Text Through Contextual Teaching And Learning (CTL) (Action Research at Second Grade of Bakti Mulya 400 Junior High School Jakarta), Skripsi, English Education Department, Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers Training, Islamic State University Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta.
Advisor: Drs. Nasrun Mahmud, M. Pd
Key Words: Contextual Teaching Learning, Descriptive text, Reading skill
This research is aimed to improve students’ reading comprehension of descriptive text by using Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) at VIII grade of SMP Bakti Mulya 400 Jakarta. This research is related to the result of a preliminary study showed that the students were still confused to comprehend the passage in reading skill; especially in descriptive text.
In conducting this study, the researcher used Classroom Action Research (CAR) as the method of the research. She used research design of Kurt Lewin which consisted of two cycles and each cycles consisted of four phases, they are: Planning, Acting, Observing and Reflecting. Each cycle conducted in two meetings. To collect and analyze the data, the researcher gained the information from observation, interview, questionnaire, documentation and the students’ achievement in pre-test and post-test in order to support the data collected.
School Jakarta), Skripsi, Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta. Pembimbing: Drs. Nasrun Mahmud, M.Pd.
Kata Kunci: Contextual Teaching and Learning, Descriptive text, Reading skill Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk meningkatkan pemahaman membaca siswa dalam teks deskriptif dengan strategi pembelajaran dan pengajaran kontekstual pada siswa kelas VIII di SMP Bakti Mulya 400 Jakarta. Penelitian ini berdasarkan pada observasi yang menunjukkan bahwa siswa masih memiliki pemahaman yang kurang pada kemampuan membaca; khususnya pada teks deskriptif.
Dalam melaksanakan penelitian ini, peneliti menggunakan metode Penelitian Tindakan Kelas (PTK). Penelitian dilakukan mengikuti Kurt Lewin, penelitian ini dilaksanakan dalam dua siklus dan masing-masing siklus terdiri dari empat tahap, yaitu: perencanaan, pelaksanaan, observasi dan evaluasi. Tiap siklus dilakukan dalam dua kali pertemuan. Instrumen yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini yaitu: observasi, wawancara, angket, dokumentasi, dan test
Hasil penelitian ini mengindikasikan bahwa pelaksanakan pembelajaran kontekstual dinyatakan berhasil dikarenakan tercapainya kriteria sukses. Kriteria pertama ialah 70% dari siswa dapat mencapai nilai 70 (KKM), hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa 73.91% sudah mencapai nilai target. Di samping itu, kriteria yang kedua ialah siswa terlihat lebih aktif dalam kegiatan belajar. Hasil dari observasi dan wawancara menunjukkan bahwa siswa terlihat lebih aktif di dalam kelas. Berdasarkan hasil yang telah di sebutkan, peneliti menyimpulkan bahwa strategi pembelajaran dan pengajaran kontekstual dapat meningkatkan pemahaman siswa dalam teks desriptif.
(Classroom Action Research in the second year of VIII-3 Class of SMP Bakti
Mulya 400 Jakarta)
“Skripsi”
Presented to the Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers’ Training in a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Strata 1 in English Education
by: Siti Zakiyah NIM: 106014000436
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF TARBIYA AND TEACHERS TRAINING
SYARIF HIDAYATULLAH STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
JAKARTA
Research at Second Grade of Bakti Mulya 400 Junior High School Jakarta), Skripsi, English Education Department, Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers Training, Islamic State University Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta.
Advisor: Drs. Nasrun Mahmud, M. Pd
Key Words: Contextual Teaching Learning, Descriptive text, Reading skill
This research is aimed to improve students’ reading comprehension of descriptive text by using Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) at VIII grade of SMP Bakti Mulya 400 Jakarta. This research is related to the result of a preliminary study showed that the students were still confused to comprehend the passage in reading skill; especially in descriptive text.
In conducting this study, the researcher used Classroom Action Research (CAR) as the method of the research. She used research design of Kurt Lewin which consisted of two cycles and each cycles consisted of four phases, they are: Planning, Acting, Observing and Reflecting. Each cycle conducted in two meetings. To collect and analyze the data, the researcher gained the information from observation, interview, questionnaire, documentation and the students’ achievement in pre-test and post-test in order to support the data collected.
School Jakarta), Skripsi, Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, Universitas Islam Negeri Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta. Pembimbing: Drs. Nasrun Mahmud, M.Pd.
Kata Kunci: Contextual Teaching and Learning, Descriptive text, Reading skill Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk meningkatkan pemahaman membaca siswa dalam teks deskriptif dengan strategi pembelajaran dan pengajaran kontekstual pada siswa kelas VIII di SMP Bakti Mulya 400 Jakarta. Penelitian ini berdasarkan pada observasi yang menunjukkan bahwa siswa masih memiliki pemahaman yang kurang pada kemampuan membaca; khususnya pada teks deskriptif.
Dalam melaksanakan penelitian ini, peneliti menggunakan metode Penelitian Tindakan Kelas (PTK). Penelitian dilakukan mengikuti Kurt Lewin, penelitian ini dilaksanakan dalam dua siklus dan masing-masing siklus terdiri dari empat tahap, yaitu: perencanaan, pelaksanaan, observasi dan evaluasi. Tiap siklus dilakukan dalam dua kali pertemuan. Instrumen yang digunakan dalam penelitian ini yaitu: observasi, wawancara, angket, dokumentasi, dan test
Hasil penelitian ini mengindikasikan bahwa pelaksanakan pembelajaran kontekstual dinyatakan berhasil dikarenakan tercapainya kriteria sukses. Kriteria pertama ialah 70% dari siswa dapat mencapai nilai 70 (KKM), hasil penelitian menunjukkan bahwa 73.91% sudah mencapai nilai target. Di samping itu, kriteria yang kedua ialah siswa terlihat lebih aktif dalam kegiatan belajar. Hasil dari observasi dan wawancara menunjukkan bahwa siswa terlihat lebih aktif di dalam kelas. Berdasarkan hasil yang telah di sebutkan, peneliti menyimpulkan bahwa strategi pembelajaran dan pengajaran kontekstual dapat meningkatkan pemahaman siswa dalam teks desriptif.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
In the name of Allah, the Beneficent, the Merciful.
All praise be to Allah, the Lord of the Universe, and Gratitude fully be to Him for the health and the strength that enable the writer to complete this ‘skripsi’. The writer believes that without His grace, blessing, and guidance, this ‘skripsi’ wouldn’t be completed. Peace and blessing be upon beloved Prophet Muhammad, his family, his companions and his followers.
There are so many people who had given valuable contributions to this writing. First of all, the writer would like to express her greatest love and honor to her beloved family: her parents, Mr. Anwar Rojali and Mrs. Siti Fatimah who give their love, care and prayer, her beloved sister and brother, and all families who always encourage her to finish this ‘skripsi’.
The writer would like to express her greatest thanks and gratitude to her advisor Drs. Nasrun Mahmud, M.Pd. for his guidance, comments, corrections and suggestions to finish this ‘skripsi’.
The writer would like to convey her sincerest gratitude for all lectures of English Department for their encouragement to the writer. Her gratitude to Drs. Syauki, M.Pd. as the head of English Education Department and her gratitude is also addressed to Prof. Dr. Dede Rosyada, M.A, as the dean of Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teachers Training.
Then, the writer would like to extend her thanks to H. Kamruz Zaman S. Pd., M.MPd. as the headmaster of SMP Bakti Mulya 400 Jakarta and Sri Lestari, S. Pd as the English teacher for the help during the research.
Last but not least, the deepest thanks to her beloved special someone, Hasyim Asy’ari and thanks to all her beloved friends in English Education Department 2006/2007 academic year, especially C class who give their motivation to finish this writing. The writer hopes Allah will always bless them all.
Jakarta, January 17th, 2011
SURAT PERNYATAAN KARYA SENDIRI... B. Limitation and Formulation of the Problem……… C. Objective of the study……… D. The Significance of Study ………....
3.Schematic Structure of Descriptive Text….. 4.Linguistic Features of Descriptive Text…… C. The Concept of Contextual Teaching and Learning
(CTL) Method………. 1. The Definition of CTL ………. 2. Principles of CTL……….. 3. The Components of CTL……….. 4. The Strategies in CTL……… 5. The Strength and Weakness of CTL ……. D. Teaching Reading Descriptive Text Through
Contextual Teaching and Learning………..
CHAPTER III: RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
A. The Setting and Subject of the Study………….. B. The design of the Study ……….. D. Technique of Collecting Data ……….
1. Findings of the Preliminary Study………
B. Suggestion………
BIBLIOGRAPHY ………
APPENDICES ………..
62
63
64
Table 2.1 Language Feature of Descriptive Text ………
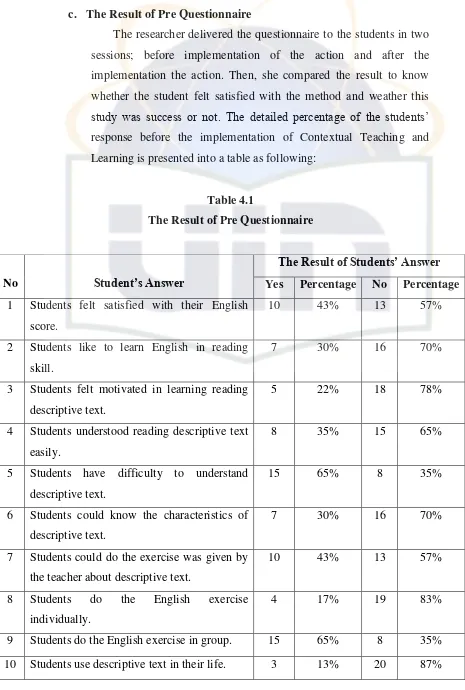
Table 4.1 The Result of Pre Questionnaire...
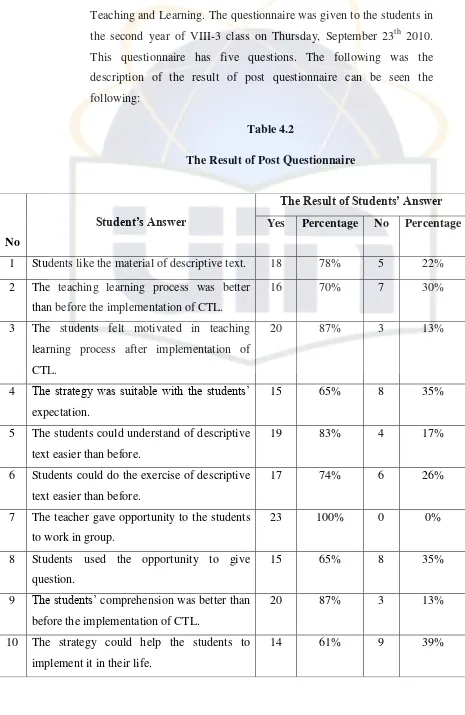
Table 4.2 The Result of Post Questionnaire ………
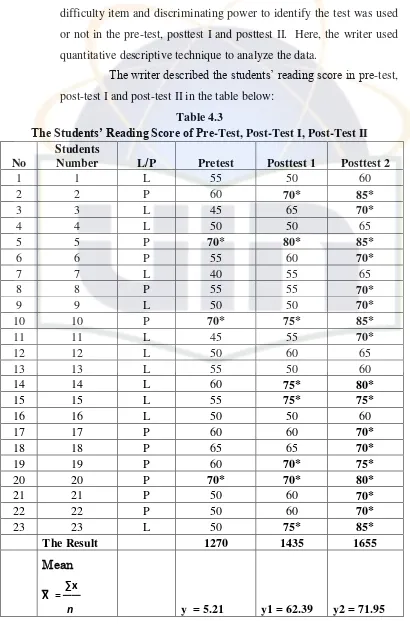
Table 4.3 The Students’ Reading Score of Pretest, Posttest I and Posttest II ………..………
16
41
50
xiii
Figure 3.1 Kurt Lewin Design ……… 31
Figure 3.2 Design of Research Cycles (Adopted from Kurt Lewin Design……….. 32
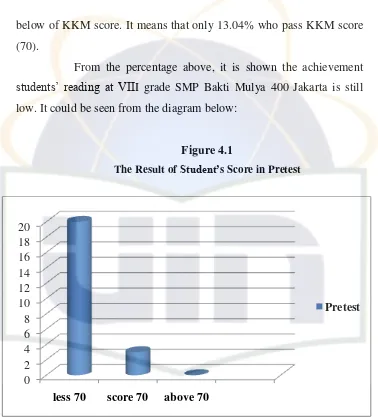
Figure 4.1 The Result of Students’ Score in Pretest ……… 54
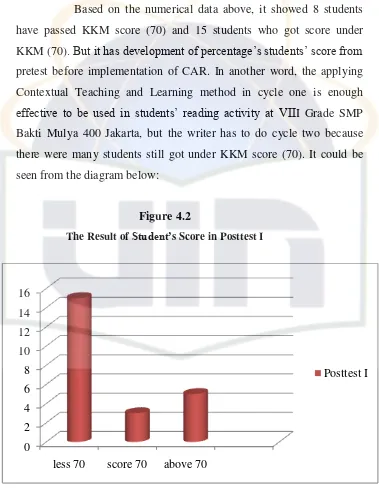
Figure 4.2 The Result of Studennts’ Score in Posttest I……….. 56
Figure 4.3 The Result of Students’ Score in Posttest II ……….. 58
Figure 4.4 The Students’ Score achievement in Pretest, Posttest I and Posttest II ……… 61
31
32
54
56
58
Appendix 2 The Question for Students (Before CAR)... 82
Appendix 3 The Question for Students (After CAR)………. 84
Appendix 4 Guideline of Teacher’s Interview (Before CAR)……… 86
Appendix 5 Guideline of Teacher’s Interview (After CAR)………. 88
Appendix 6 Observational Notes in preliminary ………. 90
Appendix 7 Observational Notes in Cycle I………. 92
Appendix 8 Observational Notes in Cycle II……… 94
Appendix 9 The Blueprint Test of Pretest……… 96
Appendix 10 The Blueprint Test of Posttest I……….. 100
Appendix 11 The Blueprint Test of Posttest II………. 104
Appendix 12 The Key Answers……… 109
Appendix 13 The Students’ Score in Pretest, Posttest I and Posttest II……… 110
Appendix 14 The Item Analysis……….. 111
Appendix 15 Surat Pengajuan Judul Skripsi………. 114
Appendix 16 Surat Bimbingan Skripsi……….. 115
Appendix 17 Surat Permohonan Izin Penelitian……… 116
Appendix 18 Surat Permohonan Izin Observasi………. 117
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
This chapter discusses and presents Background of the Study, Limitation of the Problem, Formulation of the Problem, Objectives of the Study and Significance of the study.
A. Background of Study
Language cannot be separated from life. People use language as an instrument of communication in their daily life. Language is a means of communication to express a message of the speaker’s idea to listener. There are many languages in the world but English remains the most important language. English is one of the international languages of the present in this era. As a sequence, English serves for many people as a bridge into the higher science, international trade, politics, tourism, including education. Indonesian students at Junior High School are aware of the importance of English, even if they have learned it as local content subject when they sat at 4th grade of elementary level. Besides, they will continue their study to Senior High School in which at this level English becomes a national content subject and one of the subjects to be nationally examined.
In conducting teaching learning process, the teacher should follow the curriculum recommended. It is line with the Decree of the Minister of Education number 22/ 2006 about the national content standard composed by BNSP. It is mentioned that “teaching learning process of English language consists of four skills; they are Listening, Speaking, Reading, and Writing.1 Listening and reading are called receptive skills, since they only receive the word without producing the words. Speaking and writing are called productive skills, because those skills produce words in different ways. By producing the words they can express their feeling or message in verbal or non verbal. As one of four language skills, reading has own characteristic. Reading provides some activities to help the reader comprehend the written expressions. The reader can get a lot of knowledge, information, enjoyment, or even problem solution.
Gray identifies four different steps in the reading act: word perception, comprehension, reaction, and integration. The first step is word recognition, including both the ability to pronounce the words and attach meaning to it as a concept. The second step is the ability to make individual words construct useful ideas as they are read in context. The third step requires judgmental action – a feeling about to assimilate this idea, concept, new reading, into the background of experience so that it becomes a part of the total experience of the individual. These steps are completely interdependent in the meaningful use of reading as a tool in the solutions of problems.2
Reading is one of language skills that have to be mastered. There are
Depdikbud, Kurikulum Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan 2006 Standar Isi SD,
SMP dan SMA (Jakarta: Depdikbud, 2006), p.14
2
William S. Gray, On Their Own in Reading, (Chicago: Scott, Foresman and Company,
Therefore, the problem of understanding the text in reading can be caused by many factors. One of them is the learning strategy in teaching and learning process which is ineffective in the classroom. Generally, the students only read the text but they don’t understand its meaning and identification. It is indicated that they don’t get information from text. If they don’t understand
meaningful text, they can’t answer the question based on the text and can’t
identify the structure of the text well.
Based on Competency Standard (Standar Kompetensi) and Basic Competency (Kompetensi Dasar), the second year students are expected to be able to understand and respond meaningful written texts in term of functional written text and simple short essay in the form of descriptive and recount text interact with people in the nearest environment.3 There are many types’ texts in reading, which are closely related to the purpose of each type. Descriptive text is one of the text types that taught at the second year of Junior High School.
Descriptive text has a social function is to describe a particular person, place, or thing, for instance, description of a particular building, specific animal, particular place, and specific person.4 On the other hand, descriptive text has told description and identification of something, someplace or someone. It persuades the reader to imagine the text content.
Based on the writer’s observation through conducting preliminary
study during teaching learning writing activity in the second year of 8-3 class at SMP Bakti Mulya 400 Jakarta, the writer found that many students had difficulty in reading descriptive text. It was proved by the result of the
students’ reading in preliminary study. The mean score of the students reading was 55.21, while the Minimum Mastery Criterion- Kriteria Ketuntasan Minimal (KKM) was 70. The result indicates that the students’ reading
3
Depdikbud, Kurikulum Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan 2006 Standar Isi SD,
SMP dan SMA (Jakarta: Depdikbud, 2006)
4
achievement was still low. Besides, it was supported by the result of interview to the English teacher and students’ questionnaire in preliminary study that the
students’ difficulties come from the weaknesses of student understanding in comprehend the text; therefore they did not answer the question correctly. Also, the students had difficulty in analyze the linguistic and schematic structures of descriptive. Furthermore, the students tend to be bored and low participation in reading class because the process of teaching and learning activities was monotonous. So, to make the students can improve of understanding descriptive text, there should be an effort to make reading class more interesting.
According to Harmer in his book stated that “The reading to confirm expectations’ technique is highly motivating and succesful since it interests
students, creates expectations and gives them a purpose for reading”.5
Based on this statement, the teachers assumed to teach reading in interesting learning and give the aim of reading to students.
To achieve the goal of learning, teacher must have or create a good teaching strategy to make the class effective and well-organized. Therefore, in teaching descriptive text, teacher needs good teaching strategy.
Here the writer takes her point of view that one of methods that could be used to make an easy and better understanding in learning descriptive reading is Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL). In Contextual Teaching and Learning, the teachers not only give the material, but also make the students participate in the class by connecting the material with their real life. As quoted by Nurhadi:
“Contextual Teaching and Learning is the concept of learning
where the teacher creates the real-world into the class and encourages the students making the connection between their own knowledge with is implementation in their daily life; meanwhile the students get knowledge and skill from the limited context, little by little, and from
5
Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English Language Teaching (New York: Longman
the self-constructed process, as a foundation for solving problems in
their life as member of society.”6
In accordance with the explanation above, the writer intend to conduct a classroom action research entitled: “Improving Students‟ Reading
Comprehension of Descriptive Text Through Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL) (Classroom Action Research in the Second Year of 8-3 Class
of Bakti Mulya 400 Jakarta)”.
B. Limitation and Formulation of The Problem 1. The Limitation of the Problem
Based on the background above, the writer limits the study focus on
the improving students’ descriptive reading through Contextual Teaching
and Learning in the second year of 8-3 class at SMP Bakti Mulya 400 Jakarta
2. The Formulation of the Problem
In line with the background of the study, the writer formulates the
research question as follows:” Can Contextual Teaching and Learning
improve the students’ descriptive reading in the second year of 8-3 class of SMP Bakti Mulya 400 Jakarta? And then “How does Contextual Teaching
and Learning improve the students’ descriptive reading in the second year
of 8-3 Class of SMP Bakti Mulya 400 Jakarta?”
C. Objective of the Study
According to the formulation of problem above, the objective of this study is to know whether and to know how Contextual teaching and Learning
can improve the students’ descriptive reading in the second year students of 8-3 class of SMP Bakti Mulya 400 Jakarta.
6
Nurhadi, Pembelajaran Kontekstual dan penerapannya dalam KBK, (Malang:
D. The Significance of the Study
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
This chapter covers some theories related to the study. The discussion focuses on the General Concept of Reading, Kinds of Reading, Purpose of Reading, The Definition of Descriptive Text, Purpose of Descriptive Text, Schematic Structures of Descriptive, The Definition of Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL), Principles of CTL, Components of CTL, Strategies of CTL, The Strength and Weakness of CTL, and the last discussion about Teaching Reading Descriptive Text Through CTL.
A.
Reading
1. The General Concept of Reading
Reading is a skill, so the only way people can become a good and a
fluent reader is through practice. To practice in reading, people don’t read
about the passage but also they can practice their reading to read announcement, news, or about the situation, and so on.
meaning. Accessing meaning is the rationale for reading. The simple view of reading is that reading is the product of decoding and comprehension.1 So, while the reader was doing reading, their brain has worked directly.
Then from the brain’s work, they can find the information gap of the
passage.
According to S. Pang, reading process is assumed as follow:
Reading consists of two related processes: word recognition and comprehension. Word recognition refers to the process of
perceiving how written symbols correspond to one’s spoken
language. Comprehension is the process of making sense of words, sentences, and connecting text. Readers typically make use of the background knowledge, vocabulary, grammatical knowledge, experience with the text and other strategies to help them understand written text.2
Based on the explanation above, the writer identified that the reader need many aspect to understand what they are reading. The aspect reading which support are background knowledge; they will understand of
passage’s meaning if they have more knowledge about the topic.
Vocabulary and grammatical knowledge; without two its aspect, the reader
don’t know of passage meaning. Next aspect is experience; if the readers don’t have experience about the topic, so they don’t more understand of
passage meaning.
Another resource said that reading is an exercise dominated by the eyes and the brain. The eyes receive the messages and the brain then has to work out the significance of these messages.3 It is indicated that when
1
Naomi Flynn and Rhona Stainthorp, The Learning and Teaching of Reading and
Writing, (England: Whurr Publisher Limited, 2006), p.42.
2
Elizabeth S. Pang et al, Teaching Reading, (Switzerland: International Academy of
Education, 2003), p. 6.
3
Jeremy harmer, The Practice of English language Teaching, (New York: Longman,
someone have read, their brain work together to comprehend the content of the passage.
However, in reading comprehension the readers also need to combine the information from the text with their background knowledge to
comprehend the text. Larry Lewin considered this as “prior knowledge”.
He stated that:
“prior knowledge is regarded as what the readers know toward
incoming topic concerning their past knowledge which is stored in the brain then occurring the integration of newly information to
There are two kinds of reading as below: 5 a.Intensive Reading
Intensive reading refers to detailed focus on the construction of reading text which takes place usually in classroom. In addition, Nuttal
stated that “Intensive reading involves approaching the text under the
guidance of a teacher or a task which forces the student to focus on the
4
Lary Lawin, Paving the way in Reading and Writing: Strategies and Activities to
Support Struggling Students in Grades 6-12, (San francisco: Jossey-Bass, 2003), p.23.
5
Jeremy harmer, How to Teach English, new edition (New York: Longman, 2007),
text. The aim is to arrive at an understanding, not only of what the text
means, but of how the meaning is produced.”6
In another hand, in intensive reading, as the term indicates, each vocabulary and structural item is explained and made as fact of our active language, pronunciation, and intonation are stressed, and each concept allusion is clarified. Besides intensive reading is used to gain a deep understanding of a text, which is important for the reader. The process of scanning takes a more prominent role here than skimming.
b. Extensive Reading
According to Nuttal in her book about extensive reading stated that:“It is assumed that in order to understand the whole (e.g book), the reader must first understand the parts (sentences, paragraph, chapters) of which it is made up. However, the reader can in fact often understand a text adequately without grasping every part of it; students have to be encouraged to develop this facility.”7
Based on the statement above, the reader should select a good reading material which the material related to extensive reading. In this activity, reading is for pleasure. Besides, the reader doesn’t need to understand each words because in this step the purpose of reading is merely needs to get an overall understanding of the passage or text.
3. Purpose of Reading
Generally, people read something because they want to or because they have a desire to do so and a purpose to achieve.
6
Christine Nuttal, Teaching Reading Skills in a Foreign Langauge, (London: Mcmillan,
2005),p.38.
7
There are some purposes of reading which are declared by some
experts. According to Francoise in his book stated that “there are two main reasons of reading; reading for pleasure and reading for information (to find out something or in order to do something with information you
got).”8
Moreover, the essential purpose of reading generally is to get new information or pleasure. Reading for information is reading that the reader has not stop to analyze the grammatical structures; the reader understand the structure without thinking about it. Reading for information requires that the reader understand of meaning passage.
Reading for information may range from the scanning of documents and the reading of letters to in depth understanding of articles of books. Whether we are reading for pleasure or information, the nature of the reading depends on what we want from the text.
In addition, Nuttal stated in her book that “whatever your reason for reading (excluding any reading for language learning), it is not very likely that you were interested in the pronunciation of what you read, and even less likely that you more interested in the grammatical structured used. You read because you wanted to get something from the writing.”9 This
statements also emphasizes on no matter the reader’s technique used in
reading, it aims to convey the message of the passage.
In other hand, those explanation above conclude that the general purpose in reading mainly to get something or information and make pleasure with reading from the text without attention of the technique used in reading.
8
Francoise Grellet, Developing Reading Skill: A Practical Guide to Reading
Comprehension Exercise, (Cambridge University Press, 1986), p.4
9
B.
The Concept of Descriptive Text
1. The Definition of Descriptive Text
One of genres that Junior High School students learnt is Descriptive text. Based on Competency Standard (Standar Kompetensi) and Basic Competency (Kompetensi Dasar), the second year students are expected to be able to understand and respond meaningful written texts in term of functional written text and simple short essay in the form of descriptive
and recount text interact with people in the nearest environment.10 Descriptive text is a text which describes something. According to Djuharie, he said that descriptive text is a text which describes and gives more detail information about particular people, thing, place and animal.11 It means that descriptive text tells the readers to know about something specifically by giving characteristic of something which described.
Moreover, descriptive text tells about the senses how something looks, feels, smells, tastes, and sound.12 It shows how the reader can feel and imagine the description of text. Whereas, Buscemi argued that the fundamental to describe is appealing to the senses (sight, hearing, and touch).13 Based on this statement, it means that in describing something, it needs to explain what people see, hear, and feel.
Regarding the previous explanation, the writer concludes that descriptive text is a text which describes something and includes of the characteristic and qualification of something, someone, or somewhere. It
10
Depdikbud, Kurikulum Kurikulum Tingkat Satuan Pendidikan 2006 Standar Isi SD,
SMP dan SMA (Jakarta: Depdikbud, 2006)
11
Otong Setiawan Djuharie, Gendre Dilengkapi 700 Soal Uji Pemahaman, (Bandung: Yrama Widya, 2007), p. 24.
12
Alice Oshima and Ann Hogue, Introduction to Academic Writing 3rd Edition, (New York: Pearson Longman, 2007), p. 61.
13
tells the readers with detail information that can help them to imagine and to describe in their mind about what the content of the text.
2. The Purpose of Descriptive Text
The purpose of descriptive text is to describe people, thing, place, and animal.14 Students read descriptive text might be basically to know way of describe someone, something or somewhere. It means the reader can get information about characteristic, qualification, parts, and so on. Meanwhile, According to Anderson and his sister stated that the purpose of descriptive text is to tell about subject by describing the characteristic without including personal opinions, the example of descriptive text are description of a particular building, description of a specific animal, description of a particular place, and description of a specific person.15 The aim of description is to enable the reader what something looks like. It attempts to paint a picture with words. In this sense, the description also attempts to put the reader directly in touch with the physical world within
the readers’ senses. Description helps the readers visualize a scene or a person and understand the related sensation or an emotion. It also helps students to organize their thinking as well as their writing, and to be able to communicate thoughts and ideas clearly to the reader.
Based on those statements above, descriptive text has a purpose to describe a particular person, places, animals, and things that tells about their characteristics and qualification. Then, it helps the reader to imagine what the text is about.
Mark Anderson and Kathy Anderson, Text Types in English, (South Yarra: Machmillan
3. Schematic Structures of Descriptive Text
An effective descriptive text has several significant characteristics which a reader may use as standard to guide his or her reading. The schematic structure of descriptive paragraph consists of identification and description.16 Identification mentions phenomenon to be describe, while the description describes the parts, the qualities, and the characteristics of what has been described.
In conclusion, the schematic structure is important to organize a good descriptive paragraph. It can help to see the organization of description clearly. So, the reader can easy to get imagination of description.
The example of schematic structure of descriptive text:
My Best Friend
I have a lot of friends. But my closest friend is Farida Sohia.
Farida is pleasing peer. I am happy to spend my time with her. She is always available to help her friends who are in trouble. She is never angry with any friends who try to annoy him. Because she is so smart, most of her classmates seek her to explain any difficulties in any school subjects. I am proud of having such best friend.
4. Linguistic Features of Descriptive Text
According to Hartono in his book about linguistic features of descriptive text, he assumed that the linguistic features of description are: first, focus on specific participants. Second, use of attribute and identifying processes. Next, use of epithets and classifier in nominal groups. The last, use of simple present tense.17 In addition, linguistic of descriptive text includes verb in present time, use adjective to describe the feature of the subject, and topic sentences to begin paragraph and organize the various aspect of the description. 18 Based on those statements, It mean that linguistic feature of descriptive text consist of specific participant who describe it, use simple present and also use attributive to identify itself.
The writer tries to identify linguistic feature from the previous descriptive text above. It is as following:
17
Rudi Hartono, SS, M. Pd. Genres of Text, (Unpublished Paper),(Semarang: Semarang State University: English Department Faculty of Language and Art, 2005), p.9
18
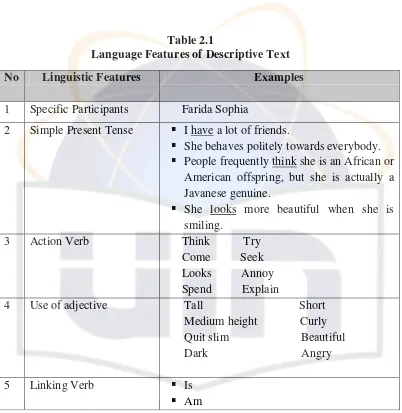
Table 2.1
Language Features of Descriptive Text
C. The Concept of Contextual Teaching and Learning Method 1. Definition of Contextual Teaching and Learning
Today, most of students in the school got a lot of material that was not in context. Therefore, they were difficult to make connection between what they are learning and how that knowledge will be use in their daily lives. The methods of the classroom teaching sometimes not really touch the learning process. The students rarely have an opportunity to experience hands-on learning.
No Linguistic Features Examples
1 Specific Participants Farida Sophia
2 Simple Present Tense I have a lot of friends.
She behaves politely towards everybody. People frequently think she is an African or
Nowadays, educators find the necessary to think over about how they teach; they feel that learning occurs only when students process new information or knowledge in such a way that it makes sense to them in their own frames or references.19 Therefore, the appropriate approach should be used in order to make the learning process really work.
There are several method proposed in order to achieve the goal pf the study. Each method offered many gains. CTL method is one of methods proposed. John Dewey was the first proposed the application of Contextual Learning was first proposed at the turn of the 20th century, Progressivism, which is believed that the students will best learn if what they have learned the materials which are related with they have already known and teaching learning process will be productive if the students are active in the process of teaching.20
According to Johnson, Contextual Teaching and Learning is an educational process that aims to help students see meaning in the academic material they are studying by connecting academic subjects with the context of their lives, that is, with context of their personal, social, and cultural circumstance.21 In this understanding, by using CTL system, students are able to connect the subject materials with the context of their daily life. It means the subject materials should go along with daily need.
In addition, Contextual Teaching and Learning is a conception of teaching and learning that helps teacher relate subject matter content to real world situation and motivates students to make connections between
knowledge and its application to their lives as family member’s citizens
19
Nur Hadi, Pendekatan Kontekstual (Contextual Teaching and Learning/CTL). Jakara:
Departemen Pendidikan Nasional, 2003) p.3.
20
Nur Hadi, Pendekatan Kontekstual (Contextual Teaching and Learning/CTL)...., p.8.
21
Elaine B Johnson, Contextual Teaching and Learning; Why It Is and Why It Is Here to
and workers and engage in the hard work that learning requires.22 Based on this statement, CTL can help the teacher relates her or his subject to real world situations and also can motivate students to connect between what is being learned and their prior knowledge.
Based on the preceding definitions, the writer conclude that CTL is a conception of teaching and learning that helps students to get a better understanding about the knowledge as they relate to the context of real life.
2. Principles of Contextual Teaching and Learning
Contextual learning assumed that students learn best actively constructing their own understanding. Related with the students individually needed, to apply the Contextual Teaching and Learning (CTL), a teacher should have these following principles below which is line with Nur Hadi stated in his book:23
a. Lesson plans that are developmentally appropriate for the students.
The relationship between curriculum content and methodology that used teach must base on the particular levels of the
students’ social condition, emotional and students’ intellectual development.
b. Making independent learning group.
Through a small group, the students able to learn cooperate each others. However, the students hoped to learn and act
22
http://www.cew.wisc.edu/teachnet/ctl/
23
Nur Hadi, Pendekatan Kontextual (Contextual Teaching and Learning / CTL )...,
actively. They hoped to improve their knowledge about the topic which discussed.
c. Preparing an environment that supports self-regulating learning.
Environment that support self-regulating learning has three general characteristic, they are: awareness thinking, the use of strategy, and continuing motivation. The students are encouraged to know their strong and their weakness to organize the learning goal and develop the strategies to achieve the goal. Therefore the teacher must create an environment where the students can reflect how they learn to help them use their thinking to guide their plans, select their performance, so they can solve the problem in good way.
d. Considering diversity of students.
In teaching and learning process, the teacher have found
students’ variety, for instance social culture, economic status, different values, perspective, their basic mother tongue, and another weakness which they have. However, a teacher is expected to help them to improve their learning purpose.
e. Using questioning to explore the students learning, problem solving development and high-thinking order.
f. Applying the authentic assessment
Contextual Teaching and Learning is intended to build knowledge and skills in meaningful ways by engaging students
in real life, or “authentic” context. Authentic assessment
evaluates the applying of knowledge and the students’ complex
thinking, it is better than just memorizing the actual information. Authentic assessment is used to monitor student progress and inform teaching practice.
3. The Components of Contextual Teaching Learning
According to Johnson mentioned that the components of Contextual Teaching and Learning. It consists of eight components as below:24
a. Making connection that hold meaning
Connecting learning to one’s life makes studies come alive. When
students can connect of an academic subject such as English, mathematics or history with their own experience, they discover meaning, and meaning gives them a reason for learning.
b. Self regulated learning
Self regulated learning is a learning process that engages students in independent action involving sometimes one person, usually a group. This independent action is designed to connect academic
24
knowledge with the context of students’ daily lives in ways that achieve a meaningful purpose.
c. Doing significant work
Doing significant work in component of Contextual Teaching Learning is engages students actively and responsibly in learning activities.
d. Collaboration
In Contextual Teaching Learning there isn’t competition, one
learner and another Lerner have collaborative to understand the meaning. From collaboration, they cultivate tolerance and compassion.
e. Critical and creative thinking
Thinking as an active, purposeful, organized process that we use to make sense of the world. According Chaffee critical thinking as thinking critically explore the thinking process itself.25 It means not only reflecting purposely, but also examining the use we and others make of evidence and logic.
f. Nurturing the individual
Contextual Teaching Learning, teachers assist every student to develop the intelligences that are challenging. Then, they encourage young people to cultivate their intelligences, releasing the talent potential residing within.
g. Reaching high standards
An important thing in contextual teaching learning system is helping all students reach high academic standards. Contextual
25
teaching learning asks students to reach high standard. Asking too little of students, lowering standard for them, manifest a callous disregard for their latent potential and future well-being.
h. Using authentic assessment
Contextual Teaching and Learning asks students to exhibit their attainment of high standard by doing authentic assessment tasks. These tasks challenge student to apply their knowledge and skill to real world situation for significant purposes.
Regarding the previous explanation the writer concludes that those components invite students to connect schoolwork with daily life in ways that hold personal meaning. When students see meaning in their schoolwork, they learn and remember it.
4. The Strategies in Contextual Teaching and Learning
As explained before that Contextual Teching and Learning is a conception of teaching and learning that helps teachers relate subject matter content to real world situations and motivates the students to make connections between knowledge and its applications to their lives. So, The teacher should know the teaching strategies which associated with contextual theory. It is needed in order to make the teaching and learning process in a good guided. Therefore, there are six strategies in using Contextual Teaching and Learning:26
a. Problem based. Contextual Teaching Learning begins with a stimulated or real problem. Students use critical thinking skill and systemic approach to inquiry to address the problem or issue.
26
Students may also draw upon multiple content areas to solve these problems
b. Using multiple contexts. Theories of situated cognition suggest that knowledge can not be separated from the physical and social context in which it develops. How and where a person acquires and creates knowledge is therefore very important. Contextual Teaching and Learning experiences are enriched when students learn skill in multiple contexts.
c. Drawing upon diversity. As the whole, the students’ population is becoming more diverse, and with increased diversity comes differences in values, social mores, and perspectives. These differences can be the impetus for learning and can add complexity to the Contextual Teaching and Learning.
d. Supporting self-regulated learning. Contextual Teaching and Learning experiences should allow for trial and error; provide time and structure for reflection; and provide adequate support to assist students to move from dependent to independent learning.
e. Using interdependent learning groups. Students will be influenced by and will contribute to the knowledge and beliefs of others. Learning groups, or learning communities, are established in workplaces and schools in an effort to share knowledge, focus on goals, and allow all to teach and learn from each other. When learning communities are established in schools, educators act as coaches, facilitators, and mentors.
f. Employing authentic assessment. Contextual Teaching Learning is intended to build knowledge and skills in meaningful ways by
engaging students in real life, or “authentic” contexts. Assessment
are blended into the teaching/learning process; and provide students with opportunities and direction for improvement. Authentic assessment is used to monitor students’ progress and inform teaching practices.
In addition, Nurhadi stated in his book that there are seven strategies in Contextual Teaching and Learning. Here they are: 27
a. Constructivism. In this teaching and learning model, students construct their own knowledge by testing ideas based on prior knowledge and experience, applying these ideas to a new situation, and integrating the new knowledge gained with preexisting intellectual constructs. Based on this statement, the teacher transfer knowledge to student and students learn step by step from the limited context and construct their own knowledge to find the deep understanding through meaningful learning experience.
b. Inquiry. Basically, inquiry is fundamental activity of Contextual Teaching and Learning. Knowledge and skill got by the students do not expect from remembering the facts, but from self inquiry. Inquiry is the regulated activities included observing, asking, analyzing, and formulating theory whether individual or in a group.
c. Questioning. The questioning technique enhances student learning and development of problem solving and other higher-order thinking skills. For CTL to achieve its aims, appropriate types and levels of question must be asked. This question not monopolized by the teacher but also asked by the students. The teacher lead the students to know something, suggest the students to get
information, asses the students’ skill of critical thinking so it
teaches the students think critically.
27
d. Learning Community. In Contextual Teaching and Learning, learning community suggest that the result of teaching and learning is resulted from doing task with other students group. Grouping can lead the students to share their experiences among friends, solve the problem together, and create better learning than learn alone.
According to Harmer, the teacher will now consider briefly the relative merits and uses of various students grouping. The teacher will consider lockstep, pair work, group work, the use of the mother tongue, and individual study.28 Its mean that many ways
to improve students’ knowledge, but it is depend on their need.
e. Modeling. Modeling is needed to give the students an example. The teacher gave the example before giving the task to the students, and demonstrate what the students must learn. Model is not only from the teacher but also can be design by the students.
f. Reflection. Reflection is also an important role in CTL. Reflection is a way of thinking on what have students done in learning that can give the description of students learning development. Its purpose to know the students developing in learning is not from the test given but from the participation of the students in learning process whether inside or outside of the class.
28
Therefore, the Center of Occupational research development (CORD) stated that there are five strategies for the teachers in applying the Contextual Teaching Learning, they are called REACT, which stands for Relating, Experiencing, Applying, Cooperating, and Transferring. More its explanation as below:29
a. Relating. Learning related with the real world experience context. b. Experiencing. Learning focused on the expiration, discovery, and
invention.
c. Applying. Learning should be presented into the context of useful. d. Cooperating. Learning through interpersonal communication
context, togetherness, etc.
e. Transferring. Learning through the use of knowledge in the situation or new context.
In sum up, for Contextual Teaching and Learning to be effective, all strategies above must be present in the teaching learning process. A teacher should integrate with other commonly accepted good teaching practices. These other practices include promoting self-regulated learning, addressing student diversity when teaching, designing authentic assessment and using questioning to develop higher order thinking skills.
5. The Strengths and the Weakness of Contextual Teaching and Learning
Contextual Teaching Learning is one of the hot topics in education these days. As an approach, Contextual Teaching and Learning has the strength and weakness in the teaching learning process. The strength is it make teacher who teach contextually become easier to reach the goal
of teaching learning process. According to Johnson, “The great power
29
of Contextual Teaching Learning is that it gives all young opportunity to develop their promise, to develop their talents, and to become
informed, capable members of a democratic society.”30
Based on that statement, Contextual Teaching Learning can develop students’
communication skill and increase students’ comprehension about
current issues which related to their live.
On the other hand, the weakness of Contextual Teaching and Learning is taking time for the preparation; in preparing the lesson
plan, teacher should recognize students’ diversity and then utilize
difference to create a rich learning environment. Besides, the authentic assessment also takes more time for teachers to develop and apply.
D. Teaching Reading Descriptive Text Through Contextual Teaching and Learning
Before the implementation of Contextual Teaching and Learning in teaching learning process, the writer prepares the suitable material. Preparing the suitable material has to do by the writer in order the teaching learning process have done successfully. In this sense, the writer prepares the material related to the Contextual Teaching and Learning method. When teacher apply Contextual Teaching Learning in the classroom, it must include its main components. Here the following are steps in teaching reading of descriptive text through Contextual Teaching and Learning.
a) Preliminary activities
Ask students related to their condition
b) Presentation
30
Explain about the concept of reading descriptive text.
Divide students into group of four
Give each group a jumble paragraph, then arrange into good
passage.
Ask the group to analyze the schematic structures and find the
linguistic features of descriptive text.
Ask the group to present their task in front of another group.
c) Closing
Give the students an evaluation. It is necessary to check their
comprehension of descriptive text.
CHAPTER III
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This chapter presented to describe methodological activities to examine the teaching of descriptive reading text through Contextual Teaching and Learning. This chapter concern with research setting and subject, research design, and research procedures.
A. The Setting and Subject of the Study
This study is conducted at SMP Bakti Mulya 400 Jakarta. The school is located at Jl. Jl.Lingkar Selatan Pondok Pinang Kebayoran Lama, South Jakarta. The research started from August to September.
This school is chosen as the field of the study because the writer has teaching learning experience during teaching practice- Praktek Profesi Keguruaan Terpadu (PPKT), so the writer knows the real condition of this school, and the writer can identify the problems in teaching reading more enjoyable. Secondly, the writer suggests that innovation is needed in improving students’ reading comprehension for the better quality of school.
class must get 70 score to fulfill the Minimum Mastery Criterion- Kriteria Ketuntasan Minimal (KKM) in English lesson.
B. The Design of the Study
The design of this study is classroom action research. The study of classroom action research indicates as a process in which teachers investigate teaching and learning to improve students’ learning problems.1 To find out students’learning problem, Mils stated that “action research is any systematic inquiry conducted by teacher researcher, principals, school counselors or other stakeholder in the teaching/ learning environment to gather information about how their particular school operate, how they teach, and how well their students learn.2 That is why action research is different from other more conventional or traditional types of research; it focused on individual or small group professional practice. Action research tries to take an action and effect positive educational change in the specific school environment that was studied.
The classroom action research design employed in this study was collaborative action research. In conducting the research, the researcher was assisted by English teacher of SMP Bakti Mulya 400 Jakarta. In this study, the writer has some roles. She becomes the practitioner who taught reading descriptive text. Besides, she makes a lesson plan and assessment in each final cycle. Furthermore, the writer also collect and analyzes data then reporting the result of study. Whereas, the collaborator (called the English teacher) becomes the observer who observed the implementation of the action.
1
www.teachingenglish.org.uk/think/methodology/action-research.html
2
Geoffrey E. Mills, Action Research: a Guide For the Teacher Researcher, 2nd ed. (Ohio:
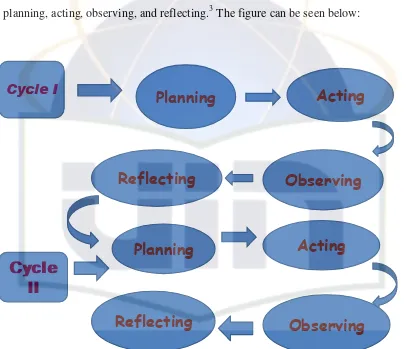
The writer uses classroom action research model proposed by Kurt Lewin. It consists of two cycles in which each cycle contains four phases; planning, acting, observing, and reflecting.3 The figure can be seen below:
Cycle I
Planning
Acting
Observing
Reflecting
Acting
Planning
Observing
Reflecting
Cycle
II
Figure 3.1 Kurt Lewin Design
3
Wijaya Kusumah dan Dedi Dwitagama, Mengenal Penelitian Tindakan Kelas, (Jakarta:
C. The Procedure of the Study
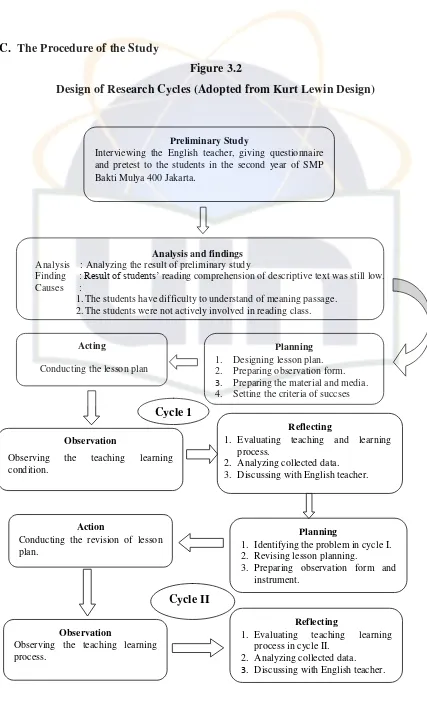
Figure 3.2
Design of Research Cycles (Adopted from Kurt Lewin Design)
Analysis and findings
Analysis : Analyzing the result of preliminary study
Finding : Result of students’ reading comprehension of descriptive text was still low. Causes :
1.The students have difficulty to understand of meaning passage. 2.The students were not actively involved in reading class.
Preliminary Study
Interviewing the English teacher, giving questionnaire and pretest to the students in the second year of SMP
4. Setting the criteria of succses
Acting
Conducting the lesson plan
Observation
Observing the teaching learning
condition.
Reflecting
1. Evaluating teaching and learning
process.
2. Analyzing collected data. 3. Discussing with English teacher.
Cycle 1
Planning
1. Identifying the problem in cycle I. 2. Revising lesson planning.
3. Preparing observation form and
instrument.
Reflecting
1. Evaluating teaching learning
process in cycle II. 2. Analyzing collected data. 3. Discussing with English teacher.
Action
Conducting the revision of lesson plan.
Observation
Observing the teaching learning process.
As mention before, this study as followed Kurt Lewin suggests four phases for classroom action research. They are planning, acting, observing and reflecting. Those four phases is called as one cycle. The researcher used more than one cycle in case of the learning problem unfinished yet. Then, the researcher used the same concept for the second cycle.
First of all, the preliminary study was done by the researcher before implementation of CAR. It was conducted on 24th – 26th August 2010. Here the researcher carried out the observation to the students’ activity in the teaching learning process in grade VIII-4 class of SMP Bakti Mulya 400 Jakarta. Then the researcher conducted an informal interview to the teacher related to the condition of teachers’ and students’ problem in teaching and learning activities of English especially on reading comprehension. After the preliminary was conducted, the researcher begins this research with the following the procedures:
1. Planning Phase
In this phase, after identifying the students the students’ problem of comprehending descriptive reading text through observing and interviewing is done, the researcher narrows the problem down so that it can be manageable. Then the researcher prepared all things concerning the implementation of CAR. The preparation consisted of designing lesson plan, preparing the instrument, and setting the criteria of CAR success.
The researcher designed lesson plan herself, it was organized for each cycle. Based on the agreement between the writer and the teacher that is each cycle consist of two meetings, the writer prepared 4 lesson plans to conduct the teaching activity. The lesson plan mentions any instruction regarding procedures of teaching, media, and resources.
questionnaire, observation note, and test for each cycle including pre-test KKM in the second posttest of second cycle.
2. Acting Phase
In this phase, the writer and English teacher are collaborating to overcome the solution finding. The researcher uses the determined strategy while the teacher observes the condition of teaching learning activity. Arikunto assumed that the acting phase should be implemented at least two cycles continuously; and at the time period for each cycle depends on the material needs that existed in the semester or formula program designed by teacher.4
Related to the statement above, the writer and English teacher agreed that the action would be implemented in two cycles. The action in first cycle was conducted on August 31st and September 2nd 2010. Therefore, the action in second cycle was conducted on September on 21st and 23rd 2010.
3. Observing Phase
The third phase of CAR is observation. In this phase, the writer gathers data which she will analyze to decide whether the solution was successful or not. In observing the implementation, there were some consideration aspect such as instrument and technique of collecting data and validity of data.
4
Suharsimi Arikunto, Peneltian Tindakan Kelas, (Jakarta: Bumi Aksara, 2009),
4. Reflecting Phase
In the last phase, the writer and English teacher discuss about the implementation and data which they gathered. If problem is unfinished in the first cycle or still might have found some problems, so they should plan again a second cycle with the same concept as the first one; re-planning, re-acting, re-observing. Hence, all the data should be analyzed by the writer.
D. Technique of Collecting Data
Technique of collecting data in this research used qualitative data and quantitative data. The qualitative data consists of observation within the physical activity in the classroom and interview to be presented for the teacher and students. On the other side, the quantitative data used is pre-test and post-test.5 The completely explanation as follows:
1. Observation
An observation is done to monitor and record the data of the students’ performance during the teaching and learning processes. The data is taken based on the students’ participation during teaching and learning activity according to lesson plan. The information obtained from these observation checklists is used as a basis to determine the planning for the following cycle. In this case, the writer carried out two sessions of the observation, they are; in preliminary and during the CAR.
2. Interview
In this research, the writer has interviewed the teacher. It is to know about the students’ difficulties in reading skill, to know the real condition in applying Contextual Teaching and Learning methods and how far the method can motivate the students in improving students’
5
Suharsimi Arikunto, Penelitian Tindakan Kelas, (Jakarta: Bumi Aksara, 2009), pp.
reading comprehension of descriptive text. This interview will conduct before and after the implementation of Classroom Action Research. 3. Questionnaire
Another way to get the data, the writer also carried out the questioner in two sessions, before and after implementation of CAR. The writer used yes/ no response as the design of the questioner. The writer wants to know students response and experience about the ideas of Contextual Teaching and Learning. Each questionnaire consist of ten questions which cover 3 categories, they are; the students feeling toward understanding the reading descriptive text, the implementation of the method and the effects of Contextual Teaching and Learning to knowledge improvement and reading skill.
4. Test
The test used in this study is pre-test and post-test. The pre-test is done before implementing the contextual teaching and learning technique. It is to measure students’ reading comprehension at first. And the post-test is implemented after using contextual teaching and learning technique. In this study, the test is done in form of multiple choices. The test is held on the second action of each cycle.
E. Technique of Data Analysis
The writer used of technique’s data analysis in this study is descriptive analysis (percentage) and the analysis qualitative data used in this research is the observation of students’ activities during teaching learning processes and the interview before and after CAR, and the situation of classroom. In this case, the researcher collected the entire data which have gained,
well the technique of contextual teaching and learning in reading comprehension of descriptive text in the classroom. It uses the formula;6
xThen, the writer tries to get the class percentages which pass the KKM 70 (seventy) of English lesson at SMP Bakti Mulya 400 Jakarta. It is the
The last, the writer analyzes the students’ reading score from pre -test up to post--test and she uses the formula:8
6
Sudjana, Metoda Statistika, (Bandung: PT. Tarsito, 2002), p. 67.
7
Anas Sudijono, Pengantar Statistis Pendidikan, (Jakarta: PT. Raja Grafindo Persada,
2008), p. 43.
8
David E. Meltzer, the Relationship Between Mathematics Preparation and Conceptual
Learning Gains in Physics: A Possible Hidden Variable in Diagnostic Pretest Score, (Iowa:
y1 - y
P = ─── X 100%
Y
Note: P : Percentage of students’ improvement y : Pre-test result
y1 : Post-test 1
y2 - y
P = ─── X 100%
Y
Note: P : Percentage of students’ improvement y : Pre-test result
CHAPTER IV RESEARCH FINDINGS
This chapter presents the research findings and the discussion based on the analysis of data collected from the implementation of Contextual Teaching and Learning to improve students’ comprehension of descriptive text in two cycles. Related to the research finding, it can be seen in three parts; data description, data analyzing and data interpretation.
A. The Description of the Data
1. Findings of the Preliminary Study a. The Result of Pre Interview
In this study, the writer conducted pre interview with unstructured interview. It held on Tuesday, 24th of August 2010 started at 9.30 a.m. to 10.00 a.m. here the writer asked some questions to the teacher. The questions talk about general condition in English class, the problem have been faced the students in reading material, and the kinds of strategies that conducted by the teacher before previously implementation of Classroom Action Research (CAR).
skill, because they did not understand the passage meaning, so they did not answer the question correctly. In this semester, they have faced recount text and descriptive text said the teacher. Then the writer asked about how many KKM (Criteria of Minimum Completeness) that concerning with school program. The students should get 70 (seventy) score in English subject. And about the methodology that the teacher have done, she tough it still less for this era, because she have taught using method traditionally.
b. The Result of Pre Observation
Based on the observation was conducted by the writer on Tuesday, 24th August 2010. It is to observe the process of teaching learning in students and teachers’ reading activities before implementation the action. It held at VIII Grade SMP Bakti Mulya 400 Jakarta. There are 23 students in the class and the teaching learning process started at 07.00 A.M up to 09.00 A.M. In this class, the teacher use teacher center during the activity because the teacher actually dominated the classroom activity then it made the students passive in the class and less motivation to learn reading material. Generally, the teacher read the text individually then the students repeat after her, after that, if they did not know about the meaning of difficult vocabulary, the teacher asked them to check it into dictionary. This activity made the students bored in English class because the teacher center method of teaching learning in reading activity.