Implementation the International Financial Reporting
Standards as a Moderating Variable of the Relationship of
Corporate Governance with Earnings Management
Agrianti Komalasari
1Abstract:
In general, this research is aimed at providing empirical evidence concerning the analysis of the adoption of IFRS as a moderating variable in the relation of corporate governance with earnings management. In particular, there are two objectives in this research, first, to provide empirical evidence concerning the analysis of the adoption of IFRS as a moderating variable in the relation between the independent of commissioners to the number of board of commissioners and earnings management; second, to analyze the adoption of IFRS as a moderating variable in the relation between the dual position audit committee members and earnings management.
The research was conducted on companies listed on the Stock Exchanges of Germany, Denmark, France, and the Netherlands from 2002 to 2013. It primarily employed agency theory. Moreover, it employed primary variables including adoption of IFRS, corporate governance, in particular the proportion of independent commissioners to the board of commissioners, dual positions of audit committee members and earnings management. The test results in this research conclude that: the results of testing of the model of accrual earnings management with the samples of companies listed on the stock exchanges of Germany, France, the Netherlands and Denmark indicated that the adoption of IFRS strengthened negative relation of the proportion of independent commissioners to the number of board of commissioners with accruals earnings management, so that the hypothesis 1 was acceptable. The hypothesis 2 stating the adoption of IFRS strengthen negative relation between the multi position of audit committee members and accrual earnings management was acceptable.
Keywords: Board of Commissioners, Independent Commissioners, Audit Committee, Adoption of IFRS, Accrual Earnings Management.
1 Faculty of Economic and Business, Lampung University-Indonesia,
Introduction
Issue elevated on this study is the impact of International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) implementation that uses proper value in assessing assets and liabilities as moderating variable between corporate governance and auditor quality with earnings management. The objectives of this study is to provide empirical evidence of the impact of IFRS implementation as moderating of relationship between corporate governance on earnings management. The crisis of finance in 2007 and 2008 provides clear picture on many companies that reports the declining of market value of company’s assets. The assessment of company’s assets based on market value may be directly affected from liquidity of low market price. This is resulting sense of skeptical of investor to perform investment named liquidity risk. Scott (2012), Kothari and Lester (2012), Khan (2010), Allegret et al. (2016), Thalassinos et al. (2010), (2013), (2014), (2015), Boldeanu and Tache (2016), Fetai (2015) and Glavina (2015) state that the liquidity risk leads to market value lower than book value. According to Scott (2012) and Thalassinos and Politis (2011) and (2012), the impact of using normal value when the liquidity is low the market price constitute main issue of normal values failure.
According to Barth et at. (2008) there is earnings management decline in the company that voluntarily adopting IFRS between 1994 until 2003. The research of Daske and Gebhardt (2006) state that there is improvement of disclosure after IFRS implementation across countries that adopting IFRS. The result of the research of Barth et at. (2008) finds that company that adopts IFRS experiencing improvement of reporting quality such as earnings management decline, the acknowledgment of on time damage and incline of value relevance. Daske et al. (2008) indicates that adoption of IFRS proven the improvement of market liquidity, reducing capital cost of company and improve equity value.
In contrary with the research result of Barth et al. (2008), other research that is performed by Christensen et al. (2008) its result indicates that the company in Germany after adopting IFRS experiencing decline of earnings management level. The decline of earnings management level mentioned earlier only for company as early adopter that has incentive to improve the transparency of reported profit rate. In relation to early adopter company, Christensen et al. (2008) find evidence that there is improvement in earnings management for company that is not implementing IFRS until IFRS becomes mandatory in Germany.
implementing IFRS in France but for Australia and England there is no improvement of earnings management. Ahmed et al. (2012) finds significant evidence that there is improvement of earnings management following relative IFRS adoption on control sample of company that is not adopting IFRS (the most comes from USA companies). Research of Ahmed et al. (2012) and Christensen et al. (2008) has different attribute for company that adopt IFRS earlier compared to sample company in Bart research et al. (2008).
Earnings management is an intension action covering all kinds of manipulation that may affect financial reporting both through profit amount or other accountant item (Scott, 2012). Apart from the accrual discretionary quality, earnings management also measured by using real activity of company. Research of Roychowdhury (2006) examines earnings management through real activity initiative starting from normal operating practice that further is motivated to meet certain targets. There are motive variety of company to perform real earnings management vary. Research of Graham et al. (2005) indicates that there is availability of manager to change discretionary expenses as well as other real decisions to achieve the objectives of financial reporting.
Some of researches examining the relationship between corporate governance and earnings management indicate that there is negative relationship between the measurement of commissioner board and earnings management. Result of Klein research (2002) and Zéghal et al. (2011) indicate that there is negative relationship between independent commissioners with profit level management. Lacker et at. (2007) researching the relationship between discretionary accrual with commissioner of board measurement. Sivaramakrishnan and Shaokun (2008) researching the effect of governance corporate structure on accrual quality. The result indicates that if the mechanism of governance corporate runs well, then the profit quality is high and the company with adequate mechanism of governance tends to have high accrual quality.
Scott (2012) states that the perspective of measurement on the financial reporting is an approach which emphasizes responsibility of the company to put normal value into financial reporting. There are three levels in determining normal price according to IFRS 13, first is an input in the form of price adopted from active market for an identical assets and liability. These prices must be applied as determining input of normal value without performing adjustment, in so far available. If it is excluded in the first level, then the second input level may be observed, directly or indirectly on assets and liability. The third level, if input can unobserved, including necessary adjusted company internal data to reflect assumptions on participant in the market.
assets assessment in IFRS application since 2005, it is expected that the application of IFRS strengthens the role of corporate governance in influencing the integrity of financial reporting. Based on that, questions of research submitted are as follows: Does the application of IFRS strengthen the negative corporate governance with earnings management?
This research is motivated by some previous researches which was the research of Bart et at. (2008), Capkun et al. (2008) and the research of Doukakis (2014). The research result of Barth et al. (2008) states that there is declining of earnings management in the company which voluntarily adopts IFRS between 1994 until 2003. Capkun et al. (2008) states that there is high earnings management in 2005 due to the adjustment of accounting standards of local accounting standards to IFRS. Doukakis (2014) with the range of data of 2000-2010 states that there is no accrual and real earnings management differences after IFRS is applied.
Previous research indicated there was relationship between corporate governance characteristic and auditor quality in reducing earnings management occurred in public company (Klein 2002; Beasley 1996; Peasnell et al., 2005; Larcker et al., 2007; Dechow et al., 1996 and Chtourou et al., 2001). The research of Marra et al. (2011) and Zéghal et al. (2011) research the influence of corporate governance and auditor quality toward earnings management in the period before and after the application of IFRS 2002-2010.
The different research of Marra et al. (2011) and Zéghal et al. (2011) with the previous research is using the application of IFRS as moderating of role of commissioner board and audit committee in reducing earnings management. Marra
et al. (2011) specifically elevate issue of corporate governance in performing new
accounting standards, due after application of IFRS the role of corporate governance and auditor quality are expected to be more effective in declining the level of earnings management. The application of IFRS that becomes main issue in this research, refers to previous research which is more focus on the setting that is exist in Europe, such as some researches that had performed by Van Tendeloo and Vanstraelen (2005), Capkun et al. (2011), Daske and Gebhardt (2006), Daske et al. (2008), Christensen et al. (2008), Marra et al. (2011) and Zéghal et al. (2011). This is due to the application of IFRS is applicable earlier in some big parts of Europe countries.
that corporate governanceis more effective to lower the earnings management after IFRS being applied.
This study elevates issue of the role of corporate governance in reducing earnings management which moderated by the application of IFRS particularly addressed to countries that implementing two-tier model in the structure model of its corporate governance. The research is performed with the enhancement of study in the initial adopters of IFRS and as countries that apply corporate governance two-tier are The Netherland, Germany, Denmark, and France. This study is different than the research of Marra et al. (2011) that only perform the study only in Italia. Marra et al. (2011) only researches on companies in one country that has only corporate governance one tier model.
The purpose of this research generally is to provide empirical evidence on analysis of application of IFRS as moderating variable of governance corporate relationship with earnings management. The result of this study is expected may provide empirical, practical and methodological contributions for academicians, regulators and communities. Empirical contribution expected may be provided by this study is presenting additional empirical evidence on analysis of application of IFRS may strengthen negative relationship between corporate governance with earnings management before and after the IFRS application period particularly for countries with corporate governance two-tier model. Using special sample for countries with corporate governance two-tier model due to different structure corporate governance model according to Othman and Zéghal (2006) will have behavior consequences in performing different earnings management.
This study particularly refers to the countries adopting IFRS and structure of two-tier council follower. This is intended to provide empirical contribution for the regulators in Indonesia due to the companies in Indonesia using the structure of two-tier council and Indonesia in 2012 begins to apply IFRS. Methodology contribution expected that may be provided on this study is the use of proxy of double post that perform by audit committee member that involves in the structure of corporate governance with other post that is in the structure of corporate governance. This study on the application of IFRS in the foregoing is as Barth et al. (2008), Lang et
al. (2003), Capkun et al. (2011), Zéghal et al. (2011), Marra et al. (2011), Daske et
al. (2008) and Doukakis (2014) only using before and after application of IFRS category to measure the application of IFRS. This study uses three levels of application of IFRS, one that has not been applied, partly applied and completely applied the IFRS. The use of these three levels of application of IFRS is expected to provide the contribution of methodology due to the difference of application of IFRS among countries in the period 2002-2013.
taken is in the form of guidance or standards that may minimizes the occurrence of accrual earnings management. Providing the evidence of empirical on the roles of auditor quality in minimizing the occurrence of accrual earnings management.
The difference of this study with the previous studies is that this study uses companies’ samples from countries using corporate governance two-tier model. Study on the application of IFRS that is performed by using the companies’ sample in many countries using control variable in the form of earnings management index per country, stock capitalism, ownership concentration, disclosure index, legal origin, corruption index and law regulation such as performed by Ahmed et al. (2012) and Christensen et al. (2008). This study uses companies from five countries that categorized based on the cluster used in the research of Leuz (2003). Leuz (2003) classifies country based on total earnings management index, stock capitalization, ownership concentration, disclosure index, legal origin, and corruption index as well as law regulation.
Literature Review
Anderson (2004) states that in the mechanism of corporate governance commissioner council is an important internal control mechanism. The stockholder delegates responsibility to the commissioner to make decision in the name of them, including the assignment to monitoring the behavior of management. Member of commissioner council must have level of high skill and have strong professional reputation. Member of independent commissioner council is expected to reduce agency issues that is in top management with the skill and professional possessed.
According to Ooghe and De Langhe (2002) there is clear cut characteristic between corporate governance models such as Anglo American model and Euro Continental model. The first difference is in Anglo American company has concentration of low stockholder, while in Euro Continental concentration of ownership by company’s group large enough from the amount of circulated stock. According to Hubert and De Langhe (2002) generally company in Germany, France, Italia, and The Netherland have concentration of ownership above 50% with the proportion of the amount company registered in Stock Exchange lesser compared to the proportion of the amount of Anglo American company registered in Stock Exchange.
The third difference is the amount of total company registered in Stock Exchange compared to the one that is not registered. In the Euro Continental Company the amount of company registered in stock exchange lesser than the amount of company that is in the Euro Continental. Investment of stock performed by individual directly to private company so that personal relationship between investor and management party tied strongly. This is different than Anglo American Company, as example system of pension leads to the availability of many funding resources that may be invested in Stock Exchange through financial institution (Miller and Choi, 2014).
The fourth difference is higher blockholding in the company of follower country of Euro Continental model with the company in Anglo American Country. This leads to high strong vote of stakeholder in euro Continental compared to in Anglo American. In the company of the follower of Euro Continental model conflict may occur between majority stakeholder and minority stakeholder. It different than the company of Anglo American that more transparent with strong regulation that limits conflict of ownership in the company.
Schipper (1989) states that earnings management is a deliberate action covers all kinds of manipulations that may affect financial reporting both through the amount of profit or other accounting item and may suits to or not suits to the standards. According to Babalyan (2004) earnings management motivation is not only a matter of bonus plan, debt covenant, or political cost but it is a result of manager motivation as well to maximize their own utility (Macijauskas and Maditinos, 2014). Maximization of manager utility is not always considered narrowly as remuneration maximization and wealth. But the intention is to meet the utilization function such as warranty job and self-respect. This occurs due to main motivation which so difficult to be measured. If the managers is respected due to their performance in the form of accounting profit, manager will make any effort to increase company’s profit that will lead to the improvement of bonus or reward through selection of certain method or procedure.
period may encourage future profit down proportionally by the increase of profit currently.
Zéghal et al. (2011) investigates the effect of mandatory IFRS adoption, corporate governance mechanism on earnings management. Sample used is 353 companies in France in 2003–2006. Zéghal et al. (2011) measures the earnings management by using discretionary accrual model used by Kothari et al. (2005). The result of the research of Zéghal et al. (2011) indicates if IFRS and corporate governance mechanism has influence on the decreasing of earnings management in Paris.
Manager is motivated by reputation and contracting to increase the company value. This encourages the creation of information to market due to the more information disclosed will decrease attention of investor on adverse selection. Information creation to the stock market may improve investor’s trust toward company and leads to the increasing of stock market price. Opposite condition occurred if manager unable to increase the value of company that its company will become subject of takeover that leads to the manager’s replacement. Diamond and Verrecchia (1991) state that the disclosure of voluntary decreases asymetric information between company and market.
According to IFRS 13 proper value is accepted price on assets selling or payment to transfer liability in transaction between interested parties on the date of measurement. IFRS 13 term requires an entity to disclose information on value techniques and inputs used to measure proper value although information on uncertain condition that covers the measurement of proper value. Input used as basic of determination of proper value consists of three levels, as follows level 1: input of adopted price from active market for identical assets and liabilities. These prices must be used as determination input of proper value without adjustment, in so far available. Level 2: inclusive at level 1, observable input, indirectly or indirectly on assets and liabilities Level 3: unobserved input, including internal data of company, necessarily adjusted to reflect assumptions on the participant at the market. IASB in 2009 provided reduction on requirement level of proper value usage that allows certain financial instrument that will be full reclassified from proper value that is issued by FASB.
Hypothesis Development
Larcker et al. (2007) examines the relationship between typical measurement of corporate governance and various accounting output and economics that are not come from one consistency set. Larcker et al. (2007) indicates positive between accrual discretionary and commissioner board measurement but there is negative relationship between absolute value of accrual and commissioner board measurement, while the issues of company management may occurred in relation to how large the member of commissioner board is. They also find abnormal accrual association that has relationship with accounting report that may describe the future performance with abnormal return stock.
Chtourou and Courteau (2001) study on the influence of company’s corporate governance practices on financial reporting quality that is published to public. This study studies the relationship between audit committee characteristic and commissioner board with company’s earnings management level that is measured by positive and negative discretionary accrual levels. Using two US companies set, one with discretionary accrual which is found relatively high and low if earnings management significantly related to corporate governance practice.
Study result of Rahman and Ali (2006) proves the contradictive with the study of Klein (2002), Anderson et al. (2004), Zéghal et al. (2011). According to Rahman and Ali (2006), the big commissioner board size will lead to the process of making decision becomes difficult. Rahman and Ali (2006) state that company with big amount of commissioner may trigger interest conflict that may constrain the monitoring the performance of company by commissioner board. Haniffa and Cooke (2002) state that there is roles of commissioner board in improving the performance of company and improving financial information quality. Klein (2002), Anderson et al. (2004) and Zéghal et al. (2011) perform study that examines relationship between corporate governance with earnings management. Their study result indicates that there is negative relationship between the sizes of independent commissioner with earnings management activity.
The study result of Cohen et al. (2012) indicates the change of manager’s behavior that performs accrual profit to be real earnings management after Sarbanes Oxley Act (SOX). Mechanism function of corporate governance in the company is providing more supervision toward management performance as well as providing accurate information and precision on the financial reporting of company. Fama (1980) and Fama and Jensen (1983) describe that commissioner board as an important mechanism in the structure of corporate governance. Their argumentation is the existence of commissioner board is a form of an effective monitoring depends on its composition.
there is negative relationship between absolute value of accrual with the size of commissioner board. Based on that hypothesis raised is:
H1: IFRS implementation strengthen the negative relationship between independent
commissioner proportion toward commissioner board with accrual earnings management.
The exploration on corporate governance that performed by Carcello et al. (2006) indicates that important role and unique of chairperson of the risk committee, chairperson of the compliance committee, chairperson of the ethics committee. Apart from that there is other important role in the corporate governance scope that is the position of chairperson of commissioner board, chairperson of the board of directors and chairperson of other committees. In line with SOX regulations of 2002, therefore regulation that regulates the existence of independent audit committee and financial expert is mandatory required by the regulators in many countries. Generally the regulation of corporate governance regulates on independency of commissioner board member with available committee in that commissioner board. The role of an audit committee is very important in conducting responsibility to present supervision report related to the credibility of financial reporting, audit and corporate governance entirely for commissioner board. The existence of audit committee in the company may provide more supervision on the performance of management and provide accurate information and exact on financial reporting of company. If a person is an audit committee member that has important responsibility to monitoring and assist on improvement of financial reporting credibility provided double post, both recruited company and other post in other company. If that audit committee member conducts double post then it is suspected to be a cause of decreasing of the performance of that audit committee member.
H2: IFRS implementation strengthen the negative relationship between audit
committee member with accrual earnings management.
Method of Study
Here is shown the research model used.
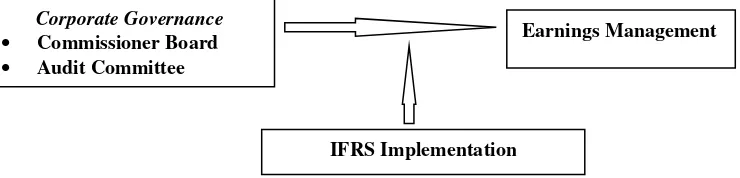
Figure 1. Model of Analysis of IFRS Implementation as Moderating Variabel of Relationship of Corporate Governance with Earnings Management
IFRS Implementation
Earnings Management Corporate Governance
• Commissioner Board
The above scheme is describing the relationship between corporate governance variable and quality of auditor that is moderated by the implementing IFRS toward earnings management. The purpose of this study is to provide empirical evidence on the analysis of implementing IFRS that moderates the relationship of corporate governance and the quality of auditor with earnings management. Corporate governance represented by two variables such as commissioner board and committee audit. Commissioner board is proxied by independent commissioner proportion toward commissioner board, while audit committee is proxied with double position of audit committee member with other position in sample company or other company.
Financial reporting data obtained from BVD OSIRIS database provided by FEB UGM taken on 01 March 2014. Other data obtained is from website of company and website of Stock Exchange of the state involved. Data used originally from the period of 2001-2013. Data of 2001 used to meet the calculation of variable that needs lag-1 data. Period of years of observation are 2002, 2003, and 2004 (three years) prior to IFRS implementation and year of 2006-2013 (eight years) for the period after IFRS implementation.
Manufacturing company is chosen as the model of earnings management calculation that uses the model component of stay depreciated in accordance with the modified Jones model used. This study is using proxy of commissioner board size by using proportion the amount of independent commissioner member toward the amount of commissioner board.
Audit committee is proxied with 1 if there is audit committee member of i company at period t perform double position with other position or in other company as an executive or commissioner board or other committee. Double position as other committee in the same company the code is 1. Double position as an executive in other company the code is 1. Double position as commissioner in other company the code is 1. If there is no double position the point is 0. Audit quality as control variable the code is 1 if it is and industrial specialist auditor and 0 if non-industrial specialist auditor. IFRS implementation level of implementing IFRS, the code is 0 for local accounting standards implementation, or accounting standards using US GAAP, the code is 0 for non-implementing, code 1 is for partly implementing IFRS, and code 2 for full implementing IFRS.
Furthermore, for the accrual income management proxy used from Jones Modified Model (Dechow, 1995) and the model for this research are:
DAit = β0 + β1Boardit + β2IFRSit+ β3ACit+ β4AUDit+ β5ROAit + β6SIZEit + β7LEVit+
β8Board*IFRSit + β9AC*IFRSit + εit
With the following explanation:
DAit: Discretionary accrual of i company in t period.
Board:it Proportion of independent commissioner toward commissioner
board in i company in t period.
IFRSit: Level of implementing IFRS with 0 code for local accounting
standard implementation, or accounting standards using US GAAP, code 1 for implementing partly IFRS, code 2 is for implementing full IFRS.
AUD it: Auditor spesialis industri pada perusahaan i pada periode t.
ACit: Audit committee member that performs multi position with other
Committee in commissioner board in i company or in other company in t period.
ROAit: Return on assets in t year, calculated from operating revenue
divided by total assets in i company in t period.
SIZEit: Natural logarithm of total assets in i company in t period.
LEVit: Total debt divided by total assets in i company in t period.
Boardit*IFRSit: Proportion of independent commissioner toward commissioner
board in i company in t period interacted with variable of implementing IFRS.
ACit*IFRSit: Audit committee member that performs double position with
other committee in commissioner board in i company or in other company in t period interacted with variable of implementing IFRS.
Results and Discussion
Table 1. Procedure of Sample Selection
Companies manufacturing code 31, 32, 33 (NAICS 2007 ) 555
Sample of 2001-2013 (13 years) 7.215
Cancelled object of observed sample of 2001 due to turns to be basic year for lag t-1,of 2005 as IFRS begins mandatory implemented
(1.110)
Number of initial sample prior to deduction unavailable data 6.105
Unavailable data (3.161)
Available data 2.944
Outlier in calculation model of regression discretionary accruals (1.475)
Total of study sample 1.469
Note: This table describes the sample selection procedure based on the completeness of the existing data according to the NAICS 2007 manufacturing code 31-33 with the 2001-2013 years of observation with some specified criteria.
The sample countries whose companies have voluntarily applied IFRS before 2005 are France at 2.5%. On the initial application of IFRS voluntarily Christensen et al. (2009) states that there are incentives for companies that voluntarily adopt IFRS that will not be granted if IFRS is required in the EU. The average value of the proportion of independent commissioners to the board of commissioners for a sample of firms listed on the German, French, Dutch and Danish stock exchanges of 0.285.
There is a difference in the level of accrual management of firms listed on the German Stock Exchange prior to the IFRS implementation of the 2002-2004 period and after the application of IFRS for the period 2006-2013. Different test results for firms listed on the German, Danish, French and Dutch Stock Exchanges show the difference between accrual earnings management before and after IFRS implementation. Companies listed on the French Stock Exchange show no difference between the accrual profit management before and after the application of IFRS.
On average earnings management on respective samples are never zero but indicates direction positive or negative. This indicates that earnings is managed to fluctuate, here is descriptive statistic presented from accrual earnings management that divided to three categories such as total earnings, positive, and negative managements. Accrual earnings 2002-2003 for registered companies in Stock Exchange of Germany, France, Denmark, The Netherland. There are different levels of earnings management before and after IFRS implementation on firms listed on the German Stock Exchange, and the Netherlands.
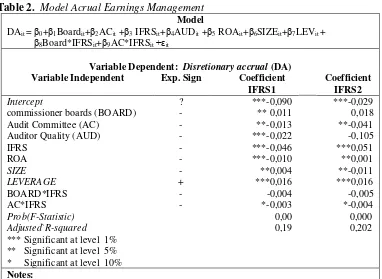
Table 2. Model Acrual Earnings Management Model
DAit = β0+β1Boardit+β2ACit +β3 IFRSit+β4AUDit +β5 ROAit+β6SIZEit+β7LEVit + β8Board*IFRSit+β9AC*IFRSit +εit
Variable Dependent: Disretionary accrual (DA) Variable Independent Exp. Sign Coefficient
IFRS1
Coefficient IFRS2
Intercept ? ***-0,090 ***-0,029
commissioner boards (BOARD) - ** 0,011 0,018
Audit Committee (AC) - **-0,013 **-0,041
Auditor Quality (AUD) - ***-0,022 -0,105
IFRS - ***-0,046 ***0,051
ROA - ***-0,010 **0,001
SIZE - **0,004 **-0,011
LEVERAGE + ***0,016 ***0,016
BOARD*IFRS - -0,004 -0,005
AC*IFRS - *-0,003 *-0,004
Prob(F-Statistic) 0,00 0,000 Adjusted`R-squared 0,19 0,202 *** Significant at level 1%
** Significant at level 5% * Significant at level 10% Notes:
This tabel discribe estimate acrual model of earnings management registered companies in Stock Exchange of Germany, France, Denmark, The Netherland. Variable dependent: disretionary accrual (DA); variable independent: Board of comisioner (Board), audit committe (AC), level of implementation IFRS (IFRS); moderating variable:
BOARD*IFRS, AC*IFRS; variable control: ROA, size, dan leverage ( LEV) and auditor quality (AUD).
Using moderated regression analysis model used constitutes one of moderating quasi as it is consists of main variable and moderating variable. Main variable is commissioner boards and audit committee. Moderating variable is moderated commissioner boards variable with degree of implementing IFRS.
The increase of highest accrual earning management occurred in companies in The Netherland in 2004, further registered companies in France Stock Exchange as well in 2005. It is different than registered companies in German Stock Exchange which its highest magnitude accrual earnings management in 2003.
sample of implemented IFRS companies unable to strengthen the negative relationship between multiple position of audit committee member with earnings management. This study result is in line with study result of Marra et al. (2011) and Zéghal et al. (2011).
Hypothesis 2 that states the implementation of IFRS weakens the negative relationship between multiple positions of audit committee member with earnings management is acceptable. The result of this study able to support the study result of Marra et at. (2011) and Zéghal et al. (2011). There is similarity of signs between predictions with the result of examination. This similarity indicates that although multiple position in audit committee occurred but mechanism of corporate governance particularly the role of audit committee may run well in reducing earnings management.
Conclusion
In general this study is aim to provide empirical study on analysis of implementing IFRS as moderating variable of corporate governance relationship with earnings management. In particular there are two objections in this study which the first one is to provide empirical study on analysis of implementing IFRS as moderating variable of the relationship between commissioner board with earnings management. Second objective is to analyze the implementation of IFRS as moderating variable of relationship between audit committee with earnings management.
Several conclusions that may be drive from the result of examination in this study is as follows accrual earnings management model examination performed by samples of registered companies in Stock Exchange of Germany, France, The Netherland and Denmark. The result of the examination indicates the implementation of IFRS strengthen the negative relationship between proportion of independent commissioner toward number of commissioner boards with accrual earnings management so that Hypothesis 1 is acceptable. Hypothesis 2 that states the implementation of IFRS strengthens the negative relationship between multiple positions of audit committee member with accrual earnings management is acceptable.
Limitations
This study uses various data source for operating cash flow reporting during 2001-2004 the author takes from various data sources. The different of data source allowing the occurrence of bias due to the difference of currency in certain period. The study uses sample from several countries that implement IFRS and its comparison country. The author has isolated the difference from those five sample countries match to the characteristic of corporate governance two tier model and the grouping of Leuz (2003) define cluster which based on total earnings management index, stock capitalization, ownership concentration, disclosure index, legal origin, corruption index and law regulation in those four countries. The sample isolation mentioned in order that there is no differences of company characteristic and sample country characteristic that may influence the result of study.
Implications
This study is expected to provide implication of study methodology as follows: first to develop the size of implementation of IFRS by using comparison of implementation per standard accounting of applicable IFRS in other countries and second a further study may use other earnings management size that is more powerful by considering the type of industrial characteristics. The implementation of IFRS is proven to moderate the role of commissioner boards and audit committees toward accrual earnings management.
References
Ahmed, A.S., Neel, M. and Wang, D. 2012. Does mandatory adoption of IFRS improve accounting quality? Preliminary Evidence. Available at SSRN:
http://ssrn.com/abstract=1502909 or doi:10.2139/ssrn.1502909.
Allegret, J.P., Raymond, H. and Rharrabti, H. 2016. The Impact of the Eurozone Crisis on European Banks Stocks, Contagion or Interdependence. European Research Studies Journal, 19(1), 129-147.
Anderson, R.C., S.A. Mansi, and D.M. Reeb. 2004. Board characteristics, accounting report integrity, and the cost of debt. Journal of Accounting and Economics 37 (3): 315-342.
Babalyan, L. 2004. Earnings management by firms applying international financial reporting standards: Implications for valuation. University of Fribour.
Barth, M.E., W.N. Landsman, and M.H. Lang. 2008. International accounting standards and accounting quality. Journal of Accounting Research 46 (3): 467-498.
Beasley, M.S. 1996. An empirical analysis of the relation between the board of director composition and financial statement fraud. The Accounting Review 71 (4): 443– 465.
Boldeanu, T.F., Tache, I. 2016. The Financial System of the EU and the Capital Markets Union. European Research Studies Journal, 19(1), 60-70.
Capkun, V., Jeny, C.A., Jeanjean, T. and Weiss. A.L. 2008. Earnings Management and Value Relevance during the Mandatory Transitition from Local GAAP’s to IFRS in Europe. Working Paper, HEC, ESSEC and Georgetown University.
Carcello, J.V., Hollingsworth, W.C., Klein, A. and Neal, L.T. 2006. Audit committee financial expertise, competing corporate governance mechanisms, and earnings management. NYU Working Paper No. 2451/27455.
Christensen, H.B., Lee, E. and Walker, M. 2008. Incentives or standards: what determines accounting quality changes around IFRS adoption? AAA 2008 Financial Accounting and Reporting Section (FARS) Paper.
Chtourou, S.M., Bedard, J. and Courteau, L. 2001. Corporate governance and earnings management. SSRN Working Paper Series, pp. 139.
Daske, H. and Gebhardt, G. 2006. International financial reporting standards and experts perceptions of disclosure quality. Abacus 42 (3-4): 461-498.
Daske, H., Hail, L., Leuz, C. and Verdi, R. 2008. Mandatory IFRS reporting around the world: Early evidence on the economic consequences. Journal of Accounting Research 46 (5): 1085-1142.
Dechow, P.M., R.G. Sloan, and A.P. Sweeney. 1995. Detecting earnings management. The Accounting Review 70 (20): 193-225.
Dechow, P.M., R.G. Sloan, and A.P. Sweeney. 1996. Causes and consequences of earnings manipulation: An analysis of firms subject to enforcement actions by the SEC. Contemporary Accounting Research 13: 1–36.
Diamond, D.W., and R.E. Verrecchia. 1991. Disclosure, liquidity and cost of capital. The Journal of Finance 46 (4): 1325-1359.
Doukakis, L.C. 2014. The Effect of Mandatory IFRS Adoption on Real and Accrual-Based Earnings Management Activities. HEC Lausanne, University of Lausanne, Switzerland, Journal of Accounting and Public Policy 33 (6): 551-572. Fama, E.F. 1980. Agency Problems and the Theory of the Firm. Journal of Political
Economy 88 (2): 288-307.
Fama, E.F, and M. Jensen. 1983. Separation of ownership and control. Journal of Law and Economics 26: 301−325.
Fetai, B. 2015. Financial Integration and Financial Development: Does Financial Integration Matter? European Research Studies Journal, 18(2), 97-106. Glavina, S. 2015. Influence of Globalization on the Regional Capital Markets and Consequences; Evidence from Warsaw Stock Exchange. European Research Studies Journal, 18(2), 117-134.
Glavina, S. 2015. Influence of Globalization on the Regional Capital Markets and
Consequences; Evidence from Warsaw Stock Exchange. European Research Studies Journal, 18(2), 117-134.
Haniffa R.M. and T.E. Cooke. 2002. Culture, Corporate Governance and Disclosure in Malaysian Corporations. Abacus: A journal of accounting, finance and business studies 38 (3): 317-349
Jeanjean, T., and H. Stolowy. 2008. Do accounting standards matter? An exploratory analysis of earnings management before and after IFRS adoption. Journal of Accounting and Public Policy 27 (6): 480-494.
Khan, U. 2010. Does fair value accounting contribute to systemic risk in the banking industry? Columbia Business School Research Paper. Available at SSRN: http://ssrn.com/abstract=1911895 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ ssrn.1911895. Klein, A. 2002. Audit committee, boards of director characteristics, and earnings
Kothari, S.P., A. Leone, and C. Wasley. 2005. Performance matched discretionary accrual measures. Journal of Accounting and Economics 39 (1): 163-197.
Kothari, S.P., and R. Lester. 2012. The role of accounting in the financial crisis: Lessons for the future. Accounting Horizons 26 (2): 335-351
Larcker, D.F., S.A. Richardson, and I. Tuna. 2007. Corporate governance, accounting outcomes, and organizational performance. The Accounting Review 82 (4): 963– 1008.
Lang, M., J. Raedy, and M. Yetman. 2003. How representative are firms that are cross-listed in the United States? An analysis of accounting quality. Journal of Accounting Research 41 (2): 363–386.
Leuz, C., 2003. IAS versus US GAAP: Information asymmetri based evidence from
Germany’s new market, Jornal of Accounting Research 41: 445-472.
Marra, A., P. Mazzola, and A. Prencipe. 2011. Board monitoring and earnings management pre-and post IFRS. The International Journal of Accounting 46: 205-230.
Macijauskas, L. and Maditinos, I.D. 2014. Looking for Synergy with Momentum in Main Asset Classes. European Research Studies Journal, 17(3), 3-16.
Ooghe, H., and Tine De Langhe. 2002. The Anglo-American versus the Continental European corporate governance model: empirical evidence of board composition in Belgium. European Business Review 14 (6): 437-449.
Othman, H.B., and D. Zéghal. 2006. A study of earnings management motives in the Anglo
American and Euro Continental accounting models: the Canadian and French Cases. The International Journal of Accounting 41: 406-435.
Paananen, M., and H. Lin. 2009. The development of accounting quality of IAS and IFRS over time: the case of Germany. Journal of International Accounting Research 8: 31-55.
Peasnell, K.V., F.P. Peter, and Y. Steven. 2005. Board monitoring and earnings management: do outside directors influence abnormal accruals? Journal of Business Finance & Accounting 32 (7-8): 1311-1346.
Rahman, R.A., and F.H.M. Ali. 2006. Board, audit committee, culture and earnings management: Malaysian evidence. Managerial Auditing Journal 21 (7): 783-804. Schipper, K. 1989. Commentary on earnings management. Accounting Horizons 3: 91-102. Schipper, K. 2005. The introduction of international accounting standards in Europe:
Implications for international convergence. European Accounting Review 14 (1): 101-126.
Scott, W.R. 2012. Financial Accounting Theory. Canada: Prentice Hall Canada Inc. Sivaramakrishnan K, and C.Y. Shaokun. 2008. On the association between corporate
governance and earnings quality. Working Paper.
Thalassinos, I.E., Deceanu, L. and Pintea, M. 2010. New Dimensions of Country Risk in the Context of the Current Crisis: A Case Study for Romania and Greece. European Research Studies Journal, 13(3), 225-236.
Thalassinos, I.E. and Politis, D.E. 2011. International Stock Markets: A Co-integration Analysis. European Research Studies Journal, 14(4), 113-129.
Thalassinos, I.E. and Politis, D.E. 2012. The evaluation of the USD currency and the oil prices: A VAR Analysis. European Research Studies Journal, 15(2), 137-146. Thalassinos, I.E., Hanias, P.M., Curtis, G.P. and Thalassinos, E.J. 2013. Forecasting
Resources and Crew Manning, Maritime Policy, Logistics and Economic Matters; Code 97318, 283-290.
Thalassinos, I.E., Liapis, K. and Thalassinos, E.J. 2014. The role of the rating companies in the recent financial crisis in the Balkan and black sea area. Chapter book in Economic Crisis in Europe and the Balkans, 79-115, Contributions to Economics, Springer International Publishing, DOI: 10.1007/978-3-319-00494-5-6.
Thalassinos, I.E., Stamatopoulos, D.T. and Thalassinos, E.P. 2015. The European Sovereign Debt Crisis and the Role of Credit Swaps. Chapter book in The WSPC Handbook of Futures Markets (eds) W. T. Ziemba and A.G. Malliaris, in memory of Late Milton Miller (Nobel 1990) World Scientific Handbook in Financial Economic Series Vol. 5, Chapter 20, pp. 605-639, (doi: 10.1142/9789814566926_0020). Van Tendeloo, B., and A. Vanstraelen. 2005. Earnings management under German GAAP
versus IFRS. European Accounting Review 14 (1): 155–180.