Faculty of Information and Communication Technology
HYBRID SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE FOR DOCTOR-PATIENT
CONSULTATION
Omar Mukhtar Bin Hambaran
Master of Science in Information and Communication Technology
HYBRID SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE FOR DOCTOR-PATIENT CONSULTATION
OMAR MUKHTAR BIN HAMBARAN
A thesis submitted
in fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Information and Communication Technology
Faculty of Information and Communication Technology
UNIVERSITI TEKNIKAL MALAYSIA MELAKA
DECLARATION
I declare that this thesis entitle “Hybrid Software Architecture for Doctor-Patient
Consultation” is the result of my own research except as cited in the references. The thesis
has not been accepted for any degree and is not concurrently submitted in candidature of
any other degree.
Signature : ………
Name : Omar Mukhtar Bin Hambaran
APPROVAL
I hereby declare that I have read this thesis and in my opinion this thesis is sufficient in
terms of scope and quality for the award of Master of Science in Information and
Communication Technology.
Signature : ………
Supervisor Name : Assoc. Prof. Dr Mohd Khanapi Abd Ghani
DEDICATION
ABSTRACT
This aim of the research is to solve an inadequate performance of the conventional approach in capturing clinical finding during doctor-patient consultation, by designing and implementing the proposed hybrid software architecture. Doctor-patient consultation is a crucial process in diagnosing and capturing clinical findings of patient problem. Currently, most doctor-patient consultation used conventional ways of capturing clinical findings by using paper‟s note, note book, manually entered digital records, and so on. With these conventional ways, the number of patient to be treated properly in the consultation process is less than the number of patients that had been registered per day. This problem most probably caused by the low performance of process and system response time, system interruption, and inadequate integrated system that make patients‟ health records difficult to be accessed seamlessly across other modules in health information system. The proposed architecture incorporates hybrid technique that could operate during online and offline situation by utilizing local and central data storage. This architecture also provide fast track search using International Clinical Diseases version 10 (ICD-10) and Read Clinical Term (CTV3) for doctors to clerk in clinical findings such as diagnosis, symptoms, medication and other related clinical notes. The research was conducted through case study approach by way of structured and semi-structured interview at Health Centre of UTeM. The findings from the data collection and validation showed that the proposed architecture is suitable to be used but requires minor modification. Application of this hybrid architecture dramatically reduces the time taken and improves response time for doctor to capture patient health record during doctor-patient consultation process.
ABSTRAK
Tujuan penyelidikan adalah untuk menyelesaikan masalah prestasi yang tidak mencukupi kepada pendekatan konvensional dalam merekod penemuan klinikal semasa rundingan doktor-pesakit, dengan menghasilkan dan menghasilkan seni bina perisian yang hybrid. Perundingan doktor-pesakit adalah satu proses yang penting dalam mendiagnosis dan merekod penemuan klinikal berkenaan masalah pesakit. Sehingga kini, kebanyakan proses perundingan antara doktor dan pesakit menggunakan cara konvensional iaitu merekod penemuan klinikal dengan menggunakan kertas nota, buku nota, rekod digital yang dimasukkan secara manual, dan sebagainya. Dengan cara-cara konvensional itu, bilangan pesakit akan dirawat dengan betul dalam proses perundingan tersebut adalah kurang daripada jumlah pesakit yang telah berdaftar setiap hari. Masalah ini kemungkinan besar disebabkan oleh prestasi proses dan tindak balas sistem yang rendah, gangguan terhadap proses sistem yang banyak, dan sistem tidak bersepadu yang membuatkan rekod kesihatan pesakit tidak bergerak lancar ke mana-mana modul lain dalam sistem maklumat kesihatan. Pendekatan metodologi yang digunakan dalam penyelidikan ini adalah menggunakan kajian kes dan alat pengukur berkomputer. Seni bina yang dicadangkan dalam kajian ini menggunakan teknik hibrid dengan storan dalam dan luar talian, termasuk Carian Laju yang menggunakan Kod Penyakit Klinikal Antarabangsa versi 10 (ICD-10) bagi doktor untuk membuat carian samada simtom-simtom yang biasa atau ubat-ubatan, dan teknik yang menggunakan pengaksesan rangkaian yang lancar untuk penyelenggaraan rekod kesihatan pesakit secara berterusan dan lancar tidak mengira apa jua keadaan kejatuhan rangkaian. Penggunaan kerangka kerja hibrid ini mengurangkan masa yang diambil secara mendadak dan meningkatkan masa tindak balas untuk doktor dalam merekod rekod klinikal pesakit semasa proses perundingan doktor dan pesakit.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First and foremost, I would like to thank Allah for the will and spirit He has given me, to further complete my study. Thank you to my family for the full support they had given me throughout my study. Thank you to my fiancé and all my lab mates that always cheering me up while my study.
Finally I would like to thank my supervisor, Assoc. Prof. Dr. Mohd Khanapi Abd Ghani who has provided excellent guidance to me throughout my research.
2.2.1.1 E-Health 28
2.2.1.2 Telemedicine 29
2.2.1.3 Tele-Health 30
2.2.1.4 Hospital Information System 32
2.2.1.5 Mobile health 34
2.2.1.6 Pervasive Health System 36
2.2.1.7 EMR and HER 36
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS xiii
LIST OF PUBLICATIONS xv
CHAPTER 1
1. INTRODUCTION 16
1.1 Overview 16
1.2 Research Objectives 17
1.2.1 To provide a critical study and comparison of the existing architecture 17 1.2.2 To develop a hybrid software architecture for doctor-patient
consultation process in clinical information system. 18 1.2.3 To validate the hybrid software architecture. 18 1.2.4 To revise a proposed architecture of the hybrid approach in a
doctor-patient consultation computerized systems from the
validated architecture. 19
2.2 Overview of Health Information System 26
2.2.1 Health Information System 27
2.2.2 Significant of Health Information System in Healthcare 37
2.2.3 The component of Health Information System 38
2.3 Evaluating of Health Information System Architecture and Framework 40 2.3.1 Early Approach to the Health Information System Framework 40 2.3.2 Review of the Health Information System Framework 44
2.3.2.1 Saman Iftikhar model: A framework based on OWL-S for
healthcare Information provision 45
2.3.2.2 Wu et al. (2014) Model: A framework for
Questionnaire-Based Healthcare Application Development 46 2.3.2.3 Jelena Mirkovic model: A framework for the development
of ubiquitous patient support systems 48
2.3.2.4 Intan Najua model: A Proposed Framework for Healthcare Portal in Malaysia to encourage Knowledge Sharing 50 2.3.2.5 Eswara Reddy model: An Efficient Cloud Framework
for Health Care Monitoring System 52
2.3.2.6 M.K. Abd Ghani framework: The Design of Flexible
Front End Framework for Accessing Patient Health Records
through Short Message Service 58
2.4 Conclusion 61
2.5 Summary 62
CHAPTER 3
3. METHODOLOGY 63
3.1 Introduction 63
3.2 Overview of Research Methodology 63
3.2.1 Research Strategy 63
3.2.2 Research Design 64
3.2.3 Research Processes and Classification 64
3.2.4 Research Methodology Process 66
3.3 Selection Methodologies 66
3.3.1 Find Research Domain 67
3.3.2 Do Literature Review on Current Research 68
3.3.3 Find and Revise Case Study on Current Architecture 69 3.3.4 Plan Instruments or Tools for Conducting Research 69
3.3.4.1 Interview & Questionnaire 70
3.3.4.2 Software to measure 70
3.3.5 Do Study on Current System and Current Data 70 3.3.6 Develop Software System based on Proposed Architecture 71 3.3.7 Conduct Scenarios and Architecture Validation 71
3.3.8 Data Analysis and Data Comparison 72
3.3.9 Revise the Architecture 73
3.4 Conclusion 73
3.5 Summary 74
CHAPTER 4
4. A PROPOSED HYBRID SOFTWARE ARCHITECTURE 75
4.1 Introduction 75
4.2 Conceptual Architecture Design 75
4.2.1 The offline components. 76
4.2.2 The online components. 76
4.3 Proposed Hybrid Architecture 77
4.4 Summary 81
CHAPTER 5
5. TESTING AND VALIDATING THE ARCHITECTURE 82
5.1 Introduction 82
5.2 Undertaking the Validation 82
5.3 System Testing 83
5.3.1 The development of E-Clinical Support System (ECSS) 83
5.3.1.1 Current Architecture 84
5.3.1.2 Proposed Architecture 86
5.3.2 Summary of system testing results 89
5.4 Discussion of the case study investigation. 91
5.4.1 Background of Case Study Organization 91
5.4.1.1 Background of Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka 91
5.4.1.2 Background of UTeM Health Centre 92
5.4.2 Feedback on the Applicability Analysis of Hybrid Software
Architecture Model for Doctor-Patient Consultation System. 94
5.5 Revised Architecture 123
5.6 Discussion and Amendments of Hybrid System Architecture 124
5.7 Summary 124
6.4 Limitations and Constraints 130
6.5 Reflections 132
6.6 Further Research 133
REFERENCES 135
APPENDICES 141
LIST OF TABLES
TABLE 2.1
TABLE
Studies on the Selected Health Information System Architecture.
PAGE 41
2.2 6 relevant models related to the research. 44
2.3 6 relevant models related to the research and related characteristic. 45
3.1 Classification of main types of research 64
3.2 Source of Information. 68
5.1 Explanations of arrow line usage in Figure 5.1 and Figure 5.2. 84
5.2 The comparison of response time between current architecture and
HybridCIS architecture. 89
LIST OF FIGURES
FIGURE TITLE PAGE
1.1 Existing architecture. 17
1.2 Research focuses area for developing the architecture. 18
1.3 Scope of HyDPC Research. 23
2.1 The six key components of a Health Information System. 38
2.2 Semantic Registry allowing central and distributed computing 46
2.3 System Context Diagram in QH framework 47
2.4 Possible usage scenarios of CONNECT 2.0 framework. 49
2.5 The CONNECT mobility framework. 50
2.6 Theoretical framework for Malaysian Healthcare Portal 51
2.7 Proposed cloud framework for healthcare monitoring system (CHMS). 54
2.8 Layered architecture of CHMS. 55
2.9 Measure of Response time in CHMS with varying no. of concurrent users. 57
2.10 Measure of throughput in CHMS. 58
2.11 The FFeF component diagram. 60
3.1 Summary of research methodology 67
4.1 Schematic diagram of HyDPC architecture. 77
4.2 Proposed Hybrid Software Architecture
(Omar Mukhtar et al. 2015). 79
5.1 Process flow during availability and non-availability of network in
UTeM clinic. 85
5.2 HybridCIS process flow during availability and non-availability of
network in UTeM clinic. 86
5.3 The interface of consultation process that use HybridCIS architecture. 88
5.4 Example of Response-Time Measurement Function in Next button. 88
5.5 Organization Chart of UTeM Health Centre. 93
5.6 Percentage of respondent by gender. 94
5.7 Percentage of respondent position. 95
5.8 Percentage of respondent working years in Healthcare Industry. 95
5.9 Percentage of respondent experience using CSS before. 96
5.10 Percentage of respondent spend time with work using ECSS. 96
5.11 Percentage of method those respondents prefer to capture clinical
records. 97
5.12 Percentage of how easy ECSS been used by the respondent. 97
5.13 Percentage of ECSS response time. 98
5.14 Percentage of how frequent network interruption happen per
month while using ECSS. 98
5.15 Percentage causes of network interruption while using ECSS. 99
5.16 Percentage of network interruption while capturing clinical records. 100
5.17 Percentage of data seamlessly across ECSS. 100
5.18 Percentage of response time while searching patient during
patient registration. 101
5.19 Percentage of system interruption while searching particular
patient during patient registration. 101
5.20 Percentage by the respondent on how accurate providing
patient's information. 102
5.21 Percentage by respondent on response time of saving process
of new patient. 103
5.22 Percentage by respondent of system interruption while saving
new patient information. 103
5.23 Percentage by respondent on accuracy of information search that
same as information on patient master index. 104
5.24 Percentage of respondent describes response time on process of
updating patient information. 105
5.25 Percentage of respondent on system interruption while updating
patient information. 105
5.26 Percentage of respondent on patient information retrieved after
updating into database is accurate as updated. 106
5.27 Percentage of respondent on describe response time of registration
process of patient into patient queue. 107
5.28 Percentage of respondent on system interruption during patient
registration process into patient queue. 107
5.29 Percentage of respondent describe response time while selecting
process of patient from queue list. 108
5.30 Percentage of respondent on system interruption while selecting
patient from queue list. 109
5.31 Percentage of respondent on accuracy of patient information
viewed in doctor-patient consultation same as retrieved from
patient queue. 109
5.32 Percentage of respondent describe response time on importing
process of patients' health record from external devices into local
storage. 110
5.33 Percentage of respondent on system interruption while importing
patients' health record from external devices into local storage. 111
5.34 Percentage of respondent on accuracy of information viewed in
doctor-patient consultation same as information copied from
external devices. 111
5.35 Percentage of respondent describes response time on search process
of clinical terminology and clinical coding. 112
5.36 Percentage of respondent on system interruption while searching
process of clinical terminology and clinical coding. 113
5.37 Percentage of respondent on accuracy of clinical terminology viewed
as information driven from database. 113
5.38 Percentage of respondent describes response time on patients'
discharge process. 114
5.39 Percentage of respondent on interruption while patient's discharge
process. 115
5.40 Percentage of respondent on accuracy of patient's medical history
viewed same as clinical records entered by the doctor. 115
5.41 Percentage of respondent describes response time on viewing
medical slips. 116
5.42 Percentage of respondent on interruption of viewing and printing
medical sips. 117
5.43 Percentage of respondent on accuracy of information printed on
medical slips is accurate as requested. 117
5.44 Percentage of respondent describes response time of order process
during doctor-patient consultation. 118
5.45 Percentage of respondent on system interruption while perform
order process during doctor-patient consultation. 119
5.46 Percentage of respondent on order information requested can be
accessed and shared across modules within ECSS. 119
5.47 Percentage of respondent describes response time on electronic
drug order arrived to pharmacy department. 120
5.48 Percentage of respondent on system interruption while receiving
electronic drug order at pharmacy department. 121
5.49 Percentage of respondent on accuracy of drug order information
received at pharmacy department same as requested. 121
5.50 Percentage of respondent on time normally taken for completing a
task for each patient. 122
5.51 The revised Proposed Hybrid Software Architecture. 123
LIST OF APPENDICES
APPENDIX TITLE PAGE
A Questionnaire of Applicability Analysis of Hybrid Software
Architecture Model for Doctor-Patient Consultation System. 140
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
HyDPC - Hybrid Software Architecture for Doctor-Patient Consultation
CIS - Clinical Information System
EMR - Electronic Medical Records
EHR - Electronic Health Records
HIS - Health Information System
UTeM - Universiti Teknikal Malaysia Melaka
PAS - Patient Administration System
HRMIS - Human Resource Management Information System
WHO - World Health Organization
WTO - World Trade Organization
ATA - American Telemedicine Association
HIT - Health Information Technology
CDS - Computerized Decision Support
LMIC - Low and Middle Income Countries
HIMSS - Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society
CTIA - Cellular Telephone Industries Association
GWAS - Genome-Wide Association Studies
HMN - Health Matrix Network
ICT - Information and Communication Technology
HIMS - Health Information Management System
PHR - Personal Health Records
IDE - Integrated Development Environment
SDK - Software Development Kit
ADT - Android Developer Tools
KM - Knowledge Management
IT - Information Technology
MOH - Ministry Of Health
FFeF - Flexible Front-end Framework
LIST OF PUBLICATIONS
Proceeding
Omar Mukhtar Hambaran, Mohd Khanapi Abd Ghani; Designing Hybrid software architecture For Capturing Clinical Findings During Doctor-Patient Consultation, E- Proceeding Of Software Engineering Postgraduates Workshop (Sepow), Pp. 47, 2013
Journal
Omar Mukhtar Hambaran, Mohd Khanapi Abd Ghani, Raja Rina Raja Ikram, Burhanuddin Mohd Aboobaider; Implementation Of Hybrid software architecture In Clinical Information System: A Case Study Of A Malaysian Clinic, Arpn Journal Of Engineering And Applied Sciences, Vol 10, Iss 20, Pp. 9891- 9895, 2015
CHAPTER 1
INTRODUCTION
1.1 Overview
Doctor-patient consultation plays a very important role in diagnosis of many clinical
findings. Currently, most doctor-patient consultation used conventional ways of capturing
clinical findings using paper‟s note, note book, manually entered digital records, and so on.
With these conventional ways, the number of patient to be treated properly in the
consultation process is less than the number of patients that had been registered per day.
This research will provide a better way to fasten the process of doctor-patient consultation
using a hybrid model of software architecture from different models from the literature
review findings.
Currently, most patients always need to go to hospitals for consultation. Thus,
because of many patients await their doctor; they need to wait till their name being called.
Plus, patients who lived in rural area will suffer a lot from travelling frequently especially
to have repeating consultation compare to those in urban area although those in urban area
affected by other factor like traffic jam that caused the travel period became long. For the
additional knowledge, the use of normal narrowband in a telemedicine system for
transporting the patients‟ health records across healthcare facilities nationwide does not
make sense due to issues of telecommunication reliability, speed and responsiveness. This
research will provide a seamlessly solution for the doctor-patient consultation process in
any condition of a network downtime.
Web-based System
1.2 Research Objectives
This research examines case studies of usage of computerized systems using hybrid
and non-hybrid approach, and feedback from subject matter experts in the doctor-patient
consultation. The objectives of the research are summarized as follows:
a. To analyze and compare Health Information System Architecture to be used as
input for developing the proposed architecture.
b. To develop Hybrid System Architecture for doctor-patient consultation (HyDPC).
c. To develop, test, and validate prototype for HyDPC.
d. To compare the result between clinical information systems that uses current
software architecture and the proposed hybrid system architecture.
A brief description of the research objectives are in the following subsections:-
1.2.1 To provide a critical study and comparison of the existing architecture
Clinical Information System
Doctor-Patient Consultation Process
Cloud Server
Online EMR
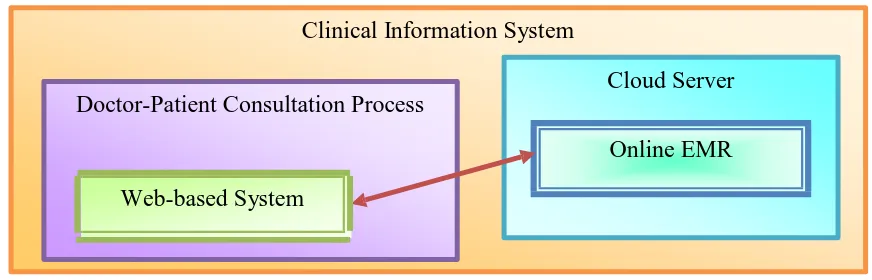
Figure 1.1: Existing architecture.
Figure shows that there exists relational between the doctor-patient consultation
process and web-based cloud system requirements. However, the scope of hybrid
computerized systems has yet to reduce online dependencies. This research objective is
vital to provide an overview to the study and identify research issues. This section shall be
addressed by a literature review of the main components of a review of doctor-patient
consultation, a review of hybrid architecture, and a review of capturing clinical findings.
Key components of the existing architecture shall be identified to establish the initial
architecture.
The scope of comparison analysis is based on current Health Information System
such as HRS, Hospital Information System, E-Health, and EMR and EHR.
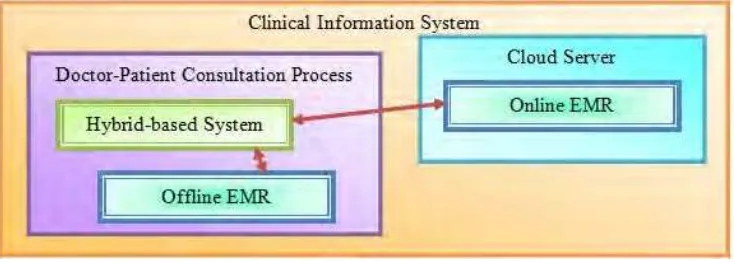
1.2.2 To develop a hybrid software architecture for doctor-patient consultation process in
clinical information system.
Based upon finding and input from first objective, the architecture will be
developed. Hybrid software architecture shall be developed based on a Subjective-
Objective-Assessment-Plan method from the critical study of the existing architecture. The
main functionality shall revolve the low response-time in the consultation process. Figure
1.2 shows the research focus area for developing the architecture. The development of
architecture shall focus on the integration and harmonization of capturing patient‟s
Electronic Medical Records (EMR) using hybrid approach to improve response-time in
doctor-patient consultation process.
Figure 1.2: Research focuses area for developing the architecture.
1.2.3 To validate the hybrid software architecture.
After the proposed architecture has been designed and developed, a validation need
to be conducted. Validation of the architecture will be performed through system prototype