0
Research Proposal
Community Sector External Review
Prepared by
Center for Health Policy and Management
Faculty of Medicine
1
Contents
List of Abbreviations ... 2
Executive Summary ... 3
Chapter 1: Background and Problem Statement ... 4
1.1. Problem Statement ... 5
1.2. Key Questions ... 5
1.3. Purpose ... 5
1.4. Result ... 6
1.5. Location ... 6
1.6. Framework of the Study ... 6
Chapter 2: Methodology ... 7
2.1. Design ... 7
2.2. Data Collection Method ... 9
2.3. Procedure of Data Collection ... 9
2.4. Data Management and Data Analysis ... 11
2.3. Quality Assurance ... 12
Chapter 3: Activities and Research Team ... 13
2.1. List of Activities and Timeline ... 13
2.2. Activity Management ... 13
Chapter 4: Budget ... 14
Reference ... 15
Annex ... 16
Annex 1. Research Instrument: Primary data Collection ... 16
2
List of Abbreviations
AIDS Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome ARC AIDS Research Center – Atmajaya University CSO Civil Society Organization
CHPM Center for Health Policy and Management CSS Community Systems Strengthening Framework CBO Community Based Organization
GF The Global Fund
GWL-Ina Jaringan Gay, Waria dan Lelaki yang Berhubungan Seks dengan Lelaki
(Network of Gay, Transgender, and Men who have Sex with Men) HIV Human Immunodeficiency Virus
IAC Indonesian AIDS Coalition IDI Ikatan Dokter Indonesia
IPPI Ikatan Perempuan Positif Indonesia
JOTHI Jaringan Orang Terinfeksi HIV (Network of People Living with HIV) KAP Key Affected Population
MARP Most at Risk Population PLHIV People Living with HIV PLWHA People Living with HIV AIDS
PKNI Persaudaraan Korban Napza Indonesia
PPK UI Pusat Penelitian Kesehatan Universitas Indonesia
3
Executive Summary
To reduce the morbidity and mortality of HIV in Indonesia, the Global Fund has initiated funds to the HIV and AIDS response program since July 2009 for intervention at 10 provinces in Indonesia. The three major objectives of the interventions includes: (1) Universal Access for HIV prevention and
STI’s ser i es, Health Syste Stre gthe i g, a d Co u ity System Strengthening.
In order to specifically review the third intervention which is the community sector strengthening, the Center for Health Policy and Management (CHPM) is proposing a research to the National AIDS Commission. This research aimed to: (1) provide a mapping of the function of community based groups in the AIDS response, (2) to measure the effectiveness of these groups intervention in terms of increasing the coverage, effectiveness and sustainability of the Indonesian AIDS response, and (3) to discover the possible strategies to increase the effectiveness of civil society in the AIDS response. The output of this study will include:
a policy analysis focusing on:
o the role and functions of civil society in the implementation of prevention and care, support and treatment programs,
o community based analysis of KAP’s perception with regards to the HIV and AIDS
services received so far,
o a map of approaches, advocacy and programs by and focusing on key populations
that contributed to the increasing the effectiveness and sustainability of HIV & AIDS programs,
case studies from each provinces focusing on highlighted issues on the role of community in the prevention, care, support and treatment of HIV& AIDS, and
recommendations of strategic approaches to increase the quality of community based
groups’ role i i reasi g o erage, effe ti e ess a d sustai a ility of the AIDS respo se.
The research method will utilize a logical framework adapted from the Community Systems Strengthening developed by the Global Fund (2014). This logical framework will enable the researchers to measure how certain inputs create functional and effective community systems, as well as for enabling the community organizations and actors to fulfill their role in contributing to health outcomes, which in this case is specific to HIV and AIDS.
The research will develop an instrument for primary qualitative data collection through interviews and focused group discussions with key informants at the national and subnational levels. Primary data will be used to provide better understanding on the aspects of input, process, and output of the CSOs using the CSS framework. While secondary data will be used to map the outcome, which is the proportion of MARP reached and served.
4
Chapter 1: Background and Problem Statement
The UN Global Repot on AIDS, 2012, noted that Indonesia is in the following groups:
Approximately 25 % increase in terms of changes in the incidence rate of HIV infection among adults 15–49 years old, 2001–2011; with Bangladesh, Georgia, Guinea-Bissau, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Philippines, Republic of Moldova, Sri Lanka
Approximately 25 % increase in terms of changes percentage change in the number of people dying from AIDS-related causes, 2005–2011
Approximately 75-100 % Reported levels of coverage of HIV testing among men who have sex with men, most recent year
Approximately 50-74% Reported levels of condom use among men who have sex with men, most recent year
Low coverage <100 - Number of syringes distributed through needle and syringe program per person who injects drugs, most recent year available
Approximately 75-100 Reported HIV testing coverage among people who inject drugs, most recent year available
The Global Fund (GF) has initiated funds to the HIV and AIDS response program since July 2009 for provinces in group A, July 2010 for provinces in group B, and July 2011 for provinces in group C. The funds is specifically addressing to 3 major objectives which includes: (1) Universal Access for HIV strengthening. In HIV and AIDS response, the o u ity’s pri ary role is to support the efforts of the government and AIDS concern groups in the prevention of HIV/AIDS at their own environment. The community has access to clear and accurate information so that it can help to prevent HIV transmission and participate actively in HIV/AIDS prevention, and create a supportive environment for PLHIV and their families.
5 Other NGOs, academics or Civil society groups either working in the field of empowering affected groups or working closely with affected groups will also be part of the response such as legal aid, IAC, PPK UI, Intuisi, Insist, ARC, etc.
1.1. Problem Statement
Following are the context of the problem:
Behaviors change among key affected populations are still low: (1) Condom use has not reached the needed level to revert the epidemic across communities: MSM, FSWs, IDUs, PLWHIV;1 (2) Levels of STIs are still high, in particular among MSMs and sex workers (3) Knowledge among the youth (15-25yo) is also low, 20.6%2
Reports of stigma and discrimination are still found, although sporadically, across the nation3 Key affected populations; most are still socially and politically marginalized groups, with lack
of access to policy-making processes, financial and other resources.
1.2. Key Questions
Following are the key questions that will guide the community sector external review: 1. What has been the function of community based groups in the AIDS response?
2. How effective has these groups been in terms of increasing the coverage, effectiveness and sustainability of the Indonesian AIDS response?
3. What are the strategies to increase the effectiveness of civil society in the AIDS response?
1.3. Purpose
The specific purposes of this review are:
1. To provide a mapping of the function of community based groups in the AIDS response, 2. To measure the effectiveness of these groups intervention in terms of increasing the
coverage, effectiveness and sustainability of the Indonesian AIDS response, and
3. To discover the possible strategies to increase the effectiveness of civil society in the AIDS response
1
IBBS 2011
2 Riskesdas
3
6
1.4. Result
The study will provide vital input to the NAC in the assessment of the current community strengthening performance, in terms of its contribution, effectiveness and sustainability. The outcome of the assessment will be a report covering:
A policy analysis focusing on:
o The role and functions of civil society, in particular community based organizations (KAP community networks and CSOs) in the implementation of prevention and care, support and treatment programs.
o A map of approaches, advocacy and programs by and focusing on key populations
that contributed to the increasing the effectiveness and sustainability of HIV & AIDS programs.
o Community-based-a alysis of KAP’s perception with regards to the HIV & AIDS services received so far
Case studies from selected provinces focusing on highlighted issues on the role of community in the prevention, care, support and treatment of HIV& AIDS. These cases could take on positive aspects as good practices or problems for lessons to be learned.
Recommendations of strategic approaches to increase the quality of community based
groups’ role in increasing coverage, effectiveness and sustainability of the AIDS response.
1.5. Location
These provinces were selected based on the local epidemic and local community based responses. These locations may be adjusted based on further discussion with the National Working Group -Community Sector External Review. However, this proposal aimed for the review to take place in 10 provinces, as follows:
Group A: West Java, East Java, Bali, North Sumatra and South Sulawesi Group B: NTB, North Sulawesi and Yogyakarta
Group C: Central Kalimantan and Bangka Belitung
1.6. Framework of the Study
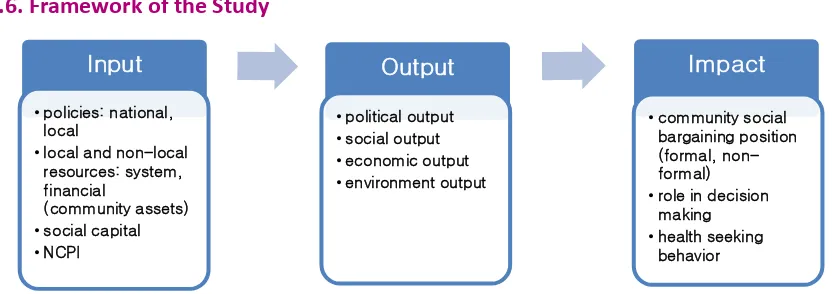
Figure 1: The Framework of the Study
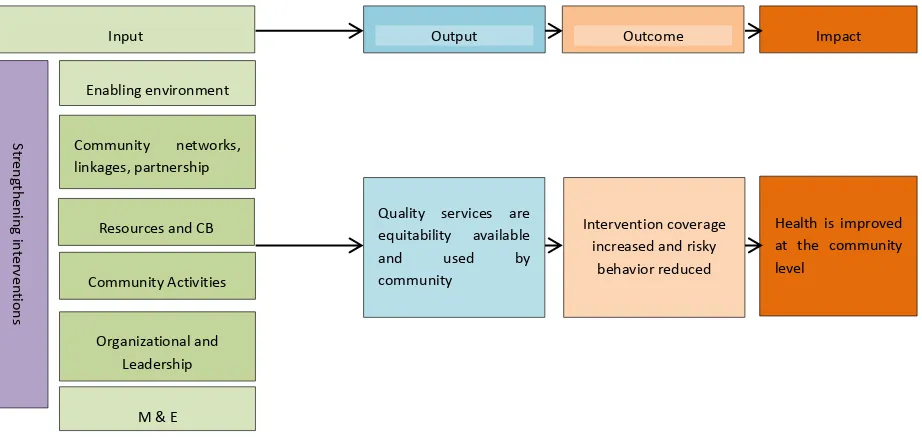
7 Guided by the proposed conceptual framework for the study (Figure 1), an operational framework (Figure 2) were developed by adopting the Community System Strengthening Framework (GF, 2014). In this framework, the role of community organizations and actors in HIV & AIDS response will be influenced by the dynamics of six core components which are considered as essential function of community systems. These six components are:
1. Enabling environment and advocacy in HIV and AIDS response. 2. Community networks, linkages, partnerships, and coordination. 3. Resources and capacity building.
4. Community activities and services delivery. 5. Organizational and leadership strengthening. 6. Monitoring and evaluation and planning.
When all of these core components are strengthened and functioning well, these will be a potential context for community system to contribute in improving their performance (service delivery area) and outcomes (availability, coverage, readiness, and use) and ultimately resulting in improved health and well-being.
Figure 2: Operationalization of the Study Framework
Chapter 2: Methodology
2.1. Design
The design of this study is a combination of quantitative and qualitative approaches. In accordance to the operational framework of the study, the data will be collected using system approach (input, process, output, and outcome) of the evaluation. Primary data will be gathered mainly for the input,
S
Quality services are equitability available
8 process, and output, while secondary data will be gathered for the outcome aspect. Following are the details of the definition and the indicators to be assessed on each aspect:
A. Input:
1. Enabling environment and advocacy in HIV and AIDS response. This refers to the community engagement and advocacy for improving the policy, legal, governance environments, and for affecting the social determinants of health. Information will be collected are:
Participation of CSOs in HIV and AIDS National Program reviews or evaluation. Policy advocacy campaign conducted by CSOs.
Supervision for CSOs using National HIV and AIDS Strategies Guideline.
Report on barriers to equitable access to HIV and AIDS services and/or implementation of National, Provincial, city/district HIV Program
2. Community networks, linkages, partnerships, and coordination. This means that functional networks, linkages, and partnership between community actors and national programs are in place for effective coordination and decision making. The indicators of this component are:
Existing referral system developed by local or national stakeholders that enablbe CSO to monitors completed referral according to National Guide (SRAN).
CSOs representation in national or provincial technical and policy bodies.
3. Resources and capacity building. This means that the actors within the community have good knowledge to develop and deliver effective community-based services, have core funding secured, and the financial resources were managed sustainably. Indicators for this component are:
Human resources with skills for service delivery, advocacy and leadership. Financial resources and competences
Material resources (infrastructure and essential commodities)
4. Community activities and services delivery. This means that the services are accessible to all who need them, evidence-informed and based on community assessments of resources and needs.
Services provided by CSOs according to national or intentional standard accepted services delivery standard.
Delivery use and its quality
5. Organizational and leadership strengthening. This includes the management, accountability and leadership for organization and community systems. The indicators of this component are:
9 Organizational capacity.
Accountability, Tranparency and Responsiveness
6. Monitoring and evaluation and planning. This includes the monitoring and evaluation system, situation assessment, evidence-building and research, learning, planning and knowledge management. The indicators of this component are:
Utilization of evidence to formulate Strategic Planning. Periodic Report to Public, Government and Donor Agencies
B. Process. The aspects that will be assessed include:
Characteristics of CSO/CBO Intervention area
Target population Structure
Types of intervention
C. Output. The aspects that will be assessed include: Number of MARPs reached by CSOs Number and type of service deliveries Equity Issues
Adequacy of Services Quality of Services
Number and types of advocacy/enhancement activity
D. Outcome. This involves the proportion of MARP reached and served and proportion of risky behavior reported by MARPs at provincial/national level
2.2. Data Collection Method
In this study, series of consultative meetings, surveys, FGDs and interviews with informants will be conducted. The informants are, among others: community based groups from key affected populations, working partners of these groups such as Human Rights NGOs, women groups, etc., and government sectors. In the field, the reviewer will visit locations of implementing partners and service providers such as public health clinics (Puskesmas) and the hotspots in the 10 designated provinces.
2.3.
Procedure of Data Collection
Primary and secondary data will be collected for this study.
1. Primary data review. The primary and data will be collected from the following informants: a. National Actors
10 CSO networks at national Level (IPPI, GWL-Ina, JOTHI, PKNI, OPSI, LBH Kes, IAC, PPK UI,
Intuisi, Insist, ARC, IDI, IBBI).
NAC secretariat officers and its members focal point at the national levels, and
International agencies who work closely with CSOs (UNAIDS, UNODC, SUM II, CHAI, HCPI) The primary data will be collected through a semi-structured interview. For collecting the primary data from the CSO networks, the sample of research instrument that will be used is available on Annex 1. Research Instrument: Primary Data Collection (please note that this instrument will still be developed further). As for the informants from NAC secretariat officers and international agencies, semi structured interview guide will be developed as an instrument to collect the data.
b. Local/Provincial Actors (10 Provinces)
Telephone interview will be conducted with 3 to 4 CSOs in each province. Telephone interview is a valid method that can be used in order to ensure that each province is represented in this study using a cost-effective way. The informant for the telephone
i ter ie ill e li ited to the lo al/pro i ial CSO’s dire tors and program managers. As for the field coordinators, financial/administrative staff, and other staffs of each CSO in the selected provinces, the data collection method that will be utilized is through the web selected key informants.
2. Secondary Data Collection
The secondary data collection will include published and unpublished reports, including Behavior and Surveillance Surveys, and other surveys, Most at Risk Population Size Estimation, HIV epidemic Projections, Policy Documents, National AIDS Spending Assessment, Operational Studies and activity reports and Minutes of meeting. The following table listed the types and sources of data that will be collected.
Data Sources of Data Institution/Publisher
Program Target and Coverage CSs Documents and Reports CSs
Institutional Resources CSs Documents CSs
HIV and AIDS Prevalence, Trend of Risk Behavior among
MARP, Intervention Coverage IBBS 2013
DOH, NAC
MARPs in the research Area MARPs Size Estimation DOH
AIDS Financing NASA UNAIDS and DOH
11
Perda Provinsi on AIDS
Perda Kota/Kabupaten on AIDS
NAC, MOH, Law and Human Right Ministry, PAC, City/District AC. Provincial, City/District Health Departments
AIDS Program Planning Minute meeting on National, Provincial, City/District Level, CSOs, and All AIDS Commission.
MOH, NAC, National
Development Planning Board, MOHA, MLRH, Provincial DPLB,
Furthermore, the secondary data will be collected by asking participant of data validation to bring their data to provincial and National focus group discussion
2.4. Data Management and Data Analysis
All the interview, consultative meeting, and focus group discussion will be recorded and transcribed verbatim. Minute meeting for every consultative meeting and FGDs will be made. The data manager will be recruited in each group area (Group A, B, and C). The data will be stored in the MS Words and MS Excel. The summary table and matrix will be made as long as the process data collection until the all data collected.
These processes below will be done throughout the data analysis:
1. Coding, categorizing, and classifying the primary data (from in-depth interview, consultative meeting and focus group discussions) based on the core components of CSS.
2. Summarizing all of primary and secondary data. The summary is the first step to know the function of community sector in response to HIV and AIDS issues.
3. Combining the primary and secondary data descriptively and classifying the themes base on the core of SCs. Triangulating and combining the primary and secondary data get description of CSs performance of the intervention (intervention outcome) which can be measured by the coverage increased and risky behavior reduced as indicators of effectiveness and suitability of the responses. Several consultations to stakeholders and community to validate the data will be conducted during the data triangulation process.
12
2.3.
Quality Assurance
Quality control of the research result will be conducted in the several steps, namely; 1. Planning, Implementing and Reporting
Quality control will be done since the planning and developing the research proposal, data collecting instrument, analyzing and reporting process. Consultation with the NAC and Provincial, and city/district AC and other stakeholders will be conducted to make sure the research process is on the right track.
2. Data validation
The principle of data validation as the important principle used in the research, which include the following activities:
Data credibility to make sure the perception of informant and researcher’s interpretation of the data are compatible. A FGD with the stakeholders as informant will be conducted in each group area.
Data dependability to make sure that all research process run logically and well documented. This step will be conducted through literature and document review related to the study. Furthermore, the peer review will also be conducted as the process of data validation and quality control of the study.
Data conformity as the process to know the main finding data for research implication and recommendation. Technically, the team will confirm the finding with the literature review of the same research issues.
13
Chapter 3: Activities and Research Team
2.1.
List of Activities and Timeline
Activities Month (2014)
1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4
Finalizing Proposal and Research Instrument
Administrative clearance
Mini Workshop for Data collection method and Procedure
Collecting Primary and Secondary Data
Analyzing Data
Submitting first draft of report
Presentations and consultation
Finalizing report
2.2.
Activity Management
This project will be managed and implemented by four personnel:
1. Research Coordinator (1 person)
Responsible for the effective and efficient management of operations of administrative resources and functions, monitoring and reporting, and achieving outputs of the research project.
Ensures that project plans and budgets are in place, that costs are kept within budgets. Coordinates with NAC especially the National Working Group - Community Sector
External Review and acts as the main contact person of the project. Conducts coordination meetings in line with the work plan.
Coordinates the researchers to ensure that the research is in line with the project objectives and scope of work.
2. Researchers (3 researchers)
Coordinate with Project Coordinator in delivering the expected output Conduct primary and secondary data collection
14
3. Research Assistant (1 person)
Help collating the secondary data
Coding and categorizing the primary data
Chapter 4: Budget
15
Reference
The Global Fund, 2011. Monitoring and Evaluation Tool Kits. Part 5: Health and Community Strengthening. Downloaded from http://www.theglobalfund.org/en/me/documents/toolkit/ Accessed at December 4th, 2014
16
Annex
Annex 1. Research Instrument: Primary data Collection
1. Enabling environment and advocacy
Definition: Enabling environment include the social, cultural, legal, financial, and political environment as well as the day to day factors that enable or hinder people search for better health.
How have the CSOs plan and develop the collaboration with HIV and AIDS stakeholder? How have the CSOs plan and develop the collaboration with others actor to monitor the
implementation of HIV and AIDS policies and its programs?
How have the CSOs participate in HIV and AIDS in national consultative strategies and plans? What were the CSOs role to analyze and document relevant issues and plan and implement in policy activities at appropriate level (National, Provincial, City/District and at lower level)? How did the community advocate for implementation and improvement of HIV and AIDS
program at appropriate level?
2. Community networks, linkages, partnership and coordination
Definition: Network is a system for connecting people with common interests. Linkage is a connection that helps to connect a person or organization to others. A Partnership is more formal agreed relationship between people and organization in which they share resources and responsibilities in order to achieve common goal.
Who were the CSOs networks in response to HIV AIDS in the area?
How did the CSOs develop the network with stakeholder of HIV and AIDS program in the area?
What kinds of network that the CSOs have in the response of HIV and AIDS issues in the area?
Did the CSOs have a joint program with others institution? What were the programs? How did the CSOs develop the joint program? What kind of resources the CSOs shared with other institution?
How did the CSOs develop and maintain the mechanism of agreements to enable the community to collaborate and work together?
3. Resources and Capacity Building
17 Did CSOs actors have good knowledge of rights, community health, social environments and barriers to access and develop and deliver effective community–based services in response the HIV and AIDS issues? How? Why?
Did the CSOs actors have core funding secured and they mobilize and manage the financial resources sustainability? How? Why?
Was the financial reporting transparent, timely and correct? How?
4. Community activities and service delivery
Definition: Community based activities and services include access and availability (delivery, use, and quality).
What are the activities of CSOs?
What are the CSO’s ser i es related to AIDS program? Who are the beneficiaries of that service?
How do the public and PLWHA accessed the services? Who run the service delivery activities?
Do the CSOs have the Standard Operational Procedure (SOP) of their HIV and AIDS services? Who developed this SOP?
Did the CSs give the effective, safe and qualified services and intervention? Are they delivered equitably to the people who in need?
5. Organizational and leadership strengthening
Definition: Organizational and leadership are essential key are that aim to build the capacity of community actors to operate and manage the core process that support their activities.
Do the organization and its leadership ensure the accountability to the all stakeholders of HIV and AIDS program in any level?
How did the CSOs provide the leadership in the development, operation, and management of HIV and AIDS programs?
6. Monitoring and Evaluation and Planning
Definition: Monitoring and Evaluation is an activity that provide the strategic information needed to make good decisions for planning, managing and improving HIV and AIDS program, and for formulating policy and advocacy massages.
How did the CSOs provide relevant programmatic qualitative and quantitative data for HIV and AIDS program in any level?
18
Annex 2. List of Informants
(Informants in each province will be selected randomly if number of CSO working for AIDS Program are more than 4)
No Institutions Position
1 NAC Institution and Partnership Deputy
2 Provincial AIDS Commission Secretary, Program Manager, Finance and administrative officer
3 City/District AIDS Commission Secretary, Program Manager, Finance and administrative officer
4 MOH P2PL
Subdit AIDS 5 Provincial Health Office P2PL
AIDS section 6 City/District Health Office P2PL
AIDS division
7 IPPI Board member
8 GWL-Ina Chairperson, board member
9 JOTHI Chairperson, member
10 PKNI Chairperson, member
11 OPSI Chairperson, member
12 LBH Kes Chairperson, Legal consultant
13 IAC Chairperson, members
14 PPK UI Researchers
15 Intuisi Chairperson, member
16 Insist Chair person, Trainers
17 ARC Researchers
19
19 IBBI Members
20 Provincial Bappeda Chair of Divisions 21 City/District Bappeda Chair of Divisions
CSO at Area Group A West Java:
22 Bahtera Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
23 Rumah Cemara Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs 24 Srikandi Pasundan Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
25 Abiayasa Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
26 PKBI West Java and PKBI East Java
Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
27 Gaya Nusantara Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
28 Perwakos Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
29 Hotline Surabaya Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
30 Bina Hati Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
31 EJA Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
32 Orbit Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
33 Sadar Hati Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
34 Bambu Nusantara Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
35 Paramitra Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
36 IGAMA Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
37 IWAMA Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
Bali:
20 (YCUI)
40 Yayasan Dua Hati Bali Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs 41 Yayasan Gaya Dewata Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs 42 Yayasan Bali Nurani Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs 43 Yayasan Hati Kita Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs 44 Yayasan Bali Plus Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs 45 Yayasan Rama Sesana Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs 46 Klinik Bali Medika Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs 47 Yayasan Bali Peduli Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
48 Yakeba Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
49 Paramacitta Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs 50 PKBI - Bali Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
North Sumatra:
51 LSM Galatea Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs 52 LSM Medan Plus Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
53 LSM GSM Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
54 LSM Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
55 H2O Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
56 PKBI Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
57 SPKS Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
58 SECI Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
59 Forum LSM kota Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
21 60 Harapan Sentosa Bitung Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
Yogyakarta:
61 JOY Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
62 Vesta Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
63 Kembang Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
64 IPPI Yogyakarta Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
65 Kebaya Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
66 LP3Y Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
67 PKBI DIY Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
68 LBH APIK Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
69 Sekber Perempuan Yogyakarta Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
CSO at Area Group C: Central Kalimantan
71 PKBI Kalteng Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
72 TBD Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs
Bangka Belitung
78 PKBI Babel Chairperson, Program Manager, Staffs