A PRAGMATIC ANALYSIS OF REQUESTS EXPRESSED BY THE MAIN
CHARACTERS IN NANCY MEYERS’STHE INTERN MOVIE
A Thesis
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Attainment of a Sarjana Sastra Degree in English Literature
Written by:
Dyotra Nurul Baiti 12211144006
ENGLISH LITERATURE STUDY PROGRAM ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT FACULTY OF LANGUAGES AND ARTS YOGYAKARTA STATE UNIVERSITY
v MOTTO
It’s never too late to start over. If you weren’t
happy with
yesterday, try something different today.
Don’t stay stuck.
Do better.
vi
DEDICATION
This thesis is dedicated to
my beloved parents who always support me in
vii
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
First and foremost, all praises be to Allah SWT by saying
Alhamdulillahirabbil’alamin for this blessed life to be gifted to me. Without His
blessings, I would never have finished my thesis.
In completing this thesis, there are many parties who have supported and
helped me. Therefore, I would like to give my deepest gratitude to:
1. Titik Sudartinah, M.A., my first supervisor, and Nandy Intan Kurnia, M.Hum.,
my second supervisor, for their support, advice, patience, and guidance in
helping me conduct this thesis, thus I could finish this thesis well;
2. Andy Bayu Nugroho, M.Hum., my academic consultant, for his motivation,
support, and patience in teaching and guiding me during my process of study;
3. all lecturers of English Education Department who have taught and guided me
during my years of study;
4. my parents, Drs. Agus Setyobudi and Ismalia Tri Ratnawati, S.Pd who always
love me sincerely, give their care to me, pray for me, teach me and support me
everytime.
5. my brother, Agra and sister-in-law, Nisa, for supporting me in the process of
writing my thesis;
6. the members of English Literature Study Program of 2012, especially E-lit G
class and Linguistics class for their support and experience;
ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL SHEET ... ii
RATIFICATION SHEET ... iii
PERNYATAAN ... iv
MOTTO ... v
DEDICATION ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS ... vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... ix
LIST OF TABLES AND FIGURES ... xi
ABSTRACT ... xii
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. Background of the Research ... 1
B. Research Focus ... 4
C. Objectives of the Research ... 6
D. Significance of the Research ... 6
CHAPTER II LITERATURE REVIEW AND CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK ... 8
A. Literature Review ... 8
1. Pragmatics ... 8
2. The Scope of Pragmatics ... 9
3. Speech Acts ... 12
4. The Act of Request ... 14
a. Definition of Request ... 14
b. Types of Request ... 16
c. Strategies of Request ... 19
d. Purposes of Request ... 24
5. The Intern Movie ... 26
6. Previous Research ... 28
x
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD ... 32
A. Research Type ... 32
B. Form, Source, and Context of Data ... 33
C. Instruments ... 33
D. Techniques of Data Collection ... 34
E. Techniques of Data Analysis ... 35
F. Data Trustworthiness ... 35
CHAPTER IV FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION ... 37
A. Findings ... 37
B. Discussion ... 39
1. Types of Requests Expressed by the Main Characters in The Intern Movie ... 40
2. Strategies of Requests Employed by the Main Characters in The Intern Movie ... 48
3. Purposes of Requests Applied by the Main Characters in The Intern Movie ... 61
CHAPTER V CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS A. Conclusions ... 69
B. Suggestions ... 72
REFERENCES ... 73
APPENDICES ... 75
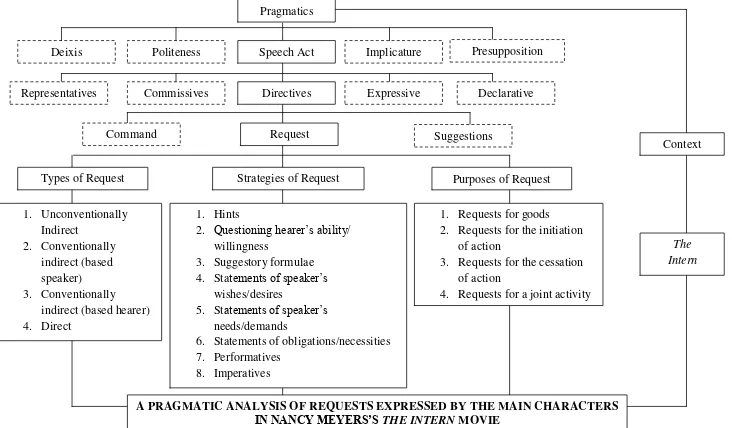
A. Data Sheet of Types, Strategies, and Purposes of Requests Employed by the Main Characters in Nancy Meyers‘s The Intern Movie ... 75
xi
LIST OF FIGURES AND TABLES
Figure 1. The Cover of The Intern movie ... 27 Figure 2. Analytical Construct ... 31
Table 1. Sample Data Sheet of Request Expressed by the Main Characters in
The Intern Movie ... 34 Table 2. Frequency of Occurrence of Types, Strategies, and Purposes of
Request Expressed by the Main Characters in Nancy Meyers‘s
xii
A PRAGMATIC ANALYSIS OF REQUESTS EXPRESSED BY THE MAIN CHARACTERS IN NANCY MEYERS’S THE INTERN MOVIE
Dyotra Nurul Baiti 12211144006 ABSTRACT
This research examines the speech acts of request presented in The Intern
movie using pragmatic approach. The objectives of this research are to find out the types of requests used by the main characters, to examine the strategies of requests used by the main characters, and to explain the purposes of requests expressed by the main characters in The Intern movie.
This research used a combination method, in which the main method was qualitative method that was supported by a qualitative method. The data were utterances, in the form of sentences, phrases, clauses or words spoken by the main characters in The Intern movie, while the contexts of the data were dialogues. The source of the data was the script of the dialogues spoken by the characters in The Intern movie. The primary instrument of this research was the researcher herself, while the secondary instrument was the data sheet. The researcher used analysis of documents by note-taking as a source of collecting data.
The results of this research are described as follows. First, there are four types of requests found in the movie: unconventionally indirect request, conventionally indirect request (hearer based), conventionally indirect request (speaker based), and direct request. Conventionally indirect request (hearer based) becomes the most prominent type of request because the main characters use this to ask their request politely. Second, there are seven strategies of requests expressed by the main characters: hints, questioning hearer‘s ability/willingness, suggestory formulae, statements of speaker‘s wishes/desires, statements of speaker‘s needs/demands, statement of obligation/necessity, and imperatives. The most dominant strategy is questioning hearer‘s ability/willingness because the main characters ask the ability to the requestee to perform the request. Therefore, they do not force the requestee to perform an action. Third, there are four purposes of request applied by the main characters: request for goods, request for the initiation of action, request for the cessation of action, and request for joint activity. The most dominant purpose of request is request for the initiation of action because the main characters often use this purpose to demand a requestee to perform an action.
1 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
This chapter consists of background of the research, research focus,
objectives of the research, and the significance of the research.
A.Background of the Research
As human beings, people need communication to socialize with others in
the society. Through it, people can share information, ask something, express
feeling, suggest anything and so forth. To achieve an effective communication,
people should understand the existence of language. Language itself basically has
two types: spoken language and written language. Written language is usually
used in texts. Meanwhile, spoken language is found in people‘s conversation.
Conversation is a real form of language use. It is part of communication which
involves few people who are doing an interaction in one situation with one topic.
A related concept of language that used as intended meaning of conversation is
known as speech acts.
According to Yule (1996:47), an action is performed through saying
something in a certain language known as a speech act. It implies that when a
speaker utters something, he/she actually wants to deliver the meaning of the
utterances, the action, and the effect of the utterances. Based on the speaker who
produces an utterance, it consists of three kinds of acts. They are locutionary act
(basic of utterances by saying something), illocutionary act (the intention via
The example is when the speaker directly says I want a book to the hearer. The locutionary act is when the speaker utters the statement (directives) that
she/he needs a book. The speaker makes an order or demand that serves as the
illocutionary act or the intention of the speaker. After the hearer understands the
intention, he/she performs an action by giving the book to the speaker in order to
comply the demand. The effect of saying something is called perlocutionary act.
There is one thing that often happened in a conversation between one
person and another in a certain situation, when a person expresses the need or
demand for hearer to fulfill it. This case is called as speech act of request. A
request can be stated by people in many occasions. It mostly happens in public
services like in the office, café, hotel, or any others. For example, when the
speaker is in the café, he/she says Could you serve me a cup of hot cappuccino? In an indirect way, the guest makes a request to order a cup of coffee and the
waiter/waitress serves him/her. It is a natural phenomenon in the society because
the guest can request many things to the waiter/waitress in the café. Thus, in
performing a request, the addressee can carry out the demand from the speaker or
not to carry out the demand based on the reason behind it.
Trosborg (1994:187) states that a request is an illocutionary act in which
the speaker wants the hearer to carry out an action that has advantages for the
speaker and, sometimes, for the hearer. It can be expressed in two ways; they are
verbal and non verbal goods and services. The verbal goods and services are a
request for information, whereas the non verbal goods and services are a request
hearer performs a future action which is an order from the speaker that has
advantages for the speaker and sometimes for the hearer. The request can be said
in direct and indirect ways. It depends on the speaker‘s utterances and what action
that the hearer may perform. Then, when a speaker utters a request, he/she needs a
strategy to convey the meaning of the request because every person is different in
understanding the utterances. Subsequently, the requester has purpose in uttering
the request which is to explicate the meaning of it.
The speech act of requests is an interesting problem to be discussed
because it can be found in daily conversation. For the representation of real life,
the researcher uses a movie because what happens in the movie mostly portrays
the society. Related to the movie, the researcher chooses The Intern as the object in this research. The story is about an old man named Ben who gets a job as an
intern and a woman named Jules who is the founder/boss in the office. Ben is a
responsible old man and he has a mature thought whereas Jules is a workhorse
and careless woman. In this movie, Ben helps his boss as an intimate intern to
accompany Jules in every occasion because she is very busy with her work and
cannot handle all of it. Jules often requests Ben to do something to fulfill her
needs any time. To cover Jules‘s activities, Ben always complies the needs of his
boss surprisingly even in the marriage or family problems which are faced by
Jules.
There are some reasons for choosing this movie as the object. First, the
researcher is interested in Jules, one of the main characters, which portrays Jules‘s
fashion company which has 220 coworkers. However, her husband decides to be a
house husband. Second, the main characters are employees and boss who have
different positions in the office. The researcher assumes that the speech acts of
requests occur in the movie. Third, the movie won an award in AARP Movies for Grownup Awards 2016 and some nominations for the best actor and actress.
Hence, this movie is considered as a great movie to be analyzed.
B.Research Focus
There are two types of communication; they are verbal and non-verbal
communication. Both of those types of communication are found in The Intern
movie. The verbal communication can be seen through the dialogues or
conversations among the characters, whereas non verbal communication can be
found in the written language which is in the script of this movie. Based on the
background of research, two topics of pragmatic approach can be used to analyze
the problems from The Intern movie.
First, the topic of politeness means a person‘s manner to avoid hurting
people. In term of politeness, the utterances in The Intern movie can be discussed since there are sociological factors such as rank of imposition, power, and degree
of intimacy which are shown by the main characters.
Second, it can be analyzed using speech acts. There are many utterances
expressed by the characters in order to deliver the purpose of the conversation.
Based on Yule (1996:53), there are three kinds of speech acts, namely
divided into five types, i.e. declarations, representatives, expressives, directives,
and commissives.
Based on the identification related to the topics, the researcher limits the
research problem. The researcher chooses one type of illocutionary acts, namely
directives. Through this type, there are command, request, and suggestion. It is
impossible to analyze all the problems because it takes too much time and
plentiful explanation. Hence, the researcher only focuses on analyzing request.
The researcher is concerned with the types of request, strategies of request and
purposes underlying the request. Thus, there are some problems in The Intern
movie dealing with request as in the following.
The first problem is the types of request that are employed by the main
characters in The Intern movie. The main characters are an employee and his boss that often demand to do something in direct or indirect ways to the other
characters.
The second problem is the strategies that are employed by the main
characters to express the request toward the other characters. To reveal the
utterances of request by the characters, there are some strategies of request that
need to be understood.
The third problem is the purpose of requests expressed by the main
characters to the other characters. It focuses on the intention of request which is
addressed to the other characters. The purposes of request are request for goods,
request for the initiation of action, request for the cessation of action, and request
From the identification and limitation of the problems, the formulation of
the problems can be arranged as follows.
1. What types of request are used by the main characters in The Intern movie? 2. What are the strategies of requests used by the main characters in The Intern
movie?
3. What are the purposes of the requests expressed by the main characters in The Intern movie?
C.Objectives of the Research
Based on the problems formulated, the objectives of the research can be
stated as follows:
1. to find out the types of request used by the main characters in The Intern
movie,
2. to examine the strategies used by the main characters to express their requests
in The Intern movie, and
3. to explain the purposes of request expressed by the main characters toward the
requestee‘s in The Intern movie. D. Significance of the Research
This research is expected to be useful and give contribution to the
following parties.
a. The Students of English Literature Study Program
It is expected that this research will serve as a valuable source of reference
enrich their knowledge and they can understand more about speech act of requests
related to the types, strategies, and the purposes of requests.
b. Readers in General
After reading this research, it is expected that this research will give more
information about speech act of requests to the readers. The researcher wants them
8 CHAPTER II
LITERATURE REVIEW AND CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
This chapter deals with literature review which covers some theories on
pragmatics concerning with speech act of requests and conceptual framework
which explains the concept of this research in accordance with the problems also
the analytical construct.
A.Literature Review 1. Pragmatics
Language is an essential part of communication. It is used to interact with
other people in daily life to share the ideas, to give opinions, or to ask someone to
do something. The use of language for communication is explained in linguistics
study which is called as pragmatics. According to Mey (2001:6), in
communication, pragmatics is the study of language used by people in order to
show the effects of the language use towards other people. It means by studying
pragmatics, people will understand how language plays a role in their lives.
There are several points of view of pragmatics proposed by Yule (1996:
3). According to him, firstly, pragmatics is the study of the speaker‘s intention. It
requires the analysis of what people mean by their sentences, phrases or words.
Secondly, pragmatics is the study of language through the intentional context. It
takes consideration on how a speaker arranges what he/she wants to say in
distance. It is assumed as the study of the relationship between the speaker and the
hearer.
In line with the definition proposed by Yule, Cruse (2006:3) states that
pragmatics concerns with the meaning of an utterance which relies on context.
Therefore, context is a necessary concept in pragmatic analysis. It is because
pragmatics focuses on the meaning of utterances or interaction which is involved
by some people to communicate with the utterances they said to others in a
particular situation.
There are two types of context offered by Nunan (1993:8), i.e. linguistic
context that is the words, sentences, or utterances accompanying a text, and non
linguistic context that is the real situation in which the text comes off. The
components of non linguistic context are the type of communication event, the
topic, the purpose of the event, the setting, the participants and the relationship
between them, and the background knowledge also the assumption underlying the
communicative event.
In short, pragmatics is the study of language use which involves how the
speaker produces his/her utterances, delivers their intention, and how the hearer
interprets them in a certain context.
2. The Scope of Pragmatics
Pragmatics as a branch of linguistic study covers several topics. They are
deixis, politeness, speech acts, presupposition, and implicature. The first topic is
deixis. Yule (1996:9) states that deixis is an expression to indicate or point
something or to refer something is called deictic expression. There are three types
of deixis. The first type is personal deixis which is used by a speaker to refer to a
person using several pronouns such as I, you, he/she, and it. The second type is spatial deixis which is used to point to a location such as there and here. The third type is temporal deixis which is an expression used to indicate the distance of
time. The terms such as now, yesterday, and tomorrow are pointing to the specific time.
The second topic is presupposition. According to Yule (1996: 25), a
presupposition is something before making an utterance which is considered by
the speaker to be the case. It means when a speaker delivers the utterances, he/she
believes that the hearer understand his/her utterances. There are six types of
presupposition. They are existensial, factive, non-factive, lexical, structural, and
counterfactual.
The third topic is implicature. Grice (in Davis, 1998:5) defines implicature
as interpreting particular things by telling different things. It explains about a
speaker‘s intended meaning behind an utterance. He divides implicature into two
types; conventional implicature and conversational implicature. Conventional
implicature talks about specific words which have correlation to the additional
meaning. Conversational implicature is the implication of the utterances based on
the context.
Politeness is the fourth topic in pragmatics. It is derived from the term
polite which is included as the behavior of a person. Related to this, Mey (2009:
by the others. In addition, Yule (1996: 60) states that to reveal the consciousness
of other person‘s public self image or face is known as politeness. There are two
types of face namely face threatening act and face saving act. Face threatening act
means the utterances of a speaker that express a threat expression to attack another
person faces whereas face saving act means the utterances of a speaker which
prevent a potential threat to another person‘s face.
Speech act is a part of the fifth topic of pragmatics deals with the meaning
of an act performed by the speaker‘s utterance in a certain context. Nunan
(1993:65) says the speaker is not only delivering the statement pointed to an
object but also conveying the functions of the statement such as requesting,
denying, introducing, apologizing, and further. In order to produce an utterance,
the circumstances are needed, thus, the hearer can recognize the intended meaning
of the utterance. The circumstances are called speech events. According to Yule
(1996: 47), speech event is used for determining the interpretation of an utterance
as related to speech act. An example is in winter situation, when someone serves a
glass of tea, thus, the speaker believes that a glass of tea is hot. On the contrary,
the speaker says This tea is really cold!The speaker‘s utterance is interpreted as a complaint. If the situation is changing into a really hot summer and the speaker is
3. Speech Acts
Austin (in Cutting, 2002: 16) defines speech acts as the actions that are
performed by utterances. It implies that people can use language by speaking
particular things to carry out something. In accordance to Austin, Yule (1996:48)
divides the speech acts into three related acts. First, a locutionary act is the
primary utterance in saying something. Second, an illocutionary act is the
intention or purpose of an utterance through saying something. The last, a
perlocutionary act is the outcome of an utterance over saying something. In other
words, a locutionary act means a simple act of saying words which are formed to
be an utterance and the meaning of saying the utterance which is uttered by the
speaker. Meanwhile, an illocutionary act means the intention behind an utterance
which is expressed by the speaker. It conveys the purpose of saying something.
Then, a perlocutionary act means the effect that emerges when the speaker says
something.
Related to the three acts above, Yule (1996: 53) also divides illocutionary
acts into five major categories, i.e. representatives, directives, expressives,
commissives, and declaratives. Representative is a kind of speech acts which have
function to describe states. The purpose is to commit the speaker to something‘s
being the case. The action are arguing, asserting, boasting, claiming, complaining,
criticizing, denying, describing, informing, insisting, reporting, swearing, etc, for
Meanwhile, directive is a kind of speech acts that a speaker uses to get the
addressee to do something. Directives express what the speaker wants toward the
hearer to commit an action. The acts of directives are ordering, commanding,
requesting, and suggesting, for example, Could you open the window, please? In this example, the speaker requests the hearer to open the window.
Then, commissive is a kind of speech acts that the speaker uses to perform
him or herself to do some future action. It expresses the speaker‘s intention to
carry out an action in a certain time. The acts are commiting, guaranteeing,
offering, promising, refusing, threatening, volunteering, vowing, etc, for example,
I’m going to get it right next time. In doing the type of commissives, the speaker promises to the hearer to get it right next time.
Thereafter, expressive is a kind of speech acts that expresses the feeling of
the speaker. Expressives express psychological states of mind such as the
pleasure, pain, like, dislike, joy or sorrow. The acts of apologizing, appreciating,
thanking, complaining, and congratulating belong to expressive, for example,
Congratulations! By presenting the example, the speaker shows his/her statement of happiness.
Later, declarative is a kind of speech acts that conveys the utterance to
bring about a change in reality. The acts are approving, betting, blessing,
christening, confirming, cursing, declaring, disapproving, dismissing, naming,
resigning, for example, I pronounce you husband and wife. By telling so, the speaker declares to the hearer/audience that there are two persons here becoming a
4. The Act of Request a. The Definition of Request
Directive covers three illocutionary forces, i.e. request, command, and
suggestion. The function of directives act is to get somebody to do something.
According to Searle (1979: 3), commands and requests have a similar purpose
which manages the hearer to carry out something. However, the illocutionary
forces are totally different. Command states directly that the speaker wants
something and the hearer should complete the desire because the hearer has a duty
to perform it. According to Cruse (2006: 62), a power should have by a
commander to control the command above the comandee.
According to Bach and Harnish (in Shams, 2011: 280), request is a part of
speech acts which express the requester‘s desires for the requestee why the
requestee should perform the action as a reason to act. Thus, requests are
performed by the requester in which aims to perform a certain thing. It is believed
that a request mostly about the requester‘s demands and the requestee‘s responses.
In addition, request is an action that is used to communicate with people in
society (Wang, 2007:11). In fact, request is usually used by people to conduct a
conversation such as someone who asks for help. People often use some verbs to
indicate a request such as ask, order, command, request, beg, plead, pray, entreat,
invite, permit, and advise (Sofwan, 2011:69). A person uses request as a way to
ask help when he/she needs a particular thing. By the definitions, it can be
concluded that request happens in daily life. It is to fulfill the requester‘s desires
In requests, when the requester wants someone to carry out him/her
interest, this is called cost of the requestee. The requester imposes on the
requestee in certain ways to comply the desires of the requester. It seems that by
imposing the requestee, the requester gets the benefits from the latter
performance. Haverkate (in Trosborg, 1995:188) states that in impositive speech
act, the requester carries out a speech act towards the requestee for gaining the
performance which has advantages for the requester. By this statement, impositive
speech act imposes the requestee to perform the requester‘s desires which is to get
lot of advantages for the requester by the circumstances. The degree in which the
requester enforces on the requestee is called degree of imposition. It makes
difference compared to demanding acts.
Imposition is determined by a number of factors. For example, if the
requester asks for something expensive such as diamond, the financial burden on
the requestee may be big. In such a case, the degree of imposition of the requested
act is high. A burden is not always financial, but it is also psychological about the
thing.
Request should be performed in appropriate circumstances. The
circumstances of speech acts are known as felicity conditions. Felicity conditions
are the conditions that need to apply in performing speech acts in order to be
appropriate (Cruse, 2006:62). Moreover, Searle (in Trosborg, 1995:191) explains
the conditions are participant roles and propositional contents. Participant roles
are actors that participate in a conversation, i.e. the requester and the requestee. A
There are four assumptions of performing request. First, the requester
wants the requestee to perform an action. Second, the requester assumes the
requestee can perform an action. Third, the requester assumes the requestee is
willing to perform an action. Last, the requester assumes the requestee will not
perform an action in the absence of the request. By these conditions, it conveys
the illocutionary forces of a request. In line with Searle, Labov – Fanshel (in
Trosborg, 1995:191) add the requester has the capacity to tell the requestee to
perform the desired act and the requestee has the responsibility to realize it.
In conclusion, request has three results. Firstly, the requester says his/her
request and wants the requestee to carry out the desired act. Secondly, the
requester may perform the desired act. Thirdly, it is indefinite that the requestee
will carry out the desired act.
b. Types of Request
Trosborg (1995) states there are two types of requesting, they are indirect
request and direct request. Indirect request is divided into three, i.e.
unconventionally indirect request, conventionally indirect request based on the
speaker, and conventionally indirect request based on the hearer. Each of them is
explained below.
1) Unconventionally Indirect Request
According to Trosborg (1995: 192), unconventionally indirect request
means a requester does not state what he/she wants to say. It has discrepancy
between what he/she says as his/her true intentions behind those utterances. It
something. The utterance must be recognized by the requester as an utterance that
conveys not only the surface meaning. In order to get the intended meaning of
request from the requester, both of the requester and the requestee must pay more
attention in a certain situation when the utterance is being produced. It is because
an indirect request has more than one meaning. In addition, both of requester and
requestee also should be aware about the intimate knowledge which is happened
in a certain situation. This type can be applied by using strategy of hints, for
example, It’s cold in here. By telling the situation, the utterance of an example may result in few interpretations.
2) Conventionally Indirect Request (based on the hearer)
A conventionally indirect request based on the hearer shows that the
requestee manages the request whether he/she will perform or refuse the request.
This type is more polite than requests formulated on request based on the speaker
(Trosborg, 1995:197). When a requester utters what he/she needs, the requestee
occupies the substantial position. A requester already knows the consequence that
he/she does not take the request. Therefore, the requestee can refuse in a polite
way to answer the request. This type can be applied on the strategies of request
which are questioning hearer‘s ability/willingness and suggestory formulae. An
example is Could you close the window? By presenting the example, the requester asks the requestee‘s willingness to close the window. In this case, the request
3) Conventionally Indirect Request (based on the speaker)
Trosborg (1995: 201) says that a conventionally indirect request based on
the speaker is the requester placing his/her wishes above the requestee in order to
make the requestee perform an act as a wish from the requester. The requester
takes an important position in this type rather than the requestee. It is because the
requester becomes the main actor of the interaction. In cooperative way, the
requestee mostly accepts the wish rather than disagrees with the requester‘s
desires. The requester has control to request; it is called demand. Thus, it makes
the requestee difficult to refuse, for example, You should wash my clothes. In this example, a requester demands to perform an action by washing his/her clothes
which is needed to comply. It is hard for the requestee to refuse the demand.
Related to this type, the statement of speaker‘s wishes and desires and the
statement of speaker‘s needs and demands are applied.
4) Direct request
Direct request is the type of request in which the requester and the
requestee instantly understand what the requester said (Trosborg, 1995:202). It is
because the requester directly says the desire to the requestee in an explicit way.
In accordance with the definition, Clark (in Achiba, 2003:7) says the illocutionary
force of direct request is only one. It clearly stated by the requester‘s utterance. In
direct request, the requester expects compliance from others. The requester tends
to have a higher position than the requestee by using performatives and imperative
statementsor modal verb expressing obligation or necessity which expresses to be
directly says to the requestee. The context is in the coffee shop, there are a guest
and a waiter. A guest, as the requester, orders a cup of coffee, thus, a waiter, as the
requestee, should comply an order from the requester. This type can be applied in
the three strategies such as statement of obligation and necessity, performatives,
and imperatives.
c. Strategies of Request
There are eight strategies of requesting stated by Trosborg (1995: 192).
They are hints, questioning hearer‘s ability/willingness, suggestory formulae,
statements of speaker‘s wishes/desires, statements of speaker‘s needs/demands,
statement of obligation/necessity, performatives, and imperatives. These strategies
are explained below.
1) Hints
Trosborg (1995: 192) states that hints strategy is a request strategy which
implicitly tells the requester‘s utterance for the desired action. This strategy can
be used for making a statement or asking a question. Thus, the requester can
express the needs to the requestee. According Achiba (2007:39), hints means that
the utterances have certain references to the object of desires for conveying the
action. By applying this strategy, the requestee should find out the intention
behind the requester utterances with certain references on the context or situation.
An example is The kitchen is a total mess. The example is clearly seen that the requester does not state the request explicitly. The requester asks the requestee to
This strategy involves some conditions; they are reasonableness,
availability, and obviousness. Reasonableness indicates the reason of request
which implicitly expresses its purpose of request. To make a successful request,
the requester should put a reason after the utterance of desire/demand is produced.
Availability is interpreted by questioning the available/existence circumstances in
request. Obviousness implies that the request is uttered through questioning an act
which has not already been performed.
According to Blum Kulka (in Jalilifar, 2009: 47), hint is divided into two
propositions. They are strong hints and mild hints. Strong hints mean the requester
says his/her wish which contains partial reference to the object. Meanwhile, mild
hints mean the requester says his/her wish which is not containing reference to the
object. The examples of mild and strong hints are I have to be at the airport in half an hour. It shows that the requester only expresses the desired action in which the requester will be at the airport in half an hour. Thus, the requestee
interprets that he/she escorts the requester to the airport before boarding. In other
examples, My car has broken down. Will you be using your car tonight? When interpreting strong hints, a requester adds his/her wish partially by completing an
utterance with Will you be using your car tonight?
2) Questioning hearer‘s ability/willingness
Trosborg (1995: 197) explains that when a requester states his/her request,
the requestee should consider that a question leads to his/her ability/willingness is
a request in order to perform the desired action. This strategy expects the
requestee can choose whether he/she wants to comply or not. When applying this
strategy, the requester uses some intensification through lexical marking such as
kind, mind, and object can enlarge the willingness pre-condition, for example,
Would you be so kind as to refrain from smoking. Here, the requester asks the requestee not to smoke near him/her.
There are two conditions included in this strategy. The first is the
condition of ability; it refers to the requestee‘s ability to perform the request. In
order to indicate ability condition, there are two indicators; the inherent capacities
of the requestee, both physical and mental, also the external circumstances related
to time, place, etc of the action. The second condition is willingness. It focuses on
the requestee‘s willingness as fulfillment to conduct the request. The example is,
Can you reach the jar for me, please. By saying so, the requester asks the capacity of the requestee whether the requestee can reach the jar or not. Another example is
Will you do the shopping today? It is a question that indirectly asking to the requestee in which the requester invites his/her to go shopping today.
3) Suggestory formulae
Achiba (2003:38) states a suggestory formulae is the utterance which
contains a suggestion to perform an action. It implies that the requester does not
ask a question directly to the requestee but he/she gives suggestion through a
question as an action of request towards the requestee. Therefore, the requester
asks the requestee‘s cooperation about certain conditions that influence the action.
The requester employs this strategy to make the request suitable to his/her own
anticipate the refusal from requestee. An example is How about lending me some of your records? By presenting this example, the requester intends to be cooperative to the requestee in borrowing the records by stating how about. This request does not force the requestee at all.
4) Statement of speaker‘s wishes and desires
As stated by Trosborg (1995:201), the statements of wishes uttered by a
requester are commonly expressed in polite but in direct way. Therefore, the
requestee thinks that he/she should comply the wishes/desires, for example, I would like to have some more coffee. From the example, the requester orders to get more coffee as his/her wish.
5) Statement of speaker‘s needs and demands
In this strategy, the requester is the focal point of the interaction.
Statement of speaker‘s needs and demands strategy contains a high degree of
impositions. Therefore, the requester expresses impolitely when requesting
something to the requestee. Trosborg (1995: 202) mentions that the direct request
by the requester above the requestee is called as demand. Demand is the
requester‘s interest that wants to be done by the requestee. Then, the requestee
feels burdened by the request, thus, it makes more difficult for the requestee to
refuse. An example of this strategy of the statement of needs and demands is I need a pen. By saying that he/she needs a pen, the word need is the main point of the utterance. A requester states his/her need and demand indirectly. It seems
In addition, this strategy can be softened by adding please, excuse me or other mitigating devices, for example, I so much want to see that film, please (let me go). By stating the utterance, a requester asks to leave the requestee because he/she wants to watch a movie. The requester makes the request more polite
because it adds please as the mitigating device. 6) Statements of obligations and necessities
In this strategy, the authority is the important point to conduct the request.
According to Trosborg (1995: 202), the requester employs his/her own authority
or authority from the outside such as institution. In addition, Blum Kulka (in
Jalilifar, 2009:47) says that the utterance consist of obligation statement to
perform an action. To show the request clearly, the strategy uses auxiliary verbs
such as should, ought to, have to, and must. To indicate moral obligation, it needs to use the verbs should and ought to, for example, You should/ought to leave now. In this sentence, the requester imposes his/her authority to the requestee since
he/she has a higher position than the requestee. Moreover, to show obligation
which delegated to the requester is using must, for example, You must leave now (because I want you to). By saying so, the requester asks the requestee to leave immediately and also it is as the requester‘s wish. Thus, the requester obliges the
requestee to comply the request. Furthermore, by applying have to, it needs to involve few obligations from outside of the requester.
7) Performative
Performative implies the illocutionary force of the utterance that is
a performative, it obviously shows an utterance as a request. The requestive
intents are asking, requesting, ordering, demanding, and commanding, etc. The
performatives is directly and usually authoritative. It seems impolite since the
authoritative element is used for requesting, for example, I request you to leave.
Here, the requester asks directly to the requestee to leave as soon as possible.
However, the requester is possible to hedge the illocutionary force which is called
as hedged performatives (Jalilifar, 2009: 47). Hedged perfomatives is used to
soften the utterance such as would, for example, I would like to ask you to leave me alone. The utterance intention is to request the requestee to leave. With the use of would, it sounds more polite.
8) Imperative
When employing imperative as a strategy, a requester directly shows that
the utterance is an order (Trosborg, 1995: 204). It seems authoritative since order
cannot be refused. The requestee must perform the requester desired to obey an
order because the requester has authority over the requestee, for example, Get out of here. It interprets that the requester demands to leave the place immediately to the requestee.
By adding tags or please and will you marker, it may softened the utterances and seems less authoritative, for example, Open the door, please. By telling so, the requestee obviously says to open the door for him/her. It sounds less
d. The Purpose of Request
The condition of the requester tries to get the requestee to do something is
called request according to Searle (in Achiba, 2003:6). Achiba (2003:94) explains
there are four purposes in conducting a request. They are requests for goods,
requests for the initiation of action, requests for the cessation of action, and
requests for joint activity. The purposes are presented below.
1) Requests for goods
The purpose of requests for goods is questioning stuff or goods by the
requester (Achiba, 2003:94). There are two contexts behind an example of the
utterance, Could I please have one choco chip? In the first context, the requestee is asked to give a chocolate chip to the requester. In the second context, the
requestee is being asked to give the requester an approval for taking a chocolate
chip. The main purpose in this type is request for delivering goods to the
requester. This purpose is achieved by focusing on the object of goods.
2) Requests for the initiation of action
Request for the initiation of action is to begin the request by saying
utterances which contain the demand for doing actions. This type is expecting
non-verbal action on the requestee (Achiba, 2003:94). The example is Could you please go to your room? A requester said so to ask the requestee to go to his/her room and the requestee carries out the request by moving to his/her room.
Meanwhile, it can be used to ask verbal action as in the utterance Say something. When uttering that example, a requester tries to ask the requestee to say
with the response of the requestee to the utterances by performing an action. To
have more statement, requests for the initiation of action is classified above
requests for goods. This purpose is achieved by focusing on the performance not
the object.
3) Requests for the cessation of action
Different from requests for initiation of action, request for cessation of
action is to stop a running action by saying utterances or avoiding certain
problems from an occurrence (Achiba, 2003:94). The example is Don’t move the table okay. A requester delivers his/her utterance to prevent the requestee moving the table. This purpose is achieved by the stoppage of action from the requestee.
4) Requests for joint activity (or invitation to join in an action)
Achiba (2003: 94) says requests for joint activity have purposes to invite
or engage the requestee to join the similar activity with the requester, for example,
shall we play with the doll-dollies? The utterance is in proposal form. By saying so, the requester persuades the requestee to play doll-dollies together. This
purpose is achieved when the requestee joins in the same activity with the
5. The Intern
Figure 1. The Cover of The Intern Movie
The Intern is the title of an American comedy movie by Nancy Meyers which was released on September 25, 2015 by Warner Bros. Some stars involve
in the production of this movie are Robert De Niro as Ben Whitaker and Anne
Hathaway as Jules. Both of them are the main characters. Meanwhile, the
supporting characters are Rene Russo, Anders Holm, Andrew Rannells, Adam De
Vine, Christina Scherer, and Zack Pearlman.
The Intern is a story about seventy-year-old widower named Ben Whittaker who is accepted as an intern senior program. The name of the company
is About the Fit, located in Brooklyn. The company runs fashion mode, whose founder and CEO is Jules Ostin. As an intern, Ben works with his boss, Jules. He
should accompany his boss in every situation, such as escorting her to meet some
clients, going to the warehouse, or staying in the office when Jules has to stay to
work overtime. Moreover, Ben and his coworkers help Jules to delete an email in
but also with her family, her daughter, Paige and her husband, Matt. Matt gives up
on his career, thus, he becomes a house husband for Paige.
Jules has crisis about her company because her investor feels that she is
unable to cope with workload. Therefore, she should hire a CEO to develop the
company. After that, Jules and Ben go to San Francisco to have an interview with
CEO candidate. At night before the interview, Jules tells that she knows about
Matt‘s cheating behind her. The problem increases that Matt has an affair with a
mother of Paige‘s friends.
6. Previous Research
There are many researchers who conduct some analysis under the study of
pragmatics focusing on speech act. In this research, the researcher uses two
previous studies as the references. There are undergraduate thesis and
international journal.
The first research is conducted by M. Rifki Fahrurrozi. The title of the
research is A Pragmatic Analysis of Speech Act of Requests Expressed by the Characters in Office Space (2015). The objectives of the research are to investigate the types of request and to identify the strategies of request employed
by the characters in the movie. Then, the research mostly uses the type of
conventionally indirect request based on the hearer. Meanwhile, the characters in
Office Space mainly use the strategy of questioning hearer`s ability and willingness.
The second research is conducted by Khalid Wahaab Jabber and Zhang
the Speech of the President of the United States Barak Obama (2013). The objective of the research is to explore the speech acts of request of political speech
which has been delivered by President Obama. The results of the research are
speech acts of request is the most frequent prevailing in the political nominated
speech and the speech acts of request is mostly happened in an indirect way.
There are some differences between two previous studies and this
research. This research intends to analyze some purposes that are different from
both of the researches. This research adds the purpose of request and The Intern
movie as the object.
Different with the journal article and thesis, this research is entitled A Pragmatic Analysis of Requests Expressed By the Main Characters in Nancy
Meyers’s The Intern Movie. The aims of this research are to describe the types of
requests expressed by the main characters in The Intern movie, to enlighten the strategies of requests expressed by the main characters in The Intern movie, and to explain the purposes of request expressed by the main characters in The Intern
movie.
B.Conceptual Framework
Since the research objectives are to find out the types, strategies and
purposes of request, this research is under the field of pragmatics in which the
researcher focuses on requests in The Intern movie. Analyzing the speech act, especially requests, is a matter of making assumption that is an utterance
interpret the meaning of the utterances expressed by the main characters in The Intern.
Yule‘s classification of illocutionary act that is based on the criterion of
what a speaker wants to imply in his/her utterances is used in this study. The
classifications are declaratives, representatives, directives, expressive and
commisives. Requests fall under directives in which speakers and hearers attempt
to indicate their desires or needs.
To answer the first and second objectives, the research employs the theory
of request offered by Trosborg (1995) to explore the types and strategies of
requests expressed by the main characters in The Intern movie. There are four types of request, i.e. indirect request, conventionally indirect request (based on
hearer), conventionally indirect request (based on speaker), and direct request.
Meanwhile, the strategies are hints, questioning hearer‘s ability/willingness,
suggestory formulae, statements of speaker‘s wishes/desires, statements of
speaker‘s needs/demands, statement of obligation/necessity, performatives, and
imperatives. In addition, to investigate the purposes of request expressed by the
main characters in the movie, the researcher uses a theory proposed by Achiba
(2003). They are requests for goods, requests for the initiation of action, requests
Figure 2. Analytical Construct
Representatives Commissives Directives Expressive Declarative
Command Request
A PRAGMATIC ANALYSIS OF REQUESTS EXPRESSED BY THE MAIN CHARACTERS IN NANCY MEYERS’S THE INTERN MOVIE
1. Requests for goods 2. Requests for the initiation
of action
3. Requests for the cessation of action
4. Requests for a joint activity Implicature
Politeness Deixis
32 CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD
This chapter is presented to describe the research method. The researcher
divided this chapter into six parts. There were type of the research – describing
the approach in conducting this research; form, source and context of data –
describing the data clearly; instruments of the research; data collection technique
– dealing with how the data were collected; data analysis technique – showing
how the data were analyzed; and data trustworthiness – describing the validity of
the data.
A.Research Type
This research was conducted by using mixed method, a combination of
qualitative and quantitative method. This research was included as descriptive
qualitative research in which the researcher described the phenomena of request in
The Intern movie by interpreting the data. According to Vanderstoep and Johnston (2009:7), qualitative research explains the description of textual phenomena. It
refers to a research design which produces descriptive data. The researcher
described the data by explaining it deeply. Moreover, Denscombe (2007:248)
states that qualitative research described the data which were taken in the form of
words by certain techniques from observations, reports and recordings. It focuses
on the explanation using written texts.
Meanwhile, this research also used quantitative method to convey the
Johnston (2009: 7) state that quantitative research focuses on statistical or numeral
assignment in certain phenomena. By using quantitative research, the researcher
could obtain the number of frequency of data in order to support the researcher‘s
interpretation to the highest or lowest frequency. Hence, the researcher could gain
the conclusion completely.
B.Forms, Sources and Context of Data
According to Denscombe (2007:286), the words or images are the data
which are analyzed or produced in qualitative research. In this research, the data
were utterances, in the form of sentences, phrases, clauses or words spoken by the
main characters in The Intern movie, while the contexts of the data were dialogues.
There were two kinds of sources namely primary source and secondary
source. The primary data source was the movie itself. Meanwhile, data sheet and
the script of the movie were the secondary data sources. In this research, the script
was taken from an internet source, i.e.
http://www.ivanachubbuck.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/02/The-Intern-Ben-Patty-Entire-Screenplay.pdf.
C.Instruments
Lincoln and Guba (in Vanderstoep, 2009:188) say that the major
instrument for qualitative research is a human. Therefore, the major instrument of
this research was the researcher herself. Meanwhile, the secondary instrument of
Table 1. Sample Data Sheet of Requests Expressed by the Main Characters
collection techniques in qualitative research. They are interviewing, ethnographic
observation, analysis of documents and material culture, and visual analysis. In
conducting research, this research used analysis of documents by note taking as a
source of collecting data. The techniques of collecting data employed by the
1. The researcher watched The Intern movie.
2. The researcher retrieved the script and checked the conformity between the
script and the dialogues in the movie.
3. The researcher took notes of the main characters‘ utterances from the dialogues
of the movie which were classified based on the objectives of the study.
4. The researcher recorded and transferred the data into the data sheet.
E.Techniques of Data Analysis
Qualitative research is included into inductive approach. Vanderstoep and
Johnston (2009:168) mention that data analysis is a process of reasoning that
observation goes first, and then followed by theory, hypothesis and interpretation.
After collecting all data, the researcher analyzed them through some processes.
1. The researcher classified the data based on the three objectives of the research.
2. The researcher applied data trustworthiness which was checked by consulting
to the linguistics students and lecturers.
3. The researcher analyzed, described, and interpreted the data.
4. The researcher obtained the conclusions from the result of the research.
F.Data Trustworthiness
According to Given (2008: 895) trustworthiness is a substantial construct
to describe the outside of qualitative terms. To gain data trustworthiness, the
researcher employed triangulation. According to Vanderstoep and Johnson
(2009:179), to produce reliability and validity of the data in the research,
triangulation is needed to reveal uncertainty of the data. It uses many
accordance to Vanderstoep and Johnson, Denscombe (2007: 296) adds that
verifying the data in qualitative research can be done through investigating the
validity, reliability, generalizability, and objectivity.
In this research, the triangulation was done by checking data source, the
method, and the theories employed in this research. The researcher used theory of
types and strategies of requests proposed by Trosborg. Meanwhile, the theory of
purposes of request was proposed by Achiba. Furthermore, the researcher
involved two experts and some of her peer reviewers to check the triangulation of
the data in this research. The researcher consulted the data to the experts who
were the researcher‘s supervisors. Moreover, the researcher also asked her peer
reviewers who were the students of linguistics major. The researcher‘s peer
reviewers read and reread the data carefully. The researcher could be helped by
37 CHAPTER IV
FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
As stated in the first chapter, the objectives of this research are to find out
the types of request used by the main characters, to examine the strategies used by
the main characters, and to explain the purposes of request used by the main
characters toward the requestee in The Intern movie. This chapter consists of two parts, namely findings and discussion to answer the problems of this research. The
findings are presented in the table of data findings. Moreover, the discussion
shows the explanation of each datum.
A.Findings
This section describes the findings of request employed by the main
characters in the movie entitled The Intern. The data are classified based on the three objectives. The first is types of request employed by the main characters in
The Intern. The types of request proposed by Trosborg occur in this movie, i.e. unconventionally indirect request, conventionally indirect request based on the
hearer, conventionally indirect request based on the speaker, and direct request.
Meanwhile, the second objective is the strategies of request used by the main
characters in The Intern. They include hints, questioning hearer‘s ability/willingness, suggestory formulae, statement of speaker‘s wishes/desires,
statement of speaker‘s needs/demands, statement of obligations/necessities, and
cessation of action, and request for joint activity. The occurrence of the types,
strategies, and purposes is presented in Table 2.
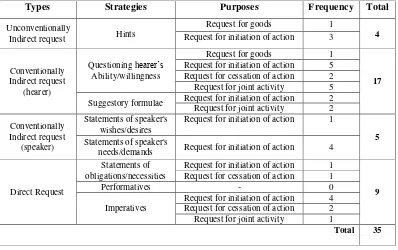
Table 2. Types, Strategies, and Purposes of Request Expressed by the Main Characters in Nancy Meyers’s The Intern
Types Strategies Purposes Frequency Total
Unconventionally
Indirect request Hints
Request for goods 1
4
Request for initiation of action 3
Conventionally
Request for initiation of action 5 Request for cessation of action 2
Request for joint activity 5
Suggestory formulae Request for initiation of action 2
Request for joint activity 2
Request for initiation of action 1
5
Statements of speaker's
needs/demands Request for initiation of action 4
Direct Request
Statements of obligations/necessities
Request for initiation of action 1
9
Request for cessation of action 1
Performatives - 0
Imperatives
Request for initiation of action 4 Request for cessation of action 2
Request for joint activity 1
characters mostly use modal verbs, i.e. can, could, will, and would for expressing the request. Furthermore, questioning hearer‘s ability/willingness becomes the
most prominent strategy which is employed by the main characters. By asking
questions, the main characters express their request. It is more polite than other
strategies since the questions use the modal verbs. Meanwhile, there is one
Statements of speaker‘s wishes/desires only occur once. When using this strategy,
the requester‘s wishes are important because the central power is on the requester.
Thus, statements of wishes/desires only occur once because the main characters
rarely use power to control their request. On the other hand, performatives is not
expressed by the main characters. This strategy is too authoritative since the
request forces the requestee to do what he/she wants. The request uses requestive
intention such as request, order, demand, and command. Following the
explanation about types and strategies, the conspicuous request‘s purpose is
request for initiation of action. The main characters often apply this type of
purposes in their request since the aim is to perform an action that a requester
wants.
Regarding the table of request above, it is clearly seen that the main
characters mostly use indirect request based on the hearer and apply questioning
ability/willingness to express their request toward the requestee. It is because the
relation of both type and strategy makes the request to be polite and sounds less
authoritative. In addition, the purpose of request is to make the requestee performs
an action, even though there is no burden to carry out the request.
B.Discussion
In this section, the researcher presents the explanation of the findings
exhaustively. There are 35 data found in The Intern movie. The main characters and the context of the movie influence the language use of requests. It can be seen
characters in The Intern movie. The detail explanation of request is presented below.
1. Types of Requests Expressed by the Main Characters in The Intern Movie The findings show that four types of request are applied by the main
characters, Jules and Ben, in The Intern. They are unconventionally indirect requests, conventionally indirect requests based on the hearer, conventionally
indirect requests based on the speaker, and direct requests. Those are explained as
follows.
a. Unconventionally Indirect Requests
Unconventionally indirect request is never formulated explicitly. It means
there is a difference between what the requester said and what is actually implied
in the utterance. The requester often makes a statement or asks a question that
indicates a request. Sometimes the requestee does not notice the request uttered by
a requester. Therefore, a requestee should be careful when interpreting the request
which is addressed to him/her by translating it by him/herself. In addition, how
close the relation between a requester and the requestee are needed to be
considered.
The conversation happens between Jules and her mom. When Ben drives
the car, Jules‘s mother calls her. Actually, she does not like a phone call from her
mom because her mom always talks about her research of sleeping habits.
However, she should hang the telephone in order to respect her mom. The