BANK INDONESIA AND CASH
Under the mandate of Act of the Republic of Indonesia
No. 23 of 1999 concerning Bank Indonesia as amended by Act
of the Republic of Indonesia No. 3 of 2004, the functions
of regulating and safeguarding the smooth operation of the
payment system are carried out by BI, the sole institution
authorised to issue and circulate the rupiah currency and
to revoke currency as legal tender, withdraw from
circulation and destroy currency withdrawn from circulation
(Article 20). In this regard, the supply of rupiah currency
begins with a macro (national) assessment of estimated
additional demand.
The estimation of nationwide additional demand for cash
takes account of economic conditions in order to facilitate
economic activity (money endogeneity). The estimation
approach used is the currency outside banks (COB) model,
which has adopted the Error Correction Model (ECM) for the
two-step Engle Granger. The ECM model is essentially a
concept for an econometric time series for synchronising
short run equilibrium with the conditions for long run
equilibrium through a process of adjustment. At the same
time the selection of independent variables in the COB
equation is more adhoc1 and assumed to be influenced by
macroeconomic variables such as GDP, inflation, interest
rates and the exchange rate.
The larger the GDP, the greater the demand for COB.
However, interest rates are assumed to have a negative
influence on COB demand. Higher interest rates will result
in lower consumption/increased savings, which weakens demand
for COB. The third factor, the exchange rate, is assumed to
have a positive impact on COB demand. Rupiah depreciation
will encourage the public to boost their present levels of
consumption to minimise future loss of purchasing power.
This will increase public demand for cash, and thus demand
for COB will rise. In addition to these macro variables,
influence on demand for COB is also assumed to come from
non-economic variables, such as celebration of religious
festivities (especially Eid-ul-Fitr and Christmas).
After selecting the variables to be used in the COB
demand equation, the next step is to perform an estimate of
the long term equation using quarterly data on GDP,
inflation, interest rates and the exchange rate beginning in
1990. The estimate thus obtained for the long-term equation
is as follows:
COB Long-Term Equation (real)
Log(cur /cpi) = -7.39 + 1.00log (GDP) – 0.06log (ir) + 0.17log (ER)
(15.42) (-3.55) (11.61)
R2=0.96
Graph 1. Fitted Value and Actual National COB Graph 2. Rolling Regression of the Long-Term Coefficient
In most cases, the estimate of the long-term equation
has the expected signs. Economic growth and the exchange
rate have a positive influence and are statistically
significant for COB demand, while interest rates have a
negative impact and are statistically significant for COB
demand. From the estimate for the long-term equation, a new
variable is established that comprises the difference
between fitted value and actual value. The new variable
(Error Correction lag 1) is then included in the short-term
equation to be estimated in conjunction with other
variables. The estimate obtained for the short-term equation
is as follows:
COB Short-Term Equation (real)
d(log(cur/cpi)) = 0.008 + 0.89d(log(GDP(-2))) + 0.07d(log(ER)) – 0.07d(log(IR(-3)))
(3.43) (2.71) (-3.16)
+ 0.04 dumleb – 0.07 dumfis – 0.40 EC (-1)
(3.76) (-4.57) (-5.80)
R2=0. 76
dw=1.59
in which:
GDP : Gross Domestic Product
CPI : Consumer Price Index (end of period for the quarter under review)
IR : 1-month Time Deposit Rate (average over 3 month period)
ER : USD/rupiah exchange rate (average over 3 month period)
Dumleb : Lebaran Dummy
(for Eid-ul-Fitr)
Dumfis : Fiscal Dummy, each Q1=1 commencing in 2000, others 0
C U R ( B a s e i n e ) CUR 140000
120000 100000 80000 60000 40000 20000 0
9 0 9 2 9 4 9 6 9 8 0 0 0 2 04
E l P D B E l I R El ER %
1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 2 0 0 1 2 0 0 2 2 0 0 3 2 0 0 4 1.2
The estimates obtained for the long-term and short-term
equations are then used simultaneously to project national COB.
The results of the COB in-sample forecast for both equations are
presented in Graph 1. To ascertain whether any change takes place
in the characteristics (preferences) of cash demand, a stability
test is conducted on the coefficient of the estimate. Rolling
regression is used on the COB model, yielding information that
the coefficient values for factors influencing cash demand are
relatively stable (Graph 2).
The estimate generated by the model will then inform the
Directorate of Currency Circulation in projecting national
cash demand in order to put together the national Currency
Distribution Plan (CDP). The CDP is an aggregation of CDPs
produced bottom up by Bank Indonesia Regional Offices2. After
harmonising the national model-based estimate (DKM) with the
national estimate based on the aggregation of data provided
by Bank Indonesia Regional Offices, a national CDP will take
shape. The national CDP will then be compared with the
minimum cash position of the Currency Distribution Section to
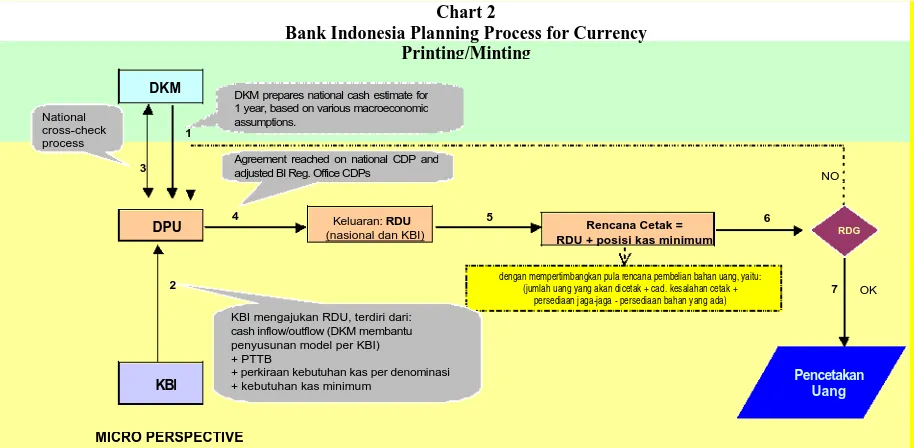
obtain the data for the Printing/Minting Plan. Based on the
Printing/Minting plan, BI will calculate the volume of
currency material to be purchased. This process is depicted
2 The CDPs at the Bank Indonesia Regional Offices are calculated beginning with the factors in cash outflow and
in schematic form in Chart 2. It is important to note that
the DKM model estimates submitted to the Currency
Distribution Section are estimates of COB, which excludes
cash-in-vault held by banks. In this context, differences can
arise between the numbers generated by the COB model and the
additional currency in circulation to be printed by the
Currency circulation section (Table 2).
[Translation of chart]
DKM = Directorate of Financial and Monetary Statistics
DPU = Directorate of Currency Circulation ---> Output: CDP (national and reg. office) --->
Printing/Minting Plan = CDP + Minimum Cash Position ---> Board of Governors’ Meeting
Also takes account of planned purchase of currency materials, i.e. (total amount to be printed/minted +
allowance for defective printing/minting + buffer – existing stock of material)
BI Reg. Offices submit CDPs consisting of cash inflow/outflow (DKM assists in development of individual Reg. Office models),
+ PTTB
+ estimated cash needs per denomination
BI Reg. Offices PRINTING/MINTING OF CURRENCY
Table 2 National
cross-check process
Chart 2
Bank Indonesia Planning Process for Currency Printing/Minting MICRO PERSPECTIVE 3 DKM DPU KBI 2 1
KBI mengajukan RDU, terdiri dari: cash inflow/outflow (DKM membantu penyusunan model per KBI) + PTTB
+ perkiraan kebutuhan kas per denominasi + kebutuhan kas minimum
4
DKM prepares national cash estimate for 1 year, based on various macroeconomic assumptions.
Keluaran: RDU (nasional dan KBI)
5
dengan mempertimbangkan pula rencana pembelian bahan uang, yaitu: (jumlah uang yang akan dicetak + cad. kesalahan cetak +
persediaan jaga-jaga - persediaan bahan yang ada) Rencana Cetak = RDU + posisi kas minimum
6 Pencetakan Uang NO 7 RDG OK Agreement reached on national CDP and
Differences between COB and Currency in Circulation
Currency Outside Banks (COB) Currency in Circulation *
Definition
Cash outside banks is cash in non-bank public circulation as reflected in the M0 money component.
All cash liabilities out side Bank I ndonesia that form part of Bank I ndonesia monetary aggregates, as reflected in the base money component (including cash held in commercial bank vaults).
Component All cash outside Bank I ndonesia and commercial
bank vaults. Money creation accounts (40x) subtracted by
1. minting of commemorative coins (402). 2
Bank I ndonesia cash accounts, i.e: Wholesale cash (010), daily cash (011), uncounted bank cash deposits (012), mobile cash and cash courier services (013), currency unfit for circulation (014), remise (016).
3 Currency used as specimens for sorting guidelines (294).
4 linkage accounts (291).