IMPROVING STUDENTS’ WRITING SKILL
IN COMPOSING SHORT FUNCTIONAL ENGLISH TEXTS BY USING GAMES
IN SMK PUTRA TAMA BANTUL
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By Maria Evita Sari Student Number: 091214049
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
i
IMPROVING STUDENTS’ WRITING SKILL
IN COMPOSING SHORT FUNCTIONAL ENGLISH TEXTS BY USING GAMES
IN SMK PUTRA TAMA BANTUL
A SARJANA PENDIDIKAN THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By Maria Evita Sari Student Number: 091214049
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION
FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
iv
Cogito ergo sum (I think therefore I am).
(René Descartes)
Always be yourself, express yourself, have faith in
yourself, do not go out and look for a successful
personality and duplicate it.
(Bruce Lee)
Things do not happen. Things are made to happen.
(John F. Kennedy)
I dedicated this thesis to
Jesus Christ
My great parents:
Pak Sumadi
and
Bu Minah
My wonderful aunty:
Simbok
My cute brother and sister:
Mas Adit and Dik Valen
My beloved man:
Bryan
v
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that this thesis, which I have written, does not contain the work or parts of the work of other people, except those cited in the quotations and the references, as a scientific paper should.
Yogyakarta, November 8th, 2013 The Writer
vi
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN
PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswa Universitas Sanata Dharma:
Nama : Maria Evita Sari
Nomor Mahasiswa : 091214049
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul:
IMPROVING STUDENTS’ WRITING SKILL
IN COMPOSING SHORT FUNCTIONAL ENGLISH TEXTS BY USING GAMES
IN SMK PUTRA TAMA BANTUL
beserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan demikian saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk media lain, mengelolakannya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistribusikan secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikannya di Internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin dari saya maupun memberikan royalty kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini yang saya buat dengan sebenarnya.
Dibuat di Yogyakarta
Pada tanggal : 18 Oktober 2013 Yang menyatakan
vii
ABSTRACT
Sari, Maria Evita. 2013. Improving Students’ Writing Skill in Composing Short Functional English Texts by Using Games in SMK Putra Tama Bantul. Yogyakarta: English Language Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
English is taught in Indonesia as a foreign language. There are four English skills, namely writing, speaking, listening and reading. In order to be successful in the global era, students have to master all of those skills. Unfortunately, many advantages in learning writing. The formulated problem of this study is: to what extent do games improve the X Accountancy 2 students’ writing skill in composing short functional English texts? Short functional English texts observed in this research were informal memos and invitation letters.
The researcher employed classroom action research to help the students improve their writing skill in composing short functional English texts. The participants of this study were 24 students of X Accountancy 2 of SMK Putra Tama Bantul. This study consisted of two cycles in which each cycle consisted of two meetings. The data were obtained by using observation sheets, field notes, students’ writings, questionnaire, and interview.
The result showed that games improved the students’ writing skill in composing short functional English texts. It could be seen from the students’ scores obtained in the preliminary study up to the second cycle of this study. The number of students who reached the passing grade increased. Games helped the students apply the elements, enrich vocabularies, and organize students’ ideas in composing short functional English texts. Games are one of media to help students learn writing. Therefore, it is suggested that teacher can use games in teaching writing.
viii
ABSTRAK
Sari, Maria Evita. 2013. Improving Students’ Writing Skill in Composing Short Functional English Texts by Using Games in SMK Putra Tama Bantul. Yogyakarta: English Language Study Program, Sanata Dhrama University.
Bahasa Inggris diajarkan di Indonesia sebagai bahasa asing. Bahasa Inggris mencakup 4 kemampuan yaitu menulis, berbicara, mendengar dan membaca. Untuk menjadi sukses pada era globalisasi ini, siswa- siswa diwajibkan menguasai keempat kemampuan tersebut. Sayangnya, banyak siswa yang berpikir bahwa menulis adalah kemampuan tersulit untuk dikuasai. Berdasarkan studi awal yang dilakukan oleh peneliti, siswa kelas X Akuntansi di SMK Putra Tama Bantul mengalami kesulitan dalam menulis teks fungsional pendek Bahasa Inggris.
Penelitian ini bertujuan untuk mengatasi masalah siswa X Akuntansi 2 dalam menulis teks fungsional pendek Berbahasa Inggris. Games ditawarkan sebagai solusi mengingat bahwa games memberikan banyak manfaat dalam belajar menulis. Rumusan masalah dalam penelitian ini adalah sejauh mana games dapat meningkatkan kemampuan menulis siswa X Akuntansi 2 dalam menyusun teks fungsional pendek Bahasa Inggris. Teks fungsional pendek Bahasa Inggris dalam penelitian ini adalah memo dan undangan tidak resmi.
Penelitian ini merupakan Penelitian Tindakan Kelas (PTK) yang bertujuan membantu siswa meningkatkan kemampuannya dalam menulis teks fungsional pendek Bahasa Inggris.Peserta dari penelitian ini adalah 24 siswa dari kelas X Akuntansi 2 di SMK Putra Tama Bantul.Peneltian ini terdiri dari dua siklus. Pada tiap siklusnya diadakan dalam dua kali pertemuan. Data dalam penelitian ini diperoleh dari lembar observasi, catatan lapangan, hasil tulisan siswa, kuesioner, dan wawancara.
Hasil analisa data menunjukkan bahwa games meningkatkan kemampuan siswa dalam menulis teks fungsional pendek Bahasa Inggris. Hal ini dapat dilihat dari nilai- nilai para siswa dari studi awal sampai siklus kedua dalam penelitian ini. Jumlah siswa yang melewati kriteria ketuntasan minimal meningkat. Gamesmembantu siswa dalam mengimplementasikan elemen, memperkaya kosakata, dan menyusun ide- ide dalam menulis teks fungsional pendek Bahasa Inggris. Games merupakan salah satu media untuk membantu siswa dalam belajar menulis. Oleh karena itu, para guru Bahasa Inggris disarankan untuk menggunakan games untuk mengajar menulis.
ix
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, I would like to express my gratitude to Jesus Christ for all of His help, blessing, love, guidance and grace during my whole life. Because of Him, I could struggle and pass all of the obstacles from planning up to reporting the thesis. Jesus is everything to me.
I would like to thank my great supervisor, C. Tutyandari, S. Pd., M. Pd.
for all her help, guidance, suggestions, patience, support, motivation, and encouragement during the research process until I reported my thesis. My supervisor always helped me when I felt stuck in doing my thesis.
Next, my gratitude is intended to Dinar Ratnasari S. Pd., who has permitted me to conduct the research in her classroom. She always gives me guidance, time and suggestions. I thank Drs. Simon Suharyanta. M. Pd., the principal of SMK Putra Tama Bantul, who has permitted me to conduct the research in SMK Putra Tama Bantul. Moreover, I thank the X Accountancy 2 students in SMK Putra Tama Bantul for their help and cooperation during the research process in their class.
x
me. I love them very much because they are the reasons why I have high spirit in doing and reporting my research.
My special thank goes to my beloved man, Florianus Bryan Aji for his support, motivation, love, joke and happiness so I could be strong. He also makes me happy in doing and reporting my research. I also express my gratitude to my besties, Karina Lega Ayu, Ratnasari Nugraheni, Yosafat Barona V., Sesilia Pramita N.S., Adria Cemara, Pipiet Dhanayu, Helen Martasari, Sekar,
Angela Kenya A., Maria Sisca I., Wilda Prandika, Shela Novitasari, Monika Nur I., Evi Tri P., Budi Prasetyo, Tunggul, Maria Ursula, Fransisca Paula Genevra, Yohanes Marwan, Yoanes Babtis Mario, Aloysius Indra, Patrisia Ayu, Mas Kojek, Ceper, Mas Frangky, and Mbak Delis. I thank them for working together and supporting each other. I thank them for their share, help, love, and laugh. I’m very glad to meet and know them all.
I am grateful to Sr. Margareth O’Donohue FCJ, Sesilia Pramita N.,
Adria Cemara., and Micahel Dian Teguh S.Pd. for their willingness, time, kindness, and suggestions in being my proof readers. I also thank Maria Imaculata W. who lent me a video recorder. I would like to say thanks to all PBI lecturers, Mbak Dhanniek, Mbak Tari, and Library staff who help me. I would like to address my gratitude to Podang 9 members, all of PBI students, all Sanata Dharma University students and all people who always motivate and support me. I am very blessed to have them all in my life.
xi
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY………... v
PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH……….. vi
LIST OF APPENDICES ………. xvii
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION Page
3.Short Functional English Texts ……… 7
xii
CHAPTER II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
A. Theoretical Description ……….. 9
1. Writing Skill ……… 9
a. The Nature of Writing ……….. 10
b. The Process of Writing ………. 11
c. Teaching Writing in EFL Classes …… 11
2. Short Functional English Texts …………... 12
a. Informal Memos ………... 12
b. Informal Invitation Letters …………... 14
3. Games in Language Learning ……….. 15
a. The Definition of Games ……….. 15
b. The Advantages of Using Games in Language Teaching ……….. 16
c. The Kinds of Games in this Study ….. 17
4. Classroom Action Research ……… 18
a. The Definition of Action Research ….. 18
b. The Characteristics of Action Research 18 c. The Advantages of Action Research … 19 d. The Model of Classroom Action Research ………... 20
B. Theoretical Framework ………... 21
CHAPTER III. METHODOLOGY A. Research Method ……… 24
xiii
1. School Setting ………. 26
2. Class Setting ………..…….. 27
C. Research Participants ……….. 27
D. Research Instruments and Data Gathering Technique……… 27
1. Observation Sheets.……….. 28
2. Field Notes ………. 28
3. Questionnaires……….. 29
4. Interviews………. 29
5. Students’ Written Texts ……….. 30
6. Students’ Reflection Sheets ……… 30
E. Data Analysis Technique ………. 31
F. Research Procedure ………. 32
1. Conducting a Preliminary Study ………… 32
2. Asking for Research Permission …………. 33
3. Conducting Classroom Action Research…. 33 CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION A. The Preliminary Study ………. 35
B. The Implementation of Games in the First Cycle 37 C. Research Findings in the First Cycle …………... 48
D. The Implementation of Games in the Second Cycle……… 52
xiv
Composing Short Functional English Texts …… 63
CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND RECOMMENDATIONS A. Conclusions ……….. 69
B. Recommendations……… 70
REFERENCES………... 72
xv
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
Table 4.1 The Students’ Scores in the First Cycle ……… 48 Table 4.2 The Students’ Scores in the Second Meeting ………... 60 Table 4.3 The Students’ Scores in the Preliminary Study, the First, and
xvi
LIST OF FIGURES
Figures Page
Figure 2.1 An Informal Memo ………. 13
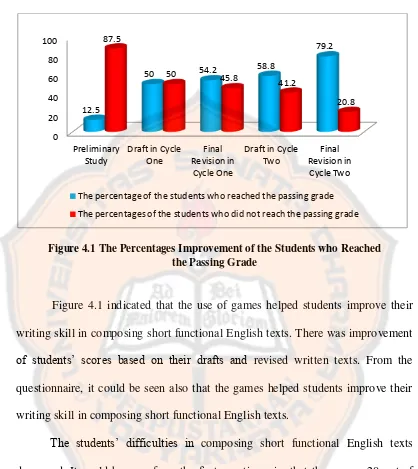
Figure 2.2 An Informal Invitation Letter ………... 15 Figure 2.3 The Model of Action Research ……….. 21 Figure 4.1 The Percentages Improvement of the Students Who
xvii
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix Page
Appendix A Covering Letter for the Head of SMK Putra Tama Bantul 75 Appendix B Research Official Statement from SMK Putra Tama
Bantul ………. 77
Appendix C Lesson Plan and Teaching Materials of Cycle One ……... 79
Appendix D Field Notes of Cycle One ………... 91
Appendix E Observation Sheet of Cycle One ……… 99
Appendix F Lesson Plan and Teaching Materials of Cycle Two ……... 104
Appendix G Field Notes of Cycle Two ……….. 113
Appendix H Observation Sheets of Cycle Two ……….. 120
Appendix I Questionnaire of the Preliminary Study ……… 125
Appendix J Questionnaire of Cycle One and Two ……… 129
Appendix K The Raw Data of Questionnaire from the Preliminary Study ……….. 133
Appendix L The Raw Data of Questionnaire from Cycle One ……….. 137
Appendix M The Raw Data of Questionnaire from Cycle Two ………. 142
Appendix N Interview Guide ……….. 147
Appendix O Interview Transcripts ………. 150
Appendix P Samples of the Students’ Reflection ………. 163
Appendix Q Compiled Rubric for Composing Short Functional English Texts ……….. 166
Appendix R Sample of a Student’s Drafts and Revised Written Text in Cycle One ………... 169
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
In this chapter, the researcher discusses the introduction of this study. There are six sections in this chapter. Those sections are the research background, research problem, problem limitation, research objectives, research benefits and definition of terms used in this study.
A. Research Background
English is the lingua franca used in the global context. Mastering English is very important because if people do not master English, they will have difficulties to communicate with others who come from other countries. It is one reason why English is taught in Indonesian schools.
The English skills that are taught in Indonesia include receptive and productive skills. The productive skills are writing and speaking. The receptive skills are reading and listening. Those skills are taught through different texts which have different functions. Therefore, there are some texts which are taught in Indonesian schools. Those texts are learned by Indonesian students start the third grade of elementary school to senior high school and vocational high school.
skills which were mentioned before. The students are expected to master all kinds of short functional English texts in all English skills. Students have different difficulties in each skill. Most students think that writing is the most difficult skill to master.
When the researcher conducted Program Pengalaman Lapangan/ PPL (Field Experience Program) in class X Accountancy 2 students of SMK Putra Tama Bantul, the researcher found that most of the students had difficulties in composing short functional English texts. It can be proved by looking at the score of their written texts. Based on the students’ writing skill scores, the researcher found that the other skills’ scores were better than the writing score. Therefore, it
can be concluded that writing skill is the most difficult skill to be mastered by the X Accountancy 2 students.
After finding the problem in class X Accountancy 2 of SMK Putra Tama Bantul, the researcher did a preliminary study to obtain more information. In the preliminary study, the researcher found that the English teacher taught informal memo and informal invitation letter by explaining them to the students. Then the students were asked to write informal memo and informal invitation letter. Most of the students got lower than the school passing grade which is 7.0.
3 used in informal memos and informal invitation. They also felt bored in learning to compose short functional English texts.
Based on the problems encountered by the students of X Accountancy 2 of SMK Putra Tama Bantul academic year 2012/ 2013 in the preliminary study, the researcher conducted classroom action research to help the students improve their writing skill in composing short functional English texts.
Games were used to overcome problems encountered by the students. Games in language learning can help the students learn English and improve their English skill. The essence of games in this research is as tools which help the students improve the students’ writing skill, understand the materials and make the learning process more enjoyable.
B. Research Problem
The problem of this study is: to what extent do games improve the X Accountancy 2 students’ writing skill in composing short functional English texts?
C. Problem Limitation
This study was Classroom Action Research (CAR) in Class X Accountancy 2 of SMK Putra Tama Bantul. The participants were twenty four students of Class X Accountancy 2 of SMK Putra Tama Bantul. This study focused on using jumbled sentences, jumbled words and flash pictures games to improve students’ writing skill in composing an informal memo and an informal invitation letter.
D. Research Objectives
5
E. Research Benefits
This study gives benefits to these following people:
1. The students of X Accountancy 2 of SMK Putra Tama Bantul
This study will help the students improve their writing skill in composing short functional English texts. They will be able to apply the elements, know the meanings of new vocabularies, organize ideas, and apply the tenses used in an informal memo and an informal invitation letter. The students will also be more active and enthusiastic in learning English. They will learn English in more enjoyable ways.
2. English Language Education Study Program Students
The English Language Education Study Program students may use this study as their additional reference. The benefits of this study can be their reference in developing techniques in teaching writing. Therefore, they can help their future students improve their students’ writing skill in composing short functional English texts.
3. English Teachers
texts. They can also teach their students in an enjoyable teaching learning atmosphere.
4. The Researcher
By conducting this study, the researcher can solve the problems encountered by the students. Besides, the researcher will be more creative in using games to teach English. The researcher also hopes that games will inspire to teachers in teaching writing short functional English texts.
5. The Other Researchers
The researcher lets the other researchers use this study for their reference in conducting their study. Therefore, the other researchers will develop the learning strategies to teach writing. The other researchers will also create more creative games in conducting their study. The researcher hopes this thesis can be beneficial to help those who design materials for the tenth grade students of vocational high schools which contain games.
F. Definition of Terms
The terms used in this study are:
1. Writing Skill
7 skill is measured from the students’ written texts score and the students’
improvement in each elements of scoring rubric.
2. Games in Language Teaching
According to Brewster, Ellis and Girard (2004), “games are not only motivating and fun but can also provide excellent practice for improving pronunciation, vocabulary, grammar and the four language skills” (p. 172). It means that games help the learners learn English and improve the learners’ English skills. In other words, games help the students learn by doing. In this study, the researcher uses three kinds of games, namely jumbled sentences, jumbled words and flash pictures. Those games are used as a media to teach writing skill in order to solve the problems encountered by X Accountancy 2 students in SMK Putra Tama Bantul.
3. Short Functional English Texts
(1977), informal invitations are invitations in a letter form to invite someone to attend some informal activities, namely dinner, lunch, and annual gatherings.
4. Students of X Accountancy 2of SMK Putra Tama Bantul
9
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
In this chapter, the researcher presents the theories that support this study. The related literatures are discussed as the basis of answering the research questiononto what extentdo games improve students’ writing skill in composing short functional English texts. There are two sections presented in this chapter, namelythe theoretical description and theoretical framework. In the theoretical framework the researcher presents the steps of implementing the related theories by using games.
A. Theoretical Description
In this section, the researcher discusses four theories which are related to the study. They are writing skill, short functional English texts, games in language learning, and classroom action research.
1. Writing Skill
a. The Nature of Writing
According to Wright et al. (2006), writing has purpose “to communicate something to somebody” by written form of language (p. 3). It means that people have to be able to write correctly if they want to communicate with others by using written language. Moreover, Brown (2007) states that writing is a kind of skill that “requires learners to product a correct written language” (p. 391). He also says, “Written products are often the result of thinking, drafting and revising procedures that require specialized skills…” (2007: 391). In other words, writing
producessome written products after employing some steps.
However, writing is the most difficult skill to master. It is supported by Tiedt (1989) who says, “… of all the language skills, writing is the most difficult and it is a hard work” (p. 6). Harmer (2011) agrees with the statement by saying “writing is a complex skill which requires some steps and takes more time” (p.
52). It shows that writing is a complex skill to master by students.
Brown (2007: 397- 398) presents the characteristics of written language as follows (all are direct quotes).
1. Permanence: written language has power to clarify the text. 2. Production time: the time in writing written language is limited. 3. Distance: the writers’ background influences their content of writing. 4. Complexity: written language has some sentences and clauses.
5. Vocabulary: in writing written language, the writers also enrich their vocabulary.
11
b. The Process of Writing
Meyers (2005) states that writing is defined as a process of discovering, thinking and organizing the ideas, putting them on the paper and revising them. Those stages require “specialized skills” (Brown, 2007: 391). According to Brown (2007), there are three stages of composing a written text. In the first stage, namely prewriting, students may obtain ideas by reading, clustering, questioning, or making outline.
After obtaining ideas, students go on to the drafting stage. In this stage, students have their time to compose sentences and paragraphs within class hour.After the students submit their wrriten texts, the teacher have to give feedback to their written texts. Then, students go to the last step, namely revising. In this step, students re-write their drafts into better written texts. The students can omit or add some important things in editing their drafts (Meyers, 2005). However, when the classroom time is limited, students may revise their drafts as homework writing assignment (Harmer, 2011). Finally, the students can submit their revised written texts to the teacher or post it.
c. Teaching Writing in EFL classes
There are some important reasons why writing is taught in Indonesia as a foreign language. Raimes (1983) says about there are three reasons why writing is important as follows:
necessarily become very involved with the language: the effort to express ideas and the constant use of eye, hand, and brain is a unique way to reinforce learning. (p. 3)
Therefore, the students learn and practice how to apply language features and construct correct sentences in writing English texts. It is more challenging to the English teachers who taught EFL classes because English is not the students’ daily language. Therefore, the students will be able to compete in global era in which English is a global language.
2. Short Functional English Texts
Based on the competency standard in School Based Curriculum (2006), some short functional English texts that are taught in vocational high school grade X are menus, public transportation departures, memos, and invitation letters. In this study, the researcher focuses on an informal memo and an informal invitation letter. Informal memos and informal invitations have similar grammatical features. Both of them focus on simple present tense and simple future tense.
a. Informal Memos
13 words” (p. 85). Based on Sularto (2008: 68), the elements of an informal memo are as follows:
1) addresse 2) addresser 3) content
4) complimentary closing 5) signature
6) sender’s name
Those elements are summarized in the following figure.
Figure 2.1 An Informal Memo Based on Sularto (2008: 68)
1
2
3
4 5
b. Informal Invitation Letters
According to Rosenblatt et al. (1977), informal invitations are invitations in a letter form to invite someone to attend some informal activities, namely: dinner, lunch, and party annual gatherings. Himstreet et al. (1993) state, “In informal invitation letters, wording should be conversational, as though were extending the invitation orally” (p. 478). In other words, the writers use informal
words in writing informal invitation letters. However, according to Raimes (1983), informal invitation letters have their “associated vocabulary, sentences structures and appropriate word choice” (p. 85). Therefore, it is important to apply correct tenses, elements and use appropriate vocabularies in writing an informal invitation letter. Rosenblatt et al. (1977) state that to show informality, the writer uses the first personal pronouns “I” and “we”. It means that informal invitation
letters are sent to people who have close relationship with the writer. For example, the letters are sent to close friends or colleagues. Based on Suryana (2006: 126), the elements of an informal invitation letter are as follows:
1) date: the day, date and year of the letters 2) greeting/ salutation
3) content/ body
4) complimentary closing 5) signature
15 Those elements are summarized in the following figure:
Figure 2.2 An Informal Invitation Letter Based on Suryana (2006: 126)
3. Games in Language Learning
There are three parts discussed in this section, namely the definition of games, the advantages of games in the language learning and the kinds of games used in this study.
a. The Definition of Games
Martin (1995: 1) as cited in Brewster et al. (2004: 172) state, “Games are fun activities which give young learners the opportunity to practice the foreign language in a relaxed and enjoyable way”. Therefore, the learners will learn in an
enjoyable situation without realizing it. It means that the learners learn the materials in a fun way.
1
2
3
4 5
b. The Advantages of Using Games in Language Learning
There are many advantages of using games in language learning. Bell and Wieckert (1985) say that games can increase students’ motivation in learning because games will make them active and participate in language learning. Moreover, Wright et al. (2006) state, “Games encourage many learners to sustain their interest and work” (p. 2).
Students’ motivation is important in the learning activities as stated by
Harmer (2007), ”Without such motivation we will almost certainly to make the necessary effort” (p. 98). Therefore, teachers are expected to be creative to improve students’ motivation. The teachers can create fun learning and good
atmosphere in class to improve students’ motivation by using games.
However, games create more than only fun in language learning. According to Brewster et al. (2004), “games are not only motivating and fun but also can provide excellent practice for improving pronunciation, vocabulary, grammar and the four English skills” (p. 172). Therefore, it is obvious that games
17
c. The Kinds of Games in this Study
Having known the problems encountered by X Accountancy 2 students, the researcher chose three kinds of games as follows.
1. Jumbled sentences
According to Raimes (1983), jumbled sentences are a kind of game in which the students are asked to put jumbled sentences into paragraph order. Raimes also says that jumbled sentences aim to help the students identify general and specific statements and understand the structures of the texts (1983).
2. Jumbled words
Jumbled words are a kind of game in which the students are asked to put the words into correct sentences. Brewster et al. (2004) say that this kind of game “is focused on memorization” then the students has to “remember and repeat in the
correct order a range of vocabulary and add their own examples”(p. 175). In this study, the researcher divides each sentence into its constituent words. Those words are put into one bind. It aims to avoid the words from getting mixed with the others.
3. Flash pictures
4. Classroom Action Research
The researcher would discuss the definition, the characteristic, the advantages and the model of classroom action research.
a. The Definition of Classroom Action Research
There are some experts that give the definition of Classroom Action Research. Elliot (1991: 69) as cited by Hopkins (2008) Classroom Action Research is the study of a social situation which is aimed to improve the quality of action within it. Ferrance supports Elliot’s theory by stating that Action Research is a process in which participants examine their own educational practice by using the techniques of study.
Kemmis (1983), as cited in Hopkins (2008) states that an action research aims to improve (a) teachers’ social and educational practices, (b) teachers understanding of the practices, and (c) teachers understanding of the real situation in which the action is carried out. Moreover, Wallace (1998) says that action research aims to develop professionals’ performances. Therefore, classroom
action research aims to improve educational practices in the specific participants and situation. The improvement is as the result of classroom action research.
b. The Characteristics of Action Research
19 done by teams, practitioners and researchers. Fourth, the changes in action research are based on the data and information obtained. From the explanation, it can be concluded that action research is done systematically in particular participants which aims to solve the problem based on the data obtained.
c. The Advantages of Action Research
Fraenkel and Wallen (2008) state that there are five advantages of action research. First, action research can be done by any professional in any type of school, at any grade. It aimed to solve any kind of problem in specific area. Second, action research improves practice in educational field. Therefore, teachers or other education professionals can improve their competent in educational practice. Third, teachers or other education professionals can practice their design in effective ways. It leads them to be able to modify and enrich their strategies and techniques. Fourth, action research helps teachers or other education professional identify problems so they can find ways to solve those problems. Fifth, action research help teachers or other education professionals share what they had learned through their own action research. It leads teachers or other education professionals to reduce the isolation feeling that they experience in the daily tasks within the school.
d. The Model of Classroom Action Research
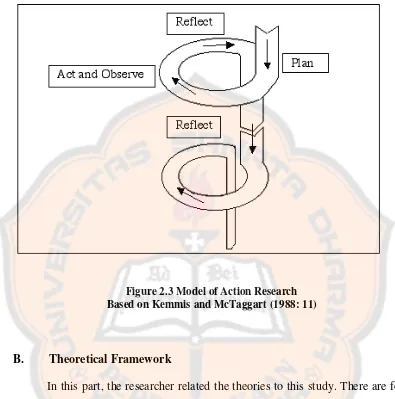
In this study, the researcher uses Classroom Action Research Model of Kemmis and McTaggart (1988), as cited in Hopkins (2008). According to Kemmis and McTaggart (1988: 10), as cited in Burns (1999: 32), action research is a spiral steps consists of four steps. They are planning, action, observation, and reflection. The model of their action research is summarized in Figure 2.3. Kemmis and McTaggart (1998: 10) as cited in Burns (1999: 32) explain that in the classroom action research, the researcher should (all are direct quotes):
1) Develop a plan of critically informed action to improve what is already happening,
2) Act to implement the plan,
3) Observe the effects of the critically informed action in the context in which it occurs, and
4) Reflect on these effects as the basis for further planning, subsequent critically informed action and so on, through a succession of stages.
21
Figure 2.3 Model of Action Research Based on Kemmis and McTaggart (1988: 11)
B. Theoretical Framework
In this part, the researcher related the theories to this study. There are four skills of English, namely writing, speaking, reading and listening. Those skills are taught through some short functional English texts. Students are obligized to master all skills. However, most students consider that writing is the most difficult skill to master. The statement is supported by Tiedt (1989: 6), who says, “of all the language skills, writing is the most difficult and it is a hard work.” Moreover,
In teaching writing, there are some texts that have to be taught in vocational high school based on competence standard in School Based Curriculum (2006). Those texts are menus, public transportation departures, memos, and invitation letters. The researcher focused on writing an informal memo and an informal invitation letter since the students of X Accountancy 2 had difficulties in writing those kinds of texts. The students had difficulties in applying elements, knowing the meanings of new words, applying tenses and organizing ideas in writing an informal memo and an informal invitation letter.
To answer the research problem, the researcher used some theories about games. Wright et al. (2006) say “Games help and encourage many learners to sustain their interest and work” (p. 2). It means that by involving actively in
games, students also learn English in an enjoyable way. Therefore, games will motivate the students in learning English. Then, they will set their mind set that writing is not difficult skill to master. It leads the students to be able to apply elements, know the meanings of new words, apply tenses and organize ideas in writing short functional English texts.
23 There were three games in this research, namely jumbled sentences, jumbled words, and flash pictures. Each game helped students in different aspects of the problems encountered. Raimes (1993) says that jumbled sentences helped the students apply the elements of an informal memo and an informal invitation letter. Brewster et al. (2004) state jumbled words helped the students make correct sentences and enrich vocabularies. According to Raimes (1983), pictures in series aimed to help the students organize their ideas in writing an informal memo and an informal invitation letter. As the result, students of X Accountancy 2 could improve their writing skill in composing an informal memo and an informal invitation letter.
24
CHAPTER III
METHODOLOGY
This chapter presents the methodology employed in this study. The researcher divides this chapter into several sections. The sections are the research method, research setting, research participants, instrument and data gathering technique, data analysis technique, and research procedure.
A. Research Method
The aim of this study was to find out to what extent games improve students’ writing skill in composing short functional English texts. The researcher
found problems of writing an informal memo and an informal invitation letter in class X Accountancy 2 of SMK Putra Tama Bantul. In this study, the researcher implemented Classroom Action Research (CAR) methodology. Wallace (1998) states that classroom action research is a process of deciding what the teacher should do in the future practice based on the data collected. Therefore, the researcher aimed to solve the problem by implementing a real action.
25
1. Planning
The researcher found the problems encountered by the students of X Accountancy 2 academic year 2012/ 2013 when the researcher did Program Pengalaman Lapangan/ PPL (Field Experience Program) in SMK Putra Tama Bantul. The problems occurred when the researcher taught writing to the students. After analyzing students’ written texts, the researcher found that they had
difficulties in composing short functional English texts. However, the researcher ensured the problem by conducting a preliminary study. The researcher conducted a preliminary study twice on February 15th, 2013 and February 22nd, 2013. The topics were writing an informal memo and an informal invitation letter. The teacher explained those texts and asked the students to compose those texts. Then, the students were asked to submit their writen texts. Their written texts showed that they had difficulties in composing an informal memo and an informal invitation letter. Moreover, the questionnaire showed that the students had difficulties in applying the elements, knowing the meanings of new vocabularies, organizing ideas and applying tenses used in an informal memo and an informal invitation letters. Having known the problem, the researcher planned to design an action that would be implemented in class X Accountancy 2.
2. Action
first meeting of each cycle was jumbled sentences. Jumbled words and flash pictures were implemented in the second meeting of each cycle.
3. Observation
The researcher conducted observation at the same time of games implementation. The researcher were helped by two co- observers to observe the researcher’s and the students’ activities during the implementation of games. The people who helped the researcher were the English teacher of class X Accountancy 2 and two students of the English Education Study Program Sanata Dharma University.
4. Reflection
Reflection was the last step of this study. The researcher analyzed what went well and what did not. It aimed to see whether students’ writing skill has improved. The researcher would go to the next cycle in order to gain better results.
B. Research Setting
There are two sections of the research setting, namely the school setting and class setting.
1. School Setting
27 learning process was carried out from 7.00 a.m. to 2.30 p.m. every Monday, from 7.00 a.m. to 2.00 p.m. every Tuesday, Wednesday and Thursday, from 7.00 a.m. to 11.15.am. every Friday and from 7.00 a.m. to 12.50 p.m. every Saturday. The school had total 24 English hours. It was handled by two English teachers.
2. Class Setting
This study was conducted in class X Accountancy 2, SMK Putra Tama Bantul. It was conducted from February 2013 to April 2013. This study was conducted in the 2nd semester of academic year 2012/ 2013. The duration of the English lesson was a hundred and twenty five minutes on Thursday and forty five minutes on Friday per class hour.
C. Research Participants
The total number of students in class X Accountancy 2 was twenty four. They had difficulties in composing short functional English texts. They had difficulties in applying the elements, knowing the meaning of new words, organizing ideas, and applying the tenses used in an informal memo and an informal invitation letter. Moreover, they felt bored in learning writing those short functional English texts.
D. Research Instruments and Data Gathering Technique
checklists, field notes, questionnaires, interviews, students’ written texts, and students’ reflection sheets.
1. Observation Sheets
The observation sheets helped the researcher and observers to observe the researcher’s and students’ activities in the English teaching learning process in
classroom. According to Best and Khan (1986), observation sheet provides list of statements that are observed during the English teaching learning process. Observation sheets were also done by co- observers who helped the researcher to obtain the information (Elliot, 1991). In this study, there were two co- observers who are two English Language Education Study Program Sanata Dharma University students.
2. Field Notes
The result of the field notes is used to support the data resulted from the observation checklist. The field notes helped the researcher reflect the implementation of classroom action research. Moreover, it helped the researcher implement the next implementation better. Those statements are supported by Fraenkel and Wallen (2008) who states “In educational research, this usually means the detailed notes researchers take in the educational setting (a classroom or a school) as they observe what is going on …” (p. 506). Therefore, the researcher and the English teacher wrote the students’ activities and conditions
29
3. Questionnaires
A questionnaire is a quick and simple way to obtain rich information about aspects of classroom and teaching method (Hopkins, 2008). In this study, the researcher distributed the questionnaires to all students of class X Accountancy 2 in the preliminary study and in the end of each cycle of games implementation. The purpose of the questionnaire was to obtain information from the students themselves whether games helped them improve their writing skill in composing an informal memo and an informal invitation letter. The researcher employed two types of item responses mentioned by Burns (1999), namely close-ended items and open- ended items. In the preliminary study, there were thirteen numbers of close- ended items and three numbers of open-ended items. In the end of each cycle, there wereeleven numbers of close- ended items and five numbers of open- ended items.
4. Interviews
The interviews helped the researcher obtain more information from the students’ opinion. Gall et al. (2007) state that interview “involves asking a series of structured questions and then probing more deeply with open-form questions to obtain additional information” (p. 246). In the preliminary study, the interview
interview was conducted to ten X Accountancy 2 students of SMK Putra Tama Bantul in the end of the second cycle.It aimed to know the students’ further opinion of games implementation whether games could improve their writing skill in composing short functional English texts. There were eight main questions used to interview the students.
5. Students’ Written Texts
The students’ written texts were the individual written texts in which the
students compose an informal memo and an informal invitation letter. The students’ written texts were used to obtain more information on the improvement of students’ writing skill in composing an informal memo and an informal
invitation letter. Those statements are supported by Burns (1999) who states that the students’ written texts help the researcher assess the students’ progress in
writing.
6. Students’ Reflection Sheets
31
E. Data Analysis Technique
The researcher aimed to answer the problem formulated and relate the theories in Chapter II. Then, the researcher used the data triangulation. Data triangulation was proposed by Elliot and Adelman (as cited in Hopkins, 2008). It involves comparison of two or more methods of data collection in the study of some aspects of human behavior (Hopkins, 2008). Therefore, the data triangulation was important in order to make the data more accurate and valid.
In order to observe whether the students got improvement in writing skill after implementing games in learning writing an informal memo and an informal invitation letter, the researcher used the students’ drafts and revised written texts as the main data. The researcher used a specific rubric from some sources which was designed by the researcher and the English teacher to measure the students’ writing skill in composing an informal memo and an informal invitation letter (see Appendix Q). Then, the researcher used the result of students’ drafts and revised written texts to see whether the students made a good improvement.
The data will be presented in two ways: percentage and description. The researcher presented the students’ answer in the questionnaire in percentage.
Then, the researcher described the data while answering the problem formulated based on the percentage.
checklists: whether some cases were supported by the observer’s observation or not.
The researcher used the students’ reflection to be the additional teacher’s
reflection in the end of each cycle. It would indicate what went well and what did not in implementing the games. Therefore, the teacher could make improvement in implementing games in the next cycle.
F. Research Procedure
This section describes the procedure of this study. There are three parts in the research procedure. Those parts are conducting a preliminary study, asking for research permission, and conducting classroom action research.
1. Conducting a Preliminary Study
The researcher conducted a preliminary study to identify the problem occurred in English class of X Accountancy 2. In the preliminary study, the researcher conducted observation. Then the researcher distributed questionnaire to all of the students to obtain more information on their problems. The researcher also collected the students’ written texts in the preliminary study. After reading
33
2. Asking for Research Permission
There were some procedures in gaining the research permission. Firstly, the researcher asked for the permission from the school (SMK Putra Tama Bantul). After being accepted by the school headmaster, the researcher asked for the permission to the Yogyakarta Governor. The researcher went to the Governor Office to get the permission letter by enclosing the permission letter from the university and the research proposal. Then the researcher sent it to BAPPEDA Bantul by enclosing the photocopy of the researcher’s student card. The staff of BAPPEDA Bantul gave the permission letter to be sent to the school and
university.
3. Conducting Classroom Action Research
In conductingclassroom action research, the researcher took some steps. Firstly, the researcher made lesson plans in implementing games to improve students’ writing skill in composing an informal memo and an informal invitation
letter. The researcher also prepared students’ worksheets, students’ handouts, observation checklists, field notes, questionnaires, interview guidelines and students’ reflection sheets.
In conducting the study, the researcher was helped by two students of the English Language Education Study Program Sanata Dharma University and anEnglish teacher of SMK Putra Tama Bantul in doing the observation. The researcher distributed questionnaires in the end of each cycle to investigate whether games improve their writing skill in composing an informal memo and an informal invitation letter. In the end of the second cycle, the researcher interviewed 10 students to whose answer in questionnaire supported the study. It aimed to obtain deeper information on their opinion and experiences towards games implemented in the English teaching learning process.
35
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The researcher presents this chapter in six parts: the preliminary study, the implementation of games in the first cycle, research findings in the first cycle, the implementation of games in the second cycle, research findings in the second cycle, the improvement of research findings in the first and second cycles. This chapter presents the research results and discussion in implementing games to improve students’ writing skill in composing an informal memo and an informal invitation letter. The research was conducted in two cycles which were applied in two meetings for each cycle. The study was conducted in March 22nd, April 4th, April 5th and April 11th, 2013.
A. The Preliminary Study
In the syllabus, the students were expected to be able to compose memos. Therefore, after discussing the answers, the teacher asked the students to composean informal memo. The passing grade of SMK Putra Tama Bantul was 70. However, most of the students of X Accountancy 2 got bad scores in theirwritten texts so they did not reach the passing grade. Lastly, the students were asked to submit their revised written texts on the next day. The researcher also collected their written texts in the preliminary study as the data for the study.
In the second preliminary study which was conducted in February 22nd, 2013, the teacher explained an informal invitation letter. The teacher explained the elements, the language features and the vocabulary used in composing an informal invitation letter. After that, the teacher gave question sheets about the elements, the language features, and vocabulary used in composing an informal invitation letter to the students. After answering the questions, the teacher and the students discussed the answers. Then, the students were asked to compose an informal invitation letter. In the second preliminary study, the researcher found that students had difficulties in composing the text. The students submitted their written texts on the next day. The researcher also collected the revised written texts of the students.
37 ideas, and applying tenses used in an informal memo and an informal invitation letter. They also felt bored in learning writing.
Therefore, the researcher tried to find the appropriate technique to teach them writing an informal memo and an informal invitation letter. Based on the observation, the researcher concluded that it was better for the students to experience the practice and use of the language rather than to listen to teacher’s explanation. Therefore, the students writing skill was expected to improve. Moreover, the students of X Accountancy 2 students felt bored easily. They needed interesting activities in learning writing.
B. The Implementation of Games in the First Cycle
The use of games in the teaching learning process in the first cycle was conducted in two meetings on Friday, March 22nd, 2013 and Thursday, April 4th, 2013. The first meeting was conducted in eighty minutes. The second meeting was conducted in a hundred and thirty five minutes. There were 24 students who joined the class. The topic in the first cycle was an informal memo. The games of this studywere implemented based on the steps of classroom action research. The steps were planning, action, observation, and reflection.
1. Planning
the researcher prepared the lesson plan and the materials. In the lesson plan, there were 3 main activities, namely: pre activities, whilst activities, and post activities. In pre activities, the researcher planned to review the informal memo that had been taught by the English teacher. The researcher planned to give some questions about elements and language features used in informal memos. These activities aimed to give the students’ view about what they were going to do in class and recalled what they have learned about an informal memo. After that, the researcher planned to distribute the students’ call card to each student in order to
help them memorize their numbers.
In whilst activities, the researcher planned to give jumbled sentences of an informal memo. The class was divided in to six groups so there would be four students each group. The researcher also planned to give some questions about elements and language features used in an informal memo. The informal memo was about a memo from Rani to Tono. The activities aimed to help the students have experience in arranging an informal memo correctly and applying the elements and language feature used in an informal memo.
39 The last game was flash pictures. It was an individual game. The researcher planned to ask the students write an informal memo after flashing the pictures in order to know their improvement in composing an informal memo. The researcher planned to flash some pictures which helped the students organize their ideas to compose an informal memo. There were seven pictures; a market, a watermelon, ten grams of grapes, a half of kilogram of carrots, a kilogram of chilies, a house and a clock shown 11 a.m. The researcher planned that the girls pretended to be mother who wrote an informal memo to their sons or daughters to buy the vegetables and ingredients. The boys pretended to be fathers who wrote an informal memo to their sons or daughters to buy the vegetables and ingredients. In conducting the study, the researcher planned to permit the students to find difficult words in the dictionary. The researcher planned to collect the students’ drafts in the in the end of the class. After that, the researcher planned to give feedback to students’ drafts. Then, the researcher planned to give the students
drafts to the students on Friday, April5th, 2013. Finally, the students were asked to submit their revised written texts on Saturday, April6th, 2013.
2.Action
The action was conducted in two meetings. The first meeting was conducted on Friday, March 22nd, 2013. The second meeting was on Thursday, April 4th, 2013. The topic was writing an informal memo.
a. First Meeting 1) Pre- Activity
In the beginning of the lesson, the researcher introduced the researcher’s name. In pre activities, the researcher began the class by greeting the students. As the introduction, the students were asked what they knew about an informal memo. Then the students accepted call cards.
2) Whilst Activities
In whilst activities, the class was divided into six groups. The names of the groups were lion, tiger, ant, dog, cat and dragon. The groups’ name helped students remember their group names. Each group consisted of four students. Then, the students were asked to play jumbled sentences in their groups. They were asked to arrange the sentences given in to the correct arrangement of an informal memo. They were asked to stick the sentences on the paper prepared. The informal memo was about a memo from Rani to Tono. They should be cooperative with their group members. The group who had finished playing the game should then write their group names on the blackboard. Then, the researcher and students discussed together the students’ arrangement of the informal memo
41 students’ worksheets. Then, the students also discussed the questions provided
including the elements and language features of an informal memo. 3) Post Activities
In post activities, the researcher reviewed what the students had learned by asking and answering questions session. Then, the researcher concluded the materials by asking the students orally. Finally, the researcher closed the meeting of that day.
b. Second Meeting
The second meeting was conducted on Thursday, April 4th, 2013. There were four days of Easter holidays so the researcher could not do the study in the previous week. There were 24 students joined the lesson. There were 3 mains activities.
1) Pre- Activities
In pre activities, the researcher began the class by greeting the students. The students answered the greeting enthusiastically. Then the researcher reviewed the material of the last meeting and distributed the call card.
2) Whilst Activity
43 3) Post Activities
In post activities, the researcher reviewed what the students had learned by asking and answering questions session. After that, the researcher distributed written reflective questions to the students. Then the researcher closed the meeting of that day.
3. Observation
The observation was conducted in two meetings on Friday, March 22nd, 2013 and Thursday, April 4th, 2013. In this stage, the researcher had roles as an observer and teacher. The researcher asked for help from two co- observers and the English teacher of the class to observe the researcher and students’ activities
during the implementation of games in teaching writing an informal memo and an informal invitation letter. The observation was done at when the implementation of games in the English teaching learning process. The data were obtained from the teachers’ activities observation sheet, the students’ activities observation sheet
and field notes. a. First Meeting
students in order to help the students understand the instructions and the materials. Besides, the teacher could not yet manage the time well.
Based on the observation sheet on the students’ activities, all of the
students followed the instructions of the researcher. The students could be managed well so all of the students involved in the teaching and learning process. All of the students paid attention to the teacher’s explanation. However, some students did not cooperate actively in their group. Some students asked for the instructions and materials that they did not understand. All of the students enjoyed the teaching learning process.
b. Second Meeting
The observation in the second meeting was conducted on Thursday, April 4th, 2013. There were 24 students in the class. It was a very hot day. The lesson was also in the last lesson hour of the day so the students looked very tired. There were four days of Easter holidays so the researcher could not do the research in the previous week.
Based on the observation sheet on the researcher’s activities, the
researcher could accomplish the activities based on the lesson plan. The researcher could manage the time wisely. Moreover, the researcher also gave feedback in the end of the discussions to the students. The researcher could accomplish the objectives of the lesson.
The observation sheet on students’ activity showed that all of the students
45 there were some students who did not pay attention to the teacher’s explanation. Some students asked the teacher to flash the pictures one more time in flash could reflect what went well and did not go well in the teaching learning process. The students paid attention to the researcher’s explanation and answered actively the researcher’s questions. As the researcher wrote in the field note:
“The students listened to her explanation and responded to her questions actively. By paying attention to the teacher’s explanation, the students understand the elements, language features and new vocabularies used in an informal memo and the rules of the game. “The students are also enthusiastic in playing the games.”
Based on the reflective questions filled in by the students, all of the students enjoyed the teaching and learning process by playing the games. They were happy in following the lesson because they had interesting experience in the teaching and learning process. Most of them wrote that they understood more materials because the games helped them. As some students wrote in the reflective sheets:
happy following the teaching and learning process by doing games.)
Student 19 :” Pengalaman hari ini sangat menyenangkan karena games yang digunakan menarik dan membuat saya memahami materi yang
diberikan guru.” (Today’s experience is very satisfying because
the games are interesting. It makes me understand more the materials given)
Student 16 :“Saya tidak bosan mengikuti pelajaran karena pelajaran diselingi games, tidak hanya penjelasan guru.” (I am not bored in following the lesson because I do not only listen to the teacher’s explanation but also play games)
Most of them wrote that it was interesting when they had to cooperate with their group members and compete against the other groups as they wrote:
Student 2 :“Pengalaman yang paling menarik adalah saat bekerja sama dengan teman sekelompok dan adu cepat dengan kelompok lain. Ittu membuat saya termotivasi untuk menyusun kata- kata dengan benar dan cepat.” (The most interesting experience is the time I cooperate with the members of my group. Then the competition makes me arrange the words correctly and quickly.)
Student 21: “Saya sangat terbantu oleh teman dalam satu kelompok membantu
saya menyusun element memos dan kata- kata.” (My group members
help me arrange the jumbled sentences and jumbled words.)
However, there were some problems in the teaching learning processes that might affect the implementation of the study. The main problem was time. There were some activities that consumed time more than that was allocated in the lesson plan. For example, students were coming late to class after taking a break. Therefore, students had not enough time to write the informal memo in the second meeting of the first cycle.
47 members who did not play the game also. Learning from the problem, the researcher planned to make the modification of the game.
The third problem was there were too many pictures flashed in flash pictures games. They made the students have difficulty in memorizing all the pictures and made them take a note of the pictures flashed by the teacher. Therefore, the researcher planned to flash three pictures in the second cycle.
The fourth problem was the paper that was used to write informal memos. The researcher gave A4 paper that hadno lines on it. It made the students’written texts untidy. It caused difficulties for the teachers to give the score to the students’ writing. In the second cycle, the researcher planned to give lined paper so the students would write tidier.
The fourth problem was the unclear flash pictures. They made the students have difficulties in observing those pictures. Therefore, in the second cycle, the researcher planned to print the pictures bigger than before and on separate papers.
The other problem was the students’ enthusiasm. Even though the
C. Research Findings in the First Cycle
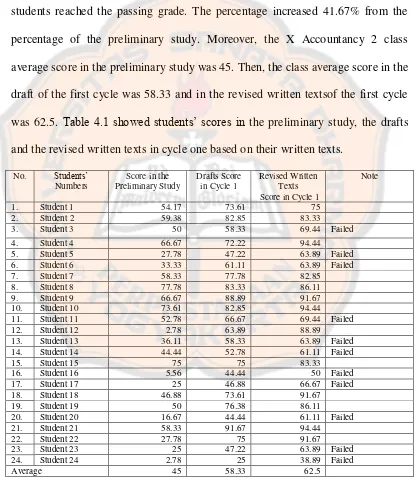
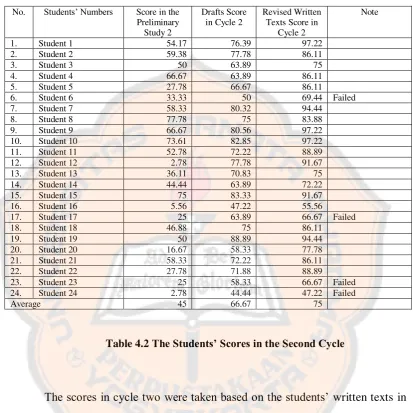
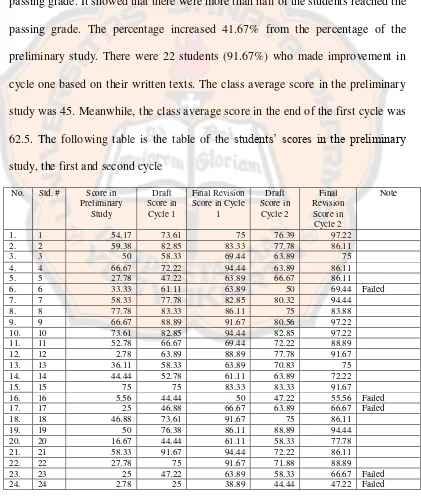
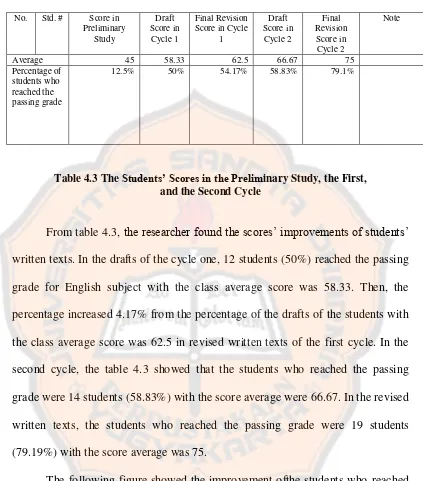
The result of the study in cycle one was13 out of 24 students (54.17%) reached the passing grade for English subject. The passing grade for English subject in SMK Putra Tama Bantul was 70. It showed that more than half of the students reached the passing grade. The percentage increased 41.67% from the percentage of the preliminary study. Moreover, the X Accountancy 2 class average score in the preliminary study was 45. Then, the class average score in the draft of the first cycle was 58.33 and in the revised written textsof the first cycle was 62.5. Table 4.1 showed students’ scores in the preliminary study, the drafts and the revised written texts in cycle one based on their written texts.
No. Students’