Financial Statement Analysis -An Introduction
1) Objective of FR
- Provide financial information to existing or potential users
- Evaluate financial position and past performance and form opinion about its future ability to earn profits
2) Financial Statement Analysis helps to make economic decisions
3) Balance sheet - Financial position at a point in time
4) Statement of comprehensive income reports all changes in equity except shareholders transactions
(Change in foreign currency translation; pension liabilities adjustments; Unrealized G/L on investments)
IFRS - Can combine with P&L
US GAAP - Can combine with statement of SH's equity
5) Statement of changes in Equity (issuing stocks; repurchase stock; paying dividend)
6) Cash flow (business activities)
- Operating CF (day to day activities)
- Investing CF (Fixed Assets)
- Financing (Debts)
7) Footnotes - Accounting methods; assumptions; estimates by management; addn information pertaining to Legal matters,
Acquisition, disposals
8) MDA - Nature of business, past and future performance; SEC requires - Effect of inflation; off b/s items; accounting policies
requires judgement by mngt
9) Audit report
Objective - To provide fairness and reliability of financial statements
Std auditors statement contains 3 parts - Independent review; Auditing stds were followed; FS prepared based on accepted
accounting principles
10) Steps in financial statement analysis framework
State the objective
Gather data
Process the data
Analyze and interpret the data
Report the conclusion or recommendations
Update the analysis
Financial Reporting Mechanics
1) Accounts - where transactions are recoreded
Chart of accounts - Detailed list of all accounts
Contra accounts - Entries offsetting some part of another account (dep on asset - Contra asset)
2) Asset = Liabilities + owner capital
Or
Asset = Liabilities + contributed capital + ending retained earnings
Or
Asset = Liabilities + contributed capital + beg retained earning + income - expenses - dividends
3) Accrual accounting
- Unearned revenue (Cash recd in adv + Service yet to be provided)
- Accrued revenue (Cash to be recd + Service provided)
- Prepaid expense (Cash paid in adv + Service yet to be recevied)
- Accrued expense (Cash to be paid + Service recevied)
4) Flow of information in accounting system
Financial Reporting Standards
1) Financial Reporting is not designed solely for valuation purposes, however it does provide important inputs for valuation purposes 2) Standard setting bodies - Establish financing reporting standards (US GAAP - FASB; IFRS - IASB)
Regulatory authorities - Legal authority to enforce compliance with financial reporting standards (US - SEC; UK - FCA) 3) 3 objectives of IOSCO1 (Intl org. of securities commission)
- Protect investors
- Ensure fairness, efficiency and transparency of mkts - Reduce systemic risk (mkt risk)
4) SEC filings
5) SEC no longer requires IFRS reporting firms to reconcile their financial statements to US GAAP 6) Qualitative characteristics
2 fundatmental characteristics - FR
- Faithful representation (Free from error and complete) - Relevance (Materiality - Can influence economic decision) 4 characteristics that enhance FR
- Comparability - Verifiability - Timeliness - Understandability
- Aggregation of similar items - No offsetting of assets
- Reporting frequency (Atleast annually) - Comparative information with prior periods 9) Barriers to financial reporting framework
- Valuation
- Standard setting (US GAAP - rule based approach ; IFRS - principal based approach i.e. judegemental) - Measurement base
10) Barriers to converge into universal accepted set of FR standard
Inventories
1) COGS = Beginning inventory + purchases - closing inventory
Or
Closing inventory = Beginning inventory + purchases - COGS
2) Calculation of cost is same as per IFRS and US GAAP
Includes:
Purchase cost (-) trade discount
Conversion cost including labour and O/H
Other cost to bring inventory to present location and condition
Excludes:
Abnormal waste
Adminstrative cost
Selling cost
3)
Methods
COGS consists of
Inventory consists of
FIFO (IFRS and US GAAP)
first purchased
Last purchase
LIFO
(US GAAP only)
last purchased
Earlier purchase
Weighted avg method (IFRS and US GAAP)
avg
avg
Specific identification method (IFRS and US GAAP)
Specific
Specific
4) Effects when prices are increasing and stable or increasing inventory level
Items
FIFO
LIFO
COGS
Lower
Higher
Ending Inventory
Higher
Lower
Gross profit
Higher
Lower
Cash flow (higher taxes)
Lower
Higher
Current Ratio
Higher
Lower
5) 2 Type of systems
- Periodic method (end of accounting period)
- Perpetual method (Updated continuously)
6)
Measurement of inventory
IFRS
Cost
Or
NRV (Selling price - selling cost)
- Loss to be recognized in P&L
- subsequent reversal in P&L to the same extent
US GAAP
Cost
2) NRV (-) normal profit margin
if Replacement cost is > NRV; den MV = NRV
if Replacement cost is <
NRV - profit margin ;
den MV = NRV - profit
margin
- Loss to be recognized in P&L
- No subsequent reversal allowed
FIFO and specific idenfication ans will be
***In certain industries - reporting inventory above historical cost is allowed
- Applies to producers of agricultural and forest products; mineral ores; precious metals
- Valued at NRV
- Changes in mkt prices to be recoreded in P&L
7) Change in method - Retrospectively and Chg to LIFO is prospectively
8) Inventory Management
Inv T/O = COGS/ Avg inventory
Low Inv T/O means slow-selling or even obsolete products
High Inv T/O means low days of inventory in hand is
desirable; however enough inventory should be in place
to satisfy demand
Long Lived Assets
1)
Expenditure providing future economic benefits over multiple accounting period is capitalized
Otherwise expensed
2)
Recorded at cost = Acq cost + other expense to prepare the asset for use
3)
Subsequent expenditure = if future economic benefit den Capitalized (Rebuilt, installation cost)
Otherwise expense (training cost, repairs and maintenance)
4)
Capitalized interest (Investing activity under CF)
- If Interest is accrued while building asset is capitalized only to the extent of debt used
- Under IFRS - income earned on temporarily investing borrowed funds reduces the interest to be capitalized
5)
Table on pg 208 - V.Imp
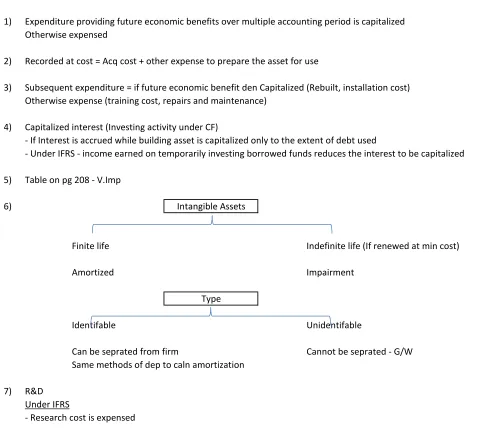
6)
Finite life
Indefinite life (If renewed at min cost)
Amortized
Impairment
Identifable
Unidentifable
Can be seprated from firm
Cannot be seprated - G/W
Same methods of dep to caln amortization
7)
R&D
Under IFRS
- Research cost is expensed
Intangible Assets
- Development cost is capitalized
Under US GAAP
- Research cost is expensed
- Development cost is expensed
S/W development cost
Under IFRS - Capitalized only after product feasibility is established (Developed for sale or own use)
Under US GAAP - Completely Capitalized (Developed for only own use)
8)
Goodwill internally developed is expensed in the period incurred
Goodwill created in business combination is capitalized
9)
Depreciation: 3 Methods
SLM
Dep = (Cost - Salvage value)/Life
Accelerated depreciation method (DDB)
Dep = 2/Life * (B.V at the beg of the year)
*** Restrict dep if B.V < salvage value
Units of prodn method
Dep = (Cost - Salvage value)/Life in units * units produced in that year
10) Change in estimates like useful life, salvage cost = effect is prospectively
11) Component depreciation - IFRS requires firms to do it; US GAAP - allowed but rarely used
12) Amortization Expense - Only for assets having definate life
If asset can be renewed at minimal cost for indefinate period, the same needs to be excluded from caln
13) Revaluation method (only IFRS allows it)
However IFRS allows to report asset at F.V if active market exists
If F.V less den cost - recored loss in P&L
Subsequent recover is allowed to the same extent and balance into SH's equity
***
No Dep Exp
***
FV to be done annually and recog P&L
14) Impairment (Both IFRS and US GAAP)
IFRS
Impaired if
Carrying value
or
Recoverable amount
Recoverable amount
F.V (-) selling cost
or
Value in use
Loss in P&L
Subsequent receoveries are allowed bt not above carrying value
US GAAP
Impaired only if events and circumstances indicates firm may not be able to recover the carrying value thru future use
Carrying value
or
Future undiscounted cash flow
15) Long lived asset held for sale
Since this has been classified as sale, hence no depreciable will now be allowed
or
NRV (-) selling cost
Loss in P&L
Subsequent receoveries are allowed bt not above carrying value
16) Long lived asset - Invt proprerties
Cost model = same
Understanding Income Statement
1) Statement of Other comprehensive income reports all changes in equity except shareholders transactions - Foreign currency translation
- Adjustment for minimum pension liability - Unrealized G/L from cash flow hedging derivatives
- Unrealized G/L from available for sale securities (Reported in B/S at F.V) IFRS - Can combine with P&L
US GAAP - Can combine with statement of SH's equity
2) Minority interest should be dedcuted from Income (Since subsidiary profits are wholly included in P&L)
3) P&L presentation - Single step statement
- Multiple step statement - Pg 49
4) Revenue Recongnition
IFRS - Sale of goods
- Risk and reward of ownership is transferred - No continuing control over goods
- Revenue can be measured - Probable flow of economic benefit - Cost can be measured
IFRS - Services
- Revenue can be measured - Probable flow of economic benefit - Cost can be measured
- Stage of completion can be measured
US GAAP - Sale of goods and services - Evidence of buyer and seller
- Product has been delivered or service has been rendered - Price is determined or determinable
- Seller is reasonably sure of collecting money
- Percentage completion method (PCM); Outcome can be measured IFRS and US GAAP
Steps:
a) % completed = Cost/Total Cost
b) Revenue to be recg = % completed * Total Revenue
- Completed contract method (CCM); Outcome cannot be measured IFRS; Revenue = Cost & profit only on completion
US GAAP; Revenue, cost and Income to be recg only when contract is completed
If loss is expected. The loss must be immediately recognized under IFRS/US GAAP
Installment Sales
US GAAP - 3 methods
- Collectibility is certain; Revenue at the time of sale
- Installment sale (Collectibility cannot be reasonably estimated) Profit = cash collected * Profit margin on sales
- Cost Recovery method (Collectibility is highly un-certain) Profit = cash received > cost
IFRS
Interest income = Installment value - Disc P.V of installment value
- Cost Recovery method (Collectibility is highly un-certain)
Barter transactions
US GAAP; Revenue = F.V if received cash for such goods, otherwise C.V of the goods IFRS; Revenue = F.V from similar non barter transaction with unrelated parties
5) Gross and Net reporting of revenue
- Primary obligator
- Bear inventory and credit risk - Be able to choose its supplier
- reasonable attitude to establish the price
6) Matching concept - Income should be recg when expense is made or vice versa (Warranty/Bad debts)
7) Inventory 8) Depreciation 9) Amortization
10) Non-Recurring Items
a) Discontinued opertaions (Reported separately, net of tax after income from continuing operations) Measurement date = Company develops a plan for disposing of operations
Phaseout period = Time between actual disposal and measurement date
On measurement date = Company will estimate loss during phaseout period and loss on sale of business; gains cannot be reported
b) Unusual or infrequent items (Included in income from continuing operations before tax) G/L from sale of business, write off
c) Extra ordinary items (Natural disaster)
US GAAP - Net of tax seprately after Income from continuing operations IFRS - Does not allow to disclose separately
11) Change in Accounting stds
- Change in accouting principles (LIFO to FIFO) - Retrospectively - Change in accouting estimates (Useful life of asset) - Prospectively - Change in prior period adjustment - re-instating prior period in FS
12) Operating and Non operating components in Income statement
Non financial firm - Interest income and dividend - not a operating income Financial firm - Interest income and dividend - operating income
13) EPS (only reported for common shares)
- Simple capital structure - No potential dilutive securities
Basic EPS = (Net income - Pref.dividend)/ weighted avg number of shares
Stock dividend and Stock split - Proportional Ownership is unchanged
Dilutive options means EPS will decrease if option is exercised
Dilutive shares = Add income in numerator and no of shares in denominator Conv Pref Shares - Add Pref dividend in numerator and no of shares in denomiator Conv Debt - Add Interest income after tax in numerator and no of shares in denomiator Stock/Warrant options - Only shares are added in denominator
Quick way to check if dilutive
Conv Pref Shares - Pref dividend/ no of new equity shares on conversion Conv Debt - Int (1-t) / no of new equity shares on conversion
Understanding Balance Sheet
1) Liquidity is the ability to meet short term obligations; Solvency is the ability to meet long term obligations
Liquidity Ratio
a) Current ratio = Current assets/Current liabilities
b) Quick ratio = (Cash + marketable securities + receivables)/current liabilties c) Cash ratio = (Cash + marketable securities)/current liabilties
Solvency ratio
a) L.T debt to equity ratio = L.T debt/Equity b) Total debt to equity ratio = Total debt/Equity c) Total debt ratio = Total debt/Assets
d) Financial leverage = Total assets/Equity
2) US GAAP needs current assets/liab and non current assets/liab to be reported seprately - Called as classified balance sheet Useful in evaluating liquidity
IFRS- Can choose to use liquidity based format - Normally banking industry use it Present Assets and Liab in order of liquidity
3) Current Asset/Liabilities: One year or
One operating cycle (Purchase inventory, Sell product and collect cash)
Current asset reveals information about operating activities of the firm Non - Current asset reveals information about firm's investing activities
Non - Current Liabilities reveals information about firm's Long term financing activities
4) Costing methods for valuation Standard costing (Predetermined cost)
Retail method (Inv cost = Sale price - Profit margin)
5) Financial Assets
- Available for sale securities
a) HTM (Debt securities)
Valued at Amoritized cost = Original issue price - principal repayment - impairment losses - amortized premium paid + amortized discount Subsequent changes in M.V is ignored
b) Trading securities (Debt,equity or derivatives) Reported at F.V in B/S
Income statement - Unrealized P&L
c) Available for sale securities (Debt and equity) Not to hold security till maturity
Other comprehensive Income statement - Unrealized P&L
*** Dividend, Interest and realized gains for all 3 types are recorded in Income statement
6) Contributed capital - Amount contributed by SH's Par value - Stated or legal value
Authorized shares - No of shares that may be sold Issued shares - Shares actually sold
Outstanding shares - Issued shares - shares acquired by firm (treasury stock which are not entitled to dividend and are not yet retired)
7) Vertical common size statements - Expressed in %
Understanding Cash flow statements
1) Cash flow is based on cash accounting (Non cash activities are not reported)
2) 3 type of activities:
Inflow Outflow
Operating activities Cash collected from customers Cash paid to suppliers and employees Interest and dividend received Cash paid for expenses
Sale proceeds from trading activities Acquisition of trading securities Interest paid
Taxes paid
Investing activities Sale proceeds from fixed assets*** Acquisition of fixed assets
Sale proceeds from debt and equity investments*** Acquisition of debt and equity investments Principal recd from loans made to others Loan made to others
Financing activities Principal amount of debt issued Principal paid on debt Proceeds from issuing stock Payment to reacquire stock
Dividend paid to SH's
*** Income from the investments are recoreded as operating activities
3) Dividend/Interest:
US GAAP Dividend paid Financing activity
Dividend recd,Interest paid,Interest recd Operating activity
IFRS Dividend paid, Interest paid Operating/Financing activity Dividend recd,Interest recd Operating/Investing activity
4) Taxes:
US GAAP Operating activities
5) Type of Methods (Same answer, however presentation of opertaing activities is different)
Direct method Pg 112 Indirect method Pg 113
6) US GAAP - Direct method must also disclose the necessary adjustment to reconcile net income to C.F from operating activities This is not the requirment for IFRS
7) FCFF = NI + NCC + [Int * (1-t)] - Fixed Cap Invt - WC Or
FCFF = CFO + [Int * (1-t)] - Fixed Cap Invt
FCFE = CFO - Fixed cap Invt + net borrowing
Financial Analysis Technique 1) Common size statements
Vertical - % of Revenue/Total Assets Horizontal - Last year will be my base i.e 1.00 2) Stacked column graph (Bar graphs) 3) Line graph
4) Regression Analysis - identify relationship between variables (GDP growth and Sales) 5) Limitations in using financial ratios for comparision of firms
- Different accounting treatment and analyst needs to adjust the data - Requires judgement for deriving at comparable value
6) Different types of ratios - Refer pg 142 - 151
Activity ratios - how well firm is utilizing its inventory and fixed assets Liquidity ratios - Ability to S.T obligations
Solvency ratios - Ability to L.T obligations Profitabality ratios
Valuation ratios - used in comparing relative valn of companies 7) Dupont Analysis
ROE = net income/equity Or
ROE = (net income/Sales)* (Sales/equity) or net profit margin * equity T/O Or
ROE = (net income/Sales)* (Sales/Asset) * (Asset/equity) or net profit margin * Asset T/O * Leverage ratio Or
ROE = (net income/EBT) * (EBT/EBIT) * (EBIT/Sales)* (Sales/Asset) * (Asset/equity) or tax burden * interest burden * EBIT margin * Asset T/O * Leverage ratio 8) Sustainable growth (g) = retention ratio * ROE
9) Business risk is std deviation of revenue, operating income and net income
CV sales/op.income/net income = (Std deviation of sales/op.income/net income)/ (mean of sales/op.income/net income) 10) 3 methods for examining variability of financial outcomes
- Sensitive analysis - "what if" - Sales increase by 3% - Scenario analysis - Lehman brothers
Income Tax
1) Income tax expense = tax payable + chg in DTL - chg in DTA
2) Def tax Liab is when Income tax expense > Income tax payable - Depreciation (Tax - DDB; Accounting - SLM) - Pg 247
Def tax asset is when Income tax expense < Income tax payable - Bad debts/Warranty liab (Income tax wont allow)
- R&D (expense in the year; Tax - capitalized and amortize over 3 years) - Customer advance but shipping left (Income tax recognized as Revenue)
3) When income tax rate changes; Def tax asset/liab reflect the new rate and find corresponding increase/decrease in tax expense If tax rate increase; increase in DTL and DTA
If tax rate decrease; decrease in DTL and DTA
4) Permenant difference is a difference between taxable income (as per tax law) and pretax income (accounting income) which cannot be reversed in future Example: Donation not allowed by income tax
Due to the above, effective tax rate are different and no financial adjustment is required
effective tax rate = income tax expense/pretax income
Temporary differences are those which can reverse in future
5) Valuation allowances - under US GAAP def tax asset and liab are shown seprately and not netted off
If >50% chances of DTA not reversing then it must be reduced and added to valuation allowance as contra account
Financial Statement Analysis
1) Credit rating improves based on below
--Scale and diversification
- Operational efficiency
- Margin stability
- Leverage
2) Inventory Accounting differences
LIFO method will have more COGS, Lower income and Low inventory
Firm needs to report LIFO reserve (difference between FIFO and LIFO COGS)
3) Off B/S financing
Capital lease are shown as liability and asset on B/s, however operating lease are not to be shown in B/s
Analyst needs to treat operating lease as liab and asset for better comparision
4) Value stock - Low price/cash ratio
Non Current Liabilities
1) Bond Terminology
- Face value - Amount that will be paid at maturity - Coupon rate - Interest rate stated
- Coupon payment - Periodic Interest payment (F.V * Coupon rate)
- Effective rate - Interest rate = P.V of future cash flow (Mkt rate required by BH's - This rate changes and is not fixed like coupon rate) - Balance sheet liability = P.V of remianing cash flow, discounted at mkt rate
- Interest exp = Book value at beginning * Mkt rate of interest
2) When mkt rate = coupon rate - Par bond When mkt rate > coupon rate - Discount bond When mkt rate < coupon rate - Premium
A premium bond is reported at B/S at more den its face value. As premium is amortized , book value will decrease and reaches face value at maturity (Interest exp decrease every year) A discount bond is reported at B/S at less den its face value. As discount is amortized , book value will increase and reaches face value at maturity (Interest exp increases every year)
Interest expense and book value are caluated using bond yeild at issue and not today's yield
3) IFRS - Effective Interest rate method is reqd (Pg 273)
US GAAP - Effective interest rate is preferred, but SLM is allowed if not materially different
4) Issuance Cost US GAAP - Capitalized IFRS - Deduct from Bond Liability
5) Debt covenants
- Affirmative covenants - Make timely payment of int and principal; maintain certain ratios and collateral - Negative covenants - Do not increase dividend and re-purchase share; do not issue more debts
6) Lease is an agreement whereby lessor (owner) allows lessee (tenant) to use the asset in return of periodic payment Finance lease - Like purchase of asset with debt (Dep + Interest Exp; Asset + Liab)
Operating lease - Rental agreement (Rental expense; No Asset + no Liab)
7) Finance lease
a) Lessee Perspective IFRS
If substantial all risk is trfd to lessee
- Title is transferred to lessee at the end of the lease
- Lessee can purchase the leased asset at price lower than fair value at some future date - Lease cover major life of asset
- P.V of lease payment = Fair value of the leased asset
- Lease asset is so specialized that only lessee can use the asset without significant modifications
US GAAP (if any 1)
- Title is transferred to lessee at the end of the lease
- Lease cover 75% or more of economic life of asset
- P.V of lease payment = 90% or more den Fair value of the leased asset
b) Lessor's Perspective IFRS
If substantial all risk is trfd to lessee, otherwise operating lease
US GAAP (if any 1 is met by lessee den finaning lease)
Operating lease - Lessor keep asset in his books
Finance lease - Lessor removes asset from balance sheet and replaces with Lease investment account
8) Reporting by Lessee
Finance lease is to be reported @ P.V of lease payment
Pg 282 or
Fair value of asset
***Total expense across operating lease and financing lease is the same Only presentation of expense in Income statement and C.F is different
Finance lease ( Int payment - Operating act; principal payment - Financing act) Operating lease ( Rental - Operating activity)
Table on 285 - Imp
9) Reporting by Lessor
Finance lease (Interest - operating act; principal repayment - investing activity)
US GAAP
a) Sales type lease (Manufacture or Dealer) and if P.V > carrying value of Asset b) Direct financing lease
IFRS do not distinguish, however if Manufacture or dealer can follow Sales type approach
Sales Type lease
Treated as a sale and difference between P.V and carrying value is gross profit Asset is removed from B/S and lease receivable account is created at P.V
Direct financing lease
No profit is recongized since P.V = carrying value
Asset is removed from B/S and lease receivable account is created at P.V
Operating lease ( Rental Income - Operating income and depreciation is claimed)
10) Disclosure requirment - Both Lessee and Lessor - General description of leasing agreement
- Nature,timing and amount to be paid in next 5 years. Lease payment after 5 years can be clubbed - Amount of lease exp/rev reporting in income statement for each period presented
- Amount receviable/unearned from lease arrangement - Restiction imposed by lease agreements
11) Pension
Pension is a form of deferred compensation for employees
a) Defined contribution plan - Company only contributes and risk is bear by employees (No future obligations as straight forward)
b) Defined benefit plan - firm will make periodic payments after retirement of employees Reporting is complicated and net pension asset and liability is key element for analysis
Financial Reporting Quality
1) Quality level of FR
- Reporting is compliant with US GAAP, earnings quality are sustainable and adequate - Reporting is compliant with US GAAP, earnings quality are low and not adequate
- Reporting is compliant with US GAAP, earnings quality are low, reporting choices and eastimates are biased - Reporting is compliant with US GAAP, earnings is actively managed
- Reporting is not compliant with US GAAP, numbers are presented on company's actual economics activities - Reporting is not compliant with US GAAP and includes fictitious numbers
2) Conservative accounting - Report losses at that point when expected and not when actually incurred Tend to decrease earnings now, but increase earnings in future
Aggressive accounting - Book all incomes immediately Tend to increase earnings now, but decreas earnings in future
3) Frauds occurs due to
- Incentives/Pressures (Salary depends on profit/share price, Competitive threats to profitability)