The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 135 ANALYSIS OF EDUCATIONAL FACTORS, INTEREST AND MOTIVATION
TOWARDS THE BEHAVIOR OF EARLY DETECTION OF CA CERVIKS IN WOMEN OF FERTILE AGE IN THE UPT HEALTH CENTER KEMBANGBAHU
LAMONGAN
Lilik Darwati1, Abdul Muhith2, Nurwijayanti Nurwijayanti2 Student Post Graduate Program1
Lecturer Post Graduate Program2
Institute of Health Science Surya Mitra Husada Kediri Email: [email protected]
ABSTRACT
CA cerviks is the most common cancer in women. Therefore necessary prevention efforts as early as possible with early detection of ca cerviks. The purpose of the study to find out the influence of factors of education, interest and motivation towards the behavior of early detection of ca cerviks in the WUS in the health Kembangbahu Lamongan design research using observational analytic with cross design sectional. The entire population is WUS 9476 in UPT Kembangbahu Lamongan with 369 samples of respondents taken with engineering porportional cluster random sampling. Free Educational variables, interests, motivation to use the questionnaire and conduct early detection terikatnya variable using observations. Data analysis with logistic regression test. From the results of the study known to almost half of the respondents in the implementation of education ca cerviks including less i.e. 130 respondents (35.2%), almost half of the respondents had a high interest in implementing early detection of ca cerviks i.e. 163 respondents (44.2%), nearly half of respondents have low motivation implement early detection of ca cerviks i.e. 149 respondents (40.4%) and most of the respondents implement early detection of ca cerviks with papsmear IE as much as 271 respondents (73.7%) of a total of 369 respondents . There are educational factors influence behaviour towards early detection of ca cerviks in the WUS (p value 0.000 < 0.05 then Ho denied), there is interest in behavioral factors influence early detection of ca cerviks in the WUS (p value 0.000 < 0.05 then Ho denied), there is the influence of motivation factors against the behavior of early detection of ca cerviks in the WUS (p value 0.05 then Ho 0.004 < rejected) and there the influence factors of education, interest and motivation towards the behavior of early detection of ca cerviks in the WUS (p value 0.000 < 0.05 then Ho denied). to make the behavior is indeed needed a variety of factors as predisposing factors include education, interest and motivation. It was concluded that educational factors, interest and motivation being the dominant factor against the behavior of early detection of ca cerviks in women of fertile age. It is recommended that place research improve outreach regarding early detection of ca cerviks in the WUS
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 136
INTRODUCTION
CA cerviks is the most common cancer in women in the world. Ca cerviks deaths are projected to increase by almost 25% over the next 10 years. More than 270,000 women's deaths due to cervical cancer every year in the developing world than in manju (WHO, 2013). True to its name, Ca cerviks is a cancer that occurs in cervical uterus, an area on the female reproductive organs that constitute the entrance towards the uterus between the womb (uterus) and liang intercourse (vagina). The term "cancer" in itself already give the impression of scary. Therefore the expected incidence rate of this cancer can be pressed as low as possible (Anurogo, 2009).
In fact the incident number Ca cerviks is still very high. CA cerviks experienced more than 1.4 million women worldwide (Ferlay in
Health RI, 2013). Each year more than 460,000 cases occurred and about 231,000 women died Ca cerviks (Parkin in Health RI, 2013). In Indonesia based on basic health Research data the year 2013 figures recorded the incident Ca cerviks on women as much as 522,354 sufferers (Trihono, 2013). In East Java, basic
health Research data based on the year of 2013 recorded the numbers of Genesis Ca cerviks on women as much as 1.6/100% o (Trihono, 2013).
In the PROVINCIAL
HOSPITAL Dr. Soegiri Lamongan Year 2016 and 2017 years recorded the numbers of Genesis Ca cerviks in women.
Table 1.1 Number Ca cerviks Events at the PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL Dr. Soegiri Lamongan
Source: outpatient Registers poli deposits. Lamongan: HOSPITALS Soegiri.
CA cerviks can be detected as early as possible with IVA test (Visual inspection Acetate) or Pap Smear. In Lamongan recorded data examination IVA or Pap Smear. Table 1.2 Scope examination of early detection of Ca cerviks in Lamongan
Source: Health Office Lamongan
While Dipuskesmas
kembangbahu IVA Test (Visual inspection Acetate) or a Pap Smear in the UPT Health Center kembangbahu area
Table 1.2 scope of Examination Early detection of Ca cerviks in the
No. Month
Px Ca cerviks 2016 2017
1 January 36 40
2 February 20 23
3 March 37
4 April 34
5 May 37
6 June 38
7 July 33
8 August 31
9 September 34
10 October 36
11 November 39
12 December 41
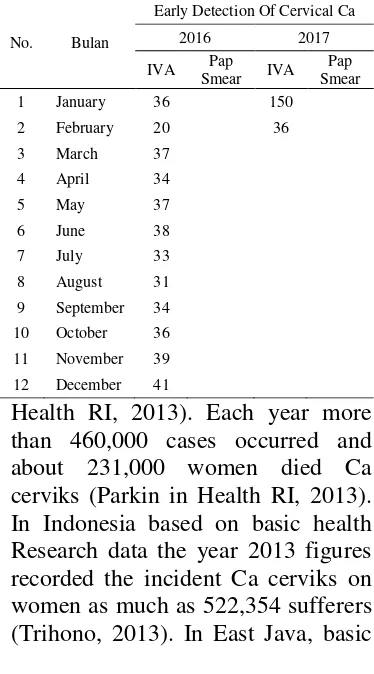
No. Bulan
Early Detection Of Cervical Ca
2016 2017
IVA Pap Smear IVA
Pap Smear
1 January 36 150
2 February 20 36
3 March 37 4 April 34
5 May 37
6 June 38 7 July 33 8 August 31 9 September 34 10 October 36 11 November 39
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 137 UPT Health Center kembangbahu
area
Source: outpatient Clinics Register Kembangbahu
Results of research Eva Sulistiowati (2012) shows as much as 3.8% of women have already done tests IVA of 3,303 respondents in Central Bogor Bogor regency.
The high incidence rate of Ca cerviks can be caused by various factors. The cause of this cancer is the Human papilloma virus (HPV), which is a type of virus that attacks humans (compass, 2008). According to the National Institute of Environmental Health Science at Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, the compound Bisphenol A that is a type of chemical substances to make hard plastic containers, such as jars of water and to coat cans of soup) can cause cancer cancer of the breast, ovaries, uterus, endometriosis, cancer and fertility problems. In pregnant women, this chemical can be forwarded to janinnya (Roman, 2013). CA cerviks occurs due to the growth of cells on an uncommon cerviks (abnormal). But before these cells into cancer cells, occur some of the changes
experienced by the cells. The cell changes usually take up to years before the last cells turn into cancer cells.
Risk factors for Ca cerviks among other things a woman never had sexual intercourse, women smoking, having a sexual partner, started sexual activity at a very young age (Riono, 2009). Risk factors that can increase the chances of cervical cancer include age the first time you have sex less than 20 years, has many partners, have experienced sexually transmitted infeski, mother or sister has cancer of the neck the uterus, the previous pap test results are normal and not smoking (Kemenkes, 2015). The research results of Sri Syatriani (2011) suggests cervical cancer risk factors can also be triggered by the use of low-quality dressing (OR = 2.320), the use of SOAP a pH > 4 (OR = 2.360), socio-economic status (OR = 4.087) and a couple of men who do not disirkumsisi (OR = 2.092). The impact occurred at an early stage is the incidence of vaginal discharge, foul-smelling pink or brownish, abnormal menstrual bleeding, and pain when sexual intercourse (Anurogo, 2009).
Given the impact that such has occurred then that should be done in an effort to avoid the Ca cerviks. The first is if ever had sexual intercourse then had to do early detection of Ca cerviks with pap smear test regularly every two years until the age of 70 years. The second case was reported abnormal symptoms such as bleeding, especially after coitus (intercourse). The third thing is don't smoke (Riono, 2009). Other methods
No. Bulan
Early Detection Of Cervical Ca
2016 2017
IVA Pap Smear IVA
Pap Smear 1 January 6 - 3 -
2 February 7 - 3 -
3 March 2 - 3 -
4 April - 108 - 105
5 May 10 -
6 June 1 -
7 July - 38
8 August - -
9 September - - 10 October - - 11 November - -
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 138 besides pap smear is by Visual
inspection with acetic acid. Current cervical cancer can also be prevented by administering the HPV vaccine. This step can provide protection against some types of HPV can cause genital warts and cerviks Ca (compass, 2008).
The problem is that there are still many Women fertile Age does not implement early detection of Ca cerviks. Many of the factors that led to the lack of implementation of early detection. The study of an aspect of behaviour according to Green (Notoatmodjo, 2010) someone wants to do something such as early detection of ca cerviks will know if the purpose and merits. After know will determine attitudes i.e. agree or disagree with that program. After that also depends on perception, values, belief. So too will depend pemungkin factors such as the presence of affordable health facilities to implement early detection, presence of social support and so on. Maslow's motivation
theory says people will be compelled do an act based on need, besides the desire or interest or motivation. A powerful motivation or impulse must be inculcated to sufferers through various approaches. The hope will be soon arose interest to implement early detection of Ca cerviks.
Based on the above description of the researchers intend to do research with formulating in the title: "analysis of Educational Factors, interest and Motivation towards the behavior of early detection of Ca cerviks in women of fertile Age in the area of District Kembangbahu UPT Health Center Lamongan ".
Research Objectives
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 139
RESEARCH METHODS
Analytic observational research design with cross sectional approach i.e. research conducted to determine the relationship between variables according to the demand without the intervention of researchers, which or the collection of data on each the subject of the study only observed once. Its population is the whole fertile age women who are on the UPT Clinic Kembangbahu Lamongan as much 9.479 married WUS. , the number of respondents as many as 369 respondents Teknikproportional cluster random sampling. Education data collection, interests, motivation to use the questionnaire and conduct early detection of ca cerviks using observations that are given on women of fertile age who are in the UPT Clinic Kembangbahu Lamongan. then analyzed by Logistic Regression.
RESULTS
Characteristics Of Respondents Table 4.1 Characteristics of respondents Based On Age
Based on table 4.1 is known to most respondents aged 35 years > i.e. as many as 186 respondents (50.4%) of a total of 369 respondents.
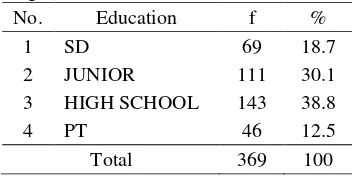
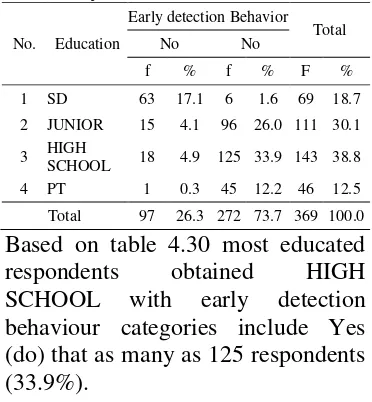
Table 4.2 the characteristics of the respondents Based On Education
No. Education f %
1 SD 69 18.7
2 JUNIOR 111 30.1
3 HIGH SCHOOL 143 38.8
4 PT 46 12.5
Total 369 100
Based on table 4.2 known HIGH SCHOOL educated respondents i.e. half as much of the 143 respondents (38.8%) of a total of 369 respondents.
Table 4.3 Characteristics of respondents based on Occupations
No. The work F %
1 Farmer 293 79.4
2 Private 62 16.8
3 PNS 14 3.8
Total 369 100
Based on table 4.3 Note most respondents working as farmers i.e. as many as 293 respondents (79.4%) of a total of 369 respondents.
Table 4.4 Characteristics of respondents based on Gravida
No. Status Of Gravida f %
1 Primigravida 164 44.4
2 Multigravida 147 39.8
3 Grandemultigravida 58 15.7
Total 369 100
Based on table 4.4 Note half the respondents including primigravida IE as much as 164 respondents (44.4%) of a total of 369 respondents.
No. Age F %
1 <20 years 32 8.7 2 20-35 years 151 40.9 3 >35 years 186 50.4
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 140 Table 4.5 Characteristics of
respondents based on early detection of Ca Cerviks
Information f %
1 Never 0 0.0
2 Ever 369 100.0
Total 369 100
Based on table 4.5 known throughout the respondents never get information about early detection of ca cerviks in women of fertile age i.e. as many as 369 respondents (100.0%) of a total of 369 respondents.
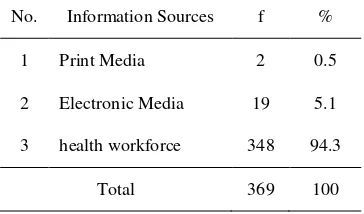
Table 4.6 the characteristics of Respondents based on information sources early detection of Ca Cerviks
No. Information Sources f %
1 Print Media 2 0.5
2 Electronic Media 19 5.1
3 health workforce 348 94.3
Total 369 100
known to the rest of the respondents get information about early detection of ca cerviks in women of fertile age from health workers that is as much as 348 respondents (94.3%) of a total of 369 respondents.
Special Data
1. Education Ca Cerviks
Table 4.7 Education Ca Cerviks in women of fertile Age
No. Education f %
1 Less 130 35.2
2 Enough 116 31.4
3 Good 123 33.3
Total 369 100
Based on table 4.7 are known to most respondents educational implementation of ca cerviks in women of fertile Age categories include less that is as many as 130 respondents (35.2%) of a total of 369 respondents.
2. Interest in the early detection of Ca Cerviks
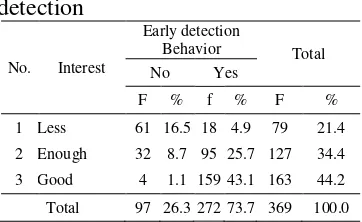
Table 4.8 interest in early detection of Ca Cerviks in women of fertile Age
No. Interest f %
1 Low 79 21.4
2 Medium 127 34.4
3 High 163 44.2
Total 369 100
Based on table 4.8 known to most respondents included have high interest to implement early detection of ca cerviks IE as much as 163 respondents (44.2%) of a total of 369 respondents.
3. Motivation towards early detection of Ca Cerviks
Table 4.9 Motivation towards early detection of Ca Cerviks in women of fertile Age
No. Motivation f %
1 Low 149 40.4
2 Medium 107 29.0
3 High 113 30.6
Total 369 100
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 141 4. Conduct early detection of Ca
Cerviks with Papsmear
Table 4.10 Conduct early detection of Ca Cerviks with a Papsmear on Fertile Age Women
No. The Behavior Of
The Papsmear f %
1 Don't do 97 26.3
2 Do 272 73.7
Total 369 100
Based on table 4.10 known to most respondents included implementing early detection of ca cerviks with papsmear i.e. as many as 272 respondents (73.7%) of a total of 369 respondents.
B.`Cross-Tabulations Between
Variables
1. Cross-Tabulated Characteristic Table 4.11 cross-Tabulate the age of respondents with Educational
Based on table 4.11 obtained most respondents aged 35 years with educational > categories include both IE as much as 77 respondents (20.9%).
No. Education
Edukasi
Total
Less Enough Good
f % F % F % f % 1 SD 60 16.3 5 1.4 4 1.1 69 18.7 2 JUNIOR 29 7.9 42 11.4 40 10.8 111 30.1
3 HIGH
SCHOOL 35 9.5 48 13.0 60 16.3 143 38.8 4 PT 6 1.6 21 5.7 19 5.1 46 12.5 Total 130 35.2 116 31.4 123 33.3 369 100.0
Table 4.12 Cross Tabulate education with Education
Based on table 4.12 obtained the most educated respondents with ELEMENTARY education including categories less and high school with both categories namely each of as many as 60 respondents (16.3%).
Cross-Tabulations table 4.13 job with Education
No. Job
Education
Total Less Enough Good
F % F % f % f %
1 Farmer 117 31.7 83 22.5 93 25.2 293 79.4
2 Private 12 3.3 25 6.8 25 6.8 62 16.8
3 PNS 1 0.3 8 2.2 5 1.4 14 3.8
Total 130 35.2 116 31.4 123 33.3 369 100.0
Based on table 4.13 obtained most of the respondents are farmers with less IE categories include education as much as 117 respondents (31.7%).
Table 4.14 Cross Tabulations Gravida with Education
No. Gravida
Education
Total Less Enough Good
F % F % f % f % 1 Primi 56 15.2 51 13.8 57 15.4 164 44.4 2 Multi 64 17.3 45 12.2 38 10.3 147 39.8 3 Grande 10 2.7 20 5.4 28 7.6 58 15.7 Total 130 35.2 116 31.4 123 33.3 369 100.0
Based on table 4.14 obtained most of the respondents were multigravida with less IE categories include education as much as 64 respondents (17.3%).
No. Age (Years)
Education
Total Less Enough Good
F % f % f % f %
1 <20 th 30 8.1 2 0.5 0 0.0 32 8.7
2 20-35 th 62 16.8 43 11.7 46 12.5 151 40.9
3 >35 th 38 10.3 71 19.2 77 20.9 186 50.4
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 142 Table 4.15 Cross Tabulate
information with Education
No. Information
Education
Less Enough Good
F % F % f %
1 Never 0 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0 2 Ever 130 35.2 116 31.4 369 33.3
Total 130 35.2 116 31.4 369 33.3
Based on table 4.15 are obtained by most of the respondents are never get information about early detection of ca cerviks with less categories include education that is as many as 130 respondents (35.2%).
Table 4.16 cross-Tabulate with Educational information resources
No. Reso- urces
Education
Total Less Enough Good
f % f % f % f % 1 Print 0 0.0 2 0.5 0 0.0 2 0.5
2 Electronic 1 0.3 12 3.3 6 1.6 19 5.1 3 Nakes 129 35.0 102 27.6 117 31.7 348 94.3
Total 130 35.2 116 31.4 123 33.3 369 100.0
Based on table 4.16 obtained most respondents get information about early detection of ca cerviks of health workers with less education includes categories i.e. as many as 129 respondents (35%).
2. Cross-Tabulated the characteristics of Respondents with an interest in early detection
Table 4.17 cross-Tabulate the age of Respondents with an interest in the early detection of Ca Cerviks in
No. Age (Years)
Interest
Total Less Enough Good
F % f % f % f % 1 <20 th 17 4.6 15 4.1 0 0.0 32 8.7 2 20-35 th 48 13.0 41 11.1 62 16.8 151 40.9 3 >35 th 14 3.8 71 19.2 101 27.4 186 50.4 Total 79 21.4 127 34.4 163 44.2 369 100.0
Based on table 4.17 obtained most respondents aged 35 years > with an interest in the early detection of ca cerviks categories include high i.e. as many as 101 respondents (27.4%), 0
Table 4.18 Cross Tabulations of education with an interest in the early detection of Ca Cerviks
No. Edu- cation
Interest
Total Less Enough Good
F % f % F % f % 1 SD 43 11.7 24 6.5 2 0.5 69 18.7 2 JUNIOR 15 4.1 33 8.9 63 17.1 111 30.1
3 HIGH
SCHOOL 20 5.4 55 14.9 68 18.4 143 38.8 4 PT 1 0.3 15 4.1 30 8.1 46 12.5 Total 79 21.4 127 34.4 163 44.2 290 100.0
Based on table 4.18 most educated respondents obtained HIGH SCHOOL with an interest in the early detection of ca cerviks high categories include IE as much as 68 respondents (18.4%).
Table 4.19 Cross Tabulations of the work with an interest in the early detection of Ca Cerviks
No. Job
Interest
Total Less Enough Good
f % f % f % f % 1 Farmers 70 19.0 100 27.1 123 33.3 293 79.4 2 Private 9 2.4 21 5.7 32 8.7 62 16.8 3 PNS 0 0.0 6 1.6 8 2.2 14 3.8
Total 79 21.4 127 34.4 163 44.2 369 100.0
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 143 Table 4.20 Cross Tabulations
Gravida with an interest in the early detection of Ca Cerviks
No. Gravida
Interest
Total Less Enough Good
f % f % f % f % 1 Primi 26 7.0 65 17.6 73 19.8 164 44.4 2 Multi 47 12.7 40 10.8 60 16.3 147 39.8 3 Grande 6 1.6 22 6.0 30 8.1 58 15.7 Total 79 21.4 127 34.4 163 44.2 369 100.0
Based on table 4.20 obtained most of the respondents is primigravida with an interest in the early detection of ca cerviks categories include high i.e. as many as 73 respondents (19.8%).
Table 4.21 Cross Tabulations of information with an interest in the early detection of Ca Cerviks
No. Infor- mation
Interest
Total Less Enough Good
F % f % f % f % 1 Never 0 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0 2 Ever 79 21.4 127 34.4 163 44.2 369 100.0
Total 79 21.4 127 34.4 163 44.2 369 100.0
Based on table 4.21 obtained most of the respondents are never get information about early detection of ca cerviks with an interest in the early detection of ca cerviks high categories include IE as much as 163 respondents (44.2%)
Table 4.22 Cross Tabulate information sources with an interest in the early detection of Ca Cerviks
No. Information Sources
Interest
Total Less Enough Good
F % f % f % f % 1 Print 0 0.0 1 0.3 1 0.3 2 0.5 2 Electronic 1 0.3 6 1.6 12 3.3 19 5.1 3 Nakes 78 21.1 120 32.5 150 40.7 348 94.3
Total 79 21.4 127 34.4 163 44.2 369 100.0
Based on table 4.22 obtained most respondents get information about early detection of ca cerviks of health workers with an interest in the early
detection of ca cerviks categories include high i.e. as many as 150 respondents (40.7%).
3. Cross-Tabulated the characteristics of Respondents with motivation Detection
Table 4.23 cross-Tabulate the age of Respondents with motivation early detection of Ca Cerviks
No. Age (Years)
Motivation
Total Low Medium High
F % f % f % f % 1 <20 th 26 7.0 6 1.6 0 0.0 32 8.7 2 20-35 th 70 19.0 40 10.8 41 11.1 151 40.9 3 >35 th 53 14.4 61 16.5 72 19.5 186 50.4 Total 149 40.4 107 29.0 113 30.6 369 100.0
Based on table 4.23 obtained most respondents aged 35 years > with motivation early detection including high category i.e. as many as 73 respondents (19.5%).
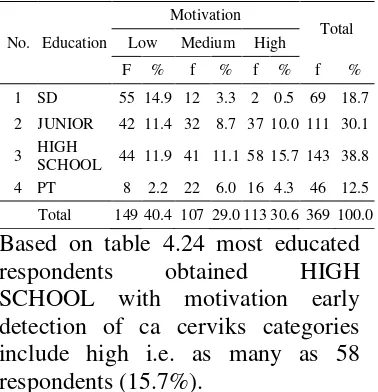
Table 4.24 Cross Tabulate Education with motivation early detection of Ca Cerviks
No. Education
Motivation
Total Low Medium High
F % f % f % f % 1 SD 55 14.9 12 3.3 2 0.5 69 18.7 2 JUNIOR 42 11.4 32 8.7 37 10.0 111 30.1 3 HIGH
SCHOOL 44 11.9 41 11.1 58 15.7 143 38.8 4 PT 8 2.2 22 6.0 16 4.3 46 12.5 Total 149 40.4 107 29.0 113 30.6 369 100.0
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 144 Table 4.25 Cross Tabulate Work
with motivation early detection of Ca Cerviks
No. Job
Motivation
Total Low Medium High
f % f % f % f % 1 Farmer 126 34.1 83 22.5 84 22.8 293 79.4 2 Private 20 5.4 17 4.6 25 6.8 62 16.8 3 PNS 3 0.8 7 1.9 4 1.1 14 3.8
Total 149 40.4 107 29.0 113 30.6 369 100.0
Based on table 4.25 obtained most of the respondents are farmers with motivation early detection of Ca Cerviks categories include low IE as much as 126 respondents (34.1%).
Table 4.26 Cross Tabulations Gravida with motivation early detection of Ca Cerviks
No. Gravida
Motivation
Total Low Medium High
F % f % f % f % 1 Primi 62 16.8 46 12.5 56 15.2 164 44.4 2 Multi 69 18.7 46 12.5 32 8.7 147 39.8 3 Grande 18 4.9 15 4.1 25 6.8 58 15.7 Total 149 40.4 107 29.0 113 30.6 369 100.0
Based on table 4.26 obtained most of the respondents were multigravida with motivation early detection of Ca Cerviks categories include low IE as much as 69 respondents (18.7%).
Table 4.27 cross-Tabulate information with Motivation early detection of Ca Cerviks
No. Infor- mation
Motivation
Total Low Medium High
f % f % f % f % 1 Never 0 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0 2 Ever 149 40.4 107 29.0 113 30.6 369 100.0
Total 149 40.4 107 29.0 113 30.6 369 100.0
Based on table 4.27 obtained most of the respondents are never get information about early detection of Ca Cerviks with motivation early detection of ca cerviks categories
include low IE as much as 149 respondents (40.4%).
Table 4.28 Cross Tabulate information resources with motivation early detection of Ca Cerviks
No. Information Sources
Motivation
Total Low Medium High
f % f % f % F % 1 Print 0 0.0 2 0.5 0 0.0 2 0.5 2 Electronic 5 1.4 8 2.2 6 1.6 19 5.1 3 Nakes 144 39.0 97 26.3 107 29.0 348 94.3
Total 149 40.4 107 29.0 113 30.6 369 100.0
Based on table 4.28 obtained most respondents get information about early detection of ca cerviks from health care personnel with motivation early detection of ca cerviks categories include low i.e. as many as 144 respondents (39%).
4. Cross-Tabulated the characteristics of Respondents conduct early detection
Table 4.29 cross-Tabulate the age of Respondents conduct Papsmear
No. Age (Years)
Early detection
Behavior Total No Yes
f % f % F % 1 <20 th 32 8.7 0 0.0 32 8.7 2 20-35 th 53 14.4 98 26.6 151 40.9 3 >35 th 12 3.3 174 47.2 186 50.4
Total 97 26.3 272 73.7 369 100.0
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 145 Table 4.30 Cross Tabulate education
with early detection Behavior
No. Education
Early detection Behavior Total
No No
f % f % F % 1 SD 63 17.1 6 1.6 69 18.7 2 JUNIOR 15 4.1 96 26.0 111 30.1 3 HIGH
SCHOOL 18 4.9 125 33.9 143 38.8 4 PT 1 0.3 45 12.2 46 12.5 Total 97 26.3 272 73.7 369 100.0
Based on table 4.30 most educated respondents obtained HIGH SCHOOL with early detection behaviour categories include Yes (do) that as many as 125 respondents (33.9%).
Table 4.31 Cross Tabulations of the work with the behavior of early detection
No. Job
Early detection Behavior Total No Yes
f % f % F % 1 Farner 92 24.9 201 54.5 293 79.4 2 Private 5 1.4 57 15.4 62 16.8 3 PNS 0 0.0 14 3.8 14 3.8
Total 97 26.3 272 73.7 369 100.0
Based on table 4.31 obtained most of the respondents is the farmer with the behavior of early detection categories include Yes (do) as much as 201 respondents (54.5%).
Table 4.32 Cross Tabulations Gravida with the early detection Behavior
No. Gravida
Early detection
Behavior Total No Yes
F % f % F %
1 Primi 40 10.8 124 33.6 164 44.4 2 Multi 54 14.6 93 25.2 147 39.8 3 Grande 3 0.8 55 14.9 58 15.7 Total 97 26.3 272 73.7 369 100.0
Based on table 4.32 obtained most of the respondents is primigravida with early detection behaviour categories
include Yes (do) as much as 124 respondents (33.6%).
Table 4.33 Cross Tabulate information with the behavior of early detection
No. Information
Early detection
Behavior Total No Yes
F % f % F % 1 Never 0 0.0 0 0.0 0 0.0 2 Ever 97 26.3 272 73.7 369 100.0
Total 97 26.3 272 73.7 369 100.0
Based on table 4.33 obtained most of the respondents are never get information about early detection of ca cerviks with the behavior of early detection categories include Yes (do) i.e. as many as 272 respondents (73.7%).
Table 4.34. Cross-Tabulate information sources with the behavior of early detection
No. Source Of Information
Early detection
Behavior Total No Yes
F % f % F % 1 Print 0 0.0 2 0.5 2 0.5 2 Electronic 0 0.0 19 5.1 19 5.1 3 Nakes 97 26.3 251 68.0 348 94.3
Total 97 26.3 272 73.7 369 100.0
Based on table 4.34 obtained most respondents get information
about early detection of ca cerviks from health workers conduct papsmear categories include Yes (do) as much as 251 respondents (68%).
5. Cross Tabulate Variables Research Table 4.35 Cross Tabulate Education with early detection Behavior
No. Education
Early detection
Behavior Total No Yes
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 146 Based on table 4.35 obtained most of
respondents with educational category of early detection of ca cerviks with the behavior of early detection categories include Yes (do) as much as 122 respondents (33.1%).
Table 4.36 Cross Tabulations of interest with Behaviors early detection
No. Interest
Early detection
Behavior Total No Yes
F % f % F % 1 Less 61 16.5 18 4.9 79 21.4 2 Enough 32 8.7 95 25.7 127 34.4 3 Good 4 1.1 159 43.1 163 44.2 Total 97 26.3 272 73.7 369 100.0
Based on table 4.36 obtained most of the respondents with high category of interest in the early detection of ca
cerviks with behavior papsmear categories include Yes (do) as much as 159 respondents (43.1%).
Table Cross-Tabulations of motivation with 4.37 behavior of early detection
No. Motivation
Early detection Behavior Total No Yes
F % f % F % 1 Less 78 21.1 71 19.2 149 40.4 2 Enough 19 5.1 88 23.8 107 29.0 3 Good 0 0.0 113 30.6 113 30.6 Total 97 26.3 272 73.7 369 100.0
Based on table 4.37 obtained most of the respondents with high motivation category about early detection of ca cerviks with behavior papsmear categories include Yes (do) as much as 113 respondents (30.6%).
C. the results of statistical tests
The results of the logistic regression test Education Factor Influences, interests and motivation towards the behavior of early detection of Ca Cerviks in women of fertile Age in the health Kembangbahu Lamongan April 12 until May 12, 2017
B S.E. Wald df Sig. Exp(B)
95% C.I.for EXP(B)
Lower Upper
Step 1a Edukation 4.430 .702 39.833 1 .000 83.940 21.207 332.234
Interes 1.877 .339 30.702 1 .000 6.532 3.363 12.687
Motivation -1.225 .595 4.231 1 .040 .294 .091 .944
Constant -7.268 .906 64.343 1 .000 .001
a. Variable (s) entered on step 1: Education, interests, motivation.
DISCUSSION
Implementation Of Education Ca Cerviks
Based on table 4.7 known to almost half of the respondents cerviks ca education implementation in women of fertile Age categories include less that is as many as 130 respondents (35.2%) of a total of 369 respondents.
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 147 deciding factor because it is a health
education given to the respondents to pay attention to the background of the client and his needs, education is providing a form of learning with a variety of lectures covering the stimulas using LCD, CD playback, sharing, peer discussion booklets, demonstration examination papsmear and counseling involving the family as supporters. Education wish and the drive to streamline internal and external factors that are owned by the respondent because of those factors that can get the behavior of early detection of cervical cancer. As research conducted by Ackerson of the year 2007 in the USA, in his research that aims to find out the factors that affect women in performing early detection of cancer, found that the behavior of early detection of cancer intrinsic factor is affected by cervical and ekstrisik factors which include age, economic status, education and knowledge.
According to Notoatmodjo (2010) says Education is the learning process of did not know about the value of health be know and from unable to cope with his own health became independent. In this case the primary role of education is to increase knowledge. The knowledge required in order to change the behavior as described in the concept of K-A-P (knowledge-attitude-practice), that the knowledge underlying attitudes and attitudes underlying the formation of behavior.
Almost half of the respondents cerviks ca education implementation in women of fertile Age categories include less. This is due to the implementation of this required cerviks ca educational facilities and infrastructure including the existence of a zpogram for this activity. Facilities and infrastructure in question is of the required learning media such as books,
magazines, newspapers or even internet public awareness by health workers. This means it is not necessarily for everyone have it. This includes the already popular is the internet, not all people use the handpone android that can be used to access the internet to read ca cerviks are common among women of fertile Age.
In addition to the above conditions the implementation of education ca cerviks in women of fertile Age are included in the category of still less can also be caused by other factors related to the characteristics of the respondents as a factor of age, educational background, employment, status of gravida, information as well as information sources. Judging from the age factor, based on the results of the analysis of the obtained most respondents aged 35 years with educational > categories include both. This is caused by the older person's age, then the accumulation of more and more certainly than the education of their young age. This possibility could occur because eduaksi can come from a variety of sources, whether from books, magazines, newspapers, internet, health workers, friends or others.
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 148 then besides includes most high than
ELEMENTARY education group. Another factor that also affects the lack of implementation of cervical cancer is educational background jobs respondents. Based on the results obtained by analysis of most respondents is a farmer with cervical cancer education categories include less. This is caused by his profession as a farmer, then rarely need education regarding ca cerviks. People with this profession generally more focus to the issue of agriculture. Information outside of the agricultural issues in general are also less attracted his attention. So in the end this most farmers groups rarely get eduaksi tentangh ca cerviks.
In addition to the above factors is also related to the status of gravida from respondents. Based on the results of the analysis of the obtained most of the respondents were multigravida with educational categories include less. This is because in general people were less concerned with preventive action regarding the disease. Including less care about the troubles of ca cerviks. Therefore despite already belongs to multigravida, besides being still about ca cerviks is still lacking.
The last factor that influence is information. Based on the results obtained by analysis of most respondents is never get information about early detection of ca cerviks with educational categories include less. This is because despite the categories never get information about early detection of ca cerviks although only one time also keep votes ever. Therefore despite already included never get information about early detection of ca cerviks then still education regarding cerviks ca judged still less. The cause is the respondent looks reluctant to seek information on their own and passive or rely solely on information from health workers.
Based on the results of the analysis of the obtained most respondents get information about early detection of ca cerviks of health workers with less education includes categories.
Interest in the early detection of Ca Cerviks
Based on table 4.8 known to almost half of the respondents including the high interest has to implement early detection of ca cerviks IE as much as 163 respondents (44.2%) of a total of 369 respondents.
The results of the research supported by the existence of a previous research results conducted Fatharani Sepa (2015) claims based on a test of paired t test is known to result in the amount of 0.005 0.000 significantly and this means there are influences counseling about cancer of the cervix against interest do the pap smear. Changes between the pre test post test with IE the number of 29 respondents. Experience increased interest in better, thus it can be concluded that the granting of extension of cervical cancer by the method of buzz group have the influence of maternal interest significantly to yg to do pap smears. With the extension of the mother's interest in doing a pap smear examination be increased, because at the time the extension this is going on the transfer of knowledge and insight about cervical cancer so that increases interest in the early detection of ca by cervik Pap smear or IVA
According to the full moon in the Mathedu (2009) outlines the characteristics of individuals who have a high interest towards something that is the existence of a large concern, have high expectations, success-oriented, have the pride, the willingness of trying and have a positive consideration
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 149 has to implement early detection of ca
cerviks can be caused by various factors such as the presence of a very difficult cancers cured and are at risk of death is already known by almost every woman. The existence of such a large threat which causes someone interested in doing preventative action. One of the ways that prevention is to implement early detection of ca cerviks.
Other factors that affect a high interest to implement early detection of ca cerviks is associated with a person's age is a factor. Based on the research results obtained by most respondents aged 35 years > interest to implement early detection of ca cerviks categories include high. This is due to the age that the older people are increasingly aware of the health risks. Included with age 35 years > for women are also increasingly at risk of experiencing ca cerviks. Therefore in this age group are most interested in implementing early detection of ca cerviks.
In addition to age, other factors also influence on high interest to implement early detection of ca cerviks is associated with the educational background of the respondents. Based on the results of the analysis of the obtained most of the respondents are highly educated HIGH SCHOOL with interest to implement early detection of ca cerviks categories include high. This is caused by the higher education of a person then the better knowledge and also wider aims. High school education can be categorized as a fairly high level of education as factors supporting a person's knowledge, so the more support the existence of high interest to implement early detection of ca cerviks.
Factors that affect height is also seen interest to implement early detection of ca cerviks is the status of gravida. The assumption is with the higher the gravida, the more so the
more positive experience to early detection of ca cerviks. However, based on the results obtained by analysis of most respondents is primigravida with an interest in the early detection of ca cerviks categories include high. This is caused by its status as a primigravida which means the number of children still owned 1 child, apparently already cause excess fear to suffer against the possibility of ca cerviks. This fear is causing the onset of a desire to implement early detection of ca cerviks. This desire is the basis of any such interest to implement early detection of ca cerviks.
Motivation towards early detection of Ca Cerviks
Based on table 4.9 is known to almost half of the respondents included have low motivation to implement early detection of ca cerviks IE as much as 149 respondents (40.4%) of a total of 369 respondents.
The results of this research are consistent with previous research by Beautiful Kurniawati (2015) which stated there is influence significant (OR = 4.700; 95% CI 1.379 hingga16,016; p = 0.013) with mother motivation behavior between checks IVA. Thus the motivation can give directions and activities that should be carried out in accordance with the outline of the objectives planned previously and selection of works, i.e. determining what works to do matching to achieve the goal, by opting out of the works that are not useful for the purpose. A selection of works that are already defined or worked on will give you the confidence that high because it is already in the process of selection.
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 150 needs according to Maslow satisfy
needs will eliminate the role those needs as a motivator. The fulfillment of the needs of the square. Obstruction of the fulfillment of the requirements will reduce the motivation of the person. There are at least four factors that affect changes in the power motive (Winardi quoted Ginting, 2008:95). Satisfy the need for eliminating the role those needs as a motivator. The fulfillment of the needs that the square will lose the motivation of the person.
The results showed almost half of the respondents included have low motivation to implement early detection of ca cerviks. This is due to the onset of the high motivation indeed must be supported by the presence of a very strong feeling of need to implement early detection of ca cerviks. Principle of encouragement or motivation will arise when there is already a feeling of need (need) of people are bersangkuitan, not just desire. The juice of this need will arise when people already know well about the purpose and the benefits of early detection of ca cerviks. Juice of need will arise when people already know the risk if late implement early detection of ca cerviks.
Such conditions would also be influenced by many factors related to the characteristics of each of the respondents, both age, education, occupation, parity as well as other factors. In terms of age factor on the basis of the research results obtained by most respondents aged 35 years > with motivation early detection of ca cerviks categories include high. This is due to the age that the older people are increasingly aware of the health risks. Included with age 35 years > for women are also increasingly at risk of experiencing cancer cerviks. Therefore in this age group the highest motivation to implement early detection of ca cerviks.
In addition to age, other factors that also affect the high motivation to implement early detection of ca cerviks is associated with the educational background of the respondents. Based on the results of the analysis of the obtained most of the respondents are highly educated HIGH SCHOOL with motivation early detection of ca cerviks categories include high. This is caused by the higher education of a person then the better anyway his knowledge and also wider aims. High school education can be categorized as a fairly high level of education as a factor that can bolster one's knowledge, so the support also of the existence of a high motivation to implement early detection of ca cerviks.
Factors that affect height also look the motivation to implement early detection of ca cerviks is the status of gravida. The assumption is with the higher the gravida, the more so the more experience a positive attitude and motivation against the efforts of early detection of ca cerviks. Based on the results of the analysis of the obtained most of the respondents were multigravida with motivation implement early detection of ca cerviks categories include low. This is caused by its status as a multigravida which means the number of children owned more than 2 children, causing mental preparedness the better so that the urge to perform detection of ca cerviks is getting low. This fear experienced semakinn berkuirang because felt is old also no signs of cervical cancer so lose the impetus to implement early detection of ca cerviks.
The behavior of early detection of Cancer Services with Papsmear Test
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 151 The behavior of the formed due
to variety of influence or stimuli in the form of knowledge and attitudes, experiences, beliefs, social, cultural, physical means. The influence of it is internal and external and is classified into factors that influence behavior where according to Lawrence predisposing factors include Green (predisposing factors), the factor pemungkin (enabling factors), and the driving factor ( reinforcing factors). Predisposing factors is internal factors in the individual, family, group or community that makes it easy to behave like individual knowledge, attitudes, values, perceptions, and beliefs. Pemungkin factor is the factor that allows individuals to behave, as due to the availability of resources, affordability, referral, and skills. Amplifier factor a factor corroborating behavior, such as attitudes and skills of health workers, peers, parents, and employers (Suliha, 2012). While according to the theory of Snehendu b. Karr in Notoatmodjo (2010) identifies five determinant of behavior, namely the existence of intention (intention) to act, support from the surrounding community (social support), terjangkaunya (information accesibility of information), the existence of autonomous community or personal freedom (personal autonomy) to take a decision and the existence of conditions and situations possible (action situation).
The results showed most respondents included already implement early detection of ca cerviks with the papsmear test or IVA. This is due to the activities of the early detection of ca cerviks with the papsmear test or IVA in General has been encouraged by health workers. In the current implementation of activities through the early detection test IVA nor the papsmear is one of the efforts to suppress the number of occurrence
of cervical cancer to society including JKN to participants/KIS. To achieve this, Health service assurance provides BPJS early detection of cervical cancer for all women age productive. The inspection can be done at the first level health facilities (health centers) for examination and Laboratory Test IVA teamed up to examination papsmear.
Other factors that also supports the majority of the respondents including implement early detection of ca cerviks with the papsmear is the age, education, occupation, status of gravida or information. In terms of age factor known to most respondents aged 35 years old with behavior > papsmear categories include Yes (do). This is due to the age that the older people are increasingly aware of the health risks. Included with age 35 years > for women are also increasingly at risk of experiencing ca cerviks. Therefore on this age group most widely implement early detection of ca cerviks.
Despite the age of the other factors that also affect the behavior of early detection of ca cerviks is associated with the educational background of the respondents. Based on the results of the analysis of the obtained most of the respondents are highly educated with HIGH SCHOOL behavior papsmear categories include Yes (do). This is caused by the higher education of a person then the better anyway his knowledge and also wider aims. High school education can be categorized as a factor that is high enough to support one's knowledge, so as to support the existence of behaviors to implement early detection of ca cerviks.
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 152 analysis of the obtained most
primigravida papsmear behavior including did. This is because with his status primigravida which means the number of children 1 child, causing concern for the better so there is encouragement implement detection of ca cerviks. Haliniyang behavior accomplishing the cause to implement early detection of ca cerviks.
Other factors that influence is information. Based on the results obtained by analisisi most respondents are never get information about early detection of ca cerviks with behavior papsmear categories include Yes (do). This is caused by never getting the information, then the respondents mengetahuan goals and benefits as well as risks if tidakmelaksanakan pap smear/therefore respondents triggered to execute a papsmear. Assuming this is in accordance with the theory of behavior expressed Notoatmodjo that the behavior manifest dengandi attitudes and attitudinal factors be preceded yangterbentuk be preceded by a factor of knowledge. While knowledge is preceded by information as a source of knowledge. Moreover, based on the results of the analysis of the obtained most respondents get information about early detection of ca cerviks from health workers conduct papsmear categories include Yes (do). This is due to the information in the dapatberasal from a reliable source.
Influence factors of Education against the behavior of early detection of Ca Cerviks
Based on table 4.38 revealed the influence of the educational factor against the behavior of early detection of ca cerviks in women of fertile age in the health Kembangbahu Lamongan (p value 0.000 < 0.05 then Ho denied).
In the concept of K-A-P (knowledge-attitude-practice), meaning that knowledge becomes a factor that precedes the attitude (attitude) of a
person. Attitude to be one of the factors that precede the formation of behavior. So in this case there is a link between a knowledge attitude behavior n da person. This opinion also supported by behavioural expert named Lawrence Green. Explained that the behavior is formed due to various influences or stimuli in the form of knowledge and attitudes, experiences, beliefs, social, cultural, physical means. Influence or stimuli that are internal and external and is classified into the factors that affect behavior. According to Lawrence predisposing factors include Green (predisposing factors), the factor pemungkin (enabling factors), and the driving factor (reinforcing factors). Predisposing factors is internal factors in the individual, family, group or community that makes it easy to behave like individual knowledge, attitudes, values, perceptions, and beliefs. Pemungkin factor is the factor that allows individuals to behave, because resource availability, affordability, referral, and skills. Amplifier factor a factor corroborating behavior, such as attitudes and skills of health workers, peers, parents, and employers (Suliha, 2012).
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 153 The results of this research are
consistent with previous research by Sri Wahyuni (2011) stating that the most dominant factor influencing the behavior of the early detection of cervical cancer is educational intervention methods wish and drive with a value of p = 0,010 and OR 3.050. This is due to the method of education wish and drive became the deciding factor because it is a health education given to the respondents to pay attention to the background of the client and his needs, education is providing a form of learning with a variety of lectures covering the stimulas using LCD, CD playback, sharing, peer discussion booklets, demonstration examination papsmear and counseling involving the family as supporters. Education wish and the drive to streamline internal and external factors that are owned by the respondent because of those factors that can get the behavior of early detection of cervical cancer. As research conducted by Ackerson of the year 2007 in the USA, in his research that aims to find out the factors that affect women in performing early detection of cancer, found that the behavior of early detection of cancer intrinsic factor is affected by cervical and ekstrisik factors which include age, economic status, education and knowledge.
Influence factors of interest in the behavior of early detection of Ca Cerviks
Based on table 4.39 revealed the influence of the factor of interest in the behavior of early detection of ca cerviks in women of fertile age in the health Kembangbahu Lamongan (p value 0.000 < 0.05 then Ho denied).
Interest as a tendency or desire a high against something. Interest makes a person try and apply yourself to it and eventually gained a deeper
knowledge of (Mubarak, et al, 2007). Sutjipto in Mathedu (2009) explains that the interest is the consciousness of a person against an object, person, problem, or situation related to her. This means that the interest should be viewed as something that is conscious. Therefore interest is the psychological aspects of a person to pay attention to high specific activity against and encourage those concerned to carry out such activities. In terms of the principal elements of interest is the concern, the thrust of each individual and pleasure (Qym, 2008). The influence of positive interest will make someone they are interested to experiment like to feel pleasure, joy, and joy. Pintrich and Schunk also mentioned that interest is an important aspect of the motivations that influence attention, learning, thinking and achievement (Mathedu, 2009).
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 154 Influence factors of Motivation
against the behavior of early detection of Ca Cerviks
Based on table 4.39 in mind there is a motivation factors influence behaviour towards early detection of ca cerviks in women of fertile age in the health Kembangbahu Lamongan (p value 0.05 then Ho 0.004 < rejected).
Tampubolon in Mathedu (2009) expressed interest in is a fusion between desire and willpower that can develop if there is motivation. Hidi & Derson in Mathedu (2009) holds an interest is a form of intrinsic motivation. The motivation comes from the latin meaning the encouragement of moreve in man to act or behave "(Notoatmodjo, 2014). The motif was the impetus that is already bound to a purpose, when one feels hungry, it means she needs or wants food. The motif refers to the systematic relationship between a response or a set of particular encouragement to the circumstances. If the impulse is innate, then the motive that the results of the learning process (Ahmadi, 2007:27). Motives (the motive) is a stimulant desire (want) a power mover and the willingness of the person. Each motif had a goal to be achieved. Motivation is the psychological process that could explain the behavior of a person. Fact of the matter is someone's orientation behavior designed to reach the goal. To achieve the necessary process of interaction of multiple items. So the motivation is the force that drives a person to do something to achieve the goal. Anthony cited Hamzah (2008:6) says that the human motivation for functions is as its driving force, determine the direction of works.
The presence of the influence factors of motivation against the behavior of early detection of ca cerviks in women of fertile age are caused by the presence of motivation then there is a power mover directing
someone to do something. In this case the presence of a strong motivation to implement early detection of cervical cancer cause someone then bend over backwards to immediately implement the early detection of cervical cancer. This happens because in general people want to do something if it's been based on certain main considerations the need, not more as a desire that sometimes can be delayed first. When something that has indeed become a necessity, then people will attempt to fill its needs it.
The results of the analysis showed niilai p value of 0.004, which means that the value of the consistency of the results of this research are 4/1000 or have an inconsistent or there's an error four times if the research is repeated as many as 1000 times. This shows a very high trust value about the influence factors of motivation against the behavior of early detection of ca cerviks in women of fertile age. Means that the results of this study provide information very credible because of the significant requirements of no more than 0.05 or there's an error 5 among 100 repetitions. The occurrence of such results can be caused by factors of motivation which is very important for the realization of one's behavior.
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 155 with papsmear test or IVA is the most
numerous on the category do the early detection of cervical cancer that is as much as 113 respondents (30.6%). This gives a real picture about the trend of the relationship between the two variables i.e. the higher the more motivation do early detection of cervical cancer and vice versa. Can be interpreted that the positive relationships that have a motivation toward behavioral detection here cervical cancer.
The results of this research are consistent with previous research by Beautiful Kurniawati (2015) which stated there is influence significant (OR = 4.700; 95% CI 1.379 hingga16,016; p = 0.013) with mother motivation behavior between checks IVA. This is in accordance with the statement of Notoatmodjo (2010) that motivation has 3 (three) function that is pushing people to do, so as the movers or the motor that releases energy. The motivation in this case is its driving force of any of the activities that will be undertaken, to determine the direction of the works, i.e. towards the goal to achieve. Thus the motivation can give directions and activities that should be carried out in accordance with the outline of the objectives planned previously and selection of works, i.e. determining what works to do matching to achieve the goal, by opting out of the works that are not useful for the purpose. A selection of works that are already defined or worked on will give you the confidence that high because it is already in the process of selection.
Influence factors of Education, interest and Motivation towards the behavior of early detection of Ca Cerviks
Based on table 4.40 revealed the influence of factors of education, interest and motivation towards the behavior of early detection of ca
cerviks in women of fertile age in the health Kembangbahu Lamongan (p value 0.05 Ho then 0.001 < rejected).
Many of the factors that led to the lack of implementation of early detection. The study of an aspect of behaviour according to Green (Notoatmodjo, 2010) someone wants to do something such as early detection of ca cerviks will know if the purpose and merits. After know will determine attitudes i.e. agree or disagree with that program. After that also depends on perception, values, belief. So too will depend pemungkin factors such as the presence of affordable health facilities to implement early detection, presence of social support and so on. Maslow's motivation theory says people will be compelled do an action based on education, interest or motivation. The hope will be soon arose interest to implement early detection of Ca cerviks.
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 156 would never think about early
detection of cervical cancer. After people already know the advantages of implementing the early detection of cervical cancer then people will want to carry it out. This interest is still psychologically based on desire. This means interest can still be lost because this desire sometimes can be delayed or thwarted. But along with the more aware of the need for early detection of ca cerviks for his health, and he increasingly felt the need (need) to carry out the early detection of cervical cancer. If it is so then the nature of these factors already include motivation is inside that person. It is this motivation that finally pushes someone to implement early detection of ca cervik
Conclusion
1. implementation of the educational variables based on ca cerviks in women of fertile Age who have the most frequency is less categories 2. Based on a variable interest that
implement early detection of ca cerviks which included a high category
3. Based on the motivational variable implement early detection of ca cerviks which includes a low category
4. Based on the variable behavior that implement early detection of ca cerviks with a papsmear do i.e. as many as 272 respondents.
5. There is the influence of the educational factor against the behavior of early detection of ca cerviks in women of fertile age of 4.430 with p value 0.000 < 0.05 then Ho denied.
6. There is interest in behavioral factors influence early detection of ca cerviks in women of fertile age 1.877 with p value 0.000 < 0.05 then Ho denied.
7. There is a motivation factors influence behaviour towards early detection of ca cerviks in women of fertile age-1.225 with p value 0.05 then Ho 0.004 < declined.
8. There are educational influence, interest and motivation towards the behavior of early detection of ca cerviks in women of fertile age in the UPT Clinic Kembangbahu Lamongan. so the dominant variables can be inferred is the educational value of the regression variables 4.430 with p value 0.000 < 0.05 then Ho denied
Advice
1. For the mother or Female Fertile Age (WUS)
For mothers in the UPT Clinic
Kembangbahu Lamongan.
expected more active to follow the guidance about ca cerviks so that mothers are willing to participate in a program of early detection of ca cerviks held by the Government. 2. For a midwife or health worker
Midwife or health worker is expected to further enhance training, mentoring, and the granting of health information especially about ca cerviks thoroughly in order to make the public understand and are aware of the importance of detecting early ca cerviks and willing to participate in a program of early detection of ca cerviks
3. place research
(Institutions/Agencies)
Recommended places research improve outreach regarding the various factors of risk of cancer to the pre cell research places in order to convey to the fertile age couples at risk so as to determine the attitude and actions of prevention ... 4. For the next Researcher
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 157 research so that the results can be
used as a comparison with the results of this research.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Abdul Muhith, Nasir, A & Ideputri, m. e. 2011. Health Research Methodology Ajuan Book, Nuha Medika: Jogjakarta Azwar's 2008. Human attitude theory
and Measurement. Yogyakarta: Liberty
Health RI. 2013. The book of reference of the prevention of cervical cancer and breast cancer. Jakarta: Directorate of disease control is not contagious, the Directorate General of Health Department PL & PP RI. Lamongan (accessed april 19.2017)
East Java Health Office, 2010. East Java Province Health Profile. www. dinkesjatim. Go. ID Health Office Lamongan. 2017.
testdikabupaten iva
implementation Report Lamongan: Health Office lamongan.
Ginting, a. 2008. The Essence Of Practical Learning & Learning. Bandung: Humanities
Husain, r. 2008. The method research for thesis and thesis. Jakarta: PT Grafindo Perdana
Kemenkes RI. 2015. The situation of cancer ",
http://www.depkes.go.id/article/view/1 5021800011/situasipenyakitkan ker.html. Lamongan (accessed april 19.2017)
Manuaba, Ida Bagus Gede. 2009. Understanding research female reproductive kesehtana. Jakarta: Arcan. Terms: 206
Martini, NK, 2012. Relationship characteristics, knowledge, and attitudes of Women of fertile Age Couples by the Act examination of Pap Smear
diPuskesmas Sukawati II, thesis, University of Udayana. Lamongan (accessed april 19.2017)
Mojgan karimi, 2009. Cervical Cancer And HPV Vaccines In Developing Countries In the Asian Pacific journal of cancer prevention.. Lamongan (accessed april 19.2017)
Mubarak. 2009. public health: theory and applications. Jakarta: Publisher Salemba Medika Myriam leyva et al, 2006. The attitudes
Towards Cervical Cancer Screening: A Study of Beliefs Among Women In Mexico in Year 2006. Thr University of texas of public health. Lamongan (accessed april 19.2017)
Notoatmodjo, s. 2010. Health education and behavioral sciences. Jakarta: Cipta Rineka. Notoatmodjo, S. 2010. Health
promotion theory and application, Jakarta: Rineka Science.
Notoatmodjo, s. 2012. Research methodology in health. Jakarta: Cipta Rineka.
Notoatmodjo, s. 2014. The Science Of Behavioral Health. Jakarta: Cipta Rineka.
Nursalam. 2014. The concept and application of Nursing Research Methodology. Salemba Jakarta Medika.
Ocviyanti. 2010. Various techniques of early detection of Breast and cervical cancer. Jakarta: Department of obstetrics and Gynecology MEDICINE
PKM Kembangbahu. 2017. Outpatient Register Book kia. PKM Kembangbahu
The Proceeding Of International Conference 2017 158 business. Bandung: Alfabeta.
Things: 72
Roman. 2013. The Inner Healing At Home (Stratagem "warding off" the source of the disease and the originator of the cancer in your home). Jakarta: PT Elex Media Komputindo Publisher Group Gramedia. Lamongan (accessed april 19.2017)
Soegiri PROVINCIAL HOSPITAL. 2017. The Register Book outpatient poli deposits.
Lamongan: HOSPITALS
Soegiri.
Saifudin, 2010. Practical Ministry Handbook of contraception. Jakarta. Yayasan Bina Sarwono Prawirohardjo Library.
Sastroasmoro & Ishmael. 2010. The basics of clinical research Methodologies. Jakarta: Sagung Seto
Sinta Oktavyany. 2015. The relationship of the level of knowledge about cervical cancer with pap smear examination of attitudes towards on pussy at clinics semanu gunung kidul.
POLTEKES Jewel Of
Indonesia. Lamongan (accessed april 19.2017)
Melville Nida Mayrita, 2012. The relationship between the incidence of cervical cancer is parity with the diyayasan cancer wisnuwardhana surabaya. wisnuwardana Cancer Foundation. Lamongan (accessed april 19.2017)
Sri Syatriani, 2011. Risk factors of cervical cancer at the Government General Hospital Dr. foreveraddictedtoyou sudirohusodo Makasar of South Sulawesi. Stikes Macassar. Lamongan (accessed april 19.2017)
Sri wahyuni. 2011. The effectiveness of educational methods wish and drive terhadapperilaku early detection of cervical cancer at kecamatanngampel kendal, Central Java. Courses on Nursing Faculty of medicine University of Indonesia. Lamongan (accessed april 19.2017)
Trihono. 2013. The Basic Health Research. Jakarta: RI Kemenkes
Widyasari. 2010. AntaraPengetahuan Relations DenganMotivasi PasanganUsia women's fertile (PUSSY) DalamMelakukan Pap Examination
Smear ManderKecamatan
TambakboyoKabupaten in the village of Tuban. DIII midwifery RSI Tuban.
The World Health Organization. Human human papillomavirus (HPV) and cervical cancer. Fact sheet. 2013 [cited September 2013]; 380: [about 3 screens] Available from:
http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsh eet/fs380/en/. Organization 2012; 90:478-478A. Lamongan (accessed april 19.2017)