Fluidization Characteristic of Sewage Sludge Particles
I Nyoman Suprapta Winaya
1, a, Rukmi Sari Hartati
2,b, I Nyoman Gde Sujana
1,c1Mechanical Engineering Department, Udayana University, Bali-Indonesia
2Electrical Engineering Department, Udayana University, Bali-Indonesia
ains.winaya@me.unud.ac.id, brshartati@ee.unud.ac.id, csujana@gmail.com
Keywords: fluidization, simulation, CFD, sewage sludge
Abstract: The main objective of this study is to determine the basic characteristics of fluidization using sewage sludge particle as non-visual phenomena which can then be modeled physically and numerically with the program of Computational Fluid Dynamic (CFD). CFD modeling using Eulerian model incorporating the kinetic theory for solid particles was applied to the gas-solid flow at various superficial velocities for different particle sizes. The transfer momentum was calculated using Syamlal-O'Brien drag function and Eulerian multiphase model was used for analysis. Two-Dimensional computational domains discretized using rectangular cells (Quad), made within the 20 iteration steps of 0,001s. The gas velocity is found to be the the most important factors that influence the formation process of fluidization; by increasing the rate of fluidization the bed expanse occurs higher as well the time of onset fluidization is shorter. The phenomenon can be explained well by modeling and simulation.
Introduction
Fluidization is one of the contacting techniques through which fine solids are transformed into a fluid using either gas or liquid. In fluidization a contact between the gas and solid particle occurs appropriately because its wide range of contact surface. Better possibilities to simulate mixing of gas and solids in fluidized beds are of interest for many researchers. One of the bed materials that can be used in fluidized bed gasification technology is sewage sludge as fuel which is obtained from wastewater treatment hospitality. In addition to the utilization of an alternative energy using sewage sludge can also reduce the environment load because potentially to contaminate natural and source disease if not treated properly. The waste water may also contain certain undesirable components, including organic, inorganic and toxic substances, such as pathogenic microorganisms. Indonesia especially Bali is one of the main tourist destination in the world in which the existing hotels with qualified supporting facility is the obligation. To support the operations of hospitality, it is necessary to provide the waste treatment process which can produce the energy for the hotel.
Computational Fluid Dynamic (CFD) offers an approach to predict the behavior of mixing phenomena in fluidized bed reactor using any type of particles as the bed material. Simulations have been developed in recent years, and CFD modeling is popularly used to simulate the hydrodynamic of fluidization regimes [1]. The program could provide the flexibility to change the design parameters without much cost, providing faster time of the trial, and also able to provide a detailed information about the flow field especially in the area of measurement which is difficult or impossible to obtain [2]. Armstrong and Luo developed a model approach Syamlal-O'Brien drag coefficient which showed more local fluctuations on the basis of particle terminal velocity with slight sensitivity to the microscopic scale [3]. Tasirin, et al. conducted an experimental study as well as modeling and it was found for a higher in gas velocity the fluidization process could be improved [4]. Fluidization behavior involves three important phases namely: the particle-dominated, predominantly gas and a mixture of both.
Applied Mechanics and Materials Vol 776 (2015) pp 294-299 Submitted: 2015-02-19
© (2015) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Accepted: 2015-04-10
Method
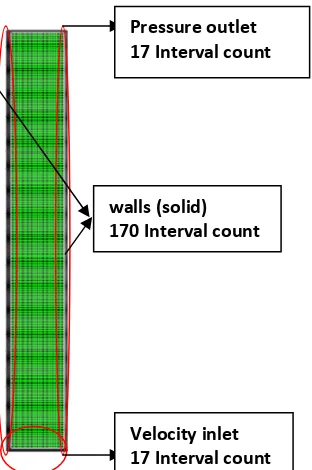
Simulation setup. The simulation process is in 2D model with mesh containing of 2,830 quadrilateral cells. Fig. 1 shows the messing and the boundary condition of the system. A solid-fluid Eulerian model has been carried out applying in the bed material of sewage sludge. Solid particle velocity was set at zero as minimum fluidization base, and gas velocity was assumed to have the same value everywhere in the bed with air velocity variation of 0.05 to 0.15 m/s. Sewage sludge properties as bed material with different particles diameter 0.5 mm, 0.6 mm, 0.7 mm which was filled to the height of 10 cm. Momentum exchange coefficients were calculated by using the Syamlal-O’Brien drag functions. The discretisation of the convective terms was carried out with the second-order upwind scheme. A time step of 0,001s was used to ensure quick convergence with 7,000 iterations.
- Total meshing = 2,890 quadrilateral cells
- Superficial velocity = 0.05 m/s, 0.10 m/s, 0.15 m/s
- Gravity force = 9,81 m/s
- Time steps = 0.001s
- Iterations = 7,000
- Air as primary phase and sewage sludge particle with density 310,48 kg/m3 of as secondary phase
Mathematical model. The interactions between gas and fluidized bed granular particles were used Eulerian granular model. The model allows for the presence of two different phases in one control volume of the grid by introducing the volume fraction variable as follows,
Solids phase:
( . ) + ∇. ( . . ) = 0 (2)
The conservation of momentum for the gas and solid phases are described as Gas phase:
Drag coefficient model Syamlal-O’Brien based on the measurements of the terminal velocities of particles in fluidized bed. These correlations give exchange coefficients in terms of the volume
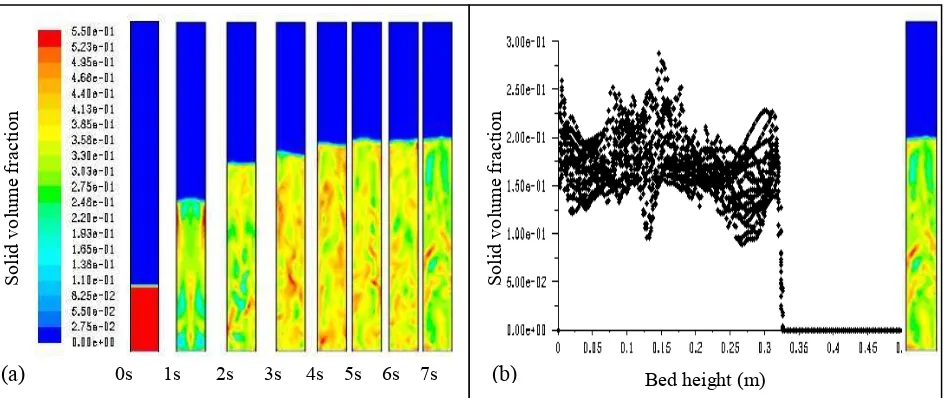
Fig. 2a shows the sample of contour of solid volume fraction along the bed reactor at fluidization velocity of 0.15 m/s at the time step of 0 to 7 s. It is observed the solid distribution continuously flowed as the velocity has just started. The degradation of the red colour is found to change as the solid fraction decreased mostly until the maximum bed height of 33cm as seen in Fig 2b. The similar behavior is observed for different fluidization velocity in which the higher velocity resulted in higher expansion of solid fraction distribution.
Fig. 2(a) Contour of solid volume fraction distribution at velocity of 0.15 m/s from 0 to 7s, (b) Solid volume fraction along the bed height after 7s
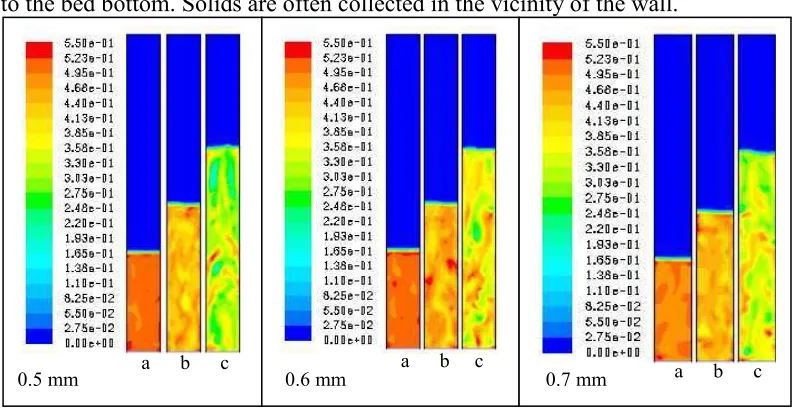
Contour of solid volume fraction. The contour of solid volume fraction during 7s of the 2D simulation at velocity of 0.05 m/s and 0.15 m/s for particle diameter variation of 0.5mm, 0.6mm and 0.7mm is shown in Fig. 3. At the lower velocity thick layers of dense suspension are observed at all conditions. A small contour layer different are found for small variation of particle size as noted as a, b and c.
Fig. 3. Contour of solid volume fraction at velocity (v) of 0.10 m/s and 0.15 m/s for particle diameter of (a) 0,5mm, (b) 0,6mm, (c) 0,7mm
In Fig. 4, the average solid volume fraction during 7s is shown clearly higher at the higher velocity. Clusters of particles are seen at higher elevations mostly at velocity of 0.15 m/s. A denser region is shown close to the bed bottom. Solids are often collected in the vicinity of the wall.
Fig. 4. Contour of solid volume fraction at particle size of 0.5, 0.6 and 0.7 mm for velocity of (a) 0.05 m/s, (b) 0.10 m/s, (c) 0.15 m/s
Bubbling characteristic. The formation bubbling in fluidization phenomena is mostly dependent on gas velocity and particle size employment. Simulation using sewage sludge as bed material with solid density ( ) of 310,48 kg/m3 and gas density ( ) of 1,225 kg/m3 for particle size of 0.5 – 0.7 mm is classified using Geldart graphic [5].
a b c a b c
v = 0,10 m/s v = 0.15 m/s
a b c a b c a b c
0.5 mm 0.6 mm 0.7 mm
Fig. 5. Particles size position of sewage sludge solid in Geldart particles classification graph
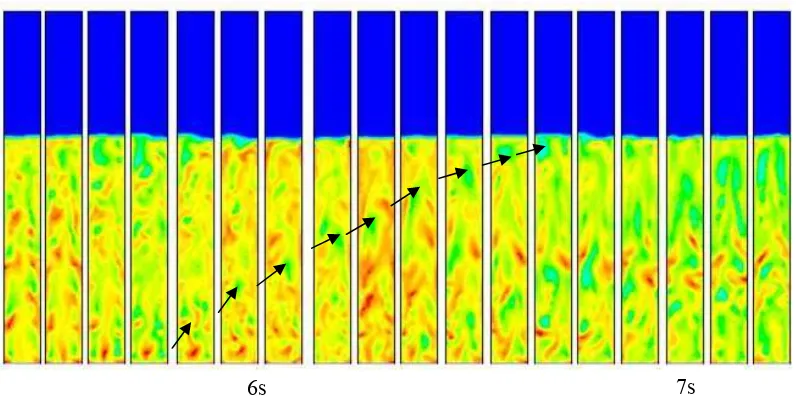
Fig. 5 shows the position of particle size of sewage sludge used for CFD simulation in the Geldart graph. Considering the density and mean diameter particles, the sewage sludge is in group of A (Aeratable) area in which the hydrodynamic behavior is specific. As the gas velocity is increased above minimum fluidization, bubbles are formed at irregular form. The formation of the bubbles can be tracked as the onset of fluidization is occurred as illustrated in Fig. 6, 7 and 8 for velocity of 0.15 m/s at particle size of 0.5, 0.6, and 0.7 mm respectively.
Fig. 6. A contour of bubble rise movement at velocity of 0,15 m/s at diameter of 0.5 mm
Fig. 6 to 8 are some example of the movement of bubble size during 7s in which bubble is considered to play an important role of the fluidization. As the gas velocity is increased the bubble rise is increased so that the added air flows into the bubble rather than into the dense bed. The movement of the particles resulting from the gas that flows into the bed restrained by material falling from the top so as to form bubbles. When a bubble reaches the top of the bed it breaks through the surface above particles.
7s 6s
Fig. 7. A contour of bubble rise movement at velocity of 0,15 m/s at diameter of 0.6 mm
Fig. 8. A contour of bubble rise movement at velocity of 0,15 m/s at diameter of 0.7 mm
Summary
From the 2D of CFD simulation, the contour of volume fraction of sewage sludge depends on gas velocity and particle size employment. The gas velocity is important factor that influence the fluidization forming as well as the bed expansion and characteristic of bubbling behavior. The sewage sludge is considered in group of A (Aeratable) area in which the hydrodynamic behavior such as bubbles are formed at irregular form. The formation of the bubbles can be tracked as the onset of fluidization using the simulation.
Acknowledgement: This study was kindly supported by Directorate of Higher Education-The Indonesia’s Ministry of Education and Culture through Hibah Desentralisasi Fundamental
2014 of Udayana University.
References
[1] Amit Kumar., 2008. CFD Modeling of Gas-Liquid-Solid Fluidized Bed. Department of Chemical Engineering National Institute of Technology Rourkela-769008,Orissa.
[2] Armstrong L.M., Gu S. dan Luo K.H., 2010. Study of Wall-to-Bed Heat Transfer In a Bubling Fluidized Bed Using the Kinetic Theory of Granular flow. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer 53, 4949-4959.
[3] Tasirin S.M., Kamarudin S.K. dan Hweage A.M.A.,2008. Mixing Behavior of Binary Polymer Particles in Bubbling Fluidized Bed. Journal of Physical Science, Vol. 19(1), 13–29.
[4] Kallio S., Gulden M., Hermason A., 2009. Experimental study and CFD Simulation of a 2D Circulating Fluidized Bed. Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Fluidized Bed Combustion, pp. 818.
[5] Kunii, Lavenspiel, 2006. Fluidization Engineering Second edition, Copyright 1991 Butterworth-Heinemann, a Division of Reed Publishing (USA) Inc.
7 s 6 s
5 s
7 s 6 s
5 s
Design of Fluidized Bed Co-Gasifier of Coal and Wastes Fuels
I Nyoman Suprapta Winaya
1,a, Rukmi Sari Hartati
2,b, I Putu Lokantara
1,c,
I GAN Subawa
3,d, I Made Agus Putrawan
1,e1Mechanical Engineering Department - University of Udayana, Bali-Indonesia
2Electrical Engineering Department - University of Udayana, Bali-Indonesia
3PT Indonesia Power UBP Pesanggaran Bali-Indonesia
ains.winaya@me.unud.ac.id, brshartati@ee.unud.ac.id, clokantara_santri@yahoo.com, dsubawa.putra@indonesiapower.co.id, agusputrawanmade@gmail.com
Keywords: fluidized bed, co-gasifier, biomass, waste
Abstract. The solid waste produced from urban area is an urgent issue to be addressed. A fluidized
bed (FB) gasification technology has been widely applied and proven effective to convert waste into clean energy and environmentally friendly. Co-gasification is a technique of mixing two or more fuels that aims to improve calorific value of the gas production. A FB gasifier reactor is designed using some previous experiments and available literature as well as from the internal experience of the research group. The gasification reactor pilot plant scale using data input of waste and biomass fuels has been fabricated with diameter of 0.7 m and a height of 1.5 m. The Tests have been performed showing that the FB gasifier is very feasible to be developed.
Introduction
The increased efforts of the need to reduce CO2 emission to prevent global warming from
power generation systems have led to an interest in biomass and wastes as fuel sources. As a potentially energy renewable resource, biomass and wastes are gaining more attention worldwide. The use of fluidized bed (FB) technology for waste and biomass fuels has expanded since the twentieth century either for energy recovery or wastes disposal. This technology is well known for its excellent gas-solid mixing and favorable emission characteristics. Pre-processing of biomass/wastes feeds to acceptable particle size and moisture content, usually necessary for conventional technologies, can then be minimized in fluidized bed operations, as long as it could be conveniently fed into the bed. FB technology is usually indicated to be the best choice, or sometimes the only choice, to convert alternative fuels to energy due to its fuel flexibility and the possibility to achieve an efficient and clean operation. It is also found that a high recovery of heat can be achieved, this is mainly due to the heat transfer coefficient in fluidized bed combustors is much greater than that of conventional combustion systems.
Looking at the future potential of urban waste, the high energy content within the waste is very urgent to utilize. Technology must find a feasible process which allows wastes to be converted as
energy in an environmental way. Fluidized bed gasification is a promising technology that can
convert energy from the low rank calorific solid fuel such as biomass and wastes into a combustible gas whose composition and heating value are greatly dictated by the type of gasifying agents. Because of the lower calorific values of waste fuels accompanied by flame stability problems, co-gasification currently holds more appeal than any of the sole source technologies including more advanced conversion options such as integrated gasification combined cycles. It is anticipated that co-gasification of waste fuels with coal will reduce flame stability problems, as well as minimize
corrosion effects. The co-gasification of coal and wastes has the potential to reduce CO2 emissions
and the amount of pollutants as NOx and SOx. Co-gasification process has been widely studied Applied Mechanics and Materials Vol 776 (2015) pp 300-306 Submitted: 2015-02-19
© (2015) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland Accepted: 2015-04-10