45 CHAPTER IV
FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter discussed the result of study. It consisted of the data finding and discussion. In data finding the research display the data which was found in the field and in discussion the researcher explained the type of error on narrative text and the cause of errors based on Heidi dulay’s theory.
A.Data Finding
Data collecting activity was conducted on 26th September, 2013. The sample was 25 students. The students were given a writing test. The data collected from the students were in form of essay. The researchers used inter rater in analyzing the writing products. There are total two examiners.
1. Types of Errors in Narrative Text Made by The Ninth Year Students of MTs Darul Amin Palangka Raya
Table 4.1
Identification and Classification of Errors Students’
code
Students’ errors
Revise Identify errors Explanation of errors Number of error Percentage of errors A1 Peas
scatter on the ground
Peas scattere d on the
ground
Omission Simple past tense incorrect Omission of –ed
1
A2 There were many kind dinosaurs There were many kind of dinosau rs
Omission Omission of
preposition
1
A3 he jumped out door
he jumped
out the door.
Omission Omission of the article
1
A4 By misty spring
By the misty spring
Omission Omission of the article
1
The cloud aren’t even what I think The clouds aren’t even what I think
Omission Failure to attach –s
1
A5 Rabbits lived in burrows the ground
Rabbits lived in burrow s in the
ground
Omission Omission of
preposition
1
A6 You have no soldier
You have no soldiers
Omission Failure to attach –s
1
A7 Sumatran tiger was smallest tiger The Sumatr an tiger was the smalles t tiger
Omission Omission of the article
A9 We doesn’t want to play with you We don’t want to play with you
Omission Disagreeme nt of subject and tense
1
A10 There were no spike on my body There were no spikes on my body
Omission Failure to attach –s
1
A11 by the misty spring.
by the misty springs
Omission Failure to attach –s
1
A12 Even smallest eagles. Even the smalles t eagles,
Omission Omission of the article
1
A13 They have no backbone They have no backbo nes
Omission Failure to attach –s
1
A14 He force himself into thinking He forced himself into thinkin g
Omission Omission of –ed
1
A16 Peas scatter on the
ground.
Peas scattere d on the ground.
Omission Omission of –ed
1
A17 But no brain
But no brains
Omission Failure to attach –s
1
A18 A reptile’s skin look slimy.
a reptile’ s skin
Omission Failure to attach –s
looks slimy, A19 Wolf
smacked his lips
The wolf smacke d his lips
Omission Omission of the article
1
A22 Golden eagles can be found in USA
Golden eagles can be found in the USA
Omission Omission of the article
1
A23 Dinosaurs were a type lizard
Dinosa urs were a type of lizard
Omission Omission of
preposition
1
A25 I’m bravest knight in your kingdom
I’m the bravest knight in your kingdo m
Omission Omission of the article
1
Total of Errors
20 51.28%
Students’ code
Students’ errors
Revise Identify errors Explanation of errors Number of error Percentage of errors A2 Dinosaurs
becomed extinct Dinosa urs became extinct Addition (regulari zation) Simple past tense incorrect Adding –ed to past already formed
1
23.07% A4 Tiger
shaked his head
Tiger shook his head
Addition Simple past tense incorrect Adding –ed to past already formed
1
A6 But taked out a leader
But took out a leader
Addition Simple past tense incorrect Adding –ed to past already formed
1
A10 Landy feeled lonely
Landy felt lonely
Addition Simple past tense incorrect Adding –ed to past already formed
1
A15 They were finded in every part They were found in every part
Addition Simple past tense incorrect Adding –ed to past already formed
1
A19 A wolf seed a goat grazing A wolf saw a goat grazing
Addition Simple past tense incorrect Adding –ed to past already
formed A21 Kodi seed
the crown behind the curtain Kodi saw the crown behind the curtain
Addition Simple past tense incorrect Adding –ed to past already formed
1
A24 He seed a frog
He saw a frog
Addition Simple past tense incorrect Adding –ed to past already formed
1
A25 A terrible dragon comed to the kingdom A terrible dragon came to the kingdo m
Addition Simple past tense incorrect Adding –ed to past already formed
1
A5 Rabbits lived in burrows the ground
Rabbits lived in burrow s in the
ground
Addition (simple addition)
Preposition 1 2.56%
Total of Errors
10 25.64%
Students’ code
Students’ errors
Revise Identify errors Explanation of errors Number of error Percentage of errors A2 There
were no tress in earth There were no tress on earth Misform ation Misuse of preposition 1
A4 Far off on the jungle Far off in the jungle Misform ation Misuse of preposition 1
A6 Gregor and him soldiers run away Gregor and his soldiers run away Misform ation Use of wrong possessive 1
A8 Some
jellyfish can glow on darkness Some jellyfis h can glow in darknes s Misform ation Use of wrong possessive 1
A9 No one
wanted to play with his No one wanted to play with him Misform ation Use of wrong possessive 1
A20 Kuku nodded him head Kuku nodded his head Misform ation Use of wrong possessive 1
A24 The scorpion remove him stinger The scorpio n remove his stinger Misform ation Use of wrong possessive 1
his basket
possessive
A16 Sat sadly
in a
branch
Sat sadly on a branch
Misform ation
Misuse of preposition
1
Total of Errors
9 23.07%
Based on the analysis result, the alternating forms misformation error occurred by 9 errors or 23.07% of total error. This result indicates that the students failed to use the correct word that totally different from the true one. The using of him in the sentence will make it ungrammatical in the deep structure.
Based on the table above the type of error frequency high to low are omission by 51.28%, addition by 25.63%, misformation by 23.07 and misordering by 0%. See the appendices for the detail of the analysis.
Figure 4.1
Types of Errors Made by the Students
51.28
25.63 23.07
0
Omission
Addition
Misformation
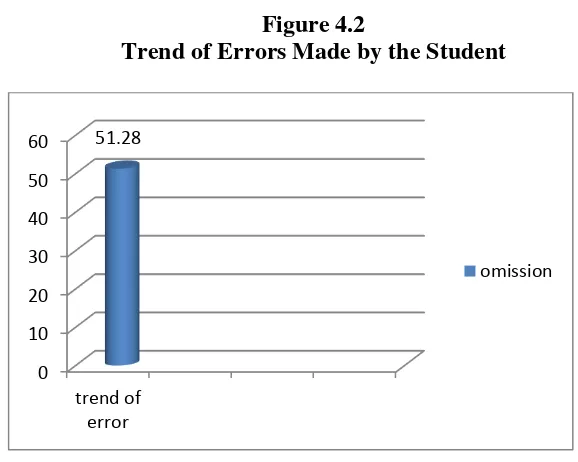
Based on the analysis result, the trend errors occurred by omission 51.28% of total errors. From the students’ writing products, the researcher found some of them omit several words in the sentences. The students wrote it by omitted such as articles, to be, and preposition. It is because they did not know the rules how to write the word in English. See the figure 4.2 for trend of errors made by the students was omission.
Figure 4.2
Trend of Errors Made by the Student
2. Cause of Errors in Narrative Text Made by The Ninth Year Students of MTs Darul Amin Palangka Raya
The students’ errors is classified into four categorizes based on the error
cause. Those are developmental, interlingual, ambiguous, and other errors.
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
trend of error
51.28
Table 4.2 Explanation of Errors Students’
Code Errors Cause of Errors
A1 Peas scatter on the ground Developmental Error
A3 He jumped out door Developmental Error
A4 By misty springs Developmental Error
A6 Gregor and him soldiers run away
Developmental Error
A7 Sumatran tiger was smallest
tiger Developmental Error
A9
We doesn’t want to play with you
Developmental Error
No one wanted to play with his
Developmental Error
A12 Even smallest eagles Developmental Error
A14 He force himself into thinking
Developmental Error
A16
Sat sadly in a branch Developmental Error A19 Wolf smacked his lips Developmental Error
A20
Kuku nodded him head Developmental Error A24 The scorpion remove him
stinger
Developmental Error
A25
He opened him basket Developmental Error A25 I’m bravest knight in your
Based on the analysis result, developmental error occurred by 38.46% of total error. This result indicated that some students are still learning the language and still in a phase where they learn English language like native speaker’s child learn the language. This cause of
errors was experienced by A25, A4, A3, A19, A12, A7, A9, A25, A20, A9, A6, A24, A1, A14 and A16 were the students who experienced this error.
Students’ Code
Errors Cause of Errors
A1 Peas scatter on the ground Interlingual Error
A2 Dinosaurs becomed extinct Interlingual Error
A4 Tiger shaked his head Interlingual Error
A6 But taked out a leader Interlingual Error
A10 Landy feeled lonely Interlingual Error
A14 He force himself into thinking
Interlingual Error
A15 They were finded in every part
Interlingual Error
A16 Peas scatter on the ground Interlingual Error
A19 A wolf seed a goat grazing Interlingual Error
A25 A terrible dragon comed to the kingdom
Interlingual Error
Based on the analysis result, interlingual error caused students’
errors by 28.20% of total error. It indicates some of the students are using their mother tongue language pattern in English writing. This cause of errors was experienced by A1, A24, A19, A2, A15, A6, A10, A25, A14, and A16 were the students who experienced this error.
Students’
Code Errors Cause of Errors
A2 There were no tress in earth Other Error
A2 There were many kind dinosaurs
Other Error
A4 Far off on the jungle Other Error
A5 Rabbits lived in burrows the
ground Other Error
A6 You have no soldier Other Error
A7 The cloud aren’t even what I think
Other Error
A11 By the misty spring Other Error
A13 They have no backbone Other Error
A16 Peas scattered in the ground Other Error
A18 A reptile’s skin look slimy. Other Error
A22 Golden eagles can be found
in USA Other Error
A23 Dinosaurs were a type lizard Other Error
Based on the analysis result, other errors caused students error by 33.33% of total error. It indicates that most of the students are making errors due to their misconception of English language. These errors can be solved by learning more about English rules in writing. This cause of errors was experienced by A18, A11, A23, A2, A7, A6, A5, A22, A16, A4, A2, A17 and A13 students. Other errors are the opposite of ambiguous errors. Those errors classified neither developmental nor interlingual.
Table 4.5
Calculation of cause of errors
Cause of Errors Number of Errors Percentage
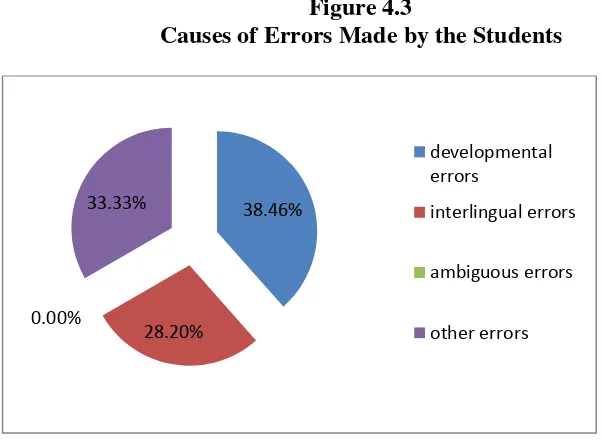
Developmental errors 15 38.46%
Interlingual Errors 11 28.20%
Ambiguous Errors 0 0.00%
Other Errors 13 33.33%
See the appendices for the detail of the analysis. Figure 4.3
Causes of Errors Made by the Students
Based on the table, developmental error occurred by 38.46% of total errors. The errors categorized as errors caused by developmental errors because the pattern of errors similar to the way of native speaker children learn their mother tongue language. Interlingual errors occurred by 28.20% of total error. This error categorized as errors caused by interlingual errors because the pattern of the sentences are similar to the pattern of the students’ mother tongue language. Other
errors occurred by 33.33% of total errors. The errors categorized as other errors because those errors couldn’t categorize neither developmental nor interlingual error.
38.46%
28.20% 0.00%
33.33%
developmental errors
interlingual errors
ambiguous errors
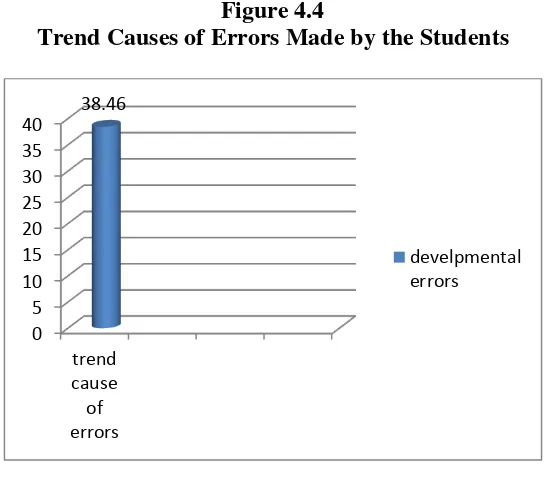
Based on the analysis result, the trend cause of errors occurred by the students was developmental error. The errors categorized as errors caused by developmental errors because the pattern of errors similar to the way of native speaker children learn their mother tongue language. See the figure 4.4 for trend cause of errors Made by the students was developmental error.
Figure 4.4
Trend Causes of Errors Made by the Students
a. Discussion
1. Types of Errors in Narrative Text Made by The Ninth Year Students of MTs Darul Amin Palangka Raya
Based on the description in the data presentation, there are several things that can be noted down. Most of the students still make errors in writing narrative paragraph. In this case, in analyzing the type of error made by the ninth year of MTs Darul Amin Palangka Raya, the writer
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
trend cause of errors
38.46
reffered to the theory recommended by Dulay that the error type based on surface strategy taxonomy. According to Dulay, a surface strategy taxonomy highlight the ways surface structured is alerted: learners may
omit necessary items or add unnecessary ones; they may misform items or
misorder them. There are four kinds of error 1) omission (content
mmorpheme, grammatical morpheme), 2) addition (double marking, simple
addition, regularization) 3) misformation (archi-forms, alternating forms,
regularization). 4) misordering.
In this study, the writer only found three kinds of error. There are omission, addition and misformation. According to the result of the
students’ product, the type of error frequency high to low are omission by
51.28%, addition by 25.63%, misformation by 23.07 and misordering by 0%.
2. Cause of Errors in Making Narrative Text Made by The Ninth Year Students of MTs Darul Amin Palangka Raya
In this case, in analyzing the cause of error made by the ninth year of MTs Darul Amin Palangka Raya, the writer reffered to the theory recommended by Dulay that the error type based on comparative taxonomy. According to Dulay, the classification of errors in a comparative taxonomy is based on comparisons between the structure of L2
errors and certain other types of constructions. This taxonomy classified
the learners’ error into developmental errors, interlingual errors,
ambiguous errors, and other errors.
In this study, the writer only found three kinds of error. There is developmental, interlingual and other error. According to the result of the students’ product, developmental error occurred by 38.46% of total errors.
The errors categorized as errors caused by developmental errors because the pattern of errors similar to the way of native speaker children learn their mother tongue language. Interlingual errors occurred by 28.20% of total error. This error categorized as errors caused by interlingual errors because the pattern of the sentences are similar to the pattern of the students’ mother tongue language. Other errors occurred by 33.33% of total errors. The errors categorized as other errors because those errors couldn’t