559 CHARACTERISTICS OF PEAT SOIL IN HOUSING AREA, TANJUNG
API-API, BANYUASIN – INDONESIA
Andriani1*, Eddy Ibrahim1, Dinar Da Putranto1, Azhar Choliq1
1
Department of Environmental Sciences, Sriwijaya University, Palembang, Indonesia
ABSTRACT
Peat soil is an accumulation of plant remnants with the condition of high natural moisture content, so peat has marginal characteristics and strongly influenced by the moisture content, the level of decomposition and organic matter content. Determination of Tanjung Api-Api as a special economic area will trigger the growth of housing and infrastructure in these locations. The development of infrastructure to support the special economic zones in the area of Tanjung Api-Api is constrained by soil type in the region. This study aimed to determine of the characteristics peat soil in Tanjung Api-Api area. Tests performed at the laboratory include physical and mechanical characteristics of peat soil with condition disturbed and undisturbed. The results showed that the development of infrastructure in the peat soil caused environmental problems, particularly environmental degradation in the region. The low bearing capacity of peat caused damage to several roads and housing floor of citizens. To overcome these problems needs to be the choice of type material embankment and foundation construction by the characteristics of peat soil.
Keywords: Bearing capacity; Characteristic of peat; Environmental degradation; Housing area.
1. INTRODUCTION
High population growth resulting in limited availability of land that can be used as a residential area. Limitations of land to agricultural, plantations, housing and industrial may cause reclamation on wetlands. Development of the wetlands began in 1980 through the transmigration program outside Java, the island of Sumatra and Kalimantan. Most areas in Sumatra and Kalimantan are consist of wetlands highly influenced by the tidal conditions and mostly of soil types consist of peat. Based on research by using a combination of analysis Landsat TM data and soil survey conducted by Wahyunto et al. (2011), peatland area in Indonesia is about 14.9 million ha, scattered in Sumatra, Kalimantan and Papua. Reclamation of wetlands conducted to obtain new land used as housing areas, agriculture, plantation and industry. The Construction over peat soil will cause various problems because the peat has a low shear strength, high deformation and coefficient of consolidation (cv) is low (Munro, 2005; Haan & Kurse, 2006; Kazemian et al., 2011; Al-Ani et al., 2013a). The high of organic content and moisture content causes great compression index (cc) on peat soil (Huat, 2006; Kazemian et al., 2011; Kalantari, 2013; Al -Ani, et al., 2013b).
The low of bearing capacity of peat could be seen from the characteristics of small bulk density and capability of high water absorbed (Wahyunto et al., 2010). The important
560 factor to determination of peat mechanical characteristics is level of peat decomposition and initial void ratio (eo) (Badv & Sayadian, 2011). The physical characteristics of peat would affect mechanical characteristics of peat (Aminur et al., 2011). The high of organic content caused by increasing the moisture content, porosity, compressibility and cohesion conversely the density would be lower (Nie, 2012; Warburton, 2015; Kononen et al., 2015). The decomposition level would determine the characteristics of peat soil. According to Rahman and Ming (2015), there were three ways to be done to determine the characteristics of peat namely: (1) classify of peat soil based weathering, (2) determine of moisture content and particle size distribution and (3) determine of pH, specific gravity and Loss on Ignition (LOI), while the testing of Atterberg's Limits is not too important to do. The level of peat decomposition and moisture content will affect the compression index (Huat, 2006; Duraisamy et al., 2007a; Kolay et al., 2012; Kalantari, 2013). The shear strength of peat was different compared to the mineral soil, because there are the fiber and organic content in the peat soil so it difficult to determine the shear strength of peat. The shear strength of peat is low greatly could be landslides (Long, 2005). Huat et al. (2014), shear strength of fibrous peat greater than amorphous peat soil.
The rapid housing construction in the wetlands causes environmental degradation, for the decreased bearing capacity of the environment due to rapid development. Determination of Tanjung Api-Api as industrial zones and international port (special economic zones) will cause to the development of housing in the wetland areas. Geographically, the area of Tanjung Api-Api is in the wetlands. The soil type in the area of Tanjung Api-Api mainly consists of peat and clay. Characteristics of the soil significantly affect the bearing capacity and environmental capacity, investigation of the properties of soil needs to be done to determine the suitability of land to avoid environmental degradation. Environmental problems often occurs in peaty areas such as forest fires, peat subsidence and rising carbon emissions as a result of the development of wetlands (Soewandita 2008; Wahyunto et al, 2010; Suryadiputra, 2012; Khusyairi, 2014). Reclamation of wetlands as housing areas may cause a reduction in water catchment areas, so that when the tidal of rapid rise and inundation the citizen housing (Dahliani, 2012; Rijal & Aldy, 2012). Reclamation of peat land would cause changes in the physical characteristics of peat. To achieve sustainability in peat lands required different methods of land management in accordance with the characteristics of peat (Kononen et al., 2015). Housing construction at peat lands should pay attention to characteristics of peat so that it could be determined sustainability of method construction to scheme housing, some of the methods that can be used in housing areas of peat include: displacement and replacement, preloading and vertical drain, lightweight foundation system, etc. (Duraisamy et al ., 2007b).
2. METHOD OF EXPERIMENT
561 natural moisture content with the properties of peat founded, so could be revealed the effect of the level of decomposition and the physical properties of peat.
(a) (b)
Figure 1 Peat Soil at Tanjung Api-Api Area (a) Condition of peat soil before sampling
(b) Condition of peat soil after sampling (disturbed condition)
Test of consolidation one dimension was performed by using Odometer on undisturbed peat samples. All tests performed in accordance with ASTM D2435 standard. The purpose of tests was to determine the time of consolidation (Tv) and settlement value (Sc) on peat soil. Water content is maintained by use of plastic. Initial loading was given on samples for 24 hours and record of changes in the deformation that occurs after the initial loading after 24 hours then performed additional burden gradually with load increment ratio (LIR) was 2 times, start of 25, 50, 100, 200, 400 kPa every interval 24 hours . The sample was drained from top and bottom. From consolidation tests will be obtained curve the relationship between the compression (%) and time (minutes). From the curve can then is calculated coefficient of consolidation (cv) using the formula below:
Besides the compression - time curve also obtained curve the relationship between the void ratio (eo) and effective pressure (logarithmic scale). From this curve will be obtained values of coefficient compression (cc) by using the slope of the straight section of the curve of e versus log p'. Formula (2) below is used to find the value of
562 and mechanical properties of peat. Characteristics of peat gave influence toward environment degradation on peat lands especially on housing area.
3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The results of physical and mechanical properties of peat are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 the Result of Physical and Mechanical Properties of Peat Tanjung Api-Api
Characteristics Range Value
Natural moisture content
Coefficient Compression (cc )
Coefficient of Consolidation, cv (m2/year) that it can be classified as peat with shallow depth and partly of peat as medium depth. Meanwhile, according to Macfarlene and Radforth (1965), peat soil at Tanjung Api-Api is amorphous peat (because the fiber content of less than 20%). According to Von Post scale (1926), including the H8 - H10 and according ASTM D - 4427, peat soil in Tanjung Api-Api area classified as organic soil because average of organic content < 75 %, the decomposition level is sapric because fiber content of 6.78% - 19.17%; the ash content is high (> 15%); formed of ferns and ability of absorb water is small.
3.2. The physical and mechanical properties of peat soil
563
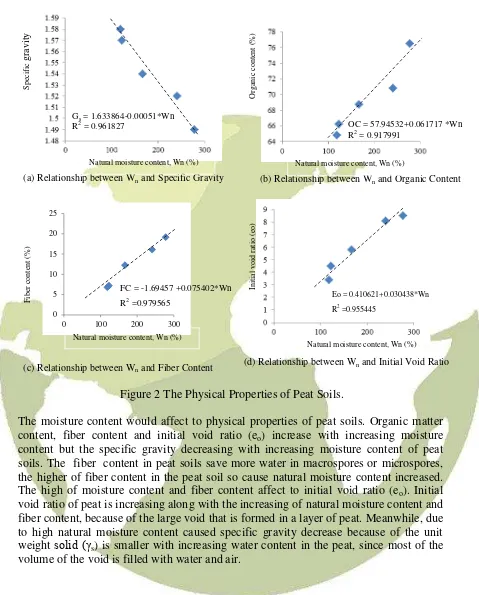
(a) Relationship between Wn and Specific Gravity (b) Relationship between Wn and Organic Content
0
(c) Relationship between Wn and Fiber Content (d) Relationship between Wn and Initial Void Ratio
Figure 2 The Physical Properties of Peat Soils.
The moisture content would affect to physical properties of peat soils. Organic matter content, fiber content and initial void ratio (eo) increase with increasing moisture content but the specific gravity decreasing with increasing moisture content of peat soils. The fiber content in peat soils save more water in macrospores or microspores, the higher of fiber content in the peat soil so cause natural moisture content increased. The high of moisture content and fiber content affect to initial void ratio (eo). Initial void ratio of peat is increasing along with the increasing of natural moisture content and fiber content, because of the large void that is formed in a layer of peat. Meanwhile, due to high natural moisture content caused specific gravity decrease because of the unit weight solid (γs) is smaller with increasing water content in the peat, since most of the volume of the void is filled with water and air.
564
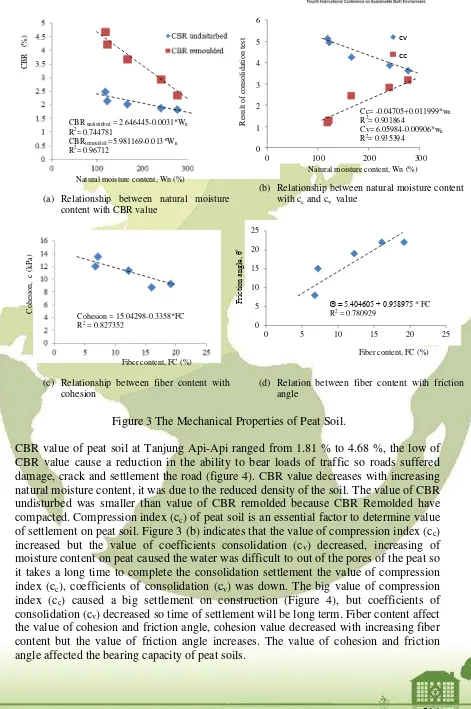
(a) Relationship between natural moisture content with CBR value
(b) Relationship between natural moisture content with cc and cv value
(c) Relationship between fiber content with cohesion
(d) Relation between fiber content with friction angle
Figure 3 The Mechanical Properties of Peat Soil.
CBR value of peat soil at Tanjung Api-Api ranged from 1.81 % to 4.68 %, the low of CBR value cause a reduction in the ability to bear loads of traffic so roads suffered damage, crack and settlement the road (figure 4). CBR value decreases with increasing natural moisture content, it was due to the reduced density of the soil. The value of CBR undisturbed was smaller than value of CBR remolded because CBR Remolded have compacted. Compression index (cc) of peat soil is an essential factor to determine value of settlement on peat soil. Figure 3 (b) indicates that the value of compression index (cc) increased but the value of coefficients consolidation (cv) decreased, increasing of moisture content on peat caused the water was difficult to out of the pores of the peat so it takes a long time to complete the consolidation settlement the value of compression index (cc), coefficients of consolidation (cv) was down. The big value of compression index (cc) caused a big settlement on construction (Figure 4), but coefficients of consolidation (cv) decreased so time of settlement will be long term. Fiber content affect the value of cohesion and friction angle, cohesion value decreased with increasing fiber content but the value of friction angle increases. The value of cohesion and friction angle affected the bearing capacity of peat soils.
Natural moisture content, Wn (%)
CBR undistrubed = 2.646445-0.0031*Wn
565 Peat soil has the ability to absorbed high of water, drainage of excess on peat soil as a result of settlements can lead to degradation of the environment by reducing the ability of peat to store water so the peat will dry quickly, to reduced water in the peat land, can trigger a peat fire and increasing emissions of greenhouse gases that resulting from the release of methane. The natural moisture content and fiber content of peat would determine the physical and mechanical properties of peat. The higher of natural moisture content and fiber content because physical and mechanical properties of peat is less favorable to building infrastructure and housing. The low of bearing capacity on peat causes the reduction to carrying the large loads. The building of housing and infrastructure on peat is potential to cause damage on the floor of the house, road damage and settlement of foundation (figure 4).
Peat soil characteristics are greatly influences the type of environmental degradation. The natural moisture content and fiber content would determine the physical and mechanical properties of peat soils. The high of natural moisture content cause the rate of degradation is also high, the low level of peat decomposition will be make of the physical and mechanical characteristics of peat soil is less favorable for the development of housing and infrastructure that will require improvement and specific of construction on peat soil, so cause the high cost of building settlements and infrastructure.
(a) (b)
Figure 4 Damage to the floor of the house (a) and the road (b).
4. CONCLUSION
566 5. REFERENCES
Annual Book of ASTM Standard, (1982), Testing of Peat and Organic Soils, Special Technical Publication820, Toronto, Canada.
Annual Book of ASTM Standard, (1994), Construction, Soil and Rocks, Volume 04.08, Section 4, Philadelphia, USA.
Al-Ani, H., Oh, E., Chai, G,. (2013a), Engineering Properties of Peat in Estuarine Enviroment. Foundation and Soft Ground Engineering Conference, Thu Dau Mot Unieversity, ICTDMU-1, Binh Duong.
Al-Ani, H., Oh, E. and Chai, G., (2013b), Characteristics of Embedded Peat in Coastal Environments, International Journal of GEOMATE, Sept, 2013, Vol.5, No. 1 (SI. No.9) ; pp. 609-618.
Aminur, M.R., Kolay, P.K., Taib, S.N.L, et al. (2011), Physical, Geotechnical and Morphological Characteristics of Peat Soils From Sarawak, Journal-The Institution of Engineers, Malaysia,Vol.72, No.4, December 2011.
Badv, K. and Sayadian, T., (2011), Physical and Geotechnical Properties of Urmia Peat, 2011 Pan-Am CGS Geotechnical Conference.
Dahliani, (2012), Konsep Pengolahan Tapak Pemukiman di Lahan Rawa, Banjarmasin. LANTING Journal of Architecture, Vol.1, No. 2 ; pp. 96-105.
Duraisamy ,Y., Huat, B.B.K., Aziz, A.A., (2007a), Engineering Properties and Compressibility Behavior of Tropical Peat Soil, American Journal of Applied Sciences 4 (10), pp. 768-773.
Duraisamy ,Y., Huat, B. B. K., and Aziz, A.A., (2007b), Methods of Utilizing Tropical Peat Land for Housing Scheme, American Journal of Enviromental Sciences 3 (4), pp. 259-264.
Huat, B. B. K., (2006), Deformation and Shear Strength Characteristics of Some Tropical Peat and Organic Soils, Pertanika Journal Science and Technology 14 (1&2), pp. 64-74.
Huat, B.B.K., Prasad, A., Asai, A. and Kazemian, S., (2014), Geotechnics of Organic Soils and Peat, CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group.
Kalantari, B., (2013), Civil Engineering Significant of Peat, Global Journal of Researches in Engineering Civil and Structural Engineering, Volume 13, Issue 2 Version 1.0
Kazemian, S., Huat, B.B.K., Prasad, A.and Barghchi, M., (2011),A State of The Art of Peat: Geotechnical Engineering Perspective, International Journal of the Physical Sciences Vol. 6 (8), pp 1974-1981.
Kolay, P.K., Sii, H.Y.and Taib, S.N.L.,(2012), Compressibility Characteristics of
Tropical Peat Using Rowe Cell Consolidation, World Journal of Engineering 9
(4), pp. 277-284.
Kononen, M., Jauhiainen, J., Laiha, R., et.al., (2015), Physical and Chemical Properties of Tropical Peat Under Stabilised Land Use Mires and Peat, Volume 16 (2015), Article 08, pp. 1–13, http://www.mires-and-peat.net/, ISSN 1819-754X .
Khusyairi, A., (2014), Kajian Lahan Gambut sebagai Calon Lokasi/ Tapak PLTN, Berkala Fisika Vol. 17, No.2. April 2014, pp. 55-60.
567 Munro, N., (2005), Dealing With Bearing Capacity Problems on Low Volume Roads
Constructed on Peat, ROADEX II Northern Periphery.
Nie, L., Lv, Y. and Li, M., (2012), Influence of Organic Content and Degree of Decomposition on The Engineering Properties of a Peat Soil in NE China, Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology and Hydrogeology, 45, 435 –446. DOI: 10.1144/qjegh2010-042.
Rahman, J.A. and Ming, C.C., (2015), Physico- Chemical Characterization of Peat at Different Decomposition Levels, Electronic Journal Geotechnical Engineeering (EJGE), Vol 20 (2015), Bund.9, pp. 4011-4019.
Rijal, M., Aldy, P., (2012), Dampak Perubahan Hidrologis dan Perkembangan Tata Guna Lahan pada Permukiman di Lahan Basah di Kota Dumai, Jurnal Arsitektur Universitas Bandar Lampung ,Vol.1, No. 3.
Soewandita, H., (2008), Studi Muka Air Tanah Gambut dan Implikasinya terhadap Degradasi Lahan pada Beberapa Kubah Gambut di Kabupaten Siak, JAI Vol. 4 No.2, pp. 103.
Suryadiputra, I.Y.N., (2012), Dampak Penabatan terhadap Pulihnya Hutan Gambut di Lokasi Blok –A Eks PLG, Warta Konservasi Lahan Basah Volume 20, No.4, Oktober 2012. 108.
Wahyunto, Dariah, A. and Agus, F, (2010), Distribution, Properties, and Stock of Indonesian Peatland, Proceeding of International Workshop on Evaluation and Sustanaible Management of Soil Carbon Sequestration in Asian Countries. Bogor, Indonesia. Sept. 28-29, 2010.
Wahyunto, Nugroho, L., Ritung, S., Sulaeman, Y., (2011), Indonesian Peatland Map : Method, Certainy and Uses. Indonesian Center for Agricultural Land Resources Research and Development. Bogor.