ii
THE USE OF NUMBERED HEAD TECHNIQUE TO IMPROVE
STUDENTS’ READING SKILLS
(A Classroom Action Research
of the Eighth Years Students of Mts
Ma’arif
Candimulyo
Magelang in the Academic Year 2015/2016)
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board Examiners as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Sarjana Pendidikan Islam (S.Pd.I) English Education Departement of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
BY:
DWI INA FAKOTIN 113 10 065
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTEMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
SALATIGA
iv
PERNYATAAN KEASLIAN TULISAN
Saya yang bertanda tangan dibawah ini: Nama : DWI INA FAKOTIN NIM : 113 10 065
Fakultas : Tarbiyah dan Ilmu Keguruan Jurusan : Tadris Bahasa Inggris
Dengan penuh kejujuran dan tanggung jawab, peneliti menyatakan bahwa skripsi ini benar-benar merupakan hasil karya saya sendiri, bukan jiplakan atau karya tulis orang lain. Pendapat atau temuan orang lain yang terdapat dalam skripsi ini dikutip atau dirujuk berdasarkan kode etik ilmiah.
vii
Motto
“
“Life cannot
become boring when we establish
contact with the one who gives happiness.”
viii
DEDICATION
This work is sincerely dedicated for:
My beloved parents, my mother (Sri Yati) and my father (Subandi) who always pray, guide, motivate me to become better person.
My husband who always support me and pray from me My child Ilyas who always support me
My beloved sisters, brothers and my big familywho fill my life with love and affection.
All of big family of Mts Ma’arif Candimulyo, the head master, all of the teachers especially Mr. Rudi Surasa, S.Pd and students of VIII B class.
My consultant Mrs. Setia Rini, M. Pd who always guides and support me.
ix
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Bismillahirrahmanirrahim,
In the name of Allah, the most gracious and merciful, the king of universe and space. Thank you to Allah because the writer could complete this thesis as one of requirement to finishthe study in English Department of States for InstituteIslamicStudiesSalatiga.
This thesis would not have been completed without support, guidance and help from individual and institution. Therefore, I would like to express special thank you to:
1. Mr. Dr. Rahmat Hariyadi, M. Pd. as the rector of State Institutefor Islamic Studies Salatiga.
2. Mrs. Noor Malihah, P. Hd the head of English Department of States Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) of Salatiga and the consultant of this thesis. Thank you for all of your suggestions, recommendations and support for this thesis from the beginning until the end.
x
4. All lecturers in the English Department of IAIN Salatiga. Thank you for all guidance, knowledge, support, and etc.
5. My beloved mother and father. Thank you for everythings (support and praying) no one better than you.
6. All my family who always cheering me.
7. Special thanks for my friends who always cheering me up.
8. All of the staffs who help the writer in processing of thesis administration.
9. Everybody who has helped me in finishing this thesis. Thank you for all supports, advices, suggestions and other helps that you all give. The writer hopes that this thesis will be useful for everyone.
Salatiga, 18 Februari 2016 The writer
xi ABSTRACT
Dwi Ina Fakotin. 2015. “THE USE OF NUMBERED HEAD TECHNIQUE TO IMPROVE STUDENTS’ READING SKILLS(A Classroom Action Research of the Eighth Years Students of MtsMa’arifCandimulyoMagelang in the Academic Year 2015/2016)”A Graduating Paper. Educational Faculty English Department State Institute of Islamic Studies (IAIN). Consultant: SetiaRini, M. Pd
Keywords: Numbered Head; reading skill; recount text
xii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE i
DECLARATION ii
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR NOTES iii
PAGE OF CERTIFICATION... iv
MOTTO v
H. Research Organization 8
CHAPTER II: THEORITICAL FRAMEWORK
A.Reading 9
1. Definition of Reading 9
2. Kind of Reading 12
3. Factors that Influence Reading ……… 13
4. Principles of Learning Reading 14
B.Reading Skill 16
1. Definition of Reading skill 16
xiii 3. Generic Structure of Recount 27 CHAPTER III: METHODOLOGY OF RESEARCH A. Setting of the Research 28 B. The Situational of the Teacher and Staff ... 29
C. The situational of the Students ... 32
D. List of VIII B ... ... 33
E. Method of Researh 35 F. Procedures of Research...………. 37
G. Technique of Collecting Data………. 38
H. Technique of Data Analysis ... 41
CHAPTER IV: DATA ANALYSIS A. Research Findings …………..………. 43
xv
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2. 1 Example of recount text 26
Table 3.1 The educational facilities of Mts Ma’arif 29 Table 3. 2 The situational teacher and staff of Mts Ma’arif 30 Table 3. 3 The situational students of Mts Ma’arif 32 Table 3. 4 List of VIII B class of Mts Ma’arif 33
Table 4.1 Group of numbered heads 46
Table 4.2 The result of pre test and post test cycle I 48 Table 4.3 The result of pre test and post test cycle II 57
Table 4.4 The mean of students’ score 62
ii CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
A. BACKGROUND OF THE STUDY
In order to communicate with others, people use language. They must use language because language is the main factor to share their ideas to the others in this life. English is regarded as an international language. It is very important because it is used broadly in the world that function as a communication means by which people from different nations or country interact. In Indonesia, it has been tought in schools from elementary school up to university.
In many foreign language teaching situations, reading seemed a special focus. There are a number of reason and one of them is many foreign language students often have as one of their most important goal. They want to be able to read for information and pleasure, for the career, and for study in purposes. In fact most EFL situations, the ability to read in a foreign language is all that students ever want to acquire (Richards, 2003: 213).
To improve students’ skill in English, there are four main skills
iii
lengthy assignments in which to know what the obligations that should they do. If they don’t know what the meaning is, so they will fail in completing the assignments.
Reading is seen as a stucture hierarchy of sequenced and separate skills which is built up to create meaning. Since it is active cognitive process, reading is closely related to other activites suc as thinking, interesting, making preception, making generalization, and of course comprehending the content (Konza, 2007: 84). Reading is complex process which involves not only the text but their experience to comprehend it.
Learning reading is more than just recognizing words in a written text. Students should be able to comprehend or understand the meaning of the text. (Duffy, 1997: 60) stated that comprehension appears to happen in two stages. The first stage occurs during the actual reading activity. The student examines the message and simultaneously recognize words and meaning through skill with the graphemic, syntactic, and semantic systems. The second stage occurs anytime during or following Stage 1. In this stage, the written message has been translated or received and can be subjected to a more thoughtful analysis.
iv
monotonous approach. The teacher also spends more time in structure than in reading skill, so the students do not have time to learn reading. The strategy is low for helping the student in learning English. The strategy should be able to motivate and interest the students to study.
From the statement above, we know that comprehension skill is needed in reading activity. However, the condition of students in Indonesia especially students in Mts Ma’arif candimulyo have poor comprehension skill. In teaching and learning process, the eighth years students of Mts Ma’arif candimulyo face some difficulties when their teacher deliver the materials. It can be seen from their reactions in learning English. Some of them are bored, sleepy and do not pay attention to their teacher explanation. Eventhough their teacher has given some strategies and methods to make the students excited in learning English. But in the reality, the students still face the difficulties in reading comprehension.
From the explanation above, it gives an inspiration to the writer to conduct a research titled on “ THE USE OF NUMBERED HEAD TECHNIQUE TO IMPROVE STUDENTS’ READING SKILLS (A Classroom Action Research Of The Eighth Students of Mts Ma’arif Candimulyo Magelang In The Academic Year of 2015/2016).
B. PROBLEM STATEMENTS
v
1. How is the implementation of students’ reading skill using numbered heads technique for the eighth years students of Mts Candimulyo Magelang in the academic year 2015/2016
2. How far is the significant difference of using Numbered Head Technique in the students’ reading skill of the eighth years students of Mts Ma’arif Candimulyo Magelang in the academic year 2015/2016
C. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
The general purpose of the study is to be able to know the effect of numbered head technique that is implemented in the classroom. The specific objectives of this study are:
1. To identify the implementation of students’ reading skill using technique for the eighth year students of Mts Candimulyo Magelang in the academic year 2015/2016
2. To find out the result of the study after using numbered head technique for the eighth students of Mts Candimulyo Magelang in the academic year 2015/2016.
D. BENEFIT OF THE STUDY 1. Theoretical advantages are:
a. The result of research can be used as the reference for those who want to conduct a research in English teaching to build students’ reading skill.
vi
a. Students’ reading skill will be better than before by understanding this technique.
b. It will give information to the teachers about using a technique to improve teaching reading quality.
E. LIMITATION OF THE STUDY
Based on the problem statement , the writer realizes that it is impossibe to carry out a classroom action research based on all the problem above. The writer limits the problem to the teacher’s monotous
technique in teaching reading skill, the writer used numbered head technique to teach reading of the eighth grade of Mts Candimulyo Magelang in the academic Year 2015/2016
F. DEFINITION OF KEY TERMS
Here are some definition as a guidence to understand the terms of this study:
1. Numbered Heads
vii 2. Technique
Technique is a way of doing something, especially one that needs special skills. (Oxford learner’s pocket dictionary, 2008: 455) 3. Improve
Improve is become or make better, make a good use of something. (Oxford Dictionary, 2003: 216)
4. Reading
Reading is a learning process in which the skills of word recognition and comprehension are mutually supportive. In reading activity, students are expected to recognize and understand about what they read especially in a text. Without understanding the text students can’t grasp the implied message in a text. (Duffy, 1977: 5) 5. Student
Student is person who studiying at the collage or university (Oxford Dictionary, 2003: 429)
6. Skill
According Dunnette (1976: 33) skills is capacity needed to implementing some tasks, which is the development of training result sand experience gained.
G. REVIEW OF PREVIOUS RESEARCH
viii
Action Research of the Second Grade Students of SMPN 09 Salatiga in the
Academic Year of 2012/2013) (STAIN Salatiga). It is written by Ulil Hidayah, a student of State Institute of Islamic Studies in the academic year 2013. She stated that the cooperative atmosphere of working in pair increase students’ motivation and their confidence using target language. This oral use of the target language may improve their speaking performance as development in reading
The second research report by Astri Rahmawati with her research paper entitled ”The Use of group investigation strategy to improve students’
reading skill” (A Classroom Action Research of X.2 Class of MAN
Tengaran,Semarang in the Academic Year of 2013/2014).There was a significant improvements. The student has lack motivation so it could influence of students reading skill. After the using group investigation strategy the students reading skill increases.
H. RESEARCH ORGANIZATION
In order to make easy to understand this thesis, the researches uses of a system of presentation as follows:
ix
Chapter II is literature review. It contains about of theories that relevant toward research, theory discretion there are: Numbered Heads method, Reading Skills and Recount text.
Chapter III is research report. It contains about general description of Mts Candimulyo Magelang.
Chapter IV is Data Analysis. Consist of cycle I, cycle II, cycle III, analysis, discussion, and result of each cycle.
x CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED THEORIES
A. Reading
1. Definition of Reading
Reading is a learning process in which the skills of word recognition and comprehension are mutually supportive. In reading activity, students are expected to recognize and understand about what they read especially in a text. Without understanding the text students can’t grasp the implied message in a text. (Duffy, 1977: 5)
According to Nunan (2003: 68), “reading is a fluent process of
readers combines information from text and their own background knowledge to build meaning”.
xi
Manzo (1996: 5) defined reading as the act of simultaneously reading the lines, reading between the lines, and reading beyond the lines. The first part, reading the lines refers to the act of decoding the words in order to construct the author’s basic message. The next part, reading between the lines, making to the act of making inferences and understanding the author’s implied message. Thus, reading beyond the
lines involves the judging of the significance of the author’s message and applying it to the other areas of the background and knowledge.
Currently, Wallace (2001), Richards (2002) argued that reading is a reader centered activity. A reader, while reading is constantly employed some strategies, helps himself to obtain whim he or she wants for reading. In other words, reading presently concerned more with the process, by which a reader attempts to understand the test he or she reads.
Reading is used to get the main point or the most important information. It is an effort to understand the content of the text, and also to know the massage from the writer. In addition reading is used to get an idea, pleasure or feeling that is expressed by the writer.
xii
There are many experts who present various definition of reading. According to Dechant (1982: 3) definitions of reading are divided into two major types:
a. Reading as Interpretation of Experience
With the first type of reading definition, in which reading is equated with the interpretation of experience generally, we might speak of reading pictures, reading faces, or reading the weather.
Spencer (1946) as quoted by Dechant (1982: 4) reading is performed whenever one experiences sensory stimulation. On the other hand, the meaning of reading based on this type is the reading- readiness program in which experience with concrete object is emphasized, visual and auditory discrimination are stressed and students are required to interpret pictures and conversation.
xiii
b. Reading as Interpretation of Graphic Symbols
In Dechant (1982: 4-5) there are presented the definition of reading by many experts. Some of them are DeBoer and Dallmann (1960: 19) consider that reading involves the comprehension and interpretation of ideas symbolized by the written or printed page. While Bond and Thinker (1967: 22) point out that reading involves the recognition of printed or written symbols which serve as stimuli for the recall of meanings built up through the reader’s past
experience.
Based on the definition above, the writer concludes that reading requires identification and comprehension. Reading involves an interaction between the writer and reader. Without a reader, communication via printed page is impossible; writing has no purpose without a reader.
2. Kind of Reading
According to Kustaryo (1988: 11), there are some kind of reading. They are:
a. Reading for meaning
Reading for meaning is reading to understand the messages which are written in the text. We didn’t read aloud during we are reading.
xiv b. Reading for comprehension
Reading for comprehension means reading with understanding about what have read.
3. Factors that Influence Reading
Cameron (2001) stated that some factors in foreign language learning context can influence the learning tasks. They are:
a. The nature of the written forms of the first language.
Each language is structured differently, so when we meet a new language, we try to apply the first language looking for familiar cues.
b. The learners’ previous experience in the first language literacy. When a young learner learns the second language, literacy, knowledge, and skill he/she only partly develops for the first language
c. The learners’ knowledge of the language.
Oral skill to learn a new language is an important factor in order to be literate. Children gain much literary experience before they come to school. The teacher of foreign language can be expanded children’s experience of literacy in the new by creating
environmental print for the classroom.
xv
There are many factors that may make learning to read a very different experience for different ages. Transferability of knowledge, skills, and strategies across language depends closely on how the two written language work: it will be different for each pair of language and for each direction of learning.
4. Principles of Learning Reading
There are some principles behind the teaching of reading (Harmer, 2001: 70), here are:
a. Reading is not passive skills
Reading is an incredibly active occupation. To do it unsuccessfully, we have to understand what the word mean, see the pictures the words are painting, understand the arguments, and work out if we agree with them. If we not do these things – and if students do not do these things – then we only just scratch the surface of the text and we quickly forget it.
b. Students need to be engaged with what they are reading
As with everything else in lessons, students who are not engaged with the reading text, not actively interested in what they are doing, are less likely to benefit from it.
c. Students should be encouraged to respond to the content of reading text, not just to the language
xvi
times they use relative clauses. But the meaning, the message of the text, is just as important and we must give students a chance to respond to that message in some way. It is especially important that they should be allowed to express their feeling about the topic d. Prediction is a major factor in reading
When we read texts in our own language, we frequently have a good idea of the content before we actually read. Books cover give s a hint what’s in the book, photographs and headlines hint at what articles are about and report look like report before single word.
e. Match the task to the topic
One decision has been taken about what reading text to the students are going to read, we need to choose good reading task, the right kind of questions, engaging and useful puzzle etc.
f. Good teachers exploit reading texts to the full
xvii B. Reading Skills
Reading skill is the ability to relate the textual material to one’s
own knowledge by comprehending the text (Fauziati, 2008: 133). The purpose of reading activity is language ideas. In reading, the process of reading activity is language ideas. In the reading the process of thinking is very urgent and vital, because the students read the text and do not morely move their eyes along the sentence they read. Instead the sometime, their minds work to get the message. Goodman (1982: 135) in Fauziati (2010: 33) states that based on psycholinguistic perceptive reading is considered as “psycholinguistic guessing game” the reader constructs a message
which is encoded by a writer. This act of meaning construction is a ongoing, cyclical process of sampling from the input text, predicting, testing, and confirming or revising these prediction and further sampling.
According to Grant (1991: 79) the aims of using a reading text at intermediate level and advance level are:
1. To teach basic reading comprehension skills
2. To teach real life reading skill such as reading for gist and reading for information
3. To develop flexible reading skills, varied according to purpose 4. To develop critical reading skills
5. To develop the students knowledge of vocabulary or idiom 6. To reinforce certain grammatical features
xviii
According to Johan (2000: 1) reading skills are grouped into: a. Deducing the meanings of Words from Context.
Deducing the meanings of words from context is way to see the words of phrases that precede or follow those words, so it can be functions as a way to know of speech, and finally the right meaning in the discourse can be known without having to look at the dictionary. b. Understanding the forms and Meaning of Non-idiomatic Phrases
It is different from idiomatic phrases that the form and meaning has been fixed, so it tends as the material which memorized so, the phrases non-idiomatic are formed based on certain rules and are unlimited.
c. Recognizing and Understanding Rhetorical Structures
Rhetorical structures is functional relationship between the meaning that described by elements of language in a reading text. This structure is basic of a text frame and closely related to the type of topic that written, the purpose of the authors, and readers are addressed by the authors.
The skills to know and understand this rhetorical structure includes an understanding of the meaning and function of words, phrases, punctuation, and specific structure that are used by the writer to describe or convey an idea or message purposed.
xix
known through the readers’ familiarity with the form of reading text
organizing in English.
This rhetorical structure found at the level of sentences, paragraphs, or intersentence, and at overall reading level.
C. Numbered heads
1. The Definition Numbered Heads
Numbered head is cooperative learning model which emphasizes students activity in which students are expected to interact with other students in the group so that they can increase their learning. Students will be divided into small groups aimed at understanding the material provided by the teacher. Students have the opportunity to the active to the process of thinking and learning activities, so there is no separation between students who have a high level of intelligence and a low. Students will each provide information about the material being studied, reviewed the materialcovered in the lesson, check or examine their understanding of the lesson content. This method was introduced by Spenser Kagan. The cooperative learning types Numbered Heads special emphasis on structures that are designed to influence the interaction patterns of students, improving their academic mastery. And also teacher social skills. It means actively asking, sharing, tasks, willing to explain ideas or opinions, the opinions of others, work in group, and so on.
xx
the number of concepts to be learned. For example if a class consist of 40 students and divided into 5 groups according to the concepts that will be the concepts that will be studied than each group consist of 8 students. Teacher gives the students a number 1-8. After the teacher gave a number of question to be answered by the students refered to the questioning. Students with their group think of the answeres called the Numbered Heads. After that the teacher called students who have same number from different groups to provide the answers. It is called the answering. Such as having heterogeneous group. Each member of the group has a different numbering, and are required are think together.
2. The Purpose of Numbered Heads
According to the Ibrahim (via Herdian: 2009), the purpose of Numbered Heads are as follows:
a. To increase students’ creativity and activity on academic .
b. acknowledgment of the diversity to students can accept their friends who have different background.
c. Development of social skills. 3. Step of Numbered Head method
According to Ibrahim (via Herdian: 2009) who developed the concepts of Kagan there are six in the implementation of Numbered Heads described bellow:
a. Preparation
xxi
Works Sheet ( LKS) in accordance with the model Numbered Heads. b. Group Formation
In the stage of formotion of a group of teachers divide students into smalls groups that do not consider the background of the students, such us race, social class, ethnicity, gender and level of students’ learning abilities. It is intended that there
is so separation between students. Teacher divides the students based on the concept to be learned. Each group consists of 3-5 students. After the group formed teacher assigns a number to each member.
c. Guide Books
The formation of each group must have books or guide books to facilited students working on a task or problem is given by the teachers
d. Discussion of issues
In group work, the teachers gave the materials to be learned or the queations that must be answered students. Then students think together and discuss the material to be learned or the questions given by the teachers with their group.
e. Calling the Numbered of Member to Give Answers
After the students finished discussing the materials studied, the next stage is the teacher calls a number, so that each group should then dialed his number raised his hand and prepare to answer question from the teacher.
f. Conclusion
xxii
4. The strengths and weakneses of Numbered Heads Method
According to lundgren (via Herdian: 2009) the strengths and weaknesses of Numbered Heads methods are:
a. the strenghts are
1. Sense of self–esterns is highers. 2. Fixing the presence.
3. Acceptance of individuals into larger. 4. Discruptive behavior become smaller. 5. Conflict between reduced personal. 6. deeper understanding.
7. Increasing cultifation kindness, sensitivity and tolerance. 8. Higher learning outcomes’
b. The weakneses of Numbered heads method D. Recount Texs
1. Definition of recount texs
Hyland (2009 : 5) state that recount text is a text that tells about past experiences or events. It can be based on the author’s personal experience (not always factual) or historical events. Recount text tells the reader about somethink that has happenned. It can be story (a fictional) recount or (factual) recount. Recount text is recall and reconstructs events, experiences and achievements from the past in a logical sequence.
xxiii
a famouse person. Recount contain a series of events that pertain to the person or event that the text focuses on. You may choose to read a recount (biography) about a famouse author to your students after you complete an author study. Other recount may present a topic through a series of time Miner and Zitnay(2012:2)
From the devinition above, it can be concluded that recount text tells about past experiences or events and specific person it can can be fictional or factual story.
2. Types of Recount teks
Sue stubs (2009 : 5)describe that types that recount teks are: a. A factual recount
A factual recount is concerned with recalling events accuratelly. It can range from everyday task such as a school accident report to a formal, structured research task such as a historical recount. The emphasis is on using language that is precise, factual and detailed, so that the reader gains the complete picture of the event, experience or achievement. Extended description, emotive language and unnecessary details are out of narration are used to give credibility to the information presented.
b. Literary or imaginative recount
Literary recounts entertain the reader by recreating the events of an imaginary world as though they are real “ A day in my life as a family pet”. For
example: emotive language, specific detail, and first person naration are used to give the writing impact and appeal.
xxiv
A procedural recount is records the steps taken in completing a task or proceduren. The use of technical terms, an accurate time sequence and first person narration (I or we) give credibility to the information provided. Example: Included a flow chart of the actions required for making bread, a storyboard of a videotaped script or advertisement, the steps taken to solvea mathematical problem.
d. A biographical recount
A biographical recount told the story the person’s life using a friend person narrator (he, she, they). In the case, of an authobiography, first person narration (I, we) is used. It is usually factually ,accurate and records specific names, timnes, places and events. A purelly factual, informative biography, however, wouldlact the appeal provided by the personal responses and memorable annecdotes. There is often an evaluation of the subject’s achievements in the final section.
3. Generic Structure of recount texts
Margaret (2009 : 25) describe that a recount has there parts, there are orientation, events, and reorientation:
1) Orientation
Orientation suyplies the background information needed to fully understand the retelling. It retablished the time, setting and who or what participating. The audience needed to know when the event occured, who was involved, what happened, where the activity or event took place and sometimes what the reason was for the event.
2) Event
xxv
orders that key happened. And it is important that students are given adequate guidelines scaffolds to assist with the structure of their reading. Students should focus and detailing who, what, where and when.
3) Re orientation
Reorientation means conclution, according to Bremmer and Sedley (1981 : 120) states that conclution to the end of basic forms is one simple variation of that patter. Reorientation at the end of the recount text and always the writer’s
cmments about the events.
4. Language feature of recount text
Language feature of recount text explaine by Kara Munn(1999:6) there are as follows:
a. Use of proper nouns and pronouns identify people, animal or things Example: Mr. Lawrence, The postman, she
b. Word families are used to build topic information Example: smoke signals, drums, telephone, television
c. Varied action verbs Are used to build word chains. These maybe synonim, antonim and repetittion.
d. Descriptive words add details about who, what, when, where and how e. Adverb and adverbial phrase sequence events in time and indicate place
Example: on 26 June 1984
f. Texts are writen in past tens to retail past events. Example: the smiled
xxvi
h. Evaluative language is used in factual personal recount. An example of recount text as follows
Table 2.1 Paragraph
1. Last month my family and I went to Toraja to attend Grandpa’s funeral. It was my first time to go to such a ceremony. We gathered there with our kin in the ceremony.
2. Overall, the ceremony was quit elaborate. It took about a week. Several days before the ceremony was done, grandpa’s body was kept in a series of houses arranged in a circular row around an open field called tongkonan. His corpse was dressed in a fine wearing.
3. First, we slaughtered the pigs and buffaloes, and then moved the corpse to face north. In this ceremony we wore black clothes. After that, the corpse was placed in a sandal wood coffin.
4. Then, it was brought out of the house and placed on an open platform beneath the granary. Meanwhile, my uncle, my brother, and I prepared the wooden puppet and a funeral tower called lakian.
Orientation
Event 1
Event 2
xxvii
5. The next phase of the ceremony was held this place. The coffin is borne from house and placed in the lakian. During the day, there were also buffalo matches. They were great matches. In the night, we were feasting, chanting, and dancing.
6. One the last day, the grandpa’s coffin were lowered from the funeral tower and brought up to the mountain side family graveyard. It was followed by great shouting and excitement from the relatives and guests. Finally, we installed the wooden puppet on a high balcony where other puppets representing the members of the whole family were already there.
The funeral ceremonies made my family and me tired. However, we were grateful because it ran smoothly.
Event 5 Event 4
xxviii CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY OF RESEARCH
A. Setting of the Research
Mts ma’arif Candimulyo is an educational organitation under
Lembaga Pendidikan (LP). The school was built in 1991, which was founded by the religious figures and community leaders the area of Candimulyo district, who are concerned with Islamic education.
The location in at Jl Barisan Candimulyo magelang Regency, Central Java. This location is strategic because it is near from high way and public society. Thus it is very fresh and this location is very condusive to conduct teaching and learning process.
The name of school is Madrasah Tsanawiyah Ma’arif candimulyo.
This is school is possessed of private. The head master of this school in the academic of 2015/2016 is Ahmad Ismail.
Mts Ma’arif Candimulyo is permanently subsidized by the government. The fasilities are text books, Marching Bands Tools, teachers and officials. The students of Mts Ma’arif Candimulyo in academic year of
xxix
Table 3. 1
The Educational Facilities of Mts Ma’arif Candimulyo in The
Academic of 2015/2016
No Facilities Total Copndition
1. Class room 10 Fine
2. Headmaster room 1 Fine
3. Teacher room 1 Fine
4. Library room 1 Fine
5. Osis room 1 Fine
6. Administrasi room 1 Fine
7. UKS room 1 Fine
8. Toilet 3 Fine
9. Language Laboratory 1 Fine
B. The Situation of the Teacher and Staffs
The situation of the teacher of the staffs of Mts Ma’arif Candimulyoin the academic year 2015/2016
Table 3. 2
The Situation Teacher and Staffs of Mts Ma’arif Candimulyo In the
Academic Year 2015/2016
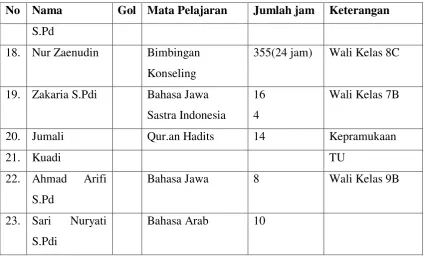
No Nama Gol Mata Pelajaran Jumlah jam Keterangan
1. A. Ismail Bahasa Arab 8 Jam Kepala Madrasah
2. Hj. Anirotun Qur’an Hadits 24 Wali Kelas
xxx
10. Ratna S.Pd p.Kewarganegaraan IPS
Pengetahuan Alam 28 Wali Kelas 7A
14. Dwi Astuti
xxxi
No Nama Gol Mata Pelajaran Jumlah jam Keterangan S.Pd
18. Nur Zaenudin Bimbingan Konseling
C. The Situation Of The Student
Table 3. 3
The Situation of The Students of Mts Ma’arif Candimulyo In
The Academic of 2015/2016
xxxii
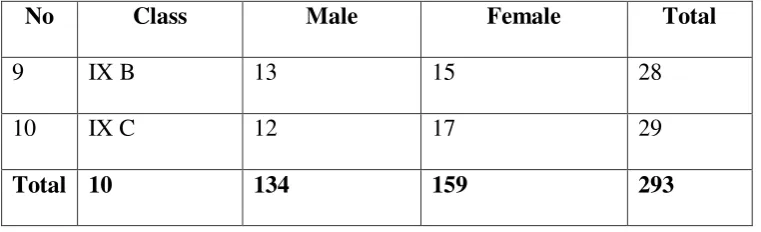
No Class Male Female Total
9 IX B 13 15 28
10 IX C 12 17 29
Total 10 134 159 293
D. List of VIII B
TABLE 3. 4
List of VIII B Class of Mts Ma’arif Candimulyo in the Academic Year Of 2015/ 2016
No Name
1 Afim Nur Arifin 2 Afrizka Diah Yuliana 3 Agus Ismanto
4 Ahmad Makhafidin 5 Aji Haryanto 6 Alfi Nur Saadah
7 Anik
8 Atik
9 Avan Tri Aviawan 10 Bayu Nugroho
xxxiii
No Name
13 Dwi Putri Rahayu 14 Eli Triyana 15 Eliatul Musrifah 16 Fitri Yaningrum 17 Heru Pamungkas 18 Ikhwan Rismanto 19 Joko Sulistiyono 20 Lisa Nur Aini 21 Luluk Mufarida 22 M. Arif Miftahudin 23 Muhammad Fajar 24 Muhammad Saefuddin 25 Muhammad Husni Mubarok 26 Nur Fadilah
27 Puji astuti 28 Tantiyati
29 Kalyana Ladi Arifah 30 Kharisma Dwi Cahyani Source: Mts Ma’arif Candimulyo 2015
E. Method of Research
xxxiv
and learning process. Manurung in Sam’s (2010: 57) stated that classroom action research is the new actions in decision and implementation process toward students in a class or another who involved in school as an alternative problem solving. While according to Arikunto (2010: 130) classroom action research is an observation toward activity that is purposely raised and occured in a class to solve the problem in that class. In this case, the researcher analyzed the problem of the student’s reading skill occurred in the learning process and found it which was then solved by Reciprocal Teaching Strategy.
Arikunto (2010: 132) stated that clssroom action research is done to improve the effectiveness of teaching methods, giving assignments for students, assessment, and so forth.
This research is focused on the teaching reading in the EFL process. The strategy of the research is regarded as the appropriate method for the students. The aim of this research is to enhance the students’ reading skill.
F. Procedures of Research
xxxv 1. Planning
Sam’s (2010: 74) stated that in the planning, there are three
activities:
a. Decide target competence
b. Design learning in cycle 1 and cycle 2
c. Design test instrument consist of multiple choice question which is taken representatively from the target competence that will be developed.
d. Make learning schedule consist of cycle 1 and cycle 2.
While according to Arikunto (2010: 138) when we compose the planning, we should explain about what, why, when, where, who, and how the action is done.
In this research, firstly researcher made lesson plan, decided the schedule, prepared material that appropriate with the strategy and made test instrument consist of pre- test and post test.
2. Action
Action is the implementation of the planning’s contain. In this stage, researcher must remember and obey the planning that h/ she made before. (Arikunto, 2010: 139)
xxxvi 3. Observation
Sam’s (2010: 74) stated that the observation is done during
the action and the teacher follows the teaching strategy that is designed by researcher.
In this research, researcher used observation guidance which consists of indicator that is designed according to the focus of research. Besides that, researcher also used some tools such camera or video recorder to help researcher in analyse the data. This observation focused on students and teacher’s activity in class such take a note what can be seen, heard, and observed during teaching and learning process.
4. Reflection
Reflection is done by analyze how far the result of students’
behavior before and after the action. (Sam’s, 2010:74)
In this research, the reflection is done by discussing with the collaborator to know the result of teaching and learning process by apply the strategy. By reflection, researcher can get input about to improve the next action in the next cycle.
G. Technique of Collecting Data
xxxvii
Arikunto (2010: 226) stated that test is used to measure the students’ basic ability and achievement. He mentions that there are two
kinds of achievement test which usually used by school:
a. Test made by the teacher; that arranged by certain procedure, but it has not been examined many times so its characteristics and strength has not been known.
b. Standardized test; a test that usually has been available in a testing institution and has been guaranteed its effectiveness.
In this research, researcher collected data by using test made by teacher because by doing test, she is able to know the improvement of student’s ability. Researcher made pre- test and post- test in each cycle. Pre- test is used to know the students’ ability in learning English especially in reading lesson. While post- test, is used to measure how far do their improvement after applying the strategy in reading lesson. Pre and post-test are to knowing the differences of the students ability before and after the teacher used the strategy.
2. Observation
Observation is written note about what is seen, heard, and experienced in collecting data and reflection toward qualitative data. Observation is used to get the certain target which is observed. (Sam’s,
2010: 93)
xxxviii
Teaching Strategy. This instrument gives monitor and records the students’ involvement during the lesson. In the observation sheet, there
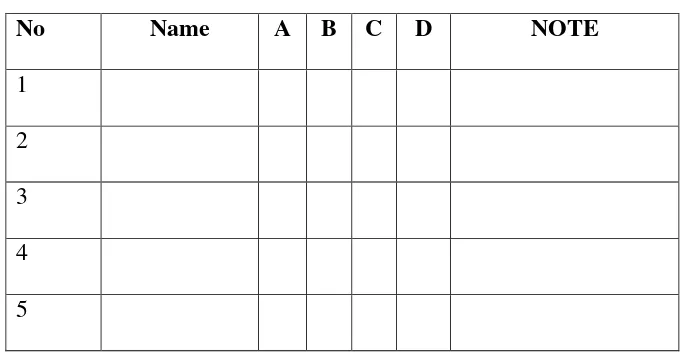
are four aspects that are consider focuses, those are: paying attention, activeness in asking question, activeness in responding question and enthusiasm in doing test. In this instrument, the teacher gives point in each aspect based on the situation of students. The table below show the example of observation sheet as follow
TABLE 3.2
STUDENTS’ OBSERVATION SHEET
No Name A B C D NOTE
1 2 3 4 5
Explanation:
A: Paying attention,
B: Activeness in asking question C: Activeness in responding question D: enthusiasm in doing test
3. Documentation
xxxix
newspapers, magazines, etc. In this method, researcher holds a check- list to look for the variable that had been decided. Whether the wanted variable is rises, then the researcher gave a check (√) in the check- list form.
In this research, researcher used camera or video recording to help the observation process. After that she would transcribe the result of observation activity.
H. Technique of Data Analysis
The researcher conducted the classroom action research of teaching reading using Reciprocal Teaching strategy at eighth years students of Mtys Ma’arif Candimulyo. In analyzing data, the researcher used mixing qualitative and quantitative approach. According to Johnson and Christensen (2007) qualitative research relies primarily on the collection
of qualitative data (i.e., nonnumeric data such as words and pictures). While Lodico (2006: 6) stated that quantitative approaches summarize data using numbers. Hypotheses and methods of data collection are created before the research begins. This technique is used to know the students’ score of reading skill in each cycle. According to Hadi (1981: 246) the formula is:
1. Mean
Where,
xl
: The sum of students’ score
: The total number of students 2. SD (Standard Deviation)
√ ( )
Where,
: Deviation Standart for one sample t-test : Different between pre-test post-test : Number of observation in sample
3. T-test
To be able to know whether there is a significant improvement or not between pre-test and post-test, researcher using t-test after calculate the SD. The formula is:
o
: T-test for the differences of pre-test and post-test : Deviation Standart for one sample t-test
xli CHAPTER IV DATA ANALYSIS
In this chapter, the writer would like to analyze the data gathered from the action research activities. The data was obtained from teaching learning process and evaluation. The data analysis is functioned to measure the students’ reading
skill improvements by applying Numbered HeadTechnique.
This chapter focuses on analyzing the collected data. The researcher gives the details of the findings. This chapter is likely the main discussion of the research conducted. It displays the finding of the collected data since in the beginning until the end of the research. In the research, the data consist of field note, the result pre-test and post-test. The action of this research consists of two cycles, cycle I and cycle II. The two cycles are treatment of implementation of the Numbered Heads in the reading skills. For the whole stages of every cycle will be explained in the description below.
A. Research Findings
xlii 1. Cycle 1
a. Planning
The writer prepared some instruments of the research, such as:
1) Lesson plan
In order to control the teaching learning process, the writer used the lesson plan as teaching guidance in learning process. a. Material
In the first cycle, the writer prepared the material about the explanation of recount text.
b. Teaching aid
The writer prepared some instrument, such as: blank paper and board marker.
c. Sheet for classroom observation
Sheet for classroom observation was prepared in order to know the condition of teaching learning process.
d. Test (pre-test and post test)
xliii b. Action
On Friday 28 August2015 in VIII B of Mts Ma’arif
Candimulyo. The researches as the teacher opened the class by salam and say good morning. The script as a follows:
T: “Assalamualaikum, warohmatullahi wa barokatuh”
S: Wa’alaikum salam warohmatullahi wa barokatuh”
T: “Good morning students, how are you today?”
S: “Good morning miss, I’m fine, and you?”
T: “I’m fine too, thank you”
After that researcher introduce herself because this meeting is the first meeting.
T: “ Ok, let me introduce my self, my name is Dwi Ina Fakotin,
you can call me bu Ina”
The researcher called the students to know their attendance in the class after that the researcher gave test to the students related with recount text.
T:”Now, I will give you a test and please complete this task S:” Aaaah mosok langsung test bu?”
T:” I need to know your competence so I give test”
xliv
T:”Now, we will discuss about recount text... who knowns about
recount text?”
S:”Teks bahasa inggris bu, menceritakan tentang liburan”
T:”Who knows about the generic structure of recount text?”
S:”Babar blas bu”
T:”Ok now we will discuss about recount text and part of recount text, there are generic structure and Language feature of recount text”.
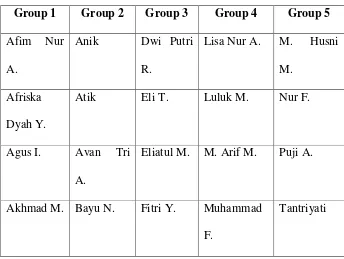
After the researcher explain about recount text then the researcher make group to use Numbered Heads technique to identify the part of recount text and the groups can be showed in the following table:
Table 4.1
Group of Numbered Heads
xlv
After the group presentation, the teacher divided to givepost-test to students to know their comprehension about narrative text, the teacher gave 20 minutes to finish it. The students submitted the answer then teacher closed the meeting.
c. Observation
The observation was carried out during the implementation of the action. In the first cycle, the teacher and her collaborator observed teaching learning process by monitoring the students’
activity and attention during the action. Observation made at the time of learning narrative text before and after using Reciprocal Teaching Technique, observation focused on students’ reading
skill.
The teacher also observed the students’ attention,
xlvi
students done the pre-test by self without ask to their friends, although they still got difficulty in understanding English text. Some students gave less attention when the teacher explained the material
d. Reflection
Based on the observation of the cycle I, the researcher had to reflect the weakness that happened in the learning process to maximize the students’ skill of reading.
1) The researcher needs to ask the students to bring dictionary to help their vocabulary difficulties.
2) The researcher needs to explain the material in detail in order make the students understand well.
3) The researcher has to motivate the students to answer the teacher’s questions using English.
Furthermore, to know there is a significant improvement in reading skills, the writer analyzes by using t-test calculation from the result of pre test and post test. Before analyzing t-test, the researcher will show the data presentation of pre test and post test.
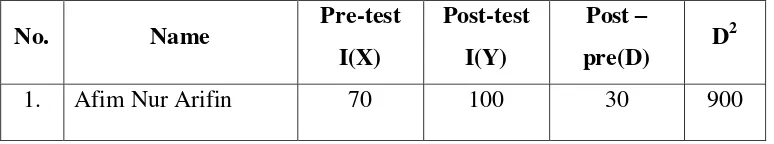
Table 4.2
The result of pre test and post test cycle I
l
T calculation is 5,46
T-table < t-calculation = 2,75< 5,46
The score of the result above shows that the students’ score increases
from the pre test to the post test. The mean of pre test is 56,1 while the mean of the post test result is .
The T-calculation also shows that there is significant influence of Numbered Heads in improving the students’ reading skill. It can be seen in
li
heads technique. It was very important to continue to the next cycle increased the students’ reading skill. The implementation of numbered heads technique in teaching reading skill did not show the good achievement. The students’ result of cycle 1 still lower than Standardized of
Minimum Score (KKM), the writer’s target was 70% but only 60% who
passed Standardized of Minimum Score (KKM). Teachers needed to continue to the next cycle by using numbered heads technique.
The researcher needed to explain the material in detail in order make the students understand well. She must guide the students to discuss and present the material in front of the class. Besides, the students must be more active to ask the teacher when they did not understand about the lesson. The researcher used the same strategy to teach reading with different topic for the next cycle to get better result
2. Cycle II
Based on the result of cycle 1, it is necessary for the researcher to continue to the next cycle:
a. Planning
The writer prepared some instrument of the research, such as:
1) Lesson plan
Lesson plan as a guide for teacher, activities in the class, so teaching and learning process can be controlled.
lii 3) Attending list
The writer prepared the attending list in order to check the attendance of the students in joining class activity.
4) Teaching aids (Reciprocal Teaching Technique). 5) Sheet for classroom observation
Sheet for classroom observation was prepared in order to know the condition of teaching learning process.
6) Test (pre-test and post-test).
Pre-test was given to the students before applying Numbered Heads Technique and post-test was given after applying Numbered Heads Technique
b. The Implementation of the Action
On Tuesday, 01September 2015 the teacher and her collaborator came to teach English. In action 2, the teacher revised the teaching learning process in cycle I where students still have difficulties in reading skill. Before began the lesson the teacher gave pre test aboutrecount text and she gave 10 minutes time to finish it. During the students did the test, her partner observed learning process in the class. After pre test, she began to teach.The teacher opened the lesson soon.
Teacher : “Assalaamu’alaikumwarohmatullahi wabarokaatuh.”
liii
Teacher : How are you today? Students : “ I am fine, and you?
Teacher : “I am very well, thank you.”
Before starting the lesson, the teacher reviewed the previous lesson. Teacher : “Did you still remember our lesson y
yesterday?”
Students : recount text Bu (Recount text Miss)
Teacher : “(Ya,, hari ini kita akan melanjutkanpembahasan tentang recount text. Apasajacontohteksrecountitu?). Today wewill continue our previous meeting about narrative text. What are the examples of recount text?”
She gave worksheet to do in pair. She asked them read example about narrative text. They try to analyze the generic structure, language feature and take some moral value from the text.
Teacher : “Now, there is example of recount text, read then analyze the generic structure, language feature and take some moral value from the text.
liv b. Observation
In the second cycle, observation was also carried out during the implementation of action. Observing the learning process that concentrated on the students’ capability which shows their understanding
of the lesson given.
Observing the students when they practiced their work in Reciprocal Teaching Technique. They can predict correctly the next story although they didn’t know the story before it and they try to answer the teacher question in English. Their confident also improved.
c. Reflection
In this cycle, the researcher and teacher as the collaborator concluded that the treatment of Numbered Heads techniquewas successful in improving the reading skill. It could be seen that the students’ reading improvement in the students’ score. They were great in
answering the questions. It means that they really comprehended the passage so they could answer the questions easily. They completed their work before the time was over. In addition, the all students seriously paid attention to the teacher’s explanation and active in engaging in the
learning process; such as asking question, responding question, and enthusiastic in doing their work.
Then, the following is score from the students’ worksheet which
lv
Table 4.3
The result of pre test and post test cycle II
lviii d. T-test calculation
T T calculation is 7,31
T-table < t-calculation = 2,75<7,31
In the cycle II, the result shows that the students’ reading
comprehension increases significantly. It is described in the result above. It displays that the mean of pre test is 67,33 and the mean of the post test 84,83.
lix
After doing the action research, it can be conclude that using clustering technique can motivated the student to active in learning reading skill. Besides, they can be active in respond the question. The result of the test was also good; the student cloud increase the score in each cycle.
The result of pre-test and post test were used to know the score. As stated before, there were cycle in this action research, east used pre-test and post-test. She gave pre-test to the students before she tough pre-test after she tough for each cycle. The student’ result of cycle 2 was show improvement; it is 81% who passed standardized of minimum score (KKM), it was reached the target. Teacher did not continue to the next to the next cycle because the students had been shown an improvement and attained the KKM.
B. Analysis and discussions
lx Table. 4.4
The Mean of Students’ Scores
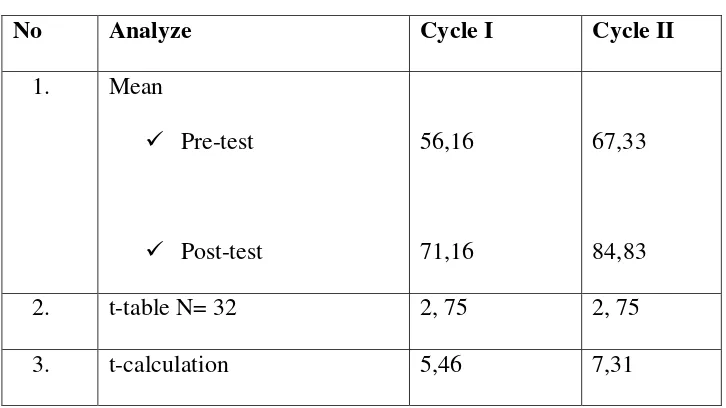
No Analyze Cycle I Cycle II
Table above shows that there is significant improvement cycle I to cycle II. The raising of students’ score is equal with their competences.
Students develop vocabulary mastery and reading skill.
lxi
The result shows that the mean of the findings in cycle I and II are higher than the standardized score (kriteria ketuntasan minimal) in score 70.The score of mean of post test in cycle I and cycle II is 71,16 and84,83.It means that in cycle I and cycle II is successful to achieve the standardized score.
Table. 4.5
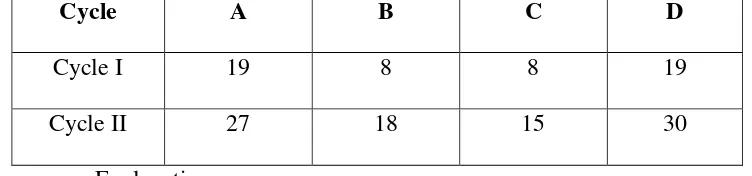
The Result of Observation Sheet Pre-Test and Post-Test in Cycle I and Cycle II
Cycle A B C D
Cycle I 19 8 8 19
Cycle II 27 18 15 30
Explanation:
A: Paying attention,
B: Activeness in asking question C: Activeness in responding question D: enthusiasm in doing test
The whole meetings are considered as the observation that may influence in the learning process. Based on the observation, the researcher can measure the other aster aspects that influence the treatment given.
lxii
Technique strategy in English learning can improve students’ motivation.
In other word. In other word, the treatments VIII B students of Mts Ma’arif Candimulyo are successful.
The implementation of Numbered Heads Technique can improve students’ reading skill. The improvement can be examined from the results
of the students’ skill by reconstructing of reading assignment in the
classroom. The students could enrich their vocabularies and be confident to predict the next story although they haven’t read the passage before.
The proof that students’ reading skill had an improvement can also
examined from the score in each cycle has increased. The students’ score
was also considered as one indicators of the improvement. The result of the students’ work in cycle I and II had improved. The students were able
lxiii CHAPTER V
CLOSURE A. Conclusions
Based on the theoretical review and implementation of study, the writer can draw the conclusion of this graduating paper as follows:
1. From the observation and implementation in classroom, the researcher could find the result of the study showing that Nmbered Heads Technique can improve students reading skill in Mts Ma’arif Candimulyo. Based on the findings of the research, it could be seen from the result of mean score of each cycle that post-test is 71,16 higher than pre-test 56,16 in the cycle I, and post-test is 84,83 higher than pre test 71,16 in the cycle II. Furthermore, the result of t-test calculation in cycle I is 5,46 and cycle II is 7,31 t table with N = 30 is 2,75. It means, there is significant difference mean on pre test and post-test. This indicates that by applying Reciprocal Teaching Technique provides significant contribution in improving the students’ reading skill
lxiv
responding the question. It means, there is improvements of students’
motivation cycle I and cycle II. The result of observational sheet in cycleII is better than cycle I. Based on the explanation, the uses of Numbered Heads Technique in English learning can improve students’ motivation. In other word, the treatments in VIII B students of Mts Ma’arif Candimulyo.
B. Suggestions
Having known the findings of the research, the researcher gives suggestions as follows:
1. To the teacher
a) In teaching learning process, teacher should make students more comfortable to enjoy the activities. The interest can raise their motivation in learning process. The teacher should use Numbered Heads Technique. This technique can build students’prior knowledge before they read a text: it helps students to improve their reading skill.
lxv 2. To the students
lxvi REFERENCE
Arikunto, Suharsimi. 2010. Prosedur Penelitian Suatu Pendekatan Praktik. Jakarta: Rineka Cipta
Arikunto, Suharsimi. et al. 2007. Penelitian Tindakan Kelas. Jakarta: PT Bumi Aksara
Baker and brown, 1984.Srategies for Constructing, Meaning http // www.educ
place.com/rdg/res/literacy/st_red 3 htmlsh: An Introduction to the Practice of English Language Teaching. England: Person Education Limited.
Elfiani, Nur Ifka. 2013. The use numbered heads together to improve students speaking skill. Unpublished Graduating paper. Salatiga: Educational Faculty STAIN Salatiga Melbourne: South Melbourne Press
Lie, Anita. 2004. Cooperative Learning: Mempraktikan Cooperative Learning di Ruang Kelas. Jakarta: PT Gramedia Widiasarana Indonesia
Lodico, Marguerite G. et al. 2006. Methods in Educational Research. US: Jossey-Bass
Muslich, Masnur. 2012. Melaksanakan PTK Itu Mudah (Classroom Action Research) Pedoman Praktis bagi Guru Professional. Jakarta: PT Bumi Aksara
Nunan, David. 2003. Practical English Language Teaching. New York: McGraw Hill
Oxford University. 2008. Oxford Learner’s Pocket Dictionary. New York: Oxford University Press
lxvii
lxviii
CURICULUM VITAE
Full Name : Dwi Ina Fakotin
Nick Name : Ina
Place/ Date of birth : Kab. Magelang/ March 13 ,1991
Address : Nglampu RT 01 RW 10, Kel.Bateh, Kec. Candimulyo, Kab. Magelang
Faculty : English Department
Educational History :
1. Mi Arrosyidin Tampir Kulon Graduated in 2003 2. Mts Ma’arif Candimulyo Graduated in 2006 3. MAN 1 Kota Magelang Graduated in 2009
4. IAIN Salatiga Graduated in 2015
Salatiga, Sept 2015
lxxi
RENCANA PELAKSANAAN PEMBELAJARAN (RPP)
Satuan Pendidikan : SMP/Mts
Nama Sekolah : Mts Ma’arif Candimulyo Magelang Kelas/Semester : VIII/1
Alokasi Waktu : 2 X 45 menit
Standar Kompetensi :Memahami makna teks tulis fungsional dan esei pendek sederhana berbentuk Recount yang berkaitan dengan lingkungan sekitar.
Kompetensi Dasar :Merespon makna dan langkah retorika dalam esei pendek sederhana secara akurat, lancar dan berterima yang berkaitan dengan lingkungan sekitar dalam teks berbentuk recount
Indikator : Langkah retorika teks recount Tujuan komunikatif teks recount
Ciri kebahasaan teks recount
I. Tujuan
Dalamakhirpembelajaran, siswadapatmengetahui:
a. Langkahretorikateksrecount
b. Tujuankomunikatifteksrecount
c. Cirri kebahasaanteksrecount
Karakter siswa yang diharapkan : Dapat dipercaya
lxxii II. Materi Pokok
Teks monolog berbentuk recount :
My Grandpa’s Funeral in Toraja
Last month my family and I went to Toraja to attend Grandpa’s funeral. It was my first time to go to such a ceremony. We gathered there with our kin in the ceremony.
Overall, the ceremony was quit elaborate. It took about a week. Several days before the ceremony was done, grandpa’s body was kept in a series of houses arranged in a circular row around an open field called tongkonan. His corpse was dressed in a fine wearing.
lxxiii
The funeral ceremonies made my family and me tired. However, we were grateful because it ran smoothly.
Generic structure of Recount text above:
Definition Recount text is a text that tell us about a part of experience
Purposeto tell the reader about a part of experience
Generic structure recount text has an orientation, a series of events in chronological and a reorientation.
Language feature
The use of nouns and pronouns
Personal pronouns Possessive
determiners
Simple past tense => S+VII+O