i
THE EFFECTIVENESS OFEDPUZZLETO IMPROVE STUDENTS’ WRITING SKILL ONRECOUNT TEXT ATSMPN 1
MOJOANYAR
THESIS
Submitted in partial fulfilment of requirement for the degree of Sarjana Pendidikan (S. Pd) in Teaching English
By Yesyika Imanniar
NIM D35212056
ENGLISH EDUCATION DEPARTMENT
FACULTY OF TARBIYAH AND TEACHER TRAINING SUNAN AMPEL STATE ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY
iii
EXAMINER APPROVAL SHEET
This thesis by Yesyika Imanniar entitled “The Effectiveness Edpuzzle to Improve Students’ Writing Skill on Recount Text
SMPN 1 Mojoanyar”has been examinated on July 25th, 2017
approved by the board of examiner.
Dean,
Prof. Dr. Ali Mudlofir, M.Ag NIP. 196311161989031003
Examiner I
Dr. Mohamad Salik, M.Ag NIP. 196712121994031002
Examiner II
M. Syaifudin, M.Ed, Ph.D NIP. 197310131997031002
Examiner III
Drs. Muhtarom, Med. Grad Dip Tesol NIP. 196512201992031005
Examiner IV
Rizka Safriyani, M.Pd NIP. 198409142009122005
ness of Text at
ix
ABSTRACTImanniar, Yesyika (2017). The Effectiveness of EdPuzzle to Improve Students’ Writing Skill on Recount Text at SMPN 1 Mojoanyar.
A Thesis. English Education Department, Faculty of Tarbiyah and Teacher Training, Sunan Ampel State Islamic University, Surabaya. Advisors: Dr.M. Salik,M. Ag
Key Words: EDPUZZLE, Writing Ability, Recount text
x
ABSTRAK
Imanniar, Yesyika (2017). The Effectiveness of EdPuzzle to Improve Students’ Writing Skill on Recount Text at SMPN 1 Mojoanyar.
Skipsi. Jurusan Pendidikan Bahasa Inggris, Fakultas Ilmu Tarbiyah dan Keguruan, Universitas Islam Negeri Sunan Ampel, Surabaya. Pembimbing: Dr.M. Salik, M. Ag
Kata Kunci: EDPUZZLE, Writing Ability, Recount text
TABLE OF CONTENT
COVER ... I APPROVAL SHEET ... II EXAMINER APPROVAL SHEET ... III MOTTO ... IV DEDICATION SHEET ... V ABSTRACT ... VI ACKNOWLEDGEMENT ... VIII PREFACE ... IX PERNYATAAN KEASLIAN TULISAN ... X TABLE OF CONTENT ... XI LIST OF TABLES ... XIV LIST OF FIGURES/GRAPHICS ... XV LIST OF APPENDICES ... XVI
CHAPTER I : INTRODUCTION ... 1
A. RESEARCH BACKGROUND ... 1
B. RESEARCH QUESTION ... 7
C. OBJECTIVE OF THE RESEARCH ... 8
D. HYPOTHESIS ... 8
E. SIGNIFICANT OF THE RESEARCH ... 8
F. SCOPE AND LIMIT OF THE RESEARCH ... 8
G. DEFINITION OF KEY TERMS ... 9
1. EDPUZZLE ... 9
2. WRITING SKILL ... 9
CHAPTER II : REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE ... 11
A. REVIEW OF THE RELATED LITERATURE ... 11
1. Edpuzzle ... 11
xii
b. Purpose of Edpuzzle... 12
c. The Advantageous and Disadvantageous of Edpuzzle ... 13
d. The Edpuzzle Implementation ... 14
2. Writing SKILL ... 15
a. General Meaning Of Writing ... 15
b. The Writing Purposes ... 17
c. Writing Process ... 18
d. Writing Assessment ... 20
3. General Concept Of Recount Text ... 22
B. REVIEW OF THE PREVIOUS STUDY ... 23
CHAPTER III : RESEARCH METHOD ... 27
A. RESEARCH DESIGN ... 27
B. THE PRESENCE OF THE RESEARCHER ... 29
C. RESEARCH VARIABLE ... 30
D. POPULATION AND SAMPLE ... 30
1. Population ... 30
2. Sample ... 31
E. RESEARCH INSTRUMENT ... 31
1. Validity Of The Test ... 32
a. Content Validity ... 32
2. Reliability Of The Test ... 33
F. DATA COLLECTION TECHNIQUE (RESEARCH PROCEDURE) ... 33
G. DATA ANALYSIS TECHNIQUE ... 36
1. Data Showing (Descriptive Statistic) ... 37
2. Analysing Data By Spss 23 ... 37
a. Normality Test ... 37
b. Homogeny Test (Levene’s Test) ... 38
c. Hypothesis Test ... 38
CHAPTER IV : FINDING AND DISCUSSION ... 39
A. RESEARCH FINDING ... 39
1. The Data Finding Description Of Edpuzzle And Conventional Method ... 39
xiii
b. The Edpuzzle And Conventional Learning
Progress ... 41
2. Normality Test ... 45
3. Homogeny Test ... 47
4. Hypothesis Test ... 48
a. Paired T-Test (The Effect Of Conventional Media By Using Lks On Recount Text Writing Skill) ... 49
b. Paired T-Test (The Effect Of Edpuzzle Media On The Recount Text Writing Skill) . 50 c. Independent Sample T-Test (The Differences Between Edpuzzle Media And Conventional Media) ... 52
d. Edpuzzle Improvement ... 54
B. DISCUSSION ... 55
CHAPTER V : CONCLUSION AND SUGGESTION ... 57
A. CONCLUSION ... 57
B. SUGGESTION ... 57
BIBLIOGRAPHY ... 59
LIST OF TABLES
Table Page
3.0 Research Procedure 33
3.1 Description of Recount Text
Learning Result Example 40
4.0 Description of Recount Text
Learning Result 43
4.1 The Learning Progress by Using
EdPuzzle 45
4.2 Conventional Learning (LKS)
Progress 46
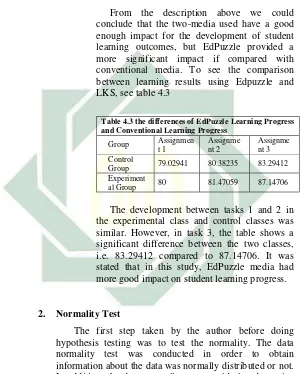
4.3
The differences of EdPuzzle
Learning Progress and
Conventional Learning Progress
48
4.4 Tests of Normality 49
4.5 Test of Homogeneity of Variances 51
4.6
Paired Samples Test (the Effect of Conventional Media by Using LKS on the Recount Text Writing Skill)
54
4.7
Paired Samples Test (the Effect of EdPuzzle Media on the Recount Text Writing Skill)
55
4.8 Independent Samples Test 57
LIST OF FIGURES/GRAPHICS
LIST OF APPENDICES
A. APPENDIX 1 (SCORING RUBRIC OF RECOUNT
TEXT) ... 63
B. APPENDIX 2 (INSTRUMENT OF THE RESEACH (PRE-TEST) ... 68
C. APPENDIX 3 (INSTRUMENT OF THE RESEARCH (POST-TEST) ... 69
D. APPENDIX 4 (LEARNING SCHEDULE) ... 70
E. APPENDIX 5 (PRE-TEST SCORE OF CONTROL GROUP AND EXPERIMENTAL GROUP) ... 71
F. POST-TEST SCORE OF CONTROL GROUP AND EXPERIMENTAL GROUP ... 77
G. APPENDIX 6 (LESSON PLAN) ... 83
PERTEMUAN PERTAMA (2JP) ... 84
PERTEMUAN KEDUA (2JP) ... 86
CHAPTER I INTRODUCTION
This chapter presents the background of the study that describes the reason why the writer conducts the study. It also contains the problem of the study, objective of the study research hypothesis, scope and limitation of the study and significance of the study. Next, significance of this study is provided. Finally, the definitions of the key term are given to avoid of those terms.
A. Research Background
In Indonesia, English was taught in any educational level, especially in junior high school. The objective of teaching English at the Junior High School/Islamic Junior High School (SMP/MTs) based on the School Based Curriculum was that the students could develop their communicative competence both in oral and written forms to achieve a certain functional stage.1 It involved four English skills; those were speaking, listening, reading and writing. Those skills were divided into productive skills and receptive skills. As Harmer stated, “Speaking and writing involve language production and were therefore often referred to as productive skills. Listening and reading, on the other hand, involve receiving massages and were therefore often referred to as receptive skills.”2From those four English skills, writing, one of productive skills, was often considered as the most difficult skill. It was also supported by Langan:
“But writing was seldom an easy, one-step journey in which a finished paper comes out in a first draft. The truth was
1
Depdiknas, “Kurikulum Tingkat SatuanPendidikan (School Based Curriculum)” (Jakarta: DEPDIKNAS, 2006), 15.
2Jeremy Harmer, The Practice of English Langage Teaching, New. (New York:
2
that writing was a process of discovery involving a series of steps, and those steps were very often a zigzag journey. Very often, writers do not discover just what they want to write about until they explore their thoughts in writing.”3
Furthermore, Hedge believed, “to have an effective writing, it required a high degree to organize development of ideas or information, a great accuracy to avoid ambiguity, a complexity grammatical use, and correctly in vocabulary choosing.”4 Despite its difficulties, Writing was an important activity in every language class. In addition, Nunan mentioned, there were three function of writing; (a) primarily for action (public signs e.g. on roads, letters, etc.); (b) primarily for information (newspapers, magazines, etc.); and (c) primarily for entertainment (comic, poetry, film subtitles, etc.).5 It was describing as skill involving complex cognitive and physical activity to form letters or combining letters and demonstrating particular linguistics aspects which consist of word, spelling, sentence structure, etc. in order to express idea, thought, opinion, and feeling.6
Teacher might face some problem in teaching English for junior high school because English was not first language in this country. So that teacher should understand about the learning strategy which could they use in teaching learning. According to Nunan, strategies were defined as the mental and communicative procedures learners use in order to learn and use language.7 Strategies might also help students elaborate language confidently, less time and energy. Learning strategy,
3
John Langan, College Writing Skills with Readings, 5th edition. (New York: McGraw-Hill Higher Education, 2011), 12.
4Tricia Hedge, Writing; Resource Books for Teachers, 1998th ed. (United
Kingdom: Oxford University Press, n.d.), 5.
5David Nunan, Language Teaching Methodology. (London: Prentice Hall, 1991),
84.
6Stoddard and Perry, Effective Writing: A Practical Grammar Review, Boston: Irwin, 1998 (Boston: Irwin, 1998), 84.
7
3
according to Oxford, were the action taken by students to make learning easier, faster, more self-directed, more effective, and transferable to new situations.8 Teacher should choose a learning strategy that enable students more active in learning process or student-centered method.
The students appeared to have many problems when writing in English. They experienced difficulties in writing for a variety of reasons. School identified that students have difficulties in planning, writing and revising text. Also, some students might have difficulty knowing how to organize their ideas, events, experiences because of limited spoken and written English and a new experience for them. Others may have difficulties in the ‘mechanical’ aspects of writing, such as handwriting, punctuation and spelling.9 For students to succeed in a foreign language, writing skill, they needed to surround themselves in a language learning environment. In the case of Indonesia, Indonesian learners have little opportunities to use the foreign language in their society.10 As a result, many problems occurred when they were in the school where the half of instruction was a foreign language like English.
On the other hand, the problem arose when the students learn about writing. The problem could be identified through these indicators: (1) The students had problem to develop the main idea into paragraph. (2) They still confused with the grammar rules such as the concept of subject, verb and so on. (3) They were difficult to compose writing that comprehensible because they have limited vocabulary. (4) The students had low motivation in writing because the teacher still
8Rebecca L. Oxford, Language Learning Styles and Strategies (United Kingdom:
Heinle & Heinle, 1990), 47.
9NSW Public Schools, Writing and Spelling Strategies: Assisting Students Who Have Additional Learning Support Needs (Sydney: NSW Department of Education and Training, 2007), 7.
10Haris Masduqi, “Critical Thinking Skills and Meaning in English Language
4
confused about teaching and media which suit to the current curriculum in writing. Consequently, students’ achievement was not equal; the smarter students got high rank, but for who had unwell in English, they got score lower. In addition, Saddler et al. wisely remarked in Westwood’s book that, good writing was not only hard work, but also it was an extremely complex and challenging mental task.11
Meanwhile, not only students often found difficulties in writing but teachers also found it. The teachers were also difficult to teach writing because it was complicated skill to teach, which, more or less, affects the students’ learning outcomes and had a long process.12 Communicating in process of writing activities started from pre-writing, drafting, revising, and editing discover and produce ideas and view. Furthermore, the teacher still used conventional teaching to teach English. The traditional or conventional teaching methods were teacher-cantered and include the use of lesson and discussions while the problem-solving element was presented or discussed with the teacher, the syllabus, the teaching materials and the students’ assessment were determined by teacher and transmitted to students in various lectures13
In order to solve the students’ problem, the teacher hoped they were able to find the solution to improve students’ writing skill. To solve the problem easier, the teacher could use media in teaching and learning process. According to Moussaid, media was very beneficial for EFL teaching and learning since it enables students to develop knowledge of material being taught, be engaged, have facilities of active learning strategies which could promote deeper
11Westwood, op.cit., p. 57
12Nguyen Ho Hoang Thuy, “Teaching EFL Writing in Vietnam: Problems and
Solutions- A Discussion from the Outlook of Applied Linguistics,” VNU Journal of Science, no. 25 (2009): 62.
5
learning.14Media could also be used to overcome the students’ boredom and to deliver information from sender to receiver which could attract their mind, feeling, attention and interest of the students, so that the teaching and learning process happened. It meant that media could develop the relation between teacher and students in the teaching and learning process effectively.
More specifically, regarding media richness and instructional appropriateness, Newby, Stepich, Lehman & Russell specifies the various characteristics of media to be considered; those were first real things, texts (hand-out, book, module), whiteboard, OHP, slide film, video, graph (picture and image), audio (tape, CD, DVD), and last software computer.15 Through media with basis of ICT, some benefits could be found such as visualizing abstract concepts, easing difficult materials, enabling interaction between learners and learning materials, handling limitation of space, time and energy, and improving users’ skill.
In Indonesia, however, there were still many schools that do not use media of ICT but still rely on traditional teaching media such as textbook and whiteboard a lot. In addition, Rahmatullah stated that students taught through textbook and whiteboard often do not pay attention during learning process since the students get bored and regard it less fun. She further states that the existence of textbook as a medium of teaching was still not optimal yet to be implemented.16 In line with this, Munir also stated that learning should not depend on textbook as only material resource since teaching process was not about accomplishing presentation of
14
Moussaid S., The Significant Role of Media in the EFL Learning Process
(Morroco: Yesmorroco.com, 2014), 16.
15
Scanlan, C.L, Instructional Media: Selection and Use, 2014, 43, http://www.umdnj.edu/idsweb/idst5330/instructional_media.htm.
16Rahmatullah, “Pengaruh Pemanfaatan Media Pembelajaran Film Animasi
6
books but helping learners to attain competence.17 Thus teachers should apply as many material resources as possible in teaching.
Learners, moreover, were viewed as proactive participants in learning, actively seeking ways to analyse question, interpret, and understand, so they need media to facilitate and express their idea in teaching and learning process; for instance, learning through technology such as Internet. Technology had allowed individuals to obtain, assemble, analyse, and communicate information more detail and at a much faster pace than ever before possible. According to Newby, in his book entitled “Instructional Technology for Teaching and Learning”, technology could build good condition during the lessons.18 Teacher and students could be cooperative to achieve the goal by asking some questions, the students look very enthusiastic respond the material. Moreover, this technology and process enhance the students’ opportunity to explore and attempt to establish meaning from the material.
Linking or browsing through internet, teacher could get a lot of newest material to teach, beside teacher could help the students to learn how to get it and increase new students’ knowledge about internet. Especially for education, the most important internet used was often found in technology, which was EdPuzzle. EdPuzzle such as e-learning had recently been implemented and given a lot of contribution towards learning process.19 It was supported by British Council in 2007 that asserts that 69% of learners around the world with strong social network performed well academically.
17Munir, Kurikulum Berbasis Teknologi Informasi Dan Komunikasi (Bandung:
Alfabeta, 2008), 29.
18Newby. (et.all), Instructional Technology for Teachinng and Learning. New
Jersey: Prentice Hall, 2000.
7
According to Jeong-Bae Son in his journal research entitled “Using Web-Based Language Learning Activities in The ESL Classroom”; he stated that most of ESL students expected that they could master English in a limited time.20 To fulfill the students’ expectations, the instructor conduct web – based learning to teach English four skills to the adult community English language program which was contain of 12 students from different countries. The result of the research was the students could be more enjoyed the Web activities and would like to use more EdPuzzle activities during and outside class time with the assistance of technology to be more actively engaged in learning.
Nowadays, almost all the people could operate technology, especially for student in junior high school. They used the technology to make them easy to access information from many online sources. This technology could help the student to get more explanation about their lesson outside the class to make them more understand.
This study focuses on the use of the combination between technology and traditional classroom. EdPuzzle became the media would be used to improve the second-grade learners of SMPN 1 Mojoanyar. A recount text was used because according to the teacher, most of her learners have lack score in this material.
A descriptive quantitative was implemented to analyse this study. The researcher would compare the learners score before and after using the EdPuzzle to investigate the progress of their learning. While the video, photo, and some paper exercise would be collected as the data validation. To measure the perspectives of the learners, the researcher would use the yes-no question.
20Son, J B., “Using Web-Based Language Learning Activities in The ESL
8
B. Research Question
Based on the background study describes above, the researcher formulated the problem as the following question:
How is the effectiveness of EdPuzzle to improve students’ writing skill on recount text?
C. Objective of the Research
The researcher achieved objective to answer the problem of the research. Based on the problem above, this study is aimed to find out the effectiveness of EdPuzzle to improve students’ writing skill in recount text
D. Hypothesis
H0 = There was no significant difference effect between EdPuzzle and Conventional learning outcomes
H1 = There were significant differences effect between EdPuzzle and Conventional learning outcomes
E. Significant of the Research
This study tried to know the writing English practices at SMPN 1 Mojoanyar, Mojokerto by EdPuzzle activities. The research was expected to give contribution to:
1. The students of SMPN 1 Mojoanyar, Mojokerto; this research could be used to know the student English achievement, especially to improve their writing competence
2. The teacher of SMPN 1 Mojoanyar, Mojokerto; this research could be used for measuring the students’ writing competence
9
F. Scope and Limit of the Research
This study only covered a limited number of students for the subject of study in the second-grade students of SMP N 1 Mojoanyar, Mojokerto.For this study, the focus was on how is the effect of EdPuzzle in teaching writing recount text from so that students might show progress in the end of the study. The population of this research was second grade of Junior High School in SMP N 1 Mojoanyar, Mojokerto.
G. Definition of Key Terms
It was important for the researcher to make clear the terms used in this paper as these followings:
1. EdPuzzle
EdPuzzle was language learning that involves the use of the Web and exploits Web materials, resources, applications or tools.21 It explained that EdPuzzle occurs with Web activities on the Web, which was important to use well-designed EdPuzzle activities to maximize language learning. EdPuzzle allowed students and teachers for flexibility of access, from anywhere and usually at any time essentially, it permitted participants to collapse time and space. According to Sarica, online learning must be done right because it had many promises but it takes commitment and resources.22
2. Writing Skill
Writing was one way to communicate with other people. It was the representation of language which was used to express and explain ideas in a textual medium through the use of signs or symbols. There were several
21Ibid., 24.
10
definitions of writing. As Meyers states that writing was an action, a process of discovering and organizing your ideas, putting them on the paper and reshaping and revising them.23 While Boardman says that writing was a continuous process of thinking and organizing, rethinking and reorganizing.24The explanation above showed that writing was a process to produce language.
23Meyers A., Gateways to Academic Writing: Effective Sentences, Paragraphs and Essays (New York: Pearson Education, 2005), 67.
CHAPTER II
REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE
This chapter explains several theories through reviewing some literatures related to this study. On this chapter, there were some main aspects studied, they were EdPuzzle, writing skill and recount text.
A. Review of the Related Literature 1. EdPuzzle
a. Definition
Nowadays, many schools and universities use E-learning in their teaching and E-learning activities. Although the word E-learning was very often to be found, people sometimes only `emphasize E-learning as a distance learning using internet. E-learning defined as the learning process through internet or other technology. The purpose of it was to make efficiency, make students more communicative, and have more time to learn and activate their knowledge.25 One media could be used in e-learning was EdPuzzle.
This research used EdPuzzle as the media of e-learning.26 EdPuzzle was a tool where you could create a video with audio, notes, and quizzes. According to Swenson it was a free service in which teachers could link to any online video, whether it was on YouTube, Vimeo, or Khan Academy, etc.27 While according to Van Horn it was a site where you could upload a video, crop it, insert
25
Krista Galyen, Joi L. Moore, and Camille Dickson-Deane, “Internet and Higher Education,” Elsevier Inc, no. 14 (October 15, 2010): 130.
26Cherie Herring, “Flipping the Elementary Music Class” (FMEA, 2016), 2. 27
12
comments or questions about the video, and allows you to see what your students have watched, when they watched it, and how much of the clip they have watched.28
The videos used could be found on YouTube or www.EdPuzzle.com. You pull a video in, add audio, create notes, and put quizzes at specific times you choose.29 The video could also be shortened to include the length that you want. The video could be shared a variety of ways. The video could be assigned to students, the link could be given to students, the video could be embedded into a website, and you could email the video, or share on the social media sites Facebook and Twitter.
When you create the video, you could make sure students do not skip the video, and set a due date. The students could go back and watch the video as many times as they like. In addition, EdPuzzle allows the user to import a video from YouTube and add interactive components, such as multiple Choices and open-ended questions.30
b. Purpose of EdPuzzle
The actual purpose of EdPuzzle was to facilitate flipping the class. It could help lecturers to deliver the course content through videos and monitor the class, but more effort was needed to motivate and encourage students to participate and prepare.31
28Shannon VanHorn, “Teaching Tips and Tools: EdPuzzle,” 2016, 1. 29
Ibid.
30Aleidine J. Moeller, Fostering Connections, Empowering Communities, Celebrating the World (2211 Dickens Road, Suite 300 Richmond, VA 23230: Robert M. Terry, 2016), 63.
31
13
c. The Advantageous and Disadvantageous of
EdPuzzle
1) Advantageous
There were some advantageous of EdPuzzle Using mentioned bellow.
a) Learners had more time to activate their learning
Because the material given by students was learned out of the class, they have more time in class to interact and discuss the material with their teacher and their classmate.
b) Teacher could monitor the learning progress of their students32
Besides giving the video, the teacher also could give questions to measure their understanding about the video. From the question have been given, teacher could measure the learning progress by the scores which were given. So, they could know accurately their students learning progress and could take more efficient step for the next learning.
2) Disadvantageous
One the lack of EdPuzzle, the teacher could not give an open-ended feedback accept the correct or false answer.33 The teacher could give a suggestion or reason why the answers of learners
14
were false or true, but they just could confirm that the answer was false or true. But it could be discussed in the classroom time.
Second disadvantageous, not all learners could follow this kind of method because of their limit.34 Some learners Might have no some facilities to access this kind of method because their house was far from city or information sources.
d. The EdPuzzle Implementation
There was a many model of flip learning implementation, but in general concept it was similar because almost of flip class uses a video as the media. For EdPuzzle, it was similar with Edmodo. For using EdPuzzle there were steps to be fulfilled by teacher and learners which were explained bellow.
1) Frist Step (Have an EdPuzzle Account)35
a) Go to WWW.EdPuzzle.com
b) Teacher should register as teacher and make a class (she/he would get class code), the code would spread out to the learners. c) Learners had to make an account of
EdPuzzle and input their class code in order to join their class
34
“Ready to Flip? Surrender Control and Structure Because Students Own Their Learning!,” in The Center on Technology and Disability was Funded by the U.S. Department of Education, Office of Special Education Programs (OSEP) under Award (presented at the U.S Office of Special Education Program, U.S: CTD, n.d.), 3.
35Educational and Technology Blue valley School, “EdPuzzle” (Blue valley
15
2) Second Step (Give a Material or Project via EdPuzzle)36
a) Teacher gave video and some question or quiz have to answer by the learners outside the classroom time
b) Learners opened the EdPuzzle, watch the video, and answer the quiz have been given. c) From the answer, teacher could monitor the
progress of their learners. And decide the activity would implement in class.
3) Get Activity in Class37
Teacher and learners did activities in class according to the learning progress have been shown in the EdPuzzle.
2. Writing Skill
As an essential language skill, writing demands students to master it well. This skill would help them to express their thoughts, feelings, ideas and knowledge. It was not an easy job to implement the best method in improving students’ writing skills.
a. General Meaning of Writing
Writing was one way to communicate with other people. It was the representation of language which was used to express and explain ideas in a textual medium through the use of signs or symbols. There were several definitions of writing, Shokrpour stated that writing was an action, a process of discovering and organizing your ideas, putting them
36Shannon VanHorn, “Teaching Tips and Tools: EdPuzzle,” 2. 37
16
on the paper and reshaping and revising them.38 While Boardman (as cited in Trang & Hoa) said that writing was a continuous process of thinking and organizing, rethinking and reorganizing.39
The explanation above showed that writing was a process to produce language. We could take more time to think and choose words in order to express our idea. We could still make a revision if it was not so clear to express what we intend to write. Writing was a complex skill, it involves a complex process done step by step to pass on knowledge or messages in our mind in a written form, in which it must have been used certain grammatical rules and choose the right words in the sentences.
Each of sentences in a paragraph must have certain correlation with each other and organize in a good order. Actually, paragraphs discuss the main ideas of the essay. The paragraph was a basic unit of organization in writing in which a group of related sentences develop one main idea. A well-written paragraph contains six elements. They are:
v Topic sentence. It states the main idea of the paragraph.
v Supporting sentences which develop the topic sentence.
v Concluding sentence. It indicates the end of the paragraph and leaves the reader with important points to remember.
38
Nasrin Shokrpour, Nikta Keshavarz, and Seyed Mohammad Jafari, “The Effect of Peer Review on Writing Skill of EFL Students,” Khazar Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences 2, no. 3 (2015): 25.
39Luong Quynh Trang and Nguyen Thi Mai Hoa, “Student Writing Process,
17
v Unity. It means that the discussion in the paragraph was only one main idea, which was stated in the topic sentence, and then each and every supporting sentence develops that idea.
v Coherence. It means that the paragraph was easy to read and understand and using appropriate transition signals connects the ideas.
v Cohesion. It means that all supporting sentences “stick together” in their support of the topic sentence.
b. The Writing Purposes
There were many purposes of writing, such as to complete the assignment, to earn a good grade, to publish their writing, and so on. Hugo (as cited in Yulianti) states that the purposes in writing activities were as follows: 40
1) Assignment Purpose
In term of this purpose, the writer actually doesn’t have the purpose of writing. It was just for completing the task given.
2) Altruistic Purpose
Here, the writer intended to entertain the reader through his writing order so they could serve the life in the easy, simple and enjoyable way.
3) Informative Purpose
The writer introduced and expressed what he really feels or thinks to the readers.
40
18
4) Creative Purpose
Through his/her writing, the writer wanted to perform artistic norms by him/herself.
5) Problem Solving Purpose
The writer wanted to explain and analyse the problem in his/her mind so that the reader understands it.
6) Persuasive Purpose
The writer wanted to persuade or convince the reader about his/her idea.
7) Self-Expression Purpose
The writer introduced and expressed what he/she really thinks to the reader.
c. Writing Process
Writing was the combination among the aspects of brain, ideas, what a writer already knows about the topic or subject and what the writer writes. A writer who wanted to produce a piece of writing must think how to make them work together in writing process. It could be said that there was no writing without a process. Boardman (as cited in Yulianti) states that writing was a continuous process of thinking and organizing. She suggests six basic steps into writing as follows:41
1) Assessing the assignment
Every student had writing assignments with different purpose, so the first step in the writing process was to understand exactly what the
19
teacher wants on a particular assignment. The most important piece of information for you to know was the topic and purpose of the assignment.
2) Generating ideas
The purpose of this step was to think about a certain topic and generate as many ideas as possible.
3) Organizing your ideas
After getting some ideas for composing paragraph, now students needed to organize those ideas. In organizing the ideas, the students need to make a topic outline. Here, the students at first have to decide the main idea of the paragraph. After that, they needed to consider which points to include in order supporting the main point.
4) Writing the first draft
Before writing the first draft the students had to generate the idea and organize the pattern of writing. Good writer should make sure to read their writing carefully in order to make changes and corrections before they consider it finished.
5) Rewriting
It was critical part of the writing process and consists of two separate processes revising and editing.
20
writing, or, better yet, set their paragraph aside for a while and go back to it later.
Editing was a process when the students make sure the spelling, capitalization, punctuation, vocabulary and grammar. Editing was somewhat mechanical because they were basically following rules. The rules of spelling, for example, were clear; a word was either right or wrong.
6) Writing the final draft
It was the last step in the writing process. In the final draft, the students write correct paragraph format based on the result of the revising step. It should have correct grammar, spelling, capitalization, punctuation and vocabulary. Keep in mind that any of the steps could be repeated at any time.
d. Writing Assessment
Assessing students’ writing ability was not simple as people imagination, it had to be clear about what will be measured from it; grammar, content, idea, punctuation, paragraph construction, or else.42 It also important to know about what kind of essay would be measured, academic writing or personal writing,43 and what kind of writing performance would be scored.44
42
H. Douglas Brown, Language Assessment: Principles and Classroom Practice
(California, n.d.), 218.
21
This kind of task given to student are writing recount text according to their experience, so it was categorized as the personal writing essay but it was design to fulfil the academic purposed. Personal writing text was a kind of essay derived from people story according to their experience or feeling, the character of this essay was personality.45 While according to the writing performance, the task given to the students for fulfil the research was categorized as the extensive writing, because the writer has skill to make a coordination between one word to others, one sentence to others, and one paragraph to others. So, the passage had been written was understandable, sync with the idea, and had good grammatical mechanism.46
According to brown, there were 4 aspects to be measured for extensive writing. First was organization aspect which was focus on the correlation between each word, each sentence, and each paragraph to others.47 Second, was developing idea. It had strong correlation with the authenticity and how the writer developed their idea into the passage.48 Third was grammar and the fourth was mechanical aspect (punctuation and others), it was related to the meaning, are the writer located the punctuation and the rules of grammar49 correctly or not, so the reader did not get miss understanding when they read the passage.
The researcher was used the writing rubric designed by Brown, because it was appropriate by the
45Ibid., 219.
46
Ibid., 20.
47
Ibid., 243.
22
factor would be measured for recount writing assignment. The focus of this study was to improve the ability of students in recount text writing, the aspect will be measured; the first was the authenticity where the students could develop their idea or not, second was the organization aspect, where the students could correlate the sentences and the paragraphs with a good way and it could be understood by the reader. Third and fourth are the grammar and punctuation aspect.
3. General Concept of Recount Text
Recount was one of the examples of story genres. In a recount text, it reconstructed past experience. It means that recount text tells about something that had happened. Anderson and Anderson (as cited in Arifan) state that recount was a piece of text that retells past events, usually in the order in which they happened; it could be speaking or writing.50 The purpose of a recount text was to give the audience a description of what occurred and when it occurred. Hartono (as cited in Arina) gives clear description about schematic structures and language features of a recount as follow:51
§ Orientation: provide the setting and introduces participants.
§ Events: tell what happened, in what sequence
§ Re – orientation: optional – closure of events
§ Language features of recount text were as follows:
50
M. Arifian Rosyadi, “Recount Text,” 2015, 507.
51Arina Muflikhati, “IMPROVING STUDENTS’ WRITING SKILLS ON
23
§ Focus on individual participant
§ Use of past tense to indicate the events in the past time.
§ Focus on temporal sequence of events.
§ Use material and action clause.
From the explanation above it could be stated that recount text deals with series of events that retell about something happened in the past. It was needed to be taught to eighth grade students of Junior High School because it was one of the requirements in the curriculum. At this level, students were expected to be able to write a text in the form of recount. However, students often faced difficulties in writing carrying out the task.
B. Review of the Previous Study
There was some study have been acted before this study. They were become the theoretical foundation to develop this study. The researcher found ten studies related to e-learning.
First was the study entitled Assessing Learning in a
Flipped Classroom52 by David Swenson. This study focused on
the learning assessment using EdPuzzle. He tries to monitoring the learners’ progress by using it, but had no specific material such as recount text in this study. The same aspect with this study were used Edpuzzle as the media. However, the differences with the researcher were only monitoring the learning progress.
Second study was acted by Hairong Mu and Dimitrios Paparas with their journal entitled Ready for the Flipped Classroom? Preliminary Experiences of the New Approach in
24
Teaching Economics to Non-Major Students.53It was explained
about the use of flip classroom in economic field. Three media were used there, one of them was EdPuzzle. The similarity of this study, the researcher used EdPuzzle as media but have different material.
Extensive Listening: Pedagogy, Resources, and Tools54 were authored by Edward Povey was the third previous study had been found by the researcher. In this study used the same media, but the differences with the researcher were used of activity in learning process. He was taken listening skill that improved using Edpuzzle. But, in this study the researcher used Edpuzzle to improve writing skill.
The fourth previous study was written by Joshua Shannon-Chastain and C. Fell-Kurban entitled just one more hit: Student engagement with pre-class videos in the evolution of English for Academic Purposes course from traditional to flipped.55This study was not used EdPuzzle but it used you tube and another source of video. This study focused on experimental research tried to change from the conventional media to the e-learning method. The differences with the researcher were focus in the method of the study. But, the similarity is used EdPuzzle as a media.
The next was Ready to Flip? Surrender control and structure because students own their learning56!published by U.S Office of Special Education Program. This study has similar media with the researcher that was Edpuzzle website.
53Hairong Mu and Dimitrios Paparas, “Ready for the Flipped Classroom?
Preliminary Experiences of The New Approach In Teaching Economics to Non-Major Students.”
54
Edward Povey, “Extensive Listening: Pedagogy, Resources, and Tools” (n.d.), accessed
February27,2017,http://www.ijeionline.com/attachments/article/56/IJEI.Vol.3.No. 7.04.pdf.
55
Shannon VanHorn, “Teaching Tips and Tools: EdPuzzle.”
56“Ready to Flip? Surrender Control and Structure Because Students Own Their
25
However, the differences with the researcher were the implementation of using Edpuzzle as flipped learning.
“Successfully flipping the ESL classroom for learner autonomy”57 was the sixth previous study written by Yu Jung Han. It talked about the successful of flipped classroom in built up the learners’ autonomy in learning. The similarity of this study was using flip class and its media such as EdPuzzle, you tube, and others. But, the differences were learners could find out their learning style according to their passion.
In addition, there was a study discussed about the effect of flip learning on traditional class which focused on the learning and teaching habitual. The different with the researcher, in this study researcher only focus on students’ learning progress. But, it has similar media used EdPuzzle as the media in learning activity. It was found on the dissertation of Jeremy F. Strayer entitled The Effect of The Classroom Flip on The Learning Environment: A Comparison in Learning Activity in A Traditional Classroom and A Flip Classroom that Used in Intelligent Tutoring System.58
The eighth was “Blended Learning: A Flipped
Classroom Experiment” was written by William R.
Slomanson. It was one of the beginner studies which use an experimental research on implementing flip learning. Focusing on the flip class but use several media, not only one media as EdPuzzle. The differences with the researcher were used one media in implementation of learning activity.
Another Study came from local area was written by Asmara Miftakhol Jannah entitled “The Effectiveness of
57
Yu Jung Han, “Successfully Flipping the ESL Classroom for Learner Autonomy,” NYS TESOL Journal 2, no. 1 (2015): 98–109.
58Jeremy F. Strayer, “The Effect Of The Classroom Flip on The Learning
26
Flipped Classroom to Improve Students’ Reading
Comprehension to The Third Grade Students of Mts Unggulan
Al-Jadid Waru Sidoarjo”59. The study was a quasi-
experimental research with two classes; experimental class and control class. The similar with this study were research design. The differences were the media and the text type. The first difference, she was taken Facebook as a media. But in this study, the researcher used Edpuzzle as media in learning activity. The second difference was text type, she was using reading comprehension but the researcher using recount text as a students’ writing skill.
While for this study was purposed to investigate the influence of flip class in improving writing skill. The differences of this study than the studies above were this study was focus on experimental research which was the flip class could improve the learners’ writing skill on recount text or not. In addition, this study was focus on using one media of flip class called EdPuzzle.
59Asmara Miftakhol Jannah, “The Effectiveness of Flipped Classroom to Improve
CHAPTER III RESEARCH METHOD
This chapter describes the features design of the fundamental research methods which were applied by the researcher. Inside it, there were any cases would be explained, they were research design, population and sample, research instruments, data collection technique, and data analysis technique.
A. Research Design
This study used quasi-experimental that applied to measure how much the effect of EdPuzzle on students’ ability to write recount text. The experimental study was held to make some investigation to the cause and effect relationship with two different groups: control group and experimental group60and the investigators accurately manipulate and control the conditions which establish the events in which they were interested.61
The experimental group would be given the treatments, but before it, the researcher would give pre-test for both groups to determine how far the students’ ability in writing recounts text. Afterwards, the students would be given treatments twice and followed by post-test.
In indicate the treatments, the random assignment would be used by the researcher, it was attended to choose which class to be control group, and another became the experimental group. It was meaning to know about the
60
Suryabrata and Sumadi, Metode Penelitian (Jakarta: PT Raja Gravindo Persada, 2011), 91.
61Sutrisno Hadi, Metodologi Research, 4 (Yogyakarta: Yayasan Penerbit Fakultas
28
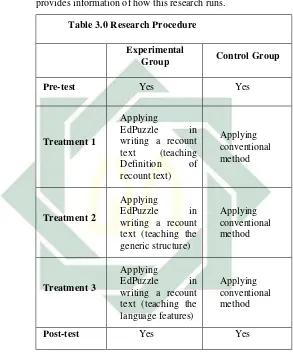
[image:41.420.71.364.85.447.2]dissimilarity result of both of the groups.62 The following table provides information of how this research runs.
Table 3.0 Research Procedure Experimental
Group Control Group
Pre-test Yes Yes
Treatment 1
Applying
EdPuzzle in
writing a recount text (teaching Definition of recount text)
Applying conventional method
Treatment 2
Applying
EdPuzzle in
writing a recount text (teaching the generic structure)
Applying conventional method
Treatment 3
Applying
EdPuzzle in
writing a recount text (teaching the language features)
Applying conventional method
Post-test Yes Yes
62
29
In this quasi-experimental study, there was Scientifics investigation which was done in manipulation on independent variable.63 In this study the researcher would use two classes to be tested. The first class would become the control group, and another one would become the experimental group. The experimental group was conditioned to use flip learning method, while the control group was using the habitual method used by the teacher.
Depend on statement of Asmadi, the experimentation was done to compare the two classes in which the control group was generally taught by the conventional or usual procedure, and the experimental group was used the new method of learning.64 Both groups would be treated with the same procedure, and given pre-test and post-test before and after the treatments with the same sets of the test.
In this study, the researcher applied cluster sampling technique by taking two classes in population. Afterward, the experimental and the control group were decided by the researcher. The pre-test would be given to both groups to find out their ability in recount text before treatments. This would be a measurement to both groups about how good they arrange sentences. Later, the researcher gave twice of treatments to experimental group. The different classes would be taught in conventional method without EdPuzzle and the experimental group would be taught by using EdPuzzle.
B. The Presence of the Researcher
In this study, the researcher played role as the teacher and data collector. The researcher gave the pre-test, treatment, and the post-test, so she mixed up directly with the research object (learners). She also was a full observer on the process of
63
L. R. Gay, Educational Research Competencies for Analsis & Application, 2nd ed. (Ohio: A Bell & Howell Company, n.d.), 298.
64Asmadi Alsa, Pendekatan Kuantitatif Kualitatif Dalam Penelitian Psikologi
30
E-learning implementation. In addition, this research had been known and permitted by the head master and the research object.
C. Research Variable
In this experimental study, both of dependent variable and independent variable had clear dissimilarity. The explanation about how the two kinds of variable associated one to another, there was a cause-effect relationship in experimental study.
Dependent variable was the effect derived from treatments from EdPuzzle learning. Meanwhile, Independent variable was similar to the cause which means that the media or the materials became the cause of the impact given after the treatments.65 It could be concluded that dependent variable was the effect on recount writing which appears after treatment using EdPuzzle and independent variable was the EdPuzzle itself. In data analysis, the researcher would calculate the mean and standard deviation to know about how effective EdPuzzle in use.
D. Population and Sample 1. Population
The population of this study was the learners on SMPN 1 Mojoanyar which was located on Jln Raya Mojoanyar no.2 Mojoanyar. The school contact numberis was (0321) 510062. For the details, there were four classes for the entire class grade. In every class, there were 34 students. The classes which the researcher applied in the research were two classes comprising VIII A and VIII B.
31
2. Sample
The samples of this research were two classes: VIII A and VIII B. The reason why the researcher take those classes as a sample because both of those classes have resembled ability in English, this statement was taken from the recommendation of the teacher on that school.
In addition, since this was a quasi-experimental research, the researcher used a purposive sampling. She gave assignment to every eighth grade of the classes, and the results two classes ;VIII A and VIII B would be the sample, both of the class have same total students; 34 students for each and they have resembled competence in English. The researcher applied purposive sampling because he could not randomize the students to be the sample in the population to represent in the study. The class would be separated into two groups, one would be the experimental group, and another would be controller group.
E. Research Instrument
In the research, the instruments were used to obtain the data from the field. Because of this study was Quasi-experimental research, it was belonging to quantitative research. The researcher needed do some tests as the instruments to collect data in the form of numbers or in quantitative way. As the instrument of research, certainly the test needed to be assessed its validity and reliability. When the instruments have proven to be valid and reliable then it could be used to collect data needed in the field.
32
Si Putu Agung Pertiwi Dewi66(see Appendix 1). The instrument in phase pre-test and post-test and the rubric was known reliable and good to apply to collect data, when the result of Pearson product moment calculation showed the score was higher than that in the table. The instrument used to measure pre-test and post test was the same rubric as in Appendix 1.
1. Validity of the Test
The data was obtained in the field could be called valid if derived from valid test as well. The validity concept was the test measure what needs to be measured.67 If the component validity namely content validity, face validity, and construct validity were included and met, the test could be considered valid.
a. Content Validity
The substance of what to measure must match the test was the content validity representation. For example, we wanted to assess speaking, but the test was not valid in its content, because the form of the test was not in the form of paper-based test with multiple choices. The data resulted from the invalid test could not represent what to assess from the individuals.68
If the test was proven to assess what skill should be assessed during the treatment, the test instrument could be said validated, for example, reading skill in recount text. The researcher cannot go beyond this boundary because the assessment must be related with the materials which in learning process.
66SI Putu Agung Pertiwi Dewi, “Kemampuan Menulis Recount Text Dengan
Menggunakan Teknik Picture Series Pada Kelas Viii Di Smp Angkasa Kuta Badung” (Universitas Udayana, 2013), 42–47.
67H. Douglas Brown, Principles of Language Learning and Teaching, 5th ed.
(White Plains, NY: Pearson Longman, 2007), 448.
33
And the material also must be appropriate with syllabus and content standard.
This research used the valid instrument because the content of the instrument appropriated with the content will be measured. Grammar, punctuation, developing idea, the correlation between each paragraph and each sentence was the content will be measured. This research used the rubric from Brown which has all of that content. According to brown, there were several aspects must be measured from writing, they are developing idea, coherent, and the writing rules (grammar and punctuation)
2. Reliability of the Test
The data research could be considered reliable or not when there was a similarity in different periods. A test could be said as reliable if the test could show the similar result in period time.69 So if the test was reliable, the test was used in the research could be used several times to measure the same data and would result the same data. The measurement of this test was using international rubric by Rebecca L. Oxford.70It meant that the test instrument was reliable.
These researches instrument also an international instrument because the instrument was ever used in many researches without change the base of the instrument.
F. Data Collection Technique (Research Procedure)
The try-out test would not be held as the first step of data collection to examine the instruments’ validity and reliability, because the tool used to be measure was an international rubric which was often use as a reference and have actual similar result. Then it was directly implement the
69Ibid., 501.
34
pre-test, treatments and ended by post-test. The Pre-test was conducted by giving an assignment to the students to write a recount text. The treatment was applied 3 times. The first treatment, teacher gave material about the definition of recount text. The second treatment teacher gave material about generic structure and the third teacher gave material about language features. The Post-test was conducted by giving an assignment to the students to write a recount text. The form of scores of pre-test, treatments, and post-test were the data collected in quasi-experimental research. The differences between pre-test and post-test was then calculated with the formula of independent t-test two tails by using Pearson correlation product moment.
Detail of Research procedure 1. Pre-test
After getting two classes, it was divided into two groups; experimental group was taught using Edpuzzle media in teaching writing recount text and Control group was taught using conventional media. Then, researcher gave pre-test to experimental group and control group. The purpose of the pre-test was to determine students’ ability for their writing in recount text. The result of this test between experimental group and control group was used to identify the differences students’ writing ability in recount text before treatment.
2. Treatment Implementation
After giving the pre-test for both of classes, then the next steps were held by giving treatment. Edpuzzle media was given to experimental group and the control group was taught using conventional media (LKS). The researcher was given three times treatments. This action had a purpose to get an accurate result of the Edpuzzle media. This research was taken a five times class meeting for both of classes.
a. Experimental class
35
steps of Edpuzzle media in teaching writing recount text were:
1. Outside the Classroom.
- Researcher shared a video teaching about recount text explanation through Edpuzzle media that the researcher has been chose. Students were able to watch the video by their laptop, smartphone or computer.
- Students watched the video at home or wherever place that the students comfort to study in. They can also study individually or peers.
- Students gave some exercise through the video about definition of Recount text, generic structure, and language features.
Note: to make sure that the students watched the video by themselves, teacher gave the students task that could be fulfilled by watching the video that have been shared in Edpuzzle. When in the class, teacher asked the students with some question about the video that have been shared.
2. Inside the Classroom.
Before Used Edpuzzle
- Teacher gave the tutorial to sign up in Edpuzzle website.
- Teacher gave the opportunity to students who wanted to ask about using Edpuzzle website.
After Used Edpuzzle
- Teacher asked what they had learned from the video and corrected the answer that the student had to answer in the video with the class.
- Teacher asked them whether there was something that they did not understand by the video.
- Teacher gave students a recount text.
36
- In group, students identified and explored the recount text of the paragraph to get the generic structure of the text.
- Using their own words, students wrote the important information from the text.
- This activity continued till the end.
- Teacher and students discussed the content of the text. Teacher can point one of the groups to share their notes about the text. Teacher controlled and provided the right answer while checking the answer.
- Teacher evaluated the learning process.
b. Control class
In the control class did not receive any treatment and the learning process was done using a conventional learning. The lesson plans for the control class were:
- Teacher explained the lesson in front of the class using conventional media.
- Teacher gave a recount text to students.
- Teacher asked the students to identify about generic structure of recount text
- Students collect the work.
3. Post-test
After the treatments, researcher was held post-test that would be given to the experimental group and the controlled group. The purpose of this test was to know the students’ achievement of both classes after getting the treatment.
After got the pre-test and post-test from both of classes, the researcher did the data analysis to found out whether students’ writing ability in recount text was an improvement or not.
G. Data Analysis Technique
37
1. Data Showing (Descriptive Statistic)
The score of the data would be shown by using this following table.
[image:50.420.71.376.145.442.2]Example of Scoring Table
Table 3.1 Description of Recount Text Learning Result Example
N Minimum Maximum Mean Std.
Deviation Variance
Post-test Control Post-test Experiment Pre-test Control
Pre-test Experiment
Valid N (list wise)
2. Analysing Data by SPSS 23
After showing data with descriptive statistic, then researcher would analyse data by using inferential statistic to test hypothesis of this research. Inferential statistics were divided into 2, parametric and non-parametric. If the data that had been taken satisfies some assumptions such as normality test and homogeneity test then the parametric statistic could be used, if the data did not meet the assumption then non-parametric statistic would be used.
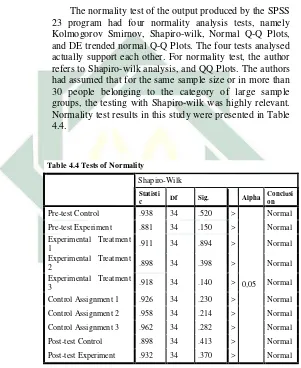
a. Normality test
38
Score.71 The data interpretation, if the Asymp, Sig. had score more than Alpha score; it was mean that the data was normally distributed.
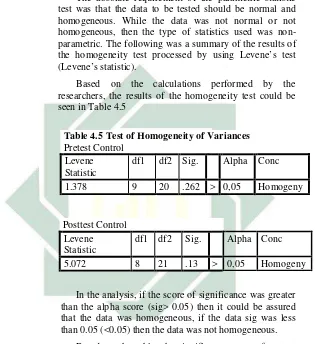
b. Homogeny Test (Levene’s Test)
In this study, a Levene’s Test was carried out to check the data Homogenous by using IBM SPSS V23. To know the result of the data was homogeny or not, it could be seen from the significant score of each variable. When the score of sig. was more than 0,05 or 5% (Alpha), it could be concluded that the data was homogeny.
c. Hypothesis Test
The hypothesis test was provided by using paired T-test to investigate the effect of EdPuzzle and LKS Media on the learning result. Then independent sample T-test was used to investigate the differences between both of that media. 72
71R. Gunawan Sudarmanto, Statistik Terapan Berbasis Komputer: Dengan Program IBM SPSS Statistik 19 (Jakarti: Mitra Wacana Media, 2013), 130.
CHAPTER IV
FINDING AND DISCUSSION
A. Research Finding
1. The Data finding Description of EdPuzzle and Conventional Method
The data had been acquired would be processed, so the score had been got meaning. Data processing in a study was conducted to find answers from the formulation of problems that have been proposed previously. Data analysis was performed using statistical software program of Computer Product Service and Service Solution (SPSS) Version 23.
The data generated through the write test recount text in the form of numbers obtained from two sample groups, namely experimental group and Control Group. Instruments were given to each group twice (at pre-test and post-test). For more details, the researcher would describe the results of the data from each group taken.
a. Recount Text Learning Result
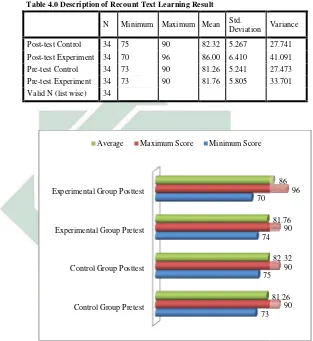
[image:52.420.70.364.128.471.2]Table 4.0 Description of Recount Text Learning Result
N Minimum Maximum Mean Std.
Deviation V
Post-test Control 34 75 90 82.32 5.267 2
Post-test Experiment 34 70 96 86.00 6.410 4
Pre-test Control 34 73 90 81.26 5.241 2
Pre-test Experiment 34 73 90 81.76 5.805 3
Valid N (list wise) 34
Figure 4.0Description of Recount Text Learning Result
Control Group Pretest Control Group Posttest Experimental Group Pretest Experimental Group Posttest
73 75 74 70
Average Maximum Score Minimum Score
40
Variance
27.741 41.091
27.473 33.701
75 74
90 90 90 96
41
Based on the tables and graphics that have been presented, the pre-test scores of the two classes had a similar average. For control group, the class had an average of 81.26 while the experimental group class had an average of 81.76. It could be said that the ability of students fr