Nurun Nayiroh, M.Si
Pertemuan ke 9MK TRANSFORMASI FASA
Hardness
Brinell, Rockwell
Yield Strength
Tensile Strength
Ductility
% Elongation
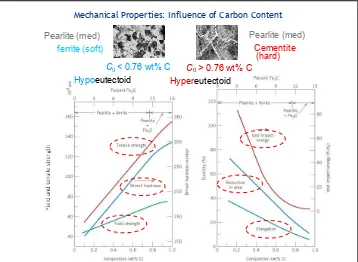
Mechanical Properties: Influence of Carbon Content
Gambar 1. Pearlit, cementit, dan ferit
Sementit bersifat lebih keras dan lebih rapuh dari perlit karena itu dengan menaikan fraksi Fe3C pada baja sementara elemen lain konstan maka material akan lebih keras dan lebih kuat, grafik sifat mekanik pearlit bisa dilihat pada Gambar 1. Ketebalan lapisan pearlit sementit juga mempengaruhi sifat mekanik sifat bahan.
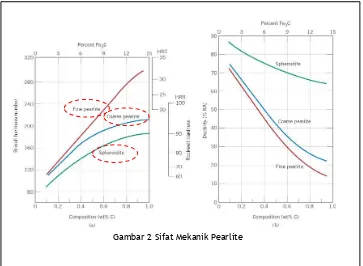
Pearlit halus lebih keras dan kuat dibandingkan dengan pearlit kasar. Hal ini dperlihatkan secara grafik pada Gambar 2. Alasan kenapa pearlit mempunyai sifat ini dikarenakan fase sementit lebih kuat dan kaku dibandingkan ferit yang lebih lunak sehingga bisa menahan deformasi dan dengan kata lain sementit sebagai penguat ferit.
Pearlite halus akan lebih kuat di bandingkan dengan pearlit kasar karena butiran pearlit halus lebih banyak sehingga luas batas fase perunit volume akan lebih besar sehingga
Gambar 2 Sifat Mekanik Pearlite
Spheroitide mempunyai kekuatan dan kekerasan
dibawah pearlit. Fenomena ini bisa diterangkan
dengan metode penguatan oleh sementit dan
hambatan gerakan dislokasi.
Luas permukaan batas butir spherodit pesatuan
volume lebih sedikit dari pearlit sehingga
kekuatannya dan kekerasannya lebih rendah.
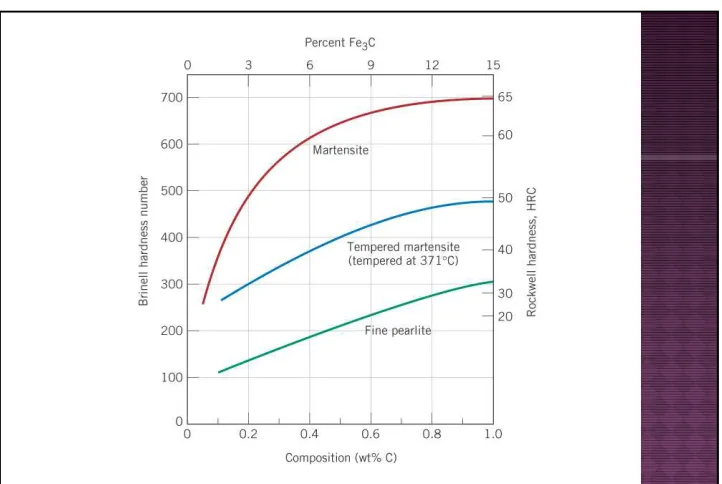
Dari bagian bentuk struktur mikro paduan baja,
martensit adalah yang paling kuat dan keras
namun paling rapuh.
Kekerasannya tergantung kandungan karbon.
Pengaruh kandungan karbon terhadap kekerasan
martensit bisa dilihat pada Gambar 3.
Kekuatan dan kekerasan martensite tidak
dikaitkan dengan struktur mikro tetapi lebih
dikaitkan dengan efektifitas atom karbon yang
larut dalam bentuk interstisi yang akan
menghalangi gerakan dislokasi dan juga karena
sistem slip yang lebih sedikit untuk kristal BTC.
Martensit bersifat keras sehingga sebagian besar tidak
bisa dipakai aplikasi.
Disamping itu tegangan internal karena proses quencning
juga memberikan efek perlemahan.
Ketangguhan dan keuletan martensit bisa ditingkatkan
dan tegangan internal bisa dibuang dengan cara
perlakuan panas yang disebut tempering.
Tempering dilakukan dengan memanaskan baja martensit
sampai temperatur di bawah eutectoid pada periode
waktu tertentu. Biasanya tempering dilakukan pada
temperatur antara 250 650 0C. Tegangan internal akan
hilang pada suhu ± 200
0C.
Proses tempering akan membentuk “tempered
maetensite”.
martensite (bct, satu fase)
→
→
→
→
tempered martensite (α + Fe3c)Foto struktur mikro tempered martensite
sama dengan spheroidit hanya partikel
sementit lebih banyak dan lebih kecil.
Tempered martensit mempunyai sifat sekeras
dan sekuat matensit namun ketangguhan dan
keuletan lebih baik.
Tempering reduces internal stresses caused by quenching. The small particles are cementite; the matrix is α%ferrite
Gambar 4. Tensile dan yield strength dan ductility versus tempering temperature untuk paduan baja yang diquenching dg minyak
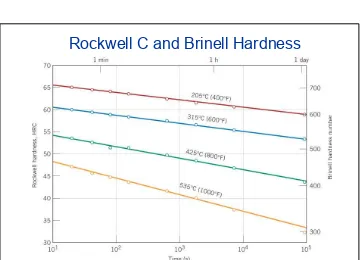
Hardness versus tempering time for a water%quenched eutectoid plain carbon steel (1080) that has been rapidly quenched to form martensite.
Pada proses tempering beberapa baja bisa mengalami
penurunan ketangguhan, hal ini disebut perapuhan
temper. Fenomena ini terjadi bila baja ditemper pada
suhu diatas 575
0C dan diikuti pendinginan lambat sampai
temperatur ruangan, atau jika tempering dilakukan pada
suhu antara 375 – 575
oC.
Perapuhaan ini disebabkan oleh kandungan elemen lain
dalam jumlah yang cukup signifikan seperti mangan,
nikel, crom dan phospor, arsen, timah putih.
Perapuhan temper bisa dicegah dengan :
1. Pengontrolan komposisi
2. Tempering diatas 575
oC atau dibawah 375
oC diikuti
dengan quenching pada temperatur ruang.
Kekuatan dan kekerasan beberapa paduan
logam dapat dikembangkan oleh pembentukan
partikel kecil terdispersi secara ekstrim dan
uniform (precipitates) pada fasa kedua dengan
matrika fasa utama.
Alloys that can be precipitation hardened or age
hardened:
Copper beryllium (Cu Be) Copper tin (Cu Sn)
Magnesium aluminum (Mg Al) Aluminum copper (Al Cu) High strength aluminum alloys
Criteria:
Maximum solubility of 1 component in the other (M); Solubility limit that rapidly decreases with decrease in temperature (M→N). Process:
Solution Heat Treatment – first heat treatment where all solute atoms are dissolved to form a single phase solid solution. Heat to T0and dissolve B phase. Rapidly quench to T1
Nonequilibrium state (αphase solid solution supersaturated with B atoms; alloy is soft, weak no ppts).
The supersaturated αsolid solution is usually heated to an intermediate temperature T2 within the α+βregion (diffusion
rates increase).
The βprecipitates (PPT) begin to form as finely dispersed particles. This process is referred to as aging.
After aging at T2, the alloy is cooled to room temperature. Strength and hardness of the alloy depend on the ppt temperature (T2) and the aging time at this temperature.
Precipitation Heat Treatment
Heat treatable aluminum alloys gain strength from
subjecting the material to a sequence of processing
steps called
solution heat treatment, quenching
, and
aging
.
The primary goal is to create sub micron sized
particles in the aluminum matrix, called
precipitates
that in turn influence the material properties.
While simple in concept, the process variations
required (depending on alloy, product form, desired
final property combinations, etc.) make it sufficiently
complex that heat treating has become a professional
specialty.
The first step in the heat treatment process is solution
heat treatment. The objective of this process step is
to place the elements into solution that will
eventually be called upon for precipitation hardening.
Developing
solution heat treatment times and
The
supersaturated solid solution
is
unstable and if, left alone, the excess
θ
will precipitate out of the
α
phase. This
process is called
aging
.
Types of aging:
Natural aging
process occurs at room
temperature
Artificial aging
If solution heat treated,
requires heating to speed up the
precipitation
After solution heat treatment the material is ductile,
since no precipitation has occurred. Therefore, it may
be
worked easily.
After a time the solute material precipitates and
hardening develops.
As the composition reaches its saturated normal state,
the material reaches its maximum hardness.
The precipitates, however, continue to grow. The
fine
precipitates disappear
. They have
grown larger
, and as
Precipitation Heat Treatment
PPT behavior is represented in the diagram:
With increasing time, the hardness increases, reaching a maximum (peak), then decreasing in strength. The reduction in strength and hardness after long periods is
overaging(continued particle growth).
Small solute enriched regions in a solid solution where the lattice is identical or somewhat perturbed from that of the solid solution are called Guinier Preston zones.
Guinier Preston (GP) zones Tiny clusters of atoms that precipitate from the matrix in the early stages of the age hardening process.
• 2014 Al Alloy:
• TS peak with precipitation time. • Increasing T accelerates
process.
precipitation heat treat time
te
1min 1h 1day 1mo 1yr
204°C
149°C
• %EL reaches minimum with precipitation time.
%
1min 1h 1day 1mo 1yr precipitation heat treat time
Effects of Temperature
Characteristics of a 2014 aluminum alloy (0.9 wt% Si, 4.4 wt% Cu, 0.8 wt% Mn, 0.5 wt% Mg) at 4 different aging
Alloys that experience significant
precipitation hardening at room temp, after short periods must be quenched to and stored under refrigeratedconditions. Several aluminum alloys that are used for rivets exhibit this behavior. They are driven while still soft, then allowed to age harden at the normal room temperature.
Several stages in the formation of the equilibrium
PPT (
θ
) phase.
0 10 20 30 40 50
composition range
available for precipitation hardening
CuAl2
A
• Particles impede dislocation motion.
• Ex:
Al%Cu system
• Procedure:
%%Pt B: quench to room temp. (retain αsolid solution) %% Pt C: reheat to nucleate
small θparticles within
αphase.
Temp.
Time
%%Pt A: solution heat treat (get αsolid solution)
Pt A (solution heat treat)
B
Pt B
C
Pt C (precipitate θ)
At room temperature the stable state of an aluminum copper alloy is an aluminum rich solid solution (α) and an intermetallic phase with a tetragonal crystal structure having nominal composition CuAl2(θ).
Aging either at room or moderately elevated
temperature after the quenching process is used
to produce the desired final product property
combinations.
The underlying
metallurgical phenomenon
in the
aging process is
precipitation hardening
. Due to
the small size of the precipitate particles, early
understanding was hampered by the lack of
sufficiently powerful microscopes to actually see
them.
With the availability of the transmission electron
microscope (TEM) with nanometer scale
resolution, researchers were able to actually
image many precipitate phases and build on this
knowledge to develop improved aluminum alloy
products.
Aluminum is light weight, but engineers want to improve the strength for high performance
applications in automobiles and aerospace.
To improve strength, they use precipitation hardening.
Quenchingis the second step in the process.
Its purpose is to retain the dissolved alloying elements in solution for subsequent precipitation hardening. Generally the more rapid the quench the better, from a properties standpoint, but this must be balanced against the concerns of part distortionand residual stress if the quench is non uniform.