IMPROVING STUDENTS’ READING
COMPREHENSION USING
(KWL) STRATEGY FOR THE SECOND GRADE
STUDENTS OF SMP NU SURUH IN ACADEMIC
Submitted to the Board of Examiners as a Partial Fulfillment of
the Requirement for Degree of
English Education
State Institute
SITI AISAH PUTRI JAMINA
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES
IMPROVING STUDENTS’ READING
COMPREHENSION USING KNOW WANT LEARN
STRATEGY FOR THE SECOND GRADE
STUDENTS OF SMP NU SURUH IN ACADEMIC
YEAR 2015/2016
A GRADUATING PAPER
Submitted to the Board of Examiners as a Partial Fulfillment of
the Requirement for Degree of
Sarjana Pendididkan Islam
Education Department of Teacher Training and
Education Faculty
State Institute for Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga
By:
SITI AISAH PUTRI JAMINA
113 11 026
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY
STATE INSTITUTE FOR ISLAMIC STUDIES (IAIN)
SALATIGA
2016
KNOW WANT LEARN
STRATEGY FOR THE SECOND GRADE
STUDENTS OF SMP NU SURUH IN ACADEMIC
Submitted to the Board of Examiners as a Partial Fulfillment of
Sarjana Pendididkan Islam
(S.Pd.I)
Teacher Training and
Salatiga
ii
DECLARATION
In the Name of Allah, the Most Gracious, the Most Merciful.
Hereby the researcher distinctly declares that this graduating paper is made
by the researcher and it does not contain materials have been written or published
by other people, except the information is from some references. In addition, the
researcher is able to account to her graduating paper if in the future it can be proved
of containing others’ idea, in fact, the researcher imitates others’ graduating paper.
iii
v
Motto
vi
DEDICATION
This graduating paper is whole-heartedly dedicated to:
1. My Allah, the Most Gracious and Most Merciful
2. My beloved parents; Mr. Risman and Mrs. Siti Zulaikha, thanks a bunch for
everything you gave to me, for your affection, education, pray, and hard work.
3. My lovely brother; Arthun Zulman Habibie and Muhammad Khoirul Anwar.
Thanks for your kindness, support, and guidance.
4. The English teachers of SMP NU Suruh who give chance for the researcher
to interviewed them.
5. All my dearest friends Dyah Koes Windarti, Nur Alita Lisnawati, Niken Arina
vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
Alhamdulillahirabbil‘alamin, thanks to the Almighty Allah. Because of
Him, the researcher can complete this research as one of the requirements for
getting the degree of Educational Islamic Studies (S,Pd.I) in English Education
Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty of State Institute for
Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga in 2016.Secondly, peace and salutation are always
given to our prophet Muhammad SAW who has guided us from the darkness to
the lightness.
However, this success will not be achieved without support, guidance,
advice, help, and encouragement from individual and institution, and the
researchersomehow realize that it is an appropriate moment to give my deepest
gratitude for:
1. Dr. RahmatHariyadi, M.Pd., as the Rector of State Institute for Islamic Studies
(IAIN)Salatiga
2. Suwardi, M. Pd, S. Pd, Dean of Teacher Training and Education Faculty
3. Noor Malihah, Ph.D., as the Head of English Education Department
4. RifqiAuliaErlangga, S.Fil. M.Hum, as the research consultant who has
educated, supported, directed and given the researcher advices, suggestions,
and recommendations for this research from beginning until the end
5. All of the lecturers in English Education Department, who taught patiently,
viii
6. All of the staffs who helped the researcher in processing of graduating paper
administration
Finally this graduating paper is expected to be able to provide useful
knowledge and information to the readers. Moreover, the researcher is pleased to
accept more suggestion and contribution from the reader for the improvement of
the graduating paper.
Salatiga, 12thMarch 2016
The Researcher
Siti Aisah Putri Jamina
ix
ABSTRACT
Jamina, Siti Aisah Putri. 2016. Improving Students’ Reading Comprehension Using Know Want Learn (KWL) Strategy For the Second Grade Students of SMP NU Suruh in Academic Year 2015/2016. A Graduating Paper.Teacher Training and Education Faculty.English Education Department. State Institute of Islamic Studies (IAIN) Salatiga. Counselor: Rr. Rifqi Aulia Erlangga S.Fil. M.hum.
Keywords :KWL Strategy, Reading Comprehension
x
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE ... i
DECLARATION ... ii
ATTENTIVE COUNSELOR’S NOTE ... iii
STATEMENT OF SERTIFICATION ... iv
MOTTO ... v
DEDICATION ... vi
ACKNOWLEDGMENT ... vii
ABSTRACT ... ix
TABLE OF CONTENTS ... x
LIST OF TABLES AND FIGURE ... xiii
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION A. Background of the Study ... 1
B. Statement of the Problems ... 5
C. Objectives of the Study ... 5
D. Significance of the Study... 6
E. Limitation of the Study... 6
F. Definition of the Key Terms ... 7
xi
H. Research Organization ... 10
CHAPTER II LITERATURE REVIEW A. Reading ... 11
1. Definition of Reading ... 11
2. Purposes of Reading ... 13
3. Types of Reading ... 15
4. Techniques of Reading ... 18
5. Principles for Teaching Reading ... 20
B. Reading Comprehension ... 21
1. Definition of Reading Comprehension ... 21
2. Reading Comprehension Skill ... 22
3. Levels for Reading Comprehension ... 22
C. KWL Strategy (KWL) 1. Definition of KWL Strategy ... 23
2. Procedures of KWL Strategy ... 25
3. Use of KWL Strategy in Teaching ... 26
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHODOLOGY A. Research Setting ... 30
xii
2. Subject of the Study ... 31
3. Research Schedule ... 31
B. Research Methodology ... 32
1. Definition of Classroom Action Research ... 32
2. Procedures of CAR ... 33
3. Techniques of Collecting Data ... 37
C. Analysis Data ... 39
1. Descriptive Qualitative Technique ... 39
2. Statistical technique (Quantitative) ... 39
CHAPTER IV RESEARCH FINDING A. Research Finding ... 42
1. Implementation of Using KWL Strategy ... 42
2. Result of Using KWL Strategy ... 56
CHAPTER VCLOSURE A. Conclusions ... 62
B. Suggestions ... 63
xiii
LIST OF TABLES AND FIGURE
Table 2.1 : KWL Instructional Scheme ... 27
Table 3.1 : Research Schedule ... 31
Table 4.1 : The result of pretest and posttest cycle 1 ... 47
Table 4.2 : The result of pretest and posttest cycle 2 ... 52
Table 4.3 : The result of pretest I, posttest I, pretest II and postest II ... 57
Table 4.4 : The Mean of Students’ Scores ... 59
14
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
A. Background of the Study
Language is avery important thinginour life. Bylanguage,
wecancommunicate with others. In the era of globalization, almost all done
with instant, indirectly we will go in the modern world. So that we do not
fall behind, we have to master the language used. English is the universal
language that is used by almost all countries as a first language or the
second, you could say this is a global language or Englishhas
beenchosenas an international language. English is an important language
that should be understood by everybody in the world. Learn English is as
preparation when we will move toward globalization life. As a means of
global communication, English must be actively controlled both oral and
written.
English is one of the subjects in school. It has become one of
subject in curriculum. Every school can develop it, especially in formal
education. . According to Catherine (1996: 11) quote by Purniati (2014:
1)There are four language skills in English, namely speaking, listening,
writing and reading.The fourthskillsare veryinfluentialin
learninglanguages, especially English. One of the ways to improve English
ability is reading. Reading is one of the language skills that should be
15
According to Moreillon (2007:10), reading is alanguage skillthat
aimsto understand theideas,and feelingsin the text. In the process ofreading
thestudents will experiencethe process ofthinking tounderstandhis
ideaswidely. Theprocess of readingis relatedto do
withfactorsdevelopmentthinking, based ontheexperience. The
experiencecan beobtained throughlistening,observationanddiscussion.
Brown as quoted Somadayo (2011 : 2) explained that, reading is an
appropriate means to promote a lifelong learning (life long learner). By
teaching children how to read, means giving the child a future, that gave a
technique, how to explore the world wherever he chose and gave the
opportunity to achieve his goal.
In reading, the students need comprehension skill. According to
Chaterine (2002:11), readingcomprehension is defined as the level of
understanding of a written language. Itis the process of simultaneously
extracting and constructing meaning throughinteraction and involvement
with a written language. Reading comprehensionis called as the result
from an interactive process between the reader and thetext. the students
should have well understanding and comprehending thecommunication
through the reading. In general, the aim of teaching reading isto develop
the students’ ability in reading the material, getting information
andunderstanding the text.The students who does not master enough
16
reading materials.It means that readingcomprehension is very important
and many students get problem in readingcomprehension.
In teaching reading, teacher must be patient and have to write a
note in teaching learning process. The teacher should make a good
technique to make students easier to understand in reading English. In
this way teacher has an important role because teacher is a key of teacher
in teaching learning process. According to Robb (2013),to improve
students’ ability in comprehending texts, the teacher must help thestudents
change their inefficient reading habits as reading word by word,
focusingtoo much attention on the form and relying heavily on dictionary.
Therefore, theactivity that the teacher applies in the class takes an
important role. English teacher has to know the strategies in order to get
better result in learning. Besides, the teachers have to know about the
strategies or models which must be used to guide the students. Strategies
are ways for learners to solve problems encountered in constructing
meaning in any context. The teacher who has important role must guide
the students to have creativity in classroom. If the strategy is not suitable
with situation in the class,the teaching and learning will not be successful.
From the discussion above, to improve students’ comprehensionin
the reading text needs an appropriate strategy for helping them as a
solutionfor their problems. In this case, the researcher wants to apply a
strategy that canhelp the students for better understanding in reading. The
17
According to Ogle (1986:565), there are three-step procedure the
K-W-L for the three basic cognitive steps required: accessing what I
Know, determining what I Want to learn, and recalling what I did learn as
a result of reading. The KWL (Know, Want and Learned) technique can
help the teachers engage their students from beginning of a reading lesson
by activating prior knowledge and keep students interested, which is very
important as they think about what they have learned.
According to Johnson (2011) ,compare to traditional method which
is usually monotone, the students only read and review the entire text but
that been improve in KWL strategy because KWL strategy divided the
main point of the text into three part; K, W and L. It makes the students
more clear about the information and elaborate with their own knowledge.
Traditional method also make the students have a less motivation to be
active questioners, read for specific purpose and reflect following reading
about whether the purpose was met. But KWL strategy can help the
students to increase their motivation, access what they know, decide what
they want to learn and whether it is likely to be in the passage, and decide
what yet needs to be done after reading.
Related to the background above, the researcher thinks that the
existenceKnow Want Learn (KWL) strategy in that school can be one of
the ways indeveloping students’ reading comprehension. Therefore, the
researcher is interested in carrying out theresearch entitled:
18
KNOW WANT LEARN (KWL) STRATEGY FOR SECOND GRADE OF SMP NU SURUH IN THE ACADEMIC YEAR 2015/2016”
B. Statement of the Problems
Based on the background of the study above, this research is aimed
to giving answer of the following problems:
1. How is the implementation of using Know, Want learn (KWL)
strategy to improve students’ reading comprehension for the Second
Grade students of SMP NU Suruh in the academic year 2015/2016?
2. How is the resultof using Know, Want learn (KWL) strategy to
improve students’ reading comprehesion for the Second Grade
students of SMP NU Suruh in the academic year 2015/2016?
C. Objectives of the Study
Based on the statements of the problems above, the intentions of
the research are as follow:
1. To find out the implementation of using Know, Want learn (KWL)
strategy to improve students’ reading comprehension for the Second
Grade students of SMP NU Suruh in the academic year 2015/2016?
2. To find out the resultof using Know, Want learn (KWL) strategy to
improve students’ reading comprehension for the Second Grade
19
D. Significance of the Study
This research is concerned with improving reading comprehension
using KWL strategy. The researcher hopes that the reasearch will be
useful. Related to the target of this research, research have two significant,
such as theoretically and practically.
Theoretically, the result of this study is expected to be able the skill
of teachers by using KWL strategy to improve student’s reading
comprehension. As reference to other researchers who want to study think
aloud strategy more intensively in teaching reading.
Practically, the result of this study is suggested to apply the KWL
strategy to improve the students’ competence in reading comprehension.
The use of KWL strategy to learn reading comprehension can make the
students are easier to understand in doing their tasks associated with the
reading materials.
E. Limitation of the Study
In this research restricted of using Know Want Learn (KWL) to
improve student’s reading comprehension for the second grade students of
SMP NU Suruh in the Academic Year of 2015/2016 at the first semester.In
order to make a focus in this research, especially in the explanation, the
researcher limits the study as follows:
1. The research is limited in using KWL Strategy.
20
3. The research is carried out to the second grade students in SMP NU
Suruh.
F. Definition of the Key Terms
The terms in this investigation is used to avoid the
misunderstanding among the readers. To make it quite clear in
comprehension the study therefore there are some key terms such
Improve, student, reading comprehension, using, Know Wont Learn
(KWL) Stategy, and SMP NUSuruh.
1. Improve
Improve is the process of becoming or making something better
(Oxford University Press, 2008 : 222).
According to Homby(1995:586) as quote by Ratminah (2014: 6)
Improving is the way to make something better.
2. Student
Student is a person who studying at a college or university or
any person interested in a particular subject (Oxford University Press,
2008 : 440).
Student is a person engaged in study; one who is devoted to
learning; a learner; a pupil; a scholar; especially, one who attends a
school, or who seeks knowledge from professional teachers or from
books; as, the students of an academy, a college, or a university; a
21 3. Reading Comprehension
Reading comprehension is widely agreed to be not one, but
many things. At the least, it is agreed to entail cognitive processes that
operate on many different kinds of knowledge to achieve many
different kinds of reading tasks. Emerging from the apparent
complexity, however, is a central idea: Comprehension occurs as the
reader builds one or more mental representations of a text message.
(Kintsch & Rawson, 2005)
We define reading comprehension as the process of
simultaneously extractingand constructing meaning through interaction
and involvement with writtenlanguage. We use the words extracting
and constructing to emphasize both theimportance and the insufficiency
of the text as a determinant of reading comprehension.
4. Know Want Learn (KWL) Strategy
The KWL strategy represents what students know about a given
topic, what they want to know about the topic, and what they have
learned about the topic. KWL strategy was created to enhance reading
comprehension in content areas. All three parts of the technique focus
on a different aspect of student’s individual learning style. KWL
strategy is also used as an organizational tool because it allows student
to identify known information about a given subject. (Jared and Jared,
22
KWL strategy is one method of teaching reading that
emphasizes the importance of background knowledge of the reader.
Where most of the educators in the field of knowledge ignore
background and interests of readers. KWL method consists of three
steps, namely the step K What I Know (what I know), step W- What I
Want to Learn (what I want to learn), and step L What I Learned (what
I have learned ). KWL is developed to know the framework teachers to
determine students' abilities
G. Review of Related Research
In this thesis, the researcher review several research papers from
the previous researches. The first was conducted by Ulil Hidayah in title
“The Use of Paired Story Telling Technique to Improve Students’ Reading
Comprehension (A classroom action research of second grade students of
SMPN 9 SALATIGA in the academic year of 2012/2013)”. In this Thesis
Ulil Hidayahexplained about the using of Paired Story Telling Technique
in SMPN 9Salatiga. She draws the conclusionthat using paired story
telling technique, the students can comprehend the text and reconstruct the
story after listen and read the text in pair then they reveal it in front the
class. In addition, the students’ cognitive skill can grow by reconstruct
what they have read in the passage into their own sentence.
In the other side, Dedy Khisbullah in his thesis “Improving the
23
(Classroom Action Research at the Third Year Students of MA Mir‟atul
Muslimien Grobogan 2012)”. The result of this study isthe improvement
of the students‟ reading comprehension is significant after the students got
reading instruction by retelling technique.
H. Research Organization
In this section, the researcher will discuss some parts of research
organization. The research consists of five chapter. Chapter I present
background of the study, statement of the study, the objective of the study,
significance of the study, the limitation of the study, the definition of
terms, and Research Organization. Chapter II is the theoretical review of
the research. Chapter III discuss about the research methodology, it
consists of research method, research schedule, the collecting data,
technique of analysis data, and the profile of the school. Chapter IV is the
result and the analysis of the research. It consists of the data presentation,
discussion, the analysis of the data, and the summary of the research.
Chapter V is closure that consists of the conclusion and suggestion. The
24
CHAPTER II
THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK A. Reading
1. Definition of reading
Reading is an activity that gives more information to the reader.
Reading is not passive activity but an active process in which readers
relate information in the text to what they already know. According
Linda (2005:6), Reading is a complex process involving a network of
cognitive actions that work together to construct meaning. Reading is an
interactive process that goes on between the reader and the text, A reader
in reading term will use his knowledge, skills, and strategies to determine
what the texts is. It means, the reader tries to recognize the words he
meets in print and finds the meaning of the written text. So, reading
brings a maximum of understanding to the author’s massage.
According to Mukhroji (2011:57) readingisthe process of
translatingthewordsspokenwhenbeginningto learn to read. Reading refers
to theprocess ofreadingwordsprintedintoa statement similar tospoken
languageeithersilentlyor out loud. Readas a translatorwho hasthe
meaningassymbolsprintedverbalwritten. This meansthat thereadingis the
resultofthe interactionbetween theperceptionof graphic symbolsandthe
ability ofthe readertounderstand theknowledge ofthe world. In this
25
Rumelhart as quoted by Mukhroji (2011:57) states "reading is
the process of understanding written language. Since reading is a process,
from seeing the surface linguistic representation and end up with certain
ideas or meaning of the message intended by the author". Reading
involves the interaction between the mind and language. This means that
the reader obtains some information and ideas, attitudes and confidence
in the results read.
In addition, Heilman, Blair, & Rupley (1981: 2) argue that the
reading can be defined as a thinking process and it can be a
communicative skill. They also define the reading is an interacting
process with the language in the printed page. This printed page should
be understood and the reader should be able to express in oral form. In
the short sentence, they defines that reading is a language process.
However, basically the nature of reading is difficult to be defined as in
the process of reading exactly. This can be pointed out in many views.
Based on explanation above, can be concludes that reading is a
process to convey the message or information. By reading, the reader will
know what they read and challenged to response the ideas of the
researcher. In order to make the messages or information that comes
from the researcher can be understood and comprehended easily by the
26
2. Purposes of Reading
The purposes of reading described by Grabe (2009:7-10) names
six academic purposes for reading. He said, “When we read for different
purposes, we engage in many types of reading, particularly in academic
settings”. All these purpose require necessary skills in order to be
accomplished efficiently. These purposes include:
a. Reading for information
To seek information can combine scanning (identifying a
specific graphic form in the text) and skimming (to search
information the reader has to build a simple quick understanding in
the text)
b. Reading for quick information (skimming)
Skimming is used the readers when they need to read many
texts. Then, they want to determine what a text about and choose
one text to focus more attention. They don’t need to read all the
materials. They just want to know some material in details.
c. Reading to learn
Reading to learn is happened in campus and professional
settings. The readers not only seek information but also keep in the
main information. The expectation of reading to learn is put the
ideas into long-term memory.
27
The type of reading to integrate information is the readers
need to synthesize and identify the different parts of long texts.
They are expected to keep the ideas into long-term memory and
create their own understanding about information.
e. Reading to evaluate, critique, and use information
In the academic setting, readers need to read many texts
and give critique or suggestion. It is more complex than reading to
integrate information.
f. Reading for general comprehension
Reading for general comprehension is the most common
purpose for reading among fluent readers and it is the default
assumption for the term reading comprehension.
3. Types of Reading
According to Harmer (2001: 210-213), reading consist of two
kinds. These are:
a. Extensive Reading
The importance of extensive reading is the development of
students’ word and their improvement as readers overall. It is not
enough to tell students to read much, teacher should offer some of
programs such as appropriate material, guidance, tasks and facilities
such as portable libraries of book. The types of extensive reading
involve:
28
One of major conditions of successful extensive reading
programmer is the students should be reading material which
they can understand. If they understand every word, they find
hard information in reading.
2) Setting up library
In order to set up an extensive reading programmer,
librarian should create library with suitable books. Although it is
look expensive to spend money but students will get good
information through various suitable books. Thus, the school
and institution have to provide fund or raise money through
other sources.
3) The role of the teacher in extensive reading programmer
Most of students will not do a lot extensive reading by
themselves unless they are encouraged to do by their teachers.
Teacher persuades the students about the advantage of extensive
reading. Teacher can organize reading programmer where they
indicate students of how many books teacher expect them to
read over a given period.
4) Extensive reading task
Students should be allowed to choose their own reading
texts by following their own likes and interesting, they will not
29
students to keep reading and encourage them to revise on their
reading.
b. Intensive Reading
In order to get students to read enthusiastically in class,
teacher should be create interest in the topic and tasks. There are
many ways for teacher when asking students to read intensively
include:
1) Organizer
In the organizer, teacher should tell students exactly
what their reading purpose or goal and give them clear
instruction about how to achieve it and how long they have
to do this in the classroom.
2) Observer
Teacher asks students to read on their own and give
them space to do. It is means restraining from interrupting
that reading, although it may need more information or
instruction. When students read, teacher can observe their
progress to know about how they do individually and
actively.
3) Feedback organizer
After students have finished the task, teacher can
provide feedback session to check how far they have
30
pairs and ask them to answer in pairs. By sharing their
knowledge, they share responsibility for their answer.
4) Prompter
When students have read a text, teacher can prompt
them, to notice language features in the text. Teacher as
controllers, direct them to pay attention about features of
text construction and clarifying ambiguities.
c. Aloud Reading
Readingaloudis alsoimportantin
teachingEnglish.Teachersshouldknowthat thetrainingof reading
aloudshould begiven to thestudentsa basic levelbecause it is
abasicword pronunciation. Whatcanteachersdo
toteachbetterandeffectively readas follows:
1) The materialpresent beforethe studentteachershould be in
accordancewith theprior knowledge ofstudentsor relatedto their
own experience.
2) Teachersshould emphasize onstresslearners.
3) Teachersshould be carefulwhenreading processis going
on.Ifany errorsmadeby learners, will correcta friendly manner.
4) Teachersshould be concernedaboutall studentsandalso pay
attentionto thedirection ofweakreaders.
5) The materialin accordancewith the level ofthe reader, so
31
d. Silent Reading
Silentreadingisan important skillin
teachingEnglish.Teachersshouldmake them readsilentlyandwhenthey
areable to readwithoutdifficulty. Itwillbe thehabitof studentsto be
active insilentreading. Teachingreadingis a skillthat isvery important
because thisisthe beginningstageof students' knowledge.
Howcanteachersmaketeachingreadingquietlyeffective reading:
1) The teacher has to tell aboutthe first topicto students,
shouldmotivate learners.
2) Teachersshould not allowstudents tomutterwhen reading.
3) The subjectshould be interested inreading material.
4. Technique of Reading
According to a Wright (1999:159) there are some techniques of
reading, such as:
a. Skimming
Skimming is building a simple quick understanding of the
text allows a reader to search for information. Skimming also used
for a variety of other reasons. We skim when we want to determine
what a text is about and whether or not we want to spend more time
reading it. We skim when we are expected to read a more difficult
text so that we have a sense of where the text will lead us and what
32
work through many texts and want to make decisions about which
texts to focus more attention.
b. Scanning
Scanning is a technique of reading to get the information
without reading the others so directly to problems are looking,
namely the specific facts and specific information. During the eyes
move quickly to see the whole material of reading, the reader does
not absorb the meaning but just to recognize that things are looking,
it clearly seems as if in bold. In daily life, reading scanning is
performed to find a phone number, look for the word in a dictionary,
look for an entry in the index, look for statistics, and see the schedule
of television broadcasts. Thus, scanning is a technique to read
quickly to get the information without reading the others.
c. Extensive Reading
Extensivereadingis a processthatwas widelyread, that
readingvariousand diverseandtime usedquickly
andsimply.Extensivereadinggoalisto understand
theessentialcontentofthe reading materialata time of rapidand brief.
For example, reading novel, newspaper, and short story.
d. Intensive Reading
Intensive reading is to read with comprehension to find the
main ideas in each paragraph, understanding the ideas manuscript of
33
reading, that are readers master the content of the text, written for
readers to know the background of the text, and the reader can have
a longer memory related to the content of the text.
5. Principles for Teaching reading
According to Harmer (2001: 70)the principle of reading instruction
includes:
a. Reading is not a passive skill. It is means that an active activity. To
be successful in reading, students have to understand what the
words mean, see the picture the words are painting, understand the
arguments and work out if we agree with them.
b. Students should to be engaged with what they are reading. In
lessons students who are not engaged with the reading text and
they are not actively interested in what they are doing. Which it is
not useful for them
c. Students need to be encouraged to respond the content of a reading
text not only in language. It is significant to study reading text for
the way they use language, the number of paragraphs they contain
and how many times they use relative clauses.
d. Teacher should match the task with the topic. By deciding about
what reading text the students are going to read. Moreover teacher
needs to choose good reading tasks, the right kind of questions,
34
e. As good teacher, they should exploit reading text completed. They
integrate the reading text into interesting class sequences, using the
topic for discussion, further tasks, using the language for study and
later activation
B. Reading comprehension
1. Definition of reading Comprehension
Dechant (1982:311) said that comprehension includes the
correct association of meanings with word symbols, the selection of the
correct meaning suggested by the context, the organization and retention
of meanings, the ability to reason one’s way through smaller idea
segments, and the ability to grasp the meaning of a larger unitary idea.
It is very important to talk about reading comprehension.
Reading comprehension is very importance for everyone who wants to
enlarge their knowledge and information. Sometimes some learners feel
difficult to comprehend the text that they have read, so they get nothing
from the text. So the teachers have to be more concern about the
problem.According to Chaterine (2002:11) reading comprehension
defined as a process of simultaneously extracting and constructing
meaning through interaction and involvement with written language. We
use the words extracting and constructing to emphasize both the
importance and the insufficiency of the text as a determinant of reading
35
In conclusion reading comprehension is a complex activity
where the reader can get knowledge from the text both of information or
message and new vocabularies; furthermore, to understand text the reader
need to find out the meaning or the correlation between the sentences that
establish in the whole text. They can retell again the information that they
have read depend on their knowledge, culture and background.
Finally, there are a lot of benefits that the reader can get from
reading. If we read a lot of books, magazines, articles, and many things
you can get a lot of knowledge and information from it.
2. Reading Comprehension Skill
According to Khoiriyah (2010:2) to make it easy to understand
the text or materials of reading, you need some reading skills. There are
various of reading skills. These skills can help you understand and
remember what you read. They are:
a. Recognizing the letters of alphabet
b. Reading group of letters as words
c. Understanding the meaning of punctuation
d. Understanding the meaning of vocabulary items
e. Understanding the grammar of a sentence
3. Levels for Reading Comprehension
According to Heilman, Blair and Rupley (1961: 246), there are
three levels of comprehension. They are:
36
Literal comprehension is an understanding the ideas and
information explicitly. The abilities of literal comprehension
consist of knowledge of word meaning, understanding of
grammatical clues and understanding of grammatical clues.
b. Interpretative comprehension
Interpretative comprehension is an understanding of ideas
and information not explicitly. The abilities in interpretative
comprehension involve inferring factual information,
summarization of story content and understanding the author’s
purpose and attitude.
c. Critical Comprehension
Critical comprehension is process analyzing, evaluating,
and personally reacting to information. The abilities can be
presented below:
1) Personal reacting to information in a passage indicating its
meaning to the reader.
2) Analyzing and evaluating the quality of written information in
terms of some standards.
C. KWL Strategy (Know, Want, and learned)
It will described about the definition of KWL strategy, the procedures
KWL strategy, and The Use of KWL Strategy in Teaching Reading.
37
According to Ogle (1986:565), K-W-L forthreebasic
cognitivemeasuresneeded: access towhat Iknow, decide whatIwantto
learn, and remember whatI Learnas a result ofreading. To performthese
steps, teachers shouldteachstudentsclearly, andteachersprovide
aworksheet for eachstudentduringthis process.
There aresomeexperts explainthe definition ofKWLstrategy.
According toMcKenna(2002: 90), KWLis a strategyin
whichstudentssettheir own goalsfor thereadnonfiction. Students aremore
activein the learning processas theydeterminetheirownlearning goals. It
also confirmsfor studentsthatreadingis athinking processandthere are
stepstotakewhen trying to understandsomething new.
Moreover, Hassard (2011:77), KWL strategy is an active
reading strategy prepares students to make predictions about what
theywill be reading, as well as engaging them withother students in a
discussion of the content ofthe topic. It means students asked to
predicttheir knowledge about the topic that given by teacher and share or
discuss it with their friends.
Based on experts’ explanation above can be concluded that
KWL is a strategy used to encourage students to be more active. This
strategy is done by preparing students to make predictions about what
they read, so the teachers can also predict their knowledge about the
topic given. Students start to write everything they know about the
38
what they know and what they do not know, so that they can explore
what they have learned. Students asked to predict their knowledge about
the topic that given by teacher and share or discuss it with their friends.
2. Procedures of KWL Strategy
There are some procedures KWL strategies that can be
implied in the teaching of reading. According to Crawford et al (2005:
23) says KWL steps are:
a. Begin by naming the topic, and ask students to think about what they
already know about it.
b. Chart K-W-L on the board or on paper charts.
c. Ask students to call out what they know about the topic. Wrote their
ideas on the fields marked KNOW.
d. Ask students to think about questions they have about the topic.
They might start by reviewing what they know, and find areas where
their knowledge is incomplete. Wrote their questions on the chart in
the column marked WANT.
e. Students have to read the text. They are reminded to seek answers to
their questions.
f. Students write the things they learned from the text. First they write
their answers to these questions, and then they write the important
ideas that they find interesting. Teachers noted these in the chart in
39
According to Ogle (1986: 565-566), KWL reading procedure
can be described as follows: Step K-what I know. The first step students
to write what they know about the topic that will be read. During this step
the teacher's role is to record every student knows about the topic. Step
W-What I want to learn? As students take the time to think about what
they already know about the topic and the general category of
information that should be known. Because not all students agree on the
same information; some conflicting information; some categories do not
have specific information available. All pre-reading activities to develop
students' own reasons to read, read to find answers to questions that will
increase their knowledge on this topic. Step L-What I have learned. After
completing the text, students are asked to write down what they learned
from reading. Students are asked to check their questions to determine
whether there is an answer to that text. Otherwise, students advised to
read more to increase their sense of curiosity.
3. Use of KWL Strategy in Teaching Reading
According to Ogle (1987: 570), KWL is a growing
instructional scheme to determine the ability of students in reading. It
gives structure to remember what learners know about the topic, note
what they want to know, and finally a list of what you have learned and
have not been studied. Learners will think about everything they know
about the topic. The relevant information recorded in the column K of the
40
what they want to know about the topic. These questions are listed in
column W. During or after reading, students answer these questions.
What they have learned is recorded in column L.
The purpose of The KWL (Know, Want, Learn) strategy provides a
structure to enable and build knowledge, establish a goal to read and to
summarize what has been learned. This strategy can help students reflect
and evaluate their learning experience, and serves as a useful assessment
tool for teachers.
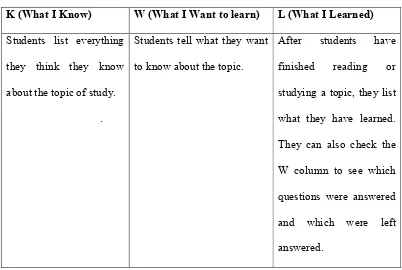
Table 2.1
KWL instructional scheme
K (What I Know) W (What I Want to learn) L (What I Learned)
Students list everything
they think they know
about the topic of study.
.
Students tell what they want
to know about the topic.
After students have
finished reading or
studying a topic, they list
what they have learned.
They can also check the
W column to see which
questions were answered
and which were left
answered.
According toBurke(2005: 16) KWLguide studentsthrough
thetext. Althoughthe process startsbefore readingactivity, the ultimate
41
procedure of theKWLstrategyinvolves threesteps.First, itprovides
studentswith the opportunity toexchange thoughts andideas ina list
ofitemsKanddetailthattheyalreadyknowaboutthe topic. Secondly,
theyreview thetopicagainandconsider whattheystillwant to knowandbe
written on theWof thechartin the formof questions.Thirdly,
whentheyreadorafterthey read, studentsadd detailsthey have learnedwhile
reading. TheywroteinpartLgraph.
KWL strategic activities:
1. K (what I know)
Teachers prepare questions in advance to help students put
their ideas. Teachers might ask them what they think of it.
2. W (What I Want to Learn)
The teacher asked a question asking for an alternative to
student responses. Questions could include: what the students
want to learn about the topic. The teacher asks the students what
they want students to learn about the topic.
3. L (What I Learned)
Teacher reminded the students that they should try to
answer their questions by filling in the L. Encourage students to
write new and exciting information they learned. Teachers advise
students to look into other sources for answers to unanswered
42
Learners who successfully use prior knowledge to new
information received, and can determine the meaning and learn on their
own. KWL strategy helps students to do this; it provides a framework that
can be used by students to understand the significance of the new material.
It is a strategy that teachers can easily modify to meet the needs of students
43
CHAPTER III
RESEACRH METHODHOLOGY
A. Research Setting
1. General Description of Location
SMP NU Suruh is one of the Islamic junior high school in
Suruh, Semarang Regency. The location of this school is very
strategic. SMP NU Suruh is located at Jl. Karanggede Suruh Km.2,
Suruh, Semarang regency, Central Java. Thisschoolwas
foundedandbegan operating(learning and teaching) inthe academic
year1979/1980. It was built on a land area of 2,345 m2 with a building
area of 1,074 m2.
SMP NU Suruh has the vision and mission. SMP NU
Suruhvisionis"Sturdy in theFaithandPiety" andto improve the skills,
innovationandpreparing forindependentgeneration ofMuslims. And
The missions of SMP NU Suruh are developing and implementing of
learning approach PAIKEM, promoting the academic achievement and
the average value of the national exam, preparing skillful Moslem
Generation, be able to develop creativity and innovation, form
students’ bahaviour become “Akhlaqul Kharimah”
2. Subject of the Study
Subject of the research is the subject that becomes the target
of researcher (Arikunto: 2010, 188). This classroom action research
44
39 students, 24 female and 15 male who are still in first semester in the
academic year of 2015/2016. The researcher chooses the Second grade
of SMP NU Suruh because the researcher finds the students’ problem
in reading comprehension. The researcher wants to apply the KWL
strategy in order to improve students’ reading comprehension. The
position of the researcher in this research is as a teacher. Moreover, the
observer of this research is the researcher’s partner. She is Nur Alita
Lisnawati, she is also students of English Department of STAIN
Salatiga.
3. Research Schedule
There is the sequences of research are done by researcher, it can
see on the table below:
Table 3.1 Research Schedule
No Activities Time
1 Preparing the research proposal
January,
Observe the teaching-learning process between English teacher and eighth grade students
September, 10th 2015
08.00 am
4 Interview to the English teacher and take data questionnare for eight grade students
45
09.45 am
A Cycle 1 implementation
September, 18th 2015
07.00 am
a Cycle 2 implementation
September, 22th 2015
07.00 am
7 Data analysis October 2015
8 Concluding the research October 2015
B. Research Methodology
1. Definition of Classroom Action Research
In this research methodology, the researcher uses Classroom
Action Research (CAR). According to Kemmis as quoted by Hopkins
(1993: 44), Classroom Action Research is a form of self-reflective
enquiry undertaken by participants in social (including educational)
situations in order to improve the rationality and justice of (a) their
own social or educational practices, (b) their understanding of these
practices, and (c) the situations in which the practices are carried out.
Besides, Arikunto (2006:2-3) informs that CAR consists of
three words, so there are three definitions, which can be explained:
a. Research-indicate an activity to observe the object by using of
ways and methodologies to get the useful data or information to
46
b. Action is a movement activity, which is done deliberately with a
certain purpose.
c. Classroom- in this case is not bound by the terms of the classroom,
but it has a more specific meaning. The word of class means groups
of students who are in the same time receive the same lesson from
the same teacher.
From the definitions above, the reseracher can conclude that
CAR is educational research that undertaken by teacher (researcher) in
order to improve quality of learning, social practice, and other aspect
of education in the class. Through CAR, the researcher can know
students’ ability: what they are needed, how far they understand about
the material, and what the way of their study. In Classroom Action
Research, the researcher focuses attention on a problem or question
about classroom.
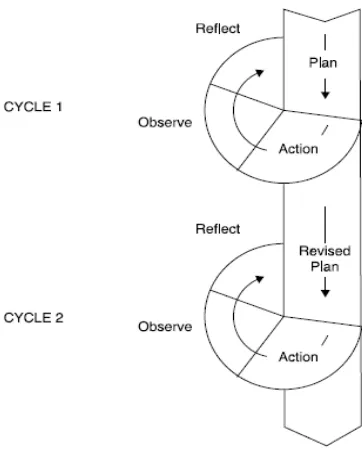
2. Procedures of CAR
This study applying Classroom Action Research as a
method, according to Kemmis as quoted by Hopkins(1985) the major
steps are planning, action, observation, and reflection. The researcher
spends two cycles in this research, and started with pre cycle. The
47
Figure 3.1 Model of Action Research ( Kemmis & McTaggert: 1988)
a. Cycle 1
1) Planning
Researcher prepared some instruments which’s support
in teaching learning process, they are:
a) Interview to their English teacher.
b) Observe the school especially class to know how to teach
the eighth grade students and how much the capability of
students.
c) Adjusting and determining the material will be teach
based on the syllaby from the English teacher, it is
descriptive text.
48
e) Prepare teaching instrument.
2) Action
The researcher implemented the Classroom Action
Research with the activities bellow:
a) Giving pre-test.
b) Explain the material.
c) Explain the material using KWL Strategy.
d) Giving the opportunity for students to ask question.
e) Giving post-test 1.
3) Observation
The reseracher invited an observer to observe
activities of teacher and students, it was wrote in observation
sheet that explain about steps of teaching-learning activity
which suitable of the lesson plan, the inhibit factors, support
factors, and the solution. It also explain the students’
responses to the teacher or the opposite. The lists of
observation sheet are:
a) Greeting students before start the lesson.
b) Praying together before start the lesson.
c) Checking the students’ attendance.
d) Apperception.
e) Inform the learning objectives.
49
g) Using KWL Strategy to teach descriptive text.
h) Giving reinforcement for students.
i) Make conclusion together.
4) Reflection
Reflecting is an activity in expressing of experience
that have by teacher as a self evaluation. After the
researcher has accomplished analyzing the observation, the
researcher will plan the next cycle. If the researcher find
problems in teaching in the first cycle, she will try to solve
the problem in the next cycle.
b. Cycle 2
1) Planning
The researcher takes planning of Cycle 2 as some steps:
a) Preparing material, making lesson plan, and designing
steps in doing action.
b) Preparing sheets for classroom observation.
c) Preparing pre-test and post-test.
2) Action
The action of cycle 2 is almost similar with cycle 1, the
activities are:
a) Giving pre-test 2
b) Teacher divide students into four groups
50
d) The teacher gives explanations and assignments to
students then reflect on the activities that have been done.
e) Giving the group assignment for students.
f) Students present their result in front of the class
g) Giving the opportunity for students to present their
assignment.
h) Giving post-test
3) Observation
The researcher invite an observer again to observe
activities of teacher and students, it is wrote in observation
sheet. The lists are similar with cycle 1.
4) Reflection
The researcher evaluated the students reading skill
improvement. After teach, the researcher make a consultation
with English teacher. English teacher gave suggestion and
advised for the future teaching performance. Besides, the
researcher asked about the students writing progress
according to the English teacher.
C. Techniques of Collecting Data
To find the result of this study, first step to do is collecting data.
This is needed to have the valid and obvious information. The collected
51
the proof of the study done. The data is collected by some procedures. The
procedures of data collection are observation, interview, and test.
1. Observation
The observation is conducted by the researcher to have
description about the subject.The reseracher got the headmaster’s
permission to collect data by doing observation in the school
classroom, it was September 10, 2015. After the permission was
given, the researcher met the English teacher to make appointment to
do the observation. Then, the researcher observe the
teaching-learning activity in the classroom to know how to teach the eighth
grade students and how much the capability of students.
2. Interview
The researcher interviewed the eighth grade’s English
teacher to know the condition of the students before conducting the
research at September 14, 2015. During the interview the researcher
asked the teacher about the english learning in the eight grade. Such
as how much the “KKM”, what are the syllabus, and what the
material was given. Then the researcher checked off it with the
material which used in the research. Between researcher and teacher,
they agree that the material which used is “Descriptive text”.
3. Test
The researcher provided pre-test in every cycle (cycle I
52
about descriptive text before applying KWL Strategy. Moreover, the
researcher gave post-test to know how far is the improvement of
students’ reading comprehension about descriptive text after
applying this method. The score’s KKM is 70, and the target of the
KKM is 70 %.
4. Documentation
The researcher needs some documentations and data to know
about the school situation of this research. Documentation included
not only the official organizational papers, report, brochures but also
the more work-day, work plans, and materials which gotten from
head master, so this research can produce good finding.
D. Analysis of Data
After collecting the data, the next step of this study is analyzing the
data. There are two ways to analyze data, they are:
1. Descriptive Qualitative Technique
A descriptive tecnique is used to know the students behavior
during the teaching learning process. In descriptive technique, the
researcher analyzes the observation sheet which has been made by her
partner (collaborator).
2. Statistical Technique (Quantitative)
A statistical technique is used to know the extent to using
53
comprehension, the result of pre-test and post-test. This research is
calculated by t-test analysis:
a. Mean
Mean is the technique to calculate the average of the
students’ score.The mean valuecan be determinedby dividingthe
amount of datawiththe number of data. The formula is:
M=
∑ ×
Clarification :
M : Mean
∑ F x : The sum of student’s score
N : The total number of student
b. SD (Standart Deviation)
The fisrt step, the researcher calculate SD. The standart
devinition is the positive square root of the variance, where the
operation of taking the square root converts the variance value
back into the original units of measurement of the observations.
The formula is:
SD =
∑D
N −
∑ D
N
Clarification :
54
D : Different between pre-test post-test
N : Number of observation in sample
c. T-test
After calculating the SD, the researcher calculate t-test to
know is there any significant differences or not between pre-test
and postest, After calculating the SD, the researcher calculate
t-test to know is there any significant differences or not between
pre-test and post-pre-test, After calculating the SD, the researcher calculate
t-test to know is there any significant differences or not between
pre-test and post-test. The Formula is :
∑
√
Clarification :
: T-test for the differences of pre-test and post-test
SD : Deviation Standart for one sample t-test
D : Different between pre-test and post-test
55
CHAPTER IV RESEARCH FINDING
In this chapter, the researcher would like to analyze the data
gathered from the action research activities. This chapter focuses on analyzing
the collected data. The data was obtained from teaching learning process and
evaluation. The function of data analysis is to measure the students’ reading
comprehension improvement by applying KWL Strategy.
In this chapter, the researcher gives the details of the findings. This
chapter is likely the main discussion of the research conducted. It displays the
finding of the collected data since in the beginning until the end of the
research. The findings consist of the results of the cycle I and cycle II. The two
cycles are treatment of the implementation of the KWL Strategy in the reading
instruction.
1. Implementation of using KWL Strategy
a. Cycle 1
1) Planning
In this activity, the researcher’s planning were:
a) Preparing the material of teaching.
b) Preparing the lesson plan as guidance in
teaching-learning activity.
56
d) Preparing the teaching instrument, it was pictures and
example of descriptive text.
e) Preparing pre- and post-test for students.
f) Preparing the observation sheet.
2) Acting
The researcher did the research on Friday,
September 18th 2015 at 07.40. It was in the class of VIII
which consists of 38 students because 1 student was not
present. The condition of class was quiet when the English
teacher, the researcher, and the observer came to the class.
Then the English teacher gave greeting for the students and
introduced researcher and observer. Fortunately, English
class beganin the first hour. So, the students still spirit, fresh
and enthusiastic to get lesson. Before the researcher began
the class she introduced herself and told the students her
purpose to do the action research. After that, the teacher
started in explaining the little material. She explained about
the definition of descriptive text, and generic stucture of
descriptive text. Then, the teacher gave the pre test for the
students. After that, the teacher gave explain new strategy in
reading, it is use Know Want Learn (KWL) Strategy. In this
strategy use KWL Chart. The beggin by naming the topic,
57
abouit it, then the teacher write the KWL Chart on the
whiteboard. The teacher gave the picture about the topic,
After that, the teacher ask the the students to call out what
want to know about the topic, and write their ideas on fileds
marked KNOW. Then the teacher ask the students to think
about questions they have about the topic. They might start
by reviewing waht they know, and find areas where their
knowledge is incomplete, wrote their questions on the chart
in the column marked WANT. After that the teacher gave the
students text about the topic, the students have to read the
text, they are reminded to seek answers to their questions.
Then the students wrote the things they learned from the text,
they wrote their answers to these questions, and they wrote
the important ideas that they find interesting, the students
noted these in the chart in the column LEARN.
After that, the teacher gave post test and the students
did it until the times up. The students submitted their paper
assigmnments. The teacher gave summary of the lesson at the
day. The students felt more entuasism with the
teaching-learning activity.
3) Observing
In the first cycle, the researcher and her partner
58
students’ activity and attention during the action. Observation
made at the time of learning descriptive text before and after
using KWL Strategy, observation focused on students’
reading comprehension.
For the results of this action, the researcher can see
that the students were unready in learning descriptive text.
Almost of them looked confused in doing the pretest. Some
of them asked the answer to their friends.
The teacher also observed the students’ activeness in
asking, answering questions, and giving feedback. In this
action, almost of them was silence in the class, only several
students who has answered the teachers’ question.
The researcher would like to analyze the students’
improvement in reading comprehension by calculating the
result of pretest and posttest. The result of both of the tests
can be seen in the table as follows: The researcher would like
to analyze the students’ improvement in reading
comprehension by calculating the result of pretest and
posttest.
Table 4.1
The result of pretest and posttest cycle I
No Names of Students Pre Test I (X) Post Test I (Y) Pos-Pre (D) D2
60
26 Setyorini 40 60 20 400
27 Shihabudin 70 60 -10 100
28 Siti Nur Wahyuni 50 60 10 100
29 Vita Lutfiana 90 90 0 0
30 Muhammad Ihsan 60 50 -10 100
31 Yuniar Hendri Widiyanti 80 80 0 0
32 Yunita Ardiyanti 50 60 10 100
33 M. Adi Saputra - - - -
34 Ria Ulfasari 60 90 30 900
35 Siti Masruroh 60 80 20 400
36 M. Soviul Mubarok 50 70 20 400
37 Eka Devi Setianingsih 50 70 20 400
38 Yasinta Faticurrahmah 70 90 20 400
39 Syifaul Qulub 40 60 20 400
Total 2280 2690 410 8500
1) Calculating Mean of Pre-test and Post-test Cycle 1
a) Mean of Pre-test 1 :
M =FxN
M =228039
M = 58,46 b) Mean of Post-test 1 :
61 M =269039
M = 68,97
Mean of pre test = 58,46
Mean of post test = 68,97
Mean of pre test ≤ than post test
There is an improvement of reading comprehension throught KWL
Strategy between pre test I ( before the action) and the post test I
(after the action)
2) Standard Deviation of post test and pre test
From the data above, the teacher calculated SD pretest and
posttest:
SD = ∑DN − ∑ DN
SD = 850039 − 41039
SD = 217,95 − 110,46
SD = √107.49
SD = 10,37
3) T-test calculation
t ∑
62
T-table < t-calculation = 2,02 <6,26
4) Reflecting
The T-calculation is bigger than T-table is 6,26, which
means that there is considerable influence in cycle I. The
T-calculation shows that The T-table is 2,02 while the T-T-calculation.
After analyzing the result of the action in cycle I, the researcher
concluded that the students’ reading comprehension was improved.
It was shown by the average of posttest, which is higher than the
average of pretest.
In other hand, the researcher needed to explain the material
in detail in order to make the students understand well. The
researcher must guide the students to discuss and present the
material in front of the class. Besides, the students must be more