Kathryn N. Rankin, Traian Sulea and Enrico O. Purisima∗
Biotechnology Research Institute, National Research Council of Canada,
6100 Royalmount Avenue, Montreal, Quebec H4P 2R2, Canada
Supporting Information
(Table S1, S2 and S3, Figure S1; 12 pages)
∗
Corresponding author. Email: [email protected]
†
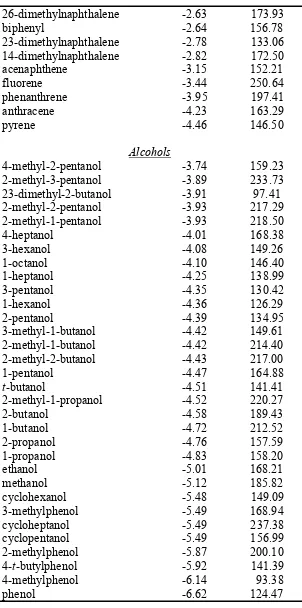
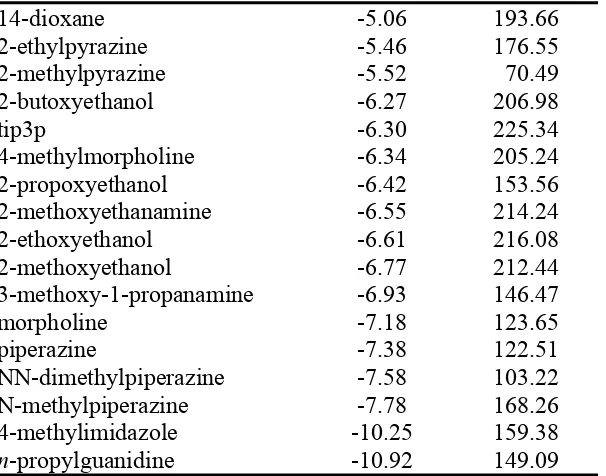
Table S1. Experimental hydration free energies11,12 (kcal/mol) and calculated molecular surface area, MSA (Ų), for the 210 neutral organic small molecules in the dataset.
Molecule exp
hydr
G MSAa
Alkanes
cyclopropane 0.75 134.81
cyclopentane 1.20 165.36
cyclohexane 1.23 277.92
cis-12-dimethylcyclohexane 1.58 215.74
methylcyclopentane 1.60 122.21
methylcyclohexane 1.71 104.80
ethane 1.83 229.44
propane 1.96 169.94
n-butane 2.08 146.79
i-butane 2.32 97.44
n-pentane 2.33 105.01
i-pentane 2.38 159.00
n-hexane 2.49 169.05
neopentane 2.50 145.22
3-methylpentane 2.51 168.02
i-hexane 2.52 138.35
22-dimethylbutane 2.59 190.57
n-heptane 2.62 165.78
224-trimethylpentane 2.85 181.03
24-dimethylpentane 2.88 168.77
n-octane 2.89 122.15
Arenes
t-amylbenzene -0.18 165.86
2-propylbenzene -0.30 176.77
butylbenzene -0.40 194.46
t-butylbenzene -0.44 162.39
2-butylbenzene -0.45 201.38
propylbenzene -0.53 144.37
ethylbenzene -0.80 231.11
p-xylene -0.81 125.47
m-xylene -0.84 146.85
124-trimethylbenzene -0.86 89.58
benzene -0.87 133.31
toluene -0.89 126.06
o-xylene -0.90 174.31
a-methylnaphthalene -2.37 161.30
naphthalene -2.39 167.59
26-dimethylnaphthalene -2.63 173.93
biphenyl -2.64 156.78
23-dimethylnaphthalene -2.78 133.06
14-dimethylnaphthalene -2.82 172.50
acenaphthene -3.15 152.21
fluorene -3.44 250.64
phenanthrene -3.95 197.41
anthracene -4.23 163.29
pyrene -4.46 146.50
Alcohols
4-methyl-2-pentanol -3.74 159.23
2-methyl-3-pentanol -3.89 233.73
23-dimethyl-2-butanol -3.91 97.41
2-methyl-2-pentanol -3.93 217.29
2-methyl-1-pentanol -3.93 218.50
4-heptanol -4.01 168.38
3-hexanol -4.08 149.26
1-octanol -4.10 146.40
1-heptanol -4.25 138.99
3-pentanol -4.35 130.42
1-hexanol -4.36 126.29
2-pentanol -4.39 134.95
3-methyl-1-butanol -4.42 149.61
2-methyl-1-butanol -4.42 214.40
2-methyl-2-butanol -4.43 217.00
1-pentanol -4.47 164.88
t-butanol -4.51 141.41
2-methyl-1-propanol -4.52 220.27
2-butanol -4.58 189.43
1-butanol -4.72 212.52
2-propanol -4.76 157.59
1-propanol -4.83 158.20
ethanol -5.01 168.21
methanol -5.12 185.82
cyclohexanol -5.48 149.09
3-methylphenol -5.49 168.94
cycloheptanol -5.49 237.38
cyclopentanol -5.49 156.99
2-methylphenol -5.87 200.10
4-t-butylphenol -5.92 141.39
4-methylphenol -6.14 93.38
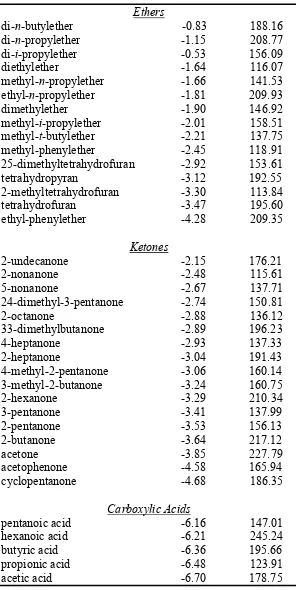
Table S1 continued.
Ethers
di-n-butylether -0.83 188.16
di-n-propylether -1.15 208.77
di-i-propylether -0.53 156.09
diethylether -1.64 116.07
methyl-n-propylether -1.66 141.53
ethyl-n-propylether -1.81 209.93
dimethylether -1.90 146.92
methyl-i-propylether -2.01 158.51
methyl-t-butylether -2.21 137.75
methyl-phenylether -2.45 118.91
25-dimethyltetrahydrofuran -2.92 153.61
tetrahydropyran -3.12 192.55
2-methyltetrahydrofuran -3.30 113.84
tetrahydrofuran -3.47 195.60
ethyl-phenylether -4.28 209.35
Ketones
2-undecanone -2.15 176.21
2-nonanone -2.48 115.61
5-nonanone -2.67 137.71
24-dimethyl-3-pentanone -2.74 150.81
2-octanone -2.88 136.12
33-dimethylbutanone -2.89 196.23
4-heptanone -2.93 137.33
2-heptanone -3.04 191.43
4-methyl-2-pentanone -3.06 160.14
3-methyl-2-butanone -3.24 160.75
2-hexanone -3.29 210.34
3-pentanone -3.41 137.99
2-pentanone -3.53 156.13
2-butanone -3.64 217.12
acetone -3.85 227.79
acetophenone -4.58 165.94
cyclopentanone -4.68 186.35
Carboxylic Acids
pentanoic acid -6.16 147.01
hexanoic acid -6.21 245.24
butyric acid -6.36 195.66
propionic acid -6.48 123.91
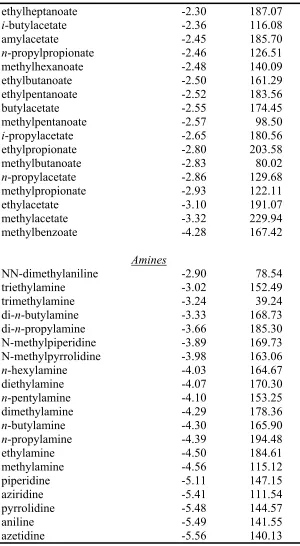
ethylheptanoate -2.30 187.07
i-butylacetate -2.36 116.08
amylacetate -2.45 185.70
n-propylpropionate -2.46 126.51
methylhexanoate -2.48 140.09
ethylbutanoate -2.50 161.29
ethylpentanoate -2.52 183.56
butylacetate -2.55 174.45
methylpentanoate -2.57 98.50
i-propylacetate -2.65 180.56
ethylpropionate -2.80 203.58
methylbutanoate -2.83 80.02
n-propylacetate -2.86 129.68
methylpropionate -2.93 122.11
ethylacetate -3.10 191.07
methylacetate -3.32 229.94
methylbenzoate -4.28 167.42
Amines
NN-dimethylaniline -2.90 78.54
triethylamine -3.02 152.49
trimethylamine -3.24 39.24
di-n-butylamine -3.33 168.73
di-n-propylamine -3.66 185.30
N-methylpiperidine -3.89 169.73
N-methylpyrrolidine -3.98 163.06
n-hexylamine -4.03 164.67
diethylamine -4.07 170.30
n-pentylamine -4.10 153.25
dimethylamine -4.29 178.36
n-butylamine -4.30 165.90
n-propylamine -4.39 194.48
ethylamine -4.50 184.61
methylamine -4.56 115.12
piperidine -5.11 147.15
aziridine -5.41 111.54
pyrrolidine -5.48 144.57
aniline -5.49 141.55
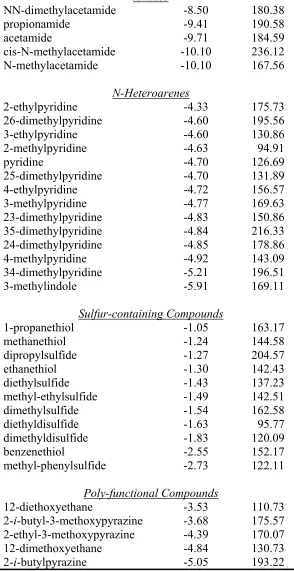
Table S1 continued.
Amides
NN-dimethylacetamide -8.50 180.38
propionamide -9.41 190.58
acetamide -9.71 184.59
cis-N-methylacetamide -10.10 236.12
N-methylacetamide -10.10 167.56
N-Heteroarenes
2-ethylpyridine -4.33 175.73
26-dimethylpyridine -4.60 195.56
3-ethylpyridine -4.60 130.86
2-methylpyridine -4.63 94.91
pyridine -4.70 126.69
25-dimethylpyridine -4.70 131.89
4-ethylpyridine -4.72 156.57
3-methylpyridine -4.77 169.63
23-dimethylpyridine -4.83 150.86
35-dimethylpyridine -4.84 216.33
24-dimethylpyridine -4.85 178.86
4-methylpyridine -4.92 143.09
34-dimethylpyridine -5.21 196.51
3-methylindole -5.91 169.11
Sulfur-containing Compounds
1-propanethiol -1.05 163.17
methanethiol -1.24 144.58
dipropylsulfide -1.27 204.57
ethanethiol -1.30 142.43
diethylsulfide -1.43 137.23
methyl-ethylsulfide -1.49 142.51
dimethylsulfide -1.54 162.58
diethyldisulfide -1.63 95.77
dimethyldisulfide -1.83 120.09
benzenethiol -2.55 152.17
methyl-phenylsulfide -2.73 122.11
Poly-functional Compounds
12-diethoxyethane -3.53 110.73
2-i-butyl-3-methoxypyrazine -3.68 175.57
2-ethyl-3-methoxypyrazine -4.39 170.07
12-dimethoxyethane -4.84 130.73
14-dioxane -5.06 193.66
2-ethylpyrazine -5.46 176.55
2-methylpyrazine -5.52 70.49
2-butoxyethanol -6.27 206.98
tip3p -6.30 225.34
4-methylmorpholine -6.34 205.24
2-propoxyethanol -6.42 153.56
2-methoxyethanamine -6.55 214.24
2-ethoxyethanol -6.61 216.08
2-methoxyethanol -6.77 212.44
3-methoxy-1-propanamine -6.93 146.47
morpholine -7.18 123.65
piperazine -7.38 122.51
NN-dimethylpiperazine -7.58 103.22
N-methylpiperazine -7.78 168.26
4-methylimidazole -10.25 159.38
n-propylguanidine -10.92 149.09
a
The molecular surface area was calculated using the SIMS molecular surface program21 and
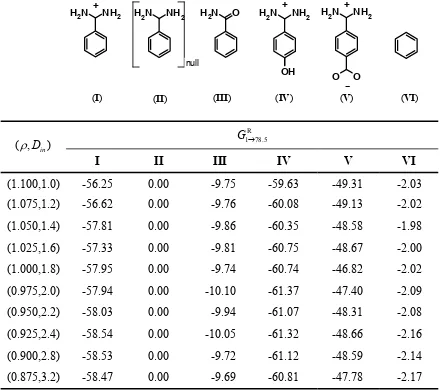
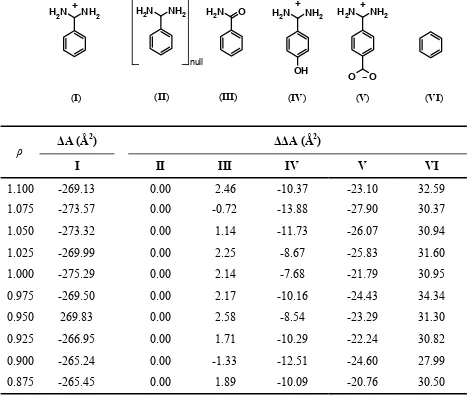
Table S2. Effect of ( ,ρ Din) parameter sets on the calculated electrostatic hydration free energy (kcal/mol) for the series of benzamidine analogs.
(0.975,2.0) -57.94 0.00 -10.10 -61.37 -47.40 -2.09
(0.950,2.2) -58.03 0.00 -9.94 -61.07 -48.31 -2.08
(0.925,2.4) -58.54 0.00 -10.05 -61.32 -48.66 -2.16
(0.900,2.8) -58.53 0.00 -9.72 -61.12 -48.59 -2.14
upon binding benzamidine to trypsin and the calculated relativea (∆∆A (Å2))change in molecular
surface area upon binding for a series of benzamidine analogs to trypsin.b
Benzamidine (I) is taken as the reference.
b
The largest variation in the relative non-polar term upon binding to trypsin (Eq (2)) is observed
for analog VI and is 0.127 kcal/mol at α = 0.020 kcal/(mol.Å2). Note that the non-polar term
Figure Captions
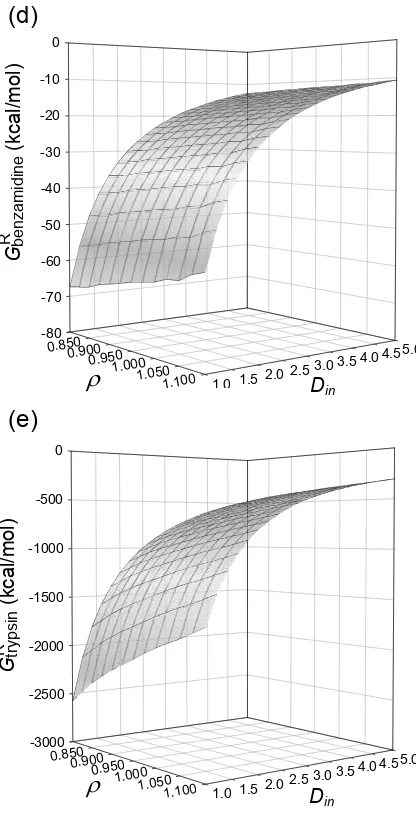
Figure S1. Dependence of the components of the calculated absolute electrostatic free energy of
binding between trypsin and benzamidine on AMBER atomic radii linear scaling factor ρ, and
solute interior dielectric constant, Din. 3D-surface representation of (a) Coulomb interaction
energy; (b) change in reaction field energy; (c) reaction field energy of tryspsin-benzamidine
-80