ENGLISH INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS
FOR THE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS
OF SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
A THESIS
Presented as Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements to Obtain the Sarjana Pendidikan Degree
in English Language Education
By
CLARA AURORA Student Number: 031214003
ENGLISH LANGUAGE EDUCATION STUDY PROGRAM DEPARTMENT OF LANGUAGE AND ARTS EDUCATION FACULTY OF TEACHERS TRAINING AND EDUCATION
A Thesis on
ENGLISH INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS FOR THE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS
OF SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
By
CLARA AURORA Student Number: 031214003
Approved by
Date Made Frida Yulia, S.Pd., M.Pd. 14 August, 2008 Major sponsor
A Thesis on
ENGLISH INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS FOR MECHANICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS
OF SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
By
CLARA AURORA Student Number: 031214003
Defended before the Board of Examiners on 22 August, 2008
and Declared Acceptable
Board of Examiners
Chairperson : A. Hardi Prasetyo, S.Pd., M.A. ____________________
Secretary : Made Frida Yulia, S.Pd., M.Pd. ____________________
Member : Made Frida Yulia, S.Pd., M.Pd. ____________________
Member : Christina Kristiyani, S.Pd., M.Pd. ____________________
Member : Carla Sih Prabandari, S.Pd., M.Hum. ____________________
Yogyakarta, 22 August, 2008
Faculty of Teachers Training and Education Sanata Dharma University
If your life seems to be going from bad to worse, sending you into depression and despair,
remember that God always hears and answers our cries, but IT’S IN HIS TIME, NOT OURS.
(Julie Ackerman Link)
*************
8
I would like to dedicate this thesis to:
God in Heaven My beloved parents
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY
I honestly declare that this thesis, which I wrote, does not contain the works or parts of the works of other people, except those cited in the quotations and the references, as a scientific paper should.
Yogyakarta, 14 August, 2008 The writer,
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN
PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH UNTUK KEPENTINGAN AKADEMIS
Yang bertanda tangan di bawah ini, saya mahasiswa Universitas Sanata Dharma :
Nama : Clara Aurora
Nomor Mahasiswa : 031214003
Demi pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan, saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma karya ilmiah saya yang berjudul :
ENGLISH INSTRUCTIONAL MATERIALS FOR THE MECHANICAL ENGINEERING STUDENTS
OF SANATA DHARMA UNIVERSITY
beserta perangkat yang diperlukan (bila ada). Dengan demikian saya memberikan kepada Perpustakaan Universitas Sanata Dharma hak untuk menyimpan, mengalihkan dalam bentuk media lain, mengelolanya dalam bentuk pangkalan data, mendistribusikan secara terbatas, dan mempublikasikannya di internet atau media lain untuk kepentingan akademis tanpa perlu meminta ijin dari saya maupun memberikan royalti kepada saya selama tetap mencantumkan nama saya sebagai penulis.
Demikian pernyataan ini yang saya buat dengan sebenarnya. Dibuat di Yogyakarta
Pada tanggal : 30 Agustus 2008
Yang menyatakan
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, I would like to express my deepest gratitude to the Almighty God. He always guides me through His way. I would thank Him especially for the strengths He gave me in getting through difficult moments in my life.
I am thankful to Made Frida Yulia, S.Pd., M.Pd., my major sponsor, and Christina Kristiyani, S.Pd., M.Pd., my co-sponsor, for their patience in guiding me to write my thesis. I would like to thank them for the corrections, suggestions, and criticism.
My deepest gratitude is addressed to C. Tutyandari, S.Pd., M.Pd., Yosef Agung Cahyanta, S.T., and Yeni Wulandari, S.Pd., who were willing to give comments and suggestions on my designed materials. I also thank my academic advisor, Drs. P. Garanim Purba, M.Pd., for giving me advice during my study. I would also like to appreciate all of the English Language Education Study Program lecturers, secretariat staff, and all of the librarians.
My sincere gratitude goes to Budi Sugiharto, S.T. M.T., the Chair Person of Mechanical Engineering Study Program, for permitting me to carry out my research. My special thanks go to the lecturers of Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University, Doddy Purwadianto, S.T., and Ir., F.A. Rusdi Sambada, M.T. I also thank all of Mechanical Engineering students of the academic year 2006 and 2004 and to the big family of Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University.
would like to thank them for allowing me to grow and learn many things together with them.
I would like to express my deepest gratitude to Dra. Sri Joeliantini and the big family of ALPA English Course, especially Yeni, Prima, Dian, Evalia, Eva, and Lita. I would like to thank them for allowing me to learn how to teach and to understand others. I would also like to appreciate them for giving me chance to develop myself, my teaching skill and my social skill.
My special gratitude goes to GenX-VanLith, especially Mitha, Maxi, Uya, Galih, Herlin, Seno, Abet, Sutaman, Resa, Esti, Dewer and Gaby. I want to express my gratitude to all of PBI-03ers, especially Nila, Nita, Arum, Indra, Dita, and Bagong. I thank my beloved friends in 9Che, especially Siska, Helmy, Paul, and Iin. I would thank frater Yuwono for the guidance of life. I would like to thank them for the time we shared together. They are the reason why I am here today.
I would like to express my deepest gratitude to Adi, for the love and hardship that bring me to be a strong and independent woman. May God always love us.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE ... i
APPROVAL PAGES... ii
DEDICATION PAGE ... iv
STATEMENT OF WORK’S ORIGINALITY... v
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS... vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS... ix
LIST OF FIGURES ... xii
LIST OF TABLES... xiii
ABSTRACT... xiv
ABSTRAK... xv
CHAPTER I: INTRODUCTION... 1
A. Background of the Study ... 1
B. Problem Formulation ... 4
C. Problem Limitation ... 4
D. Objectives of the Study... 5
E. Benefits of the Study... 6
F. Definition of Terms ... 7
CHAPTER II: REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ... 9
2. ESP... 13
a. The Characteristics of ESP ... 14
b. The Classification of ESP ... 16
c. Needs Analysis... 17
B. Theoretical Framework... 19
CHAPTER III: METHODOLOGY ... 23
A. Research Method ... 23
B. Research Participants... 26
C. Research Instruments ... 28
D. Data Gathering Technique ... 30
E. Data Analysis Technique ... 31
F. Research Procedures ... 34
CHAPTER IV: RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSIONS ... 36
A. The Steps of Designing Instructional Materials for the Mechanical Engineering Students of Sanata Dharma University ... 36
1. Analyze ... 36
2. Design ... 40
3. Evaluate ... 44
B. The Presentation of the Designed Instructional Materials... 48
CHAPTER V: CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS ... 51
REFERENCES ... 55
APPENDICES Appendix A : Surat Permohonan Ijin Penelitian... 56
Appendix B : Surat Keterangan... 57
Appendix C : The Questionnaire for Students... 58
Appendix D : The Interview Guideline ... 61
Appendix E : The Questionnaire for Teachers or Lecturers ... 62
Appendix F : The Results of the Questionnaire in Pre-Design Activities ... 64
Appendix G : The Designed Materials ... 66
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 2.1 : Kemp’s Instructional Design Model ... 12
Figure 2.2 : The Branch of ELT ... 15
Figure 2.3 : The Branch of EST... 15
LIST OF TABLES
Table 2.1 : Necessities, Lacks, and Wants... 14
Table 3.1 : Respondents of the Survey on the Designed Materials ... 26
Table 3.2 : Points of Agreement of the Respondents’ Opinion ... 30
Table 3.3 : Descriptive Data of the Respondents’ Opinion ... 31
Table 4.1 : The Necessities, Lacks, and Wants of the Mechanical Engineering Students of Sanata Dharma University... 38
Table 4.2 : The Topics and the Basic Competencies ... 39
Table 4.3 : The Topics and the Indicators... 40
Table 4.4 : The Data of the Respondents’ Opinions... 43
ABSTRACT
Aurora, Clara. 2008. English Instructional Materials for the Mechanical Engineering Students of Sanata Dharma University. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
The needs of English keep growing because many people use English to communicate and to carry out their business. Mechanical Engineering students of Sanata Dharma University are one of the examples. They need to master spoken and written English in order to survive during their study and in the working world. Unfortunately, English subject is not included yet in the curriculum of Mechanical Engineering study program of Sanata Dharma University; instead, TOEFL was the requirement for the students to conduct Thesis defense. Yet, TOEFL test will not be able to develop the students’ English in the Mechanical Engineering area. The unsuccessful policy of requiring TOEFL test to measure the students’ English ability motivates the study program to establish an English subject that will accommodate the students’ needs in mastering English in mechanical Engineering area. However, the establishment of an English subject brings the study program to a new problem, inexistence of the English instructional materials. Therefore, in this research, the writer intended to design instructional materials for the students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. There were two problems solved in this study: 1) How are English Instructional Materials for the students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University designed? 2) What do the designed English Instructional Materials for the students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University look like?
To answer those two questions, the writer employed Educational Research and Development (R & D) method. Pre-design activities were conducted in gathering the data to develop the materials. Questionnaire and interview guideline were used in pre-design activities to obtain data around the students needs and interests. The data obtained in pre-design activities were used as the basic information in developing the instructional materials. To evaluate the materials, post-design activities were conducted. In the post-design activities, questionnaire was used to obtain criticism, feedback, and comments on the designed materials.
In order to answer the first question, the writer adapted Kemp’s model. She simplified the model into three steps, they were (1) analyze, (2) design, and (3) evaluate. In the first step, learners’ characteristics were analyzed. Based on that information, instructional materials were designed. Then they were evaluated and revised. To answer the second questions, the writer presented the final version of the designed materials after making some revisions and improvements based on the result of the research in post-design activities. There were eight units in the designed materials. Each unit consists of seven activities, namely “Let’s Review” “Browse Your Idea”, “New Stuffs”, “Sharpen Your Skill”, “Language Focus”, “Act Up”, and “Let’s Conclude”.
ABSTRAK
Aurora, Clara. 2008. English Instructional Materials for the Mechanical Engineering Students of Sanata Dharma University. Yogyakarta: English Language Education Study Program, Sanata Dharma University.
Kebutuhan akan Bahasa Inggris semakin meningkat karena semakin banyak orang yang menggunakan Bahasa Inggris untuk berkomunikasi dan untuk menjalankan bisnisnya. Mahasiswa program studi Teknik Mesin adalah salah satu contohnya. Mereka perlu menguasai Bahasa Inggris dalam bentuk lisan dan tertulis agar dapat berhasil selama masa studinya dan di dunia kerja nantinya. Sayangnya, mata kuliah Bahasa Inggris belum termasuk didalam kurikulum program studi Teknik Mesin, sebaliknya, TOEFL diwajibkan bagi siswa sebagai prasyarat untuk dapat menempuh Ujian Tugas Akhir. Sayangnya, tes TOEFL tidak dapat membantu siswa untuk mengembangkan kemampuan Bahasa Inggris khususnya di bidang Teknik Mesin. Gagalnya kebijakan yang menggunakan TOEFL sebagai alat untuk mengukur kemampuan berbahasa Inggris siswa, memotivasi program studi untuk menyelenggarakan mata kuliah bahasa Inggris yang dapat mengakomodasi kebutuhan siswa untuk menguasai bahasa Inggris di bidang Teknik Mesin. Penyelenggaraan mata kuliah bahasa Inggris ini membawa masalah baru bagi program studi, yaitu ketiadaan materi. Oleh karena itu, melalui studi ini penulis bermaksud untuk merancang materi untuk pelajaran bahasa Inggris bagi mahasiswa program studi Teknik Mesin Universitas Sanata Dharma. Ada dua masalah yang dianalisa dalam studi ini: 1) Bagaimana materi untuk pelajaran bahasa Inggris bagi mahasiswa program studi Teknik Mesin Universitas Sanata Dharma dirancang? 2) Seperti apakah rancangan materi untuk pelajaran bahasa Inggris bagi mahasiswa program studi Teknik Mesin Universitas Sanata Dharma?
Untuk menjawab dua permasalahan tersebut, penulis menggunakan metode educational research and development (R & D). Aktivitas sebelum perancangan materi dilaksanakan untuk mengumpulkan data yang digunakan untuk merancang materi. Kuesioner dan panduan wawancara digunakan ditahap sebelum perancangan untuk memperoleh data seputar kebutuhan dan minat siswa. Data yang diperoleh ditahap sebelum perancangan digunakan sebagai dasar untuk menyusun materi. Untuk mengevaluasi materi, aktivitas seletah perancangan dilaksanakan. Ditahap setelah perancangan, kuesioner digunakan untuk memperoleh kritik, masukan, dan komentar tentang materi yang telah dususun.
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
In this chapter, the writer would like to discuss the background, problem formulation, problem limitation, objectives of the study, benefits of the study, and definition of terms which are employed in this study.
A. Background of the Study
The development of world has brought many effects in scientific, technical, and economic activities on international scale. As a result, trade and commerce dominate the world. This domination causes a demand on an international language that will enable people who speak different languages and who wish to carry out trade to communicate. English then obtains its role as an international language. The needs of English keep growing because many people use English to communicate and to carry out their business. People who share the same knowledge and skill also find that it is necessary for them to develop language in their own area so that they will be able to communicate effectively, precisely, and accurately. Hutchinson and Waters (1994: 6) stated:
More people know why they have to learn the language such as, businessmen and women who wanted to sell their product; mechanics who had to read instructions manuals; doctors who needed to keep up with developments in their field and whole range of students whose course of study included textbooks and journals only available in English.
Engineering students of Sanata Dharma University are one of the examples. They need to master spoken and written English in order to survive in the working world. Students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program often need to read textbooks and journals which are available in English. When they graduate, they will need to cope with the working world in which interaction with foreigners is often required. They have to read instructions manuals and they also have to keep up with developments of their profession. For Mechanical Engineering students, English mastery is required in order to enable the graduates to communicate in English when they face the working world. Therefore, English proficiency especially English in Mechanical Engineering area is the key for the students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University to survive in this developing working world. Better English ability is also their key to success. Machines mostly come from abroad; the manuals and textbooks are mostly written in English. Therefore, it is important for the Mechanical Engineering students of Sanata Dharma University to master English skill, especially reading skill, to enable them to read English textbooks and thus to support their study.
program. However, mastery of English cannot be achieved only by conducting TOEFL test. Mastery of language, in this case English, can only be achieved by practicing it actively. Though the requirement gives a good indication that the study program expects the students to conduct their own independent English study as the preparation to conduct the TOEFL test, many students, unfortunately, are not willing to do so. It is common for the students to cheat in the TOEFL test. Somehow they can obtain the answer key to the test. They prefer relying on that answer key to conduct the TOEFL preparation course.
The unsuccessful policy of requiring TOEFL test to measure the students’ English ability motivated the study program to establish an English subject that will accommodate the students’ needs in mastering their English in the area of Mechanics. The English subject is going to be a compulsory subject for the third semester students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program. Unfortunately, the establishment of an English subject brings the study program to a new problem, inexistence of the English instructional materials. Therefore, the writer tries to design instructional materials for the students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University so that it can be used in developing their English skill. Through the research, it is hoped that the English instructional materials would help the students in mastering English language and thus to achieve English proficiency especially in the area of Mechanics.
world without having English proficiency. Thus, it is highly important for the students to be equipped with English proficiency that will be useful both during their study and in their future working world. The writer’s focus is on designing the English instructional materials for the third semester students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. Hopefully, the English instructional materials can give contribution to the study program in developing English course which can facilitate the students in developing their English. Therefore the Study Program will be able to measure the students’ English ability by observing the progress they made in the English course.
B. Problem Formulation
Considering the previous explanation, there are two problems to be solved in the research:
1. How are the English Instructional Materials for the students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University designed?
2. What do the designed English Instructional Materials for the students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University look like?
C. Problem Limitation
semester students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. The writer chose Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University because she wanted to give contribution to that study program. The unsuccessful situation in which TOEFL was required to replace the English subject motivated the writer to design English Instructional Materials for the Mechanical Engineering students of Sanata Dharma University. It is known that students cannot develop their English in Mechanical Engineering area through TOEFL. Moreover, the establishment of an English subject needs to be supported by instructional materials which can develop the students’ needs of English. The third semester students were chosen due to the reason that the students still remember Basic English, which is very important to develop English around the Mechanical Engineering area. Another reason was to help the students in conducting their study by giving English in their early year. Therefore, the students will be able to read books and journals that are written in English. Besides, students will be ready to face the working world since they are already equipped with English from the beginning of their study. It is hoped that through this English Instructional Materials students can be facilitated in developing their English. However, this study focuses only on designing the materials and is not intended to be an experimental study.
D. Objectives of the Study
1. To find out how the English Instructional Materials for the students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University are designed.
2. To provide the students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University with the English Instructional Materials that would encourage them to develop their language skills and proficiency in Mechanics area.
E. Benefits of the Study
It is expected that the study may give some benefits to the students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University, the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University, and to future researchers.
1. to the students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University
2. to the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University The designed materials can give the solution to the problem when the study program establishes an English subject. Instead of requiring the students to join the TOEFL test, the Mechanical Engineering Study Program can develop the students’ ability in English through the designed English instructional materials. The study program can also facilitate the students to achieve English language proficiency.
3. to future researchers
It is hoped that the results of this study can be used as a reference to support future relevant studies done by other researchers.
F. Definition of Terms
There are two terms which are used in this study. They are instructional materials and Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University.
1. Instructional Materials
2. Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
There are two topics that will be discussed in this chapter. The two topics are theoretical description and theoretical framework.
A. Theoretical Description
There are two topics of theoretical description that are discussed in this study. The first one is related to instructional design models that will be used in designing the instructional materials and the other one is related to the theory of ESP.
1. Instructional Design Model
There are many models of design available to be used by a designer. However, in designing English Instructional Materials for Mechanical Engineering students of Sanata Dharma University, the writer uses Kemp’s Instructional Design Model.
According to Kemp (1977: 8), “the instructional design plan is designed to answer the three questions that may be considered the essential elements of instructional technology.” The questions are:
a. What must be learned? (objectives)
b. What procedures and resources will work best to reach the desired learning level? (activities and resources)
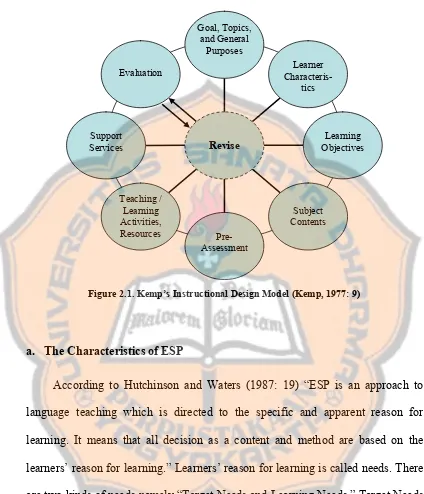
Kemp’s model consists of eight parts, namely consider goals, list topics, and state the general purposes for teaching each topic; enumerate the important characteristics of the learners for whom the instruction is to be designed; specify the learning objectives to be achieved in terms of measurable student behavioral outcomes; list the subject content that supports each objective; select teaching learning activities and instructional resources that will treat the subject content so that the students will accomplish the objectives; coordinate such support services as budget, personnel, facilities, equipment, and schedules to carry out the instructional plan; and evaluate student’s learning in terms of their accomplishment of objectives, with a view to revising and reevaluating any phases of the plan that need improvement (Kemp, 1977: 9). The explanation of each part is as follows.
a. Consider goals, list topics, and state the general purposes for teaching each topic.
In this first step, a course designer has to formulate goals. After the goals are formulated, topics are selected and arranged. The designer has to arrange the topics started from the simple or concrete levels to the complex or abstracts level. Then, general purposes for the selected topics should also be determined.
b. Enumerate the important characteristics of the learners for whom the instruction is to be designed.
learners’ characteristics; they are academic factors, such as number of learners, academic background, level of intelligence, reading level, scores on standardized achievement, etc; and social factors, such as age, maturity, attention span, special talents, relations among students, and many others. A designer should still consider some other factor in identifying the learners’ characteristics. Other factors that are also important in planning an instruction are learning conditions and learning styles. Learning conditions are the conditions which influence the ability of the learners to concentrate, absorb, and retain information. Meanwhile, learning styles are the method that the learners use in learning. Different students have different method in learning, some students might feel it more effective to use visual approach, and other students might find it easy to learn by using verbal approach, the other students might enjoy learning through experiences.
c. Specify the learning objectives to be achieved in terms of measurable student behavioral outcomes.
accomplishment. At last the course designer has to add with any criteria or conditions under which the learning must take place.
d. List the subject content that supports each objective.
There are two procedures that can be used in listing the subject content. Course designer can either list the subject content first to formulate the learning objectives, or stating the objectives first and then listing the subject content. The course designer can choose one of the procedures that is appropriate to the situation. Subject content in this instructional design plan refers to the selection and organization of the specific knowledge (facts and information), skills (step-by-step procedures, conditions, and requirements), and attitudinal factors of any topic.
e. Develop pre-assessments to determine the student’s background and present level of knowledge about the topic.
This step is done in order to plan learning activities for which the learners are prepared. It is also carried out to make sure that the learners do not waste their time to study things that they have known. There are two kinds of test that can be used in assessing the students, namely Prerequisite Test and Pretest.
f. Select teaching learning activities and instructional resources that will treat the subject content so that the students will accomplish the objectives.
course designer has to know the strengths and weaknesses of the methods in order to be able to select the appropriate method for the learners.
g. Coordinate such support services as budget, personnel, facilities, equipment, and schedules to carry out the instructional plan.
In planning an instruction, support services should be considered carefully. Support services can include budget, facilities, equipment, time, schedule, and also coordination with other activities. This has to be done so that the education program can be done smoothly and successfully.
h. Evaluate students’ learning in terms of their accomplishment of objectives, with a view to revising and reevaluating any phases of the plan that need improvement.
Evaluation is carried out in order to seek out how far the learners have achieved the objectives and also the goals of the educational program itself. It is also intended to improve the instructional plan itself. Therefore, if the objectives and goals have not been achieved, designers can revise and improve the instructional plan.
Kemp’s instructional design model is shown in Figure 2.1.
2. ESP
Evaluation
Support Services
Teaching / Learning Activities,
Resources Pre-Assessment
Subject Contents
Learning Objectives Learner
Characteris-tics Goal, Topics,
and General Purposes
Revise
Figure 2.1. Kemp’s Instructional Design Model (Kemp, 1977: 9)
a. The Characteristics of ESP
According to Hutchinson and Waters (1987: 19) “ESP is an approach to language teaching which is directed to the specific and apparent reason for learning. It means that all decision as a content and method are based on the learners’ reason for learning.” Learners’ reason for learning is called needs. There are two kinds of needs namely “Target Needs and Learning Needs.” Target Needs are what the learners need to do in the target situation. Meanwhile, Learning Needs are what the learners need to do in order to learn.
Instructional Materials for Mechanical Engineering students of Sanata Dharma University. Hutchinson and Waters (1987: 55-58) offer three terms of target needs, namely necessities, lacks, and wants.
1) Necessities: They are the type of needs that are influenced by the target situation. Necessities are things that the learner has to know in order to be able to use the language in the target situation.
2) Lacks: They are the gap between target proficiency and the learner’s existing proficiency. Therefore, it is important to seek out what the learners already know in order to be able to measure the gap with the target proficiency.
3) Wants: They are the needs from the learners’ point of view. It is important to consider the learners’ view or perception about their needs.
Table 2.1. Necessities, Lacks, and Wants (Hutchinson and Waters, 1987: 58) OBJECTIVE
(as perceived by the course designers)
SUBJECTIVE
(as perceived by learners) NECESSITIES The English needed for success in
Agricultural or Veterinary Studies
To reluctantly cope with a “second-best” situation LACKS (Presumably) areas of English
needed for Agricultural or Veterinary Studies
Means of doing Medical studies
WANTS To succeed in Agricultural or Veterinary Studies
To undertake Medical Studies
Language, which is also known as General English? The difference between ESP and General English (GE) is described in http://www.usingenglish.com/articles/ teaching-english-specialpurposes.html as follows:
The most important difference lies in the learners and their purposes for learning English. ESP students are usually adults who already have learned English before and are learning the language in order to be able to communicate well to perform particular job-related functions. An ESP program is therefore built on needs. The ESP focus is that English is not taught as a subject separated from the students' real world. ESP is integrated into a subject matter area which is important to the learners.
b. The Classification of ESP
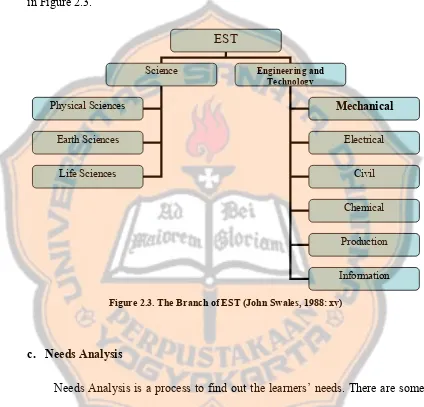
English Instructional Materials for Mechanical Engineering students of Sanata Dharma University can be included as a part in English for Science and Technology (EST). EST is the branch of English for Specific Purposes (ESP). The relationship between EST and ESP is shown in Figure 2.2.
English Language Teaching
(EMT) English as a Mother Tongue
(EFL) English as a Foreign Language
(ESL) English as a Second Language
(ESP)
English for Specific Purposes
(GE) General English (EST) English for Science and (EBE) English for Business and (ESS) English for Social
Sciences
The term of Mechanical Engineering students refers to the students who have been studying about Mechanical Engineering subject. Mechanical Engineering itself is a part of science and technology globally. It is clearly stated in Figure 2.3.
EST
Science Engineering and Technology
Mechanical
Electrical
Civil
Chemical
Production
Information Physical Sciences
Earth Sciences
Life Sciences
Figure 2.3. The Branch of EST (John Swales, 1988: xv)
c. Needs Analysis
1) Why is the language needed?
Firstly, a course designer needs to know why the language is needed by the learners. The course designer has to know whether the language is for study, work, training, or for some other purposes.
2) How will the language be used?
Next, the course designer needs to seek out how the language will be used. Will the language be used for medium use of speaking, reading, or writing? Will it be used through the channel of telephone or in a face to face interaction? Will the language be used in a lecture, informal conversation, academic texts, technical manuals, or catalogues?
3) What will the content areas be?
Content areas should also be known. A course designer needs to know whether the content areas will be about medicine, biology, architecture, shipping, commerce, or engineering. Furthermore, the course designer should know the level of the learners whether they are technician, craftsman, postgraduate, or secondary school.
4) Whom will the learner use the language with?
5) Where will the language be used?
Physical setting where the language will be used also needs to be considered carefully. A course designer needs to consider in which physical setting the language will be used. Will it be used in the office, lecture, theatre, hotel, workshop, or library? In which human context the language will be used. Will the language be used alone, in meetings, demonstrations, on telephone? In which linguistic context the language will be used. Will the language be used in own country or abroad?
6) When will the language be used?
A course designer should also consider about when the language will be used. Will the language be used concurrently with the ESP course or subsequently? Will it be used frequently? Will it be used in small or in large amounts?
B. Theoretical Framework
Kemp’s model. The model is simplified into three steps. They are analyze, design, and evaluate. The explanation of each step is as follows.
1. Analyze
In this first step the designer analyze the Mechanical Engineering students’ characteristics.
2. Design
In the second step, goals and learning objectives are developed by choosing an instructional approach, considering and then listing topics, and stating the general purposes for teaching each topic. Learning objectives are specified in this step. In this step, teaching learning activities and instructional resources that will help the students to accomplish the objectives are also selected.
3. Evaluate
In the last step, evaluation is conducted. However, evaluation in this study refers to the evaluation of the instructional materials to determine the suitability of the materials towards the students’ needs. The result of the evaluation will be used to revise any phases of the plan that need improvement.
Analyze
Design
Evaluate
Revise
CHAPTER III METHODOLOGY
This chapter discusses the method that was employed in the study. The discussion of this chapter includes research method, research participants, research instruments, data gathering technique, data analysis technique, and research procedure.
A. Research Method
Borg and Gall (1983: 772) claim that Educational research and development (R & D) is, “a process used to develop and validate educational products.” R & D cycle consists of ten steps. The steps of R & D cycle consists of (1) research and information collecting, (2) planning, (3) developing, (4) preliminary field testing, (5) main product revision, (6) main field testing, (7) operational product revision, (8) operational field testing, (9) final product revision, and (10) dissemination and implementation.
In this study the writer would refer to Borg and Gall’s steps. However, not all steps were employed due to time and place limitation. The writer employed only step 1 to step 5. The first step was named into Pre-Design Activities. She titled the second and third steps as Design Activities, then, she combined the rest of the steps into Post- Design Activities.
To enable the researcher to develop the materials, data of students’ needs and interests were needed as the basic information. Therefore, pre-design activities were conducted in gathering the data on the respondents’ needs and interests. Since evaluations, criticisms, feedback, and comments were also needed in improving the designed materials, another survey was conducted in the research. Thus, post-design activities (evaluation survey) were conducted to help the writer in gathering evaluations, criticisms, feedback, and comments on the designed materials from the respondents.
1. Pre-Design Activities
1 of R & D cycle, research and information collecting, which aimed to find out the learners’ interest and needs. In seeking for the learners’ interest and needs in learning English, questionnaire and interview were used. The questionnaire was distributed to the third semester and the seventh semester students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. The Chair Person of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University was interviewed to enrich the data around the needs of the students. The data obtained from this first part of research, both from the questionnaire and the interview, were used as the basic information in developing the instructional materials.
2. Design Activity
Based on the data found from the questionnaire and the interview, the writer designed English Instructional Materials for the students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. This activity was in accordance with the second and the third step of R & D cycle, planning and developing preliminary form of product.
3. Post-Design Activities
Study Program of Sanata Dharma University, one lecturer of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University, and one English Instructor in a private English Course. The respondents were chosen in order to enrich the researcher with evaluations, criticisms, feedback, and comments on the designed materials.
B. Research Participants
This section describes the respondents of pre-design activities and post-design activities.
1. Pre-Design Activities
In pre-design activities questionnaire was distributed to collect the data about the students’ needs and interests in learning English. The respondents of the pre-design activities were the third semester and the seventh semester students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. The sample of the third semester students were the students in Material class group A. Meanwhile, the sample of the seventh semester students were the students in Tenaga Surya class group A. The total number of the students was 55. The two groups of students were chosen due to the necessity of knowing needs of English from the students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program to achieve the understanding of overall needs of the students.
students were chosen because they were the target students whom the English subject is going to be obliged for.
Meanwhile, the seventh semester students were chosen since they had enough experience in learning in the study program; therefore they understood their needs, interests, and learning styles. In addition, the seventh semester students were also known for their being aware of the working world. They have a better awareness toward the necessity of mastering English to equip themselves in order to compete in the working world.
In order to enrich the data around the students needs from point of view of the study program, the Chair Person of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University was interviewed. He was chosen as the respondent because he understood the students’ needs. Moreover, he also knew about the purpose of establishing English subject itself.
2. Post-Design Activities
instructional materials. Respondents’ description of the post-design survey research was presented in Table 3.1.
C. Research Instruments
There were two instruments that were employed in the study. They were interview and questionnaire
Table 3.1. Respondents of the Survey on the Designed Materials
Educational Background
Teaching Experience (in year) Group of Respondents
D3 S1 S2 1-5 6-10 11-15 16-20 21-25 > 26
English Lecturer 1 1
Mechanical Engineering
Lecturer 1 1
English Teacher 1 1
1. Interview Guideline
Interview guideline was used in pre-design survey research. The interview functioned as the enrichment instrument. The Chair Person of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program was interviewed in order to obtain more information about the students’ needs in learning English and also to clarify the purpose of establishing English subject in the Study Program. The interview guideline is presented in Appendix D.
2. Questionnaires
was distributed to the third semester and the seventh semester students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. The sample of the third semester students were the students in Material class group A. Meanwhile, the sample of the seventh semester students were the students in Tenaga Surya class group A. The questionnaire in this first part of research was written in Indonesian. The purpose was to make the students understand the meaning of the questions well so that they could answer the questions appropriately. It contained both closed-ended questions and open-ended question. In part I which contained closed-ended questions, the respondents should choose the answer from the provided options. In part II which contained open-ended question about the topics they wish to learn the respondents could answer the questions and elaborate their answer freely. Therefore the questionnaire led the researcher to the understanding of the students’ needs and interests in learning English. The questionnaire used in the pre-design activities is presented in Appendix C.
questionnaire was distributed to one lecturer of the English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University, one lecturer of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University, and one English Instructor in a private English Course. It aimed to obtain rich evaluations, criticisms, feedback, and comments on the designed materials. The questionnaire used in the post-design activities is presented in Appendix E.
D. Data Gathering Technique
In the post-design activities, the questionnaire was distributed to one lecturer of the English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University, one lecturer of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University, and one English Instructor in a private English Course. Two weeks later, the writer met them to take the questionnaire that had been filled in to be analyzed. The results were used to revise and improve the designed materials.
E. Data Analysis Technique
There are two important points that will be discussed in this part. They are data analysis technique of the pre-design activities and data analysis technique of post-design activities.
1. Data Analysis Technique of Pre-Design Activities
In analyzing the data obtained from pre-design activities, the writer identified the needs and interest of the learners gained from Part I of the questionnaire employed in pre-design activities by using the percentage calculation method. The answers in the questionnaire were analyzed in order to understand the students’ needs and interests in learning English. The formula of the percentage calculation method is:
% 100 N
n
×
The data analysis from Part I and Part II of the questionnaire employed in the pre-design activities led the writer to the understanding of the learners’ needs and interest in learning English. Additional data collected from the interview were used to enrich the data from the questionnaire. The results were used as the basis to design the English Instructional Materials for the Mechanical Engineering students of Sanata Dharma University.
2. Data Analysis Technique of Post-Design Activities
In the post-design activities, the writer obtained the evaluation and feedback from one lecturer of the English Language Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University, one lecturer of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University, and one English Instructor in a private English Course by using the second questionnaire. In the post-design activities, Likert Scale was used in part I to enable the respondents to give their opinions on the designed set of materials. Points of agreement of the Likert Scale were described in Table 3.2.
Table 3.2. Points of Agreement of the Respondents’ Opinions
Points of Agreement
Meaning
1 if the respondents strongly disagree with the statement 2 if the respondents disagree with the statement
3 if the respondents neither disagree / agree with the statement 4 if the respondents agree with the statement
The data obtained in Part I of the questionnaire employed in the post-design activities were analyzed by using the central tendency (mean) of the respondents’ opinion on the designed materials. The result of the analysis of part I in the post-design activities was presented in Table 3.3.
Table 3.3. Descriptive Data of the Respondents’ Opinions (Blank)
Central Tendency
No Respondents’ Opinion on N Mean
The formula to analyze the points of agreement is written as follows:
N x
∑ = Χ
Note: Χ = mean x
∑ = the sum of values
N = the total number of values
F. Research Procedure
The research activities were divided into three major parts. They were pre-design activities, pre-design activities, and post-pre-design activities. Those three parts were in accordance with the five steps in R & D cycle.
1. Pre-Design Activities
First of all, the writer constructed the first questionnaire and a guideline for the interview. Then, the writer conducted the pre-design activities that were designed to collect the data about the students’ needs and interest in learning English, by distributing the questionnaire to the third semester students and the seventh semester students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. These activities were in accordance with the first step in R & D cycle (research and information collecting). Besides, the writer also interviewed the Chair Person of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program to enrich the data around the students needs. The information from both questionnaire and interview was analyzed and then was used to develop the English Instructional Materials that suit to the needs and interests of the students.
2. Design Activities
3. Post-Design Activities
CHAPTER IV
RESEARCH FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
This chapter consists of two parts. The first part is the steps of designing English instructional materials for Mechanical Engineering Students of Sanata Dharma University. This part answers the first question in the problem formulation. The second part is the presentation of the designed instructional materials for Mechanical Engineering Students of Sanata Dharma University. It answers the second question in the problem formulation.
A. The Steps of Designing Instructional Materials for Mechanical Engineering Students of Sanata Dharma University
Based on the data found from the questionnaire and the interview in the post-design activities, the writer designed English Instructional Materials for the students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. This activity was in accordance with the second step of R & D cycle, design. In designing the instructional materials for Mechanical Engineering Students of Sanata Dharma University, the writer applied three instructional design steps. The steps were analyze, design, and evaluate. Each of the steps will be discussed as follows.
1. Analyze
conducted by distributing questionnaire to the third semester students and the seventh semester students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. The questionnaire was distributed on 31 August 2007 and 4 September 2007. On 31 August 2007, the writer distributed the questionnaire to the third semester students in Material class group A. Then on 4 September 2007, the questionnaire was distributed to the seventh semester students in Tenaga Surya class group A. In order to obtain additional information about the learner characteristics, needs, lacks, and wants the writer conducted an interview with the Chair Person of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program on 24 August 2007.
There were eleven questions that should be answered by the students of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University in the questionnaire of the pre-design activities. In the first section of the questionnaire, the students gave their answer by crossing the choices based on their opinions. For the second section, the students wrote their answer in short sentences. Data from the first section were analyzed using percentage method. The detailed results of the questionnaire are presented in Appendix F but the general results are as follows.
ninth semester students (9%). Almost all of the students in this study program were male. The fact that most of the students in the Mechanical Engineering Study Program were male influenced the formality of the language they choose for daily speaking. They normally used informal language when they spoke to their peers. They sometimes used Indonesian while most of the time they used Javanese.
Most of the participants (96%) learned English during their SMU only. Only two respondents (4%) had once learned English during their study in the University. Therefore, it could be concluded that their level of English was still in the beginner level. Considering on the importance of English, 37 participants (67%) also stated that English was very important to support their future job. Therefore, they felt that they need to improve their English. There were 53 participants (96%) who wanted to improve their English. The rest, which was two students (4%), felt that they did not need to improve their English.
From the questionnaire it was found that the participants were enthusiastic in joining an English class. Thirty-one of them (56%) claimed that thay joined an English lecture because they wanted to improve their English. The participants wanted to improve their English because they need English proficiency that would enable them to read English textbooks. The writer found that there were 41 participants (76%) who often learned English materials from the textbooks.
participants (22%) chose role play, ten participants (18%) suggested presentation, eight participants (15%) preferred drama, and four participants (7%) chose lecture as the activity in the English class. The participants also gave their ideas on the media that they wanted to use in the English class. They wanted to use media such as TV, Radio, and Tape Recorder in learning English. The participants also gave a list of the subjects that they wanted to learn. They were: explaining how a machine works, describing a chart, English conversation, writing job application letter, grammar, the latest technology, and verb formation.
In the interview guideline, the writer prepared seven questions to be answered by the respondent. The writer obtained some additional data. They were: 1) The background why the study program is going to establish English subject was due to the ineffectiveness of TOEFL. So far, the study program obliged the students to reach certain TOEFL score for them to able to conduct the Final Examination (thesis) with the expectation that the students would be willing to conduct independent learning to improve their TOEFL score. Unfortunately, the students were not initiative enough. They neither joined TOEFL preparation course held by the university nor conducted independent learning. As a result, the students could pass the TOEFL but with a very low score.
3) English was very important for the students since they needed it for reading references that were available in English. Moreover, in their future job they would be dealing with manuals which were mostly written in English.
4) So far the methods that were employed in Mechanical Engineering classes were lecture, presentation, and discussion. Too often, there were only some students who actively participate during the discussion.
Seeing the facts, the students really needed to be facilitated in developing their English. The necessities, wants, and lacks obtained from the pre-design activities were analyzed using the target needs analysis by Hutchison and Waters to give clear information. It is presented in Table 4.1.
2. Design
As it has been mentioned in the problem formulation in Chapter I, this study focused on designing English instructional materials for Mechanical Engineering students of Sanata Dharma University. Thus, the topics of the instructional were designed to suit the students’ characteristics, needs, lacks, and wants. They were:
a. Describing procedure b. Giving instruction c. Describing chart d. Apology
e. Describing Thing
Table 4.1. The Necessities, Lacks, and Wants
of Mechanical Engineering Students of Sanata Dharma University
OBJECTIVE
(stated by the writer)
SUBJECTIVE
(stated by the Mechanical Engineering students) NECESSITIES The English that is needed to be
successful in Mechanical Engineering study and in working world
The English that is needed to read English references around Mechanical Engineering area LACKS English skills in Mechanical
Engineering area
English vocabulary around Mechanical Engineering area
WANTS To be communicatively competent in English in the intermediate level
To be able to read English references and to prepare for the future job
The Competence Standard of this course was that the students were expected to be able to communicate in English. Furthermore, the Basic Competencies are presented in Table 4.2.
Table 4.2. The Topics and the Basic Competencies
Unit Topic Basic Competencies
1 How to Use a Machine The students are able to describe a procedure in written form.
2 How a Machine Works 3 The Four-Stroke Cycle
The students are able to describe a procedure orally and in written form.
4 Rubber Plug Method of Tubeless Tire Repair
The students are able to give instruction orally and in written form.
5 Chart of a Compression Process
The students are able to describe a chart orally and in written form.
6 Phoning a Garage The students are able to apologize appropriately.
7 Hybrid Car The students are able to describe a product and persuade people to buy.
It was also necessary to state the indicators in order to make the students recognize the expected achievement after completing a particular unit. The indicators are presented in Table 4.3.
In this step, the writer selected and modified the materials from some resource books, internet sites, and newspaper. The writer also designed new materials based on her experience and knowledge. The designed materials generally contained seven activities. They were Let’s Review, Browse Your Idea, New Stuffs, Sharpen Your Skill, Language Focus, Act Up, and Let’s Conclude. The details of each part will be described below.
a. Let’s Review
In this section, students recalled their memory on what they had learned last meeting. Teacher helped them by giving questions related to the previous material. As an exception, in unit 1 students reviewed Greeting and Introduction.
b. Browse Your Idea
In the second section students brainstormed their idea around the material that was going to be learned. Pictures and charts were used to help them in brainstorming their knowledge.
c. New Stuffs
Table 4.3. The Topics and the Indicators
Unit Topic Indicators
1 How to Use a Machine
1. The students are able to select appropriate expression to describe a procedure in written form.
2. The students are able to use appropriate expression to describe a procedure in written form.
2 How a Machine Works
3 The Four-Stroke Cycle
1. The students are able to select appropriate expression to describe a procedure orally.
2. The students are able to select appropriate expression to describe a procedure in written form.
3. The students are able to use appropriate expression to describe a procedure orally.
4. The students are able to use appropriate expression to describe a procedure in written form.
4 Rubber Plug Method of Tubeless Tire Repair
1. The students are able to select appropriate expression to give instruction orally.
2. The students are able to select appropriate expression to give instruction in written form.
3. The students are able to use appropriate expression to give instruction orally.
4. The students are able to use appropriate expression to give instruction in written form.
5 Chart of a Compression Process
1. The students are able to select appropriate expression to describe a chart orally.
2. The students are able to select appropriate expression to describe a chart in written form.
3. The students are able to use appropriate expression to describe a chart orally.
4. The students are able to use appropriate expression to describe a chart in written form.
6 Phoning a Garage 1. The students are able to select appropriate expression to apologize
2. The students are able to use appropriate expression to apologize
7 Hybrid Car 1. The students are able to select appropriate expression to describe a product.
2. The students are able to select appropriate expression to persuade people to buy their product.
3. The students are able to use appropriate expression to describe a product.
4. The students are able to use appropriate expression to persuade people to buy their product.
8 Applying for a Job 1. The students are able to select appropriate expression to write an application letter.
2. The students are able to select appropriate expression to write a resume.
3. The students are able to use appropriate expression to write an application letter.
d. Sharpen Your Skill
This section contained the exercises that should be done by the students. The students were exposed to reading and listening material to help them in understanding the topic.
e. Language Focus
In this section, the grammar used was discussed. Students were also to analyze the grammatical point of the reading or listening passage.
f. Act Up
In this section, students were given the chance to perform themselves. They were to present their writing or speaking.
g. Let’s Conclude
In the last section students were to retell about what they had learned. Teacher helped them by giving questions related to the material that they had studied.
Some of the activities in the materials were done individually, others were done in pairs, and the rest were done in groups. To support the learning activities, some media were used. They were pictures, newspaper, MP3 player, and loud speaker.
3. Evaluate
one lecturer of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University, and one English instructor in a private English Course. The respondents were expected to give their evaluations and feedback on the designed materials.
Post-design activities were conducted to evaluate the materials. The research aimed to obtain the evaluations, criticisms, feedback, and comments on the designed materials which improved the designed materials. In seeking for the evaluations, criticisms, feedback, and comments questionnaire was used. The questionnaire was distributed to a lecturer of the English Education Study Program of Sanata Dharma University, a lecturer of the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University, and an English instructor. The distribution of the questionnaire was conducted on 18 February to 11 March 2008.
Table 4.4. The Data of the Respondents’ Opinions
CT
No Respondents’ Opinions on N
Mean 1 The basic competencies are well formulated. 5 4.7 2 The indicators are well formulated. 5 4.3 3 The designed materials are able to meet the goals stated in the syllabus. 5 4.3 4 The designed materials are able to meet the objectives stated in the
syllabus.
5 4.3
5 The topics are well selected. 5 4.3 6 The topics are well arranged. 5 4.3 7 The contents are relevant to the learners’ needs. 5 4.3 8 The contents are relevant to the learners’ interest. 5 4.3 9 The contents are relevant to the learners’ field. 5 4.3 10 The instructions are clear. 5 4.3 11 The instructions are easy to understand. 5 4.3 12 The contents are well elaborated. 5 4.3 13 The exercises are variously given. 5 3.7 14 The exercises are interesting. 5 3.7 15 The exercises given can help the learners understand the lesson. 5 4.3 16 The pictures provided can help the learners understand the lesson better. 5 4.7 17 The activities enable the learners to develop their English. 5 4.3 18 The media are well developed. 5 3.7
Note: N = Number of Respondents CT = Central Tendency
The instructional materials gave some chances for the students to actively participate in teaching learning process. Nevertheless, there were still weaknesses of the designed materials as stated by the respondents in their criticisms and suggestions. Considering the respondents’ opinion, the writer revised the designed materials to make them better. They were as follows.
a. The indicators and learning experiences tended to be the same and monotonous. Therefore, the writer varied the activity and the topics.
b. There was no guidance for the teacher. Since the students came from Mechanical Engineering Study Program, they knew how a machine works, but for the teacher therefore, how could the teacher know that the students had written the right procedures. Therefore, the writer made a teacher’s manual that provided the teacher with the guidance on how to implement the instructional materials. The writer also equipped the teacher’s manual with the answer key.
c. Multimedia was not yet used in the instructional materials. Therefore, the writer provided some videos that could be used during the brainstorming step (Browse Your Ideas). By having them, the students would be helped better in obtaining the illustration of how a machine works.
B. The Presentation of the Instructional Designed Materials
The presentation of the designed materials for Mechanical Engineering Students of Sanata Dharma University answers the second question in the problem formulation. The final version of the designed set of materials is presented after some revisions and improvements based on the comments, criticism, and suggestions from the respondents. The final version of the designed set materials contains eight units. Each unit is allocated for one meeting covering 2 x 50 minutes. The details of the topics in the final version of the designed materials are presented in Table 4.5.
Table 4.5. The Order of the Topics in the Designed Materials
Unit Topic Unit Title
1 Describing procedure How to Use a Machine
How a Machine Works
The Four-Stroke Cycle
2 Giving instruction Rubber Plug Method of Tubeless Tire Repair
3 Describing chart Chart of a Compression Process
4 Apology Phoning a Garage
5 Describing Thing Hybrid Car
6 Job application letter and
interview
Applying for a Job
The designed materials generally contain seven activities. They are Let’s Review, Browse Your Idea, New Stuffs, Sharpen Your Skill, Language Focus,
a. Let’s Review
In this first section, students recall their memory on what they have learned last meeting. Teacher helps them by giving questions related to the previous material. As an exception, in unit 1 students review Greeting and Introduction
b. Browse Your Idea
In the second section students brainstorm their idea around the material that is going to be learned. Pictures and charts are used to help them in brainstorming their knowledge.
c. New Stuffs
In this section students are introduced to the new vocabulary and patterns. This is done so that the students can understand the material easier.
d. Sharpen Your Skill
This section contains the exercises that should be done by the students. They are exposed to reading and listening material to help them in understanding the topic.
e. Language Focus
In this section, the grammar used is discussed. Students are also to analyze the grammatical point of the reading or listening passage.
f. Act Up
g. Let’s Conclude
CHAPTER V
CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS
This chapter consists of two parts. The first part is conclusions of the study. The second part is the suggestions for the Mechanical Engineering students, for the English lecturers, and for the future researchers who are interested in conducting similar studies.
A. Conclusions
The purpose of this study was to design English instructional materials for the Mechanical Engineering Study Program of Sanata Dharma University. The writer began the study by formulating two problems to be answered. The first problem was how the English instructional materials for the Mechanical Engineering students of Sanata Dharma University were designed. The second question was what the designed English instructional materials for the Mechanical Engineering students of Sanata Dharma University look like.
survey to gather evaluation, criticism and feedback on the designed materials before going to step five, main product revision.
In order to answer the first question, the writer adapted Kemp’s model to develop the writer’s instructional design. The writer’s model consisted of three steps. They were (1) analyze, (2) design, and (3) evaluate. The presentation of the designed materials for the Mechanical Engineering Students of Sanata Dharma University answered the second question in the problem formulation. The designed English instructional materials contained eight units. Each unit was allocated for one meeting, covering 2 x 50 minutes. They were presented as follows:
Unit 1 : How to Use a Machine Unit 2 : How a Machine Works Unit 3 : The Four-Stroke Cycle
Unit 4 : Rubber Plug Method of Tubeless Tire Repair Unit 5 : Chart of a Compression Process
Unit 6 : Phoning a Garage Unit 7 : Hybrid Car
Unit 8 : Applying for a Job
The data obtained from the questionnaire in the post-design activities were analyzed by using the statistical data computation method of central tendency. After being analyzed, the results showed that the mean ranged from 3.7 up to 4.7. It means that the designed materials are appropriate for the Mechanical Engineering Students of Sanata Dharma University to learn English.
B. Suggestions
The writer would like to offer some suggestions in this part. They were for the Mechanical Engineering students. The suggestions were also for the English lecturers who apply the designed materials, specifically for the lecturers who are teaching English to the Mechanical Engineering students. At last, the writer would offer the suggestions to the future researchers who are interested in conducting similar studies.
For the students of the Mechanical Engineering study program themselves, it is suggested that they should be active in the learning process. Since most of the activities require participation from the students, it is more beneficial if the students are willing t