Supplementary Section
The Dipole Moments of acyl halides.
The dipole moments of acyl halides are
given in Table S1.
Table S1
Molecular Structures of the larger acyl halides.
For
n-
butyryl halides,
2-methylpropionyl bromide, and the 2,2-di2-methylpropionyl halides, no experimentally
determined molecular structures have been reported. Therefore, theoretically calculated
structures (r
gbond lengths were converted from the corresponding r
ebond lengths for all
ab initio
calculations) were used for comparison purposes. For
n-
butyryl fluoride and
2,2-dimethylpropionyl fluoride, the molecular structures from
ab initio
RHF/6-31G* level
calculations were scaled by comparing the r
gstructure
19and the r
estructure (
ab initio
RHF/6-31G* method) of acetyl fluoride. For
n-
butyryl chloride and
2,2-dimethyl-propionyl chloride, the molecular structures from
ab initio
RHF/6-31G* level calculations
were scaled by comparing the r
gstructure
21and r
estructure (
ab initio
RHF/6-31G*
method) of acetyl chloride. For
n-
butyryl bromide, 2-methylpropionyl bromide, and
2,2-dimethylpropionyl bromide, the molecular structures from
ab initio
RHF/3-21G* level
calculations were scaled by comparing the r
gstructure
21and r
estructure (
ab initio
RHF/3-21G* method) of acetyl bromide.
Table S2
The calculated molecular structures of
n
-butyryl fluoride,
n
-butyryl chloride, and
n
-butyryl
bromide, compared to the scaled structures, gave rms differences of 0.001 Å and 0.51
degrees, 0.002 Å and 0.72 degrees, and 0.004 Å and 0.72 degrees, respectively, for the
bond lengths (excluding C-H bonds) and bond angles (excluding angles containing
hydrogen).
For 2-methylpropionyl fluoride, the experimentally determined r
0molecular
structure of the
gauche
conformations available from a microwave experiment.
iThe r
estructure of the
syn
form obtained from an RHF/6-31G* calculation was converted to r
gstructure. Both the experimental and
ab initio
geometries were compared to the MM3
structure. The molecular geometries for the 2-methylpropionyl halides are represented in
Table S3. The rms differences for the bond lengths (excluding C-H bonds) and bond
angles (excluding any angle containing hydrogen) were 0.008 Å and 0.6 degrees, and
0.002 Å and 0.7 degrees for the
syn
and the
gauche
forms, respectively. The MM3
derived molecular structure of 2-methylpropionyl chloride was also compared to the r
gstructure from electron diffraction.
iiaThe calculated structure for 2-methylpropionyl
chloride gave an rms difference of 0.006 Å for the bond lengths (excluding C-H bonds).
The value of the angle
∠
(C
3-C
2-C
4) from the experiment is too big, compared to either
our calculated value or to the
ab initio
value, and gave a 1.2 degrees rms deviation with
this angle excluded. The calculated molecular structures for the
gauche
and
syn
isomers
Table S3
The molecular structures for the 2,2-dimethylpropionyl halides are shown in Table
S4. The calculated molecular structures of 2,2-dimethylpropionyl fluoride, chloride, and
Table S4
bromide, compared to the scaled structures, gave rms differences of 0.004 Å and 1.16
degrees, 0.003 Å and 1.68 degrees, and 0.005 Å and 1.42 degrees, respectively, for the
bond lengths (excluding C-H bonds) and bond angles (excluding any angle containing
hydrogen).
It was found that the C-X bond lengths in 2-methylpropionyl halides and
2,2-dimethylpropionyl halides are increased, compared with the propionyl and
n
-butyryl
halides, which reflected the steric effects of the
β
-methyl groups. Introducing an
additional methyl group in the
β-position of propionyl fluoride gave no increase in the C-F
bond length from microwave studies,
26a,40but an approximately 0.003 Å increase in the
C-F bond length from our calculations and an approximately 0.001 Å increase according to
RHF/6-31G* calculations. The introduction of an additional methyl group in the
β-position of propionyl chloride resulted in a 0.007 Å increase in the C-Cl bond length
according to electron diffraction studies,
28,41aand approximately a 0.004 Å increase from
both
ab initio
quantum mechanics and molecular mechanics methods. Another methyl
Conformational analysis of the larger acyl halides.
From the low resolution
microwave spectroscopy studies,
iiiit was reported that
n-
butyryl halides exist as
syn-anti
(the first conformational symbol '
syn
' for O=C
α-C
β-C
γtorsional angle, and the second
symbol '
anti
' for C
α-C
β-C
γ-C
δtorsional angle) and
syn-gauche
conformers with roughly
the same energies. For
n-
butyryl fluoride, the less stable (about 0.3 kcal/mol)
skew-anti
conformer was characterized. More precisely, our calculations on
n-
butyryl fluoride found
that the
syn-gauche
,
skew-anti
,
skew-gauche
, and
gauche-gauche
conformers have 849,
1222, and 1656 cal/mol, respectively, higher energies than the
syn-anti
conformer. The
corresponding energy values for
n
-butyryl chloride and bromide are 850, 1341, and 1784
cal/mol, and 844, 705, and 1090 cal/mol, respectively. For the
n-
butyryl bromide,
interestingly the
skew-anti
form was more stable than the
skew-gauche
form. Each
conformer of
n-
butyryl halides are compared in Table S5.
Table S5
From the torsional potential barriers of both acetyl fluoride and propionyl fluoride
from microwave studies, Stiefvater
et al.
27in late 1960's predicted the conformations of
2-methylpropionyl fluoride to be two equivalent optical isomers,
gauche
forms (one of
methyl group eclipsing the carbonyl group) and one
syn
conformer (the
α-hydrogen
eclipsing the carbonyl group) with the
gauche
conformers being 1130 cal/mol (
∆
H
0)
stable. Recently, Durig
et al.
40determined an energy difference of 1320 cal/mol (
∆
H
0)
gauche
conformer was 1198 cal/mol (∆H
0) or 1156 cal/mol (∆E
0) more stable than the
syn.
For 2-methylpropionyl chloride, our calculations showed that the
gauche
conformer
was 1609 cal/mol (∆H
0) or 1693 cal/mol (∆E
0) more stable than the
syn
. Our energy
difference was much higher than the value from a liquid Raman study
41b(987 cal/mol,
∆H
0), from electron diffraction study
41a(700 cal/mol, ∆G
0), or from
ab initio
MP2/6-31G* level calculation
41a(910 cal/mol, ∆E
0). For 2-methylpropionyl bromide, our
molecular mechanics calculations showed that the
gauche
conformer was 672 cal/mol
(∆E
0) or 759 cal/mol (∆H
0) more stable than the
syn
conformer. The energy difference
between the stable conformers and other energy parameters for 2-methylpropionyl halides
are listed in Table S6.
Table S6
Table S1. Dipole moments (in Debye) of acyl halides
(a) formyl fluoride
HCOF
exp.a exp.b Ab initioc MM3 MM3 - exp.a RHF/6-31G* MP2/6-31G*
µtotal 2.02(4) 1.99(3) 2.39 2.49 2.24 0.22
(b) formyl chloride
HCOCl
exp.d Ab initioc MM3 MM3 - exp.d RHF/6-31G* MP2/6-31G*
µtotal 1.6(2) 2.20 2.31 2.25 0.65
(c) formyl bromide
HCOBr
Ab initioe MM3 MM3 - Ab initioe RHF/3-21G*
µtotal 2.17 2.23 0.06
(d) acetyl fluoride
CH
3COF
exp.f Ab initioc MM3 MM3 - exp.f
RHF/6-31G* MP2/6-31G*
µtotal 2.96(3) 3.09 3.26 2.69 -0.27
(e) acetyl chloride
CH
3COCl
exp.g Ab initioc MM3 MM3 - exp.g
RHF/6-31G* MP2/6-31G*
µtotal 2.713(8) 3.04 3.16 2.72 0.01
(f) acetyl bromide
CH
3COBr
Ab initioe MM3 MM3-Ab initioe
RHF/3-21G*
(g) propionyl fluoride
CH
3CH
2COF
exp.h Ab initioc
RHF/6-31G*
MM3 MM3 - exp.h
s-trans gauche s-trans gauche s-trans gauche s-trans gauche µtotal 2.90(5) 3.08 3.10 3.25 2.70 2.69 -0.20 -0.39
(h) propionyl chloride
CH
3CH
2COCl
exp.i Ab initioc
RHF/6-31G*
MM3 MM3 - exp.i MM3 - Ab initioc
s-trans s-trans gauche s-trans gauche s-trans gauche µtotal 2.63 3.11 3.25 2.725 2.717 0.10 -0.53
(i) propionyl bromide
CH
3CH
2COBr
Ab initioe
RHF/3-21G*
MM3 MM3 - Ab initioe
s-trans gauche s-trans gauche s-trans gauche
µtotal 3.02 3.18 2.717 2.710 -0.30 -0.47
(j) 2-methylpropionyl fluoride
(CH
3)
2CHCOF
exp.j Ab initioc
RHF/6-31G*
MM3 MM3 - exp.j MM3 - Ab initioc
gauche gauche syn gauche syn gauchec syn
µtotal 2.98(1) 3.18 3.32 2.699 2.692 -0.28 -0.39
a)Taken from reference 17.
b)P. Favero and J. G. Baker, Nuovo Cimento, 17, 2942 (1960).
c)Using the Gaussian 90 program, in this work. d)Taken from reference 18 a).
e)Using the Gaussian 94 program, in this work. f)Taken from reference 20.
g)R. V. Galeev, L. N. Gunderova, A. H. Mamleev, and N. M. Pozdeev, Zh. Strukt. Khim., 36, 424 (1995).
h)Taken from reference 27.
i)G. T. Martin and J. R. Partington, J. Chem. Soc., 58, 158(1936).
Table S2. Structural parameters (bond lengths in Å, and bond angles in degrees) of
n-butyryl fluoride,
n-
butyryl chloride, and
n-
butyryl bromide
a(a)
n-
butyryl fluoride
CH
3CH
2CH
2COF
Calculated,rgb MM3 MM3 - Calculatedb
r(C=O) 1.186 1.1849 -0.001
r(C-F) 1.363 1.3640 0.001
r(C1-C2)c 1.510 1.5087 -0.001
r(C2-C3) -- 1.5207
--r(C3-C4) -- 1.5319
--r(C-H)av 1.105 1.1121 0.007
∠(C-C=O) 128.79 129.315 0.52
∠(C-C-F) 110.82 110.101 -0.72
∠(O=C-F) 120.38 120.584 0.20
∠(C1-C2-C3) 113.29 112.743 -0.55
∠(C2-C3-C4) 111.95 112.381 0.43
∠(C-C-H)av 109.93 109.910 -0.02
∠(H-C-H)av 107.06 107.163 0.10
∠(C-C-C=O) 0.0 0.0 0.0
rms deviationd (bond length) 0.001
(bond angle) 0.51
(b)
n-
butyryl chloride
CH
3CH
2CH
2COCl
Calculated,rge MM3 MM3 - Calculatede
r(C=O) 1.187 1.1861 -0.001
r(C-Cl) 1.802 1.8017 0.000
r(C1-C2)c 1.513 1.5157 0.003
r(C2-C3) -- 1.5276
--r(C3-C4) -- 1.5318
--r(C-H)av 1.095 1.1124 0.017
∠(C-C=O) 127.55 127.484 -0.07
∠(C-C-Cl) 112.70 111.702 -1.00
∠(O=C-Cl) 119.75 120.814 1.06
∠(C1-C2-C3) 112.51 112.713 0.20
∠(C2-C3-C4) 111.71 112.344 0.63
∠(C-C-H)av 110.05 109.906 -0.15
∠(H-C-H)av 107.15 107.187 0.03
∠(C-C-C=O) 0.0 0.0 0.0
rms deviationd (bond length) 0.002
[image:8.612.92.522.457.701.2](c)
n-
butyryl bromide
CH
3CH
2CH
2COBr
Calculated,rgf MM3 MM3 - Calculatedf
r(C=O) 1.185 1.1833 -0.002
r(C-Br) 1.979 1.9794 0.000
r(C1-C2)c 1.522 1.5161 -0.006
r(C2-C3) -- 1.5263
--r(C3-C4) -- 1.5318
--r(C-H)av -- 1.1130
--∠(C-C=O) 127.67 127.730 0.06
∠(C-C-Br) 111.56 111.454 -0.11
∠(O=C-Br) 120.77 120.816 0.05
∠(C1-C2-C3) 111.65 112.648 1.00
∠(C2-C3-C4) 111.09 112.346 1.26
∠(C-C-H)av 109.87 109.913 0.11
∠(H-C1-H)av 107.77 107.197 -0.57
∠(C-C-C=O) 0.0 0.0 0.0
rms deviationd (bond length) 0.004
(bond angle) 0.72
a)Only the most stable syn-anti conformer is considered.
b)Converted from the re structure: (r(C=O) = 1.1691, r(C-F) = 1.3273, r(C1-C2) = 1.5005, r(C2-C3) =
1.5260, r(C3-C4) = 1.5275, and r(C-H)av = 1.0857) from ab initio RHF/6-31G* method (Gaussian 90
program, in this work). The scaling is done by comparing the rg structure from the electron diffraction experiment (reference 19) and the re structure from ab initio RHF/6-31G* method of acetyl fluoride:
(rg(C=O) - re(C=O) = 0.017, rg(C-F) - re(C-F) = 0.036, rg(C-C(O)) - re(C-C(O)) = 0.009, and rg(C-H)av
-re(C-H)av = 0.019).
c)Numbering of carbons is C4-C3-C2-C1=O.
d)For the rms deviation of bond length, the C-H bond is excluded. For the rms deviation of bond angle, any angle containing hydrogen is excluded.
e)Converted from the re structure: (r(C=O) = 1.1674, r(C-Cl) = 1.7889, r(C1-C2) = 1.5080, r(C2-C3) = 1.5275, r(C3-C4) = 1.5279, and r(C-H)av = 1.0854) from ab initio RHF/6-31G* method (Gaussian 90
program, in this work). The scaling is done by comparing the rg structure from the electron diffraction
experiment (reference 21) and the re structure from ab initio RHF/6-31G* method of acetyl chloride:
(rg(C=O) - re(C=O) = 0.020, rg(C-Cl) - re(C-Cl) = 0.013, rg(C-C(O)) - re(C-C(O)) = 0.005, and rg(C-H)av
-re(C-H)av = 0.010).
f)Converted from the re structure: (r(C=O) = 1.1866, r(C-Br) = 1.9551, r(C1-C2) = 1.5068, r(C2-C3) =
1.5360, r(C3-C4) = 1.5395, and r(C-H)av = 1.0839) from ab initio RHF/3-21G* method (Gaussian 94
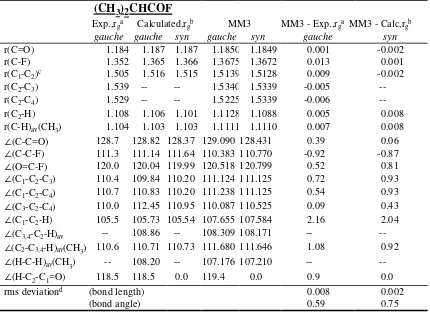
Table S3. Structural parameters (bond lengths in Å, and bond angles in degrees) of
2-methylpropionyl fluoride, 2-2-methylpropionyl chloride, and 2-2-methylpropionyl
bromide
(a) 2-methylpropionyl fluoride
(CH
3)
2CHCOF
Exp.,rga Calculated,rgb MM3 MM3 - Exp.,rga MM3 - Calc,rgb
gauche gauche syn gauche syn gauche syn
r(C=O) 1.184 1.187 1.187 1.1850 1.1849 0.001 -0.002
r(C-F) 1.352 1.365 1.366 1.3675 1.3672 0.013 0.001
r(C1-C2)c 1.505 1.516 1.515 1.5139 1.5128 0.009 -0.002
r(C2-C3) 1.539 -- -- 1.5340 1.5339 -0.005
--r(C2-C4) 1.529 -- -- 1.5225 1.5339 -0.006
--r(C2-H) 1.108 1.106 1.101 1.1128 1.1088 0.005 0.008
r(C-H)av(CH3) 1.104 1.103 1.103 1.1111 1.1110 0.007 0.008
∠(C-C=O) 128.7 128.82 128.37 129.090 128.431 0.39 0.06
∠(C-C-F) 111.3 111.14 111.64 110.383 110.770 -0.92 -0.87
∠(O=C-F) 120.0 120.04 119.99 120.518 120.799 0.52 0.81
∠(C1-C2-C3) 110.4 109.84 110.20 111.124 111.125 0.72 0.93
∠(C1-C2-C4) 110.7 110.83 110.20 111.238 111.125 0.54 0.93
∠(C3-C2-C4) 110.0 112.45 110.95 110.087 110.525 0.09 0.43
∠(C1-C2-H) 105.5 105.73 105.54 107.655 107.584 2.16 2.04
∠(C3,4-C2-H)av -- 108.86 -- 108.309 108.171 --
--∠(C2-C3,4-H)av(CH3) 110.6 110.71 110.73 111.680 111.646 1.08 0.92
∠(H-C-H)av(CH3) -- 108.20 -- 107.176 107.210 --
--∠(H-C2-C1=O) 118.5 118.5 0.0 119.4 0.0 0.9 0.0
rms deviationd (bond length) 0.008 0.002
[image:10.612.91.521.210.523.2](b) 2-methylpropionyl chloride
(CH
3)
2CHCOCl
ED.,rge Ab initiof MM3g MM3 - ED.,r
ge gauche syn
r(C=O) 1.186(3) 1.188 1.188 1.1863 0.000
r(C-Cl) 1.804(4) 1.805 1.805 1.8060 0.002
r(C1-C2)c 1.511(2) 1.522 1.523 1.5219 0.011
r(C2-C3) 1.540(2) -- -- 1.5435 0.004
r(C2-C4) 1.534(2) -- -- 1.5305 -0.004
r(C2-H) 1.088(6) 1.094 1.094 1.1117 0.024
r(C-H)av(CH3) 1.108(6) 1.094 1.094 1.1109 0.003
∠(C-C=O) 127.3(7) 127.16 126.13 127.052 -0.25
∠(C-C-Cl) 113.6(5) 113.54 114.86 112.235 -1.37
∠(O=C-Cl) 119.1 119.30 119.01 120.694 1.59
∠(C1-C2-C3) 109.9(8) 109.78 111.60 110.997 1.10
∠(C1-C2-C4) 109.7(8) 109.74 111.60 111.011 1.31
∠(C3-C2-C4) 113.8(27)j 111.97 112.19 109.581 -4.22
∠(C1-C2-H) 106.8 106.87 103.09 108.430 1.63
∠(C3,4-C2-H)av -- 109.19 108.95 108.338
--∠(C2-C3,4-H)av(CH3) 111.7(18) 110.50 110.73 111.677 0.02
∠(H-C-H)av(CH3) -- 108.24 108.18 108.332
--∠(H-C2-C1=O)h 130.1(37) 136.1 131.9 1.8
∠(H-C2-C1=O)i 0.0 0.0 0.0 0.0
rms deviationd (bond length) 0.006
(
c) 2-methylpropionyl bromide
(CH
3)
2CHCOBr
Calculated,rgk MM3 MM3 - Calculatedk
gauche syn gauche syn gauche syn
r(C=O) 1.185 1.185 1.1836 1.1838 -0.001 -0.001
r(C-Br) 1.983 1.986 1.9840 1.9843 0.001 -0.002
r(C1-C2)c 1.528 1.530 1.5227 1.5228 -0.005 -0.007
r(C2-C3) -- -- 1.5422 1.5400 --
--r(C2-C4) -- -- 1.5291 1.5400 --
--r(C2-H) -- -- 1.1152 1.1131 --
--r(C-H)av(CH3) -- -- 1.1110 1.1107 --
--∠(C-C=O) 127.66 127.30 127.052 125.460 -0.61 -1.84
∠(C-C-Br) 112.16 113.36 112.445 113.856 0.29 0.45
∠(O=C-Br) 120.18 119.34 120.486 120.684 0.31 1.34
∠(C1-C2-C3) 109.00 110.76 111.548 112.199 2.55 1.44
∠(C1-C2-C4) 109.28 110.76 110.903 112.199 1.62 1.44
∠(C3-C2-C4) 111.06 111.54 109.447 110.808 -1.61 -0.73
∠(C1-C2-H) 107.45 104.36 108.267 106.627 0.82 2.27
∠(C3,4-C2-H)av 109.98 109.59 108.287 107.337 -1.69 -2.25
∠(C2-C3,4-H)av(CH3) 110.28 110.27 111.714 111.719 1.43 1.45
∠(H-C-H)av(CH3) 108.65 108.65 107.138 107.131 -1.51 -1.52
∠(H-C2-C1=O) 133.8 0.0 127.7 0.0 -6.2 0.0
rms deviationd (bond length) 0.003 0.004
(bond angle)
1.43 1.30
a)Converted from the r0 structure: (r(C=O) = 1.180, r(C-F) = 1.338, r(C1-C2) = 1.503, r(C2-C3) = 1.537,
r(C2-C4) = 1.527, r(C2-H) = 1.098, and r(C-H)av(CH3) = 1.094) from the microwave experiment
(reference 40). The scaling is approximated by comparing the rg structure from the electron diffraction experiment (reference 19) and rs structure from the microwave experiment (reference 17) of acetyl
fluoride: (rg(C=O) - r0(C=O) = ~0.004, rg(C-F) - r0(C-F) = ~0.014, rg(C-C) - r0(C-C) = ~0.002, and rg
(C-H) - r0(C-H) = ~0.010), assuming r0 is close to rs.
b)Converted from the re structure: (r(C=O) = 1.170, r(C-F) = 1.329 (gauche) or 1.330 (syn), r(C1-C2) =
1.507 (gauche) or 1.506 (syn), r(C2-C3) = 1.538 (gauche) or 1.535 (syn), r(C2-C4) = 1.527 (gauche) or
1.535 (syn), r(C2-H) = 1.087 (gauche) or 1.082 (syn), and r(C-H)av(CH3) = 1.084) from ab initio
RHF/6-31G* level calculation (present work and reference 40). For the scaling, see Table S2 (a). c)Numbering of carbons is (C4 or C3)-C2-C1=O. C2-C4 bond is eclipsed to carbonyl group.
d)For the rms deviation of bond length, the C-H bond is excluded. For the rms deviation of bond angle, any angle containing hydrogen is excluded.
e)Taken from reference 41 a). The ratio of gauche:syn is 88:12 at 298 °K.
f) Converted from the re structure: (r(C=O) = 1.168, r(C-Cl) = 1.792, r(C1-C2) = 1.517 (gauche) or 1.518
(syn), r(C2-C3) = 1.537 (gauche) or 1.533 (syn), r(C2-C4) = 1.527 (gauche) or 1.533 (syn), r(C2-H) =
1.084, and r(C-H)av(CH3) = 1.084) from ab initio RHF/6-31G* level calculation (Gaussian 90 program, in this work). For the scaling, see Table S2 (b).
i)For the syn conformer.
j)This value of ∠(C3-C2-C4) appeared to be poorly determined, so this angle was not used in calculating
the rms deviation for the bond angle.
k)Converted from the re structures of gauche: (r(C=O) = 1.1865, r(C-Br) = 1.9593, r(C1-C2) = 1.5134,
r(C2-C3) = 1.5463, r(C2-C4) = 1.5359, and r(C2-H) = 1.0817, and r(C-H)av(CH3)= 1.0827) and syn:
(r(C=O) = 1.1869, r(C-Br) = 1.9622, r(C1-C2) = 1.5146, r(C2-C3,4) = 1.5405, and r(C2-H) = 1.0829, and
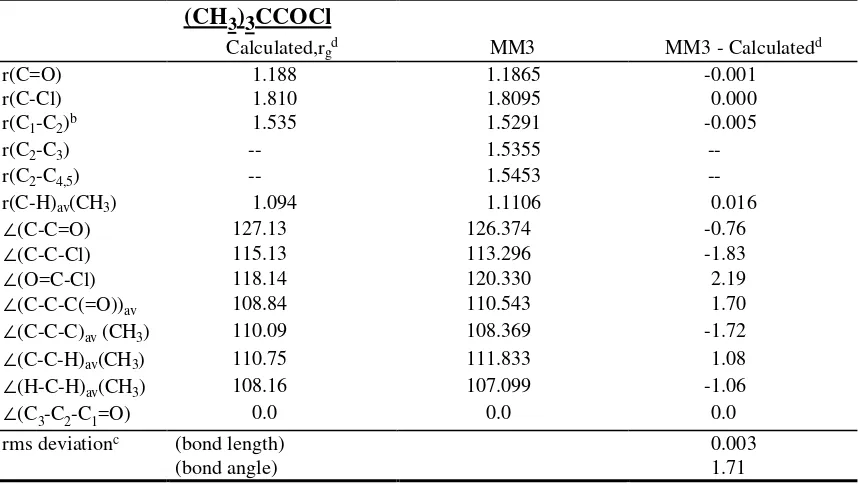
Table S4. Structural parameters (bond lengths in Å, and bond angles in degrees) of
dimethylpropionyl fluoride, dimethylpropionyl chloride, and
2,2-dimethylpropionyl bromide
(a) 2,2-dimethylpropionyl fluoride
(CH
3)
3CCOF
Calculated,rga MM3 MM3 - Calculateda
r(C=O) 1.187 1.1850 -0.002
r(C-F) 1.366 1.3696 0.004
r(C1-C2)b 1.524 1.5191 -0.005
r(C2-C3) -- 1.5272
--r(C2-C4,5) -- 1.5385
--r(C-H)av(CH3) 1.103 1.1108 0.008
∠(C-C=O) 128.77 128.918 0.15
∠(C-C-F) 111.60 110.624 -0.98
∠(O=C-F) 119.63 120.459 0.83
∠(C-C-C(=O))av 108.60 110.194 1.60
∠(C-C-C)av(CH3) 110.33 108.739 -1.59
∠(C-C-H)av(CH3) 110.75 111.786 1.04
∠(H-C-H)av(CH3) 108.16 107.060 -1.10
∠(C3-C2-C1=O) 0.0 0.0 0.0
rms deviationc (bond length) 0.004
(bond angle) 1.16
(b) 2,2-dimethylpropionyl chloride
(CH
3)
3CCOCl
Calculated,rgd MM3 MM3 - Calculatedd
r(C=O) 1.188 1.1865 -0.001
r(C-Cl) 1.810 1.8095 0.000
r(C1-C2)b 1.535 1.5291 -0.005
r(C2-C3) -- 1.5355
--r(C2-C4,5) -- 1.5453
--r(C-H)av(CH3) 1.094 1.1106 0.016
∠(C-C=O) 127.13 126.374 -0.76
∠(C-C-Cl) 115.13 113.296 -1.83
∠(O=C-Cl) 118.14 120.330 2.19
∠(C-C-C(=O))av 108.84 110.543 1.70
∠(C-C-C)av (CH3) 110.09 108.369 -1.72
∠(C-C-H)av(CH3) 110.75 111.833 1.08
∠(H-C-H)av(CH3) 108.16 107.099 -1.06
∠(C3-C2-C1=O) 0.0 0.0 0.0
rms deviationc (bond length) 0.003
[image:14.612.94.523.471.713.2](c) 2,2-dimethylpropionyl bromide
(CH
3)
3CCOBr
Calculated,rge MM3 MM3 - Calculated,e
r(C=O) 1.185 1.1839 -0.001
r(C-Br) 1.988 1.9877 0.000
r(C1-C2)b 1.538 1.5305 -0.008
r(C2-C3) -- 1.5350
--r(C2-C4,5) -- 1.5450
--r(C-H)av(CH3) -- 1.1105
--∠(C-C=O) 127.08 126.157 -0.92
∠(C-C-Br) 114.17 113.949 -0.22
∠(O=C-Br) 118.75 119.894 1.14
∠(C-C-C(=O)) av 108.67 110.643 1.97
∠(C-C-C)av(CH3) 110.25 108.263 -1.99
∠(C-C-H)av(CH3) 110.30 111.861 1.56
∠(H-C-H)av(CH3) 108.63 106.979 -1.65
∠(C3-C2-C1=O) 0.0 0.0 0.0
rms deviationc (bond length) 0.005
(bond angle) 1.42
a)Converted from the re structure: (r(C=O) = 1.1699, r(C-F) = 1.3301, r(C1-C2) = 1.5150, r(C2-C3) =
1.5312, r(C2-C4,5) = 1.5398, and r(C-H)av = 1.0842) from ab initio RHF/6-31G* method (Gaussian 94
program, in this work). For the scaling, see Table S2 (a).
b)Numbering of carbons is (C3, C4, or C5)-C2-C1=O. C2-C3 bond is eclipsed to carbonyl group.
c)For the rms deviation of bond length, the C-H bond is excluded. For the rms deviation of bond angle, any angle containing hydrogen is excluded.
d)Converted from the re structure: (r(C=O) = 1.1677, r(C-Cl) = 1.7965, r(C1-C2) = 1.5296, r(C2-C3) =
1.5349, r(C2-C4,5) = 1.5383, and r(C-H)av = 1.0838) from ab initio RHF/6-31G* method (Gaussian 94 program, in this work). For the scaling, see Table S2 (b).
e)Converted from the re structure: (r(C=O) = 1.1817, r(C-Br) = 1.9640, r(C1-C2) = 1.5227, r(C2-C3) =
1.5387, r(C2-C4) = 1.5414, and r(C-H)av(CH3)= 1.0827) from ab initio RHF/3-21G* method (Gaussian 94
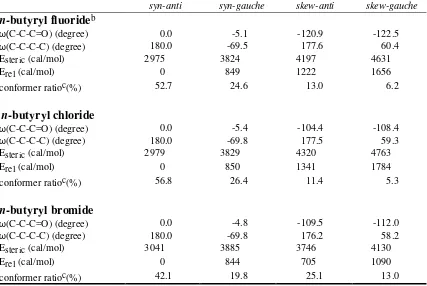
Table S5. Characteristics of conformers
aof
n-
butyryl fluoride, chloride, and bromide
found from MM3
syn-anti syn-gauche skew-anti skew-gauche
n-
butyryl fluoride
bω(C-C-C=O) (degree) 0.0 -5.1 -120.9 -122.5
ω(C-C-C-C) (degree) 180.0 -69.5 177.6 60.4
Esteric (cal/mol) 2975 3824 4197 4631
Erel (cal/mol) 0 849 1222 1656
conformer ratioc(%) 52.7 24.6 13.0 6.2
n-
butyryl chloride
ω(C-C-C=O) (degree) 0.0 -5.4 -104.4 -108.4
ω(C-C-C-C) (degree) 180.0 -69.8 177.5 59.3
Esteric (cal/mol) 2979 3829 4320 4763
Erel (cal/mol) 0 850 1341 1784
conformer ratioc(%) 56.8 26.4 11.4 5.3
n-
butyryl bromide
ω(C-C-C=O) (degree) 0.0 -4.8 -109.5 -112.0
ω(C-C-C-C) (degree) 180.0 -69.8 176.2 58.2
Esteric (cal/mol) 3041 3885 3746 4130
Erel (cal/mol) 0 844 705 1090
conformer ratioc(%) 42.1 19.8 25.1 13.0
a)Definition of conformations of butyryl halides were adopted from the literature (reference 29). b)In case of butyryl fluoride, two additional conformers, which are far less stable than syn-anti conformer, were found; the one with ω(C-C-C=O) = 90.3 degrees, ω(C-C-C-C) = 64.4 degrees, and Erel = 2355 cal/mol, and the other with ω(C-C-C=O) = 75.4 degrees, ω(C-C-C-C) = 63.3 degrees,
and Erel = 2389 cal/mol.
[image:16.612.96.523.159.445.2]Table S6. Energy parameters and energy values (cal/mol) for 2-methylpropionyl
fluoride, 2-methylpropionyl chloride, and 2-methylpropionyl bromide;
Experiment, Ab initio, and MM3
a(a) 2-methylpropionyl fluoride
energy parameter Ramanb,c Ab initiob
RHF/6-31G*
MM3
H ‡ (gauche --> syn) 1781 1784 1878
H ‡ (gauche --> gauche)
1289 1335 1439
H 0 (syn - gauche) 1320d
1240e 1198
E 0 (syn - gauche) 1038 1156
G 0 (syn - gauche) 1374
(b) 2-methylpropionyl chloride
energy parameter EDf Ramanb,g Ab initioa
RHF/6-31G*
MM3
H ‡ (gauche --> syn) 3410 3786
H ‡ (gauche --> gauche)
1010 966
H 0 (syn - gauche) 987(266) 1609
E 0 (syn - gauche) 1100 1693
G 0 (syn - gauche) 700 1978
(c) 2-methylpropionyl bromide
energy parameter Ab initioh
HF/3-21G*
MM3
H ‡ (gauche --> syn) 4002 3976
H ‡ (gauche --> gauche)
1904 1857
H 0 (syn - gauche) 759
E 0 (syn - gauche) 1397 672
G 0 (syn - gauche) 1138
a)The MM3 energy parameters were obtained in the same way for propionyl halides (see Table 6). b)Taken from reference 40.
c)From the intensity ratio of temperature-dependent Raman line of s-trans and gauche forms in the vapor phase.
[image:17.612.92.521.481.580.2]g)From the intensity ratio of temperature-dependent Raman line of s-trans and gauche forms in the liquid phase.
h)Using the Gaussian 94 program, in this work.