CHAMPASACK UNIVERSITY
JOURNAL
Submitted to
Postgraduate Program of Language study of Muhammadiyah University of Surakarta as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for Getting Master Degree of Language Study of English
By
NOKTHAVIVANH SYCHANDONE S200140054
POSTGRADUATE PROGRAM OF LANGUAGE STUDY MUHAMMADIYAH UNIVERSITY OF SURAKARTA
COMPARATIVE ERROR ANALYSIS IN ENGLISH WRITING BY FIRST, SECOND, AND THIRD YEAR STUDNETS OF ENGLISH
DEPARTMENT OF FACULTY OF EDUCATION AT CHAMPASACK UNIVERSITY
Nokthavivanh SYCHANDONE Email: [email protected]
Muhmmadiyah University of Surakarta, Indonesia.
Abstract
This study focuses on comparative error analysis in English writing made by different levels. To investigate the error types, the frequency of error types, the similarities and difference of errors and the last to find the error sources that occur in first, second and third year learners. Error analysis is one type of linguistic study and it focuses on learners’ error making. The linguistic category and surface strategy taxonomy are used to find out the types of error. The analysis the phenomenon based on Brown (1980) namely, error identification, error classification, Error description and error explanation. The data from students’ writing products, 54 pieces in three levels and the total errors are 571 erroneous sentences. There are two types of errors, namely lexical errors and syntactical errors; eight error categories and twenty-seven error cases. The second year learners made the most error 263 errors or 46, 05% while first year learners produced 229 errors or 40, 10% and third year learners made 79 errors or 13, 83%. There are similarity in errors types, five similar categories and five error cases, but there are three different error categories and eighteen error cases. The main error sources, learners had lack knowledge of English grammatical rule. The overgeneralization (265 errors or 46, 40%) influences learners’ error, language transfer (199 errors or 34, 85%) still interfere learners’ acquisition and simplification (107 errors or 18, 73%) is one factor that effect learners’ errors.
Abstrak
Penelitian ini difokuskan pada analisis kesalahan komparatif dalam menulis bahasa Inggris yang dibuat oleh tingkat yang berbeda. Untuk menyelidiki jenis kesalahan, frekuensi jenis kesalahan, persamaan dan perbedaan kesalahan dan yang terakhir untuk menemukan sumber kesalahan yang terjadi pada pertama, kedua dan ketiga pelajar tahun. Analisis kesalahan adalah salah satu jenis studi linguistik dan berfokus pada peserta didik membuat kesalahan. Linguistik kategori dan strategi permukaan taksonomi digunakan untuk mengetahui jenis kesalahan. analisis fenomena berdasarkan Brown (1980) yaitu, kesalahan identifikasi, klasifikasi error, kesalahan deskripsi dan penjelasan kesalahan. Data dari produk menulis siswa, 54 buah dalam tiga tingkat dan total kesalahan yang 571 kalimat yang salah. Ada dua jenis kesalahan, kesalahan yaitu leksikal dan kesalahan sintaksis; delapan kategori dan dua puluh tujuh kasus. Peserta didik tahun kedua membuat sebagian besar kesalahan 263 kesalahan atau 46, 05% sedangkan peserta didik tahun pertama diproduksi 229 kesalahan atau 40, 10% dan pelajar tahun ketiga membuat 79 kesalahan atau 13, 83%. Ada kesamaan jenis kesalahan, lima kategori yang sama dan lima kasus kesalahan, tetapi ada tiga kategori kesalahan yang berbeda dan delapan belas kasus kesalahan. Sumber kesalahan utama, peserta didik memiliki pengetahuan kurangnya aturan tata bahasa Inggris. The generalisasi yang berlebihan (265 kesalahan atau 46, 40%) mempengaruhi 'error, transfer bahasa (199 kesalahan atau 34, 85%) masih mengganggu peserta didik peserta didik akuisisi dan penyederhanaan (107 kesalahan atau 18, 73%) adalah salah satu faktor yang berpengaruh peserta didik kesalahan.
Kata kunci: kesalahan komparatif, kesalahan analisis, kesalahan yaitu leksikal dan kesalahan sintaksis, kesalahan sumber.
I.
INTRODUCTIONsecond learners make the error, based on James (1998: 77) said that an error arises when there was no intention to commit one; it means that learners have not mentioned to make error, but they do not avoid errors then students’ error can be classified into linguistic errors. Most second learners make more errors on writing because English writing is formal and organization of writing, concepts of English grammar, so learners face problem in writing.
Error analysis is “the first approach to the study of SLA which includes an internal focuses on learners’ creative ability to construct language” (Saville -Troike, 2006: 37). It means that is one type of linguist analysis which focused on error learner make. According to Corder (1982: 35) Error analysis is part of psycholinguistic to investigate the language of the second learner and error analysis is a one methodology of psycholinguistic. Ellis & Barkhuizen (2005: 51) described error analysis is “a set of procedures for identifying, describing and explaining learners’ errors”, Error analysis is like the process of determining the incidence, nature, cause and consequences of unsuccessful in language.
Error is one part of linguistic study because it studies the learners’ quality in second language. Saville-Troike (2006: 39) said that learners’ errors are the windows into the language learners’ mind because learners’ errors indicate teachers and researchers know about learners’ language ability. James (1998: 12) furthered that error is “tell the teacher what needs to be taught, tell the researcher how learning proceeds, and a means whereby learner test their hypotheses about the second language”. According to Corder (1967: 166) errors show that L1 and L2 learners both develop an independent system of language in using, although it is not the adult system ……..nor that of the second language, but it is evidence of a transitional competence.
Linguistic category is error classification that occurs in the English system. James (1998: 105) “carries out errors in terms of where the error is located in the overall system of the based on the linguistic item which is affected by the error”. It indicates in which component of language the error is located. Language components may include phonology (e.g. pronunciation), syntax and morphology, semantics and lexicon, and style. That error type focuses on the grammatical rule and vocabulary usage.
Surface strategy taxonomy is type of error that describes the errors appear on the omission, addition, misformation, misordering some items in the sentences. According to James (1998: 106) states that surface strategy taxonomy is based on the he ways in which the learner’s erroneous version is different from the presumed target version. The surface strategy taxonomy is the English system about omit some items, add some items that is unnecessary or incorrect, misformation uses the wrong form of structure or morpheme (run-runned, that replace those, her refers his) and the last misordering is incorrect arrangement of the sentences (what dad is doing?. He is a men tall).
According to Selinker’s theory (Fauziati, 2009: 169) describe the interlangugae system has a cognitive emphasis and a focus on the strategies that learners employ when leaning a second language. The learners’ errors are the product of the cognitive process, so that the researcher followed Selingker’s theory based on interlanguage system. He suggests that there are five processes central in leaning second language such as overgeneralization, transfer or training, strategies of second language learning, strategies of second language communication and language transfer.
unnecessary items (articles, prepositions, verbs). The character of errors related with English grammar especially part of speech and English form.
As like as Bootchuy’s work (2008) found 165 errors in students’ writing and he followed Richard (1971) to classification namely: interference error, intralingual errors and development errors. There were three high error types such as omission (subjects, verbs and other) is 37, 57%, incorrect form of compound is 23, 03% and word-order is 9, 07%. The types of errors showed the character of errors that learners made wrong in their sentences and bring to the error source. But this research is different because the researcher used more than one theory to find the type of errors.
However, this research is similar with other previous studies that based on error types on writing, but there are different something such as the research place, method to find error classification, the different theory and strategy of analysis. Moreover, this research shows the similarities and difference of errors types that is different from other, that is different from other previous studies. They found only the error types and the errors source, but they did not compare how difference the types of errors in different levels. This research is the first in Champasack University to study in students’ errors because most of researchers focused on testing the material in second language.
Second learners are in Laos who learn English as the foreign language and specific in English department of Champasack University, who learned on English major. Through researcher’s experience in English teaching there for five years then she knew that most second learners are not successful in English writing because they made some errors and they are not good in English writing. So that the researcher would like to know the types of errors and she focuses on “comparative error analysis in English writing by First, Second and Third year students of English department at Champasack University”.
process. This research is significant for improving English writing especially teachers will know the weakness of learners and they will improve their teaching strategy. Students get more benefit on this research because they know the error types and their weakness on writing, thus it stimulus to students to practice more in writing. The last, for the other researchers who are interested in writing errors, it is the one guideline to find errors and it is the deviance to support their researches.
This current study focuses on four objectives that are interesting to find out. First, researcher would identify the weather of errors types are made by three levels. Second point, she would deep to the frequencies of each types of error are made by three level. Third point, it investigates the similarities and differences of type of errors of learner on writing in First, Second, and Third year. The last point, it finds out the error sources that occurs in students’ writing in First, Second, and Third year of English Department.
II.
RESEARCH METHODA. Types of Study
According to Fraenkel, et.al (2012: 425) qualitative research is the famous method to be used in variety fields; these include comparison between alternative
methods of teaching
.
According to Moleong (Bogdan and Taylor, 2004: 36)A. Subject of Study
The subject of research is students of first, second and third year of English Department at Champasack University academic year of 2015/2016. There are 14 students in first year, 20 students in second year, and 20 students in Third year.
B. Object of Study
The object of the study is type of errors in students’ written form sentences containing errors are taken from different level of students’ composition (written production) in English Department at Champasack University academic year 2015/2016.
C. Technique of Collecting the data
The researcher used the elicitation technique to find out data because elicitation is technique to lure students to produce the writing and give instruction to writing composition. The procedure of collecting data, researcher got the data of the students’ English writing from one source: the writing task. The advantage of collecting data by asking the research participants to do a writing task is obtaining highly authentic data, but they would write in a controlled environment (giving the topic) in the same topics but it conducted in different levels, sitting in a classroom. The researcher collected data one times and distance of time is one week and one time.
D. Technique of Analyzing data
This research found out the erroneous on the sentences based on linguistic category and surface strategy taxonomy. Researcher found the total of errors about 571 erroneous sentences and it divided into groups, namely lexical errors are about 131 errors and syntactical errors are around 440 errors.
1. The Types of Errors made by First, Second and Third Year Students The first year Students were new freshmen and they had less experience in English language, so they produced errors in their sentences. The researcher found total number of errors about 229 errors or 40, 10% that made by first year learners that include from lexical errors are 45 erroneous sentences or 7, 88% and syntactical errors are 184 erroneous sentences or 32, 22 %. The second year students made the total of errors about 263 errors or 46. 05% that consists of lexical errors are 62 erroneous sentences or 10, 87% and syntactical errors are 201 erroneous sentences or 35, 20%. The third year, the errors total is 79 erroneous sentences or 13, 83% that concludes lexical errors are about 24 errors or 4, 20% and syntactical errors are 55 errors or 9, 63%.
a. Lexical Error
Lexical error is the process of converting a sequence of characters into a sequence of token means or we can say that lexical error is making the wrong choice of word for the stylistical context. The word is roughly correct, but wrong I “flavor” then choosing wrong words to complete the sentence and wrong level of formality.
1) Wrong Spelling Words
Example: Nixt, I went to take a shower at 8:30 pm
One example illustrates that learners made error on lexical error because they did not recognize English word, so they produced erroneous word. This sentence shows that error occurs in spelling word “next” but learner wrote “nixt” which is wrong form and no meaning then the correct is “next, I went to take a shower at 8:30”.
2) Wrong Selection Words
Wrong selection word is the process of choosing the wrong word to complete sentence, learners choose other word instead of the correct word such as learner mentions to write “part” but they write “park”, they want to write “nine o’clock” but they write “night o’clock” and they use wrong example “I look for any lesson” the word “any” is used in interrogative and question sentence but learners used in position sentence.
Example: I cleaned my bad
This sentence indicates that learner chose the wrong words because the characters of letters are similar but different a litter bit. Learner mentions to write “bed” but he/she wrote “bad”, so this sentence is incorrect then the correct sentence is “I clean my bed”
3) False Friend
“False friend” are words that have seemed to be the same but in fact, there are different meanings and it is often confused with the words in another language with a different meaning because the two words look or sound similar.
Example: I thing that if I can teach in my hometown
This sentence shows the similar of English words that makes student to be confused. This case is similar pronunciation “think” and “thing” the correct sentence is “I think that if I can teach in hometown”.
b. Syntactical Errors
sometimes these were called part of speech, and how to numbers of these classes go together to phrase form and sentences.
This research, writer found syntactical errors in three levels students of English Department at Champasack University and it include in five categories such as: (1) Verb “to be”, (2) Verbs, (3) Prepositions, (4) Conjunctions, and (5) Sentence constructions.
1) Verb “to be”
Verb “to be” is said to the most important of English language, constantly changing form, sometimes without much of a discernible pattern, considering that we use it so often, it is really too bad for “to be” has to be most irregular, slippery verb in the language.
Example: We are have lunch at 11:30
From example above shows that learner has lack grammatical knowledge and she/he misunderstood about simple structure, so learner puts verb “to be” in the sentence to describe activities then correct sentence is “we have lunch at 11:30”.
2) Verbs
Verb is one part of speech and sentences because all sentences structure can’t miss verb. Verb mortifies subject that makes people to understand the meaning of the speaker. Verb is part of tenses or one composition of sentences, verb predicate by using such as present simple “I drinkwater” and past simple “I drankwater” using verb in the present simple is like infinitive verb when we use verb in past simple verb character of letter.
Example: I watching TV.
TV” because the learner can’t remind English grammatical structure then she/he creates new form as similar as English form.
3) Prepositions
Preposition is one the composition of the sentences and part of speech, it used to combine between word to word and that make that sentence is meaningful and correct with English grammar. Preposition is the word which is used to show and describe the places where something is location.
Example: My family still lives in there ()
The sentence above shows that learner made error on additional unnecessary preposition because learner did not remember the preposition rule then she/he made error. The first error sentences is “My family still lives in there” the rule of using “there” does not put preposition because “there” is mean the place and it is full meaning in itself, the correct sentence is “My family still lives there”.
4) Conjunctions
Conjunction or connection idea is the part of speech that is important one because conjunction words combine between word to word, sentences to other sentences and it includes on clause. Especially English writing, the conjunction is one composition that makes writing text is perfect in context.
Example: I had party drink beer together. and
From one example indicates that learner ignored English rule when she/he wanted to combine the two clauses together such as the first error sentence is “I had big party drink beer together” there are two clauses between word “party” and “drink”, maybe learner refered to spoken language and wrote the sentence, so the correct is “I had big part and drink beer together”.
5) Sentence Construction
sentences and word phrase; it is the grammatical arrangement of words in sentences.
Example: Before go to take a shower at seven o’clock I
Three examples are omission subject case, the sentence is “before go to take a shower at seven o’clock” is similar as case in the first because learner ignore the English grammar, he/she followed spoken language and wrote the sentence. The correct sentence is “before I go to take a shower at seven o’clock”.
2. The Frequency of Error Types made by First, Second and Third Year Students
In the first year learners produced 229 errors or 40, 10%. There are two error types and seven categories. Lexical errors are 45 error or 7, 88%, it consists of three categories namely wrong spelling words (23 errors or 4, 02%); wrong selection words (15 errors or 2, 62%) and false friend (7 errors or 1, 22%). While syntactical errors are 184 errors or 32, 22% and it consists of four categories such as Verbs (109 errors or 19, 08%), prepositions (35 errors or 6, 12%); Conjunctions (21 error or 3, 67%) and sentence constructions (19 errors or 3, 32%)
The second year learners made more errors than first and third year because they do not understand the topic to writing then they used other tenses in their paragraph. The errors total is 263 erroneous sentences or 46, 05%. Lexical errors are 62 errors or 10, 87% and it has two categories, namely wrong spelling words (55 errors or 9, 63); wrong selection words (7 errors or 1, 22%) while syntactical errors (201 errors or 35, 20%) is more erroneous sentences because learners had lack of English grammar. There are five categories such as Verb “to be” (6 errors or 1, 05%); verbs (107 errors or 18, 73%); prepositions (38 errors or 6, 65%); conjunctions (17 errors or 2, 97%) and sentence construction (33 errors or 5, 77%).
made 79 errors or 13, 83%. The Lexical errors are 24 erroneous sentences or 4, 20% that consist of two categories namely wrong spelling words (20 errors or 3, 50%) and wrong selection words (4 errors or 0, 70%). Syntactical errors are 55 errors and it has four categories such as verb “to be” (3 errors or 0, 52%); verbs (24 errors or 4, 20%); prepositions (15 errors or 2, 62%) and sentence constructions (13 errors or 2, 27%), but it is found errors that relates in conjunction.
In the two types of errors indicate that most of learners made more errors on syntactical errors especially about “verb”, it means that learners had lack of English grammar and they could not use tenses in the appropriate situation. Moreover, they created the new form that is similar in the English grammar but it is incorrect. Lexical errors are the one problem for learners’ English writing because they did not reminded some spelling words because the different of letters of their mother language.
Total 229 40,10% 263 46,05% 79 13,83% 571 = 100%
The table shows that the types of error in the three levels with the number of error types and percentages are similar in error types, but they are different in the number of error and different of error categories. There are two error types, namely lexical errors and syntactical errors. Lexical errors have three categories such as wrong spelling words, wrong selection words and false friends while syntactical errors have five such as verb “to be”, verb tenses, prepositions, conjunctions and sentence constructions. The second year learners made more errors than first and third year.
3. The Similarities and Differences of Error Types made by First, Second and Third Year Students
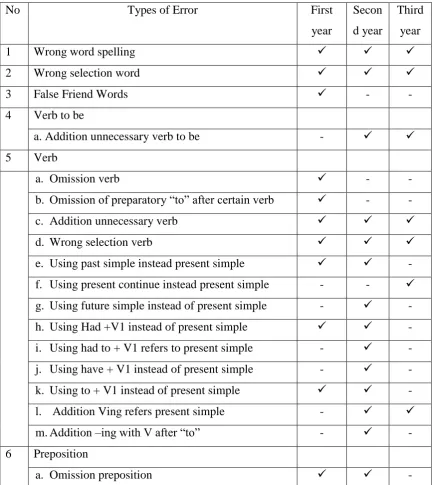
After the researcher analyzed data, she found the similar and different error types in three levels. They are important because it shows that the types of errors which learners made difference from the others. The error types are similar in three levels but they are different in categories and error cases.
In the categories have eight characteristics namely wrong spelling words, wrong selection words, false friend, verb “to be”, verb tenses, prepositions, conjunction, and sentence construction. Some of categories divided the some cases such as verb “to be” (additional unnecessary verb “to be”); verbs have 12 cases, prepositions have 3 cases, conjunctions have 3 cases and sentences constructions have 3 cases.
a. The Similarities of Error Categories and Error Cases
Similarities of error cases have five cases that three levels learners made errors in the same cases such as additional unnecessary verbs, wrong selection verbs, additional prepositions, wrong selection prepositions, and omission subjects.
b. Difference of Error Categories and Error Cases
The table above shows that there are some similarities and difference of errors which three year learners made, so that there are three thing that are different such as the different number of error (table: 1) that happen in three years, the difference of categories and difference of cases.
There are few different categories that appear in the three years and they are different from other year. There are 3 categories that some learners made on different categories namely: false friend words are found only the first year learner made this category like the verb “to be” found in second and third year, but first learners did not made errors on this category. The last, conjunctions did not find in the third year because learners did not make errors in this category.
Other error cases that learners made are different in each year, thus there are 18 cases namely: additional unnecessary verb “to be”, omission verbs, omission of preparatory “to” after certain verbs, using past simple instead present simple, using present continue instead present simple, using future simple instead of present simple, using had +V1 instead of present simple, using had to + V1 refers to present simple, using have + V1 instead of present simple, using to + V1 instead of present simple, addition V+ing refers present simple, addition V+ing after preparatory “to”, omission prepositions, omission conjunctions, additional conjunctions, wrong selection conjunctions, additional articles, and using objective pronoun replace subjective pronoun.
English grammatical rule. The learners transferred their native language structure into target language then these sentences are errors. One more errors, some learners made more errors on vocabulary or words because the different of letter character then they can’t remember the spelling words, so that is the cause of errors.
Table 2: the Similarities and Difference of Error Categories and Error Cases
No Types of Error First
year
Secon d year
Third year
1 Wrong word spelling
2 Wrong selection word
3 False Friend Words - -
4 Verb to be
a. Addition unnecessary verb to be -
5 Verb
a. Omission verb - -
b. Omission of preparatory “to” after certain verb - -
c. Addition unnecessary verb
d. Wrong selection verb
e. Using past simple instead present simple -
f. Using present continue instead present simple - - g. Using future simple instead of present simple - -
h. Using Had +V1 instead of present simple -
i. Using had to + V1 refers to present simple - - j. Using have + V1 instead of present simple - -
k. Using to + V1 instead of present simple -
l. Addition Ving refers present simple -
m.Addition –ing with V after “to” - -
6 Preposition
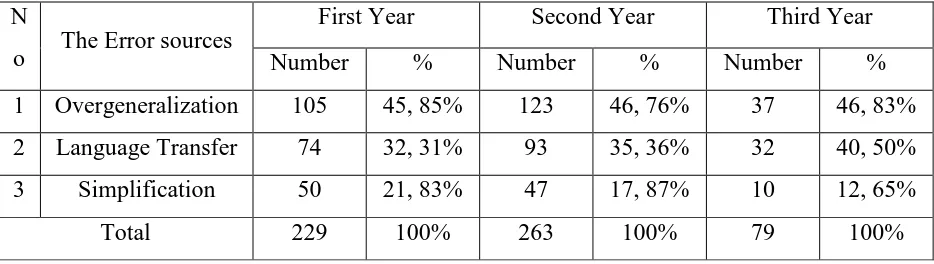
4. The Error sources made by First, Second and Third Year Students. According to Selinker’s theory based on cognitive central process, there are described into five errors causes. When researcher analyzed then it found only two error sources and one error source is new error source. Thus there are three main error sources, namely overgeneralization, language transfer and simplification.
a. Overgeneralization
This case, some of rules of interlangauge system that the result of overgeneralizations are the English grammatical rules and feature of the target language. The second learners ignore the English form that is not correct with English form, and they created new form, but there are incorrect. This cause of error occurred when the learners have mastered a general rules but they do not know the concentrations to that rule because learners’ cognitive process to comprehend in English grammar.
b. Language transfer
Language transfer is some of the rule of interlanguage and the result of transfer from learners’ first language form to target language. Sometimes it is called “influence of first language”; it is described different theoretical accounts of the role of learners’ first language in learning second language or foreign
b. Addition preposition
c. Wrong selection preposition
7 Conjunction
a. Omission conjunction -
b. Addition conjunction -
c. Wrong selection conjunction - -
8 Sentences construction
a. Addition article -
b. Omission subject
c. Using objective pronoun replace subjective pronoun
grammatical rule then they transfer native language structure into target language or some learners transfer the vocabulary. There are two major of language transfer such as: positive transfer and negative transfer. Positive transfer occur on sentences when the first language structure is used in second language form that is appropriate or correct in second language. The negative transfer is different structure between first language form and second language form then result in error.
c. Simplification
Simplification occurs when second learners absent words in the sentence, second learners omit some item to complete sentences then it is made those sentences are not correct. According to Duley, Burt and Kachen (1982:155) “Omission of content word, although typical in the early stages of L1 acquisition, is not common in sequential L2 acquisition where the learners is older and more cognitively mature” This cause occurs on sentences because learners do not remind the English structure or the cognitive process then they do not write necessary item in sentence and sometimes learners forget rule of sentence structure, then their sentences are incorrect with English grammar.
Table 3 The Error Sources Made by First, Second and Third year learners
N
o The Error sources
First Year Second Year Third Year
Number % Number % Number %
1 Overgeneralization 105 45, 85% 123 46, 76% 37 46, 83%
2 Language Transfer 74 32, 31% 93 35, 36% 32 40, 50%
3 Simplification 50 21, 83% 47 17, 87% 10 12, 65%
Total 229 100% 263 100% 79 100%
errors or 46, 76% because they created new form and used the wrong tenses in the situation. They did not remind the English form and they made the errors in the sentences.
The second error source, language transfer influences the second language learners because some learners transfer native language (Lao form and Lao language transcript) into English language. Second year learner made more errors on language transfer because they transferred their native language structure to target language about 93 errors or 35, 36%.Sometimes learners did not use English form, but they transfer to Lao form because sometimes Lao form is different from English form, so they made errors.
The last simplification is the new error source that does not have in the Selinker’s theory in cognitive processes center. In this the case, learners omit some item or morpheme in the sentence and those items are necessary to complete the sentence. The first year learners made more errors (50 errors or 21, 83%) that second and the third year. Some learners did not understand the English grammatical rule, so they omitted some items on sentences.
IV.
CONCLUSIONAfter researcher found the error in students’ writing in different levels (first, second and third years). There are 54 participates and 54 pieces from learners’ writing products. Next she followed the linguistic category and surface strategy taxonomy to find the errors and identification of error types, thus she found the total of errors about 571 errors and there are two types of errors, namely lexical errors and syntactical errors. In the lexical errors are 131 erroneous sentences or 22, 94% and syntactical errors are 440 erroneous sentences or 77, 05 %.
sentence or 1, 57%), verb tenses (240 erroneous sentence or 42, 03%), prepositions (88 error or 15, 41%), conjunctions (38 errors or 6, 65%) and sentence constructions (65 erroneous sentences or 11, 38%).
The second year learners made more errors than first and third year learners; there are 263 erroneous sentences, but second year learners produced 229 erroneous sentences and third year learners made 79 error sentences.
There are similarities of error types, namely lexical errors and syntactical errors then there are five similar error categories and five error cases. On the other hand, there are three different error categories and eighteen different error cases.
BIBILIOGRAPHY
Bootchuy, Tiptida. (2008) An analysis of error in academic English writing by a group of First-year Thai graduates majoring in English. (Master’s Thesis) Kasetsart Unversity, Thailand.
Brown. H. Douglass (1980) Principles of Language Learning and Teaching. New Jersy: Practice Hall.
Corder, S. Pit (1982) Error Analysis and Interlanguage. Oxford University Press Corder, S. Pit (1967) The Significance of Learners’ Errors. International Review
of Applied Linguistics in Language Teaching (IRAL),5(4), 161-170. http://dx.doi.org/10.1515/iral.1967.5.1-4.161
Dulay, Heidi; Marina Burt and Stephen Krashen (1982) Language Two. New York: Oxford University Press.
James, Carl (1998) Error in Language Learning and Use: Exploring Error Analysis. London: Routledge
Ellis, Rod & Gary, Barkhuizen (2005) Analysing Learner Language. Oxford University Press. UK.
Fauziati, Endang (2009) Reading on Applied Linguistics. Surakarta: Muhammadiyah University Press.
Fraenkel, R. Wallen, E. Hyun, H. (2012) How to Design and Evaluate Research in Education. McGrraw-Hill.
Moleong (1985) Metodologi Peneliatan Kualitatif. Bangdung PT Remaja Rasa Karya.
Rechard, J. (1977) Error Analysis: Perspective on Second Language Acquisition. London: Longman.
Saville-Troike, Muriel (2006) Introducing Second Language Acquisition. Cambridge: C.U.P