CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter describes the procedures of the study in order to find out the answers
of the two questions previously stated in chapter one. The chapter covers research
design, the instrument, population and sample, and data analysis.
3.1 Research Design
This study is conducted through Classroom Action Research (CAR)
method. Kemmis and Mc Taggart (1998, p.15) state that “action research is an
action which is conducted to inquire self-reflective and improve his or her
instruction by evaluating his or her own practice”. Ebutt (1985, cited in Hopkins,
2008, p.48) states that “CAR is the effort to improve the teaching learning process by a series of practical actions and to reflect toward the result of actions”. This
design is used when teachers have specific educational problems to solve in
particular scope in educationa setting such as classroom.
According to Mettetal (2003), Classroom Action Research (CAR) is a way
for instructor to discover what work best in their own classroom situation.
According to Alwasilah (2011), he also states that Classroom Action Research
helps both teacher and students to improve their performance. Thus, by using this
method, it is expected that this study can investigate, analyze, and explain
students’ reading improvement using the scanning technique. Latief (2009) states
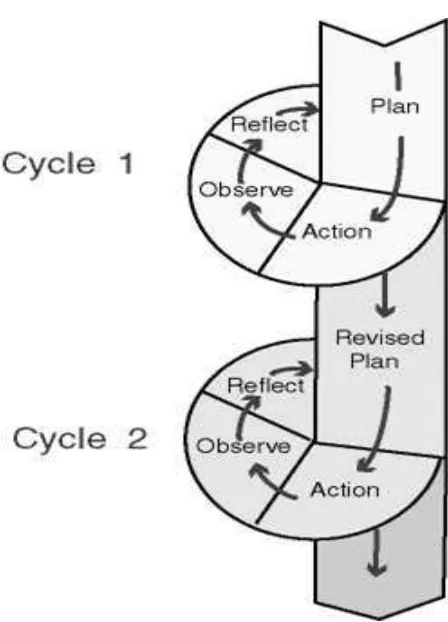
that classroom action research involves repeated cycles. It means there is
continuity from one cycle to the next cycle. Latief (2009) also supports that in
each cycle includes plan, act (do), observe, and reflect. According to Kemmis and
Mc Taggart (1990), there are four basic steps in the action research. They are
3.1.1 Planning
Planning refers to the proposed strategies to be developed and be used in
the research. The researcher arranges the schedule of the research. In the planning,
the researcher explains what, why, where, who, and how to concern the action.
The schedule of research activity as follows:
Table 3.1
Research Schedule
No Plan Activity Week
2 3 4 5 6 7
1 Preparation
Arranging action Plan X
Arranging research instrument X
Arranging schedule and task X
Preparing for class and media X
2 Implementation
Implementing Action for cycle 1 X
X
X
X
Implementing Action for cycle 2 X
X
X
X
3 Arrangement of Research Report
Formulating research report X
Arranging research report X
Planning is arranged based on the reflective observation result, such as the
this activity, the teacher will get the general description about the problem in the
class. Then, the teacher and the observer do the observation of learning process in
the classroom. The observation focuses on students’ and teacher’ attitudes in learning. The teacher’s attitude is seen from her/his way in helping students to learn. For example, the researcher notes the following things:
1. How the teacher starts the lesson.
2. How the teacher helps students (a) to understand the content/meaning of the
text and the way to reveal the meaning (the way in arranging the sentences,
spell the words, pronounce the words), (b) to communicate by using the
expressions studied. (c) to overcome the learning difficulties and motivate
them to participate in the classroom.
3. How the teacher manages the class, such as siting arrangement, light control,
volume, and activities.
4. How students respond the teacher’ efforts.
5. Other theoretical things that necessary to note.
The researcher conducts collaborative research where teacher and observer
are two different people. It is intended for maintaining the objectivity in
measuring, valuing, and deciding actions in achieving the best result. In
implementing the action research, the researcher performs as a teacher while the
English teacher performs as an observer.
3.1.2 Acting
Acting is which the teachers put the plan into actions in order to collect
information or data during teaching and learning process. According to Latief
(2009), he states that in this step, all activities made in scenario are implemented.
The researcher acts the scenario of the research while the other teacher becomes
3.1.3 Observing
Observing refers to the observation of the phenomenon occured in the
class. In observing, the data and the problem is gained through an observation
sheet in every meeting. The aim of observation itself is to collect the data which
become the indicators of success as an impact of the action that had been planed
before (Kemmis & McTaggart, 1988 in Burns 2010)
3.1.4 Reflecting
Reflecting reflects the previous action or treatments for the next cycle. In
this step, the researcher and the teacher analyzes the data and make the conclusion
act based on the data gathered then compares them to the criteria of success
(Latief, 2009). In this step, the researcher and the observer or teacher discuss the
teaching and learning process which has done by the researcher. If there is a
weakness in the previous action, the researcher and observer discuss for the
improvement in the next meeting. The reflection’ result or conclusion is used as
the source for the next action cycle.
Figure 3.1. Cycle of classroom Action Research adapted from Kemmis and
McTaggart (1990)
The research is carried out by a teacher who is also the researcher and the
teacher as the observer. This collaboration gives contribution to this study.
3.2. Participants of the Research
The subject of the research is the ninth grade students at a junior high
school in Bandung. The class consists of 31 students; 14 males and 17 females.
This grade is chosen because they will face some examinations and they need to
focus on reading the text and answering the questions. The technique is needed to
help them in comprehending the text. So, the use of scanning technique is
The researcher also uses four instruments. They are test, observation sheet,
questionnaire and documentation.
3.3.1 Observation
Observation is the act of collecting data about the performance of a subject
through five senses; sight, smelling, hearing, touching, and taste (Arikunto, 2006).
Observation sheet is used in during the teaching and learning process. Observation
sheet can be used to critically evaluate the learning process and identify the actual
data of the effectiveness strategies and techniques employed in the class (Olsen,
2008). Moreover, observation sheet can also be used to document the
phenomenon occured while using scanning technique and determine the strategies
for the next cycle. There is an observer in this study. The researcher becomes a
teacher and the teacher becomes an observer.
3.3.2 Test
Test consists of some questions based on the text that is given to students
in the teaching learning process. Students have to finish doing the task with the
limited time.
3.3.3 Questionnaire
Questionnaire is given after conducting the cycle. In this study, this is
aimed for observing students’ responses toward the use of scanning technique in
the classroom. The questionnaire consists of 10 questions about the use of
scanning technique.
3.3.4 Documentation
Documentation in this study is to find out the data that are related to the
scanning technique that will be used to help students to enhance their reading
3.4 Research Procedure
The research involved several steps described below:
3.4.1 Preparation
Before applying all procedures, the researcher makes the preparation.
After that, the teacher collects the data of students’ and class’ condition. The data are obtained from teacher’s note and observation. That is done for make sure that class and students are ready to observe and to apply the cycle. Teacher’s note and
observation explained that many students get difficulties in reading text especially
report text, and also many students get low score in English examination,
especially in reading examination.
3.4.2 Planning
After making preparation, teacher arranges the concept of the cycle in this
step.Teacher also makes a lesson plan with the scanning technique included. The
other instruments like worksheets and observation sheets are prepared too. The
researcher and the teacher discuss the topic of discussion and time of study.
Furthermore, the topic and material are discussed by the observer and teacher.
3.4.3 Acting
In this step, the researcher applies the planning of the research and it is
observed by the observer. Students and the teacher do the activities in the
classroom based on the planning that has been made before by the teacher.
However, sometimes the activities that have been planned by the teacher do not fit
the planning because the condition of the classroom affects in applying the
planning. The scanning technique is used in the activities. There are some things
that included in the acting step. The steps are:
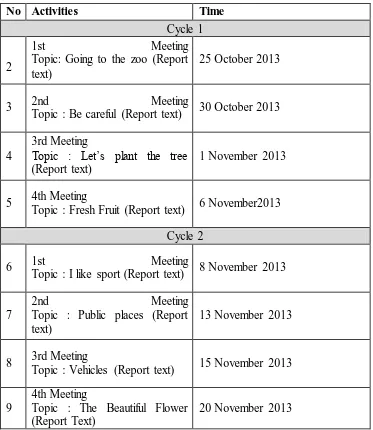
a. Teaching Material
The teacher uses 17 different report texts that are taken from internet and the
b. Teaching Method
In each cycle, the teacher uses lecturing method and scanning technique.
Lecturing method is used when the teacher explains about the scanning
technique and report texts. Besides that, Scanning technique is used when
students work in group and do the exercise.
c. Evaluation
At the end of the lesson, the teacher gives the evaluation. The evaluation
system is individual.
3.4.4 Analyzing and Reflecting
The researcher and the observer analyze and reflect the planning and acting
step by analyzing the result of observation in the class. After that, the lesson plan
is revised by the observer and the teacher. It is intended to find out the weakness
in the last activities before formulating the activities for the next cycle.
3.4.5 Feedback Discussion
In this session, the teacher and the observer do the feedback discussion.
That is a reflective collaboration between the researcher and observer toward the
class activities. They do that based on the observation sheets during the acting
step.
3.5 Data Analysis
In the research, the data are obtained through observation sheets, tests, and
questionnaire. Before analyzing, the data are transcribed and coded to make the
analysis easier. According to Alwasilah (2011), he stated that there are some
benefits of coding the data. First, it helps the researcher to simplify phenomena
identification. Second, it helps the researcher to count the frequent of
phenomenon emerging. Third, it helps the researcher to see the tendency of the
subcategorization of the inventions. After coded, the data are analyzed using
qualitative data analysis.
Meanwhile, students’ level of mastery in reading comprehension is
determined based on criteria proposed by Masidjo (1995:153) that will use criteria
referenced evaluation type 1. Furthermore, Masidjo states that students would be
considered successful if students’ score could attain at least 6,5 of the maximum
score (10). It means the ideal passing score is at least 65. However, this study will
be stopped when 90% of students, subject of this study, get 75 as the minimal
score for their reading comprehension according to the KKM (the passing
criterion) of the school. The criteria can be seen in the following table.
Table 3.3
The Criteria of Reading Score
It means:
Excellent : those students who are able toanswer the test items and get score
between 90 - 100
Very good : those students who are able to answer the test items and get score
between 80 - 89
Good : those students who are able to answer the test items and get score
between 65 - 79
Sufficient : those students who are able to answer the test items and get
score between 55 - 64
Insufficient : those students who are able to answer the test items and get score
less than 5
90 - 100 = Excellent
80 - 89 = Very good
65 - 79 = Good
55 - 64 = Sufficient
Furthermore, Alwasilah (2011) states that action research is very
qualitative seen from the research problems and research purposes. There are
three steps in analyzing the data. Those are data reduction, data display, and
conclusion (Miles and Huberman, 1984 as cited in Alwasilah, 2011).
a. Data Reduction
Data reduction is a process of selecting data that are relevant to the
research questions (Alwasilah, 2011). Reduction is done for the data that are not
necessary. It is to make the analysis easier. In this study, the data of students who
do not follow the whole process of scanning technique treatments are reduced.
b. Data Display
The result of data analysis is displayed in form of table and graph to show
the result briefly and clearly. It is explained descriptively. Alwasilah (2011) states
that descriptive technique is chosen because the data acquired in this study are
qualitaive (non numeric), not quantitative (numeric) and need to be given the
interpretation.
c. Conclusion
The last step after displaying the result of the research is making
conclusion related to research questions. The conclusion is going to be described