ABSTRACT
Ratri Wahyuningtyas. 2016. Computer-Assisted Reading Material to Enhance Reading Skills. Yogyakarta: The Graduate Program in English Language Studies, Sanata Dharma University.
Reading skill is essential to the students’ learning improvement in any subjects they have in school. Reading plays its role in providing understanding of the materials being learnt through written language. However, it is also essential also to provide the students with interesting learning materials that could help them increasing their skill, especially their reading skill. One of the alternatives is through designing the materials adapting Computer-Assisted Language Learning (CALL) theories. There are benefits of CALL that will contribute to the students’ learning progress. Those are (1) increasing students’ motivation, (2) providing self-access facility, (3) providing attractive exercises, (4) it could increase the students’ learning autonomy. Based on the fact that there was a need to introduce basic reading skills since the students are in the seven grade and the necessity of having various reading exercises, a study in developing computer-assisted reading materials was conducted.
The study used Research and Development Method which was combined with Kemp’s Instructional Design in designing the materials. The study was aimed to answer the research question What do the computer-assisted reading materials look like? In order to gather the data, research instruments were used which included an interview checklist, an observation checklist, and a set of questionnaire.
The designed materials consisted of six features, namely warming up, text exploration, vocabulary, exercises, reading skills, and puzzles. Each feature was carefully selected and chosen to accommodate the needs of the students in improving their reading skills which were in line with the principles of teaching reading and the current curriculum as the guidance. The questionnaire results from the experts showed that the mean of the designed materials was 3.8. It meant that the designed materials were able to be used with revising it first before the materials were being implemented to the students. In conclusion, the designed materials needed to be revised first before it was given to the students. Exploration towards the variety of exercises type was also needed for the sake of the materials improvement.
For the students, the learning materials were able to improve their enthusiasm in learning English, especially reading. They found out that learning reading through the help of computer could be very interesting and increase their learning motivation. Various kinds of learning exercises could be one of the reasons why they found out that the learning materials was interesting. Based on the questionnaire result, there were four exercises that the students like most, which were obtained by asking them to rank the exercises they were interested in. The exercises based on the highest to lowest rank were multiple choice, matching, crosswords, and cloze test.
ABSTRAK
Ratri Wahyuningtyas. 2016. Computer-Assisted Reading Material to Enhance Reading Skills. Yogyakarta: Kajian Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Kemampuan membaca penting dikuasai oleh siswa yang akan menunjang peningkatan pembelajaran siswa pada semua bidang studi yang mereka pelajari di sekolah. Memberikan materi pembelajaran yang menarik bagi siswa juga merupakan hal yang penting dalam kegiatan belajar mengajar sehingga dapat membantu siswa meningkatkan kemampuan mereka terutama kemampuan membaca mereka. Salah satu alternatifnya adalah mendisain materi pembelajaran yang mengadaptasi teori Computer-Assisted Language Learning (CALL). Ada beberapa manfaat dari CALL yang bisa memberikan kontribusi dalam kemajuan belajar siswa, yaitu (1) meningkatkan motivasi siswa, (2) siswa bisa mengakses sendiri materi yang ingin dipelajari, (3) menyediakan latihan-latihan yang atraktif, (4) dapat meningkatkan otonomi belajar siswa. Mengingat perlunya memperkenalkan manfaat penguasaan kemampuan membaca pada siswa kelas tujuh dan pentingnya ketersediaan berbagai jenis latihan membaca, sebuah penelitian untuk mendesain materi untuk kelas membaca dengan bantuan media komputer dilaksanakan.
Penelitian ini menerapkan metode Research and Development yang dikombinasikan dengan model desain instruksional yang digagas oleh Kemp. Penelitian ini dilakukan untuk mencari jawaban atas pertanyaan utama penelitian yaitu bagaimana desain instruksional dari materi pembelajaran kelas membaca dengan bantuan media komputer? Dalam proses pengumpulan data, instrument penelitian yang digunakan meliputi panduan wawancara, panduan pengamatan kelas, dan kuisioner.
Desain materi terdiri dari enam fitur yaitu warming up, text exploration, vocabulary, exercises, reading skills, dan puzzle. Masing-masing fitur telah diseleksi dan dipilih secara selektif supaya dapat memenuhi kebutuhan siswa dalam meningkatkan kemampuan membaca yang tentu saja sejalan dengan kurikulum yang digunakan oleh sekolah sebagai panduan. Hasil dari masukan para ahli di bidang pengajaran Bahasa Inggris dan IT menunjukkan rata-rata 3.8. Bisa diartikan bahwa desain materi yang telah dibuat dapat digunakan oleh para siswa setelah diperbaiki terlebih dahulu. Eksplorasi materi terutama tentang variasi jenis latihan juga sangat diperlukan untuk meningkatkan kualitas desain materi yang telah dirancang.
Bagi siswa sendiri, materi pembelajaran yang menarik dapat meningkatkan ketertarikan mereka dalam belajar Bahasa Inggris khususnya membaca. Mereka mendapati bahwa kelas membaca bisa menjadi sangat menyenangkan dengan bantuan komputer dan hal tersebut menambah motivasi mereka dalam belajar. Berbagai jenis latihan yang terdapat dalam materi pembelajaran menjadi salah satu faktor yang membuat materi tersebut menyenangkan. Berdasarkan hasil kuisioner, ada empat jenis latihan yang disukai siswa yang diperoleh dengan pemberian peringkat oleh siswa terhadap jenis latihan yang mereka sukai. Urutan jenis latihan berdasarkan ranking tertinggi hingga terendah adalah pilihan ganda, mencocokkan, teka-teki silang dan cloze test.
i
COMPUTER-ASSISTED READING MATERIAL TO ENHANCE READING
SKILLS
A Thesis Presented to
The Graduate Program in English Language Studies
for the Degree of Magister Humaniora (M.Hum)
in English Language Studies
by
Ratri Wahyuningtyas
136332049
Sanata Dharma University
Yogyakarta
iv
DEDICATION PAGE
When you walk through a storm Hold your head up high And don't be afraid of the dark
At the end of the storm There's a golden sky
And the sweet silver song of a lark
Walk on through the wind Walk on through the rain
Though your dreams be tossed and blown
Walk on walk on with hope in your heart And you'll never walk alone
You'll never walk alone
(You’ll Never Walk Alone – Gerry and the Pacemakers)
vii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
First of all, I would like to express my gratitude to Jesus Christ for His blessing
and guidance especially during my study and thesis completion.
I would also like to thank Dr. B.B. Dwijatmoko, MA., my thesis sponsor, for
his full guidance and patience during the thesis completion. His feedbacks and
suggestions really contributed to my thesis writing progress so I could finish it.
My sincere appreciation goes to FX.Mukarto, Ph.D., Dr. J. Bismoko, Dr.
Novita Dewi, MS., MA. (Hons), Ph.D., Patrisius Mutiara Andalas, SJ, S.S., S.T.D.,
and Widya Kiswara, S.Pd., M.Hum for all knowledge shared during my study in
English Language Studies.
I would like to thank MG. Suratmi and Pak Dodi for their warm welcome for my
research. Their sincere help is always appreciated. I owe all the teachers and students of
SMP Maria Immaculata Yogyakarta for their time and support given for my research.
My never ending gratitude goes to my parents, brother, cousins, and friends who
always gave their full supports for my study especially for my thesis completion. My
deepest gratitude goes to my special one, ang lalaki sa buhay ko, for his great supports
and encouragements during the thesis writing and completion.
viii
TABLE OF CONTENTS
TITLE PAGE ………. i
APPROVAL PAGE ……….. ii
DEFENSE APPROVAL PAGE ……… iii
DEDICATION PAGE ……….. iv
STATEMENTS OF ORIGINALITY ……….... v
LEMBAR PERNYATAAN UNTUK PERSETUJUAN PUBLIKASI KARYA ILMIAH ………. vi
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS ……….. vii
TABLE OF CONTENTS ……….. viii
LIST OF TABLES ……… xi
LIST OF FIGURES ……….. xii
LIST OF APPENDICES ……….. xiii
ABSTRACT ………. xv
ABSTRAK ………. xvi
CHAPTER I. INTRODUCTION ... 1
A.RESEARCH BACKGROUND ... 1
B. PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION ... 6
C. PROBLEM LIMITATION ... 7
D. RESEARCH PROBLEM ... 7
E. RESEARCH OBJECTIVES ... 8
ix
CHAPTER II. LITERATURE REVIEW ... 10
A. THEORETICAL REVIEW ... 10
1. Reading Skill ...….10
2. Teaching Reading ... 18
3. Computer-Assisted Language Learning ... 29
4. Material..………...……….. 32
5. Research and Development ……….………...……… 36
6. Instructional Design ... 38
B. REVIEW OF RELATED STUDIES... 41
C. THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK ... 42
CHAPTER III. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY ... 46
A. RESEARCH METHOD ... 46
B. RESEARCH DESIGN ... 49
1. Research Participants ... 49
2. Research Instruments ... 50
3. Data Gathering Techniques ... 55
4. Data Analysis Techniques ... 56
C. RESEARCH PROCEDURE ... 57
CHAPTER IV. RESEARCH RESULTS AND DISCUSSION ... 58
A. RESEARCH RESULTS ... 58
1. The Development Process of the Materials ... 59
a. Research and Information Collecting ... 59
b. Planning ... 74
x
d. The Experts’ Judgments Results... 81
e. The Analysis of the Experts’ Judgments Results ... 86
f. Final Product Revision ... 89
B. DISCUSSION ... 108
1. Features on the Designed Materials ... 108
2. Presentation of the Designed Materials ... 113
3. Administering the Designed Materials ... 114
4. The Contribution of the Designed Materials to the Students’ Improvement 116 CHAPTER V. CONCLUSIONS AND SUGGESTIONS ... 119
A. CONCLUSIONS ... 119
B. SUGGESTIONS ... 123
xi
LIST OF TABLES
Table 3.1. Blueprint of the Questionnaire and Interview Checklist ………..… 52
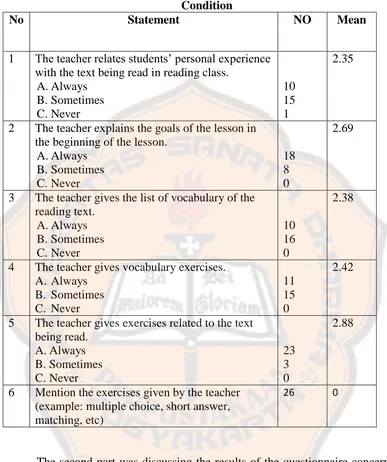
Table 4.1. Preliminary Questionnaire Results on Current Reading Class Condition .... 67
Table 4.2. Preliminary Questionnaire Results on the Use of Computer in the Reading Class ……….………. 69
Table 4.3. Preliminary Questionnaire Results on the General Comments of the Reading Class ………..… 71
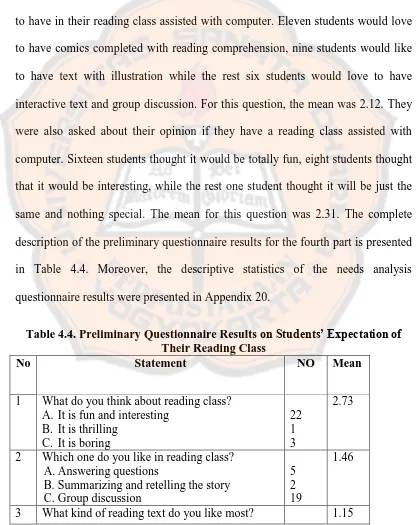
Table 4.4. Preliminary Questionnaire Results on Students’ Expectation of Their Reading Class ………..… 73
Table 4.5. Competency Standard and Basic Competences of reading for the Seventh Grade Students Semester 2 (Departemen Pendidikan Nasional, 2006) …... 75
Table 4.6. The Learning Topics ………. 75
Table 4.7. The Learning Indicators …………...……… 76
Table 4.8. The Subject Contents ……… 77
Table 4.9. The Learning Activities ………...…………. 77
Table 4.10. The Background of the Respondents ……….. 82
Table 4.11. The Results of Experts Judgments ………...……….. 83
Table 4.12. The Revision of Grammatical Mistakes ……….………… 90
Table 4.13. The Revision of Incorrect Diction ……….………. 90
Table 4.14. The Results of Post Design Survey ………...……. 95
Table 4.15. Post Design Questionnaire Result: Close Ended Questions ………..…... 105
xii
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 2.1. Curriculum Cycle (Hammond, et al, 1992)………..……… 29
Figure 2.2. The Writer’s Instructional Design Model………...……… 45
Figure 4.1. The Error Scoring System ………...……… 91
Figure 4.2. The Revised Version ……….………….. 92
Figure 4.3. Old Version Lay Out ……….……….. 93
Figure 4.4. Revised Version Lay Out ………...…………. 94
xiii
LIST OF APPENDICES
Appendix 1. Letter from the School ………...………. 128
Appendix 2. Needs Analysis Questionnaire and Interview Blueprint ………. 129
Appendix 3. Needs Analysis Classroom Observation Blueprint ………. 136
Appendix 4. English and Instructional Design Expert Validation Blueprint ……….. 137
Appendix 5. Information and Technology Expert Validation Blueprint ……….…… 140
Appendix 6. User Validation Blueprint ……….……….. 141
Appendix 7. Needs Analysis Questionnaire Form ……….…. 144
Appendix 8. Needs Analysis Interview Form ………. 147 Appendix 9. Needs Analysis Classroom Observation Form ………...…… 148
Appendix 10. English and Instructional Design Expert Questionnaire Form …...….. 149
Appendix 11. Information and Technology Expert Questionnaire Form ….………... 152
Appendix 12. User Validation Questionnaire Form ……… 154
Appendix 13. Interview Transcript ……….. 157
Appendix 14. Observation Notes ………. 159
Appendix 15. Needs Analysis Questionnaire Results ………...………….. 161
xiv
Appendix 17. Information and Technology Expert Questionnaire Results ………… 172
Appendix 18. Users’ Feedback Questionnaire Results………...……… 174
Appendix 19. User’s Feedback on Open Question……….. 177
Appendix 20. Descriptive Statistics of Needs Analysis Questionnaire Results …..… 179
Appendix 21. Descriptive Statistics of English and Instructional Design Expert
Questionnaire Results ………..…… 180
Appendix 22. Descriptive Statistics of Information and Technology Expert
Questionnaire Results ……….. 182
Appendix 23. Descriptive Statistics of Users’ Feedback Questionnaire Result.……. 183
Appendix 24. T-Test Calculation Result ………. 184
Appendix 25. Syllabus of English Subject for Seven Grade Students of
Junior High School ……….. 185
ABSTRACT
Ratri Wahyuningtyas. 2016. Computer-Assisted Reading Material to Enhance Reading Skills. Yogyakarta: The Graduate Program in English Language Studies, Sanata Dharma University.
Reading skill is essential to the students’ learning improvement in any subjects they have in school. Reading plays its role in providing understanding of the materials being learnt through written language. However, it is also essential also to provide the students with interesting learning materials that could help them increasing their skill, especially their reading skill. One of the alternatives is through designing the materials adapting Computer-Assisted Language Learning (CALL) theories. There are benefits of CALL that will contribute to the students’ learning progress. Those are (1) increasing
students’ motivation, (2) providing self-access facility, (3) providing attractive exercises, (4) it could increase the students’ learning autonomy. Based on the fact that there was a need to introduce basic reading skills since the students are in the seven grade and the necessity of having various reading exercises, a study in developing computer-assisted reading materials was conducted.
The study used Research and Development Method which was combined with Kemp’s Instructional Design in designing the materials. The study was aimed to answer the research question What does the computer-assisted reading materials look like? In order to gather the data, research instruments were used which included an interview checklist, an observation checklist, and a set of questionnaire.
The designed materials consisted of six features, namely warming up, text exploration, vocabulary, exercises, reading skills, and puzzles. Each feature was carefully selected and chosen to accommodate the needs of the students in improving their reading skills which were in line with the principles of teaching reading and the current curriculum as the guidance. The questionnaire results from the experts showed that the mean of the designed materials was 3.8. It meant that the designed materials were able to be used with revising it first before the materials were being implemented to the students. In conclusion, the designed materials needed to be revised first before it was given to the students. Exploration towards the variety of exercises type was also needed for the sake of the materials improvement.
For the students, the learning materials were able to improve their enthusiasm in learning English, especially reading. They found out that learning reading through the help of computer could be very interesting and increase their learning motivation. Various kinds of learning exercises could be one of the reasons why they found out that the learning materials was interesting. Based on the questionnaire result, there were four exercises that the students like most, which were obtained by asking them to rank the exercises they were interested in. The exercises based on the highest to lowest rank were multiple choice, matching, crosswords, and cloze test.
Key words: reading, computer-assisted language learning, CALL, seven grade students, Research and Development
xvi
ABSTRAK
Ratri Wahyuningtyas. 2016. Computer-Assisted Reading Material to Enhance Reading Skills. Yogyakarta: Kajian Bahasa Inggris, Universitas Sanata Dharma.
Kemampuan membaca penting dikuasai oleh siswa yang akan menunjang peningkatan pembelajaran siswa pada semua bidang studi yang mereka pelajari di sekolah. Memberikan materi pembelajaran yang menarik bagi siswa juga merupakan hal yang penting dalam kegiatan belajar mengajar sehingga dapat membantu siswa meningkatkan kemampuan mereka terutama kemampuan membaca mereka. Salah satu alternatifnya adalah mendisain materi pembelajaran yang mengadaptasi teori
Computer-Assisted Language Learning (CALL). Ada beberapa manfaat dari CALL yang bisa
memberikan kontribusi dalam kemajuan belajar siswa, yaitu (1) meningkatkan motivasi siswa, (2) siswa bisa mengakses sendiri materi yang ingin dipelajari, (3) menyediakan latihan-latihan yang atraktif, (4) dapat meningkatkan otonomi belajar siswa. Mengingat perlunya memperkenalkan manfaat penguasaan kemampuan membaca pada siswa kelas tujuh dan pentingnya ketersediaan berbagai jenis latihan membaca, sebuah penelitian untuk mendesain materi untuk kelas membaca dengan bantuan media komputer dilaksanakan.
Penelitian ini menerapkan metode Research and Development yang dikombinasikan dengan model desain instruksional yang digagas oleh Kemp. Penelitian ini dilakukan untuk mencari jawaban atas pertanyaan utama penelitian yaitu bagaimana desain instruksional dari materi pembelajaran kelas membaca dengan bantuan media komputer? Dalam proses pengumpulan data, instrument penelitian yang digunakan meliputi panduan wawancara, panduan pengamatan kelas, dan kuisioner.
Desain materi terdiri dari enam fitur yaitu warming up, text exploration,
vocabulary, exercises, reading skills, dan puzzle. Masing-masing fitur telah diseleksi
dan dipilih secara selektif supaya dapat memenuhi kebutuhan siswa dalam meningkatkan kemampuan membaca yang tentu saja sejalan dengan kurikulum yang digunakan oleh sekolah sebagai panduan. Hasil dari masukan para ahli di bidang pengajaran Bahasa Inggris dan IT menunjukkan rata-rata 3.8. Bisa diartikan bahwa desain materi yang telah dibuat dapat digunakan oleh para siswa setelah diperbaiki terlebih dahulu. Eksplorasi materi terutama tentang variasi jenis latihan juga sangat diperlukan untuk meningkatkan kualitas desain materi yang telah dirancang.
Bagi siswa sendiri, materi pembelajaran yang menarik dapat meningkatkan ketertarikan mereka dalam belajar Bahasa Inggris khususnya membaca. Mereka mendapati bahwa kelas membaca bisa menjadi sangat menyenangkan dengan bantuan komputer dan hal tersebut menambah motivasi mereka dalam belajar. Berbagai jenis latihan yang terdapat dalam materi pembelajaran menjadi salah satu faktor yang membuat materi tersebut menyenangkan. Berdasarkan hasil kuisioner, ada empat jenis latihan yang disukai siswa yang diperoleh dengan pemberian peringkat oleh siswa terhadap jenis latihan yang mereka sukai. Urutan jenis latihan berdasarkan ranking tertinggi hingga terendah adalah pilihan ganda, mencocokkan, teka-teki silang dan cloze
test.
1
CHAPTER I
INTRODUCTION
This chapter is the opening of the study being conducted by the writer. It
will explain anything related to the background of the study, problem
identification, problem limitation, research problem, research objectives, and
research benefits. Each sub chapter will elaborate the explanation thoroughly.
A. RESEARCH BACKGROUND
The need of using English is in a high demand during latest decade as
English is now known as lingua franca. To support the globalization ahead, non
native countries realize that mastering English would give them benefits to enter
the core of global world. Many efforts and plans are prepared by each country
especially the developing ones to get themselves in into the heart of the global
trading. One of the effective efforts which give long term benefit for the country
in preparing themselves for global world trading is by teaching their pupils
English. As a result, English is taught in schools throughout the world to prepare
people facing the challenge of globalization era. Graddol (2006) suggests that the
target model of teaching English as lingua franca is to form a fluent bilingual
speaker who preserves his national identity in terms of accent and who has the
skills to negotiate with other non natives. For this aim, schools are considered as
the best place to introduce English to non native students and make them use it.
Graddol (2006) also adds “the role of education in school is now seen as to
the future”. He also provides reasons why English is introduced to younger
learners. The reasons are to make sure that the learners have longer time to master
the language and to avoid overloaded material since secondary schools are
demanding already (Graddol, 2006). As a result, in non native countries, English
is taught since Elementary School or even Kindergarten to maximize the
knowledge absorption and make the students get used to use English in early age.
Indonesia belongs to the countries teaching English for young learners.
In Indonesia, English is one of core subjects since Junior High School. It
becomes important since English is included in the Curriculum as one of the
subjects to be tested in National Exam. It means, students’ knowledge and ability
in using English appropriately is tested and converted as mark which is written in
their certificate to notify that they pass Junior High School. There are four skills
that the students have to learn in order to master English, namely listening,
speaking, reading, and writing. According to Hirsch, Jr. (2003), reading and
writing is important as a means to possess body knowledge. When a student
knows how to read, it would be easier for them to understand any material given
by their teachers. As stated also by Wallace (1992) that reading requires response
from the readers which means readers are aware of some options. It gives proof
that reading will be beneficial in supporting their learning process. Then, reading
becomes one of the important factors for students to master anything including
English.
Problems in understanding English are also experienced by Junior High
School (JHS) students. There are two major problems in learning English. First
Education Agency (2011), that to help students developing their reading
vocabulary needs more strategies; it suddenly becomes the task of the teachers in
order to solve the first problem. Students’ vocabulary mastery is definitely
needed to support their effort in learning English. Second problem lies on their
grammar mastery. To help them understanding English text, there is a need to
improve their grammar mastery. Those two problems need to be solved by giving
more exercises so that it would give beneficial impact to students’ reading
understanding. It matches with what is being proposed by Jenkins, Fuchs, van den
Broek, Espin, & Deno (2003) that there are five elements of reading
comprehension, namely metacognition, knowledge, vocabulary, passage context,
and social context. Metacognition refers to the students’ awareness and regulation
of one’s thinking and the application of problem solving skills. It suggests
students to see reading as problem solving activity instead of words recognition
(Walczyk, 1994). Knowledge and passage context enhance students’ ability in
understanding the passage since through existing knowledge possessed by
students, they will be able to relate it with the context well. Vocabulary plays
important role in the process of reading understanding. By having strong
vocabulary mastery, students will be easier in identifying words in their reading
passage and quite faster in constructing meaning.
There are many teaching model that could be used to teach reading and one
of the teaching models is Computer-Assisted Language Learning (CALL). What
should be included in CALL, as stated by Beatty (2003), it accommodates its
changing nature in any process in which a learner uses a computer and, as a result,
teaching learning process which is also, could help teachers in providing learning
material for the students to enhance their language mastery.
There are two reasons why CALL is selected in this study. First, it supports
learner autonomy. As what has been stated by Egbert (1993), that there are
conditions of optimal language learning environment that should be attained by
teachers to maximize the learning output. The conditions of optimal language
learning environment are 1) learners have the opportunity to interact and
negotiate, 2) learners interact in the target language with an authentic audience, 3)
learners are involved in authentic tasks, 4) learners are exposed to and encouraged
to produce varied and creative language, 5) learners have enough time and
feedback, 6) learners are guided to attend mindfully to the learning process, 7)
learners work in an atmosphere with an ideal stress/anxiety level, and 8) learners’
autonomy is supported. The idea of using CALL is to improve learner’s
autonomy, involve them with tasks and atmosphere fit to their stress level, and
provide them with beneficial feedback. Rude (1986) stated that most
Computer-Assisted Instruction use wider mainframe as their attempt to improve students
achievement. This will support the usage of CALL in teaching learning process.
More statement proposed by Rude (1986) that computers used in the classroom
can be maximized to enhance reading instruction in various ways. Second,
students are interested in learning using computer. It is supported by statement
from Spencer and Baskin (1983), Merton (1983) and Fisher (1983) as cited by
Rude (1986) that children show high enthusiasm when they work with computers
and their academic motivation is usually increased. This is based on observation
the exercises given using computer. It reflects the conditions of optimal of
language learning environment which will also help teacher to deliver the material
better.
In CALL, learners are required to be able to operate computer since the
main media to communicate in computer based language learning. Computer
based language learning could be the alternative of teaching model which
emphasizes on the effectiveness and efficiency of the teaching learning process
itself. By involving media, it is hoped that learners could be more encouraged in
improving their English skills, especially their reading skill. There are benefits of
using CALL that would be very beneficial for the improvement of the students
(Prathibha, 2010). First, it could increase the students’ motivation. There are many
activities that could be done using computer; one of those is playing games.
Various options of activities in learning using computer are believed could
increase the students’ motivation and self confidence. Second, computer offers
self-access facility. It means the students have the full authority to access the
learning material and could adjust to their learning needs. Third, computer
provides more attractive exercises. By using the computer, the teacher could
create exercises a more attractive aspect by means of colors, various letter styles,
and also animated pictures. Fourth, it could increase the students’ learning
autonomy. Learning with the help of computer has given a full access to the
students in learning the material they want to learn. Moreover, in CALL teacher’s
role undergoes changing. Teacher plays role as facilitator and is free to work with
The focus of the study is to elaborate theories of using CALL in improving
JHS students’ reading mastery. The theories will be used as the foundation in
constructing the computer-assisted language learning model so that it could help
them in improving their reading mastery. Progress of the students is expected to
discover also in the study. CALL activities that will be used in the model will
include any task produced using Hot Potatoes and Eclipse, while the material are
designed using Page Breeze.
B. PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION
There are two problems found as the basis of the research conducted. First,
reading skills are definitely needed for the students in order to master English. In
fact, the seventh grade students are not yet getting more familiar with the basic
reading skills they need. As a result, introducing students to the reading skills
when they are still in their first year of Junior High School will give more benefits
to their progress of understanding English. Hence, the problem appears when the
teaching reading skills doesn’t become the urgency in the current curriculum. The
syllabus for the seven grade students doesn’t include the teaching of reading
skills. To accommodate the needs, learning material consisting the teaching of
reading skills become the alternative way. Second, the students need variety of
reading exercises. To teach the students how to read and practice the reading skills
they have learnt, having regular practice is a must. Moreover, providing adequate
reading practice will be the best solution if the teacher really wants to encourage
To make the reading material interesting, an alternative teaching media is
proposed. Computer-Assisted Language Learning is used to give new experience
to the students in learning reading skills. Based on this idea, it is then decided to
design an instructional reading material for seventh grade of Junior High School
students to improve their reading skills using computer-assisted language
learning.
C. PROBLEM LIMITATION
The limitation of the research will be about to design computer-assisted
language learning model to enhance reading skills for Junior High School
students. It will provide learning model for seven grades of Junior High School
students applying Curriculum 2006 to improve their reading skills. Seven grades
students of Junior High School are selected as the participants of the study for two
reasons. First, they will have more time to prepare for the National Examination
where they could apply the reading skills they learnt. Second, it is expected to
give beneficial advantage to teach them to be a strategic reader since they are in
the seventh grade. Moreover, the model will use CALL in which the activities are
created using Hot Potatoes and Eclipse and presented using Page Breeze.
D. RESEARCH PROBLEM
The research will try to answer research question below.
What does the computer-assisted reading material to enhance reading skill look
E. RESEARCH OBJECTIVES
There are two objectives of this research. First, it is to design and develop
computer-assisted reading model to improve reading skills for seventh grade of
Junior High School students. The model is designed according to their needs and
combined with learning objectives that they have to achieve according to
Curriculum 2006. Second, it is to give detail explanation on the features of CALL
that could help JHS students improving their reading skills. The construction of
CALL model will consider the theory and nature of teaching reading, CALL and
also use Curriculum 2006 as the guideline. The objectives stated in Curriculum
2006 and problems in learning English become the basic in designing the learning
material since the research is conducted to find the best way out to solve students’
problem by providing learning model that could accommodate them to achieve
higher understanding of English.
F. RESEARCH BENEFITS
It is hoped that the research could give alternatives of teaching learning
model which could enhance students’ English mastery. Students could experience
different learning activity that could raise their curiosity and stimulate their
problem solving activity through various reading activities. Moreover, it is hoped
that the research could be a prototype of computer-assisted language learning for
teaching reading. The prototype could be developed and adjusted to the learners’
need. There is a hope that further researchers could transform it into open source
is hoped that the research could widen the perspectives of the researchers and also
English teachers in providing interesting learning model which aims to improve
CHAPTER II
LITERATURE REVIEW
The second chapter will describe the theoretical review, theoretical
framework and hypothesis of the study. In theoretical review, all the concepts
used by the writers will be elaborated in order to find the universal truth. Then, the
relation of each concept to the study will be explained in the theoretical
framework. In short, chapter two is the writer’s plan to discover the empirical
truth.
A.THEORETICAL REVIEW
The first part of this chapter reveals all the theories used in the study. It
consists of four parts, those are reading skill, teaching reading, computer-assisted
language learning, and instructional design. Each part will elaborate the theories
in details.
1. Reading Skill
The description of reading skill theories being used in this study consists of
four parts. Those are definition of reading, purposes of reading, models of reading
process, and accessing reading text. The complete description will be presented in
the following paragraphs.
a. Definition of Reading
There are some definitions of reading used in the study. According to
Anderson as cited by Nunan (2003), reading is a receptive skill, in which readers
receive information from the writer in the text they read. It is called receptive skill
because readers do not produce anything like in speaking or writing. Readers just
need to undergo a process of understanding text being read. It is supported by the
statement from Eskey, as cited in Farrell (2009) “reading is a process of obtaining
information from a written text that does not involve the activity of converting
written language into spoken language”.
Anderson (as cited in Nunan, 2003: 68), defines that reading is a process of
understanding the text they read and combine it with their own background
knowledge to build meaning. Wallace (1992) also states that in a reading process,
readers are expected to have some attempts in order to understand the passage
being read. The attempts could be readers’ efforts in recalling their background
knowledge to understand the passage. Moreover, Hedge’s (2000) suggestion that
there is a dynamic relation between text and readers’ attempts to make meaning of
the text, adding some proofs that readers really need to do something to make the
text meaningful to them. Reading also involves the ability to recognize sentence
structure and combine it with readers’ background knowledge. As stated by Grabe
and Stoller (2002), reading is an interactive process which involves the activity of
analyzing the structure of the sentence and the activity to recall information from
b. Purposes of Reading
Reading activity is always supported by a purpose. As stated by Grabe and
Stoller (2002), that once we begin to read, there are some numbers of decisions
that we are going to make. It is whether we are going to read the whole passage or
stop it when we think we already get the information needed. Grabe and Stoller
(2002) propose that there are four main purposes of reading. First, reading to
search for simple information and reading to skim. It is also what we know as the
common reading ability, that when we read, we suppose to look for specific
information from the text. Usually, readers will scan for specific information they
need in the text. It would be time saving and more efficient compared to if readers
have to read the whole text before finally decide which information that they
need. The example could be when readers are looking for particular year in the
text, specific year or address within the text. The basic method is just the same for
skimming. In skimming, readers will use the combination strategies of guessing
where the information needed is located then followed by using the
comprehension skills they have to generate the idea (Grabe and Stoller, 2002).
Second, reading to learn from texts. According to Grabe and Stoller (2002),
reading to learn from texts required readers to (1) remember main ideas and
details elaborated in the main and supporting ideas of the text, (2) recognize and
build rhetorical frames which is organized the information in the text, (3) relate
the text to their knowledge base. Even though it comes with slow pace of reading,
reading to learn is believed to be able to strengthen readers’ ability of inferencing
their background knowledge to the texts they are reading. Third, reading to
integrate information, they need to be able to decide which one is needed and
which one is not really needed. They will build the skills on what information to
integrate and how to integrate it to reach their goals (Grabe and Stoller, 2002). For
the aim to write and to critique texts, readers are definitely needed to know what
kind of supportive and conflicting material that will be useful for their writing
process. Moreover, both purposes usually represent academic tasks that require
readers’ ability to integrate information.
Fourth, reading for general comprehension. General reading comprehension
is the most basic purpose of reading. Yet, it supports other reading purposes being
discussed before. However, general reading comprehension is more complex than
what we ever imagine. It compromises very rapid and automatic processing of
words, well-built skill in generating the main ideas, and efficient coordination of
other processes within very limited time (Grabe and Stoller, 2002). Fluent readers
will absolutely meet the requirements but it would be hard for non fluent readers.
There are many requirements that they need to accomplish for being a fluent
reader. It demands processing efficiency but once one could master general
reading comprehension, it would be easier for them to grasp meaning and ideas of
any other reading texts and genre with varied length.
c. Micro skills in Reading
According to Brown (2007), each skill consists of micro skills. In reading,
the micro skills are as follows (1) distinguish among graphemes and orthographic
writing at the efficient rate of speed to meet the purpose, (4) recognize a core of
word, and interpret the word order pattern and its significance, (5) identify
grammatical word classes, systems, patterns, rules, and elliptical forms, (6)
identify cohesive devices in written discourse and their role in signaling the
relationship between and among clauses, (7) identify the rhetorical forms of
written discourse and their significance for interpretation, (8) using world
knowledge to infer inexplicit context, (9) identify the communication function or
written text according to form and purpose, (10) identify literal and implied
meaning.
In the study, the micro skill which is included in the learning material is
mostly in identifying the communication function or written text according to
form and purpose. The material provided the information on two kinds of text and
the students learn to identify the function of the text in communication. Moreover,
the students also need to identify also the form and purpose of the text in order to
maximize the outcome.
d. Models of Reading Process
There are three models of reading process according to Anderson, as cited in
Nunan (2003). The first model is bottom-up model. This model requires learners
to start the reading process from the very beginning phase. It will start with the
fundamental basic of sound and letter recognition, and also morpheme. Then, it
one. According to Hedge (2000), bottom-up model used to explain the decoding
of the letters, words, and other language features.
In bottom-up model, the way readers understand the text they are going to
read is in a very slow pace. They build meaning or translating word by word and
add interfere using their background knowledge. As what is also stated by Grabe
and Stoller (2002) that their recognition will be started from the very basic. It will
be from letter by letter for word recognition, word by word for sentence
recognition and sentence by sentence for text recognition.
The second model is top-down model. In top-down model, learners’
background knowledge is needed in order to understand the text given. Learners’
background knowledge is believed could give contribution in understanding the
text they are reading. The activity focuses on the understanding of the learners
toward the text being read. Moreover, Hedge (2000) also states that the top-down
process is used to explain the application of prior knowledge to create meaning of
an existing text.
The idea of top-down model is the readers’ expectation toward the text
being read. It is assumed that they already have information and facts related to
the text and they are going to confirm or reject the expectations (Grabe and
Stoller, 2002). It is done by doing a kind of general monitoring mechanism in
which the readers will direct their eye to the potential place where they could find
those specific information needed.
The last model is interactive model. Interactive model assume that both
models, bottom-up and top-down model, could be beneficial in comprehending a
useful perspective from top-down model. This is the integration of bottom-up and
top-down model. The focus of this model is to invite readers to use the
perspective of bottom-up model and combine it with the key concepts of
top-down model (Grabe and Stoller, 2002). They will start with word recognition, but
in a fast and efficient way. However, strong background knowledge is highly
needed to support the readers to understand what the text is trying to convey.
In practice, readers will be given short reading passage to teach them
specific reading skills and strategies. Moreover, they will also be given longer
reading passage to practice their reading strategies. In short, fast words
recognitions technique from bottom-up model is very beneficial but background
knowledge contributes much in understanding the text, as in inferencing and
predicting what will happen next in the text.
d. Accessing Reading Text
Wallace (1992), states that there are three ways to help learners relating
their existing knowledge to the text that they are going to read. It is supported by
Farrell (2009), by stating that the teachers’ goal is to develop strategic readers and
the idea is in line with Wallace’s thought. The first activity is Pre-reading
Activities. In this activity, learners are given questions from the text which
requires learners to answer it. The activity also provides learners with task in
order to prepare them with the linguistics, cultural or conceptual difficulties.
Moreover, it also provides them with vocabulary tasks. In short, the activities in
pre-reading activities functions as an entrance for them to the reading text. Farrell
will be read. He proposes four activities that would be beneficial in order to
activate relevant background knowledge. Those are (1) word association which
determine what prior knowledge that students could bring before they read the
text, (2) direct experience which focuses on engaging students in the real
experience in building their background knowledge, (3) cinquain which requires
students to write five lines poem that reflects the affective and cognitive concept
as a response to the new concept, and (4) prediction which is linked to the strategy
to activate prior knowledge.
The second activity to access content is called while-reading activity. It is
aimed to encourage learners to be active, flexible, and reflective readers. In this
phase, a reading will be given to the learners along with a set of task to check their
understanding of the text being read. Farrell (2009) suggests three activities to
assist them in understanding the text being read. The first activity is prediction
which aims to develop students’ ability to read critically and reflectively. The
second activity is questioning which invites students to ask questions related to
the text they are reading. The last activity is summarizing which is categorized as
a reading strategy that is used to get the gist of the text being read (McEwan, as
cited in Farrell (2009)).
The last one is post-reading activities. It consists of activities that could
function as the follow up action of the text being read. It is usually in the form of
comprehension questions, while other follow up activity can be in the form of
writing or a role play. The activities in post-reading activity should be motivated
2. Teaching Reading
There are four parts provided in presenting the teaching reading theories
being used in the study. First, the study presents the principles of teaching
reading. Second, reading comprehension strategies are presented in details. Third,
it will present about Curriculum 2006 in teaching learning process. Fourth, it will
describe the learning process in Curriculum 2006.
a. Principles for Teaching Reading
1) Anderson’s Principles for Teaching Reading
Anderson (as cited by Nunan, 2003), states that there are eight principles of
teaching reading. The first principle is to exploit the reader’s background
knowledge. Background knowledge includes experiences that bring readers to the
text, such as life experience, and educational experience. Background knowledge
gives big influence in leading readers to the text and improving readers’ reading
comprehension. To enhance readers’ reading comprehension, the teacher has to
activate their background knowledge by setting goals, asking questions, making
prediction, and teaching text structure. The second principle is to build a strong
vocabulary base. Vocabulary is the basic need for the readers to build meaning of
English words or texts. In order to understand the text, the readers need to know
vocabularies related to the text. If the readers have strong vocabulary base, it will
be easier for them to understand the text.
The third principle will be to teach for comprehension. The main part of
reading process is comprehension. According to Grabe and Stoller (2002)
interpret it appropriately.” It is supported by Farrell (2009) who says “reading
comprehension is basically the English Language Learners’ ability to construct
meaning from the text through combination of prior knowledge and previous
experience with the topic, the information in the text, and the stance the reader
takes in relationship to the text”. However, the teacher needs to teach
comprehension and then monitor it. Teaching comprehension relates to the
readers’ ability to discuss with the teacher or friends what strategies they use to
comprehend the text.
The fourth principle is to work on increasing reading rate. Increasing
reading rate means that there should be a balance in improving students’ reading
rate and developing their comprehension skills. The teacher does not only focus
on the accuracy but also fluency. The teacher also has to teach students to reduce
their dependence on dictionary. The students have to spend more time on
analyzing the content and discussing it with their friends. The next principle is to
teach reading strategies. In order to be successful readers, the readers have to
know strategy of reading itself. However, knowing the strategy is not enough.
They have to know how to use and integrate strategies in their reading process.
Principle number six is to encourage readers to transform strategies into
skills. According to Anderson (as cited by Nunan, 2003:77), “strategies can be
defined as conscious actions that learners take to achieve desired goals or
objectives, while a skill is a strategy that has become automatic.” Readers should
be introduced to reading strategies in their reading process. When they use the
strategies unconsciously, they move strategies into skill. The next principle is to
can be used to measure the students’ progress in their reading class. The
assessment can be both qualitative and quantitative. Qualitative assessment
includes information from reading comprehension test and reading rate data.
Quantitative assessment includes information from reading journal responses,
reading interest surveys, and responses to reading strategies checklist.
The last principle is to strive for continuous improvement as a reading
teacher. Reading teacher should view themselves as facilitators and help the
readers to find what works best. The teacher needs to understand the nature of
reading process so that they can help the readers to understand the text.
2) Farrell’s Principles for Teaching Reading
Farrell (2009) also proposes that there are eight principles for teaching
reading. The first principle is to reflect on reading. The main point of this
principle is to invite teachers to reflect on their reading process first. They are
expected to reflect in the reading behavior and reading process they experience
when they read something. Then it would be followed by reflecting on how they
teach reading to their students through the help of fellow teachers to observe how
they teach reading in the class. The essence of this principle is to encourage
teacher to place themselves as readers first and notice on how they understand
before they decide what kind of reading class they will bring their students into.
The second principle is to teach fluency and comprehension. There are two
commonly purpose of reading, those are reading for pleasure and reading for
able to gain information from the text being read in which they have to master the
ability of understanding text and interpret it. As stated by Farrell (2009), reading
fluency is actually closely related to comprehension. As a result, the demand for
the teacher is not only to focus on the instruction to increase students’ reading
strategies, but also to make use of the ability to recognize text structure to build
both reading fluency and comprehension.
The third principle is to teach reading strategies. Reading strategies refer to
how the readers make sense of what they read and what they don’t understand
from the text (Farrell, 2009). It is the teachers’ responsibility to introduce students
to understand and use reading strategies that would be beneficial for them in the
process of understanding the text without removing the possibility of having
discussing and practice of reading strategies during the reading activity. In
addition, teacher is greatly hoped to develop strategic readers rather than to only
teach individual reading strategies. The fourth principle is to teach text structures.
In this principle, the big challenge for the teachers is to teach their students on
how to understand text organization since based on research on first language, that
readers who are able to recognize text structure found it easier to recall the
information back. From the research, it could be concluded that having the ability
to understand text structure would be so beneficial for the readers in their effort of
understanding the text. In short, it would be effective and beneficial if teachers
also teach their students how different texts are organized and structured or how
paragraphs are organized.
The fifth principle is to teach vocabulary building. To be able to understand
read new text, they know new vocabularies but it would not be beneficial if
readers do not know what to do with that. It is the teachers’ responsibility to teach
students to understand unfamiliar vocabulary so that finally it can improve their
reading understanding. By giving guessing meaning exercise or rapid
word-recognition exercise, teachers have taught their students to learn vocabulary. The
sixth principle is to promote extensive reading. The main point of this principle is
to promote alternative reading text for the students in which they are interested in.
This will be a good solution as an anticipation attempt of boredom that might be
experience by the students when they read text book.
The next principle is to plan effective reading classes. Planning an effective
reading class would be the best step that teachers could take. It is hoped that the
students are no longer learning to read but they hit the level of reading to learn. To
do so, teachers need to carefully plan the class involving all needed aspects to help
students improving their reading skill. The last principle is to use authentic
reading assessment. According to Farrell (2009), assessment here refers to both
traditional, quantitative, paper-and-pencil test which is combined with qualitative
assessment like what we could find in portfolio assessment, peer assessment, self
report and others.
b. Reading Comprehension Strategies
In order to support students to be strategic readers, it is important for
teachers to teach reading strategies to the students. The reading strategies are
for both teachers and students to reach the goal of creating strategic readers in the
reading class. Brown (2001) suggests ten strategies for reading comprehension
that could be applied in the teaching learning process. The first strategy is to
identify the purpose of reading. The aim of identifying reading purpose is to
simplify the reading activity into an efficient process. By doing so, students will
be able to know what they are looking for and what attempts that can be done to
the potential distraction information. The second strategy is to use graphemic
rules and patterns to aid in bottom-up decoding. This strategy will really help
students, especially the beginner in understanding text from the very low level,
words. By providing aids, it would be easier for the students to understand deeply
and could build meaning from the words they learn.
The third strategy is to use efficient silent reading techniques. To help
students in maximizing the use of their silent reading technique, it would be better
for them to teach using some silent reading rules. Those are, (1) reducing the habit
to pronounce each word, (2) try to virtually recognize more than one word at a
time, (3) skip anything which is not related to global understanding and try to get
the meaning from the context. The next strategy is to skim the text for the main
ideas. Skimming the whole text will give students opportunity to predict the
purpose of the text, the main topic, or probably the developing or supporting
ideas. The fifth strategy is to scan text for specific information. Scanning is the
activity of looking for certain information in the text. It is the reflection of the aim
of scanning itself that is to extract specific information without reading the whole
The sixth strategy is to use semantic mapping or clustering. It helps students
to manage ideas into meaningful clusters. By doing so, they would easily grasp
the message that is conveyed in the text. The next strategy is to guess when
uncertainty comes. There are some aims of guessing in which it could be used to
guess the meaning of a word, guess a grammatical relationship, guess a discourse
relationship, infer implied meaning, guess on a cultural reference, and guess
content messages.
The eighth strategy is to analyze vocabulary. There are several techniques
that could be used on analyzing vocabulary. It is important to look for prefixes,
suffixes, roots that are familiar, grammatical contexts which potentially give
information, and semantic context for clues. The next strategy is to be able to
distinguish between literal and implied meaning. To be able to implement the
strategy, students need to master advance top-down processing skills. Not all
language could be interpreted exactly but implied meaning usually derives from
the pragmatic information process. The last strategy is to capitalize on discourse
markers to process relationship. Discourse markers which signal relationship
among ideas are expressed through phrases, clauses, and sentences. By providing
clear comprehension on the discourse markers, it is hoped that it could help
students understanding the text being read.
c. Curriculum 2006 in Teaching Learning Process
Curriculum 2013 is the recent curriculum used in Indonesia. A pro-contra
thought from the Minister of Education which resulted to the statement to stop the
For Dinas Pendidikan Yogyakarta, some schools which had used the curriculum
for three semesters might continue using it. Otherwise, the schools need to use
Curriculum 2006. SMP Maria Immaculata Yogyakarta belongs to the schools
group using Curriculum 2013 less than three semesters. As a result, for the even
semester of 2014/2015 academic year, they are back using Curriculum 2006.
Curriculum 2006 is widely known as Kurikulum Satuan Tingkat Pendidikan
(KTSP) or School-based Curriculum. It is an operational curriculum which is
arranged and deployed by each level of education. This curriculum is developed
based on the school level, local characteristics, social and culture of the local
people and also the students itself. The development of the school-based
curriculum and its syllabus is in the hands of the school and school committee
under the supervision of education authorities. School-based Curriculum contains
Content Standards which cover the material competence level in order to achieve
the graduate competence for particular level of education. Moreover, Content
Standards consist of the basic framework and curriculum structure, learning load,
school-based curriculum, and academic calendar. Learning load could be
translated into the amount of time that the students need in order to join the
learning process which could be gained through face to face interaction in class,
structured assignments, and unstructured autonomous learning. In general,
School-based Curriculum consists of four components. Those are the educational
purposes of the school, structure and curriculum contents, academic calendar, and
also syllabus and lesson plans.
There are some terms used in School-based Curriculum. First is
form of education, attitude and skills possess by the students. Second is
Competence Standard. Competence Standard is the qualification of minimum
ability that should be possessed by the students which describe the possession of
attitude, knowledge and skills that is hoped to be achieved through particular
subjects in each level and or semester. Third is Basic Competence. It refers to the
national standard reference that should be achieved.
As stated before that the development of School-based Curriculum is given
to the schools following standard form, there are some principles in developing
the School-based Curriculum. Those are (1) the center of the curriculum
development is the potential, development, needs and interests of the students and
their environment, (2) the development should vary and integrated, (3) the
development should be up to date to the improvements of arts, science, and
technology, (4) the development should be relevant to the life needs, (5) the
development should be comprehensive and continuous, (6) the development
should reflect continuous learning, (7) the development should create a balance
between national interests and local interests. All acts done for developing the
School-based Curriculum should obey the Operational Direction of School-based
Curriculum Development based on the regulation number 24 issued by the
Minister of Education on 2006.
d. Learning Process in Curriculum 2006
According to Departemen Pendidikan Nasional (2007), there are six points
students. The teaching learning process in School-based Curriculum places
students as the centre of the teaching learning process itself. The students are
hoped to be more autonomous in learning with the help of the teacher. Second, it
develops students’ creativity. By bringing autonomous learning concept, the door
of creativity is widely opened both for the students and also the teacher. It is really
hoped that creativity could help students more in understanding the learning
material. Third, it is the task for the teacher to create fun and challenging learning
environment. If the learning environment is already fun for the students to learn, it
is hoped that it could really support the learning achievement of the students.
Fourth, the learning material should be contextual. It should give the real context
to the students so they will really understand what they are learning. Fifth, the
teaching learning process should provide various learning experiences to the
students. It would enrich the students’ experiences in learning and hopefully could
boost up their willingness to learn more and achieve more. Sixth, it should be
about learning by doing. It is related with the first point, that students are the
focus of the teaching learning process. The relation lies on the encouraging the
students to explore more by themselves. They are the doers who will do the
learning things and undergo changes for improvements.
e. Genre-Based Approach
Genre-based approach is the approach that fits to be used in teaching
learning process where the text with various genres is taught. This is the popular
of written texts (Yan, 2005). The teaching learning in genre-based approach
focuses on the understanding and production of selected type of text (Lin, 2006).
The students will have the detail explanation of certain genre text so that in the
end of the lesson, they are expected to be able to identify and produce selected
type of text in the correct form and purpose. The use of genre-based approach
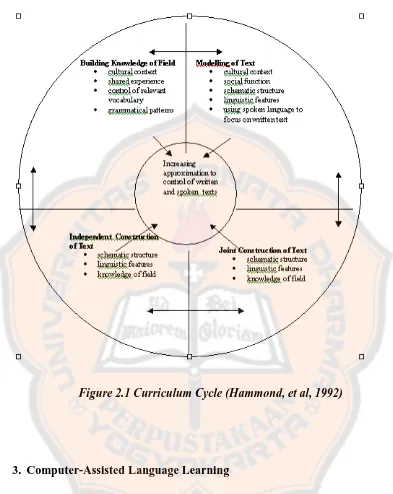
comes along with framework of teaching which is called as curriculum cycle.
Curriculum cycle consists of four main parts, namely (1) building
knowledge of the field, (2) modeling of the text, (3) joint construction of the text,
and (4) independent construction of the text (Paltridge, 2001). Building
knowledge of the field aims to bring the students to the context culture and the
social purpose of the text, introduce them to the roles and relationship or the
related components, and also the role of the language within the activity. In
modeling of the text, the students are involved in the analysis activity of the
rhetorical staging of the text and lexical and grammatical analysis as well. Joint
construction of the text aims to involve both the students and the teachers to
produce the text using the rhetoric stage introduced before. Moreover, in the
independent construction of the text, the student who are already know the correct
stages of a certain text genre are expected to be able to work on the selected text