CHAPTER II
LITERATURE REVIEW
A. Learning
According to Slameto (1984: 97), learning is an effort which is done by someone to get new language of behavior on the whole as the result of their own experience in the interaction with their environment. While Brown (1980: 2) states that learning is acquiring or getting knowledge of a subject or a skill by study, experience, and interaction. Brown (2000: 7) adds that learning involves some forms of practice, namely reinforment and change in behavior.
Kimble and Garmezy as cited by Brown (1980: 7) also state that learning is a relatively permanent change in behavioral tendency and is the result of reinforced practice. It means that there are changes of behavior in students‟ cognitive, affective and psychomotor to a positive way and it is
expected that students will be more progressive in their life.
1. Language Learning
According to Litlewood in Fadila, language learning is a natural response and communicative needs (productive and receptive). Therefore, the teacher should try to ensure that the learners are always aware of the communicative value of what they are learning.
Richards and Lockhart (2006: 12) describe the definition of language learning by relating the following theories of language learning as follows:
a. Language is taught with physical objects.
b. Language is presented by problem solving involving the material to be learnt.
c. Meaning is made clear by providing contexts, not through translation.
d. The students are provided with a lot of practice without emphasizing repetition.
The assumptions about language learning that have been developed into the four theories above could be developed into other principles depending on the teacher‟s creativity and experience.
setting rules that govern behavior and practice. So it is needed a good interaction and students‟ participation to make an interactive learning.
2. English Learning
English is a language which has an important role in the world as an international language. It is used by many people and the need of mastering English is necessary. It also plays a very important in Indonesia as a developing country. It is one of the compulsory subjects that is learnt in the schools and universities in Indonesia. It automatically has a primary status among all the other foreign languages in Indonesian formal education. James (2005: i) says that as an international language, English has several importance. If people want to be successful in the future, we need to have excellent English language skills. There are many reasons why we need to be good at English:
a. People need to be fluent if they intend to continue at university. Many textbook are written in English, and they want to use the internet for research, most research is also written in English. b. People need to be fluent if they want to have a successful career in
the future.
c. People need to be fluent in English if people want to travel and truly experience the wonders our multicultural world.
English is spoken almost everywhere. If they want to communicate with other people, they must good in English skills.
Based on the explanation above, the writer thinks that learning English is very important for students. There are many benefits that can be found. The students get more information from several resources. Therefore, the Indonesian English teachers should comprehend the principles of learning English. According to Finnochiaro (1974: 17), there are four principles in learning English. Those are:
a. English language items should be presented in situation, which will clarify their meaning through the dramatization of reasonable, feature of sound, structure, word, and the arrangement of these in the utterance used in the situation.
b. A learner must be taught the structure system of language through numerous examples. A learner must be given insight into word order, inflection, derivation, and into meaningful features of the English language learning.
d. Language learning includes learning the culture, gesture, and spoken expression, which gives added meaning to the words or sentences.
In order to master English, the students have to learn well. They must make an effort to understand, to repeat accurately, to manipulate newly understood language and use the whole range of language in conversation or written composition.
B. Involvement in Learning Process
Sadirman (2007: 99) states learning activities have important involvement. It means that good learning needs the activities. Without activities, the teaching learning process can not run well because it is a set of teaching that covers by the students where the students can ask question related the material, write, listen, think, and read which can improve the students‟ involvement.
Involvement is the act of sharing in the activities of a group, “the
teacher tried to increase his students‟ engagement in class activities
(Michele in Fadila: 2009).
Learning is an interaction between learners and environment. Therefore, the students must have a high involvement or participation in learning process to achieve optimal learning. The students' involvement is very important and determines the success of learning. Sudjana (1993: 30) says that the requirement of effective class is an involvement. Students' involvement is the first requirement of learning activities in the classroom. The students' involvement can be improved by applying various ways. For instance, the teacher gives questions to the students, accepts students' responses positively, and uses some methods that will involve many students.
Involvement in learning process is where the students can involve themselves in joining the learning process. Sukidin, et al. (2002: 154) say that there are two kinds of involvement.
a. Contributive Involvement
Table 2. 1
The Kinds of Involvement
Contributive Involvement Initiative Involvement
1. Asking questions 2. Answering questions
3. Giving opinion or suggestions 4. Giving contradicition
5. Joining the lesson actively 6. Doing structured assignment
1. Doing unstructured assignment aoutonomously or spontaneusly 2. Learning material before it is
given in the classroom 3. Making summary
1) Asking question
It means that if the students find out the difficulties in comprehending the material, they will ask questions to the teacher in order to understand the material well.
2) Answering question
It means that if the teacher gives questions to the students, they will answer the questions well.
3) Giving opinion or sugestions
5) Joining the lesson attentively
It means that the students give rebutal or rejection to other by giving a good opinion
6) Doing structured assignment
It means the teacher gives assignment that has been prepared before. Then, the students do it well.
b. Initiative Involvement
Initiatives involvement is students‟ spontaneous initiative in doing the independent unstructured task, their initiative in asking for formative repetition orally, their initiative in learning and doing a subject matter that has not been taught and will be taught, and their initiative to make quick notes. There are three initiative involvements:
1) Doing unstructured assignment autonomously or spontaneously. It means that if the students find do the task autonomously and spontaneously or without preparing before.
2) Learning material before it is given in the classroom
It means that the students learn the material well at home as basic to comprehend before joining the class.
3) Making summary
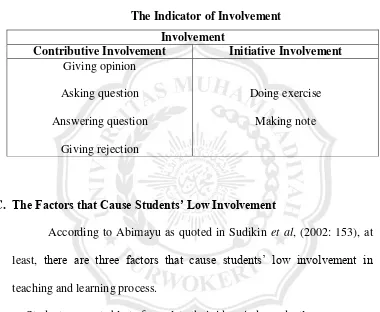
In this research, the researcher and the collaborative teacher determined the indicators of involvement. In contributive involvement the researcher will use; giving opinion, asking questions, answering question, giving rejection, and initiative involvement; doing exercise and making note.
Table 2.2
The Indicator of Involvement
Involvement
Contributive Involvement Initiative Involvement
Giving opinion Asking question Answering question
Giving rejection
Doing exercise Making note
C. The Factors that Cause Students’ Low Involvement
According to Abimayu as quoted in Sudikin et al, (2002: 153), at least, there are three factors that cause students‟ low involvement in teaching and learning process.
a. Students are not able to formulate their ideas independently. b. Students do not dare to express an opinion or idea for other.
c. Students are not accustomed to competition in expressing their opinion or idea with their friends.
Based on explanation above, the teachers need positive response objectively to improve students‟ involvement in teaching and learning
process through interactive activities. Strategies for increasing and maintaining active learners‟ involvement are important to establish
effective classroom. Students who are involved in learning activities usually respond the teacher questions most of the time. The teacher can take a benefit of this condition to attract inactive students to be involved.
Active learning through paired and group activities during a class session can promote involvement in learning. Therefore, asking students to reflect on their learning experiences is important.
The indicators that will be used are contributive involvement including giving opinion to solve problems, giving comment to other students‟ opinion, doing the task given by the teacher, receiving the
other‟s opinion. Initiative involvement includes being motivated in doing exercise and having responsibility as the member of the group.
D. Interactive Language Teaching
a. Learner to Content
Training is the planned of engaging the learner with the content. Effective organization and presentation of the content will guide the learner as they process the information into their own schemas.
Guidelines for supporting learners to content interaction include 1) providing an overview or visual map of the course content,
2) organizing material to support the sequence of the course objectives,
3) including the student guide that explains how to work through the content,
4) linking to additional or supplementary resources, and
5) incorporating, self-grading quizzes, thought provoking questions, or active practice exercise.
b. Learner to Instructor
The foundation for learner to instructor interactions is the inclusion of well-develop questions. These questions should guide learners from basic knowledge and recall material to the application and synthesis of material.
Questions should
1) be planned and sequenced to support the learning objectives, 2) keep the learners alert and attentive stimulate thinking, 3) provide testing cues,
5) help determine learners levels of understanding. c. Learner to Learner
Collaborative learning is powerful and enriching learning experience. This type of interaction encourages the development of an online learning community that supports the sharing of goals, interest, and knowledge among learners.
Web-based activities that support learner to learner interaction include 1) threaded discussions,
2) group project and presentations, 3) a discussion moderator,
4) synchronous discussion or virtual chats, and 5) “ whiteboard” design project.
Suparman as cited by Tauhari (2005:18) states that an interactive learning is a process that is able to make students actively involved in the whole of learning process both mentally and physically. Margaretha (2000: 10) says that the interactive learning focuses on the students' questions as the main characteristic by digging up the students' questions.
Asking questions activity in a learning process can be applied by the teachers to encourage guide and develop the students' thinking skills. While Lousel and Pascams as cited by Apriyani (2008: 21) state that asking questions activity in learning process has three main purposes, namely: developing students' thinking skills, checking the students' comprehension and improving students' participation in learning process.
Sagala (2007: 8) describes that asking questions activity has some purposes in a productive learning. Those purposes are to
1) dig up the students' knowledge, 2) check the students' comprehension, 3) evoke the students' responses,
4) know the students' curiosity in learning materials,
5) know the information that has been known by the students, 6) focus on the students' attentions,
7) encourage the students to ask many more questions, and 8) refresh the students' knowledges,
Suparman as cited by Tauhari (2005: 23-24) states that the learning activity has characteristics as follows:
1) There are varied classical, group and individual activities. 2) There is high mental involvement (mind and sense).
5) There is a learning condition which is flexible, democrative, challenging and focused on the learning objectives.
6) It can be applied both indoor and outdoor.
In conclusion, an interactive language teaching focuses on the students‟ participation to interact with the teacher, the other students,
and the materials given during the teaching and learning process.
1. Types of Interactive Activities
Rivers (1987:10-14) explains that in an interactive classroom, there are some activities that can be done. In an interactive classroom, there must be much listening to authentic materials. The authentic materials can be from the teacher‟s talk or audio-video tapes or film of native speakers who are interacting. Other kinds of input such as newspapers, magazines, instruction for products can also be used in the classroom. From the authentic materials, students can observe nonverbal behavior and the types of exclamation, the expressions that are used, and how they negotiate meaning.
generic term covering a multiplicity of techniques which two or more students are assigned a task that involves collaboration and self-initiated language.
Brown (2001:178) adds that there are some advantages of group work. Group work can generate interactive language. Through group work, it is possible to improve the quantity of interactive language because it provides opportunities for the students to initiate and practice to negotiate the meaning. Then, group work offers an embracing effective climate. The smaller group will make students feel secure where each individual is not so starkly on public display: Group work promotes learner responsibility and autonomy. Group work is a forward step individualizing instruction. Small group can help students with varying abilities to accomplish separate goals. The teacher can organize and capitalize upon other individual differences by careful selection of small group and by administering different task to different group.
also promote students autonomy by allowing students to make their own decision in the group without being told by the teacher.
Another technique that can be used to improve students‟
involvement is pair work. Basically, pair work is almost the same as group work, but the members of the group only consist of two people. Brown (2001:182) says that pair work is more appropriate than group work for the activities that are short, linguistically simple, and quite controlled in term of the structure of the task, for example, the practicing dialogue with partner, simple questions and answer exercise and checking written work with each other.
Harmer (2001:116) explains that the advantages of pair work are: (a) it dramatically increases the amount of speaking time anyone student gets in the class;(b) it allows students to work and interact independently without the necessary guidance from the teacher;(c) it allows the teacher to work with one or two pair work when the other students continue working;(d) it promotes the cooperation that makes the classroom become relax and friendly; and(e) it is relatively quick and easy to organize.
In conclusion, there are many interactive activities that can improve students‟ involvement during the teaching and learning
the cooperation, and give more opportunities for the students to speak and to be actively involved in the activities.
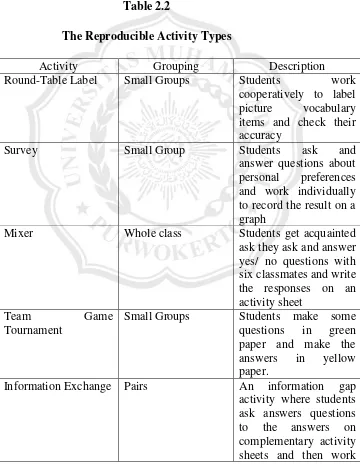
The table below lists the reproducible activity types found in Classic Classroom Activities Book (The Oxford Picture Dictionary Program by: Renee Weiss, Jayme Adelson-Goldstein, and Norma Shapiro) (2009: 8-9)
Mixer Whole class Students get acquainted ask they ask and answer
together to check their
Picture Differences Pairs Students study two almost identical scenes and work together to identify and list the differences on a chart Drawing Dictation Pairs Students take turn
describing and drawing Crossword Puzzle Small Group Students arranging
jumbled sentence to the right sentence.
2. Kinds of Interactive Activities
To maintain the students‟ involvement in the teaching and
learning process, there are some activities used
a. Questioning and Answering Activities
This activity is to attract the students‟ attention and motivate them to involve in the teaching and learning process at the begining of the lesson.
Rosenshine and Stevens in Muijs and Reynolds (2008: 67) explain that the importance of questioning and answering activities can help the students learning.
1) Questioning-answering can help the teacher to check students‟ comprehension about the material.
2) Questioning-answering makes the students have a chance to clarify their understanding about the taught concept and make them verbalize their mind, especially if they are supposed to explain the method or knowledge that they use to answer specific questions.
So, questioning-answering activity can make the students practice and master the topic taught by the teacher before they must move to the next topic.
Questioning and answering activity will be used to stimulate the students‟ motivations to learn and to speak
English. This activity will be used in the warm-up part. b. The activities used after questioning activity are:
1) Round-Table Label
In this activity, the students are divided into some groups. The students work cooperatively to label picture vocabulary items and check their accuracy. After that, the students make dialogue based on the picture.
2) Role Play
In this activity, the students are divided into some groups. The teacher asks the students to make a dialogue and act out in front of the class.
3) Team Game Tournament
In this activity, the students make some questions in green paper and make the answers in yellow paper.
4) Crossword Puzzle
Table 2.3
The Indicators of Involvement for Each Aspect
Activities Indicators
1) Round – Table Label - Giving opinion, - Answering question, - Giving rejection, - Doing exercises, and - Making a note. 2) Role Play - Giving opinion,
- Asking question, - Doing exercise, and - Making a note. 3) Team Game Tournament - Giving opinion,
- Asking question, - Answering question, - Giving rejection, - Doing exercise, and - Making a note. 4) Crossword Puzzle - Giving opinion,
The writer used some interactive activities above to build their enthusiasm to be actively involved in the teaching and learning process.
3. Basic Assumption
To improve student involvement in learning English, students need good interaction between the teacher and the students. Of course, it is difficult enough to do with the students to reach good level for all categories considering that English is only the foreign language. Therefore, the teacher has taken for innovative ways to teaching such as by using new techniques or new media.
One of them is interactive activity. Interactive activity is an interactive learning environment designed to make active student-centered learning by using media, questioning and answering activity or having group learning strategies.
By applying interactive activity, the students can involve actively in English teaching and learning process. Furthermore, it will make the students more enthusiastic because they work in pairs or groups in doing the exercise. Therefore, the problems faced in doing the exercises will be easier to be solved. It is assumed that interactive activity is one of the learning strategies that can be used to improve students‟ involvement in learning English.
process. The students are more confident in expressing their ideas and make a good interaction among each other during the lesson. It can be seen by the average the scores of students‟ involvement of Cycle 1 and Cycle 2
is 71.30%. So, interactive activity will be used to improve students‟ involvement and help the students to be active in the teaching and learning process.
4. Hypothesis of the research
Interactive activities are able to improve students‟ involvement in