ANALYSIS OF FACTORS AFFECTING SHARI’AH FINANCIAL LITERACY IN RURAL AREA, CASE STUDY OF PEKALONGAN ANALISIS FAKTOR – FAKTOR YANG MEMPENGARUHI LITERASI
KEUANGAN SYARIAH DI DAERAH PEDESAAN, STUDI KASUS PEKALONGAN
UNDERGRADUATE THESIS
Arranged By:
HAFID KHOIR MAULANA 20130430321
INTERNATIONAL PROGRAM FOR ISLAMIC ECONOMICS AND FINANCE
ANALYSIS OF FACTORS AFFECTING SHARI’AH FINANCIAL LITERACY IN RURAL AREA, CASE STUDY OF PEKALONGAN ANALISIS FAKTOR – FAKTOR YANG MEMPENGARUHI LITERASI
KEUANGAN SYARIAH DI DAERAH PEDESAAN, STUDI KASUS PEKALONGAN
UNDERGRADUATE THESIS
Arranged By:
HAFID KHOIR MAULANA 20130430321
INTERNATIONAL PROGRAM FOR ISLAMIC ECONOMICS AND FINANCE
FACULTY OF ECONOMICS AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITAS MUHAMMADIYAH YOGYAKARTA
DECLARATION
Name : Hafid Khoir Maulana
Student Number : 20130430321
With this letter I declare that this thesis entitled “ANALYSIS OF FACTORS AFFECTING SHARI’AH FINANCIAL LITERACY IN RURAL AREA, CASE STUDY OF PEKALONGAN” is consideration of my own personal effort. Where any of content presented is the result of input or data from a related collaborative research program this is duly acknowledged in the text such that it is possible to ascertain how much of the work is my own. Furthermore, I took reasonable care to ensure that the work is original, and to the best of my knowledge, does not breach copyright law, and has not been taken from other sources except where such work has been cited and acknowledged within the text.
Yogyakarta, 22 April 2017
MOTTO
“Hidup sekali hiduplah yang berarti, takut mati tak usah hidup takut hidup mati
saja”
(PMDG)
“Barangsiapa yang mendatangkan sebuah kebaikan maka ia akan mendapatkan sepuluh kali lipat dari kebaikan itu”
(Al-quranul kariim)
“Walaupun ranting pepohonan dijadikan alat tulis dan air di tujuh lautan
dijadikan tintanya maka sekali-kali tiak akan pernah cukup untuk menulis tanda
kebesaran Allah”
(Al-quranul kariim)
“Bondho,bahu,pikir lek perlu sak nyawane pisan”
(KH.Ahmad Sahal)
“Patah tumbuh hilang berganti sebelum patah sudah tumbuh sebelum hilang
sudah berganti”
(KH.Imam Zarkasyi)
“No dream no future, no regret no learning and if there is nothing to believe than nothing to achieve”
DEDICATION
I dedicated this undergraduate thesis for my parents, big family of Randukuning, teachers from my kindergarten until college, my second family “HIMIE”, my organization “FIES”, my classmate of IPIEF 2013, “PIONER” generation and all
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
All praise to Allah S.W.T the most gracious and merciful for His guidance and blessing. Peace and salutation always be to the Prophet Muhammad peace be upon him altogether with his accompanies.
After the establishment of this study on “Analysis of Factors Affecting Shari’ah Financial Literacy in Rural area, Case study of Pekalongan ”the author gives special appreciation to the parties in supporting the accomplishment of this study. In particularly they are:
1. The respectable Dr. Nano Prawoto, SE., M.Si., as Dean of Economics Faculty.
2. The respectable Alm, Dr. Masyhudi Muqorobin, SE.,Akt., M.Ec., as Director of International Program for Islamic Economics and Finance UMY.
3. The respectable Mr.Agus Tri Basuki, SE.,M.Si as my supervisor together with Mrs. Dyah Tities Kusuma W.,MIDEc. for all priceless helps, supports, advices, guidance, all material and non-material dedications. 4. Dear all IPIEF lectures and IPIEF staff: Dr. Wahdi Yudhi, Yuli Utami,
M.Ec., Dr. Abdul Hakim, Mr. Hudiyanto, Ayif Faturrahman, M.Si, Dr. Endah Saptutiningsih, Dr. Lilies Setiartiti, Mr. Hendrianto, M.Ec, Mr. Umar Fauzi, MA, Mr. Sahlan, Mrs. Linda Kusumastuti, SE
5. For my mother and Father, Rahyono S.Pd,.MSi. and Wiri S.Pd,.Sd I love you so much.
6. For my sisters, Linah Tadiya Fitriana and Juliana Rahmawati for support and accompany.
7. Mr. Suwarjo, Mrs. Subekti, Mr. Dauri, Mrs. Sau’dah and all relatives that I cannot mention one by one, may Allah bless us.
8. My high school Pondok Modern Darussalam Gontor especially my graduate Pioner Generation.
TABLE OF CONTENT
DECLARATION ... iii
MOTTO ... iv
DEDICATION ... v
AKNOWLEDGEMENT ... vi
TABLE OF CONTENT ... vii
Table of Figures ... viii
Table of Pictures ... ix
INTISARI ……… ... x
ABSTRACT ………..……. ... xi
CHAPTER I ………. ... 1
INTRODUCTION ……….…….. ... 1
Background ……….………. ... 1
Problem Limitation ………..………… ... 8
Research Question ……….………….. ... 8
Research Objective ……….………. ... 9
Research Benefits ……….…… ... 9
Research Plan ……….……. ... 10
CHAPTER II ……….……….. ... 11
LITERATURE RIVEW ……….………. ... 11
Theoretical Framework ………...……… ... 11
History of Islamic Economic in Indonesia …………..……….. ... 11
Financial Literacy ……….………. ... 12
Shari’ah Financial Institution………...…. ... 14
Factors of Financial Literacy ……….…... 15
Shari’ah Financial Product……….... ... 17
Financial Institution and Financial Literacy Classification ….…….. ... 18
Financial Literacy Consumer Attitude ……….. ... 20
Financial Literacy of Islamic Consumption Theory ………..… ... 21
Rural Area ………. ... 22
Literature Review ……….... ... 23
Research Framework ………...…… ... 34
Hypothesis ………...……… ... 35
CHAPTER III ………. ... 36
METHODOLOGY ………... ... 36
Research Object ………... 36
Type of Data ………...…… ... 36
Collecting Sample Technique ………...…..… ... 37
Population ………...……..…... 37
Sampling Method ………...………... ... 37
Data Collection ………..………. ... 38
Operational Definition of Variables ………...………… ... 40
Dependent Variable ……….………. ... 40
Independent Variables ……….………. ... 41
Quality Test of Research Instrument ……….………. ... 41
Validity Test ………. ... 41
Reliability Test ………. ... 42
Data Analysis ………....…….. ... 43
Descriptive Statistic ………... 43
Logistic Regression ……….. ... 43
CHAPTER IV ………..…. ... 45
RESEARCH OVERVIEW ………...…. ... 45
Research Overview ………...…. ... 45
Amount of Respondent ………... 45
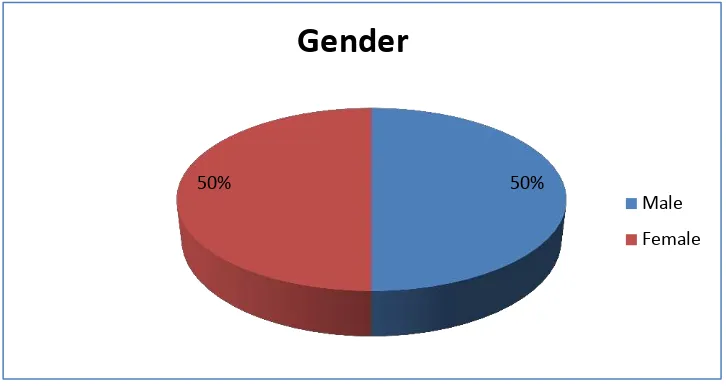
Gender ………..…… ... 47
Age Range of Respondent ………....…… ... 48
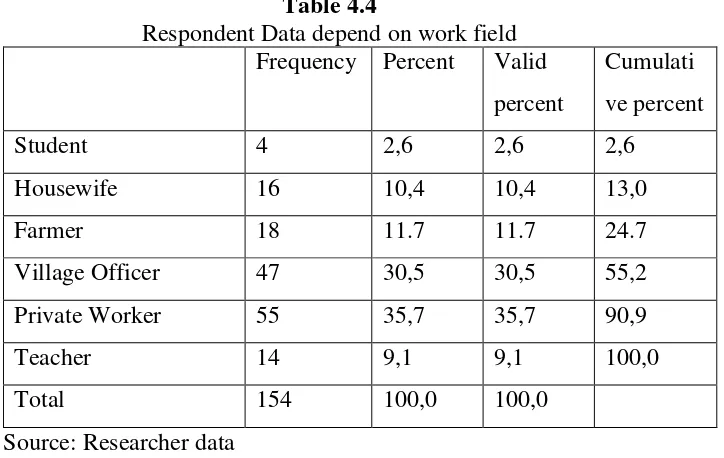
Work Field ………..…... 50
Income ………... ... 52
Education ………..…... ... 54
Financial Institution Relationship ……… ... 55
CHAPTER V ………....……. ... 58
DISCUSSION ………..………. ... 58
Instrument Data Quality Test ……….. ... 58
Validity Test ……….. ... 58
Reliability Test ……….. ... 62
Ordinal Logistic Test ………. ... 64
Discussion ………...………….… ... 68
Shari’ah Financial Literacy Level of Rural People in Pekalongam .. ... 68
Financial Literacy and Income ……….. ... 72
Financial Literacy and Education ………... ... 73
Financial Literacy and Work Field ………...…… ... 74
CHAPTER VI ………. ... 76
CONCLUSION ……….. ... 76
Conclusion ……….……… ... 76
Suggestion ……….. ... 76
Research Limitation ………... ... 77
BIBLIOGRAPHY ……….………. ... 78
APPENDIX ………..……….. ... 80
List of Table Table 1.1 Literacy and Utility Index ……… ... 4
Table 1.2 Percentage of Poor People ………... ... 6
Table 2.1 Literature Review ……… ... 6
Table 3.1 Pekalongan Population ………... ... 30
Table 3.2 Likert Scale ………... ... 36
Table 3.3 Score Conversion ……….... ... 38
Table 4.1 Respondent Amount ………... ... 45
Table 4.2 Respondent Gender ……… ... 46
Table 4.3 Age Range Table ……….... ... 47
Table 4.4 Respondent Work Field ………... 49
Table 4.5 Respondent Income Data ……….... ... 50
Table 4.7 Respondent Education ……… ... 54
Table 5.1 Respondent Relationship ……… ... 56
Table 5.2 Validity Test ………... ... 57
Table 5.3 Validity Test ………... ... 58
Table 5.4 Validity Test ………... ... 58
Table 5.6 Validity Test ………... ... 60
Table 5.7 Validity Test ………... ... 61
Table 5.8 Fitting Model ……….. ... 62
Table 5.9 Variability Test ………... ... 63
Table 5.10 Ordinal Regression Test ………... ... 64
Table 5.11 Parallel Line Test ………. ... 66
Table 5.12 Score Conversion ………. ... 67
Table 5.13 Shari’ah Financial Literacy Frequency .………... ... 67
List of Figure Figure 1.1 Pekalongan Map ……… ... 7
Figure 2.2 Frame Work ……….. ... 33
Figure 4.1 Respondent Diagram ………... 46
Figure 4.2 Gender ……….. ... 47
Figure 4.3 Age Range ……… ... 48
Figure 4.4 Work Field ……….... ... 50
Figure 4.5 Income ……….. ... 51
Figure 4.6 Education ……….. ... 53
Figure 4.7 Relation ……….... ... 54
INTISARI
Saat ini literasi keuangan menjadi salah satu isu yang sangat popular di antara kalangan para peneliti dan banyak orang yang melakukan penelitian dengan inti topic literasi keuangan, namun masih sedikit daripara peneliti yang terfokus kepada literasi keuangan syariah. Berdasarkan fakta ini, maksud peneliti dalam penelitian ini adalah untuk mengetahui tingkat literasi keuangan syariah penduduk pedesaan di kabupaten Pekalongan dan untuk mengetahui faktor – faktor yang mempengaruhi literasi keuangan syariah. dengan menggunakan data primer metode statistic deskriptif dan uji regresi ordinal peneliti mencoba untuk menemukan hubungan antara pendapatan, pendidikan, pekerjaan dan hubungan responden dengan institusi keuangan dari total 154 responden dalam 10 kecamatan di kabupaten Pekalongan.
Keyword: Shari’ah financial literacy, Descriptive statistic, Ordinal
ABSTRACT
Financial literacy today become the one of famous issues among researcher and much of people done their research with financial literacy as the concern
topic, however few of them which concern on shari’ah financial literacy.
Based on this fact, researcher aims from this research is to know the shari’ah
financial literacy level of rural people in Pekalongan regency and to know
the factors influencing shari’ah financial literacy. Using primary data with
descriptive statistic and ordinal regression test researcher try to find the relation between income, education, work field and financial relationship of the respondent from the total of 154 respondents in 10 districts of Pekalongan regency.
1 CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
A. Background
Total population number in Indonesia showed a growth rate relatively high
as an average of 1.78% per year compared to the world population growth
was 1.61% from year 1971 to 2010. In 2010 Indonesia has reached 237.64
million of total population, the community needs in term of financial product
and services are also expected increase from year to year. Data from BPS
(2012) show the number of people in productive age which from 15 to 54
years reached 59.98% or 142.54 million. This population growth is a potential
side for financial services institutions for offering their products and services.
The potential of Indonesian societies that will take financial product and
services advantages in the future are expected to be increased, considering
from year 2000 due to 2012 GDP per capita of Indonesia is increased from
Rp. 6.72 million to Rp. 33.24 million and Indonesia financial services sector
also contribute as the important role who were doing financial intermediation
Rp. 7.534.81 trillions per December year 2012. However, the role is not
optimal (OJK 2013).
The Pew Forum on Religion & Public Life (2010) set 10 Countries with
the largest Muslim population, Which placed Indonesia at the first rank with
12,7% from the world total population this statement is strengthen by Data
2
people or (87,18%) is Muslim. From its population, 150 million people have
an opportunity to access the financial product and services but in fact, only
2% who are able to access this is known by watching on Islamic banking
market share.
With the largest Muslim population Country Indonesia has the advantages
as potential place for the development of Cultural, Governmental and
Financial instrument which based on the Islamic principles. Indonesian
muslim people awareness of financial institution need which based on the Islamic principles appear in the end of 90’ Century, The emergences of
Shari’ah banks is the sign of Islamic financial system starting point in
Indonesia and also giving the refreshment air for Muslim people and as the
main foundation of Islamic financial establishment.
In the last two decade Islamic financial Institution caught by stagnation
this statement followed with the data from Otoritas Jasa Keuangan per September 2015 which shows the shari’ah financial market share in Indonesia
only 5% from the total of financial asset. Year 2013 Global Islamic Economic
Index placed Indonesia in the tenth grade when measuring the development of
Islamic Economic whole the world.
As consequences of the changing structure of an economy, financial
knowledge has become not just a convenience but an essential survival tool.
A lack of financial knowledge can contribute to the making of the poor
financial choices that can be harmful to both individual and communities
3
One of factors affecting the low of Shari’ah financial market share in
Indonesia is the low of Shari’ah financial literacy that remain in the society
(Rahmawati, 2016). The use of financial product and services has done to
fulfill individual need for consuming so individual preferences in using the shari’ah financial services determined by knowledge and understanding,
ability or skills and individual confidence to fulfill the financial need that is
called financial literacy.
Financial literacy defined as the ability to understand finance according to
(Mason and Wilson, 2000) in Sardiana, (2016) financial literacy meant as the
ability of a person to get, to understand and to evaluate relevant information
on decision-making for understanding its consequences. Financial literacy
makes a person able to make a decisions based on relevant information
therefore, the understanding of information becomes important in every
decision making process for each individuals (Sardiana, 2016). According to
Chen and Volpe, (1998) the ability to manage personal finance has become increasingly important in today’s world people must plan for long term
investment for their retirement and children’s education, they must also
decade the short term savings and borrowing for a vacation, a down payment
for a house, a car loan and other big ticket item.
It is important to know financial literacy if people want to avoid financial
scum and now days there are financial advisers and planners who look after their client’s interest also consumers bombarded with varieties of financial
4
our duty (Ahmad, 2010 in Chong, 2014). This is especially important to
middle class, where the majority of consumers of financial product belong.
According to OJK National Survey of Financial Literacy year 2013, show
financial knowledge (financial literacy) is 21, 84% or 1:5 from the total
population of Indonesia with the well literate category. Where the financial
inclusion is 59, 74% which dominated by financial product and services 57,
28%, followed by Insurance 11, 81%, funding 6, 33%, pawnshop 5, 04%,
retirement fund 1, 53% and capital market 0, 11%.
Table 1.1
Literacy Index and Utility Index of Financial Sector
Classified Finance Insurance Funding Pension
Fund
Source: National Financial Literacy Survey, 2013
Based on survey of OJK 2013, in term of society financial literacy
improvisation Indonesian society financial literacy defied into four, those are
1. Well literate (21, 84 %), those who have knowledge and believe related
financial institution products and services include advantages and risk,
right and obligation related to financial products and services, and capable
5
2. Sufficient literate (75, 69 %), those who have knowledge and believe
related financial institution products and services include advantages and
risks, right and obligation related to financial products and services.
3. Less literate (2, 06 %), those who only have a knowledge related financial
institution products and services.
Not literate (0, 41%), those who does not have knowledge and believe
related financial institution products and services include advantages and risk,
right and obligation related to financial products and services.
Financial literacy has the long term purpose for the whole of the society:
1. Increase the people literacy which less literate or not literate to the well
literate.
2. Increase the amount of financial product and services users.
People have to understand advantages and risks than believe that financial
product and services that they choose will increase their welfare than they can
determine the suitable financial product and services as they need.
For the society, financial literacy will give a benefit such as:
1. Able to determine and harness the suitable financial product and services,
and have the capability for maintaining the good financial planning.
2. Avoid people from the uncertainty investment in the financial instrument.
3. Understand the advantages and risk of financial product and services.
Financial literacy also contributed many benefit for the financial sector,
financial institution and the society need each other therefore, if the society
6
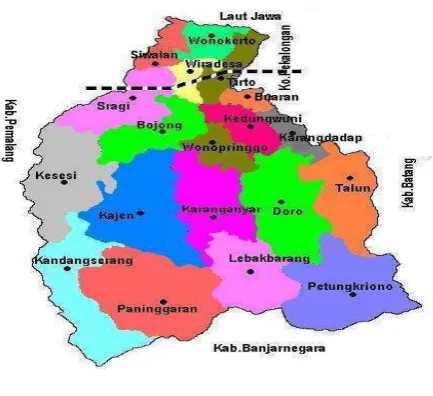
products and services. Pekalongan as one of the part of central Java labeled as
batik city and recognized at the national level. If the focus of people are
concern to the industrial product such as batik and sarong here writer try to
show how is the condition of other sector and how the poor people at
Pekalongan which is most of them work as a farmer and life in the rural area.
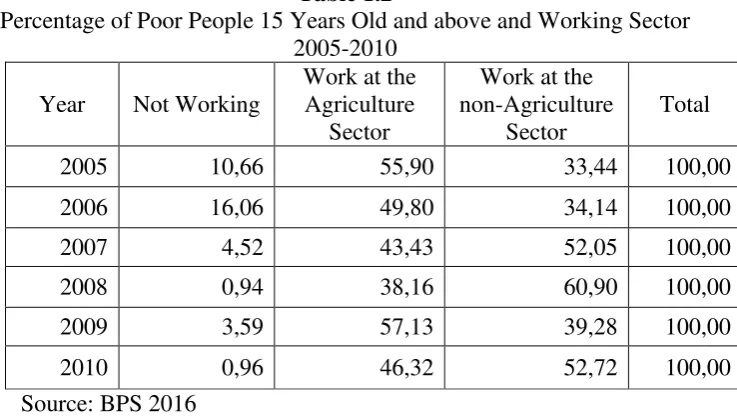
Table 1.2
Percentage of Poor People 15 Years Old and above and Working Sector 2005-2010
From above data we know most of poor people are work at the agriculture
sector which mean being a farmer, and most of people who doing an
agriculture living in the rural area with the available land. The general way to
attempted is agricultural which influence by the nature around the area such
7
Figure 1.1: Pekalongan Regency Map
According to the background above related to the lack of financial literacy
at the Indonesian society writer would like to to analyze the condition whether people are unfamiliar with the shari’ah financial literacy or in
contrary, especially in Pekalongan and writer concern on those who living at
the rural which came up with the title: “ANALYSIS OF FACTORS
AFFECTING SHARI’AH FINANCIAL LITERACY IN RURAL AREA,
STUDY CASE OF PEKALONGAN”.
B. Problem Limitation
Study limitation aims to restrict the analysis problem may occur. This
study restricted to the following limitation:
1. The dependent variable in this research is shari’ah financial literacy
2. The independent variables is income, education, work field and financial
institution relationship
3. This research used primary data and the data collection used in this
8
4. Respondent are Pekalongan people who are living in rural area.
C. Research Question
Based on the explanations that have been described above therefore, the
problems in this research are:
1. Does income affect on rural people shari’ah financial literacy in
Pekalongan?
2. Does education affect on rural people shari’ah financial literacy in
Pekalongan?
3. Does work field affect on rural people shari’ah financial literacy in
Pekalogan?
4. Does financial institution relationship affect on rural people sharaia
financial literacy in Pekalongan?
D. Research Objectives
The specific purpose of this research is to study of shari’ah financial
literacy at the specific. Based on research question, thus the objective of this
paper is:
1. To analyze the relation between shari’ah financial literacy and the income
of people who lived in the rural area of Pekalongan.
2. To analyze the relation between shari’ah financial literacy and the work
field of rural people in Pekalongan.
3. To analyze the relation between shari’ah financial literacy and the
9
4. To analyze the relation between shari’ah financial literacy and the
education in the rural area of Pekalongan.
E. Research Benefits
This study contributes useful information for parties which are interested in shari’ah literacy there are some benefits for government, financial
institution and academicians such as:
1. To the government, give benefit for government in term of conducting the
social project in financial literacy education to support financial institution.
2. To financial institution, give benefit for financial institution in term of
expanding their financial product.
3. To scholar and academicians, give benefit to provide some additional
information for further research.
F. Research Plan
The organization of the research is conducted, as follows:
1. Chapter I, Introduction. This chapter will explain the purposes and
objectives of this research, the background of this research and aims to
explore the objects of research.
2. Chapter II, Literature Review. This chapter included the theory related
with this study, also include the previous research from the expert who
was conduct similar research before with the difference object, included
10
3. Chapter III, Data Research and Methodology. Chapter three explain briefly
the data which conduct in this research, and explain Analysis quantitative
descriptive and ordinal regression methodology step to analysis the study.
4. Chapter IV, Overview. Chapter four will explain the general description and overview the Shari’ah financial literacy in rural area of Pekalongan.
5. Chapter V, Research Finding. This chapter will explain in detail the result
of analysis which conducts by an Analysis of quantitative descriptive and
ordinal regression.
6. Chapter VI, Conclusion. In this chapter will conclude the result of test in
chapter four, the recommendation for the next research and the policy
1
CHAPTER II
LITERATURE REVIEW
A. Theoretical Framework
1. History of Islamic Economic In Indonesia
Indonesia Financial System divided into two, financial system and
Non-bank financial institution. Non-Non-bank financial institution is financial that
based on the legislation law which collected the fund from the society in term
of depository financial institution and distribute in term of credit or in others
and give the services for the payment way, such as public bank and society
bank for credits. Non-bank financial institution is financial institution which
the activities not in order to collect the direct fund from the society in term of
saving, such as: pension fund, insurance, venture fund, and pawn shop.
Historically the Indonesia financial legislation system has some changing
which at first is 27 October 1988 change since 1992, those are:
a. Law No 7 Year 1992 About Finance
b. Law No 2 Year 1992 About Insurance
c. Law No 11 Year 1992 About Pension
d. Law No 8 Year 1995 About Funding Market
e. Law No 10 Year 1998 About Changing of Law No 7 Year 92 about
Finance
2. Financial Literacy
Financial literacy is an active process in which communicating
information is only the beginning and empowering consumers to take action
to improve their financial well- being is the ultimate goal (Abdullah and
Chong 2014). Financial literacy according to (Miller et.al. 2009 in Chong
2014) is the combination of consumers or investors understanding of financial
product, concept, their ability and confidence to appreciate financial risk and
opportunities to make informed choices, to know where to go for help, and to
take other effective actions to improve their financial well-being.
Financial literacy is process or activities for improving the knowledge,
confidence and skill in whole society than they can manage their financial
needs (OJK). Financial literacy defined as the ability to understand finance
according to (Mason and Wilson (2000) in Anna Sardiana (2016) financial
literacy meant as the ability of a person to get, to understand and to evaluate
relevant information on decision-making for understanding its consequences.
Nevertheless, studies on financial literacy have not come up with a
consensus definition of financial literacy. However, (Remund, 2010 in Ma’ruf, 2015) was able to pin point that many conceptual definitions of
financial literacy fall into five categories:
1) Knowledge of financial concept
2) Ability to communicate about financial concept
4) Skill in making appropriate financial decisions
5) Confidence in planning effectively
In addition according to Remund 2010 in Ma’ruf, 2015, financial literacy
is a measure of the degree to which one understands key financial concepts
and possesses the ability and confidence to manage personal finances through
appropriate, short term decision making and sound, long range financial
planning, while mindful of life events and changing economic condition.
3. Shari’ah Financial Literacy
Shari’ah financial literacy is related to knowing product and financial
services able to differ between shari’ah and conventional bank also can
influence manner of the people in order to take economic decision according
to shari’ah. Shari’ah finance is kind of finance based on shari’ah or Islamic
principles. Shari’ah which mean “road to the water springs”, filled with moral
goals and tough of truth. Therefore shari’ah is more than the role of law. The
fact, shari’ah represented the argument that every people and governance
obey to the justice under the law (Rahmawati, 2012).
Abdul Hamid and Bordin, (2001) in Azmi and Anderson, (2015) state a
study conducted in Malaysia in 1994, regarding knowledge in Islamic
banking showed that almost 100 percent Muslim population was aware of the
Islamic bank , however out of this 27,3 percent completely understood the
differences between Islamic bank and conventional banks and only 38,7
4. Shari’ah Financial Institution
Financial institution is a business entity which the wealth basically such as
financial asset or financial claims compared to the non-financial assets or rill
assets, financial institution give the credits to the costumers and plant their
fund in term of securities (Siamat, 2001). Shari’ah finance is a financial form based on shari’ah or Islamic law principles. Indeed, shari’ah represented an
idea that all of people and governance is submissive under the justice of law.
This is one of term which summarized the way of life that Allah’s tough to
his creature include all of things related to business contract until worship, term of “suitable with the shari’ah” in picturing all allowed things in Islam
(Abdullah and Chee, 2012). In general, shari’ah bank is financial institution
which the basic business is give the people credits and other services in line of payment and the operation of cash flow suited with the shari’ah principles
Sudarsono (2008).
The movement of modern Islamic financial institution started with a local
saving bank non-interest that operated in Mit Ghamir village, blank of Nil
river Egypt at 1696 by Dr. Hamid An-nagar in Muhammad (2011).
The need of Islamic private bank in rural and international, followed by
the existence of other supporting institution such as insurance, pawn shop and
baitul mal wa tamwil. That based on Islamic principles and lately Dow jones came out what we called by Islamic Index which cover the stock index that
5. Factors of Financial Literacy
The social research center, (2011) in Sari, (2015) factors which describe
the differences of financial literacy level:
a. Age, there are positive affect on the attitude as an indicator of financial
literacy at 25-34 years old which at 18-24 there is no influence. This is in
line with the more knowledge of financial products they have the more
financial transaction used for their needs.
b. Financial knowledge have a positive relation to mathematics ability,
people who has the knowledge will be able to control their financial
expenses. This show with the general financial knowledge and
mathematics ability people able to choose the suitable financial products,
watching the financial condition, and know the latest condition of financial
situation.
c. Financial attitude has the positive and negative relation to the finance
indicators.
d. House hold income, has the positive significant relation to financial
control which mean more income lead to the better financial control.
e. Education and work field has a relation with some of the financial
indicators, because in some point that education and work field is
Bushan and Medhury, (2013) in Margaretha and sari, (2105) found
financial literacy level influenced by gender, education level, income, kind of
job or nature of employment, and work field, where not influenced by
geography and age (Margaretha and Sari, 2015)
a. Financial literacy and income
Financial literacy increases trough with the income increases
(Scheresbergh, 2013) in Margaretha (2015). There is a significant
influence between financial literacy and the income of people
(Margaretha and Sari, 2015). Amount of income has the significant influence with the level of shari’ah financial literacy (Rahmawati, 2016).
b. Financial literacy and education
More the education of people will influence to the more understanding of
financial literacy (Nidar and Bestari, (2012) in Margaretha and Sari
(2015). Financial literacy and education have the significant relationship
(Margaretha and Sari, 2015). Variable of education level positively affect
on financial literacy (Amaliyah and Witiastuti, 2015). The Educational
background has the significant influences with the shari’ah financial
literacy (Rahmawati, 2016).
c. Financial literacy and work field
Financial literacy level is influenced by work field (Bushan and
Medhury, 2013) in Sari (2015). Education and work field has a relation
d. Financial literacy and financial institution relationship
The respondent relationship trough financial institution has the significant influences to the shari’ah financial literacy (Rahmawati,
2016).
6. Shari’ah Financial Products
For the sufficient of capital and financing, shari’ah bank has the different
requirement with a conventional bank. In general, the devices of shari’ah
bank consist of three categories:
a. Financing products
b. Funding products
c. Services products
Financing products:
a. Wadi’ah (giro).
b. Mudarabah (saving and deposit). Funding products:
a. Profit sharing (mudarabah dan musarakah).
b. Buy and sell (murabahah, istisna’, salam, dan ijarah). c. Services (rahn, wakalah, kafalah, hawalah, qard)
Non- Bank (services) products:
Islamic banks have the purposes those are, guide the society economic
activities for interaction in term of Islamic value, to build the balance and
justice system in term of economic investment, to develop the social living
standard with the easiness for poor people, poverty alleviation, to maintain
the economic stability and become savior of the society from konventional
bank dependency (Sudarsono, 2008).
7. Financial Institution and Financial Literacy Classification a. Depository financial institution or depository intermediary.
Financial institution collecting the fund directly from the society in term of
deposits such as giro, saving, or time deposit which accepted from
depositor or unit of surplus such as: Corporation, Government and
household with the surplus income after the consumption expenses.
b. Non-Depository financial institution or non-bank financial institution.
Financial institution included of this category is financial institution
which the business activity where characteristically has a contract or
contractual institution which is collecting the fund from the society with
offering the contract for consumers protection from the uncertainty risk
such as insurance and pension program than called by insurance company
According to Chen and Volpe (1998) in Farah and Sari (2015) financial
literacy categorized into three groups bellow:
a. < 60% which is those people who have the low financial literacy.
b. 60%–79%, which mean people who have the medium financial literacy.
c. 80% which mean those are people who have the high financial literacy.
Based on the Indonesia financial literacy national strategy, people
financial literacy are classified into 4, those are:
a. Well Literate, Those who have knowledge and believe related financial
institution products and services include advantages and risk, right and
obligation related to financial products and services, and capable to use
financial product and services.
b. Sufficient Literate, Those who have knowledge and believe related
financial institution products and services include advantages and risk,
right and obligation related to financial products and services.
c. Less Literate, Those who only have the knowledge related financial
institution products and services.
d. Not Literate, Those who does not have knowledge and believe related
financial institution products and services include advantages and risk,
8. Financial Literacy Consumer Attitude
The consumer attitude toward a products or services, according to the
theory of three component attitude model determined by three attitude
components:
a. Cognitive
b. Affective
c. Conative
From the three components that can affect the attitude are confident and
feelings. Engel (1995) in Anna (2016) said on some product or services
attitudes only depend on the confidence while other products or services
attitude depend on evaluation of product or services. Meanwhile, the
relationship between attitude or conative or interest can be described as a
cause and effect relationship where the attitude of person can affect to certain
moralities (Mardiana, 2016).
An attention describes the conative attitude components that related to
some preferences to perform regarding specific attitude. Based on some
interpretations, conative components can be included the attitude (real)
behavior itself.
9. Financial Literacy of Islamic Consumption Theory
In Islamic consumption analysis that people manner of consumption not
only to fulfill their body needs but also for fulfill their spirit needs. So in term
of manner of consumption a Muslim always pay their attention to the Islamic
what is the purposes behind the consumption, how is the moral and manner as
a Muslim when they consume something and how is the consumption of a
Muslim is related to their society.
Islamic economy aims to realize the long term of economic growth and
maximizing the welfare or falah. Falah mean the personal needs of people is fulfilled trough the company of social balance and concern at the family
values also attitude (Chapra, 2000) in Sudarsono, (2008). For the
consequences some of basic attitude is needed in the economy to achieve the
concept of falah (Naqwi, 1994) in Sudarsono, (2008), those are first, the existence of god (Allah) as the control center of the economic activities
because of the limited knowledge of people in contrary with god. Second,
balances in term do not very excessive, balance of distribution nor the
individual and social needs. Third, in term of freedom of choices but it is
bordered with the obligation of each people (Sudarsono, 2008).
10. Rural Area
The 1996 census defines “rural areas” as sparsely populated lands lying
outside urban areas which urban have the minimum populations of 1.000 and
population densities of 400 or more people per square kilometer (Statistic
Canada, 1999) in Canada Statistic, (2002).Rural and small town refers to the
population living outside the commuting zones of larger urban center
specifically outside census metropolitan area (Medelson and Bollman, (1998)
Law number 2 year 1999, Rural area is the unity of society law which have
an authority to manage and organize society needs based on the origin custom
that recognized by the national governance system and include in the area.
Law number 6 year 2014, Rural is rural and custom rural or called by
another name next called by rural, is unity of society law which has the limit
of area obligated to manage and organize the government jobs, society needs
according to society initiative, origin right, and or traditional right which
recognized and be respected by the governance national system of republic of
Indonesia.
B. Literature Review
Financial literacy is first and foremost about empowering and enlightening
consumers so that they are knowledgeable about finance in a way that is
relevant to their lives and enables them to use this knowledge to evaluate
product and informed decisions. As the consequences of the changing product
of economy, financial knowledge has become not just convenience but an
essential survival tool. A lack of financial knowledge can contribute in
making of poor financial choices that can be harmful to both individual
communities. Mounting evidence shows that those who are less financially
literate are more likely to have problems with debt, are less likely to save, are
more likely to engage in high cost mortgages, and are less likely to plan for
retirement. Without a certain level of financial literacy, consumers might not
purchase the financial products and services they need and might be
consumers, and to understand and appropriately manage the variety of risk
(Kefela, 2011:9) Financial literacy called as the ability of people to get,
understand, and evaluate the relevant information for the decision making
with the understanding of financial consequences that appear Krisna (2010),
in Amaliyah and Witiastuti (2015).
Looking to the economic condition today, financial literacy contribution is
important. People need the basic knowledge of finance and skill for
processing the effective financial resources for the welfare of their life,
especially for the entrepreneur which is commonly face with the financial
decision making and more which related to the financial corporation. Less of
access will lead to the low of access to the financial institution (Amaliyah and
Witiastuti, 2015).
The research result shows that Islamic financial literacy significantly
affected to the shari’ah financial services usage. At the more research, the
knowledge indicators shows half of them are significant to the financial literacy preference usage, ability indicator and self not affect on shari’ah
financial literacy preferences (Sardiana, 2016).
The financial crisis has also led to the renewed focus of the world to
Islamic finance. The Islamic financial industry has been flooded with various
different types of financial instruments and asset for not only Muslim
investors but also the non-Muslim investors to choose from. Hence, an
assets are pertinent in order of invertors irrespective of whether they are
Muslim or non-Muslim to manage their portfolio. With respect to making
these Islamic financial products acceptable to wider spectrum of investors and
business people alike, the governor of central bank of Malaysia several years
ago has pointed that enhanced financial literacy on Islamic financial products
will facilitate transactions, with a clear understanding and appreciations of the
unique characteristics and features of Islamic finance and its real economic
value (Abdullah and Anderson, 2015).
Margaretha and Sari, (2015) said many people with the financial problem
in one side just not because of the low of their income rather than because of
the false in income allocation, the low of financial literacy cause unwise
income allocation therefore with the financial ability will lead to the right
choices. Financial literacy in term of understanding to the all aspect of
finance is not burden or to tide people on doing their life but with the
financial ability will lead people for the better life (Warsono, (2010) in
Margaretha and Sari, (2015).
The financial literacy index of financial institution that exist in Indonesia
at the FEB Unsoed students still low at only $4.76 for student who are well
literate and amounted to 95.24% in banking products and services and the
cause of these is they do not get the financial education from the family as a
child (80%), not taught in formal education as a child (77%), not to get the
be used to invest in products and services of financial institutions (93%)
(Lestari, 2015).
It was several years ago when the governor of central bank of Malaysia
pointed out that in order to make Islamic financial acceptable to a wider
spectrum of investors and business people alike, financial literacy on Islamic
financial products need to be enhanced, This is in order to facilitate
transactions, with a clear understanding and appreciation of the unique
characteristics and features of Islamic finance and its real economic value
(Abdullah and Chong, 2014).
Financial education is important to both the security of individuals and the
security of nation. Enlightened societies today strive to ensure social cohesion
as an integral part of economic progress, Interesting and well-paid jobs are
central pillars of social cohesion, but so are savings and the building of
capital to provide individuals with financial security, especially for their
retirement. That cohesion can be seriously undermined by major imbalanced
of wealth within nations. Major inequalities between elements of society,
especially along ethnic or racial lines, can be recipe for disaster. One way to
avoid that catastrophic scenario is to ensure that everyone participated in
wealth, both in its creation and distribution. Along with good employment
prospect, financial education can play a key role in helping individuals and
families build their assets. Just as health education in primary and secondary
schools helps children develop good life-long dietary and hygiene habits,
Moreover, well-informed financial consumers ultimately lead to better
financial markets, where rogue products are forced from the market place and
confidence is raised (Johnston, 2005).
In this few of years, in the whole part of the world financial literacy issue
is concerned to discuss. An exclusive attention to the financial literacy
because of the willingness of such country for having the good quality people
and financial good understanding, will affect to the finance and economic
condition, this financial literacy is related to the ability of people at the
management and doing the planning which related to the finance (Ma’ruf and
Desiyana, 2015).
Halal literacy and Islamic literacy are two crucial concepts where it can
lead to the behavior of person toward its decision especially in adopting the
Islamic financing, literacy has been studied widely in many fields including
in consumer behavior context. Literacy usually associated with knowledge
and it shows that knowledge is one element things that lead to the behavior of
a person in the Holy Qur’an in surah Al-an’am also states that knowledge or
literacy is necessary to that a Muslim can differentiate what is lawful and
prohibited in Islam “why should you not eat of (meats) on which Allah’s
name hath been pronounced, when he hath explain to you in detail what is
forbidden to you – except under compulsion of necessity? but many do
Consumptive life style influenced by many factors one of those is the
easiness of transaction, industries development and life style which is
adopted, these things make many people irrational in term of their
consumption moreover today money is unnecessary when people want to buy
any kind of product or services because the existence of credits card and it is
popular in the society (Margaretha and Sari, 2015)
Lisa Xu and Bilal Zia (2012) in Lestari, (2015) said that term of financial
literacy include the concept which is start from the awareness and
understanding about financial products, financial institution, and concept of
financial ability such ability to count compound interest payment and the
general financial ability such as money management and financial planning. According to Lusardi and Mitchell (2000) in Ma’ruf (2015) that gender is one
of factor in the financial literacy, they explain the gender differences in
Sweden which female is rarely make any decision at the house hold. Kefela
(2011) said financial literacy a broad concept that include both the
information and behavior it is relevant for all consumers regardless of their
wealth or income. Bank in the developing countries have to provide financial
literacy to their consumers because of the positive direct impact this can have
an access to finance and saving which in return support livelihood, economic
growth, sound financial system and poverty reduction.
The understanding of individual finance is needed with this people able to
decide any products and services that suitable with their current condition,
lead them to the negative cash flow. Therefore knowledge and the good
understanding is absolutely needed by the people in their daily life to
maximize the uses of a financial instrument, financial product that and able to
decide the correct decision in other word every people need to have the good
financial literacy (Mendari and Kewal, (2013) in Margaretha and Sari (2015).
Financial literacy topic become important among expert because of 2008
crisis, the expert said that the main cause of the economy global crisis is the
low of financial literacy. On that time people became more consumptive more
than what they able to earn for income, they have much of credits with the
high rate of credit card user because of this financial institution lost their
liquidity and bankrupt (Lestari, 2015).
In every people daily life, there are 3 financial decision commonly used
those are:
1. How much the amount they should consume in every period of time.
2. Is there any surplus of income and how to maintain this surplus for
investment
3. How to earn for consumption and this investment.
In order to achieve the financial welfare, people have to have a knowledge
and attitude through the healthy individual financial implementation.
Knowledge, manner and individual financial implementation at the financial
Term of Financial literacy is an ability of people for taking decision of their own finance. Remund (2010) in Ma’ruf (2015) explained five domain of
financial literacy is:
1. Knowledge of financial concept.
2. Ability to communicate related to financial concept.
3. Ability to maintain the individual finance.
4. Ability to take any financial decision.
5. Believe in order to plan future finance (Margaretha and Pambudhi, 2015).
According to the researchers INDEF Aviliani, the need for education to
the community of financial products both banks and nonbank very urgent to
people not be deceived by those who are not responsible. Research conducted
Gonthor, et al (2006) from Bapepam-LK in terms of understanding the capital
markets, 80% of respondents were familiar with capital markets, 50% of them
knew the capital markets of the news media, 25% of the respondents knew
and 50% claims to know enough about capital market products (Nidar and
Table 2.1
Summary of Literature Review
No Books & Journals Analysis Tool Research Output
1 Juliana Rahmawati
(2016) “Faktor Yang of SMe in Yogyakarta is intermediate with
and people attitude in term of economic
activity.
3 Riski Amaliyah dan Rini
Setyo Witiastuti of logistic biner regression method.
Research shows financial literacy level
of owner of SMe in Tegal city include the
high category with mean of 11,79. Gender and education affect on financial literacy level. children in house wife
No Book and Journal Analysis Tool Research Output
This research use the primary data from majority of SMe has the
intermediary financial literacy level with 73,8%. Beside of that the ability of SMe has the intermediary level
too with 57,5%.
6 Farah Margaretha dan
Reza Arief Pambudhi (2015) “Tingkat Literasi
Keuangan Pada Mahasiswa S-1 Fakultas
Ekonomi”.
This research use the primary data from questionnaire with descriptive statistic
and chi- square analysis and ANOVA
test. student FED Unsoed is
low because well literate include 4,76 % and financial products knowledge 95,24%. Cause of it is they do not got the financial education from the child or their parent
are no concern of it .
8 Yulia Indrawati (2014),
“Determinan dan
Research show in term of aggregate financial literacy level of urban people in Jember is low
whether basic financial literacy and advanced
financial literacy.
9 Anastasia Sri Mendari & Suramaya Suci Kewal (2013), “Tingkat Literasi
Keuangan di Kalangan
Mahasiswa STIE MUSI”.
Statistic Descriptive The indication for financial decision in some cases show the low of knowledge of long investment term
No Book and Journal Analysis Tool Research Output View of banking and
Islamic banking Halal Literacy: The Way Forward in Halal literacy can help the policy maker in
12 Sardiana, Anna. 2016. The Impact of Literacy
To Shari’ah Financial
Literacy.
Descriptive research Research shows Islamic financial
No Book and Journal Analysis Tool Research Output 14 Johnston, Donald. 2005.
Important of Financial Literacy in The Global Economy. Kuala Lumpur.
Financial education is important to both the security of individuals and the security of nations.
15 Abdullah, M.A. and
Chong, Rosita. 2014. Financial Literacy: An Exploratory Review of The Literature and Future Research.
Much of the current works have been on the literacy on
conventional financial knowledge. Since there is a renewed interest in in islamic finance, more studies should be undertaken in order to determine the level of people literacy of people
C. Research Framework
This research aims for analyzing the shari’ah financial literacy at the rural
people of Pekalongan, Central Java Province. The figure that describes how
the framework of research would be conducted can be seen as below.
D. Hypothesis
Based on the review and discussion related to the previous study, this
study developed the hypothesis:
H1: There is positive and negative significant relationship between income and the shari’ah financial literacy.
H2: There is positive significant relationship between education and the shari’ah financial literacy.
H3: There is positive and negative relationship between work field and the shari’ah financial literacy.
H4: There is positive significant relationship between financial institution
CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
A. Research Object
The object of this research is the relation between some variable such as income, work field, education and financial relationship trough shari’ah
financial literacy variable used in this research consist of one dependent
variable and four independent variables.
The dependent variable is:
1. Shari’ah financial literacy
And the independent variables are:
1. Income
2. Work field
3. Education
4. Shari’ah financial institution relationship
B. Type of Data
This research used a primary and secondary data with the primary data as
the based, primary data is data which obtained from the research subject. This
data is information obtain from the respondent explanation, questionnaire answers and direct interview to the respondent related to the shari’ah financial
And secondary data obtained from the journals, articles, internet and
previous study related to the research variable.
C. Collecting Sample Technique
1. Population
Population is a generalization area contained of object or subject which
has the quality and any characteristic determined by the researcher for being
studied and taking conclusion from that Sugiyono (2014). Population that will
be included in this research is people who lived in the rural area of
Pekalongan, Central Java with the different background. Population of
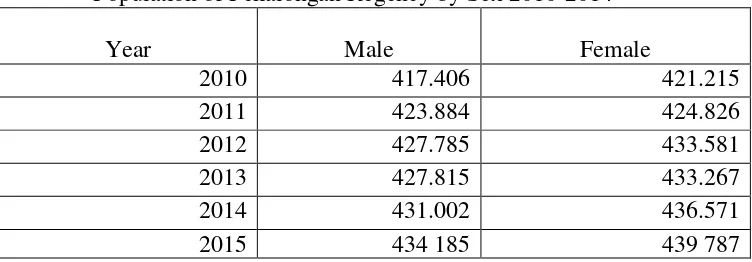
Pekalongan people in term of year 2010 up to 2014 is increasing by 6491
people with the growth rate of 0,75 in year 2014.
Table 3.1
Population of Pekalongan Regency by Sex 2010-2014
Year Male Female
2010 417.406 421.215
2011 423.884 424.826
2012 427.785 433.581
2013 427.815 433.267
2014 431.002 436.571
2015 434 185 439 787
Source: BPS 2015
2. Sampling Method
Sample is a part of amount and characteristic own by the population.
Sample taken from the population have to represent of population (Sugiyono,
Sample taking technique used in this research is simple random sampling. Simple random sampling technique is a simple technique because member
taking sample from the population is random without paying attention to the
society level. This way is taken if the member of population considered as
homogeny (Sugiyono, 2014).
Sample random sampling is choosing process of unit sampling in such a
way than every unit of sampling in the population has the same chance for
being choosing in to the sample. Taking sample with this way can be done
with the lottery or random table (Sanusi, 2012)
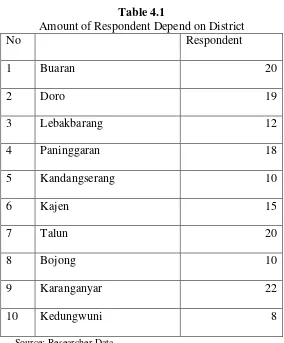
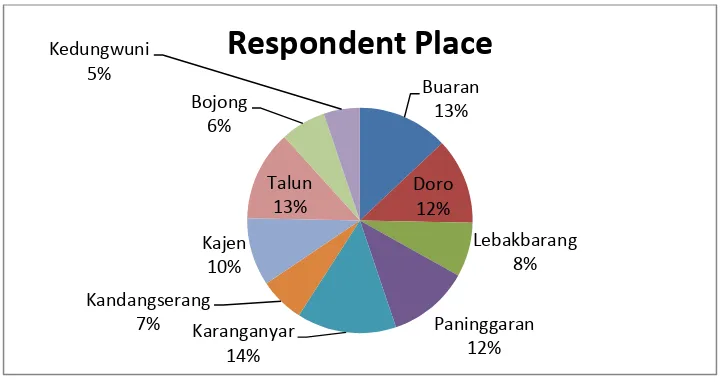
Amount of sample used in this research is 154 respondents which separate
in 10 districts from the total of 19 in Pekalongan Central Java Province. The
minimum respondent that delivered by long is 100 than writer decided that in
this research use more than the minimum amount of respondent (Gudono,
2014) in Rahmawati, (2016).
D. Data Collection
Data collection technique in this research is using the questionnaires.
Questionnaire is data collection technique with giving the bunch of written
questions or statements for the respondent to answer (Sugiyono, 2014).
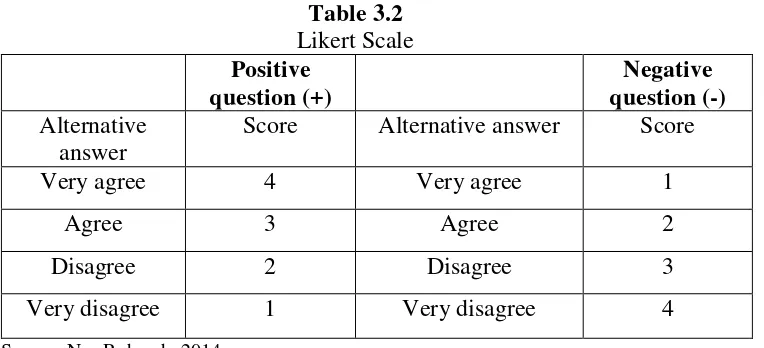
Questionnaire used in this research is likert scale. Likert scale is an ordinal measurement used to measure manner, opinion, and people perception related
to social phenomenon. Therefor for knowing the measurement of respondent
researcher use the likert scale (likert’s summated ratings) Sugiono in Basuki
(2015). Result range that given is 1 up to 4.
Likert Scale is scale based on additional respondent attitude in responding
the questions related to indicators from the concept or measured variable. In
this condition, respondent asked to agree or disagree in each of questions
(Sanusi, 2012). This range used for standardize the appraisal of respondent,
directly stuffed by the people who lived in the Pekalongan rural area.
Table 3.2
Score Alternative answer Score
Very agree 4 Very agree 1
Agree 3 Agree 2
Disagree 2 Disagree 3
Very disagree 1 Very disagree 4
Source: Nur Rohmah, 2014
For interpreting the result of research data collected is conversed to the
likert scale category using the guidance result conversion as below:
Table 3.3
Guidance of Score Conversion
Score Conversion Formula Category
1 X>Mi+1 (SDi) High
2 Mi-1 SDi ≤X≤Mi + 1 (SDi) Moderate
3 X<Mi-1 (SDi) Low
Explanation:
X = Total Score
SDi = Ideal Standard Deviation
= 1/6 (ideal maximum score – ideal minimum score)
Mi = Mean Ideal
= ½ (ideal maximum score + ideal minimum score)
E. Operational Definition of Variables 1. Dependent Variable
In this research the bound variable is shari’ah financial literacy, which is
ability of people for managing the finance in corresponding with shari’ah
principles. For measuring shari’ah financial literacy variable, questionnaire
will be spread with the questions and statements related to shari’ah financial
literacy.
2. Independent Variables
Unbound variables that used in this research is: (1) Income which this
variable explain the respondents earning each month that will classified into
four groups: < 1 million, 1 million - 5 million, 5 million - 10 million & >10
million; (2) Education: This variable explain educational level of respondents,
which classified into: Elementary School, Junior High School, senior High
School, Diploma, Strata 1, Strata 2; (3) Work Field: explain the jobs of
respondents which stay in this ten districts. (4) Financial institution
F. Quality Test of Research Instrument 1. Validity Test
Validity Test is used for measuring the legitimacy and validity of the
questionnaires. Called valid if the question can express the something that
will measure with the questionnaire Ghazali (2001). The validity measure
used in this research is construct validity by SPSS version 15.0. Construct
validity is validity that asking whether the question point at the instrument is
suitable with the related knowledge concept (Nurgiyantoro, 2009) in
Rahmawati, (2012).
Validity determination related to the questions with seeing the column
corrected column correlation, significant examination is using r table in significant level 0.05. If result of r arithmetic ≥ r table so item called valid, if
r arithmetic < r table so item called not valid. In this research using 0, 1330 as
the data measurement of validity, based on the total respondent which is 154
respondents as a sample of the citizen of Pekalongan.
2. Reliability Test
Reliability test is a test to measure questionnaires as indicator of variable
or construction. A questionnaire called reliable if the respondent answers
related to the question is consistent or stabile from time to time.
Reliability measurement used in this research by the cronbach alpha > 0.07 that categorized as the sufficient level of reliability Nunnally, (1994) in
the result of the reliability test on data at the level of moderate Basuki,
(2017).
3. Hypothesis Test
a. F - Test (Simultaneous Test) for the first hypothesis. This test used to know if the independent variable has the significant influences to the
dependent variable together. With the comparison result of F count and F
table in error degree at 5% its mean if result of F count > from F table,
than all of the independent variables has the significant influences together
to dependent variable or the first hypothesis is accepted.
b. T - Test (Partial Test) for the second hypothesis. This test used to know if the independent variable has the significant influences to the dependent
variable. With the comparison result of t count of every independent variables and t table in error degree at 5% its mean if result of t count > from t table, than the independent variables has the significant influences to dependent variable or the first hypothesis is accepted.
G. Data Analysis
1. Descriptive Statistic
Descriptive statistic is statistic used for data analysis by describing or
drawing the collected data as it is without any additional and intentional to
conclude the collected data applied for general or generalization. (Sugiyono,
2014). Descriptive statistic give the description related to the data looked
from the mean, standard deviation, varian, maximum, minimum, sum, range,
Descriptive research is research design in order to arrange the systematic
picturing related to scientific information which came from object or subject
of research. Descriptive research focused in the systematic explanation with
the fact obtainable from the research, if researcher intent to describing the
data from one of variable of research, the researcher can use the descriptive
statistic (Sanusi, 2012).
2. Logistic Regression
Logistic regression is closely similar with discriminant analysis which we
want to test the probability of dependent variable is it explained by the
independent variable, truly in this such of case can be solved by using discriminant analysis but normal multivariate distribution assumption can’t be
filled because of independent variable is mixed between matric variable and
non- matric variable. In this case logistic regression used because no need to
use normality test of the independent data (Ghozali, 2011).
Such as an multinominal logistic regression, if the category of dependent
variable is an ordinal (rating) for an example the condition of bank healthy,
healthy enough, unwell and not healthy where healthy have the higher value
than healthy enough, and healthy enough have the higher value than not
healthy so logistic analysis must be using ordinal regression or called PLUM