Index 10 max 10 max 11 min 11 min
Plasticity Index 10 max 10 max 11 min 11 min
Usual types of significant constituent materials
General subgrade rating
Clayey soils Fair to poor
Silty soils
* For A-7-5, PI ≤ LL - 30